Author: Alan Weissberger
OpenAI and Broadcom in $10B deal to make custom AI chips
Overview:
Late last October, IEEE Techblog reported that “OpenAI the maker of ChatGPT, was working with Broadcom to develop a new artificial intelligence (AI) chip focused on running AI models after they’ve been trained.” On Friday, the WSJ and FT (on-line subscriptions required) separately confirmed that OpenAI is working with Broadcom to develop custom AI chips, a move that could help alleviate the shortage of powerful processors needed to quickly train and release new versions of ChatGPT. OpenAI plans to use the new AI chip internally, according to one person close to the project, rather than make them available to external customers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Broadcom:
During its earnings call on Thursday, Broadcom’s CEO Hock Tan said that it had signed up an undisclosed fourth major AI developer as a custom AI chip customer, and that this new customer had committed to $10bn in orders. While Broadcom did not disclose the names of the new customer, people familiar with the matter confirmed OpenAI was the new client. Broadcom and OpenAI declined to comment, according to the FT. Tan said the deal had lifted the company’s growth prospects by bringing “immediate and fairly substantial demand,” shipping chips for that customer “pretty strongly” starting next year. “The addition of a fourth customer with immediate and fairly substantial demand really changes our thinking of what 2026 would be starting to look like,” Tan added.
Image credit: © Dado Ruvic/Reuters
HSBC analysts have recently noted that they expect to see a much higher growth rate from Broadcom’s custom chip business compared with Nvidia’s chip business in 2026. Nvidia continues to dominate the AI silicon market, with “hyperscalers” still representing the largest share of its customer base. While Nvidia doesn’t disclose specific customer names, recent filings show that a significant portion of their revenue comes from a small number of unidentified direct customers, which likely are large cloud providers like Microsoft, Amazon, Alphabet (Google), and Meta Platforms.
In August, Broadcom launched its Jericho networking chip, which is designed to help speed up AI computing by connecting data centers as far as 60 miles apart. By August, Broadcom’s market value had surpassed that of oil giant Saudi Aramco, making the chip firm the world’s seventh-largest publicly listed company.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Open AI:
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has been saying for months that a shortage of graphics processing units, or GPUs, has been slowing his company’s progress in releasing new versions of its flagship chatbot. In February, Altman wrote on X that ChatGPT-4.5, its then-newest large language model, was the closest the company had come to designing an AI model that behaved like a “thoughtful person,” but there were very high costs that came with developing it. “We will add tens of thousands of GPUs next week and roll it out to the plus tier then. (hundreds of thousands coming soon, and i’m pretty sure y’all will use every one we can rack up.)”
In recent years, OpenAI has relied heavily on so-called “off the shelf” GPUs produced by Nvidia, the biggest player in the chip-design space. But as demand from large AI firms looking to train increasingly sophisticated models has surged, chip makers and data-center operators have struggled to keep up. The company was one of the earliest customers for Nvidia’s AI chips and has since proven to be a voracious consumer of its AI silicon.
“If we’re talking about hyperscalers and gigantic AI factories, it’s very hard to get access to a high number of GPUs,” said Nikolay Filichkin, co-founder of Compute Labs, a startup that buys GPUs and offers investors a share in the rental income they produce. “It requires months of lead time and planning with the manufacturers.”
To solve this problem, OpenAI has been working with Broadcom for over a year to develop a custom chip for use in model training. Broadcom specializes in what it calls XPUs, a type of semiconductor that is designed with a particular application—such as training ChatGPT—in mind.
Last month, Altman said the company was prioritizing compute “in light of the increased demand from [OpenAI’s latest model] GPT-5” and planned to double its compute fleet “over the next 5 months.” OpenAI also recently struck a data-center deal with Oracle that calls for OpenAI to pay more than $30 billion a year to the cloud giant, and signed a smaller contract with Google earlier this year to alleviate computing shortages. It is also embarking on its own data-center construction project, Stargate, though that has gotten off to a slow start.
OpenAI’s move follows the strategy of tech giants such as Google, Amazon and Meta, which have designed their own specialized custom chips to run AI workloads. The industry has seen huge demand for the computing power to train and run AI models.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ft.com/content/e8cc6d99-d06e-4e9b-a54f-29317fa68d6f
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/openai-broadcom-deal-ai-chips-5c7201d2
Reuters & Bloomberg: OpenAI to design “inference AI” chip with Broadcom and TSMC
Open AI raises $8.3B and is valued at $300B; AI speculative mania rivals Dot-com bubble
OpenAI announces new open weight, open source GPT models which Orange will deploy
OpenAI partners with G42 to build giant data center for Stargate UAE project
Generative AI Unicorns Rule the Startup Roost; OpenAI in the Spotlight
Will the wave of AI generated user-to/from-network traffic increase spectacularly as Cisco and Nokia predict?
Network operators are bracing themselves for a wave of AI traffic, partially based on a RtBrick survey, as well as forecasts by Cisco and Nokia, but that hasn’t happened yet. The heavy AI traffic today is East to West (or vice-versa) within cloud resident AI data centers and for AI data center interconnects.
1. Cisco believes that AI Inference agents will soon engage “continuously” with end-users, keeping traffic levels consistently high. has stated that AI will greatly increase network traffic, citing a shift toward new, more demanding traffic patterns driven by “agentic AI” and other applications. This perspective is a core part of Cisco’s business strategy, which is focused on selling the modernized infrastructure needed to handle the coming surge. Cisco identified three stages of AI-driven traffic growth, each with different network demands:
- Today’s generative AI models produce “spikey” traffic which spikes up when a user submits a query, but then returns to a low baseline. Current networks are largely handling this traffic without issues.
- Persistent “agentic” AI traffic: The next phase will involve AI agents that constantly interact with end-users and other agents. Cisco CEO Chuck Robbins has stated that this will drive traffic “beyond the peaks of current chatbot interaction” and keep network levels “consistently high”.
- Edge-based AI: A third wave of “physical AI” will require more computing and networking at the edge of the network to accommodate specialized use cases like industrial IoT.
“As we move towards agentic AI and the demand for inferencing expands to the enterprise and end user networking environments, traffic on the network will reach unprecedented levels,” Cisco CEO Chuck Robbins said on the company’s recent earnings call. “Network traffic will not only increase beyond the peaks of current chatbot interaction, but will remain consistently high with agents in constant interaction.”
2. Nokia recently predicted that both direct and indirect AI traffic on mobile networks will grow at a faster pace than regular, non-AI traffic.
- Direct AI traffic: This is generated by users or systems directly interacting with AI services and applications. Consumer examples: Using generative AI tools, interacting with AI-powered gaming, or experiencing extended reality (XR) environments. Enterprise examples: Employing predictive maintenance, autonomous operations, video and image analytics, or enhanced customer interactions.
- Indirect AI traffic: This occurs when AI algorithms are used to influence user engagement with existing services, thereby increasing overall traffic. Examples: AI-driven personalized recommendations for video content on social media, streaming platforms, and online marketplaces, which can lead to longer user sessions and higher bandwidth consumption.
The Finland based network equipment vendor warned that the AI wave could bring “a potential surge in uplink data traffic that could overwhelm our current network infrastructure if we’re not prepared,” noting that the rise of hybrid on-device and cloud tools will require much more than the 5-15 Mbps uplink available on today’s networks. Nokia’s Global Network Traffic 2030 report forecasts that overall traffic could grow by 5 to 9 times current levels by 2033. All told, Nokia said AI traffic is expected to hit 1088 exabytes (EB) per month by 2033. That means overall traffic will grow 5x in a best case scenario and 9x in a worse case.
To manage this anticipated traffic surge, Nokia advocates for radical changes to existing network infrastructure.
- Cognitive networks: The company states that networks must become “cognitive,” leveraging AI and machine learning (ML) to handle the growing data demand.
- Network-as-Code: As part of its Technology Strategy 2030, Nokia promotes a framework for more flexible and scalable networks that leverage AI and APIs.
- 6G preparation: Nokia Bell Labs is already conducting research and field tests to prepare for 6G networks around 2030, with a focus on delivering the capacity needed for AI and other emerging technologies.
- Optimizing the broadband edge: The company also highlights the need to empower the broadband network edge to handle the demands of AI applications, which require low latency and high reliability.
Nokia’s Global Network Traffic 2030 report didn’t mention agentic AI, which are artificial intelligence systems designed to autonomously perceive, reason, and act in their environment to achieve complex goals with less human oversight. Unlike generative AI, which focuses on creating content, agentic AI specializes in workflow automation and independent problem-solving by making decisions, adapting plans, and executing tasks over extended periods to meet long-term objectives.
3. Ericsson did point to traffic increases stemming from the use of AI-based assistants in its 2024 Mobility Report. In particular, it predicted the majority of traffic would be related to the use of consumer video AI assistants, rather than text-based applications and – outside the consumer realm – forecast increased traffic from “AI agents interacting with drones and droids. Accelerated consumer uptake of GenAI will cause a steady increase of traffic in addition to the baseline increase,” Ericsson said of its traffic growth scenario.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Dissenting Views:
1. UK Disruptive Analysis Founder Dean Bubley isn’t a proponent of huge AI traffic growth. “Many in the telecom industry and vendor community are trying to talk up AI as driving future access network traffic and therefore demand for investment, spectrum etc., but there is no evidence of this at present,” he told Fierce Network.
Bubley argues that AI agents won’t really create much traffic on access networks to homes or businesses. Instead, he said, they will drive traffic “inside corporate networks, and inside and between data centers on backbone networks and inside the cloud. “There might be a bit more uplink traffic if video/images are sent to the cloud for AI purposes, but again that’s hypothetical,” he said.
2. In a LinkedIn post, Ookla analyst Mike Dano said he was a bit suspicious about “Cisco predicting a big jump in network traffic due to AI agents constantly wandering around the Internet and doing things.” While almost all of the comments agreed with Dano, it still is an open question whether the AI traffic Armageddon will actually materialize.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
RtBrick survey: Telco leaders warn AI and streaming traffic to “crack networks” by 2030
https://www.fierce-network.com/cloud/will-ai-agents-really-raise-network-traffic-baseline
Mulit-vendor Open RAN stalls as Echostar/Dish shuts down it’s 5G network leaving Mavenir in the lurch
Last week’s announcement that Echostar/ Dish Network will sell $23 billion worth of spectrum licenses to AT&T was very bad news for Mavenir. As a result of that deal, Dish Network’s 5G Open RAN network, running partly on Mavenir’s software, is to be decommissioned. Dish Network had been constructing a fourth nationwide U.S. mobile network with new Open RAN suppliers – one of the only true multi-vendor Open RANs worldwide.

Credit: Kristoffer Tripplaar/Alamy Stock Photo
Echostar’s decision to shut down its 5G network marks a very sad end for the world’s largest multivendor open RAN and will have ramifications for the entire industry. “If you look at all the initiatives, what the US government did or in general, they are the only ones who actually spent a good chunk of money to really support open RAN architecture,” said Pardeep Kohli, the CEO of Mavenir, one of the vendors involved in the Dish Network project. “So now the question is where do you go from here?”
As part of its original set of updates on 5G network plans, Dish revealed it would host its 5G core – the part that will survive the spectrum sale – in the public cloud of AWS. And the hyperscaler’s data facilities have also been used for RAN software from Mavenir installed on servers known as central units.
Open RAN enters is in the fronthaul interface between Mavenir’s DU software and radios provided by Japan’s Fujitsu. Its ability to connect its software to another company’s radios validates Mavenir’s claims to be an open RAN vendor, says Kohli. While other suppliers boast compatibility with open RAN specifications, commercial deployments pairing vendors over this interface remain rare.
Mavenir has evidently been frustrated by the continued dominance of Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia, whose combined RAN market share grew from 75.1% in 2023 to 77.5% last year, according to research from Omdia, an Informa company. Dish Network alone would not have made a sufficient difference for Mavenir and other open RAN players, according to Kohli. “It helped us come this far,” he said. “Now it’s up to how far other people want to take it.” A retreat from open RAN would, he thinks, be a “bad outcome for all the western operators,” leaving them dependent on a Nordic duopoly in countries where Chinese vendors are now banned.
“If they (telcos) don’t support it (multi-vendor OpenRAN), and other people are not supporting it, we are back to a Chinese world and a non-Chinese world,” he said. “In the non-Chinese world, you have Ericsson and Nokia, and in the Chinese world, it’s Huawei and ZTE. And that’s going to be a pretty bad outcome if that’s where it ends up.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Open RAN x-U.S.:
Outside the U.S., the situation is no better for OpenRAN. Only Japan’s Rakuten and Germany’s 1&1 have attempted to build a “greenfield” Open RAN from scratch. As well as reporting billions of dollars in losses on network deployment, Rakuten has struggled to attract customers. It owns the RAN software it has deployed but counts only 1&1 as a significant customer. And Rakuten’s original 4G rollout was not based on the industry’s open RAN specifications, according to critics. “They were not pure,” said Mavenir’s Kohli.
Plagued by delays and other problems, 1&1’s rollout has been a further bad advert for Open RAN. For the greenfield operators, the issue is not the maturity of open RAN technology. Rather, it is the investment and effort needed to build any kind of new nationwide telecom network in a country that already has infrastructure options. And the biggest brownfield operators, despite professing support for open RAN, have not backed any of the the new entrants.
RAN Market Concentration:
- Stefan Pongratz, an analyst with Dell’Oro, found that five of six regions he tracks are today classed as “highly concentrated,” with an HHI score of more than 2,500. “This suggests that the supplier diversity element of the open RAN vision is fading,” wrote Pongratz in a recent blog.
- A study from Omdia (owned by Informa), shows the combined RAN market share of Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia grew from 75.1% in 2023 to 77.5% last year. The only significant alternative to the European and Chinese vendors is Samsung, and its market share has shrunk from 6.1% to 4.8% over this period.
Concentration would seem to be especially high in the U.S., where Ericsson now boasts a RAN market share of more than 50% and generates about 44% of its sales (the revenue contribution of India, Ericsson’s second-biggest market, was just 4% for the recent second quarter). That’s partly because smaller regional operators previously ordered to replace Huawei in their networks spent a chunk of the government’s “rip and replace” funds on Ericsson rather than open RAN, says Kohli. Ironically, though, Ericsson owes much of the recent growth in its U.S. market share to what has been sold as an open RAN single vendor deal with AT&T [1.]. Under that contract, it is replacing Nokia at a third of AT&T’s sites, having already been the supplier for the other two thirds.
Note 1. In December 2023, AT&T awarded Ericsson a multi-year, $14 billion Open RAN contract to serve as the foundation for its open network deployment, with a goal of having 70% of its wireless traffic on open platforms by late 2026. That large, single-vendor award for the core infrastructure was criticized for potentially undermining the goal of Open RAN which was to encourage competition among multiple network equipment and software providers. AT&T’s claim of a mulit-vendor network turned out to be just a smokescreen. Fujitsu/1Finity supplied third-party radios used in AT&T’s first Open RAN call with Ericsson.
Indeed, AT&T’s open RAN claims have been difficult to take seriously, especially since it identified Mavenir as a third supplier of radio units, behind Ericsson and Japan’s Fujitsu, just a few months before Mavenir quit the radio unit market. Mavenir stopped manufacturing and distributing Open RAN radios in June 2025 as part of a financial restructuring and a shift to a software-focused business model.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Arguably, Kohli describes Echostar/ Dish Network as the only U.S. player that was spending “a good chunk of money to really support open RAN architecture.”
Ultimately, he thinks the big U.S. telcos may come to regret their heavier reliance on the RAN gear giants. “It may look great for AT&T and Verizon today, but they’ll be funding this whole thing as a proprietary solution going forward because, really, there’s no incentive for anybody else to come in,” he said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/open-ran/echostar-rout-leaves-its-open-ran-vendors-high-and-dry
AT&T to to buy spectrum Licenses from EchoStar for $23 billion
AT&T to deploy Fujitsu and Mavenir radio’s in crowded urban areas
Dell’Oro Group: RAN Market Grows Outside of China in 2Q 2025
Mavenir and NEC deploy Massive MIMO on Orange’s 5G SA network in France
Spark New Zealand completes 5G SA core network trials with AWS and Mavenir software
Mavenir at MWC 2022: Nokia and Ericsson are not serious OpenRAN vendors
Ericsson expresses concerns about O-RAN Alliance and Open RAN performance vs. costs
Nokia and Mavenir to build 4G/5G public and private network for FSG in Australia
Hyperscaler design of networking equipment with ODM partners
Networking equipment for hyperscalers like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Oracle, Meta, and others is a mix of in‑house engineering and partnerships with specialized vendors. These companies operate at such massive scale to design their own switches, routers, and interconnects — but rely on Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) and network silicon providers to build them.
In‑House Networking Design:
Hyperscalers have dedicated hardware teams that create custom network gear to meet their unique performance, latency, and power‑efficiency needs.
- Google – Designs its own Jupiter and Andromeda data center network fabrics, plus custom top‑of‑rack (ToR) and spine switches. Uses merchant silicon from Broadcom, Intel (Barefoot Tofino), and others, but with Google‑built control planes and software.
- Amazon (AWS) – Builds custom switches and routers for its Scalable Reliable Datagram (SRD) and Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA) HPC networks. Uses in‑house firmware and network operating systems, often on ODM‑built hardware.
- Microsoft (Azure) – Designs OCP‑compliant switches (e.g., SONiC network OS) and contributes to the Open Compute Project. Uses merchant silicon from Broadcom, Marvell, and Mellanox/NVIDIA.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) – Designs its own high‑performance RDMA‑enabled network for HPC and AI workloads, with custom switches built by ODM partners.
- Meta – Designs Wedge, Backpack, and Minipack switches under OCP, manufactured by ODMs.
Manufacturing & ODM Partners:
While the hyperscaler’s network equipment designs are proprietary, the physical manufacturing is typically outsourced to ODMs who specialize in hyperscale networking gear:
| ODM / OEM | Builds for | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Quanta Cloud Technology (QCT) | AWS, Azure, Oracle, Meta | Custom ToR/spine switches, OCP gear |
| WiWynn | Microsoft, Meta | OCP‑compliant switches and racks |
| Celestica | Multiple hyperscalers | High‑end switches, optical modules |
| Accton / Edgecore | Google, Meta, others | White‑box switches for OCP |
| Foxconn / Hon Hai | AWS, Google | Large‑scale manufacturing |
| Delta Networks | Multiple CSPs | Optical and Ethernet gear |
Network Silicon & Optics Suppliers:
Even though most hyperscalers design the chassis and racks, they often use merchant silicon and optics from:
- Broadcom – Tomahawk, Trident, Jericho switch ASICs
- Marvell – Prestera switch chips, OCTEON DPUs
- NVIDIA (Mellanox acquisition) – Spectrum Ethernet, InfiniBand for AI/HPC
- Intel (Barefoot acquisition) – Tofino programmable switch ASICs
- Cisco Silicon One – Used selectively in hyperscale builds
- Coherent optics & transceivers – From II‑VI (Coherent), Lumentum, InnoLight, etc.
Hyperscaler Networking Supply Chain Map:
| Layer | Key Players | Role | Example Hyperscaler Relationships |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Silicon (ASICs / DPUs) | Broadcom (Tomahawk, Jericho), Marvell (Prestera, OCTEON), NVIDIA/Mellanox (Spectrum, InfiniBand), Intel (Barefoot Tofino), Cisco (Silicon One) | Core packet switching, programmability, congestion control | Google (Broadcom, Intel), AWS (Broadcom, Marvell), Microsoft (Broadcom, Marvell, NVIDIA), Oracle (Broadcom, NVIDIA) |
| Optics & Interconnects | Coherent (II‑VI), Lumentum, InnoLight, Source Photonics, Broadcom (optical PHYs) | 400G/800G transceivers, co‑packaged optics, DWDM modules | All hyperscalers source from multiple vendors for redundancy |
| ODM / Manufacturing | Quanta Cloud Technology (QCT), WiWynn, Celestica, Accton/Edgecore, Foxconn, Delta Networks | Build hyperscaler‑designed switches, routers, and chassis | AWS (QCT, Foxconn), Google (Accton, QCT), Microsoft (WiWynn, Celestica), Meta (Accton, WiWynn), Oracle (QCT, Celestica) |
| Network OS & Control Plane | In‑house NOS (Google proprietary, AWS custom OS, Microsoft SONiC, Oracle custom), OCP software | Routing, telemetry, automation, SDN control | Google (Jupiter fabric OS), AWS (custom SRD/EFA stack), Microsoft (SONiC), Oracle (OCI NOS) |
| Integration & Deployment | Hyperscaler internal engineering teams | Rack integration, cabling, fabric topology, automation pipelines | All hyperscalers do this in‑house for security and scale |
Design Flow:
- Chip Vendors → supply merchant silicon to ODMs or directly to hyperscaler design teams.
- Hyperscaler Hardware Teams → design chassis, PCB layouts, thermal systems, and specify optics.
- ODMs → manufacture to spec, often in Asia, with hyperscaler QA oversight.
- Optics Vendors → deliver transceivers and cables, often qualified by hyperscaler labs.
- In‑House NOS → loaded onto hardware, integrated into hyperscaler’s SDN fabric.
- Deployment → rolled out in data centers globally, often in multi‑tier Clos or AI‑optimized topologies.
Major Trends:
- Disaggregation – Hyperscalers separate hardware from software, running their own Network Operating System (NOS), (e.g., SONiC, Google’s proprietary OS) on ODM‑built “white‑box” or “bare metal” switches.
- AI‑Optimized Fabrics – New designs focus on ultra‑low latency, congestion control, and massive east‑west bandwidth for GPU clusters.
- Optical Integration – Co‑packaged optics and 800G+ transceivers are becoming standard for AI and HPC workloads.
- AI Cluster Networking – NVIDIA InfiniBand and 800G Ethernet fabrics are now common for GPU pods.
- Co‑Packaged Optics – Moving optics closer to the ASIC to reduce power and latency.
- Open Compute Project Influence – Many designs are OCP‑compliant but with proprietary tweaks.
- Multi‑Vendor Strategy – Hyperscalers dual‑source ASICs and optics to avoid supply chain risk.
References:
How it works: hyperscaler compute server in house design process with ODM partners
Cloud‑resident high performance compute servers used by hyperscale cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), Meta, and others use a mix of custom in‑house designs and ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) ‑ built hardware.
In‑House Design Teams:
- Amazon (AWS) – Designs its own Nitro System–based servers, including custom motherboards, networking cards, and security chips. AWS also develops Graviton (Arm‑based) and Trainium/Inferentia (AI) processors. HPC instances use Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA) for low‑latency interconnects.
- Google (GCP) – Builds custom server boards and racks for its data centers, plus TPUs (Tensor Processing Units) for AI workloads. GCP builds custom HPC server boards and racks, plus TPUs for AI workloads. It uses high‑speed interconnects like Google’s Jupiter network for HPC clusters.
- Microsoft Azure – Designs Azure‑optimized servers and AI accelerators, often in collaboration with partners, and contributes designs to the Open Compute Project (OCP). It integrates InfiniBand and/or 400 Gbps Ethernet for HPC interconnects.
- Oracle – Designs bare‑metal HPC shapes with AMD EPYC, Intel Xeon, and NVIDIA GPUs, plus RDMA cluster networking for microsecond latency.
- Meta – Designs its compute servers, especially for AI workloads, by working closely with ODM partners like Quanta Computer, Wiwynn, and Foxconn.
Manufacturing Partners (ODMs/OEMs):
While the hyperscaler compute server designs are proprietary, the physical manufacturing is typically outsourced to Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) who specialize in hyperscale data center gear as per these tables:
| ODM / OEM | Known for | Cloud Customers |
|---|---|---|
| Quanta Cloud Technology (QCT) | Custom rack servers, HPC nodes | AWS, Azure, Oracle |
| WiWynn | OCP‑compliant HPC servers | Microsoft, Meta |
| Inventec | HPC and AI‑optimized servers | AWS, GCP |
| Foxconn / Hon Hai | Large‑scale server manufacturing | Google, AWS |
| Celestica | HPC and networking gear | Multiple hyperscalers |
| Supermicro | GPU‑dense HPC systems | AWS, Oracle, Azure |
| ODM / OEM | Role in Hyperscale Cloud |
|---|---|
| Quanta Cloud Technology (QCT) | Major supplier for AWS, Azure, and others; builds custom rack servers and storage nodes. |
| WiWynn | Spun off from Wistron; manufactures OCP‑compliant servers for Microsoft and Facebook/Meta. |
| Inventec | Supplies compute and storage servers for AWS and other CSPs. |
| Foxconn / Hon Hai | Builds cloud server hardware for multiple providers, including Google. |
| Delta / Celestica | Provides specialized server and networking gear for hyperscale data centers. |
| Supermicro | Supplies both standard and custom AI‑optimized servers to cloud and enterprise customers. |

The global server market expected to reach $380 billion by 2028. Image credit: Alamy
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Here’s a supply chain relationship map for cloud‑resident high‑performance compute (HPC) servers used by the major hyperscalers:
Hyperscale HPC Server Design & Manufacturing Landscape:
| Cloud Provider | In‑House Design Focus | Key Manufacturing / ODM Partners | Notable HPC Hardware Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Custom Nitro boards, Graviton CPUs, Trainium/Inferentia AI chips, EFA networking | Quanta Cloud Technology (QCT), Inventec, Foxconn | Arm‑based HPC nodes, GPU clusters (NVIDIA H100/A100), ultra‑low‑latency RDMA |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Custom server boards, TPU accelerators, Jupiter network fabric | Quanta, Inventec, Foxconn | TPU pods, GPU supernodes, liquid‑cooled racks |
| Microsoft Azure | OCP‑compliant HPC designs, Maia AI chip, Cobalt CPU, InfiniBand networking | WiWynn, QCT, Celestica | Cray‑based HPC clusters, GPU/FPGA acceleration |
| Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) | Bare‑metal HPC shapes, RDMA cluster networking | QCT, Supermicro | AMD EPYC/Intel Xeon nodes, NVIDIA GPU dense racks |
| Meta (for AI/HPC research) | OCP‑based AI/HPC servers | WiWynn, QCT | AI Research SuperCluster, liquid cooling |
| Alibaba Cloud / Tencent Cloud | Custom AI/HPC boards, Arm CPUs | Inspur, Sugon, QCT | GPU/FPGA acceleration, high‑bandwidth fabrics |
Meta’s ODM Collaboration Model:
- Quanta Computer: Meta has partnered with Quanta for final assembly of its next-gen AI servers. Quanta is responsible for building up to 6,000 racks of the Santa Barbara servers, which feature advanced cooling and power delivery systems.
- Wiwynn & Foxconn: These ODMs also play key roles in Meta’s infrastructure. Wiwynn reportedly earns more than half its revenue from Meta, while Foxconn handles system assembly for NVIDIA’s NVL 72 servers, which Meta may also utilize.
- Broadcom Partnership: For chip supply, Meta collaborates with Broadcom to integrate custom ASICs into its server designs.
Hyperscaler/ODM Collaboration Process:
- Design Phase – Hyperscalers’ hardware teams define the architecture: CPU/GPU choice, interconnect, cooling, power density.
- ODM Manufacturing – Partners like Quanta, WiWynn, Inventec, Foxconn, Celestica, and Supermicro build the servers to spec.
- Integration & Deployment – Systems are tested, integrated into racks, and deployed in hyperscale data centers.
- Optimization – Providers fine‑tune firmware, drivers, and orchestration for HPC workloads (e.g., CFD, genomics, AI training).
Industry Trends:
- Open Compute Project (OCP) – Many designs are shared in the OCP community, allowing ODMs to build interoperable, cost‑optimized hardware at scale. Open Compute Project designs speed up deployment and interoperability.
- Vertical Integration – Hyperscalers increasingly design custom silicon (e.g., AWS Graviton, Google TPU, Microsoft Maia AI chip) to optimize performance and reduce dependency on third‑party CPUs/GPUs.
- AI‑Optimized Racks – New designs focus on high‑density GPU clusters, liquid cooling, and ultra‑low‑latency networking for AI workloads.
- Vertical integration: More custom silicon to optimize performance and cost. See Specialized HPC components below.
- Liquid cooling: Increasingly common for dense GPU/CPU HPC racks.
Specialized HPC Components:
- CPUs – AMD EPYC, Intel Xeon Scalable, AWS Graviton (Arm), custom Google CPUs.
- GPUs / Accelerators – NVIDIA H100/A100, AMD Instinct, Google TPU, AWS Trainium.
- Networking – Mellanox/NVIDIA InfiniBand, AWS EFA, Oracle RDMA cluster networking.
- Storage – Parallel file systems like Lustre, BeeGFS, IBM Spectrum Scale for HPC workloads
References:
ODM Sales Soar as Hyperscalers and Cloud Providers Go Direct
The future of US hyperscale data centers | McKinsey
100MW+ Wholesale Colocation Deals: Inside the Hyperscaler Surge
Hyperscaler design of networking equipment with ODM partners – IEEE ComSoc Technology Blog
Liquid Dreams: The Rise of Immersion Cooling and Underwater Data Centers
Analysis: Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia network equipment for AI data centers
Both telecom and enterprise networks are being reshaped by AI bandwidth and latency demands of AI. Network operators that fail to modernize architectures risk falling behind. Why? AI workloads are network killers — they demand massive east-west traffic, ultra-low latency, and predictable throughput.
- Real-time observability is becoming non-negotiable, as enterprises need to detect and fix issues before they impact AI model training or inference.
- Self-driving networks are moving from concept to reality, with AI not just monitoring but actively remediating problems.
- The competitive race is now about who can integrate AI into networking most seamlessly — and HPE/Juniper’s Mist AI, Cisco’s assurance stack, and Nvidia’s AI fabrics are three different but converging approaches.
Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia are designing AI-optimized networking equipment, with a focus on real-time observability, lower latency and increased data center performance for AI workloads. Here’s a capsule summary:
Cisco: AI-Ready Infrastructure:
- Cisco is embedding AI telemetry and analytics into its Silicon One chips, Nexus 9000 switches, and Catalyst campus gear.
- The focus is on real-time observability via its ThousandEyes platform and AI-driven assurance in DNA Center, aiming to optimize both enterprise and AI/ML workloads.
- Cisco is also pushing AI-native data center fabrics to handle GPU-heavy clusters for training and inference.
- Cisco claims “exceptional momentum” and leadership in AI: >$800M in AI infrastructure orders taken from web-scale customers in Q4, bringing the FY25 total to over $2B.
- Cisco Nexus switches now fully and seamlessly integrated with NVIDIA’s Spectrum-X architecture to deliver high speed networking for AI clusters
HPE + Juniper: AI-Native Networking Push:
- Following its $13.4B acquisition of Juniper Networks, HPE has merged Juniper’s Mist AI platform with its own Aruba portfolio to create AI-native, “self-driving” networks.
- Key upgrades include:
-Agentic AI troubleshooting that uses generative AI workflows to pinpoint and fix issues across wired, wireless, WAN, and data center domains.
-Marvis AI Assistant with enhanced conversational capabilities — IT teams can now ask open-ended questions like “Why is the Orlando site slow?” and get contextual, actionable answers.
-Large Experience Model (LEM) with Marvis Minis — digital twins that simulate user experiences to predict and prevent performance issues before they occur.
-Apstra integration for data center automation, enabling autonomous service provisioning and cross-domain observability
Nvidia: AI Networking at Compute Scale
- Nvidia’s Spectrum-X Ethernet platform and Quantum-2 InfiniBand (both from Mellanox acquisition) are designed for AI supercomputing fabrics, delivering ultra-low latency and congestion control for GPU clusters.
- In partnership with HPE, Nvidia is integrating NVIDIA AI Enterprise and Blackwell architecture GPUs into HPE Private Cloud AI, enabling enterprises to deploy AI workloads with optimized networking and compute together.
- Nvidia’s BlueField DPUs offload networking, storage, and security tasks from CPUs, freeing resources for AI processing.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of how Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia are approaching AI‑optimized enterprise networking — so you can see where they align and where they differentiate:
| Feature / Focus Area | Cisco | HPE / Juniper | Nvidia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core AI Networking Vision | AI‑ready infrastructure with embedded analytics and assurance for enterprise + AI workloads | AI‑native, “self‑driving” networks across campus, WAN, and data center | High‑performance fabrics purpose‑built for AI supercomputing |
| Key Platforms | Silicon One chips, Nexus 9000 switches, Catalyst campus gear, ThousandEyes, DNA Center | Mist AI platform, Marvis AI Assistant, Marvis Minis, Apstra automation | Spectrum‑X Ethernet, Quantum‑2 InfiniBand, BlueField DPUs |
| AI Integration | AI‑driven assurance, predictive analytics, real‑time telemetry | Generative AI for troubleshooting, conversational AI for IT ops, digital twin simulations | AI‑optimized networking stack tightly coupled with GPU compute |
| Observability | End‑to‑end visibility via ThousandEyes + DNA Center | Cross‑domain observability (wired, wireless, WAN, DC) with proactive issue detection | Telemetry and congestion control for GPU clusters |
| Automation | Policy‑driven automation in campus and data center fabrics | Autonomous provisioning, AI‑driven remediation, intent‑based networking | Offloading networking/storage/security tasks to DPUs for automation |
| Target Workloads | Enterprise IT, hybrid cloud, AI/ML inference & training | Enterprise IT, edge, hybrid cloud, AI/ML workloads | AI training & inference at hyperscale, HPC, large‑scale data centers |
| Differentiator | Strong enterprise install base + integrated assurance stack | Deep AI‑native operations with user experience simulation | Ultra‑low latency, high‑throughput fabrics for GPU‑dense environments |
Key Takeaways:
- Cisco is strongest in enterprise observability and broad infrastructure integration.
- HPE/Juniper is leaning into AI‑native operations with a heavy focus on automation and user experience simulation.
- Nvidia is laser‑focused on AI supercomputing performance, building the networking layer to match its GPU dominance.
- Cisco leverages its market leadership, customer base and strategic partnerships to integrate AI with existing enterprise networks.
- HPE/Juniper challenges rivals with an AI-native, experience-first network management platform.
- Nvidia aims to dominate the full-stack AI infrastructure, including networking.
Omdia on resurgence of Huawei: #1 RAN vendor in 3 out of 5 regions; RAN market has bottomed
Market research firm Omdia (owned by Informa) says Huawei remains the number one RAN vendor in three out of five large geographical regions. Far from being fatally weakened by U.S. government sanctions, Huawei today looks as big and strong as ever. Its sales last year were the second highest in its history and only 4% less than it made in 2020, before those sanctions took effect. In three out of the five global regions studied by Omdia – Asia and Oceania, the Middle East and Africa, and Latin America and the Caribbean – Huawei was the leading RAN vendor. While third in Europe, it was absent from the top three only in North America where it is banned.
Spain’s Telefónica remains a big Huawei customer in Brazil and Germany, despite telling Krach in 2020 that it would soon have “clean networks” in those markets. Deutsche Telekom and Vodafone, two other European telco giants, are also still heavy users of Huawei. Ericsson and Nokia have noted Europe’s inability to kick out Huawei while alerting investors to “aggressive” competition from Chinese vendors in some regions.
“A few years ago, we were all talking about high-risk vendors in Europe and I think, as it looks right now, that is not an opportunity,” said Börje Ekholm, Ericsson’s CEO, on a call with analysts last month. The substitution of the Nordic vendors for Huawei has not gone as far as they would have hoped. Ekholm warned analysts one year ago about “sharply increased competition from Chinese vendors in Europe and Latin America” and said there was a risk of losing contracts. “I am sure we’ll lose some, but we do it because it is right for the overall gross margin in the company. Don’t expect us to be the most aggressive in the market.”
There are few signs of European telcos replacing one of the Nordic vendors with Huawei, or of big market share losses by Ericsson and Nokia to Chinese rivals. Nokia’s RAN market share outside China did not materially change between the first and second quarters, says Remy Pascal, a principal analyst with Omdia (quarterly figures are not disclosed but Nokia held 17.6% of the RAN market including China last year). Huawei appears to have overtaken it because of gains at the expense of other vendors and a larger revenue contribution from Huawei-friendly emerging markets in the second quarter. Seasonality and the timing of revenue recognition were also factors, says Pascal.
Huawei is still highly regarded by chief technology officers for the quality of its products. It was a pioneer in the development of 5G equipment for time division duplex (TDD) technology, where uplink and downlink communications occupy the same frequency channel, and in massive MIMO, an antenna-rich system for boosting signal strength. It beat Ericsson and Nokia to the commercialization of power amplifiers based on gallium nitride, an efficient alternative to silicon, according to Earl Lum, the founder of EJL Wireless Research.
Sanctions have not held back Huawei’s technology as much as analysts had expected. While the company was cut off from the foundries capable of manufacturing the most advanced silicon, it managed to obtain good-enough 7-nanometer chips in China for its latest smartphones, spurring its resurgence in that market. Network products remain less dependent on access to cutting-edge chips, and sales in that sector do not appear to have suffered outside markets that have imposed restrictions.
Alternatives to Huawei’s dominance have not materialized in a RAN sector that was already short of options. Besides evicting Huawei from telco networks, U.S. authorities hoped “Open RAN” would give rise to American developers of RAN products. That has failed badly.
- Mavenir, arguably the best Open RAN hope the U.S. had, became emblematic of the Open RAN market gloom after it recently withdrew from the market for radio units as part of a debt restructuring. The company has sold its Open RAN software to DISH Network and Vodafone, it has not achieved the market penetration it initially targeted. Mavenir has faced significant financial challenges that led to a restructuring in 2025, significant layoffs and a major shift in strategy away from developing its own hardware.
- Parallel Wireless makes Open RAN software and also provides Open RAN software-defined radios (SDRs) as part of its hardware ecosystem, focusing on disaggregating the radio access network stack to allow operators flexibility and reduced total cost of ownership. Their offerings include a hardware-agnostic 5G Standalone (SA) software stack and the Open RAN Aggregator software, which manages and converges multi-vendor RAN interfaces toward the core network.
Stefan Pongratz of Dell’Oro Group forecasts annual revenues from multi-vendor RAN deployments – where telcos combine vendors instead of buying from a single big supplier – will have reached an upper limit of $3 billion by 2029, giving multi-vendor RAN less than 10% of the total RAN market by that date. He says five of six tracked regions are now classed as “highly concentrated,” with an Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) score of more than 2,500. “This suggests that the supplier diversity element of the open RAN vision is fading,” Stefan added.
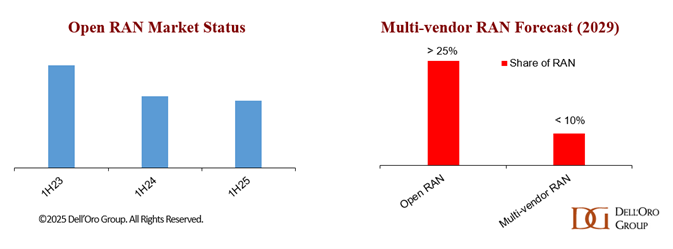
Preliminary data from Dell’Oro indicate that Open RAN revenues grew year-over-year (Y/Y) in 2Q25 and were nearly flat Y/Y in the first half, supported by easier comparisons, stronger capex tied to existing Open RAN deployments, and increased activity among early majority adopters.
Open RAN used to mean alternatives to Ericsson and Nokia. Today, it looks synonymous with the top 5 RAN vendors (Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, and Samsung). In such an environment of extreme market concentration and failed U.S. sanctions, the appeal of Huawei’s RAN technology is still very much intact.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Omdia’s historical data shows that RAN sales fell by $5 billion, to $40 billion, in 2023, and by the same amount again last year. In 2025, it is guiding for low single-digit percentage growth outside China, implying the RAN market has bottomed out. This stabilization suggests the market may be transitioning into a phase of flat-to-modest growth, though risks such as operator capex constraints and uneven regional demand remain. However, concentration of RAN vendors
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/huawei-overtakes-nokia-outside-china-as-open-ran-stabilizes-
Omdia: Huawei increases global RAN market share due to China hegemony
Malaysia’s U Mobile signs MoU’s with Huawei and ZTE for 5G network rollout
Dell’Oro Group: RAN Market Grows Outside of China in 2Q 2025
Dell’Oro: AI RAN to account for 1/3 of RAN market by 2029; AI RAN Alliance membership increases but few telcos have joined
Network equipment vendors increase R&D; shift focus as 0% RAN market growth forecast for next 5 years!
vRAN market disappoints – just like OpenRAN and mobile 5G
Mobile Experts: Open RAN market drops 83% in 2024 as legacy carriers prefer single vendor solutions
Huawei launches CloudMatrix 384 AI System to rival Nvidia’s most advanced AI system
U.S. export controls on Nvidia H20 AI chips enables Huawei’s 910C GPU to be favored by AI tech giants in China
AT&T to buy spectrum licenses from EchoStar for $23 billion
Executive Summary:
Embattled EchoStar Corp, parent company of Dish Network [1.], has agreed to sell spectrum licenses to AT&T Inc. for about $23 billion in a deal that will help the company stay out of bankruptcy and fend off regulatory concerns about its airwave use. The sale will expand AT&T’s wireless network and add about 50 MHz of low-band and mid-band spectrum in an all-cash transaction, the Dallas, Texas-based telecommunications company said in a statement on Tuesday. The deal is expected to close by mid-2026, pending regulatory approval.
Note 1. Dish Network is one of only two U.S. wireless telcos that have commercially deployed 5G SA core network on Amazon’s AWS public cloud.. The EchoStar subsidiary has also deployed 5G OpenRAN.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Key Takeaways:
- $23 billion acquisition will add an average of approximately 50 MHz of low-band and mid-band spectrum to AT&T’s holdings – covering virtually every market across the U.S. and positioning AT&T to maintain long-term leadership in advanced connectivity across 5G and fiber
- Transaction powers improved and capital-efficient long-term growth by accelerating the Company’s ability to add converged subscribers with both 5G wireless and home internet services in more places
- Leading AT&T network will enable continued EchoStar participation in wireless industry through long-term wholesale network services agreement
AT&T said the acquisition of approximately 30 MHz of mid-band spectrum and 20 MHz of low-band spectrum will strengthen the company’s ability to deliver 5G and fiber services across the US. EchoStar will operate in the US market as a hybrid mobile network operator under its Boost brand, the company said in the statement. AT&T will be its primary network partner for wireless service. AT&T has been spending heavily to expand its fiber-optic network across the country and previously said it would use cash savings from Trump’s tax and spending bill to accelerate those plans. In May, it agreed to buy the consumer fiber operations of Lumen Technologies Inc. for $5.75 billion, expanding its fast broadband service in major cities like Denver and Las Vegas. AT&T intends to finance the EchoStar deal with a combination of cash on hand and borrowings. Jefferies Financial Group Inc. advised AT&T on the EchoStar acquisition.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Backgrounder:
Federal regulators have been pushing EchoStar to sell some of its airwaves after concerns it had failed to put valuable slices of wireless spectrum to use, Bloomberg reported in July. The FCC launched an investigation in May into whether EchoStar was meeting its obligations for its wireless and satellite spectrum rights. The company skipped bond payments and considered filing for bankruptcy, saying the probe had stymied its ability to make decisions about its 5G network. In a June meeting, first reported by Bloomberg, Trump urged EchoStar Chairman Charlie Ergen and FCC Chairman Brendan Carr to cut a deal to resolve the dispute. EchoStar shopped the assets to other would-be buyers, including Elon Musk’s Starlink, Bloomberg earlier reported.
The purchase price is $9 billion more than EchoStar paid for the spectrum and $5 billion more than the appraised value used in securitizing the assets, New Street Research’s Philip Burnett said in a research note Tuesday. While $1.5 billion shy of New Street’s valuation, he said the sale price was “nevertheless a great mark on value.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Quotes:
EchoStar CEO Ergen described the sale and related agreement to work with AT&T as “critical steps toward resolving the FCC’s spectrum utilization concerns.”
FCC spokesperson Katie Gorscak said “We appreciate the productive and ongoing discussions with the EchoStar team. The FCC will continue to focus on ensuring the beneficial use of scarce spectrum resources.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/t-buy-echostar-spectrum-licenses-160830548.html
https://about.att.com/story/2025/echostar.html
FCC to investigate Dish Network’s compliance with federal requirements to build a nationwide 5G network
FCC approves EchoStar/Dish request to extend timeline for its 5G buildout
New FCC Chairman Carr Seen Clarifying Space Rules and Streamlining Approvals Process
Dish Network & Nokia: world’s first 5G SA core network deployed on public cloud (AWS)
Dish Network to FCC on its “game changing” OpenRAN deployment
DISH Wireless Awarded $50 Million NTIA Grant for 5G Open RAN Center (ORCID)
A 1959 re-invention of Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radar
by Jeffrey Pawlan, Chairman of IEEE SCV Life Members Affinity Group, with Alan J Weissberger (member of IEEE SCV Life Members Affinity Group)
Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radar, is currently a hot topic in the IEEE Microwave Theory and Technology Society. It is a type of radar system that measures distance and velocity by continuously transmitting a radio wave whose frequency changes over time (a “chirp” signal). This allows FMCW radar to determine both the distance to a target and its velocity by analyzing the frequency difference between the transmitted and received signals. It also measures the Doppler frequency (due to the Doppler effect) for calculating the speed of the object.
Below is a short summary of my 1959 invention related to FMCW, but first some historical background and applications:
- The earliest known use of FMCW was in 1920s for ionospheric research.
- First patent for an FMCW radar was filed in 1928 for altitude measurement from an aircraft. – Bentley, J. O., “Airplane Altitude Indicating System,” U.S. Patent No. 2,011,392 , issued August 13, 1935, application August 10, 1928.
- Most theoretical work were published between the late 1940s and early 1960s. – Luck, D. G. C., Frequency Modulated Radar, New York, McGraw-Hill, 1949. – J.R. Klauder, A.C. Price, S. Darlington, and W.J. Albersheim, “The Theory and Design of Chirp Radars,” Bell Syst.Tech. J. 39 (4), 1960, pp. 745–808
- Applications include: Radar altimeter, Radar navigation , Vehicle collision warning systems, Level-indication in tanks, aviation (altimetry, weather), industrial automation (distance, speed, level sensing), and healthcare (vital sign monitoring).
- Its low power, compact size, and cost-effectiveness suit short-range applications, enabling features like blind-spot detection, drone navigation, and non-contact medical measurements.
Advantages of FMCW Radar:
- mm-wave FMCW radars offer high-resolution distance measurement (resolution of 2 cm can be easily achieved over 20-30 meters)
- Measures the target range and velocity simultaneously
- FMCW provide quick updating of measurement compared to pulsed radar system (because FMCW mm-wave radars are continuously transmitting the signal)
- Functions well in many types of weather & atmospheric conditions such as heavy rain, humidity, fog, and dusty conditions.
- Immune to effects from temperature differences or high temperatures.
- Better electrical and radiation safety
- FMCW radars offer a good range compared to other non-radio technologies such as visible or infrared light spectrum or those using ultrasonic waves due to the superior signal propagation.
- Can be mounted invisibly (behind radome)
- Can penetrate into a variety of materials; hence, FMCW radar can be used for measurement or detection of concealed or covered targets
- Better at detecting tangential motion than Doppler-based systems.
My 1959 re-invention of FMCW radar:
Surplus stores were common in large cities like Los Angeles (where I lived) from 1950 to 1970. Those stores purchased World War II radios and parts from the U.S. government at a very low cost. The stores then sold those items to hobbyists and collectors. That’s how microwave radio parts were acquired – mostly by hobbyists.
In most cases, one complete X-band radar unit and one partial unit were purchased. Each unit contained a reflex klystron [1.] for the receiver’s local oscillator. The magnetron in the transmitter was not used because it could’ve generated a dangerous level of RF power. Pieces of WR90 waveguide were used to construct a low-power (20 milliwatts) transmitter with one klystron and a receiver with the other. These klystrons were type 723A/B.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Note 1. A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937, which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. A reflex klystron is a low-power vacuum tube oscillator that generates microwave oscillations by using a single resonant cavity and a repeller electrode to reflect an electron beam back through the cavity. The electron beam is velocity-modulated by the cavity, causing electrons to bunch together and produce a microwave RF output as they return through the cavity gap. It consists of an electron gun, a single cavity that functions as both a “buncher” and “catcher,” and a repeller that pushes the electrons back.
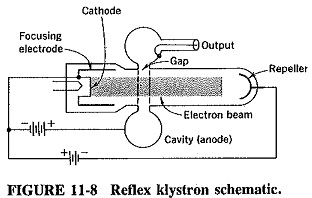
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Frequency Modulation (FM) was used to modulate the signal. This was achieved by adjusting the negative voltage of the klystron tube’s repeller which is a negatively charged electrode located at the far end of the tube from the electron gun. Its function is to create a high negative potential that repels the electron beam, causing it to reverse direction and pass back through the resonant cavity, a process necessary for the device to oscillate and generate microwave energy.
This repeller was approximately -105V at a very low current. I used a vacuum tube radio “B” battery to provide the repeller power. I did not use AC-operated power supplies, because they produced too much ripple which caused an unacceptable amount of hum in the signal. A transformer was placed in series with the repeller voltage.
In my amateur radio experimentation, I used audio from my microphone amplifier. I cannot explain how my brain got the idea that I might be able to make a radar by using triangular wave modulation. I confirmed that idea by looking at the resulting frequency difference of the return microwave signal bouncing off of a nearby wall. It worked!
I modulated the klystron with a triangular wave and then determined the distance to the wall by comparing the timing of the reflected signal with the time of the transmitted signal. The triangular wave varied the wavelength of the signal over time so I could see the time difference based on the point on the triangle waveform. Since I was so young, I did not have access to the previously published papers, patents, and books so I could not copy or reference them. Therefore, I did not invent FMCW radar, but claim I independently re-invented it.
In 1959, I was a subscriber to Microwaves magazine. I penned a short letter to that publication and described what I had done and included a few diagrams. They had no idea that I was only 14 years old. They wrote back a typed letter stating they would like me to submit a full article on this new radar system. The problem for me was that even though I was excellent at reading even technical books, I was absolutely terrible expressing myself in writing. So I did not reply to them. I saved that letter from the editor of Microwaves magazine for decades but when I moved the last time I threw it out.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Postscript:
At 79 years old, I recently designed a unique antenna feedhorn for 47 GHz. I submitted a 12-page write-up to the Microwave Journal which will publish it in 2026.
References:
https://data.cresis.ku.edu/education/tutorial_2006/fmcw_6-28-06_1pm.pdf
https://www.everythingrf.com/community/what-is-a-fmcw-radar
Nokia introduces new Wavence microwave solutions to extend 5G reach in both urban and rural environments
SoftBank’s Transformer AI model boosts 5G AI-RAN uplink throughput by 30%, compared to a baseline model without AI
Softbank has developed its own Transformer-based AI model that can be used for wireless signal processing. SoftBank used its Transformer model to improve uplink channel interpolation which is a signal processing technique where the network essentially makes an educated guess as to the characteristics and current state of a signal’s channel. Enabling this type of intelligence in a network contributes to faster, more stable communication, according to SoftBank. The Japanese wireless network operator successfully increased uplink throughput by approximately 20% compared to a conventional signal processing method (the baseline method). In the latest demonstration, the new Transformer-based architecture was run on GPUs and tested in a live Over-the-Air (OTA) wireless environment. In addition to confirming real-time operation, the results showed further throughput gains and achieved ultra-low latency.
Editor’s note: A Transformer model is a type of neural network architecture that emerged in 2017. It excels at interpreting streams of sequential data associated with large language models (LLMs). Transformer models have also achieved elite performance in other fields of artificial intelligence (AI), including computer vision, speech recognition and time series forecasting. Transformer models are lightweight, efficient, and versatile – capable of natural language processing (NLP), image recognition and wireless signal processing as per this Softbank demo.
Significant throughput improvement:
- Uplink channel interpolation using the new architecture improved uplink throughput by approximately 8% compared to the conventional CNN model. Compared to the baseline method without AI, this represents an approximately 30% increase in throughput, proving that the continuous evolution of AI models leads to enhanced communication quality in real-world environments.
Higher AI performance with ultra-low latency:
- While real-time 5G communication requires processing in under 1 millisecond, this demonstration with the Transformer achieved an average processing time of approximately 338 microseconds, an ultra-low latency that is about 26% faster than the convolution neural network (CNN) [1.] based approach. Generally, AI model processing speeds decrease as performance increases. This achievement overcomes the technically difficult challenge of simultaneously achieving higher AI performance and lower latency. Editor’s note: Perhaps this can overcome the performance limitations in ITU-R M.2150 for URRLC in the RAN, which is based on an uncompleted 3GPP Release 16 specification.
Note 1. CNN-based approaches to achieving low latency focus on optimizing model architecture, computation, and hardware to accelerate inference, especially in real-time applications. Rather than relying on a single technique, the best results are often achieved through a combination of methods.

Using the new architecture, SoftBank conducted a simulation of “Sounding Reference Signal (SRS) prediction,” a process required for base stations to assign optimal radio waves (beams) to terminals. Previous research using a simpler Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) AI model for SRS prediction confirmed a maximum downlink throughput improvement of about 13% for a terminal moving at 80 km/h.*2
In the new simulation with the Transformer-based architecture, the downlink throughput for a terminal moving at 80 km/h improved by up to approximately 29%, and by up to approximately 31% for a terminal moving at 40 km/h. This confirms that enhancing the AI model more than doubled the throughput improvement rate (see Figure 1). This is a crucial achievement that will lead to a dramatic improvement in communication speeds, directly impacting the user experience.
The most significant technical challenge for the practical application of “AI for RAN” is to further improve communication quality using high-performance AI models while operating under the real-time processing constraint of less than one millisecond. SoftBank addressed this by developing a lightweight and highly efficient Transformer-based architecture that focuses only on essential processes, achieving both low latency and maximum AI performance. The important features are:
(1) Grasps overall wireless signal correlations
By leveraging the “Self-Attention” mechanism, a key feature of Transformers, the architecture can grasp wide-ranging correlations in wireless signals across frequency and time (e.g., complex signal patterns caused by radio wave reflection and interference). This allows it to maintain high AI performance while remaining lightweight. Convolution focuses on a part of the input, while Self-Attention captures the relationships of the entire input (see Figure 2).
(2) Preserves physical information of wireless signals
While it is common to normalize input data to stabilize learning in AI models, the architecture features a proprietary design that uses the raw amplitude of wireless signals without normalization. This ensures that crucial physical information indicating communication quality is not lost, significantly improving the performance of tasks like channel estimation.
(3) Versatility for various tasks
The architecture has a versatile, unified design. By making only minor changes to its output layer, it can be adapted to handle a variety of different tasks, including channel interpolation/estimation, SRS prediction, and signal demodulation. This reduces the time and cost associated with developing separate AI models for each task.
The demonstration results show that high-performance AI models like Transformer and the GPUs that run them are indispensable for achieving the high communication performance required in the 5G-Advanced and 6G eras. Furthermore, an AI-RAN that controls the RAN on GPUs allows for continuous performance upgrades through software updates as more advanced AI models emerge, even after the hardware has been deployed. This will enable telecommunication carriers to improve the efficiency of their capital expenditures and maximize value.
Moving forward, SoftBank will accelerate the commercialization of the technologies validated in this demonstration. By further improving communication quality and advancing networks with AI-RAN, SoftBank will contribute to innovation in future communication infrastructure. The Japan based conglomerate strongly endorsed AI RAN at MWC 2025.
References:
https://www.softbank.jp/en/corp/news/press/sbkk/2025/20250821_02/
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/softbank-claims-its-ai-ran-tech-boosts-throughput-by-30-
https://www.telecoms.com/ai/softbank-makes-mwc-25-all-about-ai-ran
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/transformer-model
https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-M.2150/en
Softbank developing autonomous AI agents; an AI model that can predict and capture human cognition
Dell’Oro Group: RAN Market Grows Outside of China in 2Q 2025
Dell’Oro: AI RAN to account for 1/3 of RAN market by 2029; AI RAN Alliance membership increases but few telcos have joined
Dell’Oro: RAN revenue growth in 1Q2025; AI RAN is a conundrum
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
OpenAI announces new open weight, open source GPT models which Orange will deploy
Deutsche Telekom and Google Cloud partner on “RAN Guardian” AI agent




