Author: Alan Weissberger
Is a new 5G Patent War in the works? Expert Opinion + Review of 5G patent studies
Introduction:
A recent Bloomberg article sees an increasing amount of patent litigation arising from the use of 5G and other (unnamed) wireless technologies. Wireless telecom patent producers, like Qualcomm and Nokia (along with many others not mentioned in the article) may reap royalties from many different types of products that communicate using wireless networks. Examples include “talking cars” (aka V2V or V2X), and IoT devices [1.] being planned in agriculture, medicine, appliances and other sectors.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Note 1. The 5G/IMT 2020 use case “Massive Machine to Machine communications” is the wireless connectivity used in the IoT. Note that IMT 2020.SPECS includes NB-IoT as one of the Radio Interface Technologies supported by 3GPP, China, Korea, and India/TSDSI.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“So many different types of companies have to find a way to get these deals done,” said Joe Siino, president of Via Licensing, a Dolby Laboratories Inc. unit that works with audio, wireless, broadcast and automotive industries. “It’s taking the problems we had with smartphones and multiplying it by 10.”
After noting the “4G smartphone patent wars,” Bloomberg says the new wireless patent disputes are potentially more lucrative, as sales of 5G devices is forecast to grow to $668 billion globally in 2026 from $5.5 billion this year, according to Allied Market Research. Here’s a review of recent court rulings, again from Bloomberg:
Courts in the U.S. and Europe have in the past few weeks rejected efforts claiming the telecommunications companies’ licensing policies violated antitrust laws and confirmed their ability to limit the use of fundamental wireless technology by those who refuse to meet their licensing demands.
Those rulings have already favored the telecoms in cases brought by the automobile industry in Europe and the U.S. over the current wireless standards
In the past few weeks, judges in Germany sided with Sharp Corp.’s request to limit Daimler AG sales in its home country for using its mobile technology without a license. In an unrelated case a federal judge in Texas threw out an antitrust lawsuit filed by Continental AG, a Daimler parts supplier, against a patent-licensing pool (aka Patent Troll) set up as a one-stop shop for access to patents.
That pool, Avanci LLC, handles licensing patents owned by Qualcomm, Nokia, Sharp and other telecom companies. It charges $15 per vehicle for a range of patented inventions needed to comply with 2G, 3G and 4G standards, and is developing a plan to charge for the next generation, known as 5G.
In a letter to the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC), Daimler and Ford Motor Co. warned that an appeals court ruling won by Qualcomm could “destabilize the standards ecosystem by encouraging the abuse of market power acquired through collaborative standard-setting.”
And a few selected quotes:
“Patent owners want to get paid because they are proud of what they created and continue to innovate,” Kasim Alfalahi, founder and CEO of Avanci. “You have to find a middle ground, you have to find a place where these things can meet.”
“The fact that more and more industries are going to start incorporating technology that has to be standardized means it’s going to be even more important to resolve these issues,” said Katie Coltart, a patent lawyer with Kirkland & Ellis’s London office.
“You’ve got a handful of companies that are investing billions of dollars in research,” said Mark Snyder, deputy general counsel for Qualcomm. “In a functioning market, you want people to engage in earnest negotiation. FRAND is a two-way street.”
Telecoms.com Scott Bicheno wrote: “Around half of Huawei’s 5G patent applications seem to have been made in China, and they account for half of all such applications made in China. While there’s nothing intrinsically wrong with that, it’s worth noting that Samsung and LG, which are in the top three 5G patent applicants alongside Qualcomm, have hardly filed any applications in Korea. It’s almost as if the barrier to entry for patent filing in China is lower.”
5G Patent Expert Yigang Cai, PhD [2.] Comments:
- Currently, most companies generating 5G patents aim to license royalty revenues rather than to protect the intellectual property they have created.
- A high percentage of the many patents granted are not essential (professionals call them garbage patents), or only quite least claims among those patents are useful. It is kind of a waste of financial expenses and resources worldwide.
- Restrictions on the use of 5G patents will hurt most industries in the future, when 5G use cases and industry vertical applications are being developed.
Note 2. Among other honors, Yigang Cai, PhD was awarded the first ever Alcatel-Lucent “Distinguished Inventor Award” (2013) with his inventive accomplishments and patent contributions throughout his career with the company. Yigang has filed a total of 1000+ patents globally, of which 669 are granted patents (including 196 U.S. granted patents as of this week). Many of his inventions in wireless networks have been built into products and systems of 2G/3G/4G and 5G, and deployed worldwide. He is one of the pioneers and leaders in developing the principles and components of Machine Type Communications (MTC). Dr. Cai generated many 5G inventions, including 5G New Radio (NR), 5G end-to-end architectures and use cases (both Access Networks and Core Networks), Network Slicing, MEC, 5G Machine Type Communications (MTC), and Device-to-Device Communications.
Review of 5G Patent Studies:
1. In a 2019 study by GreyB, a research company, Huawei was found not only to hold more 5G-related patents than any other company (some 13,474), but also to hold the bigger share of standard-essential patents (or SEPs) – about 19% of them vs 15% for Samsung, 14% for LG, 12% for each of Nokia and Qualcomm, and just 9% for Ericsson.
Authors of the study wrote: “Huawei holds the most 5G patents i.e. 13473 followed by Qualcomm and then Samsung with 12719 and 9299 respectively. China wants to have an upper hand in 5G therefore, it won’t come as a surprise to see Chinese companies such as Huawei and ZTE surpass some of the top companies worldwide.”
Here is the list of top 10 companies holding most 5G patents: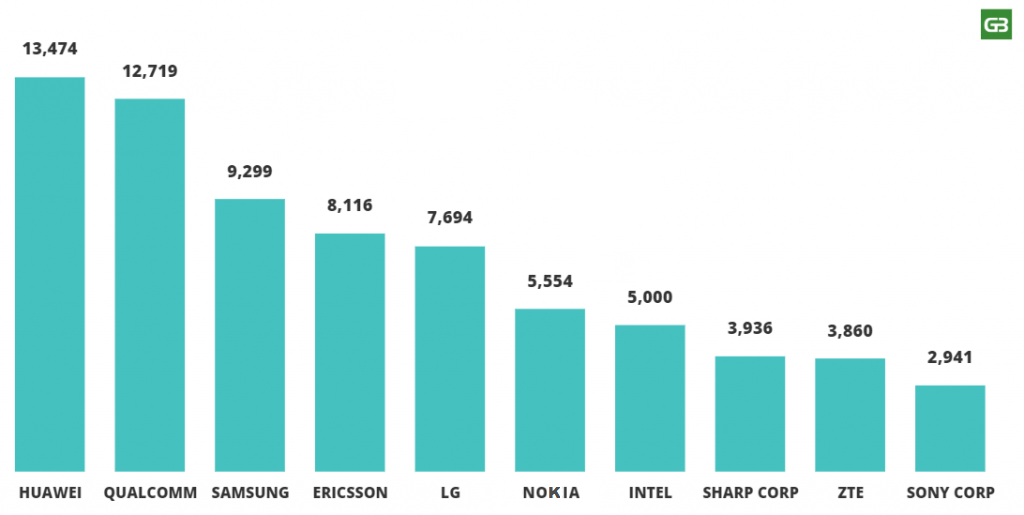
2. In a January 2020 released study, Berlin, Germany based Iplytics found that the 5G standard is highly patented. In total 95,526 5G
declarations patents have been declared for 5G which breaks down to 21,571 unique patent families. Only 44% of these patent families have yet been granted.
As most 5G patents have been recently filed, we would expect the rate of granted patents to further increase in the next few years. Most 5G patents where declared between 2017 and 2019 showing a sharp increase year by year. And as the 5G standard development is not yet completed (that includes IMT 2020.SPECS and 3GPP Release 16) further patent declarations are expected in the upcoming years.
It’s also interesting that 24% of the patents declared for 5G have before already been declared for 4G. This shows that some 4G technologies are still relevant for the new 5G specifications. As of January 1st, 2020 Huawei (CN) has declared most 5G patents followed by Samsung (KR), ZTE (CN), LG (KR), Nokia (FI), Ericsson (SE) and Qualcomm (US). All of those top 5G patent owners have already been active in the 4G standard development.
The study identified new market players. Here the Chinese companies Guangdong Oppo (CN), Vivo Mobile (CN), FG Innovation (CN), Spreadtrum Communications (CN) and the Taiwanese ASUSTeK Computer (TW) are new in the top patent owner list comparing 5G and 4G. The study shows however that the larger share of the Chinese newcomers’ patent portfolios is yet filed locally in China and are yet not granted. Given that 5G is a recent technology the study shows that the patent portfolios of these Chinese companies are still very young and could very well still be filed and granted internationally.
This study also investigated companies’ participation in the standards development, where technical contributions submitted to the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) – the spec writing organization that develops complete radio and non-radio telecommunications specs for 3G, 4G and 5G – were counted and analyzed.
The main 4G standard developers such as Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, Qualcomm, ZTE or Samsung and LG are again strong players for the 5G development. Here again the data shows increasing participation from new and upcoming Chinese players. When counting only approved 5G standard contributions, Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia and Qualcomm are the strongest players.
3. As of February 2020, The Times of India says that Huawei has filed the most 5G patents, but Samsung has been GRANTED the most.
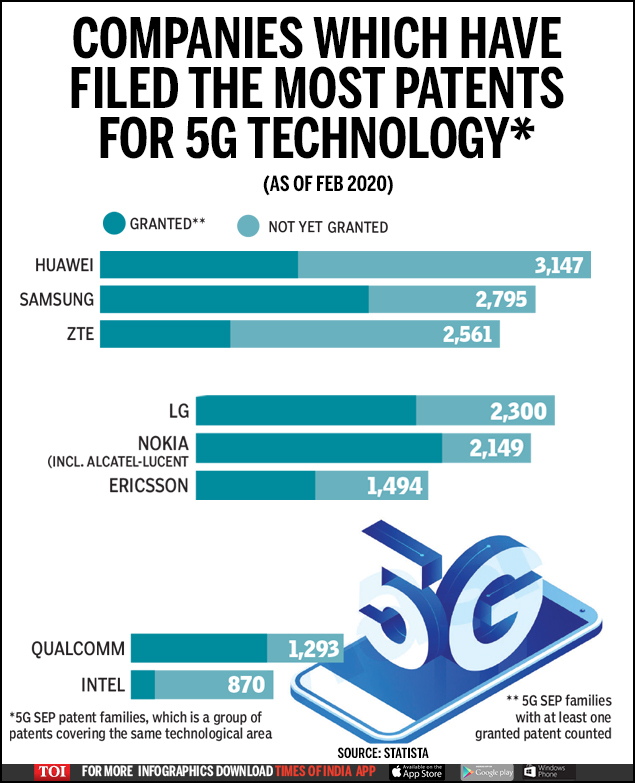
Conclusions:
Bloomberg believes that there may be some “bumps in the road” for 5G and other wireless patent owners. A Chinese court has issued an order that would limit InterDigital Inc.’s powers in a royalty spat with handset maker Xiaomi Corp., even though the legal fight is in India. And judges in Dusseldorf indicated they want the European Union’s top court to weigh in on the dispute between Nokia and Daimler, which could turn the tide against the former handset maker if the EU top judges side with the carmaker.
The concern is that if there isn’t enough money for patent owners, they won’t work together to develop a single system that can be used for anyone. Too much money, though, means manufacturers will increase their prices or opt to pass on using the latest technology, said Mauricio Uribe, a patent lawyer with Knobbe Martens in Seattle. “Neither extreme is good for consumers,” he said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
FCC increases 3.45-3.55 GHz spectrum for 5G and local wireless services
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has approved the release of more mid-band spectrum for mobile broadband services. An additional 100 MHz in the 3.45-3.55 GHz range will be made available for 5G services, while 50 MHz in the 4.9 GHz range will be available for state licensing of local wireless services.
The release of the 3.5 GHz spectrum remains subject to public consultation. If approved, the frequencies would be available for flexible-use service. The public review seeks comment on an appropriate regime to coordinate non-federal and federal use and proposes a band plan, as well as technical, licensing and competitive bidding rules for the band. Lastly, it seeks comment on details regarding the processes for relocating non-federal radiolocation operators to the 2.9-3.0 GHz band and sunsetting amateur use in the 3.3-3.5 GHz band.
Today’s FCC announcement follows last month’s by the White House and Department of Defense (DoD) that 100 megahertz of contiguous mid-band spectrum would be made available in the 3450-3550 MHz band for 5G commercial use while simultaneously minimizing impact to DoD operations.
With this 3.45 GHz band item, the upcoming December C-band auction of 280 megahertz of spectrum, and the recently completed auction for Priority Access Licenses in the 3.5 GHz band, the Commission is on track to make a wide swath of 530 megahertz of continuous mid-band spectrum available for 5G. Combined with the Commission’s work to make low- and high-band spectrum available for flexible use as well as its successful efforts to expedite the deployment of wireless infrastructure and fibe Federal Communications Commission r, the FCC is establishing a strong foundation for wireless innovation and investment and helping the United States lead the world in 5G.
The additional spectrum for 5G is made possible by an agreement earlier this year with the Department of Defense to vacate the 3.45-3.55 GHz range. This adds to the 3.55-3.65 GHz range just auctioned and the 3.7-3.98 GHz band planned for the FCC December auction.
The FCC said the latest announcement means that a total of 530 MHz in the range 3.45-3.98 GHz is set for release for 5G services.

Under the new rules for the 4940-4990 MHz frequency range, states are allowed to lease this spectrum to third parties to boost wireless broadband, improve critical infrastructure monitoring, and facilitate public safety use cases. The frequencies are currently designated for public safety use, but are rarely used, and the FCC is hoping the new rules will increase applications of the spectrum.
The rules adopted establish a framework for states to allow new partnerships with electric utilities, AT&T FirstNet and commercial operators to increase usage of this spectrum, while protecting existing public safety operations. The wider possibilities are expected also to contribute to more equipment for the band being developed, a problem that has limited the spectrum’s use to date.
References:
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-367236A1.pdf
https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-seeks-facilitate-5g-345-355-ghz-band
Media Contact:
Cecilia Sulhoff at (202) 418-0587, email: [email protected]
5G launch in Israel with 3 network operators awarded licenses; fiber optic programs of 2 others are approved
Israeli Communications Minister Yoaz Hendel has announced that Partner Communications, Pelephone and Hot Mobile have been awarded licences to operate 5G communications networks in the country, Globes reported. It would appear that Pelephone, Partner and Hot Mobile will receive the full grant since they finished setting up the first 250 cellular sites in the third quarter. Those who did not receive the license to operate the 5G network this morning are the last group in the tender, which includes Cellcom, Golan Telecom and Expon.
Hendel said it was important to award the licenses quickly so that 5G services could begin as soon as possible. The minister said that Israel was going through a difficult period, and that it was good that there were some hopeful signs of progress and growth. He also said that his ministry would put an emphasis on transparency on 5G coverage as well as on other matters. Hendel will extend the work of the frequencies’ committee to award more frequencies to be used for 5G networks.
- Pelephone CEO Ran Guron said that his company’s subscribers would be able to receive 5G services immediately in 150 towns and cities in Israel.
- Partner CEO Itzik Benbenishti said that today’s announcement was very significant news for all Partner’s subscribers, especially at the beginning of the new year in the Jewish calendar.
- Hot Mobile CEO Ilan Brook said that his company was very excited, and that from today the company’s subscribers, both business and private, would be able to benefit from 5G services.
Pelephone claims that “hundreds of sites” have been deployed in about 150 cities and localities, including: Tel Aviv, Haifa and the Krayot, Raanana, Dimona, Kiryat Shmona and more. According to the company, there is at least one mobile site that supports 5G in every city and locality in the country. Therefore, even if you have a smartphone that supports 5G, it is not certain that you will be able to find the few sites that have been established in all of Israel.
In contrast to Pelephone and Partner, which announced that all their customers who own supported 5G mobile devices will be able to use the new network at no extra charge, Hot Mobile asked its customers who want to join the 5G network to join the company’s new 5G subscriber programs (TBD).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Two other important telecom events in Israel are the entry of HOT Telecommunication Systems Ltd. into the fiber-optic venture IBC (Israel Broadband Company), and government approval for Bezeq Israeli Telecommunication Co. Ltd.’s fiber-optic program. Earlier in September, Bezeq said it would invest billions of shekels in the coming years to accelerate deployment of a nationwide fiber optics network, with connections to ultra-fast Internet to begin in a few weeks.
These two events, together with the award of 5G licenses in the mobile market and the forthcoming abolition of the split in the Internet market between infrastructure and service provision, set out new borderlines for the Israeli telecommunications market. The main aim is to narrow the gap between Israel and the rest of the world when it comes to (Internet/web) surfing speed. This will facilitate the development of digital services and greater innovation in the economy.
The Hot-IBC deal would never have happened were it not for the approval given to Bezeq’s fiber-optic proposal, and even more so were it not for the failure of the deal whereby Hot was to have acquired Partner. The aim of that deal was to overcome Hot’s difficulty (some would say its owner’s refusal) to enter on investment in a fiber-optic project without partners.
However you look at it, Hot has become a strange sort of telecommunications company, with no infrastructure that it owns outright. An unnatural hybrid has been created here, the result of continual regulatory distortions together with an owner, Patrick Drahi, who has utterly despaired of the local regulators. As a result, he has decided to invest the bare minimum in Israel, and to concentrate his main efforts on the rest of the world. Ultimately, Hot accounts for only a small fraction of the global business of Drahi’s Altice, so that there is a limit to the resources that can be devoted to it.
Bezeq finds itself where it likes to be. It comes to life when it has a big infrastructure project before it. After many delays, crises, and disputes with the Ministry of Communications, the company is back to dealing with such a project. The question is whether it was right to wait for all the conditions to mature, or whether it should have embarked on the project earlier.
The implication is that State of Israel has lagged behind in the field of telecom infrastructure for more than three decades. Perez wrote that “Israel has deteriorated by all measures of telecommunications efficiency, and important reforms have not been made, because of the regulator’s desire to punish Bezeq for past sins.”
References:
https://en.globes.co.il/en/article-pelephone-partner-hot-mobile-receive-5g-licenses-1001343883
https://en.globes.co.il/en/article-Israel-narrows-the-telecoms-gap-1001344146
AT&T Deploys Dis-Aggregated Core Router White Box with DriveNets Network Cloud software
AT&T today announced that Israeli start-up DriveNets is providing its software-based, disaggregated core routing solution for the carrier’s IP-MPLS backbone network. AT&T also said it had deployed its “next gen long haul 400G optical transport platform, giving AT&T the network infrastructure needed to transport the tsunami of demand that will be generated by 5G, fiber-based broadband and entertainment content services in the years ahead.” [Long haul is for distances >= 600km. AT&T did not name its 40G optical transport equipment vendor]
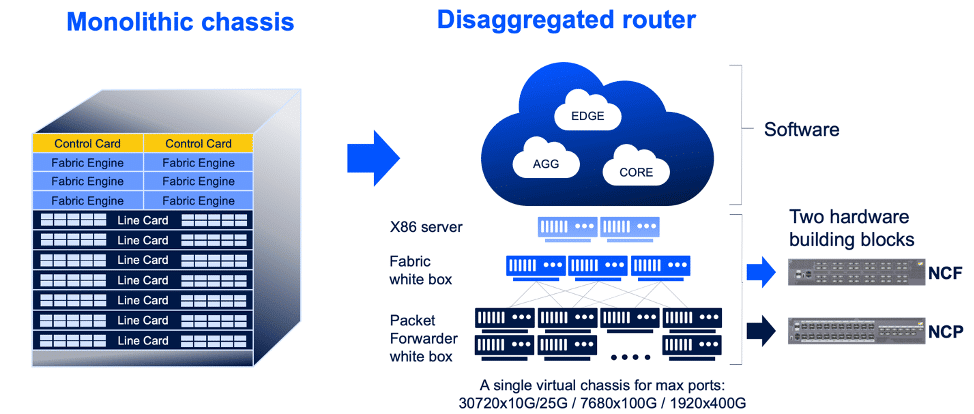
DriveNets says their Network Cloud solution perfectly fits the vision of AT&T and other leading service providers and cloud hyper-scalers for the evolution of the network to be open, agile, cost effective and software based. DriveNets Network Cloud is cloud-native software (not open source software). It’s a software solution which runs over a cluster of low-cost white box routers and compute servers. It has its own Network Operating System (NOS) and turns the physical network into a shared resource supporting multiple network services in the most efficient way.
Indeed, Network Cloud runs on standard white boxes built by ODM partners like UfiSpace who provided the white boxes to AT&T, based on the Jericho2 chipset from Broadcom. This approach creates a new economic model for the networking industry, lowering cost per bit and improving network profitability.
“We’re thrilled about this opportunity to work with AT&T on their next gen core network, and proud of our engineers for meeting AT&T’s rigorous certification process that field-prove the quality of our solution,” said Ido Susan, CEO of DriveNets. “This announcement demonstrates to those who questioned the disaggregated network model that our Network Cloud is more scalable and cost-efficient than traditional hardware-centric routers. DriveNets is transforming the network in the same way that VMware transformed the compute and storage industry” he added.
“I’m proud to announce today that we have now deployed a next gen IP/MPLS core routing platform into our production network based on the open hardware designs we submitted to OCP last fall,” said Andre Fuetsch, AT&T’s CTO of Network Services, in his keynote speech at the Open Networking and Edge Summit (ONES). “We chose DriveNets, a disruptive supplier, to provide the Network Operating System (NOS) software for this core use case.”
One year ago, AT&T contributed an open source specification for a distributed disaggregated chassis (DDC)to the Open Compute Project (OCP). The DDC was intended to define a standard set of configurable building blocks to construct service provider-class routers, ranging from single line card systems, a.k.a. “pizza boxes,” to large, disaggregated chassis clusters. It is a a white box design based on Broadcom’s Jericho2 silicon. AT&T said the Jericho2 chip set provide the density, scale and features needed to support the requirements of a service provider.
The white box hardware was designed and manufactured by Taiwan based UfiSpace. It consists of three components: a 40x100G line card system, 10x400G line card system, and a 48x400G fabric system. These building blocks can be deployed in various configurations to build routers with capacity anywhere between 4 Tbps to 192 Tbps.
DriveNets Network Cloud solution and its innovative Network Operating System (NOS) software is NOT open source/open networking. It provides the management and control of the white box hardware. It supports a sophisticated set of traffic engineering features that enable highly reliable and efficient MPLS transport for our global, multi-service core backbone. The software then connects into AT&T’s centralized SDN controller that optimizes the routing of traffic across the core.
DriveNets Network Cloud offers extreme capacity and scale for networking service providers and cloud hyperscalers, supporting small to largest core, aggregation and peering network services. DriveNets Network Cloud runs over scalable physical clusters ranging from 4 Tbps (single box) to 768 Tbps (large cluster of 192 boxes), acting as a single router entity. This model is designed to offer both network scaling flexibility, similar to cloud architectures, as well as the ability to add new service offerings and scale them efficiently across the entire network.
“We are pleased to see the broad adoption of Jericho2 products across the networking industry combined with the innovative DriveNets Network Cloud software,” said Ram Velaga, senior vice president and general manager, Core Switching Group, Broadcom. “AT&T’s submission of the Distributed Disaggregation Chassis white box architecture based on Jericho2 is making a big impact on driving the networking industry forward,” he added.
“UfiSpace has been among the first who committed to opening the networking model, starting with our disaggregated cell site gateway routers which we have already demonstrated with AT&T at the Open Networking Summit (ONS) last April.” said Vincent Ho, CEO UfiSpace. “We are proud that AT&T’s core routing platform will utilize our white box solution where we can take part in the largest live Dis-Aggregated network in the world.”
In an email to Light Reading, Drivenets’ Mr. Susan wrote: “This is the largest backbone network in the U.S. and DriveNets Network Cloud is deployed across the entire network, running over multiple large white box clusters in many core and aggregation locations of the AT&T network. Each one of these large clusters contains 192 white boxes from UfiSpace. The DriveNets Network Cloud Network Operating System (NOS) turn these large clusters of 192 white boxes into a single router entity. These large router entities are deployed in many locations at the AT&T network.”
Performing as the best in class router when it comes to stability, reliability and availability, DriveNets Network Cloud is the largest router in the market today. DriveNets is engaged with 18 service providers and hyperscalers and is already on the path to becoming one of the leading networking vendors in the market. Last week, DriveNets announced lab testing of a 192Tbps distributed router by a European operator.
DriveNets Network Cloud created a new SaaS-based network economic model that detaches network growth from network cost, lowering cost per bit and improving network profitability. This disruptive business model assists service providers and cloud hyperscalers in reducing both network CapEx and OpEx.
“AT&T has a rigorous certification process that challenged my engineers to their limits, and we are delighted to take the project to the next level with deployment into the production network,” said Drivenets’ Susan.
Today’s white box with core routing software announcement is just the first of many from AT&T we may see in the near future. AT&T’s Fuetsch wrote in the press release, “In the coming weeks, we’ll announce additional software suppliers for other use cases operating on the same hardware, demonstrating the maturity of the eco-system and power of openness.”
Expect forthcoming AT&T white box related announcements to be on Provider Edge routers for which the carrier alluded to when releasing its DDC spec to the OCP.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2020/open_disaggregated_core_router.html
https://about.att.com/story/2019/open_compute_project.html
DriveNets Network Cloud: Fully disaggregated software solution that runs on white boxes
US, India, Japan, Australia to explore common approach to 5G with trusted vendors
The U.S., India, Japan and Australia are considering a common approach on 5G telecom technology, expanding their strategic cooperation under the framework of Quadrilateral coalition or “Quad,” which was primarily focused on the Indo-Pacific region.
Officials of the four countries discussed the issue at a virtual meeting of the ‘Quad’ on Friday. The announcement comes as a significant number of countries in Europe and elsewhere continue to permit Chinese telecommunications giant Huawei Technologies to operate in their countries, despite U.S. pressure to ban the telecom giant. Huawei has targeted India as a major market for its 5G technology.
Noting the importance of digital connectivity and secure networks, the officials discussed ways to promote the use of trusted vendors, particularly for 5G networks. They explored ways to enhance coordination on counterterrorism, maritime security, cyber security, and regional connectivity, as well as quality infrastructure based upon international best practices, such as the G20 Principles for Quality Infrastructure Investment. Participants also highlighted the need to improve supply chains in sectors including critical minerals, medical supplies, and pharmaceuticals.
The officials reaffirmed their countries’ strong support for ASEAN centrality and ASEAN-led regional architecture. They explored ways to work together in the Mekong sub-region, in the South China Sea, and across the Indo-Pacific to support international law, pluralism, regional stability, and post-pandemic recovery efforts. The four countries committed to continuing regular consultations, including at the senior officials’ and Ministerial levels.

Image Credit: ANI
India and Japan are already cooperating on the development of 5G technology.
“India and Japan have agreed to closely cooperate and develop the 5G and advanced technologies with US and Australia ramping up technological support. We are also taking help from Israel. There are discussions on within the government and our 5G policy will take a final shape in the coming days. But Japan will be a close partner nevertheless,” said an official involved in the discussions.
Cooperation was extensively discussed during the first foreign and defense ministerial dialogue between the two strategic partners in November last year.
People familiar with the issue said the proposed cooperation on 5G technology between India and Japan will be discussed at the annual India-Japan summit which is likely to take place by end of this year. The discussion on the 5G technology at the Quad meeting also reflected how serious the four countries have been on the issue, people familiar with the issue said.
In November 2017, the four countries formalized the long-pending proposal of setting up the “Quadrilateral” coalition or “Quad” to develop a new strategy to keep the critical sea routes in the Indo-Pacific free of any influence. However, the coalition is now expanding the sphere of their cooperation to other issues having geopolitical ramifications like 5G networks.
The anonymous sources said the issue of 5G technology is expected to figure prominently at a meeting of foreign ministers of the Quad member countries in Tokyo next month. The issue of “risks” posed by Chinese communication networks was discussed at a high-level meeting between India and the U.S. last year.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.state.gov/u-s-australia-india-japan-consultations-the-quad-3/
German Telecom Regulator awards 5G private network licenses in the 3.7GHz to 3.8GHz band
Germany’s telecommunications regulator Bundesnetzagentur (Federal Network Agency or BNetzA) announced earlier this week that it has awarded 74 licences to applicants for deploying private 5G networks (called “campus or local networks” in Germany, or “lokale Netze”) using 3.7GHz-to-3.8GHz spectrum. This more than doubled the 33 licences it had awarded as was announced in April.
According to the BNetzA press release, the regulator expected the frequencies to be primarily used for Industry 4.0, “but also in the agricultural and forestry sector,” Jochen Homann, President of BNetzA, said in the press release, “by awarding spectrum for local 5G networks, we are creating scope for innovation for enterprises. There has been a great amount of interest in the spectrum, and we are anticipating a large number of applications still to come,” he added.
Editor’s Notes:
- Private LTE and 5G networks can ensure guaranteed connectivity and privacy (e.g. safeguarding data), while supporting a wide range of applications and usage scenarios. Small-scale private LTE and 5G-ready networks are also beginning to be deployed in industrial IoT (Internet of Things) settings – where LTE and 5G can fulfill the stringent reliability, availability and low latency requirements for connectivity in industrial control and automation systems, besides supporting mobility for robotics and machines.
- The Bundesnetzagentur is an authority under the responsibility of the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy. Its core tasks include supervising the energy, telecommunications, postal and railway markets. As part of its mandate, the Bundesnetzagentur ensures that as many undertakings as possible can use the infrastructure in these sectors so that consumers benefit from competition and favourable prices. The authority employs over 2,900 people at its headquarters in Bonn and Mainz and its 46 regional offices.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In a separate document, BNetzA published a list of the names and addresses of 35 licensees. Presumably the other recipients have not granted the agency the permission to make their names public. There are system integrators (NTT DATA Deutschland GmbH), specialised engineering companies closer to core telecoms technologies (Rohde & Schwarz, Corning Services), car makers (Audi, Mercedes), broadcasters (Bayerischer Rundfunk), event company (Deutsche Messe AG which operates the Hannover trade fairs), etc.
Huawei – Germany, based in Düsseldorf, is also a recipient. It isn’t clear what the Chinese telecom network equipment maker will use the frequency for, but likely for 5G related R&D work.
There are a number of other companies that have publicly stated that they have bought spectrum for private 5G networks, but for whatever reasons their names did not appear on the BNetzA list. According to an earlier report by The Wall Street Journal, that group included car makers BMW and Volkswagen, the industrial conglomerate Robert Bosch GmbH, the chemistry company BASF, and the German airline Lufthansa.
Meanwhile BNetzA has just concluded the consultation process, started in July, on how best to make the 26GHz, specifically the 24.25 – 27.5 GHz, also available for “local 5G networks”. When this band is open to applications, BNetzA expects to see more active participation thanks to the high bandwidth this frequency can enable, especially from sectors like infrastructure development, Industry 4.0, and IoT.
On the other hand, when enterprises and public sector entities are actively building their own private 5G networks in countries where it’s permitted, one might question the 5G operators’ ambition to support business use cases with their public 5G networks, including the much hyped end-to-end network slicing capabilities which will only be achieved by a 5G SA core network.
Some network operators are building 5G private networks. Vodafone Deutschland for example has been working with Lufthansa Technik to build the 5G network at an aircraft hangar at Hamburg Airport. In most cases, mobile operators are entirely bypassed. Nokia said publicly that no operator was involved in its private 5G project for Deutsche Bahn, Germany’s national railway service.
By opening 5G frequencies to private bidders, BNetzA and its peers in countries like Japan and the UK are helping popularize 5G in the business world and expediate enterprises’ embrace of the new technology. However, the telecom operators that have made big 5G investment may not be the biggest or primary beneficiaries. This means those 5G network operators need to ask themselves some hard questions on how to strengthen their value propositions to their business customers, especially when the transition to 5G standalone mode is just now beginning.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
Ericsson on 5G Private Networks:
The next five to seven years will see an explosion of 5G private networks catering to different industry verticals like automotive, ports, mines, manufacturing and a plethora of mission-critical services. Ultra-high reliability, ultra-low latency, 99.999 percent availability, and very high security are some of the characteristics 5G private networks will be capable of.
What are private networks and why are they so important for Industry 4.0?
Private 4G networks have been around for years, but they’re still few and far between. However, with 5G’s sub-millisecond latency, ultra-high throughput, the business case for the proliferation of private 5G networks is expected to be more widespread. 3GPP calls them non-public networks or NPN, and are intended for the sole use of a private entity, be it a big enterprise or government. Use cases for such private networks are:
- Mission-critical functions like public safety and national security, emergency response and government systems
- Digitalization of industries like oil rigs, mining, retail, and so on
- Enabling an Industry 4.0 ecosystem. For example, smart manufacturing, warehouses, and autonomous fleet management
- Critical infrastructure like ports, airports, healthcare, and railways
References:
https://telecoms.com/506639/germany_likely_-to_-see_many_-private_5g_networks/
https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2020/7/5g-private-network-operations
Samsung introduces 5G mmWave small cell for indoor use with Verizon as 1st customer
Samsung Electronics unveiled a new integrated 5G mmWave small cell for indoor use as part of the company’s full suite of 5G in-building products, Samsung Link. Samsung said its new 5G indoor small cell dubbed “Link Cell” will help provide enhanced 5G experiences to users in indoor environments. It provides 5G-powered applications within enterprises, including manufacturing or distribution facilities, corporate offices, and entertainment or public venues (such as shopping centres, stadiums or hotels). Link Cell is among the first commercial products available globally that provides wireless operators with a mmWave indoor small cell. It includes the Qualcomm 5G RAN platform, which builds on the collaboration between Qualcomm Technologies and Samsung.
Durga Malladi, Senior Vice President and General Manager, 4G/5G, Qualcomm Technologies said:
“Small cells are an excellent vehicle to deliver the incredible speed, capacity and low latency benefits of 5G mmWave to indoor locations. We are very pleased to continue our long standing relationship with Samsung to support development of high-performance 5G small cell infrastructure that addresses the challenging power and size requirements for enterprise deployments, using Qualcomm Technologies’ 5G RAN Modem-RF technology.”
Link Cell gives wireless network operators a way to extend 5G service into businesses and venues. It’s also a critical component for future private 5G networks in enterprises, such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail and warehouse facilities. That’s a market segment AT&T wants to penetrate for its 5G services, including extending their 5G network indoors.

Photo Credit: Samsung Electronics
Verizon will be the first U.S. wireless network operator to commercially deploy Samsung’s Link Cell, which the wireless provider will use to extend the footprint of its 5G Ultra Wideband network. This marks a new phase in delivering enterprise private 5G networks, and advancing next generation mobile technology use cases and applications. Verizon recently said lab trials were underway with Samsung to test the product, along with field tests of an in-building 5G cell site from Corning.
The first version of Samsung’s Link Cell will support 28GHz and has the functionality to combine four 100MHz bandwidth of frequencies, offering high capacity and ultra-fast download speeds. Moreover, it brings together a radio, antenna and digital unit into one compact box, and is less than 4 liters in volume, one of the smallest in the industry.
Link Cell offers fast and easy indoor installation; it can be discretely placed on walls or ceilings, similar to a Wi-Fi access point, while minimising noise through fanless convection cooling. Designed to self-organise, Link Cell will adjust for optimal RF performance, allowing mobile applications to operate within a facility or—as applications transition from a macro 5G network outside to the in-building network—maintain high-quality communications continuity. Link Cell is available now for wireless operators to purchase for use in commercial rollouts.
Commenting on the Link Cell, Jaeho Jeon, Executive Vice President and Head of R&D, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics, said:
“Today, we are excited to unveil Samsung Link for wireless operators to expand the capabilities of 5G networks and seamlessly link together outdoor and indoor 5G experiences. As one of the first commercial 5G mmWave indoor small cells, Link Cell will enable wireless operators and enterprises to bring 5G services to various offices, facilities and venue locations.”
“Verizon continues to rapidly advance our 5G deployment, and the addition of indoor cell sites will extend the availability of the fastest 5G service in the U.S. This is a key step in providing industry-changing, scalable, latency-sensitive, robust 5G solutions for enterprises,” said Adam Koeppe, senior vice president of Technology Planning and Development at Verizon, in a statement. “The addition of indoor cell sites will extend the availability of the fastest 5G service in the U.S,” he added.
Verizon was the first to deploy Samsung’s 5G NR integrated mmWave access unit, which helped hit 4.2 Gbps speeds during a live network demo in February. Samsung is also working with Verizon on network virtualization, providing its commercial 5G vRAN solution. That might be part of the $6.65B contract Samsung recently was awarded by Verizon.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The new Samsung Link portfolio features several products to help businesses address indoor 5G service needs. In addition to Link Cell, Samsung will deliver products supporting other indoor needs and spectrums. Link Hub and Link HubPro provide low and mid-band support to operators and enterprises.
Link Hub is designed for venues with existing Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS), providing low and mid-band 5G service across an existing in-building infrastructure. Link HubPro is an active antenna system, which includes a hub and indoor radios for mid-to-large enterprises with support for various spectrum options. Link Hub and Link HubPro are expected to begin commercial rollouts beginning 1Q 2021.
References:
https://news.samsung.com/us/5g-indoor-mmwave-small-cell/
https://www.neowin.net/news/samsung-reveals-its-indoor-5g-small-cell-solution/
https://www.fiercewireless.com/tech/samsung-debuts-indoor-5g-mmwave-small-cell
AT&T plans to deploy 5G SA this year; “cloud native” 5G core benefits, assessment and status
Status of AT&T 5G SA:
Speaking Tuesday at the Big 5G Event hosted by Light Reading, Yigal Elbaz, SVP of wireless and access technology at AT&T said that its 5G+ mmWave network has been deployed in 35 cities (densely populated, campuses, etc) and AT&T will continue to expand beyond those cities.
‘The new (transformational) 5G architecture being introduced is a cloud native architecture and software for the 5G core and RAN. We’re moving to a disaggregated and open architecture which will allow AT&T to introduce additional players in the ecosystem and drive further innovations. These capabilities manifest themselves in 5G Stand Alone (SA) core.”
5G SA core brings many benefits, through a true end to end 5G network. This is achieved via a virtualized “cloud native 5G core network,” the implementation of which has not been standardized .[1] or even completely specified in 3GPP Release 16.
Yigal said one important benefit of 5G SA core is network slicing, which supports different use cases and quality of experiences. A better way to optimize spectrum and increase 5G coverage [2.] are other important benefits. Most importantly, is the ability to introduce agility and capabilities of iterating development and pushing software, in the same way it was introduced in IP based network systems.
Note 1. Because there is no standard for implementing a 5G SAcore, every 5G SA network operator works with its 5G core vendors to agree on a detailed implementation specification which is then created as software, mostly running on “cloud native” compute servers.
Note 2. By decoupling 5G spectrum from the LTE network used in 5G NSA, 5G coverage area can be increased. Please see Note 3. for further drill down details.
Elbaz described AT&T’s move toward standalone 5G as an important evolutionary step. “Like anything else in 5G, this is a journey,” he explained. He said standalone 5G can support network slicing, improved latency (?) and improved coverage (by decoupling 5G spectrum from the LTE network used in 5G NSA as per the Note 3. below).
Yigal said that with 5G SA extended architecture, AT&T could now more easily extend the 5G network into the enterprise premises. AT&T has more than 3M enterprise customers of different sizes. With multi-access edge compute on prem, those enterprise customers could then have a cost effective 5G network that could keep sensitive data in house, yet still realize 5G benefits, like “low latency.” Vertical industry types for this hybrid inside/outside 5G network include: manufacturing, health care, robotics, military, education, and others.
Regarding the 5G SA core timeline, Elbaz said AT&T is currently developing and testing 5G Stand Alone (SA) operation now and will deploy it by the end of the year. He added that AT&T would work on “scaling” the technology throughout 2021.
Light Reading’s Phil Harvey tried to get Yigal to be more specific. He asked, “When will 5G SA from AT&T be deployed nationwide?”
Yigal replied, “You need to think about the complete capabilities of the ecosystem that needs to evolve. It’s not just the core….Everything needs to be in place to support the scale of 5G SA and supports the use cases that come with it.”
After repeating his remarks about the 5G SA timeline noted above, Yigal said they don’t have specific dates for 5G SA deployment as it is a “journey.”
AT&T did not disclose its standalone 5G core network vendors. Neither has Verizon (see below), which has hinted it would also deploy 5G SA by the end of 2020. [T-Mobile’s 5G core vendors are Cisco and Nokia; Dish Network recently said Nokia would supply its forthcoming 5G core; Rakuten is working with NEC for their 5G core; Reliance Jio says it’s doing its own 5G core].
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
From Ericsson – Standalone 5G facts:
- Target 5G network architecture option
- Simplified RAN and device architecture
- New cloud-native 5G Core
- Brings ultra-low latency (not true until 3GPP Release 16 URLLC for the core network and RAN are completed and tested)
- The only option to provide same 5G coverage for low band as legacy system
- Supports advanced network-slicing functions (and others like virtualization, orchestration, and automation)
Note 3.: Another benefit of 5G SA, noted by AT&T above is improved coverage. That is because the 5G spectrum used is decoupled from the LTE network that is required for 5G NSA. Thereby, that 5G spectrum may be used to reach areas outside of the LTE coverage area. T-Mobile plans to use their 5G SA 600MHz spectrum to achieve wider coverage than would be possible with 5G NSA. The catch is for the 5G only coverage areas there is no fallback to 4G LTE if something goes wrong.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In an August 25th press release, Verizon said:
“Instead of adding or upgrading single-purpose hardware, the move to a cloud-native, container-based virtualized architecture with standardized interfaces leads to greater flexibility, faster delivery of services, greater scalability, and improved cost efficiency in networks.”
“Virtualizing the entire network from the core to the edge has been a massive, multi-year redesign effort of our network architecture that simplifies and modernizes our entire network,” said Adam Koeppe, Senior Vice President of Technology and Planning for Verizon. “Verizon has been on the leading edge of virtualizing the core over the past few years and has been bullish in the design and development of open RAN technology, as well as in the testing of that technology with great success.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Samsung says the 5G core network is further leveraging the cloud concept by migrating to a cloud native core, in which network functions are modularized and containerized to enable highly flexible scaling and function lifecycle management. The cloud native core provides capabilities that allow the network to adapt to changing demands and support new services with minimal interactions required by operational teams. Samsung’s cloud native 5G core implementation includes the following types of software: microservices, containers and a container engine, stateless operation, intelligent orchestration, and efficient NFVi (NFV Infrastructure).
With its 5G core, network operators will be able to rapidly develop services, launch them on time, and adapt the network frequently according to market demands. Open source can accelerate this innovation by providing platform services with features commonly used by 5G core functions such as monitoring, database activities, and high availability related features.
Samsung collaborates with many operators and partners in efforts to create 5G core solutions and to expand the 5G ecosystems through active participation in the following organizations:
- Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), which leads the de-facto standard for cloud technology, and
- Open Network Automation Platform (ONAP), a telco-oriented open source project
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Other Voices on 5G SA:
Ericsson’s Peter Linder, head of 5G marketing in North America told RCR Wireless:
“When we accelerated the standard and said we can do 5G at the end of 2018 rather than the end of 2020, we did not have the ability then to do both core and radio at the same time. We said, ‘Let’s focus on doing all the radio stuff first in way that it’s as easy as we can possibly make it to connect into an existing EPC that’s upgraded with 5G capabilities.”
“The difference between EPC and 5G core is essentially an architectural difference and how you operate and execute around that,” Linder said. “When we looked at all the different migration options…we came to the conclusion that the only way you could secure a smooth evolution for service providers is to combine EPC and 5G core. The dual mode is essentially about giving the option of doing either EPC or 5G core or EPC and 5G core combined.” In that combined scenario, “You can cut and freeze the investment in the current physical and virtualized platforms. Over time you can start phasing out both physical and virtualized EPC and have everything supported by the 5G core.”
“The move from virtualized to cloud-native eliminates integration steps. People went through so much pain depending on which virtualization [solutions]they used on which hardware. Right now, moving toward cloud-native, that takes away a lot of that cost.” Another key factor Linder identified was OPE. With standalone, “The biggest thing that will have an impact on the total costs is the automation. You have to automate as much as you possibly can.”
Speaking on Arden Media’s “Will 5G Change the World?” podcast, Oracle’s John Lenns, vice president of product management, sized up the transition to 5G SA based on three types of network operators: early adopters, fast followers and the mass market. With early adopters (like T-Mobile US, AT&T, Verizon), “You’ll see some standalone architecture networks going live this calendar year.” The fast followers are “putting out requests for information to prepare themselves for issuing RFPs, and the mass market is still further out into the future.”
Lenns highlighted security and rapid security responsiveness and cost efficiencies both capital and operating. “From a capex perspective, they are looking for an efficient transition through virtualization to cloud-native. They don’t want to pay twice. From an opex perspective, they are recognizing that assembling this 5G solution…is a challenge. It’s not easy…The CSPs are looking for solutions that make that opex journey less expensive. How that manifests itself is they are looking for a solution that offer them efficiencies of deployment, more automation, more embedded test tools, more self-healing behavior.”
HPE’s VP and GM of Communications and Media Solutions Phil Mottram tied 5G core adoption to new service-based revenue opportunities. “Investing in a new 5G network before the revenue streams are there is a financial and technical challenge for many carriers, but… telcos can start deployments today and pay for the infrastructure as their revenue grows.”
Omdia (market research firm owned by Informa) expects that few commercial 5G SA core deployments of scale will take place this year. They expect COVID-19 to have delayed deployment timelines by as much as six months as most converged operators prioritized 4G capacity upgrades and fixed broadband investments given the unprecedented rise in home working during the pandemic, and some mobile carriers lowered or deferred capex to prepare for the potential financial shock of fewer net adds and much reduced roaming revenue.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/atandt-to-launch-standalone-5g-later-this-year/d/d-id/764109?
https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2019/7/standalone-and-non-standalone-5g-nr-two-5g-tracks
T-Mobile Announces “World’s 1st Nationwide Standalone 5G Network” (without a standard)
T-Mobile US: 5G SA Core network to be deployed 3Q-2020; cites 5G coverage advantage
Why It’s IMPORTANT: Telefonica, Rakuten MOU on Open RAN, 5G Core Network and OSS
EU Recommendations on very high capacity broadband network infrastructure and a joint approach to 5G rollouts
Summary:
On September 18th, the European Commission (EC) released a recommendation on how all 27 European Union (EU) member states could ensure a timely and more cost-effective way of deploying very high-capacity broadband connectivity infrastructure and develop a “joint approach” to 5G rollouts. The EC says that 5G is the most fundamental block of the digital transformation and an essential pillar of the recovery.
The EC says “the timely deployment of 5G networks will offer significant economic opportunities for the years to come, as a crucial asset for European competitiveness, sustainability and a major enabler for future digital services.”
The EC’s joint approach to 5G is by means of a “toolbox” that defines best practices, including “realistic measures” to assign radio spectrum for 5G networks under investment-friendly conditions. The Commission aims to facilitate the deployment of very high capacity fixed and wireless networks “by, for example, removing unnecessary administrative hurdles and streamlining permit granting procedure.”
The objective is to agree on a toolbox by March 30, 2021. The commission has requested each member state provide it with a roadmap for implementation by April 30, 2021, reporting back by the same date the following year. Please refer to detail timeline in Next steps below.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In parallel, and closely linked to this Recommendation, the Commission proposed a new Regulation for the European High Performance Computing Joint Undertaking to maintain and advance Europe’s leading role in supercomputing technology to underpin the entire digital strategy and to ensure the Union’s competitiveness in the global setting.
The commission said the proposal “would enable an investment of €8 billion in the next generation of supercomputers – a substantially larger budget compared to the current one.” The EC noted that the COVID-19 crisis “has shown that connectivity is essential for people and businesses,” and that “very high capacity networks” have been enabling remote working and schooling, healthcare, and personal communication and entertainment. The EC said the pandemic “has changed the economic outlook for the years to come. Investment and reforms are needed more than ever to ensure convergence and a balanced, forward-looking and sustainable economic recovery.”

Executive Vice-President for a Europe fit for the Digital Age, Margrethe Vestager, said:
“Broadband and 5G connectivity lay the foundation for the green and digital transformation of the economy, regardless if we talk about transport and energy, healthcare and education, or manufacturing and agriculture. And we have seen the current crisis highlight the importance of access to very high-speed internet for businesses, public services and citizens, but also to accelerate the pace towards 5G. We must therefore work together towards fast network rollout without any further delays.”
Commissioner for the Internal Market, Thierry Breton, added:
“Digital infrastructures have proven to be crucial during the pandemic to help citizens, public services and businesses get through the crisis and yet recent investments have slowed down. At a time when access to broadband Internet represents both a fundamental commodity for Europeans and a geostrategic stake for companies, we must – together with Member States – enable and accelerate the rollout of secure fibre and 5G networks. Greater connectivity will not only contribute to creating jobs, boosting sustainable growth and modernising the European economy, it will help Europe building its resilience and achieve its technological autonomy.”
The Commission invites Member States to come together to develop, by 30 March 2021, a common approach, in the form of a toolbox of best practices, for the timely rollout of fixed and mobile very high-capacity networks, including 5G networks. Such measures should aim to:
- Reduce the cost and increase the speed of deployment of very high capacity networks, notably by removing unnecessary administrative hurdles;
- Provide timely access to 5G radio spectrum and encourage operators’ investments in expanding network infrastructure;
- Establish more cross-border coordination for radio spectrum assignments, to support innovative 5G services, particularly in the industry and transport fields.
The Recommendation also sets out guidance for best practices to provide timely access to radio spectrum for 5G as well as ensure stronger coordination of spectrum assignment for 5G cross-border applications. This is particularly important to enable connected and automated mobility, as well as the digitisation of industry and smart factories. Enhanced cross-border coordination will help to provide Europe’s main transport paths, particularly road, rail and in-land waterways, with uninterrupted 5G coverage by 2025. However, until mid-September 2020, Member States (and the UK) had assigned on average only 27.5% of the 5G pioneer bands. It is therefore essential that Member States avoid or minimise any delays in granting access to radio spectrum to ensure timely deployment of 5G.
The Recommendation also highlights the need to ensure that 5G networks are secure and resilient. Member States have worked together with the Commission and the EU Cybersecurity Agency (ENISA) on a respective toolbox of mitigating measures and plans, designed to address effectively major risks to 5G networks. In July, a progress report was published.
Sustainable network deployment for improved connectivity:
The Recommendation also builds upon the Broadband Cost Reduction Directive. It promotes the rollout of high-speed networks by reducing deployment costs through harmonised measures to ensure network providers and operators can share infrastructure, coordinate civil works and obtain the necessary permits for deployment. The Recommendation is calling on Member States to share and agree on best practices under this Directive, to:
- Support simpler and more transparent permit-granting procedures for civil works;
- Improve transparency on existing physical infrastructure, so that operators can access more easily all relevant information on the infrastructure available in a certain area, and facilitate permit-granting procedures, through a single information point in the administration of public authorities;
- Expand network operators’ rights to access existing infrastructure controlled by public sector bodies (i.e. buildings, street lamps and those belonging to energy and other utilities) to install elements for network deployment;
- Improve the effectiveness of the dispute resolution mechanism related to infrastructure access.
Improved connectivity can also minimise the climate impact of data transmission and thus contribute to achieving the Union’s climate targets. Member States are encouraged to develop criteria for assessing the environmental impact of future networks and provide incentives to operators to deploy environmentally sustainable networks.
Next steps:
The Recommendation calls for Member States to identify and share best practices for the Toolbox by 20 December 2020. The Member States should agree on the list of best practices by 30 March 2021.
As announced in its strategy “Shaping Europe’s digital future” in February, the Commission plans two further actions in this area:
- The update of its action plan on 5G and 6G in 2021. The updated plan will rely and expand on the spectrum-related actions in this Recommendation. It will look at the progress made so far, and set new, ambitious goals for 5G network roll-out.
- The revision of the Broadband Cost Reduction Directive. The next steps in this process are the launch of an open consultation in autumn 2020 and of a dedicated study to evaluate the current Directive and assess the impact of several policy options.
The Recommendation will contribute to the achievement of the objectives set out in the Broadband Cost Reduction Directive as well as the European Electronic Communications Code. The Code, which needs to be implemented into national law in Member States by 21 December 2020, aims to promote connectivity and access to very high-capacity networks by all citizens and businesses.
The Commission’s strategy on Connectivity for a European Gigabit Society sets the EU’s connectivity objectives. By 2025, all main socio-economic drivers (i.e. schools, hospitals, transport hubs) should have gigabit connectivity, all urban areas and major terrestrial transport paths should be connected with uninterrupted 5G coverage, and all European households should have access to connectivity offering at least 100 Mbps upgradable to Gigabit speeds.
Other EU Projects and Country Plans:
As announced in June 2020, the EU is funding 11 new technology and trial projects to enable 5G connectivity and pave the way for autonomous driving on main road, train and maritime routes in Europe.
Individual EU member states are also grappling with their own post-pandemic recovery plans. For example, France is earmarking €240 million ($284 million) for fiber networks as part of its €100 billion ($118 billion) stimulus package.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_20_1603
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ec-pins-recovery-hopes-on-5g-and-supercomputing/d/d-id/764064?
ITU-R work in progress: Providing enhanced mobile broadband services to remote sparsely populated and underserved areas
Editor’s Note: This is an excerpt of an ITU-R working document, subject to significant revision(s). It has no official status and has NOT been approved by ITU-R WP5D. ITU TIES account holders may access the document on the ITU-R WP 5D website as an October 2020 meeting contribution .
ATDI proposes to insert text (not included here) at Section 4 ‘Solutions that support remote sparsely populated areas providing high data rate coverage’ of the Draft Working Document.
Why this is an important topic:
Many people in developing countries like India live in villages or rural areas. In most cases they have little or no mobile broadband coverage.
In the U.S., the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) estimates that 26.4% of rural America, or 16.9 million people, lack access to a broadband connection of 25Mbps downstream/3Mbps upstream. This has been proven to be a highly conservative estimate because of the way the FCC collects broadband data. More accurate studies suggest the FCC’s estimates could be off by upwards of 50%. A 2017 study by Microsoft, for instance, found that half of all Americans, or 162.8 million people, lack access to broadband. Also, many wireless telcos are hesitant to roll out mobile broadband to rural America because of a perceived lack of return on investment.
According to data from the FCC, 39% of people living in rural areas in the United States lack access to high-speed broadband, compared with just 4% of urban Americans.
In addition to using IMT 4G/5G for mobile communications (discussed in the draft report below), 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) will make a significant impact on global markets, both developing and developed. In the U.S., sparsely populated, rural areas currently lag far behind metro area cities in broadband access. As there is no standard for 5G FWA, it will likely be based on the enhanced Mobile Broadband use case for IMT 2020, or proprietary versions of IEEE 802.11ax (WiFi 6).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Introduction:
On a global basis, the total number of mobile subscriptions was around 8 billion in Q3 2019, with 61 million subscriptions added during the quarter, the mobile subscription penetration is at 104 percent. There are 5.9 billion unique mobile subscribers using mobile networks, while 1.8 billion people remain unconnected. In year 2025 it is forecasted to be 2.6 billion 5G subscriptions and 8.6 billion mobile subscriptions globally at a penetration level of about 110%1. In year 2025 there may be up to 6.8 billion unique mobile subscribers using mobile networks, while 1.5 billion people remain unconnected, many of whom are below the age of nine.
The prospect of providing mobile and home broadband services for most of the 1.5 billion unconnected people, living in such underserved rural areas, is largely related to techno-economic circumstances.
This Report provides details on scenarios associated with the provisioning of enhanced mobile broadband services to remote sparsely populated and underserved areas with a discussion on enhancements of user and network equipment.
1 Ericsson Mobility Report, November 2019, mobile broadband includes radio access technologies HSPA (3G), LTE (4G), 5G, CDMA2000 EV-DO, TD-SCDMA and Mobile WiMAX.
Background:
Deploying networks in remote areas is normally more expensive, and at the same time, expected revenues are lower in comparison with deployments in populated areas. A further reason for not being incentivized to deploy new IMT broadband (e.g. IMT-2020/5G) Base Stations (BS) in these areas is the expected number of new BS sites. Therefore, the total economic incentives to deploy traditional networks in sparsely populated areas are consequently narrowed.
The competition model, applying to densely populated areas, is normally not providing rural coverage expansion at a speed that society wish. Connectivity in underserved remote areas is important to national policy makers facing needs of consumers, to service providers for reasons of branding, and to satisfy regulatory conditions in countries.
When expanding coverage in remote areas, it may imply an undesirable local monopoly, suggesting that only one service provider would expand in to such a remote area due to a low consumer base.
Rural coverage might in the future be driven by the need for national security and public safety connectivity, intelligent traffic systems, internet of things, industry automation and end users need for home broadband services as an alternative to fiber connections. In order to fulfil the needs of rural coverage, it is a matter of urgency to identify viable solutions for mobile and home broadband services.
Solutions that support remote sparsely populated areas providing high data rate coverage:
Possible technical solutions to achieve both extended coverage as well as high capacity in remote areas could be to use dual frequency bands at the same time, one lower band for the uplink (UL) and one higher band for the downlink (DL), in aggregated configurations.
Combining spectrum bands in the mid-band range and the low-band range on an existing grid can provide extended capacity compared to a network only using the low-band range.
An alternative technical solution to provide extended coverage in a remote area using a reduced number of terrestrial BS sites, aiming to bringing cost down, requires careful selection of proper locations and technical characteristics compared to configurations of suburban networks. Realizing such extended network configuration for coverage, several considerations need to be taken into account, both at a BS site and at customer premises. Considerations of accommodating BSs on high towers in sparsely populated areas could be further studied. Such opportunities rest with traditionally high tower used for analogue or digital television with an average inter-site distance (ISD) of the order of 60 km to 80 km designed to provide blanket coverage of national terrestrial television services.
Other sections of this report:
- Analyzing configurations for an IMT broadband network operating in dual bands
Combining spectrum bands in the mid-band range 3.5 GHz and the low-band range, e.g. 600 MHz, 700 MHz or 800 MHz, on an existing grid can provide extended capacity compared to a network only using the low-band range. The reason being that the mid-band range offer access to more spectrum bandwidth, and the low-band range combined, can provide the coverage for cell edge users in a unified manner.
- Analyzing configurations for an IMT broadband network operating only in the band 3.5 GHz
In underserved remote areas, the DL capacity performance can be significantly improved by using the band 3.5 GHz whilst the UL coverage is representing the bottleneck in attempts of satisfying needs for coverage. With potential upgrades of BS and consumer premises UE configurations, the feasibility of providing improved remote area coverage is considered by using only the band 3.5 GHz.
References:
ITU-R Report: Terrestrial IMT for remote sparsely populated areas providing high data rate coverage


