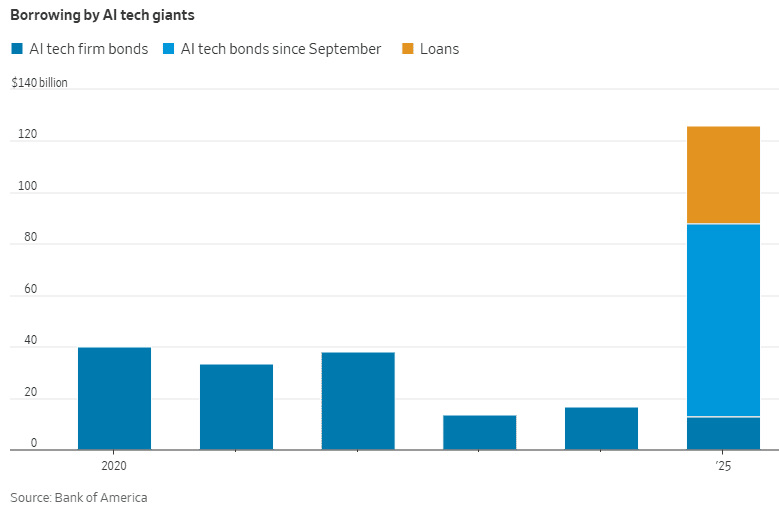Author: Alan Weissberger
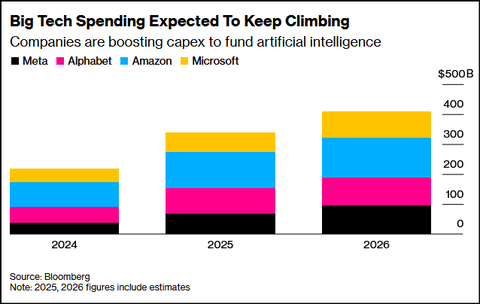
AI spending boom accelerates: Big tech to invest an aggregate of $400 billion in 2025; much more in 2026!
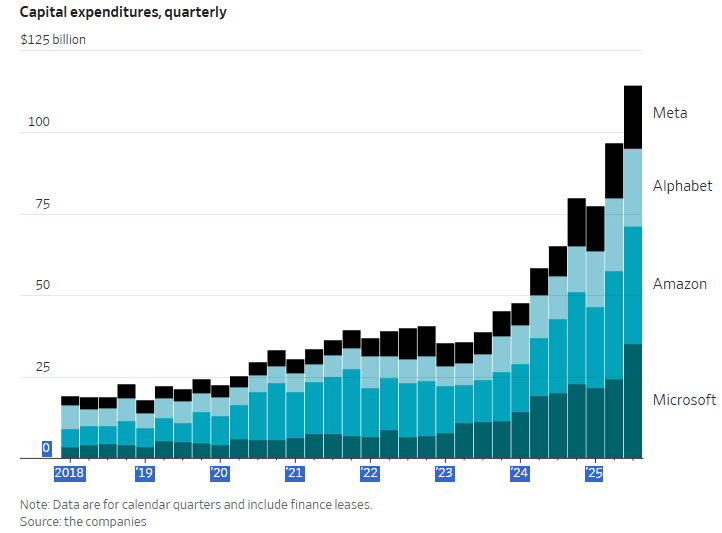
- Meta Platforms says it continues to experience capacity constraints as it simultaneously trains new AI models and supports existing product infrastructure. Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg described an unsatiated appetite for more computing resources that Meta must work to fulfill to ensure it’s a leader in a fast-moving AI race. “We want to make sure we’re not underinvesting,” he said on an earnings call with analysts Wednesday after posting third-quarter results. Meta signaled in the earnings report that capital expenditures would be “notably larger” next year than in 2025, during which Meta expects to spend as much as $72 billion. He indicated that the company’s existing advertising business and platforms are operating in a “compute-starved state.” This condition persists because Meta is allocating more resources toward AI research and development efforts rather than bolstering existing operations.
- Microsoft reported substantial customer demand for its data-center-driven services, prompting plans to double its data center footprint over the next two years. Concurrently, Amazon is working aggressively to deploy additional cloud capacity to meet demand. Amy Hood, Microsoft’s chief financial officer, said: “We’ve been short [on computing power] now for many quarters. I thought we were going to catch up. We are not. Demand is increasing.” She further elaborated, “When you see these kinds of demand signals and we know we’re behind, we do need to spend.”
- Alphabet (Google’s parent company) reported that capital expenditures will jump from $85 billion to between $91 billion and $93 billion. Google CFO Anat Ashkenazi said the investments are already yielding returns: “We already are generating billions of dollars from AI in the quarter. But then across the board, we have a rigorous framework and approach by which we evaluate these long-term investments.”
- Amazon has not provided a specific total dollar figure for its planned AI investment in 2026. However, the company has announced it expects its total capital expenditures (capex) in 2026 to be even higher than its 2025 projection of $125 billion, with the vast majority of this spending dedicated to AI and related infrastructure for Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- Apple: Announced it is also increasing its AI investments, though its overall spending remains smaller in comparison to the other tech giants.
As big as the spending projections were this week, they look pedestrian compared with OpenAI, which has announced roughly $1 trillion worth of AI infrastructure deals of late with partners including Nvidia , Oracle and Broadcom.
Despite the big capex tax write-offs (due to the 2025 GOP tax act) there is a large degree of uncertainty regarding the eventual outcomes of this substantial AI infrastructure spending. The companies themselves, along with numerous AI proponents, assert that these investments are essential for machine-learning systems to achieve artificial general intelligence (AGI), a state where they surpass human intelligence.
Yet skeptics question whether investing billions in large-language models (LLMs), the most prevalent AI system, will ultimately achieve that objective. They also highlight the limited number of paying users for existing technology and the prolonged training period required before a global workforce can effectively utilize it.
During investor calls following the earnings announcements, analysts directed incisive questions at company executives. On Microsoft’s call, one analyst voiced a central market concern, asking: “Are we in a bubble?” Similarly, on the call for Google’s parent company, Alphabet, another analyst questioned: “What early signs are you seeing that gives you confidence that the spending is really driving better returns longer term?”
Bank of America (BofA) credit strategists Yuri Seliger and Sohyun Marie Lee write in a client note that capital spending by five of the Magnificent Seven megacap tech companies (Amazon.com, Alphabet, and Microsoft, along with Meta and Oracle) has been growing even faster than their prodigious cash flows. “These companies collectively may be reaching a limit to how much AI capex they are willing to fund purely from cash flows,” they write. Consensus estimates of AI capex suggest will climb to 94% of operating cash flows, minus dividends and share repurchases, in 2025 and 2026, up from 76% in 2024. That’s still less than 100% of cash flows, so they don’t need to borrow to fund spending, “but it’s getting close,” they add.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Google, which projected a rise in its full-year capital expenditures from $85 billion to a range of $91 billion to $93 billion, indicated that these investments were already proving profitable. Google’s Ashkenazi stated: “We already are generating billions of dollars from AI in the quarter. But then across the board, we have a rigorous framework and approach by which we evaluate these long-term investments.”
Microsoft reported that it expects to face capacity shortages that will affect its ability to power both its current businesses and AI research needs until at least the first half of the next year. The company noted that its cloud computing division, Azure, is absorbing “most of the revenue impact.”
Amazon informed investors of its expedited efforts to bring new capacity online, citing its ability to immediately monetize these investments.
“You’re going to see us continue to be very aggressive in investing capacity because we see the demand,” said Amazon Chief Executive Andy Jassy. “As fast as we’re adding capacity right now, we’re monetizing it.”
Meta’s chief financial officer, Susan Li, stated that the company’s capital expenditures—which have already nearly doubled from last year to $72 billion this year—will grow “notably larger” in 2026, though specific figures were not provided. Meta brought this year’s biggest investment-grade corporate bond deal to market, totaling some $30 billion, the latest in a parade of recent data-center borrowing.
Apple confirmed during its earnings call it is also increasing investments in AI . However, its total spending levels remain significantly lower compared to the outlays planned by the other major technology firms.
Skepticism and Risk:
While proponents argue the investments are necessary for AGI and offer a competitive advantage, skeptics question if huge spending (capex) on AI infrastructure and large-language models will achieve this goal and point to limited paying users for current AI technology. Meta CEO Zuckerberg addressed this by telling investors the company would “simply pivot” if its AGI spending strategy proves incorrect.
The mad scramble by mega tech companies and Open AI to build AI data centers is largely relying on debt markets, with a slew of public and private mega deals since September. Hyperscalers would have to spend 94% of operating cash flow to pay for their AI buildouts so are turning to debt financing to help defray some of that cost, according to Bank of America. Unlike earnings per share, cash flow can’t be manipulated by companies. If they spend more on AI than they generate internally, they have to finance the difference.
Hyperscaler debt taken on so far this year have raised almost as much money as all debt financings done between 2020 and 2024, the BofA research said. BofA calculates $75 billion of AI-related public debt offerings just in the past two months!
In bubbles, everyone gets caught up in the idea that spending on the hot theme will deliver vast profits — eventually. When the bubble is big enough, it shifts the focus of the market as a whole from disliking capital expenditure, and hating speculative capital spending in particular, to loving it. That certainly seems the case today with surging AI spending. For much more, please check-out the References below.
Postscript: November 23, 2025:
In this new AI era, consumers and workers are not what drives the economy anymore. Instead, it’s spending on all things AI, mostly with borrowed money or circular financing deals.
BofA Research noted that Meta and Oracle issued $75 billion in bonds and loans in September and October 2025 alone to fund AI data center build outs, an amount more than double the annual average over the past decade. They warned that “The AI boom is hitting a money wall” as capital expenditures consume a large portion of free cash flow. Separately, a recent Bank of America Global Fund Manager Survey found that 53% of participating fund managers felt that AI stocks had reached bubble proportions. This marked a slight decrease from a record 54% in the prior month’s survey, but the concern has grown over time, with the “AI bubble” cited as the top “tail risk” by 45% of respondents in the November 2025 poll.
JP Morgan Chase estimates up to $7 trillion of AI spending will be with borrowed money. “The question is not ‘which market will finance the AI-boom?’ Rather, the question is ‘how will financings be structured to access every capital market?’ according to strategists at the bank led by Tarek Hamid.
As an example of AI debt financing, Meta did a $27 billion bond offering. It wasn’t on their balance sheet. They paid 100 basis points over what it would cost to put it on their balance sheet. Special purpose vehicles happen at the tail end of the cycle, not the early part of the cycle, notes Rajiv Jain of GQG Partners.
References:
Market research firms Omdia and Dell’Oro: impact of 6G and AI investments on telcos
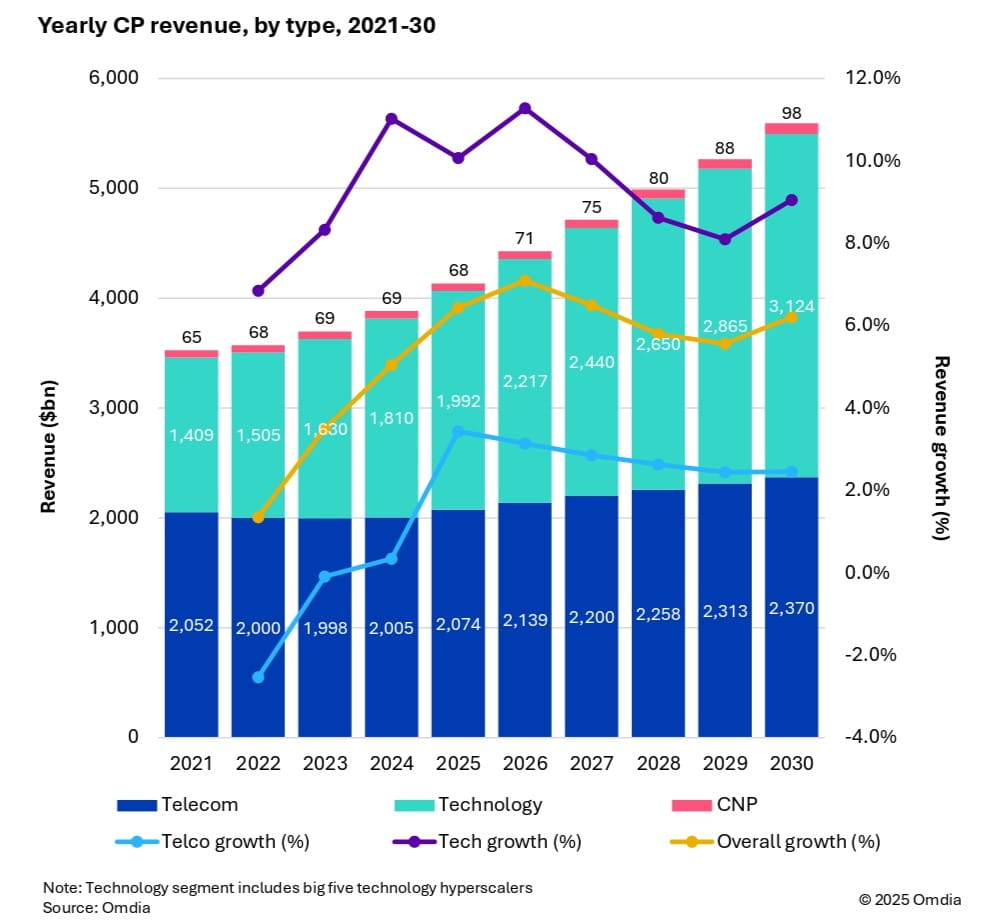
Market research firm Omdia (owned by Informa) this week forecast that 6G and AI investments are set to drive industry growth in the global communications market. As a result, global communications providers’ revenue is expected to reach $5.6 trillion by 2030, growing at a 6.2% CAGR from 2025. Investment momentum is also expected to shift toward mobile networks from 2028 onward, as tier 1 markets prepare for 6G deployments. Telecoms capex is forecast to reach $395 billion by 2030, with a 3.6% CAGR, while technology capex will surge to $545 billion, reflecting a 9.3% CAGR.
Fixed telecom capex will gradually decline due to market saturation. Meanwhile, AI infrastructure, cloud services, and digital sovereignty policies are driving telecom operators to expand data centers and invest in specialized hardware.
Key market trends:
- CP capex per person will increase from $74 in 2024 to $116 in 2030, with CP capex reaching 2.5% of global GDP investment.
-
Capital intensity in telecom will decline until 2027, then rise due to mobile network upgrades.
-
Regional leaders in revenue and capex include North America, Oceania & Eastern Asia, and Western Europe, with Central & Southern Asia showing the highest growth potential.
 Dario Talmesio, research director at Omdia said, “telecom operators are entering a new phase of strategic investment. With 6G on the horizon and AI infrastructure demands accelerating, the connectivity business is shifting from volume-based pricing to value-driven connectivity.”
Dario Talmesio, research director at Omdia said, “telecom operators are entering a new phase of strategic investment. With 6G on the horizon and AI infrastructure demands accelerating, the connectivity business is shifting from volume-based pricing to value-driven connectivity.”
Omdia’s forecast is based on a comprehensive model incorporating historical data from 67 countries, local market dynamics, regulatory trends, and technology migration patterns.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Dell’Oro Group sees 6G capex ramping around 2030, although it warns that the RAN market remains flat, “raising key questions for the industry’s future.” Cumulative 6G RAN investments over the 2029-2034 period are projected to account for 55% to 60% of the total RAN capex over the same forecast period.
“Our long-term position and characterization of this market have not changed,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President of RAN and Telecom Capex research at Dell’Oro Group. “The RAN network plays a pivotal role in the broader telecom market. There are opportunities to expand the RAN beyond the traditional MBB (mobile broadband) use cases. At the same time, there are serious near-term risks tilted to the downside, particularly when considering the slowdown in data traffic,” continued Pongratz.
Additional highlights from Dell’Oro’s October 2025 6G Advanced Research Report:
- The baseline scenario is for the broader RAN market to stay flat over the next 10 years. This is built on the assumption that the mobile network will run into utilization challenges by the end of the decade, spurring a 6G capex ramp dominated by Massive MIMO systems in the Sub-7GHz/cm Wave spectrum, utilizing the existing macro grid as much as possible.
- The report also outlines more optimistic and pessimistic growth scenarios, depending largely on the mobile data traffic growth trajectory and the impact beyond MBB, including private wireless and FWA (fixed wireless access).
- Cumulative 6G RAN investments over the 2029-2034 period are projected to account for 55 to 60 percent of the total RAN capex over the same forecast period.
Dell’Oro Group’s 6G Advanced Research Report offers an overview of the RAN market by technology, with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue for total RAN over the next 10 years. 6G RAN is analyzed by spectrum (Sub-7 GHz, cmWave, mmWave), by Massive MIMO, and by region (North America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, China, Asia Pacific Excl. China, and CALA). To purchase this report, please contact by email at [email protected].
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/6g-momentum-is-building
6G Capex Ramp to Start Around 2030, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/6g-course-correction-vendors-hear-mno-pleas
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/what-at-t-really-wants-from-6g
New Verizon CEO Dan Schulman to overhaul strategy; “cost reductions will be a way of life”
Verizon’s 3Q2025 Results:
Verizon lost a net 7,000 postpaid phone connections in the 3rd quarter of 2025, missing expectations of adding 19,000. However, the company reported a profit of $5.06 billion, or $1.17 a share, compared with $3.41 billion, or 78 cents a share, a year earlier. Stripping out certain one-time items, adjusted per-share earnings were $1.21 a share, just ahead of the $1.19 a share that analysts had forecast, according to FactSet. Revenue ticked 1.5% higher to $33.82 billion vs Wall Street analysts expectation of $34.26 billion.
Wireless service revenue—Verizon’s largest business—rose 2.1% year-over-year to $21 billion. The company added 306,000 broadband connections, ending the latest quarter with more than 13.2 million connections. It has also added 261,000 new fixed-wireless access connections.
Broadband:
- Delivered 306,000 broadband net additions in third-quarter 2025.
- Total fixed wireless access net additions were 261,000 in third-quarter 2025, bringing the base to nearly 5.4 million fixed wireless access subscribers.
- Delivered 61,000 Fios internet net additions in third-quarter 2025, the best quarterly result in two years.
- Total broadband connections grew to more than 13.2 million as of the end of third-quarter 2025, representing a 11.1 percent increase year-over-year.
Forward Guidance: Verizon expects total wireless-service revenue growth of 2% to 2.8%, while adjusted per-share earnings are projected to rise 1% to 3%.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Verizon’s New Strategy & Focus:
Dan Schulman was named CEO of Verizon on October 6, 2025, replacing former CEO Hans Vestberg. The new CEO plans to overhaul the company’s strategy, focusing on customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Schulman, who stepped into the CEO role earlier this month, said in a letter to employees that Verizon hasn’t been able to translate its years of heavy network investment into customer growth, especially amid fierce competition that has pressured pricing. Schulman attributed Verizon’s lagging performance to a strategy that relied too heavily on price increases without corresponding subscriber growth.
“Verizon has deep strengths and incredible potential, but the blunt truth is we haven’t captured the customer growth opportunities this strong foundation enables. “Our plan will not be about incremental change. We intend to aggressively transform the culture and financial profile of our company operating under the principles of being bold, customer centric and executing with financial discipline, with a focus on shareholder value,” he said.

Verizon will aim to fundamentally change its culture and cost structure to focus on customer satisfaction, operational efficiency and profitable expansion. Schulman plans to simplify offers and improve the customer experience, in part by leveraging artificial intelligence to tailor marketing and reduce costs. Verizon also intends to exit or streamline legacy businesses that don’t offer clear paths to profitability: “We will be a simpler, leaner and scrappier business,” Schulman said on the company’s earnings call.

Source: Jordi Boixareu
His assessment, is that while the #1 U.S. mobile operator by subscribers has been busy building out fiber and 5G, somewhere along the way it forgot about customers and has not been giving them good enough reasons to stay. “Despite investing significantly in network leadership, we have not been able to translate that into winning in the market, and, consequently, we are not generating the financial profile necessary for share price appreciation. Every year it gets harder to grow as we lap past price increases and experience higher churn. This cannot continue, and there is no question that meaningful change is needed,” Schulman said. “This is not a course correction, it is a fundamental change in our strategic approach to customers,” he said, noting that “raising rates without corresponding value rarely, if ever, delights customers.”
He stressed that attracting and retaining customers for the long-term will not come through “promotional activities” but rather a focus on and investment in value and customer experience to improve loyalty, “grow through retention,” and “make it much easier to do business with us.” Schulman’s goal is to have the lowest churn rate in the industry. “Verizon will no longer be the hunting ground for competitors looking to gain share,” he said. “We will be a simpler, leaner and scrappier business. This work is overdue and will be multi-year … Cost reductions will be a way of life for us,” he added.
As Verizon redirects investment to specific growth areas, it will also “aggressively” shut down or exit legacy businesses that are not profitable, which would “unleash margin improvement.” But as to which businesses he has in mind, more will be revealed at the operator’s next investment update in January 2026.
AI will be leveraged to “simply offers” and reduce churn “through smart, consistent and more personalized marketing,” while reducing cost and complexity across processes, he said. Verizon will continue to invest in growth areas – namely, its fiber build and C-band spectrum rollout. But it will also keep an eye out for other opportunities that might come along, noting that it has the financial flexibility in its balance sheet to do so. Schulman did not divulge what types of investments he might be interested in so we will have to wait till January for that information.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In a research note published today, MoffettNathanson analyst Craig Moffett said Schulman “described a shift towards being a customer-centric company, with the ‘best value proposition’ in the market. There is a clear focus on subscriber metrics. He called it a ‘full reboot.’ The obvious question is… how? Verizon is no longer perceived to have the best network. And it is perceived to have the highest prices. His promise to reverse subscriber losses without relying on promotions and price strikes us as more of a wish than a strategy.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/new-verizon-playing-to-win
https://www.verizon.com/about/investors/quarterly-reports/3q-2025-earnings-conference-call-webcast
https://www.wsj.com/business/earnings/verizon-backs-outlook-as-profit-revenue-rise-f92e4a6c
https://www.lightreading.com/broadband/verizon-ceo-dan-schulman-calls-for-full-reboot-
Verizon’s commercial agreement with Eaton Fiber to accelerate fiber/mobile convergence
AT&T deploys nationwide 5G SA while Verizon lags and T-Mobile leads
Verizon’s 6G Innovation Forum joins a crowded list of 6G efforts that may conflict with 3GPP and ITU-R IMT-2030 work
Verizon partners with Nokia to deploy large private 5G network in the UK
AT&T and Verizon cut jobs another 6% last year; AI investments continue to increase
Verizon and AT&T cut 5,100 more jobs with a combined 214,350 fewer employees than 2015
U.S. Cellular to Sell Spectrum Licenses to Verizon in $1 Billion Deal
Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
Point Topic: Global Broadband Subscribers in Q2 2025: 5G FWA, DSL, satellite and FTTP
Overview:
Global broadband subscribers surpassed 1.53 billion in Q2 2025, marking a 1.1% growth. Broadband subscriptions[1] declined in 24 countries[2], compared to 22 in Q1 2025. In some of these markets consumers are migrating to mobile broadband, others are experiencing economic headwinds or are already highly saturated. Some are still in the midst of conflict. Globally, the growth in Q2 2025 has increased slightly, compared to the same quarter of 2024.
Notes:
[1] Whenever Point Topic refers to ‘broadband’ in this report, they mean fixed broadband. Also, ‘subscriptions’ and ‘connections’ are used interchangeably.
[2] It is possible there will be restatements in the coming quarter/s and single period data should be viewed in that light. Decline in some markets can be due to changes in methodology used by national regulatory authorities.
Key Points:
-
In terms of growth, India remained at the top of the largest 20 fixed broadband markets with a 6.7% quarterly growth rate.
-
The share of FTTH/B in the total fixed broadband subscriptions increased further and stood at 72.68%. Broadband connections based on other technologies saw their market shares shrink again, with an exception of satellite and fixed wireless access (FWA).
-
Year-on-year, FTTH/B connections grew by 7.2%. Satellite and FWA saw an even higher annual growth (41.6% and 31% respectively).
-
Legacy copper subscriptions declined by 12.1% y-o-y, while FTTx lines (mainly VDSL) went down by 6%, with Spain becoming one of the first countries in the world and the first major European economy to shut down its copper network completely.
-
5G FWA take-up accelerated, especially in India and the US, as a result of aggressive investments by Reliance, Bharti Airtel, T-Mobile, Verizon and AT&T.

In Q2 2025, the global fixed broadband subscriber figure grew by 1.1%, exceeding 1.53 billion. In line with seasonal trends, the growth rate was slower than in the previous quarter but it was slightly higher than in the respective quarter of 2024 (Figure 1. above and Table 1. below).
Table 1. Global broadband subscribers and quarterly growth rates. Source – Point Topic

South and East Asia continues to claim the largest share of net adds in global fixed broadband subscribers, though it dropped slightly quarter-on-quarter from 63.5% to 62.3%. This was largely due to the slower quarterly growth in China, the largest broadband market of the region[3], which is inevitable due to the increasing market saturation (Table 2. below).
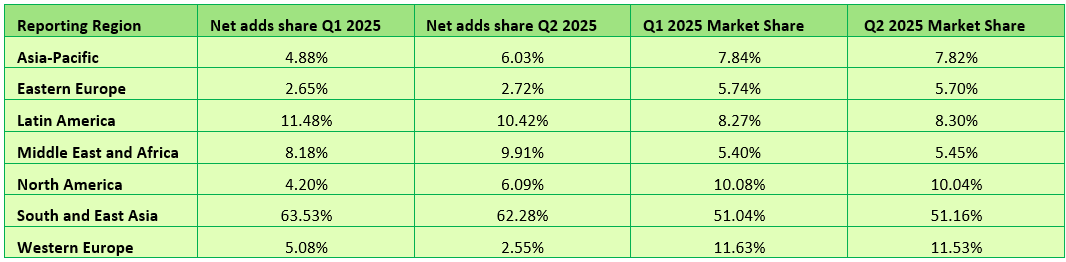
Other regions saw their net adds shares expand, with an exception of Latin America and Western Europe. In Western Europe, whose net adds share halved, most of the Scandinavian countries, the UK and some others saw a decline in fixed broadband subscribers, as the extent of migration to gigabit capable technologies was not sufficient to offset the decline in copper based subscriptions.
For the largest twenty broadband markets, once again all except the UK saw fixed broadband subscriber growth in Q2 2025 (Figure 5). The UK saw a -0.05% decline (compared to -0.3% in the previous quarter), as the FTTP growth was not sufficient to offset the decline in DSL, FTTx and cable broadband connections. For several quarters now India is at the top of this cohort, with a 6.7% growth, continuing to show huge growth potential due to the low fixed broadband penetration (16% of households) and the fast growing economy. Along with Canada, India also saw the largest increase in quarterly growth, compared to Q1 2025.

Globally, healthy quarterly FTTH/B growth rates were spread around the world, with the less advanced economies and more youthful fibre markets generally exhibiting higher growth. In the last 12 months to the end of Q2 2025, the number of DSL lines saw another decline (-12.1%), while FTTH/B connections grew by 7.2%. The decline in FTTx was -6%, while cable (HFC) broadband subscribers dropped by -0.9%.
The decline in copper and FTTx (mainly VDSL) is not surprising. When it comes to cable/HFC, it is not immune to competition from other technologies either. The US is a good example, being the largest cable market globally. There the decline has continued as major players such as Comcast, Charter, Cox, Altice and others are losing customers. Competition from telcos who are rapidly expanding their fibre footprints (AT&T, Verizon, Frontier, Lumen, Consolidated Communications) and offering symmetric bandwidth, superior upload speeds and lower latency is partly to blame. At the same time, cable broadband prices have risen steadily due to promotional offer expirations, ‘network fees’, and equipment costs. Finally, 5G FWA home broadband from T-Mobile, Verizon and AT&T has exploded, with their customer numbers jumping year-on-year by 31%, 34% and 194% respectively.
Globally, wireless broadband (FWA, 5G FWA and LTE fixed) connections also continued to grow – they went up by 31% year-on-year, largely impacted by an explosive growth of 5G FWA in India (332% year-on-year) as well as the US (39%). In India, Reliance and Bharti Airtel are marching ahead with 5G FWA rollouts, capitalising on the huge potential of the enormous broadband hungry market.
Point Topic expects this trend to continue due to the fact that FWA networks are easier to scale after the initial investment, FWA broadband services being generally cheaper for consumers than the alternatives, easy to self-install, and being ‘good enough’ for streaming, remote work, and average household use, as well as the demand for connectivity in remote and underserved areas. Having said that, this applies primarily to the more advanced FWA, especially 5G based. They are also seeing a decline in subscriptions based on older FWA variants in some markets.
Point Topic: FTTP broadband subs to reach 1.12bn by 2030 in 29 largest markets
U.S. broadband subscriber growth slowed in 1Q-2024 after net adds in 2023
Point Topic Comprehensive Report: Global Fixed Broadband Connections at 1.377B as of Q1-2023
Point Topic: Global Broadband Tariff Benchmark Report- 2Q-2022
Point Topic: Global fixed broadband connections up 1.7% in 1Q-2022, FTTH at 58% market share
Cable broadband subscriber growth slows while FTTx and FWA gain ground
Nvidia pays $1 billion for a stake in Nokia to collaborate on AI networking solutions
This is not only astonishing but unheard of: the world’s largest and most popular fabless semiconductor company –Nvidia– taking a $1 billion stake in a telco/reinvented data center connectivity company-Nokia.
Indeed, GPU king Nvidia will pay $1 billion for a stake of 2.9% in Nokia as part of a deal focused on AI and data centers, the Finnish telecom equipment maker said on Tuesday as its shares hit their highest level in nearly a decade on hope for AI to lift their business revenue and profits. The nonexclusive partnership and the investment will make Nvidia the second-largest shareholder in Nokia. Nokia said it will issue 166,389,351 new shares for Nvidia, which the U.S. company will subscribe to at $6.01 per share.
Nokia said the companies will collaborate on artificial intelligence networking solutions and explore opportunities to include its data center communications products in Nvidia’s future AI infrastructure plans. Nokia and its Swedish rival Ericsson both make networking equipment for connectivity inside (intra-) data centers and between (inter-) data centers and have been benefiting from increased AI use.

Summary:
- NVIDIA and Nokia to establish a strategic partnership to enable accelerated development and deployment of next generation AI native mobile networks and AI networking infrastructure.
- NVIDIA introduces NVIDIA Arc Aerial RAN Computer, a 6G-ready telecommunications computing platform.
- Nokia to expand its global access portfolio with new AI-RAN product based on NVIDIA platform.
- T-Mobile U.S. is working with Nokia and NVIDIA to integrate AI-RAN technologies into its 6G development process.
- Collaboration enables new AI services and improved consumer experiences to support explosive growth in mobile AI traffic.
- Dell Technologies provides PowerEdge servers to power new AI-RAN solution.
- Partnership marks turning point for the industry, paving the way to AI-native 6G by taking AI-RAN to innovation and commercialization at a global scale.
In some respects, this new partnership competes with Nvidia’s own data center connectivity solutions from its Mellanox Technologies division, which it acquired for $6.9 billion in 2019. Meanwhile, Nokia now claims to have worked on a redesign to ensure its RAN software is compatible with Nvidia’s compute unified device architecture (CUDA) platform, meaning it can run on Nvidia’s GPUs. Nvidia has also modified its hardware offer, creating capacity cards that will slot directly into Nokia’s existing AirScale baseband units at mobile sites.
Having dethroned Intel several years ago, Nvidia now has a near-monopoly in supplying GPU chips for data centers and has partnered with companies ranging from OpenAI to Microsoft. AMD is a distant second but is gaining ground in the data center GPU space as is ARM Ltd with its RISC CPU cores. Capital expenditure on data center infrastructure is expected to exceed $1.7 trillion by 2030, consulting firm McKinsey, largely because of the expansion of AI.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang said the deal would help make the U.S. the center of the next revolution in 6G. “Thank you for helping the United States bring telecommunication technology back to America,” Huang said in a speech in Washington, addressing Nokia CEO Justin Hotard (x-Intel). “The key thing here is it’s American technology delivering the base capability, which is the accelerated computing stack from Nvidia, now purpose-built for mobile,” Hotard told Reuters in an interview. “Jensen and I have been talking for a little bit and I love the pace at which Nvidia moves,” Hotard said. “It’s a pace that I aspire for us to move at Nokia.” He expects the new equipment to start contributing to revenue from 2027 as it goes into commercial deployment, first with 5G, followed by 6G after 2030.
Nvidia has been on a spending spree in recent weeks. The company in September pledged to invest $5 billion in beleaguered chip maker Intel. The investment pairs the world’s most valuable company, which has been a darling of the AI boom, with a chip maker that has almost completely fallen out of the AI conversation.
Later that month, Nvidia said it planned to invest up to $100 billion in OpenAI over an unspecified period that will likely span at least a few years. The partnership includes plans for an enormous data-center build-out and will allow OpenAI to build and deploy at least 10 gigawatts of Nvidia systems.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Tech Details:
Nokia uses Marvell Physical Layer (1) baseband chips for many of its products. Among other things, this ensured Nokia had a single software stack for all its virtual and purpose-built RAN products. Pallavi Mahajan, Nokia’s recently joined chief technology and AI officer recently told Light Reading that their software could easily adapt to run on Nvidia’s GPUs: “We built a hardware abstraction layer so that whether you are on Marvell, whether you are on any of the x86 servers or whether you are on GPUs, the abstraction takes away from that complexity, and the software is still the same.”
Fully independent software has been something of a Holy Grail for the entire industry. It would have ramifications for the whole market and its economics. Yet Nokia has conceivably been able to minimize the effort required to put its Layer 1 and specific higher-layer functions on a GPU. “There are going to be pieces of the software that are going to leverage on the accelerated compute,” said Mahajan. “That’s where we will bring in the CUDA integration pieces. But it’s not the entire software,” she added. The appeal of Nvidia as an alternative was largely to be found in “the programmability pieces that you don’t have on any other general merchant silicon,” said Mahajan. “There’s also this entire ecosystem, the CUDA ecosystem, that comes in.” One of Nvidia’s most eye-catching recent moves is the decision to “open source” Aerial, its own CUDA-based RAN software framework, so that other developers can tinker, she says. “What it now enables is the entire ecosystem to go out and contribute.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Quotes:
“Telecommunications is a critical national infrastructure — the digital nervous system of our economy and security,” said Jensen Huang, founder and CEO of NVIDIA. “Built on NVIDIA CUDA and AI, AI-RAN will revolutionize telecommunications — a generational platform shift that empowers the United States to regain global leadership in this vital infrastructure technology. Together with Nokia and America’s telecom ecosystem, we’re igniting this revolution, equipping operators to build intelligent, adaptive networks that will define the next generation of global connectivity.”
“The next leap in telecom isn’t just from 5G to 6G — it’s a fundamental redesign of the network to deliver AI-powered connectivity, capable of processing intelligence from the data center all the way to the edge. Our partnership with NVIDIA, and their investment in Nokia, will accelerate AI-RAN innovation to put an AI data center into everyone’s pocket,” said Justin Hotard, President and CEO of Nokia. “We’re proud to drive this industry transformation with NVIDIA, Dell Technologies, and T-Mobile U.S., our first AI-RAN deployments in T-Mobile’s network will ensure America leads in the advanced connectivity that AI needs.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Editor’s Notes:
1. In more advanced 5G networks, Physical Layer functions have demanded the support of custom silicon, or “accelerators.” A technique known as “lookaside,” favored by Ericsson and Samsung, uses an accelerator for only a single problematic Layer 1 task – forward error correction – and keeps everything else on the CPU. Nokia prefers the “inline” approach, which puts the whole of Layer 1 on the accelerator.
2. The huge AI-RAN push that Nvidia started with the formation of the AI-RAN Alliance in early 2024 has not met with an enthusiastic telco response so far. Results from Nokia as well as Ericsson show wireless network operators are spending less on 5G rollouts than they were in the early 2020s. Telco numbers indicate the appetite for smartphone and other mobile data services has not produced any sales growth. As companies prioritize efficiency above all else, baseband units that include Marvell and Nvidia cards may seem too expensive.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Other Opinions and Quotes:
Nvidia chips are likely to be more expensive, said Mads Rosendal, analyst at Danske Bank Credit Research, but the proposed partnership would be mutually beneficial, given Nvidia’s large share in the U.S. data center market.
“This is a strong endorsement of Nokia’s capabilities,” said PP Foresight analyst Paolo Pescatore. “Next-generation networks, such as 6G, will play a significant role in enabling new AI-powered experiences,” he added.
Iain Morris, International Editor, Light Reading: “Layer 1 control software runs on ARM RISC CPU cores in both Marvell and Nvidia technologies. The bigger differences tend to be in the hardware acceleration “kernels,” or central components, which have some unique demands. Yet Nokia has been working to put as much as it possibly can into a bucket of common software. Regardless, if Nvidia is effectively paying for all this with its $1 billion investment, the risks for Nokia may be small………….Nokia’s customers will in future have an AI-RAN choice that limits or even shrinks the floorspace for Marvell. The development also points to more subtle changes in Nokia’s thinking. The message earlier this year was that Nokia did not require a GPU to implement AI for RAN, whereby machine-generated algorithms help to improve network performance and efficiency. Marvell had that covered because it had incorporated AI and machine-learning technologies into the baseband chips used by Nokia.”
“If you start doing inline, you typically get much more locked into the hardware,” said Per Narvinger, the president of Ericsson’s mobile networks business group, on a recent analyst call. During its own trials with Nvidia, Ericsson said it was effectively able to redeploy virtual RAN software written for Intel’s x86 CPUs on the Grace CPU with minimal changes, leaving the GPU only as a possible option for the FEC accelerator. Putting the entire Layer 1 on a GPU would mean “you probably also get more tightly into that specific implementation,” said Narvinger. “Where does it really benefit from having that kind of parallel compute system?”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Nokia and Nvidia will partner with T-Mobile U.S. to develop and test AI RAN technologies for developing 6G, Nokia said in its press release. Trials are expected to begin in 2026, focused on field validation of performance and efficiency gains for customers.
References:
https://nvidianews.nvidia.com/news/nvidia-nokia-ai-telecommunications
https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/nvidia-make-1-billion-investment-finlands-nokia-2025-10-28/
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/nvidia-takes-1b-stake-in-nokia-which-promises-5g-and-6g-overhaul
https://www.wsj.com/business/telecom/nvidia-takes-1-billion-stake-in-nokia-69f75bb6
Analysis: Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia network equipment for AI data centers
Nvidia’s networking solutions give it an edge over competitive AI chip makers
Telecom sessions at Nvidia’s 2025 AI developers GTC: March 17–21 in San Jose, CA
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
FT: Nvidia invested $1bn in AI start-ups in 2024
The case for and against AI-RAN technology using Nvidia or AMD GPUs
Highlights of Nokia’s Smart Factory in Oulu, Finland for 5G and 6G innovation
Nokia & Deutsche Bahn deploy world’s first 1900 MHz 5G radio network meeting FRMCS requirements
Will the wave of AI generated user-to/from-network traffic increase spectacularly as Cisco and Nokia predict?
Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison and Nokia use AI to reduce energy demand and emissions
Verizon partners with Nokia to deploy large private 5G network in the UK
Verizon’s commercial agreement with Eaton Fiber to accelerate fiber/mobile convergence
Verizon has announced a commercial fiber agreement with Eaton Fiber LLC [1.], an affiliate of Tillman Global Holdings, that will enable Verizon to sell fiber-based services outside its current wireline footprint and beyond the areas it will gain via its pending acquisition of Frontier Communications. It’s another important step to accelerate Verizon’s broadband and mobility convergence strategy, which has also been embraced by AT&T and T-MobileUS.
Note 1. “Eaton Fiber is a wholesale-only FTTP network provider powering ISPs with fast, frictionless access to future-ready fiber. Our open-access platform makes it easy for ISPs to expand across key U.S. markets—without building or managing the network. Our open-access platform makes it easy for ISPs to expand across key U.S. markets – without building or managing the network. You bring the service. We deliver the speed,” Eaton Fiber states on its website.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Eaton Fiber will fund and build the network and take care of network maintenance and installation, while Verizon will be responsible for sales and marketing and end-user customer service. The agreement will expand Verizon’s premium broadband offering, complementing the company’s ongoing fiber builds and planned acquisition of Frontier. The agreement is expected to bring ultra-fast, high-capacity fiber service to homes and customers in markets outside of Verizon’s and Frontier’s current fiber-to-the-home footprint.

Image Credit: Eaton Fiber
“Our strategy is clear: lead the market in premium mobility and broadband convergence, and fiber is the foundation of that leadership,” said Sowmyanarayan Sampath, Executive Vice President for Verizon and CEO for Verizon Consumer. “This agreement allows us to rapidly enter new markets, accelerate deployment speed and ensure we maintain the necessary flexibility to capture growth opportunities across the country.”
“We are pleased to partner with a world-class provider in Verizon,” Sanjiv Ahuja, Founder, Chairman, and CEO of Tillman Global Holdings. “Marking a significant expansion of Tillman’s fiber deployments, this announcement underscores our shared commitment to expanding next-generation infrastructure nationwide.”
Missing from the press release: Verizon did not say where Eaton Fiber has built networks, where it intends to build, or how many homes and businesses Verizon eventually will be able to serve off of Eaton’s platform. Verizon also neglected to say when it will start to offer services via Eaton Fiber’s networks. It’s also not clear if Verizon is considered an anchor tenant or will represent one of multiple tenants that will sell services over Eaton Fiber’s network.
Tillman Fiber, builds and operates symmetrical gigabit-capable services over fiber-to-the-premises networks. The company was founded in 2021, and its backers include Tillman Global Holdings and Northleaf Capital Partners. In July, Tillman Fiber launched fiber networks serving parts of Northport, Kissimmee and Deltona and Hernando County in Florida. T-MobileUS is offering services on that network as part of a broader fiber Internet strategy that’s also underpinned by partnerships and acquisitions of Lumos, Metronet and US Internet.
Both Tillman Fiber and Eaton Fiber note on their respective websites that their fiber networks use an open access model that sells wholesale access to other Internet service providers (ISPs).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
New Street Research David Barden remarked in a research note (registration required) that Eaton Fiber has not yet revealed its leadership. But given that Verizon referenced Frontier in today’s announcement, he wondered if Veronica Bloodworth, a former AT&T exec who has been serving as Frontier’s EVP and chief network officer since 2021, or Vishal Dixit, Frontier’s EVP of strategy and wholesale, “could be on a short list.” Barden also suggested that today’s announcement with Eaton Fiber is more about intent rather than specifics. “Given that this agreement was seen as worthy of a press release, especially within a month of Dan Schulman taking over the reins of the company, this release is also very likely about ambition as well,” Barden wrote.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Verizon’s new agreement with Eaton Fiber is proceeding as the company approaches the finalization of its $20 billion acquisition of Frontier Communications.
The integration of Frontier’s assets is expected to boost Verizon’s fiber network, increasing its reach to serve about 25 million premises throughout 31 states and Washington, D.C.. In addition to constructing 500,000 new FiOS locations this year, Verizon has set a strategic goal of achieving over 30 million fiber passings by 2028 and is exploring an eventual expansion to 35-40 million homes and businesses.
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-expanding-broadband-new-strategic-fiber-agreement
https://www.lightreading.com/broadband/verizon-taps-into-eaton-fiber-to-broaden-fiber-reach
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-acquisition-starry
Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
Reuters: US Department of Energy forms $1 billion AI supercomputer partnership with AMD
The U.S. Department of Energy has formed a $1 billion partnership with Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) to construct two supercomputers that will tackle large scientific problems ranging from nuclear power to cancer treatments to national security, U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright and AMD CEO Lisa Su told Reuters.
The U.S. is building the two machines to ensure the country has enough supercomputers to run increasingly complex experiments that require harnessing enormous amounts of data-crunching capability. The machines can accelerate the process of making scientific discoveries in areas the U.S. is focused on.

U.S. Energy Secretary Wright said the systems would “supercharge” advances in nuclear power, fusion energy, technologies for defense and national security, and the development of drugs. Scientists and companies are trying to replicate nuclear fusion, the reaction that fuels the sun, by jamming light atoms in a plasma gas under intense heat and pressure to release massive amounts of energy. “We’ve made great progress, but plasmas are unstable, and we need to recreate the center of the sun on Earth,” Wright told Reuters.
The second, more advanced computer called Discovery will be based around AMD’s MI430 series of AI chips that are tuned for high-performance computing.
184K global tech layoffs in 2025 to date; ~27.3% related to AI replacing workers
As of October, over 184,000 global tech jobs were cut in 2025, according to a report from Silicon Valley Business Journal. 50,184 were directly related to the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation tools by businesses. Silicon Valley’s AI boom has been pummeling headcounts across major companies in the region — and globally. U.S. companies accounted for about 123,000 of the layoffs.
These are the 10 tech companies with the most significant mass layoffs since January 2025:
- Intel: 33,900 layoffs. The company has cited the need to reduce costs and restructure its organization after years of technical and financial setbacks.
- Microsoft: 19,215 layoffs. The tech giant has conducted multiple rounds of cuts throughout the year across various departments as it prioritizes AI investments.
- TCS: 12,000 layoffs. As a major IT firm, Tata Consultancy Services’ cuts largely affected mid-level and senior positions, which are becoming redundant due to AI and evolving client demands.
- Accenture: 11,000 layoffs. The consulting company reduced its headcount as it shifts toward greater automation and AI-driven services.
- Panasonic: 10,000 layoffs. The Japanese manufacturer announced these job cuts as part of a strategy to improve efficiency and focus on core business areas.
- IBM: ~17,000 to 19,700 layoffs as part of a restructuring effort to shift some roles to India and align the workforce with areas like AI and hybrid cloud. The layoffs were reportedly concentrated in certain teams, including the Cloud Classic division, and impacted locations such as Raleigh, New York, Dallas, and California.
- Amazon: 14,000 layoffs in October 2025. Cuts have impacted various areas, including the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud unit and the consumer retail business.
- Salesforce: 5,000 layoffs. Many of these cuts impacted the customer service division, where AI agents now handle a significant portion of client interactions.
- STMicro: 5,000 cuts in the next three years, including 2,800 job cuts announced earlier this year, its chief executive said on Wednesday. Around 2,000 employees will leave the Franco-Italian chipmaker due to attrition, bringing the total count with voluntary departures to 5,000, Jean-Marc Chery said at a June 4th event in Paris, hosted by BNP Paribas.
- Meta: 3,720 layoffs. The company has made multiple rounds of cuts targeting “low-performers” and positions within its AI and virtual reality divisions. More details below.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..

Image Credit: simplehappyart via Getty Images
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Feb 3, 2026 Update from Light Reading:
- Verizon’s new CEO Dan Schulman in October said that 13,000 employees would soon be laid off. When results were published last week, as reported by Light Reading, they showed that 10,300 jobs had been cut from the total in the final three months of the year, leaving Verizon with 89,900 employees on New Year’s Eve.
- AT&T eliminated about 8,000 jobs in 2025, finishing the year with 133,000 employees.
- That total net loss of 17,700 jobs at AT&T and Verizon was equal to about 7% of the combined workforce at the end of 2024.
Last year’s job losses were not an isolated event but the continuation of a decade-old trend that has gutted the telco workforce. At its high point for staff numbers in 2017, AT&T employed as many as 280,000 people, including those it would acquire with its $85 billion takeover of Time Warner. Around 147,000 jobs have subsequently disappeared, showing the workforce has more than halved in just eight years.
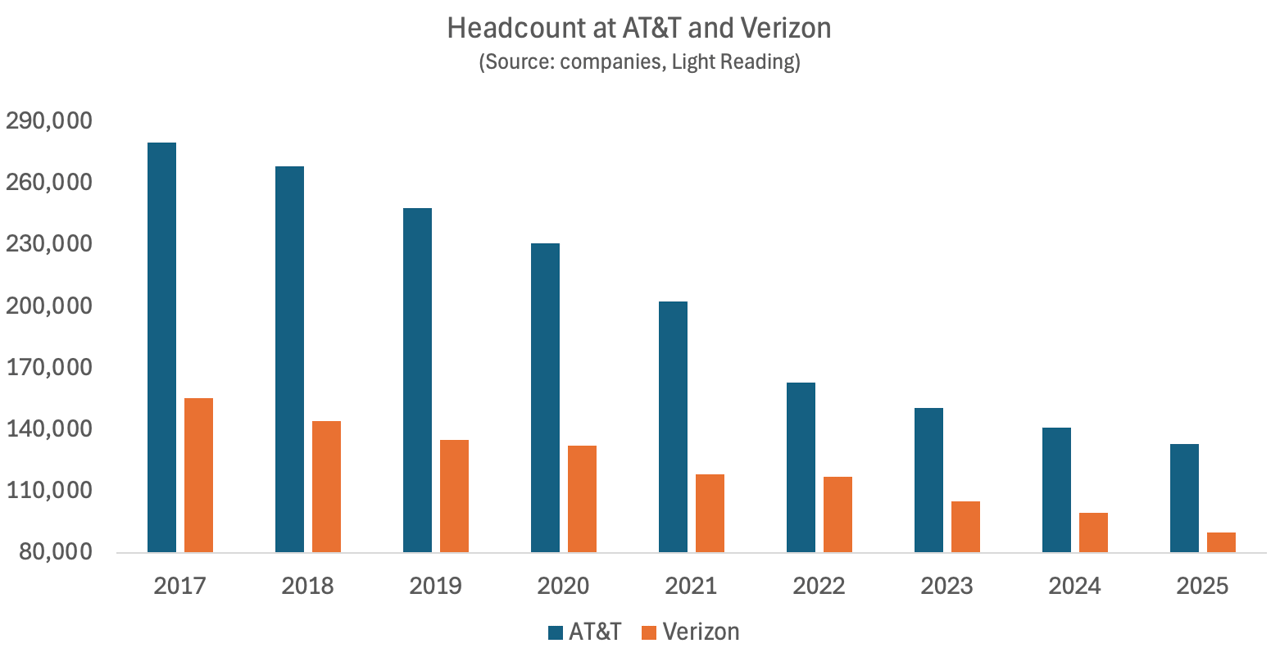
Pie Chart Credit: Light Reading
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In a direct contradiction in August, Cisco announced layoffs of 221 employees in the San Francisco Bay Area, affecting roles in Milpitas and San Francisco. This occurred despite strong financial results and the CEO’s previous statement that the company would not cut jobs in favor of AI. The cuts, which included software engineering roles, are part of the company’s broader strategy to streamline operations & focus on AI.
About two-thirds of all job cuts — roughly 123,000 positions — came from U.S.-based companies, with the remainder spread across mainly Ireland, India and Japan. The report compiles data from WARN notices, TrueUp, TechCrunch and Layoffs.fyi through Oct. 21st.

- Shift to AI and automation: Many companies are restructuring their workforce to focus on AI-centric growth and are automating tasks previously done by human workers, particularly in customer service and quality assurance.
- Economic headwinds: Ongoing economic uncertainty, inflation, and higher interest rates are prompting tech companies to cut costs and streamline operations.
- Market corrections: Following a period of rapid over-hiring, many tech companies are now “right-sizing” their staff to become leaner and more efficient.
References:
Report: Broadcom Announces Further Job Cuts as Global Tech Layoffs Approach 185,000 in 2025
Tech layoffs continue unabated: pink slip season in hard-hit SF Bay Area
HPE cost reduction campaign with more layoffs; 250 AI PoC trials or deployments
High Tech Layoffs Explained: The End of the Free Money Party
Massive layoffs and cost cutting will decimate Intel’s already tiny 5G network business
Big Tech post strong earnings and revenue growth, but cuts jobs along with Telecom Vendors
Telecom layoffs continue unabated as AT&T leads the pack – a growth engine with only 1% YoY growth?
Cisco restructuring plan will result in ~4100 layoffs; focus on security and cloud based products
Cloud Computing Giants Growth Slows; Recession Looms, Layoffs Begin
AT&T’s convergence strategy is working as per its 3Q 2025 earnings report
AT&T reported a 1.6% increase in third-quarter revenue to $30.7 billion, driven by its convergence strategy which combines wireless and fiber services. This strategy attracted profitable customers, as evidenced by 405,000 postpaid phone net additions and 550,000 new subscribers for AT&T’s advanced broadband services, including Fiber and Internet Air. The growth in these areas offset a decline in business wireline revenue.
“We have the key building blocks in place to give our customers the best connectivity experience in the industry and we’re winning the race to lead in convergence,” said John Stankey, AT&T Chairman and CEO.
“We continue to add highly-profitable customers that are choosing AT&T for all their connectivity needs on the country’s fastest and largest wireless and fiber networks. It’s clear our differentiated investment-led strategy is working, and we remain on track to achieve all of our 2025 consolidated financial guidance.”

Here are a few AT&T 3Q 2025 highlights:
- Postpaid Phone Subscribers: Gained 405,000 net additions.
- AT&T Fiber: Added 288,000 new subscribers.
- AT&T Internet Air: Added 270,000 new subscribers, marking a strong quarter for broadband net additions overall.
- Total Revenue increased 1.6% year-on-year to $30.7 billion.
- Mobility Revenue grew 3.1% year-over-year, supported by higher equipment sales and subscriber additions.
- Latin America Revenues were up 7.1% year on year to USD 1.10 billion amid subscriber and ARPU growth, higher equipment sales and the favourable effects of foreign exchange rates.
- Consumer Wireline Revenue increased 4.1%, led by an 8.2% rise in broadband revenue and strong fiber growth.
- Business Wireline Revenue declined 7.8%, mainly due to reductions in legacy services, though this was partially offset by growth in fiber and advanced connectivity services.
- The strategy is working because customers who bundle fiber and wireless services have lower churn and higher lifetime values, according to AT&T CEO John Stankey.
- More than 41% of AT&T Fiber households also have an AT&T Mobility service, which shows the success of this strategy.
- The company is on track to achieve its consolidated financial guidance for the year.
Stankey on AT&T’s competitive advantage (from Earnings Call transcript):
“We offer fast and reliable connectivity for 5G and fiber at attractive price points. More people are choosing AT&T for both wireless and home internet services. Today, more than 41% of AT&T Fiber households also choose AT&T for wireless. And the pace of this convergence trend within our customer base continues to grow. These customers remain our most valuable, with the lowest churn profile and highest lifetime values.
Our success with convergence also extends to fixed wireless. More than half of our Internet Air subscribers also choose AT&T for their wireless service. Similar to fiber, these customers exhibit lower churn and drive higher lifetime values than customers with stand-alone services.
The EchoStar spectrum we agreed to acquire will improve our 5G wireless performance in a cost-efficient manner, while allowing us to grow Internet Air at a faster pace. We’re already making great progress, delivering on our commitment to deploy this valuable spectrum for the benefit of American consumers and businesses.
We started deploying the 3.45 GHz spectrum that we have agreed to acquire from EchoStar under a short-term spectrum manager lease. Based on our current rate and pace, we expect these mid-band licenses will be deployed in cell sites covering nearly two-thirds of the US population by mid-November.
This should position us to further expand the availability of Internet Air 5G FWA) in our sales channels in 2026. Our ability to move this quickly reflects the great work of our teams and the FCC’s pro-investment and supportive policy environment. We’re also making great progress in preparing to close our transaction with Lumen. Most of the senior leadership team has been identified, and we now expect to close this transaction in the early part of 2026.
As I’ve said before, where we have fiber, we win with both fiber and 5G, and we plan to win even more as our investments in these assets bring advanced connectivity to more Americans. The supportive (FCC) policy environment is also making it easier for us to transition away from outdated legacy infrastructure and invest in the AI-ready connectivity that Americans want and need.
The bottom line is that we now have the right building blocks in place to realize our scaled fiber and fixed wireless ambitions, complete our wireless modernization, and successfully transition away from legacy infrastructure. As we complete our key investments, acquisitions, and transformation initiatives, we expect to increase our fiber and convergence penetration rates and see a majority of incremental revenue growth originate from converged customer relationships.”
Outlook & Financial Guidance:
AT&T reiterated its guidance for the 2025 financial year, with service revenue growth in the low single-digit range and mobility service revenue growth of 3 percent or better. It still foresees consumer fibre broadband revenue growth in the mid-to-high teens. Annual adjusted EBITDA growth should be 3 percent or better. Mobility EBITDA growth will be about 3 percent. Business wireline EBITDA will decline at a low double-digit rate and EBITDA growth for consumer wireline is still forecast in the low to mid-teen range. FY capital investment will be in the USD 22 billion to USD 22.5 billion range. AT&T predicts free cash flow in the low-to-mid USD 16 billion range. It continues to forecast FY adjusted EPS of USD 1.97 to USD 2.07.
AT&T reiterated its long-term financial guidance of service revenue growth in the low-single-digit range annually from 2026-2027, adjusted EBITDA growth of 3 percent or better annually, and adjusted EPS accelerating to double-digit percentage growth in 2027. AT&T foresees capital investment in the range USD 23 billion to USD 24 billion annually from 2026-2027. It predicts free cash flow of USD 18 billion or more in 2026 and USD 19 billion or more in 2027.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/3q-earnings.html
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/att-says-convergence-boosts-q3-revenue-and-profitability–1551778
AT&T deploys nationwide 5G SA while Verizon lags and T-Mobile leads
AT&T to buy spectrum licenses from EchoStar for $23 billion
AT&T grows fiber revenue 19%, 261K net fiber adds and 29.5M locations passed by its fiber optic network
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
T-Mobile’s new CEO Srini Gopalan faces fierce competition from AT&T, Verizon and MVNOs
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
AT&T and Verizon cut jobs another 6% last year; AI investments continue to increase
Omdia: How telcos will evolve in the AI era
Dario Talmesio, research director, service provider, strategy and regulation at market research firm Omdia (owned by Informa) sees positive signs for network operators.
“After many years of plumbing, now telecom operators are starting to see some of the benefits of their network and beyond network strategies. Furthermore, the investor community is now appreciating telecom investments, after many years of poor valuation, he said during his analyst keynote presentation at Network X, a conference organized by Light Reading and Informa in Paris, France last week.
“What has changed in the telecoms industry over the past few years is the fact that we are no longer in a market that is in contraction,” he said. Although telcos are generally not seeing double-digit percentage increases in revenue or profit, “it’s a reliable business … a business that is able to provide cash to investors.”
Omdia forecasts that global telecoms revenue will have a CAGR of 2.8% in the 2025-2030 timeframe. In addition, the industry has delivered two consecutive years of record free cash flow, above 17% of sales.
However, Omdia found that telcos have reduced capex, which is trending towards 15% of revenues. Opex fell by -0.2% in 2024 and is broadly flatlining. There was a 2.2% decline in global labor opex following the challenging trend in 2023, when labor opex increased by 4% despite notable layoffs.
“Overall, the positive momentum is continuing, but of course there is more work to be done on the efficiency side,” Talmesio said. He added that it is also still too early to say what impact AI investments will have over the longer term. “All the work that has been done so far is still largely preparatory, with visible results expected to materialize in the near(ish) future,” he added. His Network X keynote presentation addressed the following questions:
- How will telcos evolve their operating structures and shift their business focuses in the next 5 years?
- AI, cloud and more to supercharge efficiencies and operating models?
- How will big tech co-opetition evolve and impact traditional telcos?
Customer care was seen as the area first impacted by AI, building on existing GenAI implementations. In contrast, network operations are expected to ultimately see the most significant impact of agentic AI.
Talmesio said many of the building blocks are in place for telecoms services and future revenue generation, with several markets reaching 60% to 70% fiber coverage, and some even approaching 100%.
Network operators are now moving beyond monetizing pure data access and are able to charge more for different gigabit speeds, home gaming, more intelligent home routers and additional WiFi access points, smart home services such as energy, security and multi-room video, and more.
While noting that connectivity remains the most important revenue driver, when contributions from various telecoms-adjacent services are added up “it becomes a significant number,” Talmesio said.
Mobile networks are another important building block. While acknowledging that 5G has been something of a disappointment in the first five years of the deployment cycle, “this is really changing” as more operators deploy 5G standalone (5G SA core) networks, Omdia observed.
Talmesio said: “At the end of June, there were only 66 telecom operators launching or commercially using 5G SA. But those 66 operators are those operators that carry the majority of the world’s 5G subscribers. And with 5G SA, we have improved latency and more devices among other factors. Monetization is still in its infancy, perhaps, but then you can see some really positive progress in 5G Advanced, where as of June, we had 13 commercial networks available with some good monetization examples, including uplink.”
“Telecom is moving beyond telecoms,” with a number of new AI strategies in place. For example, telcos are increasingly providing AI infrastructure in their data centers, offering GPU as-a-service, AI-related colocation, AI-RAN and edge AI functionality.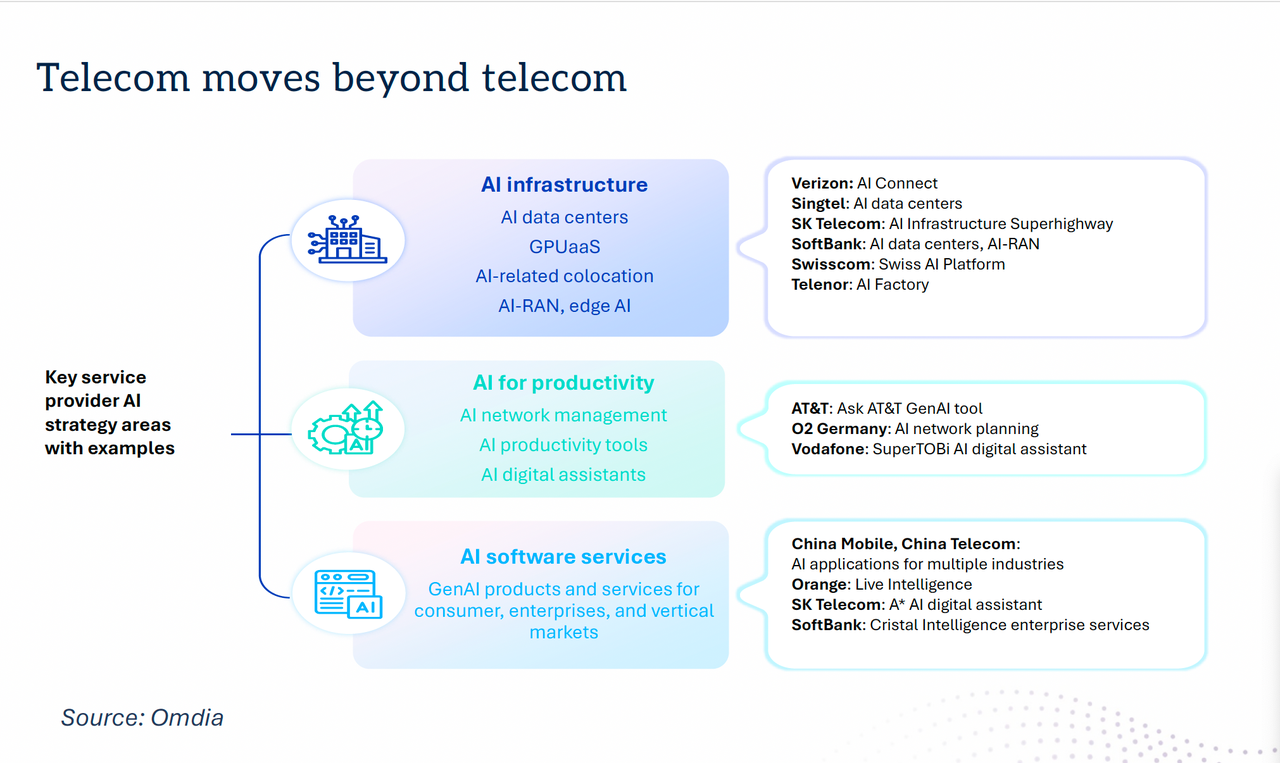

Dario Talmesio, Omdia
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
AI is also being used for network management, with AI productivity tools and AI digital assistants, as well as AI software services including GenAI products and services for consumer, enterprises and vertical markets.
“There is an additional boost for telecom operators to move beyond connectivity, which is the sovereignty agenda,” Talmesio noted. While sovereignty in the past was largely applied to data residency, “in reality, there are more and more aspects of sovereignty that are in many ways facilitating telecom operators in retaining or entering business areas that probably ten years ago were unthinkable for them.” These include cloud and data center infrastructure, sovereign AI, cyberdefense and quantum safety, satellite communication, data protection and critical communications.
“The telecom business is definitely improving,” Talmesio concluded, noting that the market is now also being viewed more favorably by investors. “In many ways, the glass is maybe still half full, but there’s more water being poured into the telecom industry.”
References:
https://networkxevent.com/speakers/dario-talmesio/
https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/technology-media-and-telecommunications/our-insights/pushing-telcos-ai-envelope-on-capital-decisions
Omdia on resurgence of Huawei: #1 RAN vendor in 3 out of 5 regions; RAN market has bottomed
Omdia: Huawei increases global RAN market share due to China hegemony
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Omdia: Cable network operators deploy PONs