Author: Alan Weissberger
Dell’Oro: FWA revenues on track to advance 35% in 2022 led by North America
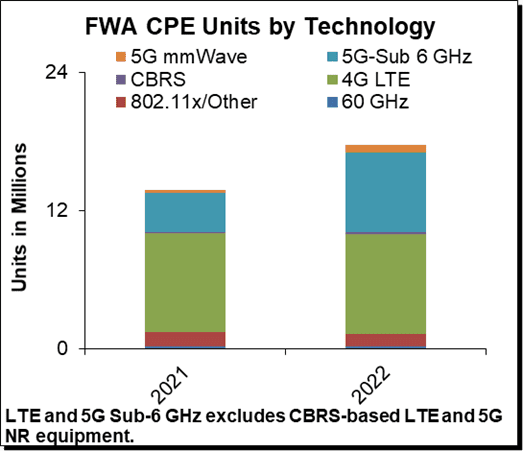
Dell’Oro Group announced today the launch of its new Fixed Wireless Access Infrastructure and CPE advanced research report (ARR). Preliminary findings suggest total Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) revenues, including both RAN equipment and CPE revenue remain on track to advance 35% in 2022, driven largely by subscriber growth in North America.
“Fixed Wireless Access has become a key component to bridging the digital divide and connecting rural and underserved markets globally. What we are also seeing is that FWA can effectively compete with existing fixed broadband technologies, especially with the advent of 5G and other higher-throughput, non-3GPP technologies,” said Jeff Heynen, Vice President and analyst with the Dell’Oro Group.
“Right now, CPE for fixed wireless access using 5G sub-6GHz technologies are growing the fastest. We do expect these units to tail off over time as current investments in fiber networks, along with cable’s DOCSIS 4.0 and fiber upgrades, will limit the addressable market for large-scale fixed wireless services,” Jeff added.
Additional highlights from the Fixed Wireless Access Infrastructure and CPE Advanced Research Report:
- Global FWA revenues are projected to surpass $5 B by 2026, reflecting sustained investment and subscriber growth in both 3GPP- and non-3GPP-based network deployments.
- The North American market remains the most dynamic in terms of deployed FWA technology options, with CBRS and other sub-6GHz options growing alongside 5G NR and 60GHz options.
- Long-term subscriber growth is expected to occur in emerging markets in Southeast Asia and MEA, due to upgrades to existing LTE networks and a need to connect subscribers economically.
- The Satellite Broadband market will also be a key enabler of broadband connectivity in emerging markets, thanks to LEOS-based providers including Starlink, OneWeb, and Project Kuiper.
The Dell’Oro Group Fixed Wireless Access Infrastructure and CPE Report includes 5-year market forecasts for FWA CPE and RAN infrastructure, segmented by technology, including 802.11/Other, 4G LTE, CBRS, 5G sub-6GHz, 5G mmWave, and 60GHz technologies. The report also includes regional subscriber forecasts for FWA and satellite broadband technologies, as well as Gateway forecasts for satellite broadband deployments. To purchase this report, please contact us by email at [email protected].
Note: The IEEE Techblog has featured many FWA success stories and that FWA is probably the top 5G use case to date. The main reason is that a 5G FWA network doesn’t involve roaming or a 5G SA core network for which there are no ITU/ETSI standards or 3GPP implementation specs. As long as the FWA CPE supports 5G NR (via ITU M.2150 recommendation or 3GPP Release 16) all the other functions can be customized in software which only has to work with the network provider offering the FWA service.
References:
JC Market Research: 5G FWA market to reach $21.7 billion in 2029 for a CAGR of 65.6%
Juniper Research: 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) to Generate $2.5 Billion in Global Network Operator Revenue by 2023
Samsung achieves record speeds over 10km 5G mmWave FWA trial in Australia
5G FWA launched by South Africa’s Telkom, rather than 5G Mobile
Nokia and Safaricom complete Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial
Huawei aims to lead Africa’s 5G digital transformation, as U.S. and Europe lockouts continue
Faced with continuing bans in the U.S. and Europe, Huawei is focusing network equipment sales in Africa, which in turn is emphasizing “digital transformation.”
“As the third wave of the global 5G market, Africa will open the 5G era in 2023,” Benjamin Hou, president of Huawei’s northern Africa business, told the Africa 5G summit, that took place in Bangkok, Thailand on October 24th. The event was seen as a platform to draw African countries to 5G tech powered by Shenzhen-based Huawei.
Hou said: “Huawei will further increase its investment in Africa to support the steady development of 5G to facilitate digital transformation in the region. In Africa, for Africa, Huawei will continue to deepen cooperation with industry partners to support customers’ business success in the 5G era.”

Huawei has already built massive information and communications technology (ICT) infrastructure across Africa, but faces challenges in the United States and other Western countries in the northern hemisphere over security concerns. The Trump administration banned tech exports to Chinese companies including Huawei Technologies, ZTE and China Telecom over alleged ties to Chinese military or surveillance networks, and lobbied allied nations to do the same. President Biden took his predecessor’s restrictions forward last year, signing a law to block Chinese companies including Huawei. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has named Chinese telecoms firms China Unicom and Pacific Networks Corp as threats to U.S. national security, with a formal ban likely to go through soon.
China’s foreign ministry said: “What the U.S. did violates the rules of the market economy … and seriously hurts the interests of Chinese companies.” “China firmly rejects this. We urge the U.S. side to immediately change its wrong course of action and stop hobbling and suppressing Chinese companies.” In Africa, however, local operators have invested heavily in Chinese equipment and infrastructure, with Beijing often providing funding to build ICT infrastructure including data centers, fiber optic cables and cloud services.
Huawei also faces headwinds in Europe, where Britain and some European Union countries have blacklisted the company from supplier lists for mobile networks, including 5G.
Delivering the keynote speech at the Bangkok summit, Coulibaly Yacouba, CEO of the Ivory Coast mobile spectrum authority, hailed the advent of the 5G era in his country – due to host the Africa Cup of Nations in early 2024.
“The government and local operators are making comprehensive preparations for the commercial launch of 5G in the country. People are expected to enjoy the ultimate service experience brought by innovative 5G technologies during the next Africa Cup of Nations,” he said.
Late last month, two more African mobile network operators – in South Africa and Kenya – launched 5G networks powered by Huawei. South Africa’s partly state-owned Telkom followed smaller data-only network Rain – which in 2019 became Africa’s first telecoms to deploy a commercial 5G network using Huawei. In Kenya, largest mobile network operator Safaricom became East Africa’s first telecoms company to commercially launch 5G high-speed internet services, with infrastructure built by Huawei and Finland’s Nokia.
Deploying multiple vendors, as Safaricom has done, is seen as a way for African operators to get around US or European sanctions and calls to avoid Chinese technology. In South Africa, Vodacom – a subsidiary of Britain’s Vodafone – uses Nokia alongside Huawei as a network provider, while MTN uses tech from Sweden’s Ericsson as well as Huawei and ZTE.
Abishur Prakash, co-founder and geopolitical futurist at the Centre for Innovating the Future, a Canada-based advisory firm, said the Western pushback had made Huawei realise that some countries were “off limits”, with its most lucrative business lines, like 5G, being banned or restricted from India to Japan to Britain. “Now, Huawei is focusing on markets that are less under the thumb of the West – like Africa and the Middle East,” Prakash said. What Huawei was experiencing was part of a new era of “vertical globalisation”, he said. “The world is no longer open and accessible, as it has been for decades … In this new design of the world, Huawei cannot operate freely, the way [America’s] IBM and GE once did.” The US-China rivalry was revealing a new African position, Prakash noted. “African nations are willing to put their own interests first. Take Kenya. It will continue buying from Huawei, even if the US doesn’t want this. It’s this attitude, where Africa is willing to ignore the US, that’s encouraging Huawei to focus more on the continent. Of course, none of this comes without challenges.” Prakash said that while Africa was acting independently, it was also ceding sovereignty as U.S. and Chinese technology companies dominated their societies.
“[As] for the West, it will have to contend with the footprint China is building in Africa, and how this drives Chinese power in the 21st century.”
No government in Africa has banned operators from using Huawei technology. In 2019, South African President Cyril Ramaphosa hinted his country would choose Huawei for its 5G roll-out, and also criticized the U.S. government. “Because they have been outstripped, they must now punish that company and use it as a pawn in the fight they have with China. We want 5G and we know where we can get 5G.”
Those sentiments are also supported by operators in Africa. According to Stephane Richard, CEO of French telecoms giant Orange, Africa’s No 2 operator after MTN: “We’re working more and more with Chinese vendors in Africa, not because we like China, but we have an excellent business relationship with Huawei. They’ve invested in Africa while the European vendors have been hesitating,” Richard told Reuters during last year’s Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Spain.
New Zealand-based Kenyan telecoms and IT consultant, Peter Wanyonyi, said US and European warnings to African and other developing countries against using Huawei had nothing to do with security or spying. “It’s all about geopolitical power and protectionism – and the West’s fear of a rising China,” Wanyonyi said.
He maintains that the West saw Huawei – and other leading Chinese companies – as threats to the dominance that Western companies had enjoyed in Africa and the Global South for 200 years. The economies of scale meant Huawei could bring leading-edge products onto the market much faster than Western rivals could, and China’s pro-business outlook encouraged investment in research and development at rates that the West simply could not match, he said. “The result is that Huawei technologies are more affordable and now more robust than what the West has to offer, and African countries are jumping at the opportunity afforded by Huawei to modernise their technology infrastructure.” Chinese investments in Africa were not charity, he added.
“To many Africans, it is a relief to just be able to do business without having to deal with the paternalism and historical baggage that Western companies carry around with them when doing business in Africa. “Huawei technology is affordable, available, unconditional and does the job – and will thus continue to be the technology of choice for many African telecoms.” Dobek Pater, business development director at the market research firm Africa Analysis, said Huawei equipment has improved significantly over the years and was very competitive in terms of quality and price with traditional “Western” equipment.
“Particularly in the case of 5G, Huawei has invested a lot in R&D. This makes Huawei often a preferred supplier,” Pater said. “Moreover, in many instances the mobile network operators or fixed-line operators already have quite a bit of Huawei kit installed in their networks and it makes sense to continue building out networks with Huawei equipment,” Pater said. He said some of the operators followed a strategy of using multiple suppliers of new technologies.
“In the case of 5G, there are only really three main providers of [radio access network] equipment. Huawei is one of them. Therefore, it naturally becomes a choice in many instances,” Pater said. Another advantage for Huawei was the Chinese government’s willingness to advance soft loans to help in infrastructure development. However, Huawei has not gone without controversy in Africa, he added.
n 2018, French newspaper Le Monde reported Huawei had bugged the African Union headquarters in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia – claims that were rejected by the company. The following year, Huawei lodged a protest with The Wall Street Journal after it reported that the Chinese company had helped the Ugandan and Zambian governments spy on political opponents. Huawei denied the allegations.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/technology-insights/publications/huawei-tech/202203/5g-business-success
https://www.connectingafrica.com/author.asp?section_id=728&doc_id=778960
Samsung achieves record speeds over 10km 5G mmWave FWA trial in Australia
South Korea’s Samsung Electronics says it has achieved record-setting average downlink speeds of 1.75 Gbps and uplink speeds of 61.5 Mbps over a 10 km (6.2 miles) 5G mmWave network in a recent field trial conducted with Australia’s NBN Co. As the farthest 28 GHz 5G mmWave Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) connection recorded by Samsung, this milestone demonstrates the expanded reach possible with this powerful spectrum, and its ability to efficiently deliver widespread broadband coverage across the country.

Source: Accton
To achieve average downlink speeds of 1.75 Gbps at such extended range, the trial by Samsung and NBN utilized eight component carriers (8CC), which is an aggregation of 800MHz of mmWave spectrum. The potential to support large amounts of bandwidth is a key advantage of the mmWave spectrum and Samsung’s beamforming technology enables the aggregation of such large amounts of bandwidth at long distance. At its peak, the company also reached a top downlink speed of 2.7Gbps over a 10km distance from the radio.
“The results of these trials with Samsung are a significant milestone and demonstrate how we are pushing the boundaries of innovation in support of the digital capabilities in Australia,” said Ray Owen, Chief Technology Officer at NBN Co. “As we roll out the next evolution of our network to extend its reach for the benefit of homes and businesses across the country, we are excited to demonstrate the potential for 5G mmWave. nbn will be among the first in the world to deploy 5G mmWave technology at this scale, and achievements like Samsung’s 10km milestone will pave the way for further developments in the ecosystem.”
There’s a total of AUD $750 million investment in the nbn Fixed Wireless network (made up of AUD $480 million from the Australian Government and supported by an additional AUD $270 million from nbn). NBN will use software enhancements and advances in 5G technology, and in particular 5G mmWave technology, to extend the reach of the existing fixed wireless footprint by up to 50 percent and introduce two new wholesale high-speed tiers. The nbn FWA network covers nearly 650,000 premises in the country. The company wants to add at least 120,000 locations in Australia that are currently served by a satellite-based service.
“This new 5G record proves the massive potential of mmWave technology, and its ability to deliver enhanced connectivity and capacity for addressing the last mile challenges in rural areas,” said Junehee Lee, Executive Vice President and Head of R&D, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “We are excited to work with nbn to push the boundaries of 5G technology even further in Australia and tap the power of mmWave for customer benefit.”
As demonstrated in the trials, 5G mmWave spectrum is not only viable for the deployment of high-capacity 5G networks in dense urban areas, but also for wider FWA coverage. Extending the effective range of 5G data signals on mmWave will help address the connectivity gap, providing access to rural and remote areas where fiber cannot reach.
For the trial, Samsung used its 28GHz Compact Macro and third-party 5G mmWave customer premise equipment (CPE). Samsung’s Compact Macro is the industry’s first integrated radio for mmWave spectrum, bringing together a baseband, radio and antenna into a single form factor. This compact and lightweight solution can support all frequencies within the mmWave spectrum, simplifying deployment, and is currently deployed in commercial 5G networks across the globe, including Japan, Korea and the U.S.
Since launching the world’s first 5G mmWave FWA services in 2018 in the U.S., Samsung has been leading the industry, offering an end-to-end portfolio of 5G mmWave solutions — including in-house chipsets and radios — and advancing the 5G mmWave momentum globally.
The nbn® network is Australia’s digital backbone that helps deliver reliable and resilient broadband across a continent spanning more than seven million square kilometers. nbn is committed to responding to the digital connectivity needs of people across Australia, working with industry, governments, regulators and community partners to increase the digital capability of Australia.
Samsung has pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions including chipsets, radios and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio from RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company is currently providing network solutions to mobile operators that deliver connectivity to hundreds of millions of users around the world.
Nokia had previously announced it was supplying 5G FWA mmWave CPE equipment for nbn’s efforts that also operates in the 28 GHz band with similar performance characteristics stated by Samsung for its test, including a range of up to 6.2 miles from the transmission tower. However, Samsung said that Nokia’s equipment was not part of its test.
Nokia noted that its CPE includes an antenna installed on the roof of a premises that is linked using a 2.5 Gb/s power over Ethernet (PoE) connection to an indoor unit that powers the on-premises internet connectivity.
Related Articles:
- Samsung Electronics Supports NTT East’s Continued Expansion of Private 5G Networks in Japan
- Samsung Electronics Tapped To Support Comcast’s 5G Connectivity Efforts
- Samsung Electronics To Deliver Private 5G Network Solutions to Korea’s Public and Private Sectors
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/samsung-nokia-power-5g-mmwave-potential/2022/11/
Sabotage or Accident: Was Russia or a fishing trawler responsible for Shetland Island cable cut?
Most telecom professionals, analysts, and media don’t realize how dependent the world is on a limited number of fiber-optic subsea cables that form the internet’s spine and electronically link our continents and islands. Currently 95% of international internet traffic is transmitted by undersea cables. Satellites, in comparison, convey very little internet traffic.
There are still only about 200 cables around the world, each the size of a large hose pipe and capable of data transfers at about 200 terabytes per second. These cables lie on the ocean floor, while nearer to the shore they are buried under the seabed for additional protection. They carry an estimated $10 trillion worth of financial transactions every day and come together at 10 or so international chokepoints, which are particularly vulnerable.
On October 20th, the subsea cable connecting Shetland and the Faroe Islands was damaged with a separate cable linking Shetland with the Scottish mainland also being cut. BT Group, which provides communications services through the cables, said engineers had been working “flat out” to repair the damage – which had primarily impacted mobile and broadband connections.
A BT spokesperson said: “While both cable links are being repaired by subsea engineers, engineers were able to reconnect all services via a temporary solution on Thursday afternoon.”
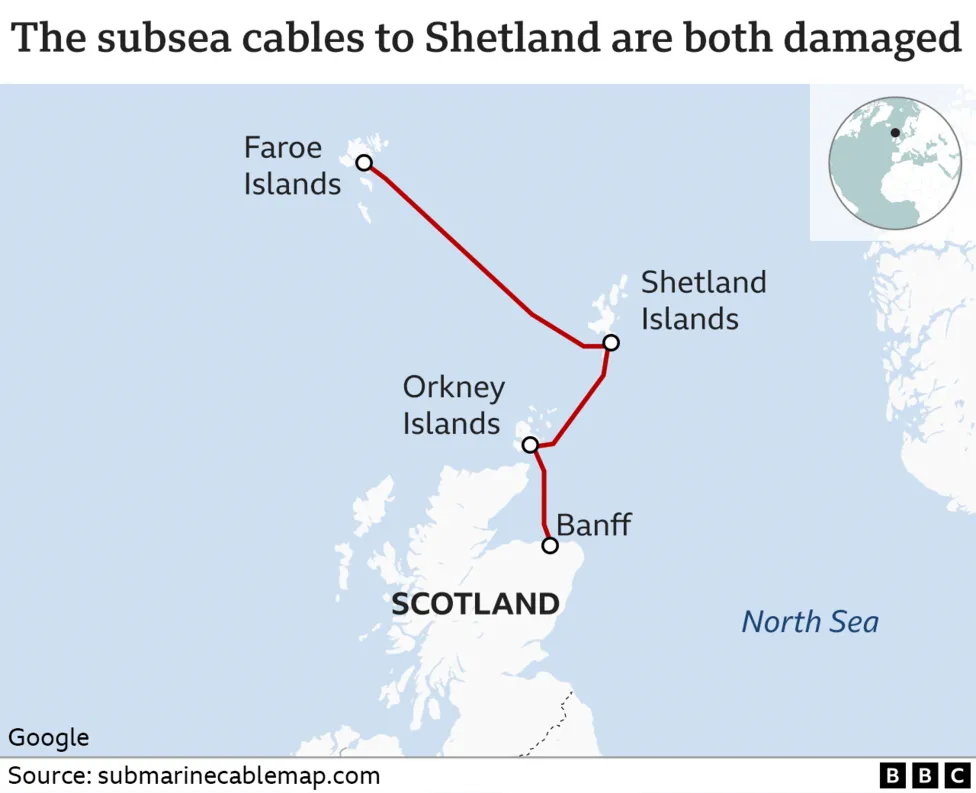
Although the BBC attributed the Shetland subsea cable damage to a fishing trawler, there is speculation that Moscow may have been the culprit. The Financial Times (and other sources) reported that Russia’s Boris Petrov scientific research ship, was tracked in the vicinity of the Shetland Isles cables when they were cut. Since it’s designated a ‘vessel of interest’ by western navies, there’s every chance the fault could have been an example of Russia’s hybrid warfare.
The FT wrote: “The presence of a Russian underwater research ship, and the recent trio of underwater explosions that severed the Nordstream gas pipeline, make Moscow sabotage far more plausible.
Lord West, the former head of the Royal Navy, told Talk Radio: “In the Shetlands recently, where power was lost a couple of times and I’m sure it was probably a dredger or a trawler did it. “But actually there was a Russian ship of the type that can cause damage to damaged pipelines in that region. And hopefully, we are monitoring very closely making sure we’re seeing what they are doing.”
Alexander Lord, a Europe and Eurasia analyst at Sibylline told Express.co.uk: “I think in the instance of the Shetland Islands I think that’s a really interesting one to watch. Obviously, accidents do happen, and these undersea cables do occasionally get damaged by fishing trawlers, for example.
“But I think it is notable and indeed local officials have noted that it’s highly unusual that two cables were damaged in quick succession and that’s what we’ve seen this week, it is what’s caused some of the problems in Shetland. In terms of the vulnerability of European critical infrastructure, maritime assets, for example, including undersea cables will remain particularly vulnerable, undersea pipelines as well.”
The FT noted that UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak wrote a paper in 2017 on the growing sabotage threat to subsea cables. From that paper: “In the digital age of cloud computing, the idea that steel and plastic pipes are integral to our life seems anachronistic,’ wrote Rishi Sunak. ‘But our ability to transmit confidential information, to conduct financial transactions and to communicate internationally all depend upon a global network of physical cables lying under the sea.’ And what if those cables are cut? The threat is nothing short of existential.”
In his 2017 paper, Sunak made several recommendations for fortifying the security of undersea cables. These included incentivising private businesses such as Google and Facebook, which own or finance much of the global cable network, to back up systems and distribute cables more widely. But nothing was done.
The UK has around 60 undersea cables. If several of these were cut or disrupted, the consequences would be disastrous. Now that Sunak is the UK PM, will he invest in protective maritime and submarine capabilities as he recommended in his 2017 paper?
This past January, Admiral Tony Radakin, the head of the British Armed Forces, observed that ‘Russia has grown the capability to put at threat those undersea cables and potentially exploit undersea cables.’ It’s now crunch time for the UK!
References:
https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-scotland-north-east-orkney-shetland-63337473
https://www.ft.com/content/0ddc5b48-b255-401b-8e9f-8660f4eab37b
https://www.spectator.co.uk/article/the-threat-to-britains-undersea-cables/
Cable One invests $50 million in Ziply Fiber after its JV called Clearwire Fiber
Cable One [1.] has invested $50 million to acquire a minority stake in northwestern U.S. wireline network operator Ziply Fiber [2.]. Although the investment was made on September 6th, it was first announced Thursday November 3rd when Cable One Chair and CEO Julie Laulis revealed the investment during the company’s Q3 2022 earnings call. She referred to Ziply Fiber as Cable One’s “newest strategic growth partner.” A Ziply representative confirmed the sum from Cable One was part of the $450 million in new funding it announced on September 8th.
Note 1. Cable One is an American broadband communications provider. Under the Sparklight brand, it provides service to 21 states and 900,000 residential and business customers. It is headquartered in Phoenix, Arizona, though it does not serve that metro area.
Note 2. Ziply Fiber was formed from the acquisition of Frontier Communications operations in Washington, Oregon and Montana. Ziply has an ambitious fiber buildout/upgrade plan with the launch of symmetrical, multi-gigabit broadband speed tiers.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In a 10-Q filing, Cable One stated it invested an initial $22.2 million in Ziply in November 2022 and expects to invest the remaining $27.8 million before the end of September 2023. Its investment netted the company less than a 10% equity interest in Ziply.
“We are investing alongside proven operational and financial leaders that we have maintained long-term trusted relationships with and they continue to demonstrate the ability to deliver strong results and shareholder returns that align with our rigorous standards,” a Cable One spokesman told Light Reading.

Other highlights from Cable One’s Q3-2022 results and earnings call:
- Total revenues were $424.7 million in the third quarter of 2022 compared to $430.2 million in the third quarter of 2021. Year-over-year, residential data revenues increased 6.3% and business services revenues decreased 11.5%. Revenues for the third quarter of 2022 included $4.9 million from CableAmerica(1) operations. Revenues for the third quarter of 2021 included $16.3 million from operations that were contributed to Clearwave Fiber(1) and from the Divested Operations, of which a substantial majority consisted of business services revenues.
- Net income was $70.6 million in the third quarter of 2022, an increase of 35.1% year-over-year. Adjusted EBITDA was $224.6 million in the third quarter of 2022, an increase of 1.9% year-over-year. Net profit margin was 16.6% and Adjusted EBITDA margin(2) was 52.9%.
- Revenues decreased $5.5 million, or 1.3%, to $424.7 million for the third quarter of 2022 due primarily to the contribution of operations to Clearwave Fiber and the disposition of the Divested Operations during 2022 that collectively generated $16.3 million of revenues in the prior year quarter, predominantly consisting of business services revenues, and decreases in residential video and residential voice revenues. The decrease was partially offset by increases in higher margin residential data and business services revenues from continuing operations and the addition of CableAmerica operations.
- Cable One, like other cable operators, is seeing a slowdown in consumer move activity across its footprint. The operator posted an organic gain of just 1,800 broadband subs in the quarter, according to MoffettNathanson, a division of SVB Securities.
- Sell-in for 1-Gig service has accelerated to nearly 32%.
- Cable One’s average revenue per user (ARPU) rose 15%, to $80.46, as customers migrated to faster, higher-priced services or took an unlimited data plan.
- Rate increases are “absolutely on the table,” Laulis said.
- Average data usage reached about 580 gigabytes per month in Q3, up 19% year-over-year.
- Cable One, which has DOCSIS 4.0 on its roadmap, has tested symmetrical multi-gigabit speeds, but did not say when it might launch such services.
- FWA adoption in Cable One’s markets “remains low,” Laulis said.
- Video losses hit 18,000, widened from a year-ago loss of 8,000. Reflecting Cable One’s de-emphasis on video and its laser-focus on broadband, the company’s video base eroded by another 28% year-over-year.
At the start of 2022, Cable One along with three private equity companies formed a joint venture called Clearwave Fiber, aiming to reach 500,000 rural locations by 2027. Cable One contributed assets from its Illinois-focused Clearwave Communications and South Carolina-based Hargray Communications businesses as part of the deal. Shortly after its formation, Clearwave Fiber acquired the assets of Kansas-based operator RG Fiber to gain a foothold in the state.
Earlier this week, Clearwave Fiber revealed it has already crossed the 100,000 passings mark. By the end of this year, the company said its services will be available in a total of 35 markets across four states: Illinois, Kansas, Georgia and Florida.
References:
Cable One joint venture to expand fiber based internet access via FTTP
Ziply Fiber deploys 2 Gig & 5 Gig fiber internet tiers in 60 cities – AT&T can now top that!
Frontier Communications and Ziply Fiber to raise funds for fiber optic network buildouts
https://www.lightreading.com/cable-tech/cable-one-invests-$50m-in-ziply-fiber/d/d-id/781591
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/broadband/cable-one-doubles-down-fiber-50m-ziply-investment
FCC establishes Space Bureau dedicated to satellite industry oversight
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has set up a new bureau dedicated to improving the agency’s oversight of the satellite industry. It is one of two new offices to come out of an internal reorganization at the FCC, which has also created a standalone office of international affairs.
According to the FCC, the changes will help the agency fulfill its statutory obligations and to keep pace with the rapidly changing satellite industry and global communications policy. Establishing a standalone Space Bureau will elevate the importance of satellite programs and policy internally, and will also acknowledge the role of satellite communications in advancing domestic communications policy, according to the agency.
“The satellite industry is growing at a record pace, but here on the ground our regulatory frameworks for licensing them have not kept up. Over the past two years the agency has received applications for 64,000 new satellites. In addition, we are seeing new commercial models, new players, and new technologies coming together to pioneer a wide-range of new satellite services and space-based activities that need access to wireless airwaves,” said FCC Chairwoman Rosenworcel in her prepared remarks.
After identifying space tourism, satellite broadband, disaster recovery efforts and more, Rosenworcel said the interest in space as a new market for investment and a home for new kinds of services is vast. She noted that “private investment in space companies has reached more than $10 billion in the last year, the highest it has ever been.”
She also said that “the space sector has been on a monumental run. Satellite operators set a new record last year for the number of satellites launched into orbit, a record they will surpass again.”
Under the Communications Act of 1934, the FCC licenses radio frequency uses by satellites and ensures that space systems reviewed by the agency have sufficient plans to mitigate orbital debris.
The FCC said also that creating the two new separate offices will allow expertise to be more consistently leveraged across the organization’s different bureaus.
Commenting on the reorganization, FCC Chairwoman Rosenworcel said: “The satellite industry is growing at a record pace, but here on the ground our regulatory frameworks for licensing them have not kept up. Over the past two years, the agency has received applications for 64,000 new satellites. In addition, we are seeing new commercial models, new players, and new technologies coming together to pioneer a wide-range of new satellite services and space-based activities that need access to wireless airwaves.”
“Today, I announced a plan to build on this success and prepare for what comes next,” she added. “A new Space Bureau at the FCC will ensure that the agency’s resources are appropriately aligned to fulfill its statutory obligations, improve its coordination across the federal government, and support the 21st century satellite industry.”
Jennifer Warren, VP of technology, policy and regulation at Lockheed Martin, said during a panel following Rosenworcel’s announcement that the stakes are much bigger than broadband satellite launches. This new regulatory framework can clear the way for the US to be a leader in “the commercialization of space,” she said. “It’s not for the faint-hearted.”
The FCC bureau reorg “also gives encouragement to new space actors that there will be staff accessible to answer the many questions they must have as they try to enter this exciting industry,” according to Julie Zoller, Head of Global Regulatory Affairs, Project Kuiper at Amazon. “It’s a complex process, but it is one that is full of opportunity and benefits to consumers, as Chairwoman Rosenworcel mentioned. The number of broadband satellite systems is really supercharging the ability to bridge the digital divide curve at home and abroad.”
In August, the FCC signed a joint memorandum of understanding with the NTIA aimed at improving the coordination of federal spectrum management and efficient use of radio frequencies.
References:
FCC establishes new bureau dedicated to satellite industry oversight
https://www.lightreading.com/satellite/the-fcc-takes-its-bureaucracy-beyond-stars/d/d-id/781568
Frontier’s Big Fiber Build-Out Continued in Q3-2022 with 351,000 fiber optic premises added
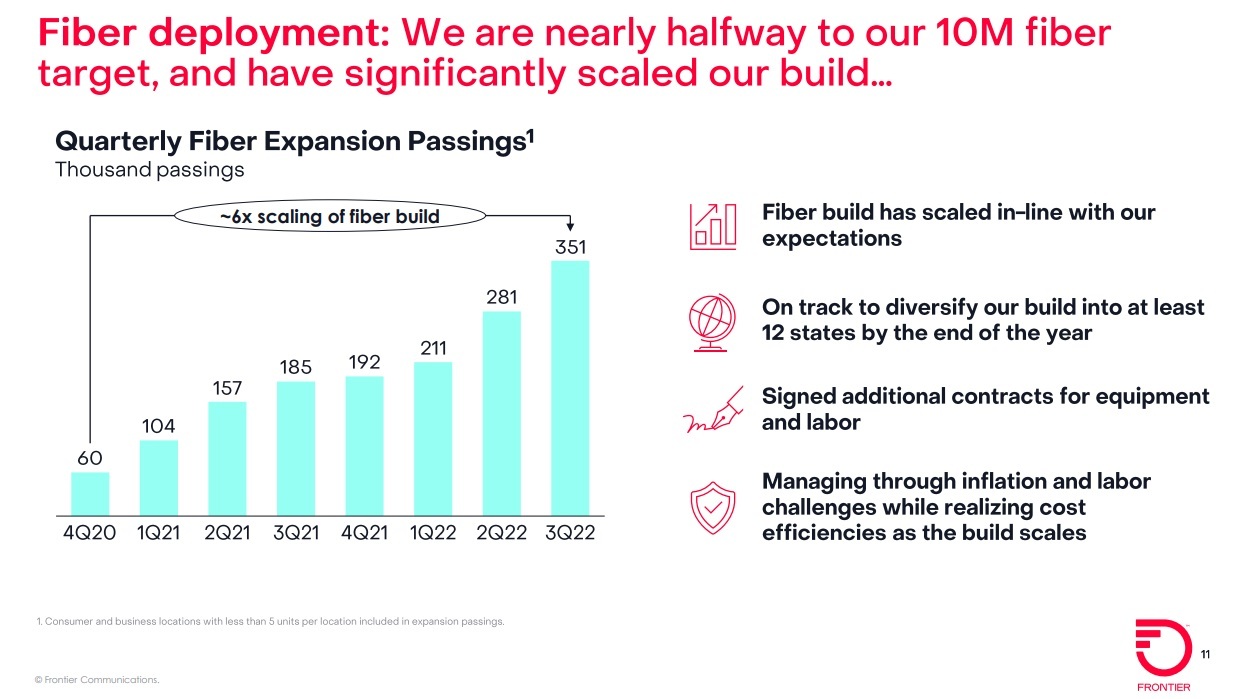
Frontier Communicatons massive fiber build-out continued in the third quarter (Q3-2022), as the company added record number of fiber subscribers to reach a total of 4.8M fiber locations. Frontier is poised to reach 5 million locations passed with fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) networks this month, putting it at the halfway point toward a goal to reach at least 10 million locations with fiber by the end of 2025. The company added a record 64,000 fiber subscribers, beating the 57,000 expected by analysts. That helped to offset greater than expected copper subscriber losses of -58,000. Consumer fiber Q3 revenue climbed 14% to $424 million while consumer copper fiber dropped 3% to $361 million.
Frontier built FTTP to a record 351,000 fiber optic premises in Q3-2022, handily beating the 185,000 built out in the year-ago quarter and the 281,000 built in Q2 2022. Frontier ended Q3 with 1.50 million fiber subs, up 16% versus the year-ago quarter.
“We delivered another quarter of record-breaking operational results,” said Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier. “Our team set a new pace for building and selling fiber this quarter. At the same time, we radically simplified our business and delivered significant cost savings ahead of plan. This is a sign of a successful turnaround.
“Our team has rallied around our purpose of Building Gigabit America and is laser-focused on executing our fiber-first strategy. As the second-largest fiber builder and the largest pure-play fiber provider in the country, we are well-positioned to win.”
Third-quarter 2022 Highlights:
- Built fiber to a record 351,000 locations to reach a total of 4.8 million fiber locations, nearly halfway to our target of 10 million fiber locations
- Added a record 66,000 fiber broadband customers, resulting in fiber broadband customer growth of 15.8% compared with the third quarter of 2021
- Revenue of $1.44 billion, net income of $120 million, and Adjusted EBITDA of $508 million
- Capital expenditures of $772 million, including $18 million of subsidy-related build capital expenditures, $442 million of non-subsidy-related build capital expenditures, and $170 million of customer-acquisition capital expenditures.
- Net cash from operations of $284 million, driven by healthy operating performance and increased focus on working capital management
- Nearly achieved our $250 million gross annual cost savings target more than one year ahead of plan, enabling us to raise our target to $400 million by the end of 2024
In Frontier’s “base” fiber footprint of 3.2 million homes (in more mature areas where fiber’s been available for several years), penetration rose 30 basis points in Q3 to 42.9%. “When we look at the growth over the past year, we see a clear path to achieving our long term target of 45% penetration in our base markets,” Frontier CEO Nick Jeffery said.
Penetration rates in Frontier’s expansion fiber footprint for the 2021 cohort is on target and is exceeding expectations in the 2020 expansion fiber footprint, he said.
Fiber ARPU (average revenue per user) was up 2.6% year-over-year, but came a little short of expectations thanks in part to gift card promotions. Frontier’s consumer fiber ARPU, at $62.97, missed New Street Research’s expectation of $63.67 and a consensus estimate of $64.51. Copper ARPU, however, beat estimates: $49.65 versus an expected $48.57.
Frontier CEO Jeffery said faster speeds remain a top ARPU driver, with 45% to 50% of new fiber subs selecting tiers offering speeds of 1Gbit/s or more. Fiber subs taking speeds of 1Gbit/s or more now make up 15% to 20% of Frontier’s base, up from 10% to 15% last quarter, he said.
Frontier currently has no plans to raise prices due to inflation and other economic pressures, but the company left the door open to such a move.
“We’ll be a rational pricing actor in this market,” Jeffery said. “If those [inflationary pressures] don’t moderate, then of course we maybe consider pricing actions to compensate…just as we’re seeing others doing.”
Frontier also has no immediate plans to strike an MVNO deal that would enable it to use mobile in a bundle to help gain and retain broadband subscribers – a playbook already in use by Comcast, Charter Communications, WideOpenWest and Altice USA.
As churn rates remain stable and low, Jeffery explained, “the argument for using some of that scarce capital to divert into an MVNO to solve a problem that we don’t yet have, I think, would probably not make our shareholders super happy.” Importantly, Frontier has experience in the mobile area from execs who previously worked at Vodafone, Verizon and AT&T.
“We’re watching it very closely and if consumer behavior changes or if the market changes in a material way that impacts us such that moving some of our scarce capital to build or partner with an MVNO would be a smart thing to do, we’ll do it and we’ll do it very quickly,” Jeffery said. “But now isn’t the moment for us.”
Frontier ended the quarter with $3.3 billion of liquidity to fund its fiber build. Beasley said Frontier has additional options if needed, including taking on more debt, selling non-core real estate assets, access to government subsidies and the benefits of a cost-savings plan that has exceeded the target (from an original $250 million to $400 million).
References:
The conference call webcast and presentation materials are accessible through Frontier’s Investor Relations website and will remain archived at that location.
https://events.q4inc.com/attendee/387527166
https://www.lightreading.com/broadband/frontiers-big-fiber-build-nears-halfway-point-/d/d-id/781503?
JC Market Research: 5G FWA market to reach $21.7 billion in 2029 for a CAGR of 65.6%
Introduction:
According to JC Market Research, the 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) market was valued at US $296 million in 2021. In a new report ““Worldwide 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) Industry Analysis,” the market research firm forecasts that global 5G FWA rеvеnuе will rеасh а vаluе оf UЅ$ 21,710 million іn 2029. That’s a remarkable CAGR of 65.6% over the forecast period.
Yesterday, we posted an article on South Africa’s Telkom deploying 5G FWA before 5G mobile and it appears that 5G FWA is a stronger use case than 5G mobile.

Glоbаl 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) Industry Dуnаmісѕ:
In many of smart cities, 5G IoT will be the technology of choice for niche applications. Smart cities, with applications such as HD cameras to monitor safety, Smart energy, such as smart grid control, smart security, including the provision of emergency services and connected health, such as mobile medical monitoring is possible with the help of 5G networks. Advanced sensing for environmental monitoring can be done using this module.
The increasing adoption of connected devices such as smartphones, laptops, and smart devices in several commercial and residential applications such as distance learning, autonomous driving, multiuser gaming, videoconferencing, and live streaming, as well as in telemedicine and augmented reality, is expected to generate the demand for 5G fixed wireless access solutions to achieve extended coverage.
Global 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) Industry Analysis Маrkеt Drіvеrѕ Rеgіоnаl Ѕеgmеntаtіоn аnd Аnаlуѕіѕ:
Rеgіоn-wіѕе ѕеgmеntаtіоn in the global 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) industry іnсludеѕ North Аmеrіса, Еurоре, Аѕіа Расіfіс, Ѕоuth Аmеrіса, аnd the Міddlе Еаѕt & Аfrіса. North Аmеrіса ассоuntѕ for hіghеѕt rеvеnuе ѕhаrе in the global 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) industry analysis market, аnd іѕ рrојесtеd tо rеgіѕtеr а rоbuѕt САGR оvеr thе fоrесаѕt реrіоd. While serving rural markets and developing nations is still a costly proposition, governments around the globe stand ready to provide aid. In the USA, phase two of the Connect America Fund (CAF) is supporting broadband initiatives in underserved communities. The connecting Europe Broadband fund is performing a similar role for underserved populations in EU member countries.
The report also indicated that North Аmеrіса, Еurоре, Аѕіа Расіfіс, Ѕоuth Аmеrіса аnd the Міddlе Еаѕt & Аfrіса as FWA market leaders.
JC Market Research is not the only research firm exploring the potential growth of the FWS market; ABI Research forecasts that the total number of FWA subscriptions will grow from 81 million globally in 2021 to slightly over 180 million in 2026, representing a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 17%. Consequently, ABI Research believes that global FWA Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) shipments will reach 47 million annually by 2026, with 5G FWA CPE making up the majority of shipments by the same year.
References:
https://jcmarketresearch.com/report-details/1538805/discount
5G FWA launched by South Africa’s Telkom, rather than 5G Mobile
5G fixed wireless access market to reach $22 million in 2029: Report
LightCounting: Optical components market to hit $20 billion by 2027+ Ethernet Switch ASIC Market Booms
|
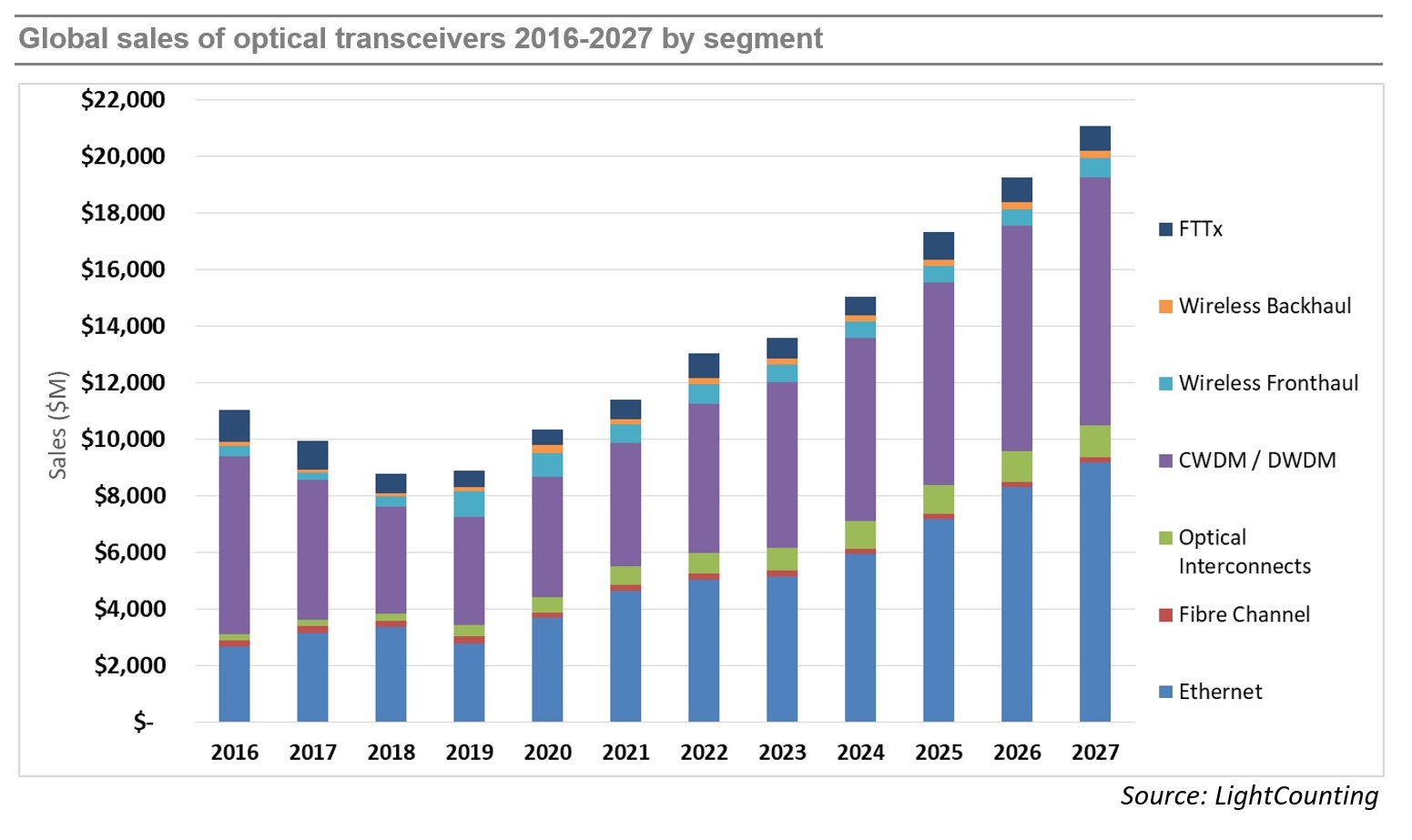
The optical communications industry entered 2020 with very strong momentum. Demand for DWDM, Ethernet, and wireless fronthaul connectivity surged at the end of 2019, and major shifts to work-at-home and school-at-home in 2020 and 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic created even stronger demand for faster, more ubiquitous, higher reliability networks.
While supply chain disruptions continued, the industry was able to largely overcome them, and the market for optical components and modules saw strong growth in 2020 and 2021, as shown in the figure below. Light Counting believes the transceiver market is on track for another year of strong (14%) revenue growth in 2022, after increasing by 10% in 2021, and 17% in 2020. However, market growth is projected to slow to 4% in 2023, prior to recovering in 2024-2025.
Demand for optics is strong across all market segments, but continuing bottlenecks in the global supply chain negatively impacted sales of 400G DR4 and 100G DR1+ transceivers to Amazon in the first 9 month of 2022. Meta increased its deployments of optics sharply this year, but its latest forecast for 2023 has been reduced substantially. We suspect that Amazon and other cloud companies may moderate their investments in 2023, if the current economic slowdown continues to negatively impact their advertising, streaming, and retail businesses.
|
 |
|
LightCounting’s latest forecast projects a 11% CAGR in 2022-2027, not very different from the 13% CAGR in the forecast published in October 2021. Strong sales of DWDM and Ethernet optics accounted for most of the market growth in 2021 and these segments are projected to lead the growth in 2022-2027. Sales of optical interconnects, mostly Active Optical Cables (AOCs), will also increase at double digit rates over the next 5 years. PON sales for FTTx networks will remain steady, as the China market ends its 10G cycle and North America and Europe ramp up 10G PON deployments, driven by government funding programs. 25G and 50G PON provide new growth later in the forecast period. Wireless fronthaul is one area of weakness, since 5G network deployments in China are reaching completion. This segment will return to growth in 2026-2027 with the onset of 6G deployments (which we don’t think will happen till many years later).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
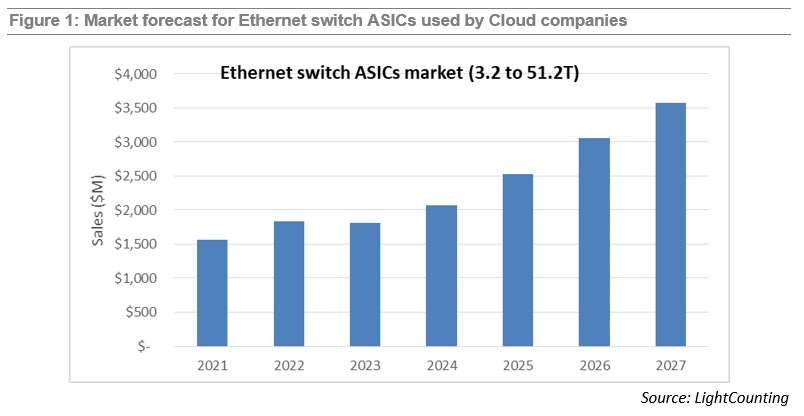
Demand for Ethernet switches from Cloud companies created a new market segment for very high bandwidth switches and switch ASICs. It also transformed the industry supply chain as Cloud companies started using internally designed Ethernet switches and opening these “white box” designs to a broader community. LightCounting’s report on Ethernet switch ASICs was first published in April 2022, and today the first update has been released. The report covers the most interesting segment of the switching ASIC market – high bandwidth (3.2T and above), low latency chips deployed in Cloud datacenters. The report offers brief profiles of the leading suppliers of merchant switch ASIC and system integrators, offering products to Cloud companies, and includes a forecast for sales of 3.2 to 51.2T switch ASICs. The updated report now includes 3.2T/6.4T chips in addition to the higher speed products. This change added close to $1 billion to the total market size compared to our April estimate. The forecast includes chips sold in the merchant market as well as chips used by Cisco in their own equipment (captive market). A lower forecast for 2023 compared to our April 2022 edition reflects reduced guidance by the leading Cloud companies for datacenter upgrades planned for next year. Despite a reduced forecast, the overall market is expected to roughly double in size from $1.8 billion in 2023 to $3.6 billion in 2027.
References:
|
5G FWA launched by South Africa’s Telkom, rather than 5G Mobile
South African telecommunications operator Telkom [1.] has launched its 5G high speed Internet network using technology from China’s Huawei Technologies. The partially state-owned operator said it will initially use the network to provide fixed wireless Internet via 5G rather than focusing on mobile 5G.
“At launch Telkom will primarily focus on providing super fast 5G fixed wireless access solutions, as the demand for mobile 5G increases, we will supplement this with suitable mobile propositions,” Telkom Consumer and Business CEO Lunga Siyo explained.
Note 1. Telkom is South Africa’s third largest network operator with 17.6 million users in the third quarter of 2022, according to statistics from market research company Omdia. Vodacom remains South Africa’s largest operator with over 52 million users while MTN has about 36 million customers.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Telkom joins its competitors Vodacom, MTN and Rain in the quest to provide high speed Internet in South Africa. Data-only network Rain rolled out its 5G services in 2019 and Vodacom and MTN followed with commercial launches in 2020.
Telkom said it will use its 125 5G base stations located in the provinces of Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal, Eastern Cape and Western Cape at launch.
The telco’s managing executive Lebo Masalesa said the company is rolling out 5G nationally and in smaller towns, with the intention to build network where it is needed.
“Once there is a greater proliferation of 5G capable mobile devices on Telkom’s network, it will launch 5G services for mobile users,” he added.
“5G stands head and shoulders above 4G and LTE through faster and more reliable connection it provides, however it was critical for us to make sure that our existing 4G ecosystem remains strong whilst introducing 5G into the market,” continued Siyo.
The South African network operator invested 2.1 billion South African rand (US$116 million) for 42MHz of frequencies in the spectrum auction by the Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA), supporting its network upgrades.
“The COVID pandemic has driven significant lifestyle changes for South Africans, due to work from home or school from home, online shopping and an ‘always on’ kind of culture,” said Fortune Wang, Carrier Business Director for Huawei South Africa.
“At launch Telkom will primarily focus on providing super fast 5G fixed wireless access solutions, as the demand for mobile 5G increases, we will supplement this with suitable mobile propositions,” said Lunga Siyo, chief executive officer of Telkom Consumer and Business.
Shunned in the global north due to security concerns, which Huawei has denied, the Chinese company dominates in Africa as a supplier of equipment to many telecoms operators.
Telkom SA’s commercial 5G rollout comes on the back of Safaricom in Kenya making a similar announcement last week about a focus on retail and enterprise customers for 5G rather than mobile, as it launched its 5G Internet service following trials that started in March 2021.
Furthermore, the commercial 5G launch comes after MTN walked away from talks to acquire Telkom. The talks between the two companies stalled when the data-only network operator Rain offered its network up to Telkom SA to acquire, in a move that stood in the way of MTN’s plans to buy Telkom.

References:
https://www.euronews.com/next/2022/10/27/telkom-sa-huawei-tech-5g