Author: Alan Weissberger
Telco business models must change as Big Tech generates the majority of internet traffic
In a blog post today, network intelligence firm Sandvine states that Google, Facebook, and other ‘top-6’ digital brands generate more than 56% of global network traffic. The company’s upcoming 2022 “Global Internet Phenomenon Report,” takes this a step further by showing that the top-6 – Google, Facebook, Netflix, Amazon, Microsoft, and Apple – are generating more than 56% of global network traffic.
For the first time, the biggest digital players account for more traffic than everyone else (telcos, MSOs/cablecos, satellite internet, state & local governments, municipalities, etc), combined! And that trend is likely to continue to increase. as OpenVault recently reported that average monthly home internet data consumption in the U.S. rose to 434.9 GBytes in the third quarter of 2021, up 13% over the same period in 2020.
The chart below shows the percentage of traffic that the six biggest Internet companies generated across global networks.
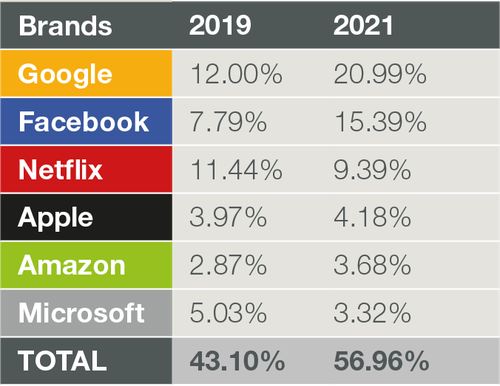
Source: Sandvine
For Communications service providers (CSPs), this is a watershed moment: they must deliver the benefits of 5G (are there any?), cloud, the IoT, AR/VR, AI, the metaverse (?), etc. and they must assure a good QoE (Quality of Experience) for the current and next generation of apps.
Sandvine believes the shift to more mission-critical enterprise and industry services will trigger a need for flawless connectivity (ultra high reliability/availability) and optimal performance for manufacturing robotics, remote healthcare, autonomous driving, public safety, and other critical services.
Recently, the CEOs of Deutsche Telekom, Telefonica, Vodafone, and 11 other influential service providers published an open letter stating that “a large and increasing part of network traffic is generated and monetized by Big Tech platforms.”
They cited the fact that it is the telecommunications sector that is bearing the “continuous, intensive network investment and planning” that ultimately drives the unprecedented profitability of the biggest tech brands.
“A large and increasing part of network traffic is generated and monetized by Big Tech platforms, but it requires continuous, intensive network investment and planning by the telecommunications sector,” the CEOs said in the joint statement seen by Reuters.
In other words, telcos are subsidizing Big Tech who reap the benefits of those same telco networks. MSOs/cablecos broadband internet providers, like Comcast, Charter, and Cox Communications, could likely make the same argument.
The CEOs did not mention any big tech firms by name, but Reuters understands that U.S.-listed giants such as Netflix and Facebook are companies they have in mind.
According to Reuters, the investments in Europe’s telco sector rose to 52.5 billion euros ($59.4 billion) last year, a six-year high. Those investments include the networks, 5G trials, licenses, planning, and deployment that fuel app QoE. In return, the European telcos received modest usage fees from subscribers.
In addition to wanting a fair ROI for their substantial investments, CSPs also want to protect their networks and brands. The recent Facebook, AWS, and Tesla outages demonstrated how pronounced and far reaching the impacts on networks can be now that apps and services are far more intertwined and interdependent than ever before. QoE for both related and unrelated apps and services were affected.
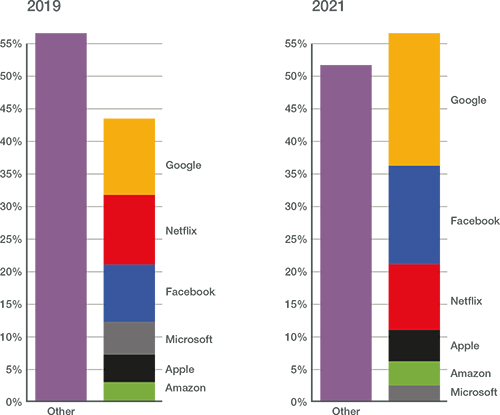
Source: Sandvine
Sandvine says CSPs need predictive insights that help identify macro trends across their millions of subscribers, billions of devices, and thousands of applications to answer key questions that can drive business actions and outcomes.
Here are a few such questions CSPs should address, according to Sandvine:
- Which apps are consuming and generating the most traffic, downstream and upstream?
- What’s the impact of app complexity in terms of mashups, embedded video, payments, chat, and other features?
- How are QUIC (a new multiplexed transport built on top of UDP), HTTP/3, iCloud Private Relay, and encryption affecting the network?
- Who are the “heavy users” in the upgrade from 4G to 5G?
The above questions are just some that Sandvine will explore in detail in their upcoming “Global Internet Phenomenon Report.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Meanwhile, a growing number of professionals are calling for “Big Tech” to contribute to the Universal Service Fund (USF). The FCC instituted the USF in 1997 to help fund the construction of broadband networks in rural and unserved areas of the country, and to help low-income Americans afford telecom services. But the primary sources of funding for the USF are network operators (which redirect the USF fees paid by their customers each month).
FCC Commissioner Brendan Carr said that the best way to fund the FCC’s Universal Service Fund advanced communications subsidies is to make Big Tech pay the freight. Citing a new study from economist Hal Singer and Ted Tatos, Carr said that the current method of assessing dwindling traditional telecom services is unsustainable, and that shifting to assessing wireless broadband would continue to hit consumers in the pocketbook–the USF fees are passed on by telecoms onto their customers’ bills.
Car argues that the FCC should make Big Tech companies like Google and Facebook pay the USF fees, which would be very difficult for them to pass on to consumers and which would, “significantly reduce consumers’ costs, properly align incentives, and unlike assessing wireline broadband revenues, would not raise consumers’ monthly bill for internet services,” Carr said citing the study,
References:
https://www.sandvine.com/blog/telco-business-models-reaching-tipping-point-in-digital-era
https://www.nexttv.com/news/fccs-carr-make-big-tech-pay-for-usf-subsidies
Dell’Oro: 3Q21 Total Telecom Equipment Market up 6% year-over-year & 9% year-to-date
Dell’Oro Group just completed their 3Q21 reporting period for all the Telecommunications Infrastructure programs covered. Those include: Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core & Radio Access Network (RAN), SP Router & Switch.
The data contained in these reports suggest that the positive trends that characterized the broader telecom equipment market in the first half of 2021 extended into the third quarter, propelling the overall telecom equipment market to a sixth consecutive quarter of year-over-year (Y/Y) growth in revenues.
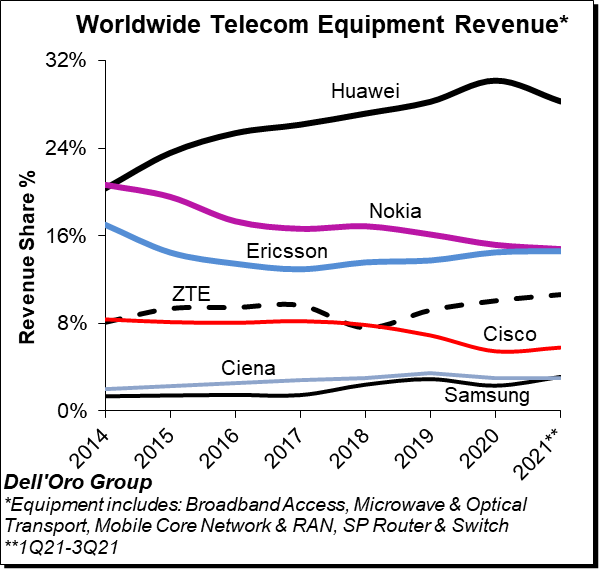
Preliminary estimates suggest the overall telecom equipment market advanced 6% Y/Y in the quarter and 9% Y/Y year-to-date (YTD). The growth in the quarter was underpinned by healthy demand for both wireless and wireline equipment.
While the majority of the suppliers were able to navigate the supply chain situation fairly well in the first half, supply chain disruptions had a greater impact in the third quarter, though clearly this was not enough to derail the positive momentum that has characterized the market over the past six quarters.
The analysis contained in these reports suggests the collective global share of the leading suppliers remained relatively stable between 2020 and 1Q21-3Q21, with the top seven vendors comprising around ~80% of the total market.
Ongoing efforts by the US government to curb the rise of Huawei is starting to show in the numbers, especially outside of China. At the same time, Huawei continued to dominate the global market, still nearly as large as Ericsson and Nokia combined.
Overall, we believe ZTE and Samsung are trending upward while Huawei is losing some ground YTD relative to 2020.
Additional key takeaways from the 3Q21 reporting period include:
- Positive market sentiment in the third quarter was driven by strong growth in RAN and Broadband Access, which was more than enough to offset weaker trends in Optical Transport.
- RAN and Broadband Access are also the strongest growth vehicles for the YTD period, fueled by surging demand for 5G, PON, and FWA CPEs.
- With the pandemic resurging and the visibility surrounding the supply chain weakening, the Dell’Oro analyst team is expecting near-term growth to decelerate – the overall telecom equipment market is now projected to advance 2% in 2022, down from 8% in 2021.
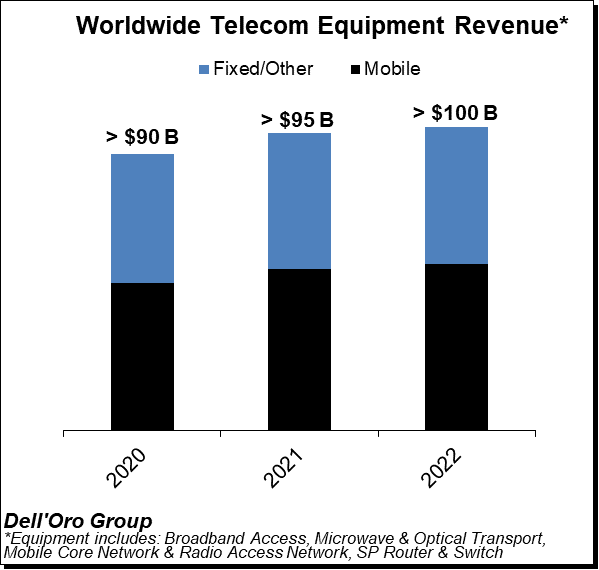
Dell’Oro Group telecommunication infrastructure research programs consist of the following: Broadband Access, Microwave Transmission & Mobile Backhaul, Mobile Core Networks, Radio Access Network, Optical Transport, and Service Provider (SP) Router & Switch.
Dell’Oro: Ethernet adapter port shipments declined in Q3-2021 but expected to grow in 2022
After declining in the 3rd quarter of 2021, Ethernet adapter port shipments are forecast to return to double-digit growth in 2022, as supply restrictions ease, and as Smart NICs create growth opportunities.
“Ethernet adapter port shipments declined 7% year-over-year in 3Q 2021, as vendors faced various component sourcing challenges, with lead-times extending beyond 52 weeks in some extreme cases,” said Baron Fung, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group.
“In contrast, Ethernet controller shipments have approached record levels, as we believe server vendors are increasing their inventories of controllers in anticipation of stronger cloud and enterprise demand ahead,” added Fung.
Additional highlights from the 3Q 2021 Ethernet Controller and Adapter report include:
- Total Ethernet controller and adapter revenue forecast to grow 27 percent in 2021.
- Major cloud service providers are upgrading server connectivity to 100 and 200 Gbps port speeds in conjunction with network upgrades.
- Smart NICs developed internally by cloud service providers, such as Amazon and Microsoft, for their data centers have accounted for the majority of the shipments.
- Vendors such as Marvell and Nvidia, are expected to increase their share in 2022 as customer qualifications make progress.
“Outside of the hyperscale cloud service providers, the smartNIC market is still in its early stages,” Fung said, as customers explore viable use cases for them in their data centers.
Most adapter vendors today either offer smartNICs or are sampling them. Besides cloud providers, smartNIC vendors include Marvell, Intel, Xilinx, Nvidia, Napatech, Pensando, Fungible, Ethernity, and Broadcom.
Most of them “are trying to grow their smartNIC share in the tier two cloud, enterprise, and telco segments,” Fung said.
The Dell’Oro Group Ethernet Controller and Adapter Quarterly Report provide complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue; average selling prices; and unit and port shipments by speed (1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, 25 Gbps, 40 Gbps, 50 Gbps, 100 Gbps, and 200 Gbps) for Ethernet controllers and adapters. The report also covers Smart NIC controllers and adapters. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
References:
Ethernet Adapter Shipments Stalled by Supply Constraints in 3Q 2021, According to Dell’Oro Group
Synergy Research: Microsoft and Amazon (AWS) Dominate IT Vendor Revenue & Growth; Popularity of Multi-cloud in 2021
Synergy Research Group’s detailed review of 2021 IT markets identified 13 vendors that generated over $25 billion in annual revenues from sales of technology to enterprises and service providers. Microsoft was the leader by a wide margin with annual revenues of $120 billion from its enterprise customers, followed by IBM, Amazon, Huawei and Cisco.
Amazon Web Services led the way in annual revenue growth, with 36% growth. Salesforce and Microsoft followed with each grew their revenues by well over 20%. None of the other leaders managed to achieve double-digit growth rates, with Cisco coming the closest.
At the other end of the spectrum Huawei saw its revenues from enterprise and service provider customers fall by 9%, as it was hurt by geopolitical issues and technology supply restrictions. While Huawei’s revenues dropped, business levels at both Ericson and Nokia were mostly flat, demonstrating the relative weakness of service provider sales compared with the enterprise sector.

2021 Vendor Ranking. Source: Synergy Research Group
In aggregate the thirteen vendors generated 2021 revenues of $613 billion from enterprise and service provider customers, up 10% from 2021. The analysis is based on Synergy’s detailed quarterly tracking data for a comprehensive range of enterprise IT markets. The full-year 2021 revenue numbers represent actual data for the first three quarters of the year and a forecast of Q4 activity levels. The larger market segments include cloud infrastructure services, collaboration, enterprise software/SaaS, data center infrastructure, service provider infrastructure and enterprise IT services. Segments with the highest growth rates are cloud infrastructure services, SaaS, hosted & cloud collaboration and service provider data center infrastructure.
“The performance of the technology titans was a bit of a mixed bag in 2021, but the good news is that only Huawei saw its revenues decline and that was due to factors that were largely beyond its control. Across a broad swathe of enterprise technology markets, vendors saw double-digit revenue growth,” said John Dinsdale, Chief Analyst at Synergy Research Group. “Cloud and software-oriented markets were the standout performers, driving stellar growth for AWS, Microsoft and Salesforce. Vendors whose sales are focused primarily on more traditional on-premise products or infrastructure will continue to have a hard time generating exciting levels of growth.”
About Synergy Research Group:
Founded in 1999, Synergy provides market intelligence and analytics for the networking and telecoms industry for over 30 technology markets. We publish comprehensive quantitative market data that is updated every 90 days. Through annual subscription services, Synergy offers worldwide, regional, and country-level market share data including vendor revenue, shipments, subscribers, end user sizing, detailed market segmentation, forecasts and analysis.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Cloud Computing Trends in 2021 – Multi-cloud, Hybrid and Cloud Migration:
2021 was another big year for multi-cloud, thanks not only to the continued demand for cloud services but also the number of strong options users have. The advantage of using multi-cloud when there are multiple strong options available is that an organization can run workloads across multiple clouds, instead of choosing just one cloud for all of its needs.
The multi-cloud trend in 2021 also extended to hybrid cloud deployments – a mix of public cloud resources alongside on-premises deployments. Moving from one deployment model to another, either from on-premises to the public cloud or from one public cloud to another, has been a common topic of discussion across vendors in 2021, as they try to grow share.
What 2021 proved was that organizations are continuing and will continue to turn to the cloud and there is no shortage of options, technologies and vendors from which IT pros can choose.
References:
Ookla: Q3 2021 Satellite Internet performance finds Starlink still #1 but average download speed decreased
Satellite internet is making headlines all over the world. Starlink continues to launch service in new countries while Viasat plans to acquire Inmarsat.
Ookla continues their ongoing series on satellite internet performance around the globe with fresh data from Q3 2021 to see if Starlink’s performance is holding up and how satellite internet compares to fixed broadband in 12 countries.
In the U.S., satellite internet performance was mostly flat when comparing Q3 2021 to Q2 2021.
- Starlink’s median download speed decreased from 97.23 Mbps during Q2 2021 to 87.25 Mbps in Q3 2021, which could be a function of adding more customers.
- HughesNet followed distantly at 19.30 Mbps (comparable to the 19.73 Mbps we saw in Q2 2021)
- Viasat third at 18.75 Mbps (18.13 Mbps in Q2 2021).
For comparison, the median download speed for all fixed broadband providers in the U.S. during Q3 2021 was 119.84 Mbps (115.22 Mbps in Q2 2021).
Starlink continues to far out perform satellite-based competitors in general, and even clocks faster speeds than wireline networks in some countries. For U.S. users during the third quarter of this year, Ookla found that median download speed decreased slightly, from 97.23 Mbps during the second quarter of 2021, to a median of 87.25 Mbps in the third quarter. Ookla noted that this “could be a function of adding more customers.”
Starlink’s median upload speed of 13.54 Mbps (down from 13.89 Mbps in Q2 2021) was much closer to that on all fixed broadband (18.03 Mbps in Q3 2021 and 17.18 Mbps in Q2 2021). Viasat and HughesNet followed at 2.96 Mbps (3.38 Mbps in Q2 2021) and 2.54 Mbps (2.43 Mbps in Q2 2021), respectively.
Starlink, which uses low earth orbit (LEO) satellites, was the only satellite internet provider with a median latency anywhere near that seen on fixed broadband in Q3 2021 (44 ms and 15 ms, respectively). Viasat and HughesNet, which both utilize higher “geosynchronous” orbits, had median latencies of 629 ms and 744 ms, respectively.
Ookla analyzed Starlink performance in 304 counties in the U.S. While there was about a 100 Mbps range in performance between the county with the fastest median download speed (Santa Fe County, New Mexico at 146.58 Mbps) and the county with the slowest median download speed (Drummond Township, Michigan at 46.63 Mbps), even the lower-end speeds are well above the FCC’s Baseline performance tier of at least a 25 Mbps download speed.

Starlink’s critics will be watching closely to see if its slight decrease in performance becomes a trend. Since the company received nearly $900 million in government subsidies for broadband service as part of the Rural Digital Opportunities Fund (RDOF), other industry observers and players have argued about whether it’s actually possible for Starlink to deliver what it has promised.
In April of this year, satellite competitor Viasat went so far as to provide technical analysis that it says demonstrates in multiple ways that even if SpaceX deploys the full number of satellites that it has plans for, “significant shortfalls in Starlink capacity exist” due to a combination of limitations on spectrum re-use and the geographic density of the areas it bid on and provisionally won in the RDOF process. Starlink responded by scoffing at the analysis and said it was full of factual errors and incorrect assumptions.
As far as the existing service that Starlink is providing, though, it is still the best of the satellite internet providers. While Ookla’s data found that Starlink’s median download speed in the U.S. decreased to around 87 Mbps, the other the satellite internet providers were only able to provide a fraction of that speed. HughesNet and Viasat were a distant second and third, respectively, at 19.30 Mbps and 18.75 Mbps.
……………………………………………………………………………………………
Request: If you’re using satellite internet, take a Speedtest to help Ookla provide an accurate picture of real-world performance.
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.speedtest.net/insights/blog/starlink-hughesnet-viasat-performance-q3-2021/
“5G smart hospital” launched in Thailand; Joint Innovation Lab to incubate 5G applications
The Office of The National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission (NBTC) in Thailand, Siriraj Hospital, and Huawei jointly launched the “Siriraj World Class 5G Smart Hospital” on Sunday, December 10th. This is the first and largest 5G smart hospital project in the ASEAN region. It will deliver a more efficient and convenient experience to patients by introducing technologies such as 5G, cloud, and artificial intelligence. Meanwhile, Siriraj Hospital and Huawei will establish a Joint Innovation Lab to incubate over 30 innovative 5G applications that will be promoted nationwide from 2022.
General Prayut Chan-o-cha, Prime Minister, addressed the national policy on 5G and digital economy. “Thailand understands the importance of technology, and today is an important first step in the utilization of digital technologies and 5G in the medical field. We are thankful for the long-lasting friendship and collaboration between Thailand and China. We admire Siriraj Hospital and Mahidol University, and would like to thank Huawei, NBTC, and all other partners. We hope the project will act as a blueprint for all smart hospitals in Thailand going forward.”
Han Zhiqiang, Ambassador of the People’s Republic of China in Thailand, emphasized that China will leverage technology to help Thailand fight the pandemic. “China and Thailand’s 5G cooperation has become a model in the region, helping Thailand become the first country in Southeast Asia to launch 5G commercial use. China will continue to support Huawei and other Chinese companies in advancing Smart Hospitals and bringing better lives for Thai and Chinese people.”
Prof. Dr. Prasit Watanapa, MD, Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University, and Colonel Natee Sukonrat, Ph.D., Vice-Chairman of NBTC emphasized that with the “smart hospitals” model, people in remote areas will have better opportunities to access advanced health care services.
Abel Deng, CEO of Huawei Thailand, said, “Huawei has collaborated with Siriraj Hospital to transform it into a world class 5G Smart Hospital, and introduced the Innovation Lab at Srisavarindira Building as part of its 5G infrastructure project for Siriraj Hospital last year. This signifies a model for upgrading Thailand’s public health industry in the future and contributes to Siriraj’s transition to becoming a smart hospital, in line with Huawei’s mission to Grow in Thailand, Contribute to Thailand.”

Thailand’s Prime Minister Prayut Chan-o-cha touring the Siriraj hospital. Image courtesy of Huawei Technologies
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
This cross-sector collaboration will enhance and upgrade the services of Siriraj Hospital to progress it to become a smart medical center using digital technologies based on 5G, AI, big data infrastructure, and cloud edge processing for the purpose of patient tracking, disease diagnosis by AI on cloud, data storage and analysis, and allocation of resources.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, Siriraj Hospital and Huawei have established long-term cooperation in 5G technology development and application. In June 2020, Siriraj Hospital cooperated with Huawei Thailand to launch 5G self-driving vehicles for contactless delivery of medical supplies.
Siriraj Hospital and Huawei signed a five-year MoU in December 2020 to accelerate the use of 5G and cloud technologies. In June, 5G unmanned vehicles were introduced for contactless medical supplies delivery. Last year, Siriraj received the CommunicAsia “Most Innovative 5G Trial in Asia Pacific Region” award.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/us/news/2021/12/smart-hospital-thailand-5g-siriraj
https://www.itnews.asia/news/thailand-launches-first-5g-smart-hospital-in-asean-574247#
Thailand partners with Huawei to launch ASEAN’s first 5G smart hospital
MEF New Standards for SD-WAN Services; SASE Work Program; Dec 2022 UPDATE!
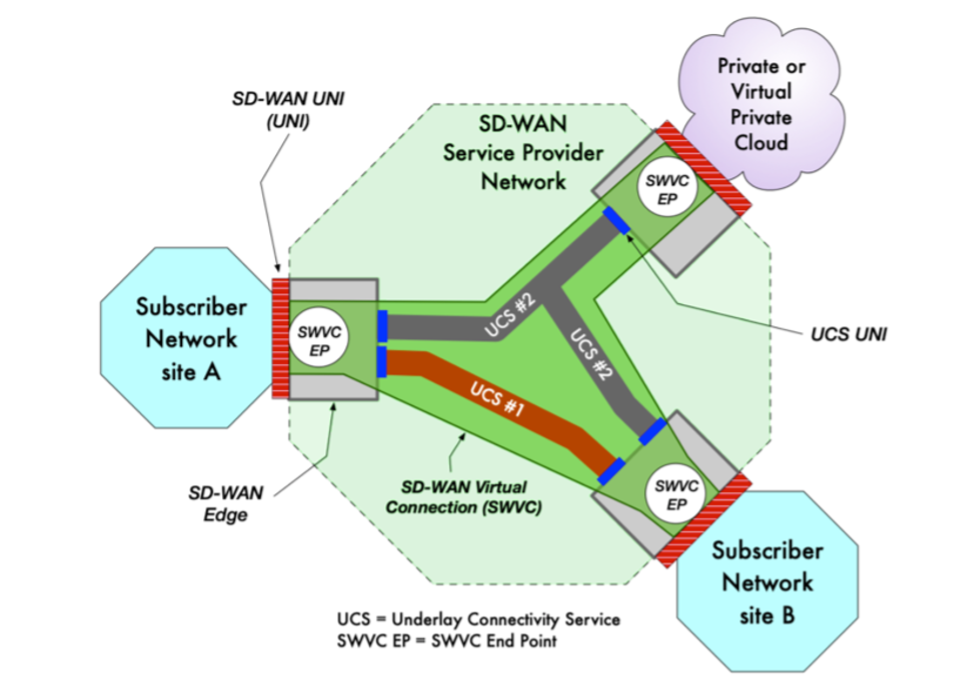
The Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) [1.] has published new SD-WAN standards that add critical enhancements, including new service capabilities for underlay connectivity, important application performance metrics, and security zones for service providers deploying SD-WAN managed services.
Note 1. The MEF is an industry forum empowering enterprises to transform digitally with standard services and APIs for network, cloud, and technology providers. While initially focused on Carrier Ethernet, the MEF scope has broadened to encompass overlay services like SD-WAN. The ITU-T does not have an active SD-WAN standardization program so the industry must look to the MEF for service definitions and standards for that subject.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The new MEF standards include:
- MEF 70.1 updates MEF 70, the industry’s first global SD-WAN standard, to include new service attributes for underlay connectivity services, new measurable performance metrics that provide visibility into an application’s performance within the provider network and across multiple service providers, and the infrastructure to support application-based security defined in MEF 88 (see below).
- MEF 88, MEF’s first security standard, enhances an SD-WAN service to add security functions. These include defining threats, malware protections, security policy terminology and attributes, and describing what actions a policy should take in response to certain threats.
- MEF 95 provides a unified policy framework for MEF’s SD-WAN (MEF 70.1), Network Slicing (MEF 84), and SASE (MEF W117) and Zero Trust (MEF W118) standards coming in 2022.
“We’re seeing a healthy uptick in SD-WAN deployments driven by work from anywhere, as more users are connecting to the cloud and cloud-based applications. We estimate the global SD-WAN service market will grow from $2.85B in 2020 to $14.5B in 2025 (CAGR of 38%),” said Roopa Honnachari, vice president of research & global program leader – network & edge services, Frost & Sullivan.
“MEF’s work in standardizing and certifying SD-WAN managed services is helping to drive that adoption, and we believe certified services and professionals will continue to play an important role in moving the market forward.”
“MEF develops standards and certifications to provide clarity and assurance and remove complexity for SD-WAN managed services.
The new standards define the service behavior and associated policy language needed to deliver high-performance, secure SD-WAN managed services,” said Pascal Menezes, CTO, MEF.
Source: MEF
……………………………………………………………………………………..
“These standards, and the forthcoming SASE and Zero Trust standards, benefit both customers and providers—customers know what to expect when purchasing SD-WAN managed services from a provider, and providers have the tools needed to deliver secure SD-WAN services that drive customer satisfaction,” Pascal added.
Both service providers and vendors can attain certification for MEF’s SD-WAN standards in the MEF 3.0 SD-WAN certification program which validates compliance with MEF standards for delivering managed SD-WAN services and the underlying technology. The objective is to eliminate market confusion, and enable faster SD-WAN market adoption.
In 2022, secure SD-WAN requirements will be added to the MEF 3.0 certification program. Currently, 17 companies have achieved MEF 3.0 SD-WAN certification. In addition, the MEF-SDCP Professional Certification training and certification provides an opportunity for the engineers, architects, product managers, and others deploying SD-WAN solutions to demonstrate their expertise in MEF 3.0 service standards.
- Worldwide, there are over 700 MEF-SDCP professionals employed by more than 120 companies.
- Over 60 service providers have either the Carrier Ethernet or SD-WAN certification within the MEF 3.0 framework, and a handful have both.
- AT&T, Verizon, Comcast Business and Windstream are among the service providers with MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Certification. Those companies also rank within the top five of Vertical Systems Group’s 2020 US Carrier Managed SD-WAN Leaderboard.
MEF SASE Work:
MEF will also be releasing SASE (MEF W117) and Zero Trust (MEF W118) standards in 2022. MEF started developing its secure access service edge (SASE) framework last fall to clarify the service attributes and definitions for SASE.
The SD WAN market has already become bogged down by different SASE definitions, which has led to confusion among enterprise customers and frustration for service providers.
MEF defines SASE as a “service connecting users (machine or human) with their applications in the cloud while providing connectivity performance and security assurance determined by policies set by the Subscriber.” The networking and security functions within a SASE service include routing, VPN, path selection, traffic shaping, firewall, threat prevention and more.
Yet finding one vendor that meets all those requirements, and delivers a SASE service that is simple to deploy, is proving challenging for service providers that want to provide SASE as a managed service to enterprise customers.
“The ideal is one vendor, right? That’s the ideal, we all agree with it. But at least for enterprise customers, we’d haven’t found a single vendor solution that meets their needs yet from a SASE perspective,” said Verizon’s Vincent Lee.
MEF Media Contact: Melissa Power [email protected]
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
MEF Introduces New Standards for High-Performance, Secure SD-WAN Services
https://www.mef.net/service-standards/overlay-services/sase/
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
December 2022 UPDATE:
MEF SD-WAN and SASE Standards:
In August 2019, the MEF published the industry’s first global standard defining an SD-WAN service and its service attributes. SD-WAN Service Attributes and Services (MEF 70). The MEF SD-WAN standard describes requirements for an application-aware, over-the-top WAN connectivity service that uses policies to determine how application flows are directed over multiple underlay networks irrespective of the underlay technologies or service providers who deliver them. However, it does not address interoperability because it does not specify either a UNI or NNI protocol stack.
MEF 70 defines:
- Service attributes that describe the externally visible behavior of an SD-WAN service as experienced by the subscriber.
- Rules associated with how traffic is handled.
- Key technical concepts and definitions like an SD-WAN UNI, the SD-WAN Edge, SD-WAN Tunnel Virtual Connections, SD-WAN Virtual Connection End Points, and Underlay Connectivity Services.
SD-WAN standardization offers numerous benefits that will help accelerate SD-WAN market growth while improving overall customer experience with hybrid networking solutions. Key benefits include:
- Enabling a wide range of ecosystem stakeholders to use the same terminology when buying, selling, assessing, deploying, and delivering SD-WAN services.
- Making it easier to interface policy with intelligent underlay connectivity services to provide a better end-to-end application experience with guaranteed service resiliency.
- Facilitating inclusion of SD-WAN services in standardized LSO architectures, thereby advancing efforts to orchestrate MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services across automated networks.
- Paving the way for creation and implementation of certified MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services, which will give users confidence that a service meets a fundamental set of requirements.
In December 2022, MEF published two Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) standards defining 1.] SASE service attributes, common definitions & a framework and 2.] a Zero Trust framework that together allow organizations to implement dynamic policy-based actions to secure network resources for faster decision making and implementation for enterprises. MEF’s SASE standard defines common terminology and service attributes which is critically important when buying, selling, and delivering SASE services. It also makes it easier to interface policy with security functions for cloud-based cybersecurity from anywhere. MEF’s Zero Trust framework defines service attributes to enable service providers to implement and deliver a broad range of services that comply with Zero Trust principles.
- SASE Service Attributes and Service Framework Standard: specifies service attributes to be agreed upon between a service provider and a subscriber for SASE services, including security functions, policies, and connectivity services. The standard defines the behaviors of the SASE service that are externally visible to the subscriber irrespective of the implementation of the service. A SASE service based upon the framework defined in the standard enables secure access and secure connectivity of users, devices, or applications to resources for the subscriber. MEF’s SASE standard (MEF 117) includes SASE service attributes and a SASE service framework.
- Zero Trust Framework for MEF Services: The new Zero Trust Framework for MEF Services (MEF 118) defines a framework and requirements of identity, authentication, policy management, and access control processes that are continuously and properly constituted, protected, and free from vulnerabilities when implemented and deployed. This framework also defines service attributes, which are agreed between a subscriber and service provider, to enable service providers to implement and deliver a broad range of services that comply with Zero Trust principles.
ETSI MEC Standard Explained – Part II
by Dario Sabella, Intel, ETSI MEC Chair
Introduction:
This is Part II of a two part article series on MEC. Part I may be accessed here.
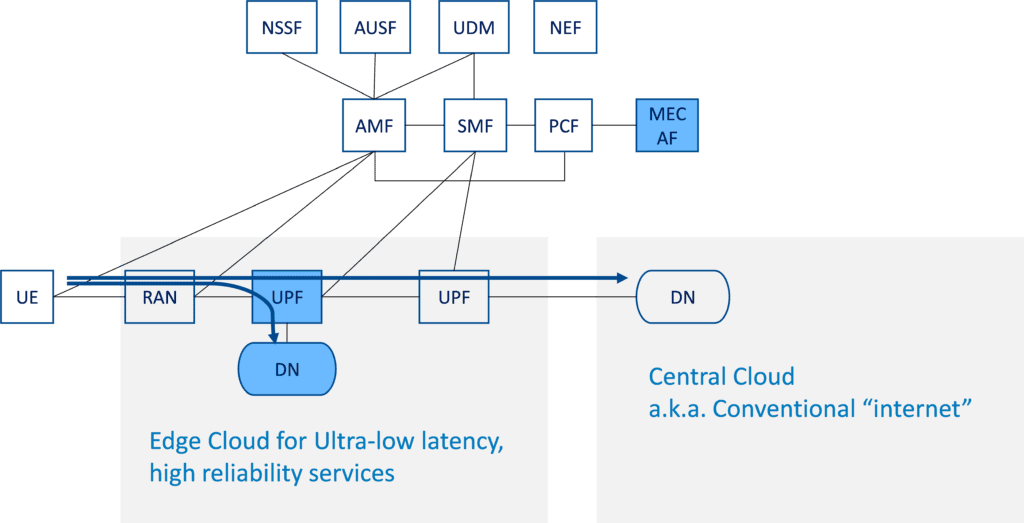
Access to Local and Central Data Networks (DN):
Figure 5. below illustrates an example of how concurrent access to local and central DN (Data Networks) works. In this scenario, the same UP session allows the UE to obtain content from both the local server and central server (service continuity is enabled by IP address anchoring at the centralized UPF, with no impact on UE by using Uplink Classifier -ULCL).
Figure 5. Concurrent access to local and central Data Networks (DN)
In this context it is assumed that MEC is deployed on the N6 reference point, i.e. in a data network external to the 5G system. This is enabled by flexibility in locating the UPF. The distributed MEC host can accommodate, apart from MEC apps, a message broker as a MEC platform service, and another MEC platform service to steer traffic to local accelerators. Logically MEC hosts are deployed in the edge or central data network and it is the User Plane Function (UPF) that takes care of steering the user plane traffic towards the targeted MEC applications in the data network.
The locations of the data networks and the UPF are a choice of the network operator who may choose to place the physical computing resources based on technical and business parameters (such as available site facilities, supported applications and their requirements, measured or estimated user load etc). The MEC management system, orchestrating the operation of MEC hosts and applications, may decide dynamically where to deploy the MEC applications.
In terms of physical deployment of MEC hosts, there are multiple options available based on various operational, performance or security related requirements (for more details, see the ETSI paper “MEC in 5G networks” [6] and the more recent study on “MEC 5G integration” [7]).
Moving forward with 5G (3GPP Release 17 onwards):
Given the increase of 5G adoption, and the progressive migration of network operators towards 5G SA (Stand Alone) networks this above MEC deployment is naturally becoming a long-term option considering the evolution of the networks. A major joint opportunity for MEC 5G integration, is on one hand for MEC to benefit from the edge computing enablers of the 5G system specification, and for 3GPP ecosystem to benefit from the MEC system and its APIs as a set of complementary capabilities to enable applications and services environm5 ents in the very edge of mobile networks. IN this perspective, also in the view of more mature 5G deployments, ETSI MEC is aligning with 3GPP SA6, defining from Rel.17 an EDGEAPP architecture (ref. 3GPP TS 23.558).
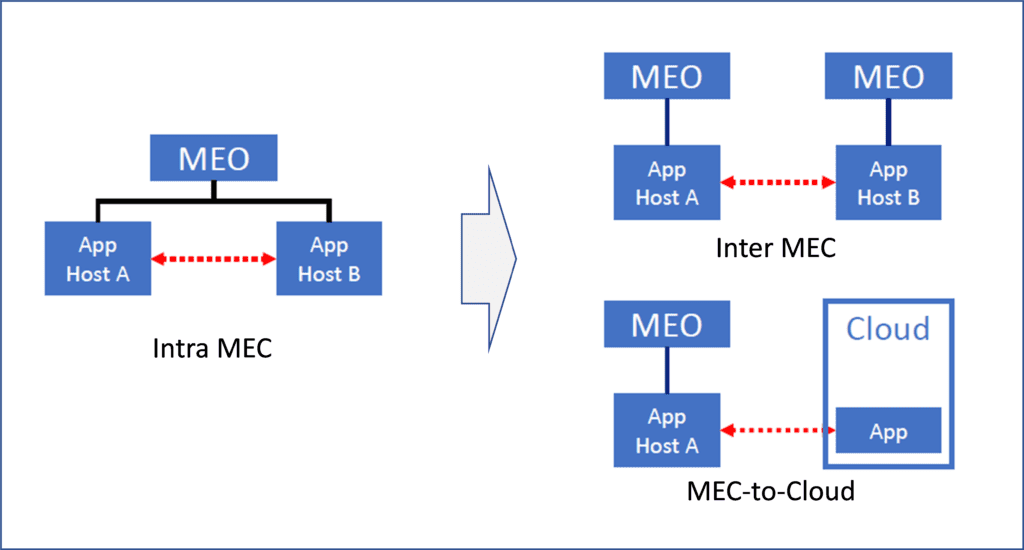
In this perspective, an ETSI white paper [3] provides some first information on this ongoing alignment, which is introducing a Synergized Mobile Edge Cloud architecture supported by 3GPP and ETSI ISG MEC specifications. This is an ongoing alignment, also in the view of future Rel.18 networks, and with respect to MEC federation and the related expansion (for MEC Phase 3 specifications) from intra-MEC communication to inter-MEC and MEC-Cloud coordination (as depicted in Figure 6). A very first study in this field has been published by ETSI MEC with the ETS GR 035 report [8].
Figure 6. MEC Phase 3: Expansion from intra-MEC to inter-MEC and MEC-Cloud
The MEC 035 study on “Inter-MEC systems and MEC-Cloud systems” was a major effort in ETSI MEC, mainly driven by the need of operators to form federated MEC environments. For example, to achieve V2X (vehicle to X) service continuity in multi-operator scenarios, to enable edge resource sharing among the federating members, and in general offer edge computing infrastructure as an asset to provide global services benefiting of better performance and low latency environments. Many use cases in MEC 035 are in need of MEC federation. Many are also based on the ETSI MEC requirements in MEC 002 (e.g. use cases like “V2X multi-stakeholder scenario” and “Multi-player immersive AR game,” among others).
This work carefully aligns with a GSMA publication introducing requirements for their “Operator Platform” concept. [The GSMA Operator Platform defines a common platform exposing operator services/capabilities to customers/developers in the 5G-era in a connect once, connect to many models. The first phase of the platform focuses on Edge which will be expanded in future phases with other capabilities such as connectivity, slicing and IPComms.] In this scenario, multiple operators will federate their edge computing infrastructure to give application providers access to a global edge cloud which may then run innovative, distributed and low latency services through a set of common APIs.
Currently ETSI MEC is working on the related normative work to enable and support this concept of MEC Federation, by defining a suitable MEC architecture variant in MEC GS 003, updating other impacted MEC specifications in Phase 3, and by introducing proper “MEC Federation Enablement APIs” (MEC GS 040) [9].
Enablement of MEC Deployment and Ecosystem Development:
MEC adoption is critical for the ecosystem. In this perspective, ETSI ISG MEC has established a WG DECODE dedicated to MEC Deployment and Ecosystem engagement activities. As a part of that (but not limited to it!) MEC is publishing and maintaining a MEC Wiki page (mecwiki.etsi.org), including links to several examples of MEC adoption from the ecosystem:
- MEC Ecosystem, with 3rd party MEC Applications and Solutions
- Proof of Concepts (PoCs), with a list and description of past and ongoing PoCs, including the ISG MEC PoC Topics and PoC Framework (and Information about process, criteria, templates….)
- MEC Deployment Trials (MDTs), with a list and description of past and ongoing MDTs (and the MDT Framework, clarifying how to participate)
Additionally, the MEC Wiki also includes: information on MEC Hackathons, MEC Sandbox, OpenAPI publications for ETSI MEC ISG API specifications, and outreach activities (e.g. MEC Tech Series of video and podcasts).
Summary and Conclusions:
- MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) “offers to application developers and content providers cloud-computing capabilities and an IT service environment at the edge of the network” (see Ref 1. below).
- The nature of the ETSI MEC Standard (as emphasized by the term “Multi-access” in the MEC acronym) is access agnostic and can be applicable to any kind of deployment, from Wi-Fi to fixed networks.
- MEC is also serving multiple use cases and providing an open and flexible standard, in support of multiple deployment options, especially for 5G networks.
- MEC is focused on Applications at the Edge, and the specified MEC service APIs include meaningful information exposed to application developers at the network edge, ranging from RNI (Radio Network Information) API (MEC 012), WLAN API (MEC 029), Fixed Access API (MEC 028), Location API (MEC 013), Traffic Management APIs (MEC015) and many others. Additionally, new APIs (compliant with the basic MEC API principles) can be added, without the need for ETSI standardization.
- The ongoing ETSI MEC work in alignment with 3GPP includes aspects related to MEC 5G Integration and future evolution, including the standardization work on MEC Federation. Also, carefully aligning the MEC work with requirements from GSMA OPG (Operator Platform Group).
Finally, since MEC adoption is critical for the IT ecosystem, ETSI ISG MEC has established a WG dedicated to MEC Deployment and Ecosystem engagement activities.
There is also a dedicated MEC Wiki page (mecwiki.etsi.org) which provides several examples of MEC adoption from the ecosystem (PoCs, trials, MEC implementations). It also includes information on MEC Hackathons, MEC Sandbox, OpenAPI publications for ETSI MEC ISG API specifications, and outreach activities (e.g. MEC Tech Series of video and podcasts).
………………………………………………………………………………………….
Previous References (from Part I):
Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) Market, Applications and ETSI MEC Standard-Part I
[1] ETSI MEC website, https://www.etsi.org/technologies/multi-access-edge-computing
[2] ETSI GS MEC 003 V2.1.1 (2019-01): “Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC); Framework and Reference Architecture”, https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/mec/001_099/003/02.01.01_60/gs_mec003v020101p.pdf
[3] ETSI White Paper #36, “Harmonizing standards for edge computing – A synergized architecture leveraging ETSI ISG MEC and 3GPP specifications”, First Edition, July 2020, https://www.etsi.org/images/files/ETSIWhitePapers/ETSI_wp36_Harmonizing-standards-for-edge-computing.pdf
[4] ETSI GS MEC 009 V3.1.1 (2021-06), “Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC); General principles, patterns and common aspects of MEC Service APIs”, https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/MEC/001_099/009/03.01.01_60/gs_MEC009v030101p.pdf
[5] ETSI White Paper No. 24, “MEC Deployments in 4G and Evolution Towards 5G”, February 2018, https://www.etsi.org/images/files/ETSIWhitePapers/etsi_wp24_MEC_deployment_in_4G_5G_FINAL.pdf
[6] ETSI White Paper No. 28, “MEC in 5G network”, June 2018, https://www.etsi.org/images/files/ETSIWhitePapers/etsi_wp28_mec_in_5G_FINAL.pdf
[7] ETSI GR MEC 031 V2.1.1 (2020-10), “Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC); MEC 5G Integration”, https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gr/MEC/001_099/031/02.01.01_60/gr_MEC031v020101p.pdf
[8] ETSI GR MEC 035 V3.1.1 (2021-06), “Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC); Study on Inter-MEC systems and MEC-Cloud systems coordination”, https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gr/MEC/001_099/035/03.01.01_60/gr_mec035v030101p.pdf
[9] ETSI DGS/MEC-0040FederationAPI’ Work Item, “Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC); Federation enablement APIs”, https://portal.etsi.org/webapp/WorkProgram/Report_WorkItem.asp?WKI_ID=63022
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Additional References:
https://mecwiki.etsi.org/index.php?title=Main_Page
https://www.gsma.com/futurenetworks/5g-operator-platform/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2021/05/19/o2-uk-and-microsoft-to-test-mec-in-a-private-5g-network/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2021/07/06/att-and-google-cloud-expand-5g-and-edge-collaboration/
Orange installs Private 4G/5G Network at Nokia factory in Poland
Orange Poland has announced that it has been selected as the partner in the creation of a private 4G and 5G network at Nokia’s factory and R&D facility at Bydgoszcz, Poland, which includes a factory and three R&D centers. Orange said the 5G private network will benefit from various innovations and edge computing applications.
The network will cover the entire 13,000 square metre facility, providing the location’s 6,000 employees with access to faster, more reliable communications. This, in turn, will enable numerous efficiency improvements within the factory itself, including facilitating automated guided vehicles to transport products internally, drones for surveillance and monitoring, and the widespread deployment of IoT devices. The network will also allow for greater reliability when it comes to inter-facility communications, including group push-to-talk and push-to-video applications. As a private network, it will not be incorporated with Orange Polska’s wider network.
“Private 5G networks are undoubtedly the future of an effective industry. I am glad that we can boast a unique experience on the Polish market, collected during the implementation of already operating implementations of this type, which pay off in subsequent projects, such as the one with Nokia,” said Julien Ducarroz, president of Orange Polska.
“It is a solution enabling the maximum adjustment of communication to the customer’s needs, safe and increasing the efficiency of processes.”

Orange has had a busy couple of months when it comes to 5G. Last month, the company launched its first 5G Lab in Antwerp, the Netherlands, a move that further expands the operator’s presence in the city. Orange has a well-established private 5G standalone network set up in Port of Antwerp, set up back in 2020, where they have been trialling a variety of 5G use cases. At around the same time, Orange was also launching their first Open RAN lab in Paris, with CTO Michael Trabbia notably arguing that interoperable RAN tech would be central to creating a stronger European vendor ecosystem and offering the continent greater technical sovereignty. Further 5G developments are going on in Orange’s other markets too. Just yesterday, Orange Spain announced a new 5G fixed wireless access trial in Galicia, as part of Orange’s wider commitment to the Spanish government’s National 5G plan.
References:
Algar Telecom deploys 1st 5G network in Brazil using 2.3GHz band
Brazilian network operator Algar Telecom announced that it launched what it claims to be the first commercial 5G network in the country. It’s a commercial Non Standalone (NSA) 5G service using its newly acquired 2.3GHz spectrum. The 5G network went live on 15 December and covers selected parts of Uberlandia and Uberaba, as well as Franca in Sao Paulo, with initial coverage reaching some 40 districts in these three cities.
Algar had carried out demonstrations of 5G technology two weeks ago in Uberaba via an implementation carried out together with Nokia and with a focus on agribusiness. According to the company, investments were made in transport network structures, network core and service platforms.
Brazil’s Minister of Communications, Fábio Faria, had anticipated in his hearing before the Senate last week that Algar would be the first telco to launch 5G services in the country.
“For this almost immediate launch to be possible, intensive planning prior to the 5G auction was essential, ensuring the acquisition of the 2.3 GHz frequency, which does not require spectrum cleaning. In addition, the company already had a good part of its infrastructure adequate or easily adapted to offer 5G. We made investments in backhaul structures, network core and service platforms,” the telco said in a release.
In the 5G auction, which ended on November 5, Algar Telecom had secured seven regional slots: five on the 26 GHz frequency, one on the 3.5 GHz frequency and one on the 2.3 GHz frequency. All slots obtained are in Algar Telecom’s original area of operation, where the company has operated since 1954, and which covers 87 municipalities in the states of Minas Gerais, São Paulo, Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul.
The government of Brazil raised a total of 47.2 billion reals ($8.5 billion) in its recent 5G spectrum auction, making it the second largest auction of assets in the country’s history, according to the government.
Through this auction, the government offered spectrum in the 700 MHz, 2.3 GHz, 3.5 GHZ and 26 GHz bands.
The country’s main mobile operators, Vivo, Claro and TIM, secured 5G spectrum as well as telecoms operators Algar Telecom and Sercomtel. Also, six new entrants secured 5G spectrum in the auction.
The new entrants that secured licenses in the auction are Winity II Telecom, Brisanet, Fly Link, Neko Serviços e Comunicações and Entertainment and Education, Consórcio 5G Sul and Cloud2U Indústria e Comércio de Equipamentos Eletrônicos.
Brazilian Communications Minister Fabio Faria said that the government will schedule a new 5G spectrum auction in 2022 to sell batches that did not attract interest, mainly in the 26 GHZ spectrum band. Faria noted that the 26 GHZ spectrum did not attract interest due to uncertainties in the business model.
The rules previously approved by telecommunications watchdog Anatel stipulate that 5G should be deployed across Brazilian state capitals by July 31, 2022.
Brazilian cities with more than 500,000 inhabitants will have 5G by July 31, 2025, while the deadline for the rollout of the service in locations with more than 200,000 inhabitants is July 31, 2026. Also, Brazilian cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants will have 5G by July 31 2027, and the service will be available in locations with more than 30,000 inhabitants by July 31, 2028.
TeleGeography notes that Algar acquired regional spectrum in the 2.3GHz, 3.5GHz and 26GHz bands in the country’s 5G spectrum auction. Unlike the 3.5GHz band, the 2.3GHz band does not require cleaning for interference before 5G use. Algar executive Marcio De Jesus commented: “The company already had a good part of its infrastructure adequate or easy to adapt to the 5G offer. We made investments in backhaul structures, network core and service platforms.”
References:
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20211216/5g/algar-telecom-activates-first-5g-network-brazil
https://www.commsupdate.com/articles/2021/12/16/algar-telecom-launches-5g-using-2-3ghz-band/
https://www.gsma.com/spectrum/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/5G-and-3.5-GHz-Range-in-Latam.pdf
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20211108/5g/brazil-raises-total-8-billion-5g-spectrum-auction