Bharti Airtel working with partners to enable 5G use cases in India
Bharti Airtel said that it is engaging new partners to enable 5G use cases for various consumer and enterprise use cases in India. It will also start a campaign to educate users about their next 5G smartphone to ensure if they can get the best experience with support to all relevant bands.
A handset to support all possibilities of 5G is very important, Bharti Airtel’s chief technology officer Randeep Sekhon told ET. Airtel will come out with a campaign for users who want to buy 5G handsets informing them about various checks of their particular handsets to make sure the handset works well in India across not just 5G but various other bands and carrier aggregation. “This is important when you choose a 5G handset to get the best experience,” he said.
The Sunil Mittal-led telecom operator had recently urged the India Department of Telecommunications to bring uniform guidelines to develop the 5G smartphone ecosystem. It recommended that any new 5G handset sold in India must support all existing bands in India for 5G, including the mmWave bands.
Indian telecom operators have spectrum in the 2G, 3G and 4G bands which can be refarmed and used for 5G NSA or 5G SA and also use Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) for fast deployment. They want handset brands to support all existing spectrum bands like 1800/2100/2300 MHz and sub-GHz bands 800/900 Mhz.
The telecom operator said that it successfully conducted a cloud gaming session on its 5G trial network in Manesar using the 3.5GHz spectrum band. Sekhon said that “immersive entertainment” will be another major consumer use case of 5G. “But, for A/R and V/R, content needs to be created and be personalized at the edge. We are seeing how we can make it real.”
Airtel is currently using the 3.5 GHz spectrum band for 5G trials in Delhi-NCR and Mumbai. Sekhon said that the telco hasn’t started 5G trials using mmwave band. “As and when we will get equipment, we will try that too. 3.5 GHz anchored with traditional 4G bands are currently being used for trials.”
“For the B2B, industry 4.0, high speed, high latency and mass concurrency around IoT cloud and 5G are required.. We are working with many of our industry customers on creating fir infra, FMCG, factory, mining. This will be relevant,” Sekhon added.
The CTO said that telecom operators can’t do everything by themselves and their main focus is to build the best infrastructure to enable partners. Airtel, he said, will have various partners to enable 5G use cases like education, e health and for industries.
“Some partnerships are for initial 5G trials and some will for massifying the roll out. The 5G real experience will happen when all stakeholders ecosystem partners are available,” Sekhon said.

Dell’Oro Group increases Open RAN radio and baseband revenue forecast
Dell’Oro Group has revised their Open RAN radio and baseband forecast. Total cumulative Open RAN revenues are now projected to approach $10B to $15B between 2020 and 2025.
“The momentum with both commercial deployments and the broader Open RAN movement continued to improve during 1H21, bolstering the thesis that Open RAN is here to stay,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President and analyst with the Dell’Oro Group. “We are adjusting the forecast upward to reflect the higher baseline and the improved pipeline,” continued Pongratz.
Additional highlights from the Dell’Oro Group Open RAN Advanced Research Report:
- Open RAN revenues are expected to account for more than 10 percent of the overall RAN market by 2025, reflecting healthy traction in multiple regions with both basic and advanced radios.
- Open RAN Massive MIMO projections have been revised upward to reflect the improved competitive landscape and the improved market sentiment with upper mid-band Open RAN.
- The shift towards Virtualized RAN (V-RAN) is progressing at a slightly slower pace than Open RAN. Still, total V-RAN projections remain relatively unchanged, with V-RAN expected to approach $2 B to $3 B by 2025.
Separately, Stefan wrote:
The long-term open RAN vision is built on three key pillars including open interfaces, virtualized technologies and vendor neutral multi-vendor deployments. In addition to leading the industry toward open and interoperable interfaces, the long-term roadmap maximizes the use of COTS hardware and minimizes the reliance on proprietary hardware (O-RAN Alliance).
Taking into consideration that one of the primary objectives is to capture the overall movement toward open RAN and the fact that it will take some time to realize the broader vision, it is somewhat implied that there will be room for interpretation when it comes to capturing this movement and tracking the open RAN market.
And within each of these pillars, there will be various degrees of compliance. Multi-vendor deployments are often associated with mixing and matching baseband and radio suppliers. But when Mavenir introduced the term “True Open RAN,” it meant true mixing and matching across the board – they want to work with anyone with any component. If someone gives them a radio they should be able to integrate it with their software. And vice versa, if another supplier provides the software “True Open RAN” would enable them to make it work with their Massive MIMO radios.
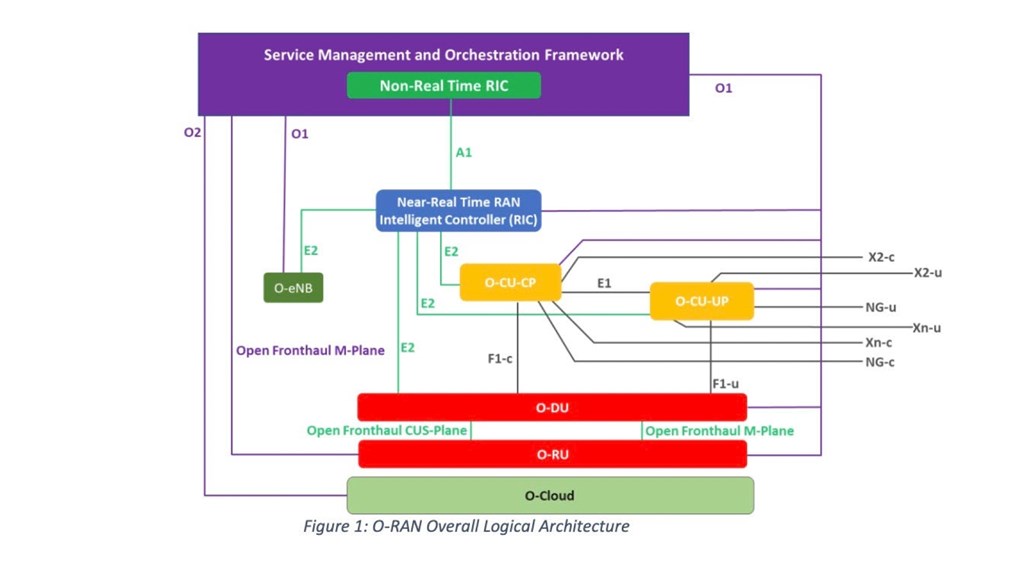
Not surprisingly, there is room for interpretation with the other building blocks as well. Open RAN compatible radios are now proliferating across the supplier landscape. But it is not always clear after browsing the data sheets what this entails from an open RAN specifications, customization and coverage perspective. With five interfaces (A1, E2, O1, O2, Open FH), multiple functions (SMO, Non-Real time RIC, Near-Real-Time RIC), and a confluence of profiles, there is not an abundance of confidence that the open RAN maturity would be consistent across the board.
The Dell’Oro Group Open RAN Advanced Research Report offers an overview of the Open RAN and Virtualized RAN potential with a 5-year forecast for various Open RAN segments including macro and small cell, regions, and baseband/radio. The report also includes projections for virtualized RAN along with a discussion about the vision, the ecosystem, the market potential, and the risks.
To purchase this report, please contact [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Rebuttal: Open RAN Forecasts Way too High!
While not a market analyst cranking out forecasts, this author believes the Open RAN market will be a huge disappointment and revenues will be much lower than Dell’Oro and other market research firms forecast.
As Light Reading has correctly said, Open RAN is trading one type of vendor lock-in for another.

Trading one version of vendor ‘lock-in’ for another? Image Credit: Light Reading
That’s because the O-RAN Alliance specs have not led to vendor neutral interoperability, but rather partnerships amongst vendors to provide a complete Open RAN solution.
O-RAN Alliance Threatened:
The O-RAN Alliance is in a crisis because of U.S. sanctions against Chinese vendors in the group has troubled Nokia and Ericsson. In particular, the recent addition to the American “entity list” of three Chinese members of the Alliance. Kindroid, a semiconductor company, Phytium, a supercomputing company, and Inspur, a compute server vendor, have been accused of working with the Chinese military, and have joined 260 other Chinese companies, including, Huawei, on the entity list.
A few days after Nokia decided to suspend its technical activity with the O-RAN Alliance, in fear of American punishment over its engagement at the forum with companies recently put on the American “entity list,” Ericsson expressed similar concerns.
It should not be a surprise that, given O-RAN Alliance’s legacy (born out of a merger of the American-led xRAN Forum and the Chinese-led C-RAN Alliance), there are a strong Chinese contingency. According to Strand Consult, by the end of 2020, 44 of the 200 odd Alliance members are companies from China. Also of concern is this post by Mr. Strand, What NTIA won’t tell the FCC about OpenRAN.
References:
Open RAN Forecast Revised Upward, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.fiercewireless.com/tech/not-all-open-ran-same-industry-voices-pongratz
https://techblog.comsoc.org/?q=Open%20RAN#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=Open%20RAN&gsc.page=1
https://techblog.comsoc.org/?q=Open%20RAN#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=Open%20RAN&gsc.page=2
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2020/12/04/omdia-and-delloro-group-increase-open-ran-forecasts/
Ericsson and Vodafone deploy new energy-efficient, light 5G radio in London
This week, Ericsson installed a new antenna-integrated radio solution (AIR 3227) on the roof of Speechmark, Vodafone UK’s central London office that, according to the telecom vendor, reduced the site’s daily network energy consumption by an average of 43% in direct comparison to previous generations of radio technology, and as much as 55% at off-peak times.
Designed for future-proof and sustainable networks, Ericsson’s new radio is 51 percent lighter than existing radio’s [1.] and its more compact design and improved energy management features will help to optimize overall site footprint, making 5G rollout and 4G upgrades faster and easier.
Note 1. The comparison is with the 64TR antenna units from Ericsson that Vodafone has been rolling out so far, which are very heavy (about 60 kilos) and less energy efficient, noted Vodafone UK’s Head of Performance and Radio, Ker Anderson, at a media briefing earlier this week.
“Vodafone is looking for ways to deploy 5G in a more energy-efficient way. When we started rolling out 5G we were using a 64-by-64 [64TR] panel from Ericsson and it’s close to 60 kilos in weight and burns electricity for fun,” noted Anderson, who added that the new AIR 3227 unit, while on paper having half the capacity of the 64TR units, “performs just as well… two years of technology evolution means we can now get the same performance from a 32-by-32 that we got with the first generation 64-by-64. Plus, they’re half the weight, and we’ve got a 43% energy reduction. So it’s been a real godsend for us for this product to come along and it’s the right thing for us to deploy – it’s cheaper, it’s faster, burns less electricity and the performance is really, really good,” Anderson said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
1,500 of the new energy efficient Ericsson radios will be deployed across Vodafone’s network by April 2022, helping to reduce Vodafone’s forecasted energy consumption of its future 5G network and support a sustainable and responsible 5G rollout.
Andrea Dona, Chief Network Officer, Vodafone UK, says: “Our strategy is simple; turn off anything we don’t need, replace legacy equipment with up-to-date alternatives and use the most energy efficient options available. The success of this trial allows us to explore new ways we can more effectively manage the energy consumption of our network with our partner Ericsson. There is no silver bullet to manage our network energy consumption – it is about putting sustainability at the heart of every decision and adding up all the small gains to make a material difference.”
Björn Odenhammar, Chief Technology Officer, Networks and Managed Services, Ericsson UK and Ireland, says: “Building on the success of an award-winning 5G network in London, it is another fantastic achievement for Vodafone and Ericsson to reduce network energy consumption by a daily average of 43 percent. Sustainability is central to Ericsson’s purpose and our new radio will help Vodafone to reduce network energy consumption, simplify network rollout and efficiently manage the expected growth in data traffic of both current and future 5G networks. Together we are building the 5G network of the future – one that delivers the highest possible performance with improved resource efficiency and low environmental impacts.”

Ericsson and Vodafone UK first launched commercial 5G services in 2019. The strong working partnership was recognised for a high performing best-in-class 5G network in London in 2020. In June 2021, it was announced that Ericsson will be supporting Vodafone’s entire cloud-native 5G Core Standalone for packet core applications – a critical milestone to deliver 5G Standalone connectivity services.
The two companies have also been collaborating to reduce the environmental impact of site upgrades and speed up network deployment through the use of drones and Ericsson’s Intelligent Site Engineering service.
RELATED LINKS:
References:
2021 World 5G Convention in Beijing: “5G+ By All For All”
The 2021 World 5G Convention, themed “5G+ By All For All, ” kicked off in Beijing Etrong International Exhibition & Convention Center on 31st August 2021. With more than 1,500 experts, scholars and entrepreneurs from 20 countries participating online and offline, the convention aims to discuss the future application of 5G in the fields of “industry”, “economy” and “innovation” .
Co-hosted by The People’s Government of Beijing Municipality, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Science and Technology and Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the three-day event features forums, exhibitions and a 5G-based application design competition.
According to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), since 5G came into commercial use in China, 993,000 5G base stations have been built. With more than 392 million households connected to 5G terminals, 5G base stations has covered all prefecture-level cities, more than 95% of counties and 35% of townships.
By now, over 10,000 5G application cases have covered 22 important industries and related fields of China’s economy, including steel, electric power and mining. Besides, a large number of colorful application scenarios are becoming new engines leading China’s high-quality development.
The convention unveiled 10 projects for 5G applications, all of which best represented 5G industrial practices and cutting-edge business patterns.
Eight white papers and research reports on 5G technologies were released during the event, and 18 strategic cooperative projects including the application of 5G technologies in Beijing’s municipal parks were signed at the closing ceremony.
As the host city of the event, Beijing will step up efforts to promote the construction of 5G network, industrial internet, and big data platform, accelerating the use of 5G technologies in telemedicine, self-driving vehicles, high-definition live streaming, and other fields during the 14th Five-Year Plan period (2021-2025).
Li Meng, Vice Minister of Science and Technology, said that at present, the new generation of information technology, represented by the mobile Internet, artificial intelligence, big data and supercomputing, is booming and evolving at a faster pace, bringing significant and far-reaching impact on economic development, the improvement of people’s livelihood and the environment and ecology of all countries.
“As China enters a new stage of development, implementing new development concepts, building a new development pattern and achieving high-quality development, sci-tech innovation are more than ever needed,” Li said. “At the same time, the huge potential market, diversified consumer demands and emerging industrial forms will also provide more diversified application scenarios and broader space for sci-tech innovation.”
As for how to promote the maturity of 5G enhanced technology, Li elaborated, “We are willing to continuously uphold the idea of opening up and cooperation, mutual benefit and win-win result, with more open attitudes and more pragmatic approaches, further strengthen the international cooperation of the evolution of 5G technology.”
Visitors experience 5G stereo photography at a venue of the 2021 World 5G Convention in Beijing, capital of China, Sept. 1, 2021. (Photo: China News Service/Yi Haifei)
Relying on 5G application technology and industrial base, exploring the secondary technology development system of 5G vertical industry application system, with joint efforts, we are endeavoring to address imperative needs of 5G frequency expansion and coverage enhancement, carry out standards of 5G enhanced technology and equipment R&D, and enhance the adaptability of 5G vertical industry applications, noted Li.
Li stressed that the Ministry of Science and Technology warmly welcomes entrepreneurs, universities and research institutions from all over the world to join in the future R&D of 5G, seizing the new trends and opportunities of global information technology development. With joint efforts and deep cooperation, create more breakthrough and leading technological achievements.
The World 5G Convention is claimed by China Daily to be the world’s first international conference in the 5G field. The first edition of this event took place in Beijing in 2019.
SOURCE: Science and Technology Daily
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
http://www.china.org.cn/business/2021-09/02/content_77729828.htm
http://en.people.cn/n3/2021/0902/c90000-9891257.html
https://global.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202109/01/WS612f435ba310efa1bd66cac6.html
Analysts: Combined ADTRAN & ADVA will be a “niche player”
ADTRAN is positioning its acquisition of ADVA as building a complementary combination of assets that can better capitalize on what it sees as an unprecedented investment cycle in fiber. However, analysts argue that the new combined company would still be just a “niche player” in the market.
On Monday, ADTRAN wrote in an email to this author (and many others):
ADTRAN has entered into a business combination agreement with ADVA, a Germany-based global leader in business ethernet, metro WDM, Data Center Interconnect and network synchronization solutions, to combine our two companies.We believe our combination will create many opportunities to better serve end-to-end fiber networking solutions spanning metro edge, aggregation, access and subscriber connectivity. Additionally, we anticipate that by utilizing our collective world-class R&D teams, we will be better positioned to accelerate innovation and offer differentiated solutions.Going forward, it will be business as usual and all existing customer, partner and supplier relationships will remain intact. Until we receive all required regulatory approvals and close the transaction, ADVA and ADTRAN will continue to operate as separate companies. As we integrate the two companies, we will be focused on the best ways to offer our enhanced value proposition and partner with you.
Highlights of the Deal:
- Combination expands product offering and strengthens position as a global fiber networking innovation leader with combined revenue of $1.2B
- Highly complementary businesses create a global, scaled end-to-end provider to better serve customers with differentiated fiber networking solutions, spanning metro edge, aggregation, access and subscriber connectivity
- Creates a stronger and more-profitable company, poised to benefit from the unprecedented investment cycle in fiber, an expanded market opportunity and increased scale
- Meaningful value creation with over $50 million in annual run-rate cost synergies
- All-stock transaction with ADTRAN shareholders to own approximately 54% and ADVA shareholders to own approximately 46% of the combined company, assuming a tender of 100% of ADVA shares
- Combined company to be dual-listed on the NASDAQ and Frankfurt Stock Exchange
 The two vendors produced a combined $1.2 billion in revenues last year. However, ADTRAN’s presentation in support of the deal showed that market heavyweights Nokia, Ciena, and smaller player Infinera had much higher revenues over that same time period.
The two vendors produced a combined $1.2 billion in revenues last year. However, ADTRAN’s presentation in support of the deal showed that market heavyweights Nokia, Ciena, and smaller player Infinera had much higher revenues over that same time period.
“It’s not going to reshape the optical networking industry,” John Lively, principal analyst at LightCounting, told SDxCentral about the deal. “ADTRAN and ADVA are going to improve their position in combination, [but] don’t really threaten the large players.”
Companies that are potentially threatened by this deal are smaller competitors such as Infinera ($1.4 billion in 2020 revenues) and Calix ($500 million in 2020 revenues), Lively noted.
“The challenges pressured by the global pandemic have clearly shown that fiber connectivity has become an essential foundation for the modern digital economy,” ADTRAN Chairman and CEO Thomas Stanton explained to investors about the deal. “This transformation will significantly increase the scale of the combined businesses, enhancing our ability to serve as a trusted supplier to our customers and worldwide.”
Stanton added that “our combination will make us one of the largest western suppliers for the markets we serve. Our greater size will increase cross-selling opportunities to existing customers, accelerating our combined growth, and allowing us to further penetrate our target markets.”
Although ADTRAN will remain a mid-tier player after the deal closes, LightCounting’s Lively and Dell’Oro Group VP Jimmy Yu both think in general, “it’s a good move.”
Yu noted that industry mergers can destroy value if too many products and workforces overlap. But in this case, ADTRAN and ADVA are from adjacent markets of fixed access and optical layer, and both sides will help each other grow the product line, so “it seems like a complementary combined company that’s going to come out of this,” he added.
Jimmy had this general comment on optical network trends:
“Disaggregated DWDM systems outperformed the broader market, demonstrating the growing adoption of this platform type. Really what we see is that this type of platform architecture, where transponder units are independent of the line systems, is being more widely embraced beyond the Internet content providers. Also, it is no longer just for metro applications. Recently, the highest growth rates have been from long-haul applications,”
Lively noted that there is almost no overlap in the product line, and “for the networks, the two companies logically fit together [as] ADTRAN makes access to equipment and ADVA makes the gear that connects the access equipment to the core.”
“So if you are a smaller service provider, and you want to upgrade to 10 Gb/s internet service for your customers, you could potentially buy everything you need from the new ADTRAN, from the passive optical networking, all the way through to connect to the core,” he said.
Yu also mentioned that the deal will help increase the scale and diversity in products as ADTRAN will be able to offer access and a backhaul solution, especially in tier-two and tier-three markets where most service providers want to work with one solution company instead of multiple vendors.
“2022 should be positive for sales,” argued the analysts at WestPark Capital in a note to investors earlier this month, following the release of Adtran’s second quarter results.
The WestPark Capital analysts pointed out that ADTRAN stands to gain ground in part from government broadband funding, as well as moves by some American and European network operators away from China’s Huawei.
The Raymond James analysts concurred on the Huawei opportunity. “We believe that the Huawei backlash outside of China presents among the largest opportunities,” they wrote on Monday.
The combined company will maintain ADTRAN’s global headquarters in Huntsville, Alabama. It will maintain ADVA’s headquarters in Munich, Germany, as its European base. Currently, ADTRAN has a geographical revenue split of 74% in the Americas, 21% in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, and 5% in Asia Pacific, while ADVA is split 62% in EMEA, 29% in the Americas, and 9% in Asia Pacific, according to Stanton.
The deal expands ADVA’s presence in North America and ADTRAN’s ability to reach the European market more effectively, Lively said. One of the drivers for this combination is “we see our customers making significant capital investments to transition their supply chains to trusted vendors with our roots in the U.S. and Germany, our company will be viewed favorably by customers who increasingly specify Western vendors,” Stanton explained.
“It’s kind of a race to build out their digital infrastructure to make the country competitive,” which presents a real opportunity for the new ADTRAN and also its competitors, Lively added.
Juniper to integrate RAN Intelligent Controller with Intel’s FlexRAN platform for Open RAN
Juniper Networks today announced plans to integrate its radio access network (RAN) intelligent controller (RIC) with Intel’s FlexRAN platform for Open RAN development.
This joint initiative between two companies is part of Juniper’s continuing efforts to bring openness and innovation to a traditionally closed-off part of the network, providing a faster route-to-market for service providers and enterprises to deliver 5G, edge computing and AI. Juniper views open RAN as an opportunistic endeavor and claims it’s currently testing the RIC integration in labs and trials with some tier-one operators. Juniper’s RIC takes direction from the O-RAN Alliance and adheres to open interfaces and APIs, but the specialized features it adds on top are proprietary.
Juniper has made major investments to lead the shift to Open RAN, beginning with the exclusive IP licensing agreement with Netsia (a subsidiary of Turk Telekom Group), and continuing with significant involvement in the O-RAN Alliance. Juniper is heavily engaged in expanding integrations with key partners and is part of the innovation team building joint customer solutions in Intel’s 5G Lab.
Spending on Radio Access Networks (RAN) is a significant amount of service providers’ CapEx, primarily due to limited vendor choice and closed architectures which lead to lock-in. Juniper recognizes that the RAN is a domain that demands openness and best-of-breed innovation to ensure the best experience for network operators and their customers, and is determined to lead the industry toward that vision.
Juniper’s collaboration with Intel includes the following:
- Juniper RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) and Intel FlexRAN platform are pre-integrated and pre-validated to enhance usability of a full ORAN-compliant Intelligent RAN system
- Collaborative R&D work with Intel Labs for RIC platform-specific apps to improve customer experience, maximize ROI and drive rapid ORAN ecosystem innovation
- Joint customer testbeds with Intel to validate performance-improving implementation and speed of time-to-market
Juniper is an active member of the O-RAN Alliance, contributing to six working groups and serving as chair and co-chair of the slicing and use-case task groups, respectively. Juniper is also an editor of RIC specifications within the alliance.
Quotes:
“Juniper has always been committed to open infrastructures, which is why we are excited to support the work that Intel has undertaken with their FlexRAN ecosystem. By collaborating with Intel, we are able to deliver cloud-native routing, automation, intelligence and assurance solutions and services that are optimized for our customers’ needs, speeding time-to-market and enabling them to monetize faster.”
– Constantine Polychronopoulos, VP of 5G and Telco Cloud at Juniper Networks
“RIC is like the brain for open RAN, and we also call it essentially the operating system of the RAN,” said Jai Thattil, director of strategic technology marketing at Juniper Networks. Juniper intends to differentiate its RIC from others by pre-integrating and validating the technology so operators can adopt it as part of a more comprehensive offering combined with other services. “Juniper is kind of in a unique position, compared to a lot of other vendors” because of its experience in 5G transport, network cores, service management and orchestration, according to Thattil.
“The virtualization of the RAN continues to gain momentum across the industry as operators take advantage of cloud economics and the delivery of new services. This collaboration with Juniper and the validation of FlexRAN and RIC solutions will assist service providers to overcome integration challenges and accelerate time-to-market for future deployments.”
– Caroline Chan, VP Intel Corporation, GM of Network Business Incubator Division
O-RAN Alliance Threatened:
The O-RAN Alliance is in a crisis because of U.S. sanctions against Chinese vendors in the group has troubled Nokia and Ericsson. In particular, the recent addition to the American “entity list” of three Chinese members of the Alliance. Kindroid, a semiconductor company, Phytium, a supercomputing company, and Inspur, a compute server vendor, have been accused of working with the Chinese military, and have joined 260 other Chinese companies, including, Huawei, on the entity list.
A few days after Nokia decided to suspend its technical activity with the O-RAN Alliance, in fear of American punishment over its engagement at the forum with companies recently put on the American “entity list,” Ericsson expressed similar concerns.
It should not be a surprise that, given O-RAN Alliance’s legacy (born out of a merger of the American-led xRAN Forum and the Chinese-led C-RAN Alliance), there are a strong Chinese contingency. According to Strand Consult, by the end of 2020, 44 of the 200 odd Alliance members are companies from China. Also of concern is this post by Mr. Strand, What NTIA won’t tell the FCC about OpenRAN.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/juniper-nudges-open-ran-ric-into-intel-flexran/2021/09/
Additional Resources:
Media Relations:
Lori Langona
Juniper Networks
+1 (831) 818-8758
[email protected]
IDC: Global Smartphone Shipments +7.4% in 2021, led by Emerging Markets
IDC forecasts that global smartphone shipments are set to increase by 7.4% this year, marking a return to growth after the Covid-19 pandemic hit the industry in 2020, according to new analyst figures. IDC estimates worldwide smartphone shipments at 1.37 billion units in 2021, which represents “minimal growth” compared with pre-pandemic 2019. Its data for 2019 shows shipments of 1.372 billion, then a 5.9% decline to 1.29 billion the following year. Making comparisons with 2019 (pre-COVID) gives a more accurate picture of the state of the market.
The 7.4% growth can be attributed to a healthy 13.8% growth from iOS devices combined with 6.2% growth from Android. Although COVID-19 drastically impacted 2020 shipments, 2021 shipments have managed to display minimal growth compared to 2019 (pre-pandemic) volumes, giving us a more accurate view of the state of the market. The world’s largest markets – China, the United States, and Western Europe – will still be down from 2019, but growing markets such as India, Japan, the Middle East, and Africa are fueling the recovery.
“The smartphone market was better prepared from a supply chain perspective heading into 2020 given almost all regions were expecting to grow and vendors were preparing accordingly,” said Ryan Reith, group vice president with IDC’s Mobility and Consumer Device Trackers. “2020 was a bust due to the pandemic but all of the top brands continued forward with their production plans with the main difference that the timeline was pushed out. Therefore, we are at a point where inventory levels are much healthier than PCs and some other adjacent markets and we are seeing the resilience of consumer demand in recent quarterly results.”
5G shipments continue to be a primary driver of 2021 growth as both vendors and channels focus on 5G devices that carry a significantly higher average selling price (ASP) than older 4G devices. The ASP of a 5G smartphone will reach $634 in 2021, which is flat from $632 in 2020. However, 4G devices continue to witness a massive price decline as the ASP drops to $206, representing a nearly 30% decline from last year ($277). As a result, the total 5G shipment volume will grow to 570 million units, up 123.4% from last year.
China will continue to lead the smartphone market with 47.1% of the 5G global market share, followed by the USA at 16%, India at 6.1%, and Japan at 4.1%. By the end of 2022, 5G units are expected to make up more than half of all smartphone shipments with a 54.1% share.
“Despite the ongoing issues surrounding the pandemic and the Delta variant, consumers are continuing to upgrade to more premium smartphones this year,” said Anthony Scarsella, research director, Mobile Phones at IDC. “Premium smartphones (priced at $1000+) continued to grow in the second quarter as the segment displayed 116% growth from last year. Moreover, ASPs across the entire market climbed 9% as buyer preferences trend towards more costly 5G models than entry-level devices.”
Closing Comment: We don’t share IDC’s enthusiastic forecast for 5G smartphones, because they do not support any new features, applications or use cases without a 5G SA core network. As 95% of deployed 5G networks are NSA (requiring a 4G anchor/core network), 5G smartphones that use 5G NSA networks are only a little faster [1.] than 4G-LTE phones with no noticeable improvement in latency. Also, there’s no roaming, so users must fall back to 4G-LTE when outside of their 5G carrier serving area. Mobile subscribers will soon realize that and stop buying 5G smartphones.
Note 1. PC magazine has tested smartphones on 5G networks from AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon. Their report Fastest Mobile Networks 2021 found that T-Mobile’s new mid-band 5G network is the only U.S. nationwide 5G that’s markedly faster than 4G
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About IDC Trackers
IDC Tracker products provide accurate and timely market size, vendor share, and forecasts for hundreds of technology markets from more than 100 countries around the globe. Using proprietary tools and research processes, IDC’s Trackers are updated on a semiannual, quarterly, and monthly basis. Tracker results are delivered to clients in user-friendly Excel deliverables and on-line query tools.
For more information about IDC’s Worldwide Quarterly Mobile Phone Tracker, please contact Kathy Nagamine at 650-350-6423 or [email protected].
References:
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS48194821
https://www.idc.com/tracker/showproductinfo.jsp?containerId=IDC_P8397
https://www.pcmag.com/news/fastest-mobile-networks-2021
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2021/08/22/juniper-research-5g-smartphone-trends/
Verizon starts private 5G mobile edge services with Microsoft Azure cloud
Verizon announced the availability of an on-premises, private edge compute service with Microsoft Azure, building on their collaboration formed last year. Verizon 5G Edge with Microsoft Azure Stack Edge is a cloud computing platform that brings compute and storage services to the edge of the network at the customer premises. This should provide enterprises with increased efficiencies, higher levels of security, and the low lag and high bandwidth needed for applications involving computer vision, augmented and virtual reality, and machine learning, Verizon said. Here are the highlights:
- Through its relationship with Microsoft, Verizon is now offering businesses an on-premises, private edge compute solution that enables the ultra-low latency needed to deploy real-time enterprise applications.
- Solution leverages Verizon 5G Edge with Microsoft Azure Stack Edge to bring compute and storage services to the edge of the network at the customer premises, providing increased efficiencies, higher levels of security, and the low lag and high bandwidth needed for applications involving computer vision, augmented and virtual reality, and machine learning.
- Ice Mobility has used Verizon 5G Edge with Microsoft Azure to help with computer vision-assisted product packing to improve on-site quality assurance. The company is now exploring additional 5G Edge applications that provide tangible, material automation enhancements to its business, such as near real-time activity-based costing.
Some of the applications possible with the on-site 5G and edge computing include in-shop information processing in near real time to help retailers manage inventory, or factory data processing and analytics to minimize downtime and gain visibility across manufacturing processes.
Logistics company Ice Mobility has used Verizon 5G Edge with Azure Stack Edge to help with computer vision-assisted product packing to improve on-site quality assurance. The company is exploring additional 5G applications that leverage initial computer vision and 5G edge investments to provide automation enhancements, such as near real-time activity-based costing. This would allow the company to assign overhead and indirect costs to specific customer accounts, pick and pack lines, and warehouse activities to enhance efficiencies and improve competitiveness.
“This announcement aligns with IDC’s view that an on-premises, private 5G edge compute deployment model will spur the growth of compelling 4th generation industrial use cases,” said Ghassan Abdo, Research VP at IDC. “This partnership is a positive development as it leverages the technology and communications leadership of both companies.”
“Our partnership with Microsoft brings 5G Edge to enterprises, dropping latency at the edge, helping critical, performance-impacting applications respond more quickly and efficiently,” said Sampath Sowmyanarayan, Chief Revenue Officer of Verizon Business. “5G is ushering in next-generation business applications, from core connectivity to real-time edge compute and new applications and solutions that take advantage of AI transforming nearly every industry.”
“Business innovation demands powerful technology solutions and central to this is the intersection between the network and edge” said Yousef Khalidi, corporate vice president Azure for Operators at Microsoft. “Through our partnership with Verizon, we are providing customers with powerful compute and storage service capabilities at the edge of customers’ networks, enabling robust application experiences with increased security.”

Verizon offers a similar service with Amazon Web Services (AWS which provides private multi-access edge computing (Private MEC) for enterprises. Private MEC integrates edge computing infrastructure with private networks deployed on or near the customer’s premises.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/node/921923
Watch this video to learn more about how Ice Mobility is using Verizon 5G Edge. Learn more information about Verizon 5G Edge and Verizon’s 5G technology
Amazon AWS and Verizon Business Expand 5G Collaboration with Private MEC Solution
India lagging in 5G unless spectrum prices decrease & 5Gi standard debate is settled
Bloomberg says India risks lagging in the rollout of the 5G wireless networks unless the government makes airwaves cheaper in an upcoming spectrum auction, a local telecom industry body said, citing the financial stress in the sector.
“The reserve prices are fixed so high that almost 50-60% of the spectrum may go unsold,” S.P. Kochhar, director general of Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI), said in an interview August 27th. “It is not viable because we are not passing on the extra price to the consumer as we continue to bleed. We have to reduce our cash outflow and one of the major things money goes into is auctions.”
Proceeds from the 5G airwaves auction, likely early next year, is an important source of revenue for the Indian Exchequer (UK term for Treasury Dept.) especially as the Narendra Modi-led government looks to spur India’s pandemic-hit economy. Too high a reserve price for spectrum risks putting off wireless network operators whose financial health has been battered by a brutal tariff war after the entry of billionaire Mukesh Ambani’s Reliance Jio Infocomm Ltd. in 2016. Most operators since have quit, gone bankrupt or merged.
Lowering the base price for auctioned spectrum and other government levies have been a longstanding industry demand. The local telecom industry is paying about 32% of its total revenue as levies and taxes and that’s “too high,” said Kochhar. “It’s the highest in the world.”
India’s government has set the reserve price for 5G airwaves at 4.92 billion rupees ($67.2 million) per megahertz of spectrum in 3,300 to 3,600 Mhz bands which are most suitable for the new technology. Kochhar expects the auction to happen in January or February 2022.
High reserve prices have hindered spectrum sales in some categories in the past. The 700 megahertz band, which is suitable for 5G technology, didn’t receive any bids in the March auction.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Sidebar: TSDSI’s 5Gi standard (included in ITU-R M.2150 recommendation/IMT 2020.specs)
Another important aspect of 5G in India deployments has been the deliberation on the development of specific 5G India standards (5Gi or LMLC). While the Telecommunications Standards Development Society of India (TSDSI) has been keen on pushing telcos to undertake trials based on 5Gi, a homegrown standard with a Large Cell Low Mobility enhancement for wider coverage in rural areas, the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) has argued for the implementation of the global 3GPP specification (5G NR in Release 15 & 16) for 5G in India. They remain convinced that 5Gi could lead to interoperability issues. This ongoing debate is further delaying the 5G launch in India.

Source: The Economic Times
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
India remains a relative latecomer in the 5G space compared to some countries, including China and South Korea, which already have 5G networks in place.
If the government can “somehow have the right price point for spectrum,” it would boost the growth of 5G network traffic as well as the devices, Bharti Airtel Ltd. Chairman Sunil Mittal said in an investor call Monday. “We need to invest in fiber backhaul now.”
The market leader Jio and Bharti Airtel, India’s no. 2 operator, have been conducting 5G trials in preparation for a nationwide roll out once the airwaves are sold.
Debt-laden Vodafone Idea Ltd. — the only other private sector wireless operator left in India — has been posting losses for several quarters and is struggling to stay afloat. Bharti and Vodafone Idea also have to come up with billions of rupees in back dues to the government after India’s top court rejected their petitions seeking relief.
“At this point, the payouts in telecom are so excessive that even survival is becoming a problem,” said Kochhar. That strongly implies there will be only two 5G network operators in India- Jio and Bharti!
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
BSNL is aiming to upgrade the 4G network to 5G non-standalone (NSA) by 2022 (pending 5G spectrum to be purchased at the long delayed auction) and to 5G standalone (SA) by 2023. What about that? Almost every country has already deployed 5G NSA while operators are slowly evolving to 5G SA using different software technologies in the absence of any standard or implementation spec.
Light Reading says BSNL is unlikely to meet to this timeline, with shortlisted 4G network vendors still conducting tests. It is likely to be another year before BSNL can roll out a 4G network, while private-sector companies are gearing up for a 5G launch in the coming year.
References:
Singtel discloses new 5G SA uses cases for enterprises and residents in Singapore
At its ‘Powering Up Singapore With 5G’ event, Singtel (the leading network operator in Singapore) revealed a number of 5G Standalone (SA) use cases, according to a press release. The new use cases span a variety of sectors from entertainment to mobility and bring to life the benefits of 5G by redefining live, work and play experiences with blazing fast speeds and near-instantaneous response times.
Singtel said it continues to expand its 5G network, which now covers over two-thirds of Singapore, adding sites in densely populated areas like Choa Chu Kang, Punggol, Sembawang and Tampines. In addition, it has expanded its 5G indoor coverage to more major shopping malls island-wide such as Funan, West Mall, Tampines Mall, Northpoint City and Waterway Point.
Minister for Communications and Information Mrs Josephine Teo highlighted the role of 5G, “Mobile networks and data exchanges are key building blocks for the digital infrastructure. 5G, which promises to be ultra-fast and supports near-zero latency, can change the way we live and work in profound ways, and become essential for the digital developments of the future. Building a digital future is certainly about the hardware, software, systems and standards. It is equally about the people and skills. For that, the Government will continue to invest in reskilling and upskilling our people so that they can achieve not just digital literacy but digital mastery. This way, everyone can benefit from the infrastructure.”
Yuen Kuan Moon, CEO of Singtel said: “With the maturing of 5G technology, we’re excited to unlock the benefits of a 5G-enabled reality for consumers and enterprises. Its potential to transform business models and deliver enhanced products and services on a scale like never before, will spur Singapore’s digital economy as the country moves into post-COVID recovery. As part of our strategic reset to focus on 5G, we are accelerating our roll-out and the creation of new services.”

Ookla® recently declared Singtel the ‘Fastest 5G mobile operator in Singapore’ in H1 2021 for clocking in the highest median mobile network speed.
Singtel said the arrival of 5G has proved timely against a backdrop of accelerated digital adoption as a result of safe distancing and remote working. With more people using digital channels to go about their lives, there has been a corresponding increase in demand for fast and reliable connectivity. This is reflected in a recent Singtel survey, in which majority of consumers indicated that 5G-enabled services such as augmented reality books and virtual reality entertainment events appeal to them.
The new use cases powered by Singtel’s 5G SA network include:
- 5G-powered Remote Racing: Partnering with Formula Square to deliver an immersive, lag-free experience racing remote-controlled cars powered by 5G at Southside, Sentosa;
- 4K Live Streaming: Working with S.E.A. Aquarium to bring Singapore’s first underwater 5G livestream of the S.E.A. Aquarium to UNBOXED, Singtel’s unmanned pop-up retail store, where visitors can immerse themselves in the aquatic wonders of the aquarium, viewing manta rays, sharks and shoals of fishes in vivid 4K resolution;
- Enhancing the Arts and Culture Experience: Collaborating with the National Gallery Singapore and Esplanade – Theatres on the Bay to deliver cultural and art experiences over 5G, from the Singtel Special Exhibition Gallery and the Singtel Waterfront Theatre when it opens officially next year. This will enable more people with opportunities to get up close and personal with local artists and performers amid prevailing safe distancing measures;
- Co-creating the future of hybrid work: Teaming up with Samsung and Zoom to introduce a Productivity Data Pass plan offering data-free usage of Zoom, enabling customers to connect to family and colleagues seamlessly and lag-free. This, coupled with Samsung devices such as DeX, will enable customers to set up virtual workstations easily.
Singtel has also signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Ericsson and global industry partners to collaborate on the development and deployment of advanced 5G enterprise solutions in Singapore. The agreement will allow companies to leverage Ericsson’s technology expertise and Singtel’s 5G network, test facilities and capabilities to innovate solutions and scale them up for global deployment.
Singtel launched its 5G SA network in May, via a partnership with South Korea’s Samsung. The 5G SA sites run on 3.5 GHz spectrum. Singtel had initially launched its 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) network in September of 2020, using spectrum in the 3.5 GHz frequency as well as existing 2.1 GHz spectrum.
As part of its 5G SA deployment, Singtel has already deployed over 1,000 5G sites across Singapore in strategic locations such as Orchard Road, the Central Business District, Marina Bay, Harbourfront and Sentosa, as well as major residential areas including Sengkang, Punggol, Pasir Ris, Jurong East and Woodlands.
Singtel also demonstrated at the event how 5G is empowering industries and businesses with greater productivity and operational efficiency. Key to this is multi-access edge computing (MEC), an infrastructure that maximizes 5G’s low latency, high bandwidth benefits and enables functions like real-time computing, data storage, data analytics and AI services at the edge. MEC supports massive and faster connectivity of devices, bringing to life more mission critical enterprise applications than before, such as real-time asset tracking and automated quality inspection in factories and smart city planning.
During the event, Guest of Honor Mrs Josephine Teo, Minister of Communications and Information and IMDA’s Chief Executive Mr Lew Chuen Hong were ‘teleported’ into the venue via Singtel’s 5G network, in which their high-resolution likeness were beamed from a separate location. The network’s ultra-low latency meant that Minister Teo and Mr Lew could ‘interact’ seamlessly with Mr Yuen on stage.
Singtel aims to intensify its 5G SA deployment across the island in the coming months as handset manufacturers progressively roll out 5G SA software updates for existing 5G handsets and launch more 5G SA-compatible models in Singapore later this year.
References:
https://www.singtel.com/personal/products-services/mobile/5g#5g1
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20210830/5g/singtel-unveils-new-use-cases-5g-sa-technology-singapore
Singtel starts limited deployment of 5G SA; only 1 5G SA endpoint device; state of 5G SA?





