Month: February 2024
Charter Communications: surprise drop in broadband subs, homes passed increased, HFC network upgrade delayed to 2026
Charter Communications posted a surprise drop in broadband subscribers in the Q4-2023, the company announced on Friday. Charter’s internet customers decreased by 61,000 (-62,000 residential and +1,000 business) in the 4th quarter, with nearly all of the decline from residential customers. That was much worse than expectations for 17,290 additions, according to Visible Alpha and a year-ago gain of +105,000. The broadband subscriber drop was especially disappointing given Charter’s homes passed growth accelerated to 2.5% year-over-year, Craig Moffett said in a research note.
“Internet growth in our existing footprint has been challenging, driven by admittedly more persistent competition from fixed wireless and similar levels of wireline overbuild activity,” CEO Chris Winfrey said on a post-earnings call, adding that new investments will help drive growth despite the “temporary challenges.” Chief Financial Officer Jessica Fischer had warned in December that the company could lose internet customers in the quarter. At the time, speaking at an analyst conference, she said the company was facing short-term challenges and that results would be in line with the rest of the industry.
Charter was not the only cableco/MSO to report decreased broadband internet subscribers in the 4th quarter. Last week, rival Comcast reported a loss of 34,000 broadband customers, fewer than expectations, but exceeding the 18,000 broadband customers it lost in the previous quarter.
Stiff competition across broadband and wireless mobile and the decline of traditional television have been causes of concern, with Charter trying to expand its reach into rural areas in an effort to boost subscriber and earnings growth. Charter is facing heightened competition from Verizon and T-Mobile’s wireless home internet offerings, and the cable company could soon lose even more subscribers when a key government program runs out of funding in April, JPMorgan analysts say in a research note. In particular, the end of the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP), which provided up to $30 per month to eligible customers to put toward their internet bills, could hurt Charter more than its peers. If ACP is not refunded, “we’ll work very hard to keep customers connected,” Winfrey said. Charter has more than 5 million ACP recipients, the highest in the industry. The majority of them were Charter broadband subscribers before the program began.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Charter added 142,000 broadband subs via its rural subsidy program in Q4, for a total of 420,000, and an overall penetration rate of 33.8% – up from 27.2% in the year-ago quarter. The company posted $74 million in rural revenues, up from $39 million a year earlier. Charter pulled in subsidy revenues of $29 million in Q4. Total capex for the project in Q4 was $426 million, down from $567 million in the year-ago quarter. Charter plans to activate 450,000 new subsidized rural passings in 2024. With all programs rolled up, Charter has committed to build 1.75 million subsidized rural passings.
Charter expects to complete its Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) builds by the end of 2026 – two years ahead of schedule. Charter also intends to participate in the much larger $42.45 billion Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) program.

……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Completion of Charter’s hybrid fiber/coax (HFC) network upgrade has been delayed to 2026 due in part to a lengthier certification process for distributed access architecture (DAA) technology. Charter’s original plan was to complete its HFC upgrades by the end of 2025. Charter’s HFC evolution plan consists of three steps:
- An upgrade to 15% of its network to 1.2GHz with an upstream-enhancing “high-split” using traditional integrated cable modem termination systems (CMTSs). That enables multi-gigabit downstream speeds and upstream speeds up to 1 Gbit/s.
- An upgrade to 1.2GHz with DAA and a virtual CMTS in 50% of the HFC footprint, enabling downstream speeds up to 5 Gbit/s and upstream speeds up to 1 Gbit/s.
- A full DOCSIS 4.0 upgrade by deploying 1.8GHz with DAA and a vCMTS to 35% of the HFC footprint. That’ll put Charter in position to deliver up to 10 Gbit/s downstream and at least 1 Gbit/s upstream.
Speaking on today’s Q4 2023 earnings call, Charter CEO Chris Winfrey said the operator has launched symmetrical speed tiers in two markets (Reno and Rochester, Minnesota, an official confirmed), with deployments in six additional markets underway that, once completed, will fulfill the phase one plan. Charter expects to start DAA deployments in its phase two markets later this year, Winfrey said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Charter added 546,000 mobile lines in Q4, down from a gain of +615,000 in the year-ago quarter and +594,000 in the prior quarter. Analysts were expecting Charter to add 594,000 mobile lines in the 4th quarter and +2.5 million lines for full 2023, up from 1.7 million in full 2022. The MSO ended 2023 with 7.76 million mobile lines. Charter is also expanding its deployment of CBRS spectrum to help the company offload MVNO costs in high-usage areas. Winfrey said “thousands” of CBRS units have been deployed in one “large” market (believed to be Charlotte, North Carolina). Charter expects to roll CBRS to an additional market later this year, he said.
References:
Charter Communications adds broadband subs and raises CAPEX forecast
Precision Optical Technologies (OT) in multi-year “strategic partnership” to upgrade Charter Communications optical network
Charter Communications selects Nokia AirScale to support 5G connectivity for Spectrum Mobile™ customers
T-Mobile and Charter propose 5G spectrum sharing in 42GHz band
Comcast Xfinity Communities Wi-Fi vs Charter’s Advanced Wi-Fi for Spectrum Business customers
IEEE President’s Priorities and Strategic Direction for 2024
by Tom Coughlin, 2024 IEEE President; edited & augmented by Alan J Weissberger, IEEE Techblog Content Manager
 Let’s examine each of these issues and initiatives for IEEE this year:
Let’s examine each of these issues and initiatives for IEEE this year:
1. IEEE has a lot of college student members but, like many other professional organizations, the majority of these student members don’t continue as full IEEE members. One reason is the much higher cost – $218/yr for full IEEE membership vs. $32/yr for IEEE student membership. This is a big financial burden as many college graduates carry student loans after graduation. Another reason is they don’t see much if any value in being an IEEE member. We need to change that perception by revitalizing IEEE such that is relevant to young members careers in both industry and academia.
In order for the IEEE to remain vital and relevant we need to convert more of our student members to full IEEE members and then engage and retain them. One thought is to encourage them to volunteer at the section, chapter, or global level.
I am creating a special task force in the IEEE to address this problem and do surveys, focus groups and pilot programs to find ways that we can attract and retain our younger members.
2. IEEE needs to create stronger ties and provide greater value to industry and to those engineers and scientists who work in industry. This goal is closely related to the first goal since most of our student members end up working in industry.
IEEE has an Industry Engagement Committee and I have asked them to work with the IEEE Student Activities Committee and IEEE Young Professionals to find value in the IEEE for younger people working in industry. In addition, I am personally reaching out to companies to speak with senior technical people about how IEEE is useful now and what else we can do to provide value, particularly for younger people working in industry.
3. IEEE needs to reach out to the broader world to let them know who we are and what we do. Today, most people that have heard of IEEE think of it as ONLY a standards organization, e.g. for IEEE 802.11 WiFi and IEEE 802.3 Ethernet. They don’t realize that IEEE is by far, the largest tech non-profit organization.
We have in our IEEE membership experts in all technologies, who can provide insights and guidance for public policy, convene meetings and create new and valuable standards.
IEEE is by far the most cited source for prior art in patents worldwide, it has created documents and standards on ethical design of intelligent and autonomous systems (AI) and our volunteers write, review and publish much of the worlds technical literature and put on conferences on every conceivable technical topic.
IEEE also creates future directions committees on emerging technologies, pursue technical megatrends and create and publish technology roadmaps on semiconductor and other important technologies.
4. IEEE needs to invest in new products and services. In particular, applying AI and other computer algorithms to IEEE content that will enable new ways to find, understand and advance technologies that can serve our members and our customers.
In 2024, IEEE will start an Ad hoc committee, working with relevant groups outside of the IEEE, on educating future generations of workers who will be using new tools such as AI, working in outer space and in virtual environments and who will work for many organizations and technologies during their career.
IEEE should be able to leverage technical tools to help people learn in the best way for them and to provide lower costs for continuous education which can enable those from underserved communities to participate in and benefit from technical education.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
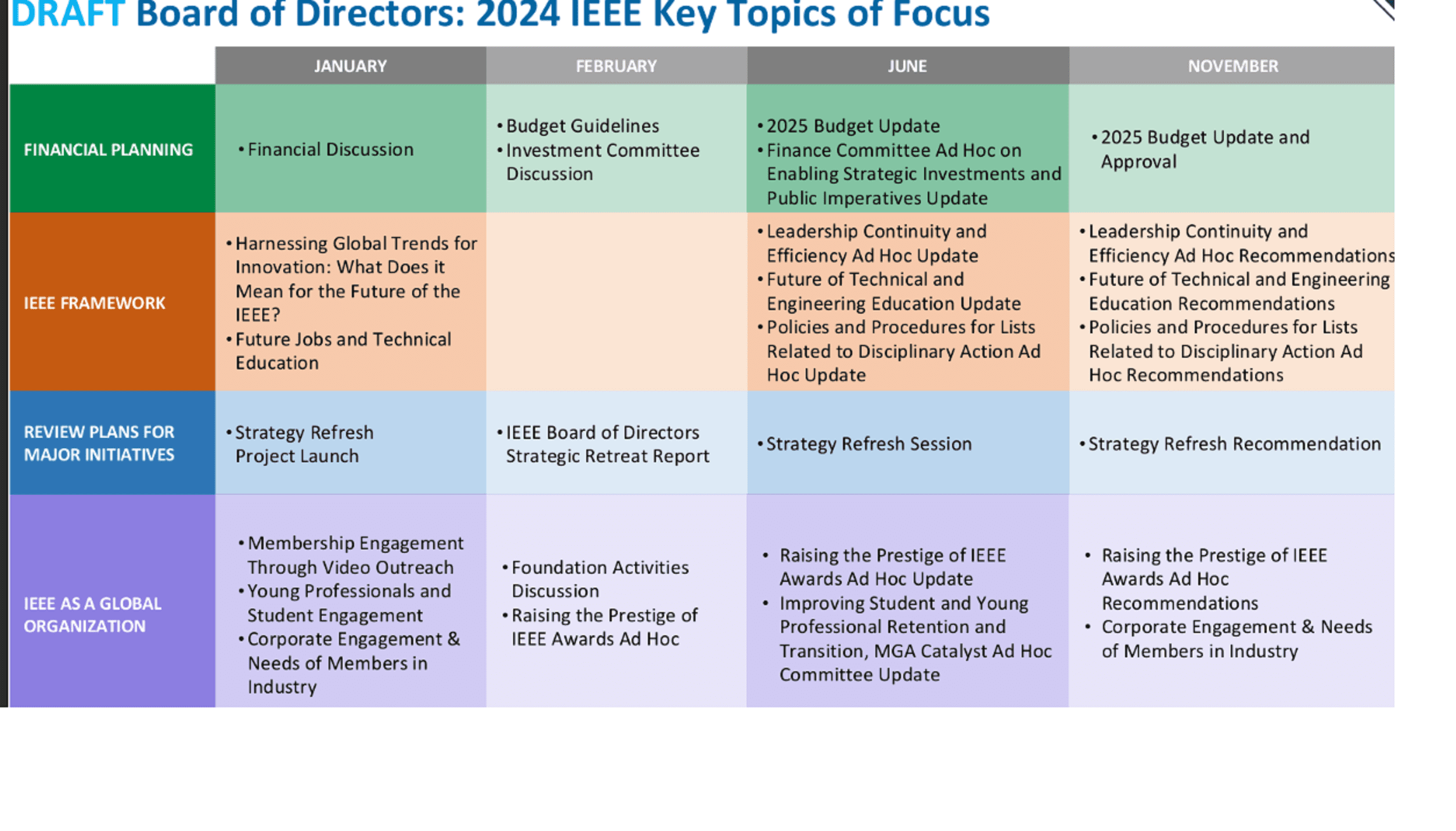
2024 IEEE Key Topics of Focus Overview:
- Provides a roadmap for the year in terms of areas of focus and provides year over year continuity.
- Discussed and adopted on an annual basis by the IEEE Board of Directors at the January meeting.
- A living document that evolves throughout the year and is updated for every Board meeting as progress is reported.
I know the time will go by fast in my one year term as IEEE President. I look forward to meeting more of our members in more places and having the chance to understand and support these members. I also hope that I can help create stronger ties to those who work in industry and keep more of our younger members and provide greater value to the world. Most of all I will support the IEEE’s mission to advance technology for the benefit of humanity!
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
IEEE President Elect: IEEE Overview, 2024 Priorities and Strategic Plan
SK Telecom, Intel develop low-latency technology for 6G core network
In collaboration with Intel, SK Telecom (SKT) has successfully developed technology to reduce communication delays necessary for the evolution of 6G Core Network Architecture. The Core network is the gateway through which all voice and data traffic generated from a customer’s mobile device passes through to access the Internet network. It is a mobile communication service system that is responsible for security and service quality through the inter-connection of various systems.
Editor’s NOTE: Of course, 6G is currently undefined with only the features and functions being defined by ITU-R WP 5D which is meeting this week in Geneva. The 6G core network specifications will be done by 3GPP and NOT ITU-T as was the case for 5G core.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The 6G Core Architecture is required to have higher flexibility and safety than previous generations of wireless communications, and to provide stable AI service quality and technologies to customers by embedding intelligent and automation technologies.
As Core network technology continues to develop, the various systems that make up the network and the detailed functions that provide various services are also explosively increasing. As network complexity continues to increase, the process of sending and receiving messages is frequently recreated. Therefore, communication delays will increase compared to before. It is difficult to address these limitations with communication standard technologies (service communication proxies) for interconnection between unit functions within the existing Core network.
Inline Service Mesh, a low latency technology the two companies developed utilizing Intel Xeon processors with built in AI, is capable of increasing the communication speed within the Core network by reducing latency between unit function without Proxy.
Through this technology development, AI, which requires a large amount of computation, can be applied to the Core network in a wider variety of models. SKT has already commercialized a technology that reduces wireless resources by 40% and improves connectivity by analyzing movement patterns of real users in real time. Through this cooperation, the two companies will be able to reduce communication delays by 70% and increase service efficiency by 33% in the Core network through the application of the 6G Core Architecture.
SKT aims to apply the results of this study to commercial equipment next year. A technical white paper has been published by Intel that describes the technology, development process and benefits.
SKT and Intel have been continuing to cooperate for research on the development of key wired/wireless mobile communication technologies for the past 10 years. Based on the results of this study, the two companies plan to continue research and development for traffic processing improvement technologies incorporating AI technology in various areas of the Core network.
“We have made another technical achievement through continuous technology development cooperation with Intel to secure leadership in 6G,” said Yu Takki, Vice President and Head of Infra Tech at SKT. “We will continue our research and make efforts to commercialize AI-based 6G Core Architecture.”
“Our research and development efforts with SK Telecom continue to deliver innovations that have been deployed by Communications Service Providers worldwide”, said Dan Rodriguez, Corporate Vice President of Intel Network & Edge Solutions Group. “By leveraging the latest Intel Xeon processors with built in AI features, our companies are able to drive both performance and efficiency improvements that will be vital to the future Core networks.
Last March, SKT and NTT DOCOMO released a white paper addressing the requirements for future 6G networks.
The South Korean carrier said the new white paper contains its views on 6G key requirements and 6G evolution methodology, along with its opinions on the latest trends in frequency standardization. The 6G white paper also provides analysis, development directions and methodologies pertaining to promising 6G use cases, technology trends as well as and candidate frequencies.
The 6G White Paper reviews the following:
- Performance requirements and implementation scenarios for each frequency band, taking into account the characteristics of each frequency
- Issues concerning coverage and devices in high-frequency bands
- Standardization for migration to 6G architecture and application of cloud-native / open architecture

References:
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?idx=1597¤tPage=1&type=&keyword=
NTT DOCOMO & SK Telecom Release White Papers on Energy Efficient 5G Mobile Networks and 6G Requirements
https://www.docomo.ne.jp/english/corporate/technology/rd/docomo6g/whitepaper_dcmskt.html#title02
Ericsson and IIT Kharagpur partner for joint research in AI and 6G
Ericsson and the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur have announced a partnership for a long-term cooperation for joint research in the area of radio, computing and AI (artificial intelligence). Both organisations have signed two milestone agreements. As part of the agreements, researchers from IIT Kharagpur and Ericsson will collaborate to develop novel AI and distributed compute tech for 6G. Leaders from IIT Kharagpur and Ericsson participated in discussing the developments and advancements for the future of networks and communications at the GS Sanyal School Telecommunications (GSSST).

Ericsson members from left: Rupa Deshmukh, Mikael Prtz, Kaushik Dey, Mikael Hook, Bo Hagerman,Magnus Frodigh, Director – Prof V. k Tewari, Deputy Director – Prof Amit Patra, Anil R Nair
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Two key initiatives finalized by Ericsson and IIT were:
a) Compute offload and Resource Optimisation at edge compute: The project aims to explore resource optimization, dynamic observability and sustainable distributed and Edge computing technologies.
b) RL-based Beamforming for JCAS: Safe, Causal, and Verifiable: The project aims to explore causal AI methods for joint communication and sensing (JCAS).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
AI and Compute Research is instrumental to Ericsson’s 6G networks as the compute offload needs to be managed dynamically at edge and the policies would primarily be driven by AI. These themes of research are well aligned with IIT Kharagpur and both organizations view this partnership as a way to push the boundaries of fundamental and applied research in the Radio domain.
Editor’s Note:
Ericsson laid off 8,500 employees last year as part of its cost-cutting initiatives and reduced total costs by 12 billion Swedish crowns ($1.15 billion) in 2023.
Telecoms equipment suppliers are expecting a challenging 2024 as 5G equipment sales – a key source of revenue – are slowing in North America, while India, a growth market, may also see a slowdown. Ericsson’s fourth-quarter net sales fell 16% to 71.9 billion Swedish crowns ($6.89 billion), missing estimates of 76.64 billion.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Magnus Frodigh, Head of Ericsson Research, says: “This collaboration strengthens our R&D commitments in India and is pivotal to Radio, Compute and AI research. We are excited to partner with IIT Kharagpur and look forward to collaborative research in fundamental areas as well as translational research for our Future Network Platforms”. Dr Frodigh also presented Ericsson’s vision on 6G which aims to blend the physical and digital worlds enabling us to improve the quality of life by incorporating widespread Sensor-based communications between humans and machines through digital twins.
Nitin Bansal, Managing Director of Ericsson India said, “Ericsson is well poised to lead 6G innovation and we are making significant R&D investments in India in line with our commitment to the country. Given our 5G and technology leadership, our research initiatives are geared to provide affordable network platforms for ubiquitous connectivity all across the country.”
Virendra Kumar, Director at IIT Kharagpur, said, “In the commitment towards Digital India and making India the hub of technological innovation, this collaboration with Ericsson will be effective for next-generation technology significantly. 6G networks integrated with artificial intelligence will enable AI-powered applications to run faster and more efficiently. In the 6G era, IIT Kharagpur aims to contribute to Radio Access Technology and Network, Core Network, RF & Device Technologies, VLSI Design, Neuromorphic Signal Processing, Services and Applications.”
About Ericsson;
Ericsson enables communications service providers to capture the full value of connectivity. The company’s portfolio spans Networks, Digital Services, Managed Services, and Emerging Business and is designed to help our customers go digital, increase efficiency and find new revenue streams. Ericsson’s investments in innovation have delivered the benefits of telephony and mobile broadband to billions of people around the world. The Ericsson stock is listed on Nasdaq Stockholm and on Nasdaq New York. www.ericsson.com
About IIT Kharagpur:
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur (IIT KGP) is a higher educational and academic institute, known globally for nurturing industry ready professionals for the world and is a pioneer institution to provide Excellence in Education, producing affordable technology innovations. Set up in 1951 in a detention camp as an Institute of National Importance, the Institute ranks among the top five institutes in India and is awarded, “The Institute of Eminence”, by the Govt. of India in 2019. The Institute is engaged in several international and national mission projects and ranks significantly in research output with about 20 academic departments, 12 schools, 18 centers (including 10 Centre of Excellence) and 2 academies with vast tree-laden campus, spreading over 2100 acres having 16,000+ students. Currently, it has about 750+ faculty, 850+ employees and 1240+ projects.
To know more visit: [http://www.iitkgp.ac.in/]
Ericsson, IIT Kharagpur Partner to Joint Research in AI and 6G
Ericsson’s India 6G Research Program at its Chennai R&D Center
India unveils Bharat 6G vision document, launches 6G research and development testbed
India creates 6G Technology Innovation Group without resolving crucial telecom issues
https://www.cnbc.com/2024/01/23/ericsson-warns-of-2024-market-decline-despite-q4-earnings-beat.html