Month: July 2021
India approves backhaul satellite connectivity via VSAT for telecom services; BharatNet tender coming soon
India’s Digital Communications Commission (DCC), formerly the Telecom Commission, has authorized use of satellite connectivity in telecom networks to provide services in remote areas where it is difficult to lay fiber optic cable. As a result, VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminals) operators will now be able to provide satellite-based cellular backhaul connectivity to telcos in India. That enables Indian wireless telecom communications service providers, like Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vodafone Idea, to use satellite capacity from VSAT license holders, such as Hughes, Nelco and BSNL, to connect their cell sites.
“With a view of ease of doing business, the DCC has approved provision of cellular backhaul connectivity via satellite through VSAT for telecom services as per Trai recommendation,” said India’s Telecom Secretary Anshu Prakash.
VSAT backhaul can also help Indian telcos cost-effectively extend coverage in rural and remote areas that are yet to be connected with fiber. Around 50% of India’s population is not yet connected to the Internet.

Several global LEO satellite providers, including Elon Musk’s Starlink, Bharti backed OneWeb and Amazon’s Project Kuiper, have recently started exploring the Indian market. OneWeb specifically will offer satellite capacity for cellular backhaul, but will need a VSAT permit to provide satellite-based backhaul services to the telcos.
Starlink and Project Kuiper have different business models, focusing on providing satellite-based broadband Internet directly to end users.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Telecom Secretary Anshu Prakash also said that the DCC has also cleared the Request for Proposal (RFP) for the rollout of BharatNet project for broadband services in villages in 16 Indian states in public private partnership mode with viability gap funding of Rs 19,041 crore (or US$ 2,544,834.60). “DoT (Department of Telecom) will come out with the tender for the PPP mode rollout of BharatNet in 16 states in seven days,” Prakash said.
India Telecom Secretary Anshu Prakash Photo Credit: Shiv Kumar Pushpakar
BharatNet project objectives are to:
- To carry on the business of establishment, management and operation of National Optical Fiber Network (NOFN) which has been envisaged by the Government of India to provide high speed broadband connectivity to all gram panchayats.
- To provide access to bandwidth in a non discriminatory manner to all eligible service providers to enable them to provide services in rural areas.
Comment and Analysis:
Just as India’s 5G spectrum auction has been the victim of one delay after another, so has the BharatNet project. The timeline for 2nd phase of the BharatNet project, earlier slated to be completed by August 2021, was extended with no definitive completion date.
“The BharatNet phase-II project was envisaged to be completed by August 2021. However, this time will now be extended as the pace of completion is affected by lockdown and restrictions on movement imposed by the various Governments due to COVID-19,” said India Minister of State for Communications Sanjay Dhotre.
“The delay in the implementation by the states is also adversely affecting the completion of the project. For other states, not being implemented under state-led model, the implementation strategy is under the process of review,” he added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
AT&T and Google Cloud Expand 5G and Edge Collaboration
Just one week after outsourcing their 5G SA/Core network software and IP to Microsoft (Azure public cloud), AT&T and Google Cloud announced new initiatives across AT&T’s 5G and Google Cloud’s edge computing portfolio, including AT&T’s on-premises Multi-access Edge Compute (MEC) solution, as well as AT&T Network Edge capabilities through LTE, 5G, and wireline.
For over a year, AT&T and Google Cloud have been developing edge solutions for the enterprise. Now, the two companies are taking the next step to deliver transformative capabilities that help businesses drive real value and build industry-changing experiences in retail, healthcare, manufacturing, entertainment and more — with the ability to use Google Maps, Android, Pixel, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), and other solutions across Google for more immersive customer experiences. For example:
- Enabling video analytics services to help businesses across industries with theft prevention, crowd control, and queue prediction and management.
- In retail: Streamlining and automating inventory management, connecting brick-and-mortar, and ecommerce and backend systems for near real-time visibility into operations.
- In healthcare: Scaling access to services like telehealth-based therapy, using AR and VR for remote care either from patients’ homes or at an onsite facility.
- In manufacturing: Accelerating operations with remote support and quality control checks at plant locations, and optimizing bandwidth usage by streaming video on the edge rather than on-device.
- In entertainment: Enhancing in-venue experiences for concerts and sporting events, with solutions ranging from immersive AR and VR experiences, smart parking and ticketless entry, to contactless food and souvenir payment.
The companies are also working together to evaluate how network APIs could optimize applications, using near real-time network information at the Google Cloud edge. If successful, this would allow them to optimize the user experience at the edge and drive meaningful outcomes for businesses.
AT&T Multi-access Edge Compute (MEC) with Google Cloud combines AT&T’s existing 5G and fully managed MEC offering with core Google Cloud capabilities, including Kubernetes, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), data analytics, and a robust edge ISV ecosystem. With the solution, enterprises can build and run modern applications close to their end users, with the flexibility to manage data on-prem, in a customer’s data center, or in any cloud. All this can help customers to increase control over data, improve security, lower latency and provide higher bandwidth.
AT&T Network Edge (ANE) with Google Cloud will enable enterprises to deploy applications at Google edge points of presence (POPs), which will be connected to AT&T’s 5G and fiber networks. In this low-latency compute and storage environment, businesses can deliver faster, more seamless enterprise and customer experiences. AT&T and Google Cloud are focusing on a multi-year strategy to bring the solution to 15+ zones across major cities, starting with Chicago this year. We expect to roll out the solution next in Atlanta, Dallas, Miami, and San Francisco.
“By combining the power of AT&T 5G and Google Cloud technologies, we are helping enterprises create new customer experiences and business services that were previously impossible,” said George Nazi, Vice President, Global Telecom, Media and Entertainment Solutions, Google Cloud. “Together with AT&T, we are committed to enabling our customers to build and deliver next-generation applications, whether on-premise or on AT&T’s leading mobile network.”
“With premises-based 5G and network edge computing, we give our customers even greater control of where their data goes and how they use it – at higher speeds and with lower latency. These capabilities allow businesses to deliver unique experiences to their customers, today and into the future,” said Rasesh Patel, Chief Product and Platform Officer, AT&T Business. “We’re bringing forth a new era where the latest technological advancements, including 5G and edge computing, make it possible to transform, innovate and prepare for whatever the future holds.”
“5G, cloud services and edge compute each have a tremendous amount of promise as standalone technologies,” says Jason Leigh, research manager for 5G and Mobile Services Research at IDC. “But coupling these three as complimentary, enabling technologies both accelerates and extends the promise of digital transformation in many more business settings.”
You can learn more about AT&T’s work in on-premises edge computing here, and network-based edge computing here. To learn more about Google Cloud’s work driving transformation and 5G adoption, visit here.
AT&Ts collaboration with Google extends beyond business and reaches the hands of the consumer. Together, the two companies are combining the power of AT&Ts 5G and fiber networks with Google cloud gaming platform.
Comment: It’s quite interesting that AT&T has outsourced its 5G SA core network to Microsoft Azure, but is using Google Cloud for edge computing for its 5G and fiber optics networks. AT&T claims a cohesive cloud strategy, but the network operator’s various alliances with cloud providers are confusing, according to Kathryn Weldon, research director at GlobalData. AT&T previously announced 5G edge partnerships with IBM, Microsoft, Accenture, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, and Deloitte.
The different goals AT&T hopes to achieve with each cloud or edge vendor and how they will jointly provide specific aspects of edge computing for each remains unclear, Weldon said.
“There have been so many announcements regarding operators’ relationships with hyper-scalers for 5G edge that it would be helpful to get really specific about use cases. The immersive experience examples are a bit generic. It’s time for actual customer use cases to be cited, even if they are only in trial,” she wrote in a report. Google Cloud and AT&T said joint customers will gain near real-time access to features packed into Google’s cloud and some of its most popular services.
“While the new initiatives leverage more Google capabilities, the announcement begs the question as to what things the partners have been working on for the last year. It isn’t clear why the listed Google elements could not have been brought in before,” Weldon added.
References:
AT&T 5G SA Core Network to run on Microsoft Azure cloud platform
MoffettNathanson: AT&T, Verizon set to lose wireless market share to Cablecos; 5G to disappoint – no real use cases
Our esteemed colleague Craig Moffett of MoffettNathanson says that the wireless market is now growing fast enough for both telcos and cablecos to meet their expectations. However, longer term growth that’s much above population growth is clearly unsustainable.
The market research firm has long argued that above-population phone growth in a more or less fully penetrated
market owes to the industry’s willingness to give away free phones in return for additional lines, even when those additional lines aren’t needed and won’t be used.
MoffettNathanson had earlier reported that it expects cablecos to continue to take wireless market share from telcos, bolstered by what is now much more competitive pricing from Comcast.
Craig wrote in a note to clients [we recommend you become one if not truly interested in telecom and/or cable]:
That leaves AT&T and Verizon to bear the brunt of the impact. AT&T has been growing its market share of late, but only because Verizon had been slow to match their aggressive retention offer. Now that Verizon has finally introduced its own, similar, retention offer, the two are likely to be in closer equilibrium… …which is to say, we believe they are likely to now both lose equally. Both companies have guided to low-single digit consolidated revenue growth in the near term, accelerating to the mid-single digits over the coming years.
With continued contraction in the Business Wireline segment all but a given, that means growth in wireless will have to be even faster than that. How? Their guidance seems awfully optimistic to us. We are also projecting significant losses for prepaid as low-priced post-paid plans accelerate pre-paid to post-paid conversions.
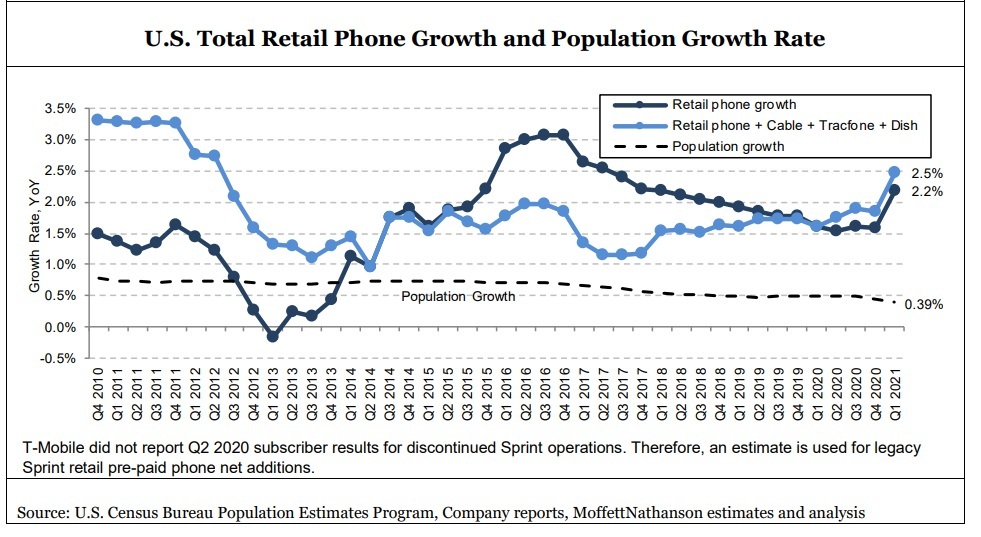
Moffett’s revised estimates are for mobile phone subscriber net additions to drop from about 6 million this year to approximately 4.5 million per year in the next few years. That works out to 5.8 million postpaid net adds vs. a loss of 1.3 million prepaid subscribers.
Moreover, the phone subscriber loss for mobile telcos will become more acute if the growth rate recedes from a recent increase of 2.5% year-over-year (a number five times higher than population growth), to more moderate levels – down to about 1.4% by 2025, according to Moffett’s forecast.
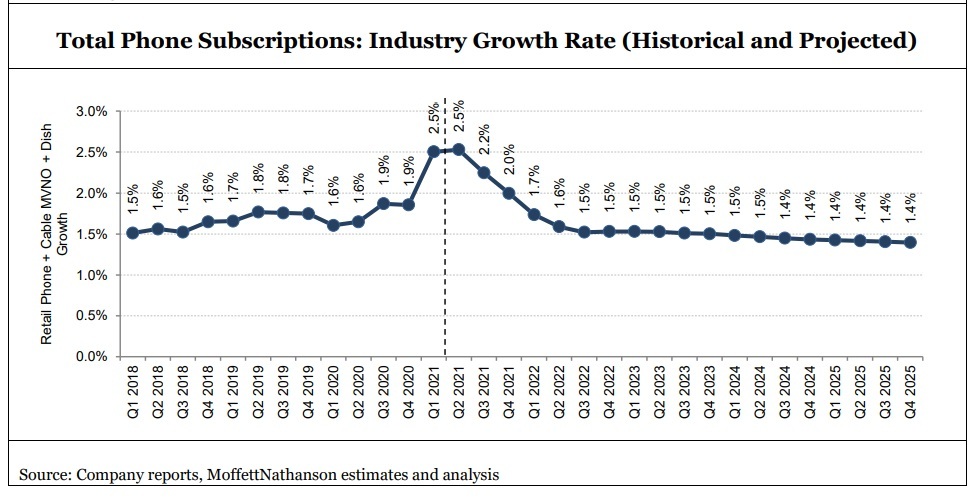
Moffett has significantly lowered his estimates for postpaid phone net adds for both AT&T and Verizon. T-Mobile’s sub growth will slow to a smaller degree, reflecting “greater competition from cable operators,” Moffett wrote.
- AT&T: For 2022, Moffett has cut an original forecast of 1.05 million postpaid net adds, to net adds of 505,000. Looking to 2025, he has lowered an original forecast of 888,000 postpaid adds, to 261,000.
- Verizon: For 2022, the analyst cut original expected postpaid adds of 1.03 million to 673,000. For 2025, he now expects Verizon, which does benefit from Comcast’s and Charter’s mobile businesses thanks to the aforementioned MVNO agreements, to pull in postpaid adds of 306,000, versus an original 1.09 million.
- T-Mobile: For 2022, Moffett has reduced his original postpaid net adds of 2.93 million, to 2.73 million. For 2025, he has lowered T-Mobile’s expected postpaid net adds to 2.97 million, versus an original 3.35 million.
Ahead of its national 5G network build, Dish Network remains largely a prepaid operator following its acquisiton of the Boost business from T-Mobile, along with a mix of pre- and post-paid subs coming from last year’s Ting deal. Moffett expects to see a faster decline at Dish’s Boost prepaid business as the company prepared to “compete more vigorously in post-paid.”
The wireless industry hasn’t grown mid-single digits in years, and, with competitive intensity rising, there is little reason to expect that to change. Unfortunately, MoffettNathanson is skeptical (to say the least) that 5G will create incremental revenue streams that fundamentally alter the industry’s growth trajectory. [1.]
Note 1. With URLLC performance requirements not met by either 3GPP Release 16 or IMT 2020 (M.2150), no ITU standard or 3GPP implementation spec for 5G SA core network (which is required for all 5G features like network slicing), no 5G SA roaming, and no ITU-R agreement on 5G mmWave frequencies (revision to M.1036 companion recommendation for M.2150), we think there are very few legitimate use cases for 5G at this time. Furthermore, the network build out costs, especially for hundreds of thousands of small cells with fiber backhaul) will overwhelm any revenue increases and result in a net LOSS for almost all wireless telcos that deploy 5G SA (T-Mobile may be an exception for many reasons).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Craig continues:
And if AT&T and Verizon are both going to be share losers – this seems to us to be a relatively non-controversial assertion – in an industry that barely grows, then how on earth will they achieve faster than mid-single digit growth?
In sum, our calculation suggests industry phone growth – again, to be clear, this is before the minting of unneeded and unused additional lines – should be about 1.2% per year.
With Cablecos taking a bite out of that smaller pie, Craig expects growth of incumbent telco’s – AT&T and Verizon, in particular – to suffer.
References:
MoffetNathanson July 6, 2021 Report: Cable Wireless: The Impact on TelCos (subscribers only)
Nokia and TPG Telecom launch 5G SA 700MHz network in Australia; 700MHz 5G status report
Nokia and TPG Telecom today announced that they have switched on a live 5G standalone (SA) network in Australia on the 700MHz spectrum band – the first time this has happened in the world. Low band 5G coverage at 700MHz, which is the lowest 5G frequency band deployed in Australia with the largest range, will enable TPG Telecom to provide wide outdoor 5G services, as well as deep indoor 5G coverage in urban and suburban areas to its customers.
Under the partnership, Nokia is supplying equipment from its latest ReefShark based AirScale product range including its unique triple band remote radio unit that supports 700, 850 and 900 MHz bands. The unit also supports 3G, 4G and 5G simultaneously across all TPG Telecom’s low-band frequencies. TPG Telecom’s 5G SA service is now successfully activated in parts of Sydney and this means that the operator’s customers will benefit from having 5G available in more places.
Low band 5G goes further outdoor and deeper into buildings than existing 5G deployments and will allow operators like TPG Telecom to bring 5G to even more customers. TPG Telecom may be targeting the Internet of Things (IoT) with its 700MHz service, because that frequency provides a broader coverage area. Australian homes will contain over 47 million smart devices by 2022, estimates the country’s National Science and Technology Council.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Other network operators are pursuing 700MHz 5G service.
- Japan’s KDDI said in March that it is using Samsung equipment operating in the 700MHz spectrum as part of its goal of covering 90% of Japan’s population by early 2022.
- CBN/China Mobile have put out tender requests bids for 480,397 5G macro base stations in the 700 MHz band. China granted a 5G license for use of the 700 MHz frequency to CBN, the country’s fourth telecoms operator, in June 2019.
- AT&T’s 5G “low band” network mostly uses 850MHz, but its 700 MHz FirstNet public safety network uses hardware “that can be upgraded to 5G with a simple software release.” AT&T has not publicly announce when that might be done.
The 700MHz spectrum provides “deep indoor penetration, a reliable uplink and large coverage,” notes a Nokia white paper. 700Mhz spectrum was referred to as “beachfront property” in 2007-2008.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Barry Kezik, Executive General Manager Mobile and Fixed Networks at TPG Telecom, said: “We’re excited to be the first network in the world to realize the true potential of low band 5G SA at 700MHz. TPG Telecom’s low band 5G will expand our 5G coverage, supporting our goal of reaching 85% of the population in Australia’s top six cities by the end of the year and changing the way people and things connect to the TPG Telecom 5G network.”
Dr Robert Joyce, Chief Technology Officer at Nokia Oceania, said: “Nokia is proud to support another 5G world first. We have a long-standing partnership with TPG Telecom, and we have jointly developed our unique triple band radio solution specifically for them. Today we get to see the result of that joint effort and collaboration which will deliver premium wide area 5G SA coverage for TPG Telecom and its customers.”
Other 5G networks in Australia: Telstra’s 5G covers 200 towns and cities, and Optus recently announcing it has connected 1 million 5G devices to its network
References:
https://www.rrt.lt/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Nokia_5G_Deployment_below_6GHz_White_Paper_EN.pdf
Other Resources:
Activate massive 5G capacity with Nokia AirScale
AirScale baseband | Nokia
AirScale Active Antennas | Nokia
AirScale Radio | Nokia
Facebook and Liquid Intelligent Technologies to build huge fiber network in Africa
Facebook Inc. and Africa’s largest fiber optics company, Liquid Intelligent Technologies, are extending their reach on the continent by laying 2,000 kilometers (1,243 miles) of fiber in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The two companies intend to build an extensive long haul and metro fiber network. Apparently, this is part of Facebook’s effort to “connect the unconnected,” especially in 3rd world countries.
The move will make Facebook one of the biggest investors in fiber networks in the region. The cable will eventually extend the reach of 2Africa, a major sub-sea line that’s also been co-developed by Facebook, the two companies said in a July 5th statement.

Facebook will invest in the fiber build and support network planning. Liquid Technologies will own, build and operate the fiber network, and provide wholesale services to mobile network operators and internet service providers. The network will help create a digital corridor from the Atlantic Ocean through the Congo Rainforest, the second largest rainforest after the Amazon, to East Africa, and onto the Indian Ocean. Liquid Technologies has been working on the digital corridor for more than two years, which now reaches Central DRC. This corridor will connect DRC to its neighboring countries including Angola, Congo Brazzaville, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia.
The new build will stretch from Central DRC to the Eastern border with Rwanda and extend the reach of 2Africa, a major undersea cable that will land along both the East and West African coasts, and better connect Africa to the Middle East and Europe. Additionally, Liquid will employ more than 5,000 people from local communities to build the fiber network.
“This is one of the most difficult fiber builds ever undertaken, crossing more than 2,000 kilometers of some of the most challenging terrain in the world” said Nic Rudnick, Group CEO of Liquid Intelligent Technologies. “Liquid Technologies and Facebook have a common mission to provide affordable infrastructure to bridge connectivity gaps, and we believe our work together will have a tremendous impact on internet accessibility across the region.”
Liquid Intelligent Technologies is present in more than 20 countries in Africa, with a vision of a digitally connected future that leaves no African behind.
“This fiber build with Liquid Technologies is one of the most exciting projects we have worked on,” said Ibrahima Ba, Director of Network Investments, Emerging Markets at Facebook. “We know that deploying fibre in this region is not easy, but it is a crucial part of extending broadband access to under-connected areas. We look forward to seeing how our fibre build will help increase the availability and improve the affordability of high-quality internet in DRC.”
Facebook has been striving to improve connectivity in Africa to take advantage of a young population and the increasing availability and affordability of smartphones. The social-media giant switched to a predominantly fiber strategy following the failed launch of a satellite to beam signal around the continent in 2016.
About Liquid Intelligent Technologies:
Liquid Intelligent Technologies is a pan-African technology group present in more than 20 countries, mainly in Sub-Saharan Africa. Liquid has firmly established itself as the leading provider of pan-African digital infrastructure with an extensive network covering over 100,000 km. Liquid Intelligent Technologies is redefining network, cloud, and cybersecurity offerings through strategic partnerships with leading global players, innovative business applications, smart cloud services and world-class security on the African continent. Liquid Intelligent Technologies is now a comprehensive, one-stop technology group that provides customized digital solutions to public and private sector companies across the continent under several business units including Liquid Networks, Liquid Cloud and CyberSecurity and Africa Data Centers. For more information contact: Angela Chandy [email protected]
References:
Huawei investment subsidiary buys 40 companies in 3 years to reconstruct semiconductor supply chain
According to financial magazine Caijing (Chinese), Huawei has been building an independent and controllable silicon industrial capability in the last two years as it attempts to rebuild its supply chain. Investments cover virtually every part of the semiconductor industry, including IC design, electronic design automation (EDA) software, packaging and testing, and materials.
On June 23rd, Tianyancha, an enterprise information query platform, revealed that Shenzhen Hubble Investment Partnership (Limited Partnership), a subsidiary of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd [1.], became a shareholder of Qiangyi Semiconductor (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. The registered capital of the latter increased from 65.943 million yuan to 73.165 million yuan. This is the first company in mainland China that has the ability to independently design vertical probe cards and has achieved mass production of MEMS probe cards.
The probe card is the core component of the chip test link, accounting for 70% of the total cost of the entire test fixture. As a test interface, the probe card will test the bare chip and screen out defective products. For a long time, the semiconductor test probe market has been monopolized by foreign manufacturers.
Note 1. Shenzhen Hubble Investment Partnership (Limited Partnership), which was established in April this year and is an investment institution controlled by Huawei Investment Holdings Co., Ltd., which is the same as Hubble Technology Investment Co., Ltd., which was established in April 2019.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Hubble Technology Investment Co., Ltd., which has been established for three years, has made faster and more detailed investments. In May, it invested in Shenzhen Yunyinggu Technology. On June 23 and 24, it successively invested in Qiangyi Semiconductor and Chongqing Xinjing Special Glass. There are 37 companies in its investment portfolio, of which 34 are related to semiconductors, involving chip design, EDA, testing, packaging, materials and equipment All links.
Before the establishment of Hubble Investment in 2019, Huawei had always followed the long-term principle of not investing in any company. Hubble’s mission is closely linked to the production of Huawei chips via wholly-owned subsidiary HiSilicon. Huawei CEO Ren Zhengfei had insisted the company would not invest in or partner with suppliers in order to ensure it was free to choose the best technologies.
In 2019, after Huawei was sanctioned by the U.S. government, the chips designed by HiSilicon could not find a foundry company (e.g. TMSC, Samsung, etc) that would make those chips for them. Those U.S. sanctions have changed Ren’s stance on investments/acquisitions. So Hubble Investment’s mission was directed at Huawei’s survival needs.
According to market research firm Strategy Analytics report, in the first quarter of 2021, the global smartphone processor market grew by 21% year-on-year, and Huawei HiSilicon’s smartphone processor shipments dropped by 88% compared to the same period last year. The sharp decline in data also indicates the urgency of self-help to make HiSilicon designed chips.
As tech blogger Kevin Xu pointed out: “Habo is a way to find and invest in the best companies in China who can be suppliers and partners, and groom them to be world class quality. That’s why Huawei gives them its business — there’s no better training than serving a real (and big) customer.”
Huawei’s executive director and CEO of consumer business, Yu Chengdong, once admitted that it was a mistake to only choose the field of chip research and development and ignore the asset-heavy chip manufacturing field.
The investment focus has shifted several times as it has built out its prospective supply chain partners, Caijing says. In late 2019 and the first half of 2020, its targets were materials and opto-electronic chip firms. In the latter part of 2020 and early 2021, it shifted to EDA software. In recent months it has targeted advanced equipment. In early June it invested 82 million yuan (US$12.7 million) in Beijing RSLaser Opto-Electronics Technology Co, specialist in light source systems for lithography machines.
Caijing confirmed with many people familiar with the matter that Huawei will build its first wafer fab in Wuhan. It will need a series of related materials, equipment, software, etc., which cannot be researched by Huawei alone. This means that Hubble’s investment in the semiconductor industry chain in the past three years will play an important role, and this will also be a crucial step for Huawei to achieve self-help in the supply chain.
Most of the companies invested by Hubble are in the early stages, and their scale is still far from the leading companies in the industry. Huawei tends to grow together with a company. Therefore, even some technologies that have not yet been commercialized in large quantities will receive investment from Huawei. This is for the controllable layout of Huawei’s industrial chain.
Although the information released to the outside world is extremely limited, many sources indicate that Hubble is closely connected with Huawei’s overall strategic plan. Bai Yi, the chairman and general manager of Hubble Investment, is also the president of Huawei’s Global Financial Risk Control Center and formerly vice president of Huawei’s strategy department.
A Huawei employee revealed to a reporter from Caijing that Hubble’s personnel are simple, “only a few dozen people”, but some of them also belong to Huawei’s strategic department in terms of administrative planning. For a long time before this, the decision-making power of Hubble’s foreign investment was not in the hands of the investment company itself, but was determined by the business department related to the invested company.
A semiconductor investor told a reporter from Caijing that sometimes they will look at projects with Hubble Investment. In many projects, Huawei’s procurement VP will directly participate in investment negotiations. At the same time, some of the invested companies are also Huawei’s upstream suppliers. . Some companies have business cooperation with Huawei, but Hubble has only deepened business cooperation.
The most obvious manifestation of the in-depth business cooperation is the order. In addition to investment, Huawei will also support the invested companies in order.
Take analog chip manufacturer Si Ruipu as an example. In the prospectus disclosed, customer A is the number one customer of Si Ruipu, which accounts for 57.13% of the operating income of the company. According to some related information, it is speculated that this customer A is Huawei. According to the prospectus, Si Ruipu established a cooperative relationship with Huawei in 2016 and obtained the certification of Huawei as a qualified supplier in 2017. In 2019, Hubble Investment, a subsidiary of Huawei, through private placement, became a shareholder of Seripul, and furthered the cooperation, and Huawei became the number one customer of Siripul.
Another example is Can Qin Technology. In 2019, Can Qin Technology became Huawei’s strategic core supplier and the largest supplier of Huawei’s 5G base station filters. Its orders from Huawei accounted for 91.34% of its operating income. In 2020, Hubble Investment will invest in Canqin Technology through equity transfer, with a shareholding ratio of 4.58%.
For small and medium-sized start-ups, the most worrying thing before is that no manufacturers are willing to use the product. Obtaining Huawei’s orders means stable sales revenue and strong ecological support, and it also gives these companies the opportunity for iterative trial and error. Many semiconductor companies in the United States have gradually developed by relying on powerful semiconductor manufacturers.
As previously noted, Huawei was not receptive to domestic suppliers in the early days. In addition to its strong style, Huawei did not give many domestic companies opportunities in the early years of the company. Their suppliers will still be the world’s first-class manufacturers. Today, the situation is quite different, but it gives tech companies in mainland China a rare opportunity.
In addition to orders, if some companies say that products or technologies may not be developed until next year, Huawei will also say that as long as the company can produce products in the future, Huawei promises to use it. This is a strong driving force for China’s independent semiconductor industry chain.
Once Huawei’s wafer fab is completed, its IDM model will go through, and a closed loop of the ecological industry chain will be realized. Now, Huawei is hiring talents in chip manufacturing and equipment. At the same time, Huawei is also paying attention to some domestic material companies, such as photoresist, silicon wafer, gas and other companies, which will serve for the construction of fabs in 2 to 3 years.
Becoming a supplier of Huawei is not an easy task. Huawei has very high requirements on suppliers. Accepting Huawei’s orders is a very energy-consuming task. At the same time, invested companies may also face the choice of giving up other customers. If there is a problem with Huawei, a major customer, the company’s operations will also be strained.
Today, Huawei is planning to build its own wafer fab and adopt the IDM model. If completed, Huawei’s semiconductor ecosystem will gradually form a closed loop. Huawei also hopes that the companies it invests in will be used for its production lines in the next 3 to 5 years.
References:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/16JJ4h5JXckwoowvLe4gYw
OneWeb Launches 36 LEO satellites, 254 in orbit, funding deals & UK coverage too!
OneWeb, the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite communications company, announced the successful launch of another 36 satellites to mark the completion of its ‘Five to 50’ mission.
The latest launch takes OneWeb’s in-orbit constellation to 254 satellites, or 40% of OneWeb’s planned fleet of 648 LEO satellites that will deliver high-speed, low-latency global connectivity. OneWeb intends to make global service available in 2022.
With this major milestone, the company is ready to deliver connectivity across the United Kingdom, Canada, Alaska, Northern Europe, Greenland, and the Arctic Region. Commercial satellite Internet service should be rolled out by the end of 2021 with a global service following next year, the company said.
Service demonstrations will begin this summer in several key locations – including Alaska and Canada – as OneWeb prepares for commercial service in the next six months. Offering enterprise-grade connectivity services, the Company has already announced distribution partnerships across several industries and businesses including with BT, ROCK Network, AST Group, PDI, Alaska Communications and others, as OneWeb expands its global capabilities.
The company continues to engage with telecommunications providers, ISPs, and governments worldwide to offer its low-latency, high-speed connectivity services and sees growing demand for new solutions to connect the hardest to reach places.
The launch of the latest 36 satellites was conducted by Arianespace from the Vostochny Cosmodrom. Liftoff occurred on 1 July at 13:48 BST. OneWeb’s satellites separated from the rocket and were dispensed in 9 batches over a period of 3 hours 52 minutes with signal acquisition on all 36 satellites confirmed.

Image Source: Source: Roscosmos, Space-Center-Vostochny and TsENKi
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, the Rt. Hon. Boris Johnson, MP, said: “This latest launch of OneWeb satellites will put high-speed broadband within reach of the whole Northern Hemisphere later this year, including improving connectivity in the remotest parts of the UK.
“Backed by the British Government, OneWeb proves what is possible when public and private investment come together, putting the UK at the forefront of the latest technologies, opening up new markets, and ultimately transforming the lives of people around the world.”
Sunil Bharti Mittal, Founder and Chairman of Bharti Enterprises, Executive Chairman of OneWeb, said: “Today’s momentous milestone demonstrates that OneWeb is now a leader in LEO broadband connectivity, serving a wide range of stakeholders across the Northern Hemisphere. This fifth launch amid the unprecedented global pandemic is truly remarkable and I congratulate the management team and fellow shareholders on the success.
“Bharti’s doubling of its investment earlier this week is testament to the commitment to OneWeb’s mission. We now look forward to the next chapter in OneWeb’s story, preparing the company for commercial service in the less than six months to deliver our global connectivity solutions to communities around the world.”
The Rt. Hon. Kwasi Kwarteng, MP, Secretary of State, BEIS, added: “Today’s launch is an exciting milestone in providing some of the world’s most remote locations with fast, UK-backed broadband less than a year since British government investment made this possible. With yet another successful mission, the people of the UK can be proud that this country is at the heart of the latest advances in small satellite technology.
“OneWeb’s coverage across the Northern Hemisphere now puts the United Kingdom at the forefront of the latest developments in Low Earth Orbit technology, and we will capitalise on the company’s unique position within this growing market to build a strong domestic space industry and cement our status as a global science and technology superpower.”
Neil Masterson, OneWeb CEO, said: “This is a truly historic moment for OneWeb, the culmination of months of positive momentum in our ‘Five to 50’ programme, increased investment from our global partners and the rapid onboarding of new customers. We are incredibly excited to start delivering high-speed, low-latency connectivity first to the UK and the Arctic region and to see our network scale over the coming months as we continue building to global service. Thanks to all our incredible partners who have been with us on this journey and are instrumental to making OneWeb’s mission a success.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Funding Deals:
OneWeb resumed satellite launches in December 2020 after emerging from bankruptcy protection with $1 billion in equity investment from a consortium of the British government and India’s Bharti Enterprises. It has also received investment from Japan’s Softbank and Eutelsat Communications, and further financing from Bharti. OneWeb said on Tuesday it was fully-funded and had secured $2.4 billion in total.
Earlier this week, OneWeb secured another $500 million in funding, bringing its total funding to $2.4 billion. This new cash injection came from Bharti under a Call Option agreement and is expected to be completed in the second half of this year. According to the BBC, the funding will see Bharti take a 39% stake in OneWeb, making it the company’s biggest shareholder. The UK government, Eutelsat and SoftBank will each own 19.3% of the firm.
“In just a year and during a global pandemic, together we have transformed OneWeb, bringing the operation back to full-scale,” said Bharti Global’s managing director Shravin Mittal. “With this round of financing, we complete the funding requirements.”
The funding announcement came on the heels of news that OneWeb had struck a deal with BT as the UK incumbent operator looks to improve its coverage of more remote areas.
References:
https://www.oneweb.world/media-center/oneweb-completes-its-five-to-50-mission
Webcast playback Launch highlights available View on OneWeb YouTube
Launch Imagery Launch #8 Media Kit
Launch Partner Arianespace and Glavkosmos
Launch Facility Soyuz Launch Complex, Vostochny Cosmodrome
RootMetrics touts 5G performance in Korea while users complain; No 5G SA in Korea!
A new report released by RootMetrics (owned by IHS Markit), shared the 5G performance results in four major South Korean cities in the first half of 2021. Three South Korean operators, KT, LG Uplus and SK Telecom, claim to have provided users with widespread access to 5G, remarkable speeds, and low latency.
According to the report, LG Uplus’s 5G network in Seoul has the fastest speed, the shortest latency, and the best coverage, providing end users with an optimal 5G experience. This is the third consecutive year that LG Uplus has maintained their position as a 5G industry leader. Of note, the report stated that LG Uplus made the most efficient use of the spectrum, despite only 80 MHz of 5G bandwidth, less than that of KT and SK Telecom, with 100 MHz each.
South Korea’s 5G availability and user speed, which are the two key components of a consumer’s 5G experience, are ahead of most of the rest of the world. RootMetrics considers LG Uplus in Seoul to be the best 5G network based on the 5G report results in four cities (see image below):
- Best 5G coverage: LG Uplus provides coverage in all scenarios, including outdoor, indoor, high-speed railway, metro, hot spots etc., with 95.2% 5G availability. That means the network is providing ubiquitous 5G access, far more than cities like New York and London city.
- Fastest 5G speed: The median speed of 5G users is 640.7 Mbps, which is much higher than in other cities with 5G access.
LG Uplus has built 5G networks with high-bandwidth massive MIMO, deployed 64TRx Massive MIMO at scale for outdoor scenarios and LampSite+distributed Massive MIMO for indoor scenarios to build “Everywhere” Massive MIMO. In addition, 5G AI+ has also been introduced. Together these technology build the strongest and most intelligent 5G network, according to RootMetrics.
The report says that the performance of the other two major operators in South Korea is also impressive. The 5G availability of the three operators has increased to over 93% and the median speed is over 461 Mbps, which means end users can access the 5G network no matter their location to enjoy the ultimate 5G experience. RootMetrics can’t help praise: South Korea is winning the global 5G race, with availability and speeds that are far, far ahead of others.
“5G is becoming the foundation of our connected communities and as important a piece of infrastructure as is water, roads, or electricity. We’ve tested performance in South Korea over many years. Our results continue to show that South Korean operators have taken a leading position in delivering the type of 5G experience that can help fuel new consumer and business activity,” said Patrick Linder, Chief Marketing Officer at RootMetrics. “As 5G continues to expand across the globe, the implementation strategies and performance seen in South Korea have set an impressive standard for other operators to follow.”
Reference:
https://rootmetrics.com/en-US/content/5g-in-south-korea-1H-2021
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In sharp contrast to RootMetrics’ glowing praise for 5G in South Korea, many 5G customers there are extremely dissatisfied as per this Light Reading article:
Their gripe is that 5G is little better than 4G in terms of speed, while coverage is annoyingly patchy. Worst of all, they’re locked into much more expensive two-year contracts when compared to LTE tariffs.
Rather than just put up with their 5G lot, this unhappy crew is intending to take part in a collective lawsuit and seek compensation of at least KRW1 million ($890) each. South Korean law firm Joowon is spearheading the legal action.
“Considering that monthly 5G plans are around 50,000 won more expensive than 4G LTE plans, we expect around 1 million won in compensation for users subscribed to two-year plans,” explained Kim Jin-wook, a Joowon lawyer.
Kim indicated that South Korea’s “big three” had a case to answer. They initially advertised 5G download speeds as being 20 times faster than 4G LTE, when they first came out of the 5G traps in April 2019, but a government report last year apparently found that average 5G download speeds were just four times faster than 4G.
Korea Bizwire points out that the Korea National Council of Consumer Organizations, a consumer advocacy group, recommended last October that carriers pay as much as KRW350,000 ($309) in compensation to users who filed for mediation over what they saw as a mediocre 5G service.
As of January the number of 5G subscribers in South Korea was just shy of 13 million, which was less than 20% of all mobile network users in the country.
5G customer dissatisfaction is a worldwide phenomenon. In May, Reuters reported that “about 70% of (global 5G) users are dissatisfied with the apps and services bundled with their 5G plans, according to a study carried out by Ericsson ConsumerLab in 26 markets around the world.
“While early adopters are pleased with 5G network speeds, they are already expressing dissatisfaction with a lack of bundled new and innovative apps and services, which they feel were promised in the marketing pitch for 5G,” Ericsson said.
“Service providers need to offer exclusive content and services that could differentiate a 5G experience from 4G and promote a sense of novelty and exclusivity,” Ericsson said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Finally, none of the South Korea carriers have deployed a 5G SA/Core network, despite Samsung’s bogus claim of November 4, 2020: “Samsung and KT announced they have successfully deployed Korea’s first 5G Standalone (SA) and Non-Standalone (NSA) common core in KT’s commercial network. KT will commercially launch its SA network when 5G SA-capable devices become available in the market.”
Well, that hasn’t happened yet, so KT’s 5G SA network has yet to be deployed! The major benefits of 5G, like network slicing, automation, secure communications, new QoS model, etc. are ONLY realized via a 5G SA core network.
The 5G SA architecture connects the 5G Radio (base station or small cell) directly to the 5G core network, and the control signaling does not depend on the 4G network as it does in 5G NSA. The full set of 5G Phase 1 services (defined in 3GPP Release 15) are ONLY supported in 5G SA mode.
GSMA has identified 12 5G SA networks worldwide. None are in South Korea:
At least 12 operators in nine countries/territories are understood to have launched (or close to launch) public 5G SA networks:
- China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom have all launched 5G SA networks (China Telecom and China Unicom sharing some of the network construction). China Mobile has deployed or upgraded 400,000 base stations to support standalone services, while China Telecom announced its service launch covering more than 300 cities.
- T-Mobile in the USA has launched 5G SA nationwide using spectrum at 600 MHz.
- RAIN has launched 5G SA in parts of Cape Town in South Africa to support 5G FWA services and DIRECTV in Colombia has launched 5G SA for FWA in parts of Bogota. China Mobile Hong Kong announced the launch of 5G SA in late 2020.
- Mass Response (Spusu) has launched a limited network in Austria and is progressing with a wider regional deployment and, most recently.
- Telefonica and Vodafone have launched 5G SA networks in Germany.
- STC has announced a commercial launch in Kuwait.
- Singtel has announced its launch in Singapore (with other operators in Singapore expected to go live very soon).
- In Saudi Arabia, STC has announced that it has activated its 5G SA networks, although GSA is waiting for confirmation of availability of commercial services for customers before classifying its 5G SA networks as launched. Also, in Saudi Arabia, ITC has announced a soft launch of a 5G SA network.
- In Australia, Telstra has deployed a 5G core network and has stated it is ready to launch its 5G SA network once a sufficient range of suitable devices is available in the Australian market.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Qualcomm’s designing custom CPU’s for dominance in laptop markets; CEO: “We will go big in China”
Qualcomm’s new CEO believes that by next year his company will supply CPU chips for laptop makers competing with Apple. Last year, the Cupertino, CA based company introduced laptops using a custom-designed central processor chip that boasts longer battery life. Longtime processor suppliers Intel Corp and Advanced Micro Devices have no chips as energy efficient as Apple’s.
Qualcomm Chief Executive Cristiano Amon told Reuters on Thursday he believes his company can have the best chip on the market, with help from a team of chip architects who formerly worked on the Apple chip but now work at Qualcomm. In his first interview since taking the top job at Qualcomm, Amon also said the company is also counting on revenue growth from China to power its core smartphone chip business despite political tensions.
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/RRPGOKG4OVID5I2WPBB3GWCY2Q.jpg)
“We will go big in China,” he said, noting that U.S. sanctions on Huawei Technologies Co Ltd (HWT.UL) give Qualcomm an opportunity to generate a lot more revenue.
Amon said a cornerstone of his strategy comes from a lesson learned in the smartphone chip market: It was not enough just to provide modem chips for phones’ wireless data connectivity. Qualcomm also needed to provide the brains to turn the phone into a computer, which it now does for most premium Android devices.
Now, as Qualcomm looks to push 5G connectivity into laptops, it is pairing modems with a powerful central processor unit, or CPU, Amon said. Instead of using computing core blueprints from longtime partner ARM Ltd, as it now does for smartphones, Qualcomm concluded it needed custom-designed chips if its customers were to rival new laptops from Apple.
As head of Qualcomm’s chip division, Amon this year led the $1.4 billion acquisition of startup, whose ex-Apple founders help design some those Apple laptop chips before leaving to form the startup. Qualcom will start selling Nuvia-based laptop chips next year.
“We needed to have the leading performance for a battery-powered device,” Amon said. “If ARM, which we’ve had a relationship with for years, eventually develops a CPU that’s better than what we can build ourselves, then we always have the option to license from ARM.”
ARM is in the midst of being purchased by Nvidia Corp for $40 billion, a merger that Qualcomm has objected to with regulators.
Amon said Qualcomm has no plans to build its own products to enter the other big market for CPUs – data centers for cloud computing companies. But it will license Nuvia’s designs to cloud computing companies that want to build their own chips, which could put it in competition with parts of ARM.
“We are more than willing to leverage the Nuvia CPU assets to partner with companies that are interested as they build their data center solutions,” Amon said.
Smartphone chips accounted for $12.8 billion of its $16.5 billion in chip revenue in its most recent fiscal year. Some of Qualcomm’s best customers, such as phone maker Xiaomi Corp are in China.
Qualcomm is counting on revenue growth as its Android handset customers swoop in on former users of phones from Huawei, which was forced out of the handset market by Washington’s sanctions.
Kevin Krewell, principal analyst at TIRIAS Research, called it a “political minefield” due to rising U.S.-China tensions. But Amon said the company could do business as usual there.
“We license our technology – we don’t have to do forced joint ventures with technology transfers. Our customers in China are current with their agreements, so you see respect for American intellectual property,” he said.
Another major challenge for Amon will be hanging on to Apple as a customer. Qualcomm’s modem chips are now in all Apple iPhone 12 models after a bruising legal battle. Apple sued Qualcomm in 2017 but eventually dropped its claims and signed chip supply and patent license agreements with Qualcomm in 2019. Apple is now designing chips to displace Qualcomm’s communications chips in iPhones.
“The biggest overhang for Qualcomm’s long-term stock multiple is the worry that right now, it’s as good as it gets, because they’re shipping into all the iPhones, but someday, Apple will do those chips internally,” said Michael Walkley, a senior analyst at Canaccord Genuity Group.
Amon said that Qualcomm has decades of experience designing modem chips that will be hard for any rival to replicate and that the void in the Android market left by Huawei creates new revenue opportunities for Qualcomm.
Another challenge for Amon, a gregarious executive who is energetic onstage during keynote presentations, will be that Qualcomm is not well known to consumers in the way that Intel or Nvidia are, even in Qualcomm’s hometown.
“I flew into San Diego and got an Uber driver at the airport and told him I was going to Qualcomm. He said, ‘You mean the stadium?'” Krewell said, referring to the football arena formerly home to the San Diego Chargers.
Amon has started a new branding program for the company’s Snapdragon smartphone chips to try to change that. “We have a mature smartphone industry today. People care what’s behind the glass,” he said.
References:
https://www.reuters.com/technology/qualcomms-new-ceo-eyes-dominance-laptop-markets-2021-07-01/
China Broadcasting Network tender for 480,400 5G macro base stations & multi-band antenna products
China Broadcasting Network (CBN), China’s fourth mobile operator, has issued a tender for the radio access portion of its national 5G network via its network partner China Mobile. Previously, the two companies entered into a 5G Network Co-construction and Sharing Collaboration Agreement along with other 5G collaborations.
The CBN/China Mobile tender requests bids for 480,397 5G macro base stations in the 700 MHz band which is roughly equivalent to the number of 2.6 GHz base stations already deployed by China Mobile. Based on past big 3 (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom) tender results, Huawei and ZTE are expected to win approximately 85% of the business. That would leave only 15% for Ericsson or other well known 5G base station vendor, but probably NOT Nokia which was shut out of the last China 5G contract awards.
China granted a 5G license for use of the 700 MHz frequency to CBN, the country’s fourth telecoms operator, in June 2019. The other three obtained 5G licenses for 2.6 GHz and 4.9 GHz. Founded in 2014, Beijing-based CBN is the most recently established, so lacks users and infrastructure, which is partly why it is cooperating with China Mobile on 5G.
Concurrently, a bidding announcement for the centralized procurement of multi-band (including 700MHz) antenna products was also issued. This project is a centralized bidding project. The purchased products are multi-band (including 700M) antenna products. There are three types of 6 antennas: 4+4+4 antennas (700/900/1800MHz), divided into ordinary gain and high gain; 4+4+ 4+8 antennas (700/900/1800/FA), divided into long and short models; single 4 antenna (700MHz), divided into normal gain and high gain. The procurement scale is approximately 1.74 million antennas, of which 4.448 antennas require 1.14 million antennas, and the remaining model antennas such as 444 are 600,000 antennas.
China Mobile will complete the deployment of 700MHz 400,000 stations within this year. In the first half of 2022, they plan to open 480,000 seats and fully support 5G broadcasting services. Within two years full network coverage will be achieved.
There are now nearly 100 5G mobile phones supporting the 700MHz frequency band, covering high, middle and low end consumer groups. China Mobile earlier made it clear that in 2021, it will promote the joint construction and sharing of 700MHz to achieve 700MHz commercialization. It requires: starting from March 1, 2021, terminals of 4,000 yuan and above must support 700MHz; from October 1, 2021, The newly added terminal must support 700MHz.

The tender is a milestone for the China telecom sector, marking the start of the rollout of the new entrant, who is also the first network operator not linked to the Ministry of Industry and IT. CBN said the network will be configured around video and streaming to serve its existing cable TV customer base and to provide differentiation from the incumbent telcos. The rollout will include 5G mobile broadcasting capabilities, including 3,000 transmission towers.
The 700MHz frequency band is part of the wider ultra-high frequency (UHF) band used previously for terrestrial broadcasting. The 700MHz frequency band will improve connectivity in rural areas thanks to its ability to support better coverage in open spaces. Moreover, with its wide territorial reach and good penetration in buildings, the 700MHz band will help service providers meet the rising consumer demand for audiovisual content and other broadband services over wireless networks.
Li Shuang, Deputy Director of Department of Technology Development, CBN, said: “CBN always extensively cooperates with domestic and international industry partners with innovation-driven, open and win-win concepts in mind, promoting continuous maturation of the global industry chain of 5G 700MHz network and committed to building a high-quality nationwide 5G network in China. The successful test by Ericsson based on the 3GPP 5G specifications contributed by CBN, including the 700MHz technology standard and n28 band terminal enhancements standard, has improved the 700MHz network capability efficiently, which is of great significance to the innovation of low-band 5G networks in various scenarios.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
CBN and China Mobile are reportedly promising to deploy 400,000 base stations this year.
Robert Clark of Light Reading wrote, “That seems unlikely – it took the incumbent operators nearly two years to reach that mark – but it seems certain that CBN will offer its first commercial services late this year or early 2022. The bid documents state that the tender is fully funded, a positive sign for the cash-strapped CBN.
As Rakuten in Japan is learning, it is not easy to compete against big legacy players each with a large installed base and deep marketing channels. Even in the capital markets, CBN may find itself competing again with its industry rivals.”
References:
http://www.cctime.com/html/2021-6-30/1579416.htm
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/cbn-issues-massive-5g-base-station-tender/d/d-id/770623?



