5G Advanced
Huawei pushes 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) but there are no completed 3GPP specs or ITU-R standards!
During MWC 2024, Huawei held a new product solution launch event, where George Gao, President of Huawei Cloud Core Network Product Line, released the 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) intelligent core network solution.
Huawei claims 2024 is the first year for commercialization of 5.5G (this author strongly disagrees- 3GPP 5G Advanced specs are not nearly complete and ITU-R standards work hasn’t even started yet).
“The first year of commercial use of 5.5G has officially arrived, and the commercial rollout of 5.5G is accelerating worldwide,” the China based vendor said. “While Middle Eastern operators have achieved scaled 5.5G commercialization, operators across Europe, Asia Pacific, and Latin America are verifying 10 Gbps [1.], preparing for 5.5G commercialization in 2024,” Huawei added.
Note 1. CCS Insight wrote last month, “operators are deploying greenfield networks in new cities, such as STC in Bahrain and Zain in Saudi Arabia, both of which have achieved 10 Gbps downlink speeds on their 5G-Advanced test networks.”
The company says announced their 5.5G intelligent core network as an important part of 5.5G, incorporating service intelligence, network intelligence, and O&M intelligence.
The claim is that 5.5G technology will improve both business value and development potential. We seriously doubt that!
Service Intelligence Expands the Profitability of Calling Services:
In 2023, New Calling [2.] was put into commercial use for serving up to 50 million subscribers across 31 provinces in China. It has also been verified in Europe, Latin America, the Middle East, and Asia Pacific, and is set to be commercialized in these regions in 2024.
Note 2. New Calling essentially combines voice calls with other elements – fun calling with avatars, for example, or calling with real-time translation or speech-to-text. It is backed by the GSMA (which is NOT a standards body), but to date has been deployed only in China.
As stated by George, the industry’s first New Calling-Advanced solution launched by Huawei embraces enhanced intelligence and data channel-based interaction capabilities. Huawei says that will take us to a multi-modal communication era and helping operators reconstruct their service layout. In addition, Huawei also introduced the Multi-modal Communication Function (MCF) to allow users to control digital avatars through voice during calls, delivering a more personalized calling experience. An enterprise can also customize their own avatar as an enterprise ambassador to promote their branding.
Network Intelligence Enables Experience Monetization and Differentiated Operations:
For a long period of time, operators have strived to realize traffic monetization on MBB networks. However, there are three technical gaps: not assessable user experience, no dynamic optimization, and no-closed-loop operations. To bridge these gaps, Huawei has launched the industry’s first Intelligent Personalized Experience (IPE) solution, aiming to help operators add experience privileges to service packages and better monetize differentiated experiences.
In the industry, the user plane on the core network usually processes and forwards one service flow using one vCPU. As heavy-traffic services increase, such as 2K or 4K HD video and live streaming, microbursts and elephant flows frequently occur. It is, therefore, more likely that a vCPU will become overloaded, causing packet loss. To address this issue, Huawei releases the Intelligent UDG. According to George, this is the industry’s first Intelligent UDG product that can deliver ubiquitous 10 Gbps superior experiences.
O&M Intelligence Achieves High Network Stability and Efficiency:
Empowered by the multi-modal large model, the Digital Assistant & Digital Expert (DAE) reduces O&M workload and improves O&M efficiency. It reshapes cloud-based O&M from “experts+tools” to intelligence-centric “DAE+manual assistance”. With DAE, 80% of trouble tickets can be automatically processed, which is much more efficient than 100% manual processing as it used to be. DAE also enables intent-driven O&M, avoiding manual decision-making. Before, it usually took over five years to cultivate experts in a single domain, however, the multi-modal large model is now able to be trained and updated within just weeks.
Huawei published eight innovation practices which cover key 5.5G technology areas, including antenna evolutions, mmWave bandwidth, network intelligence in the RAN, and energy efficiency. The full list is here, along with details of Huawei’s proposed 5.5G offerings.
With the 2024 commercial launch of 5.5G, Huawei is collaborating with wireless network operators and partners around the world to pursue exciting new innovation in networks, cloud, and intelligence. Huawei plans to drive its 5G business and foster a thriving industry ecosystem, creating a new era for intelligent digital transformation.
For more information, please visit: https://carrier.huawei.com/en/events/mwc2024.
Closing Comments:
This author feels it’s extremely dangerous to announce any IMT products in advance of 3GPP specifications and ITU-R standards. It unrealistically raises expectations and of course there’s no interoperability without specs/standards.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2024/2/5ga-practices-multipath
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
Nokia plans to investment €360 million in microelectronics & 5G Advanced/6G technology in Germany
Nokia exec talks up “5G Advanced” (3GPP release 18) before 5G standards/specs have been completed
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
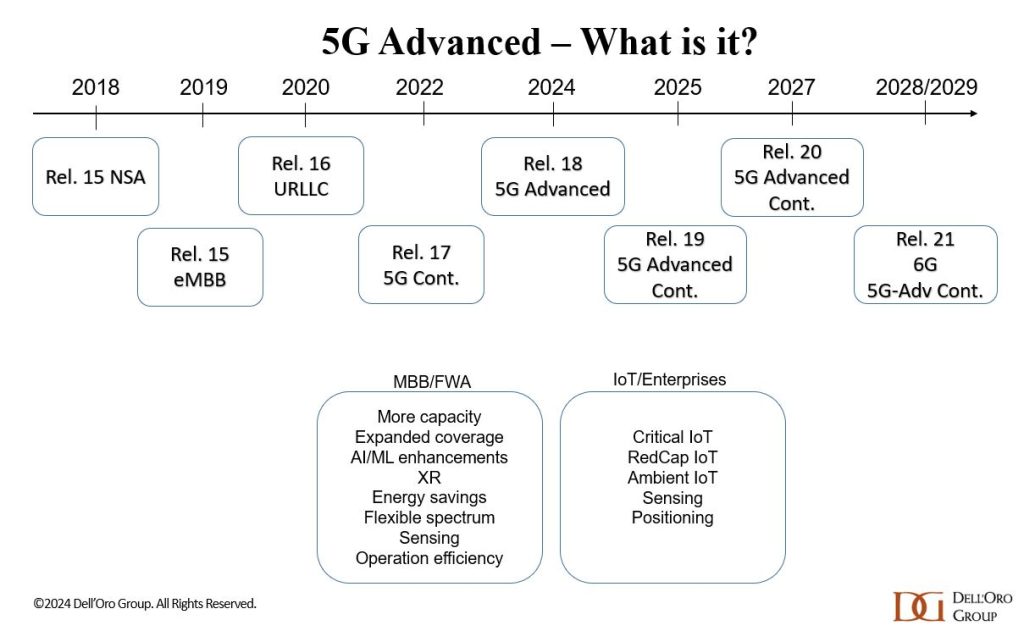
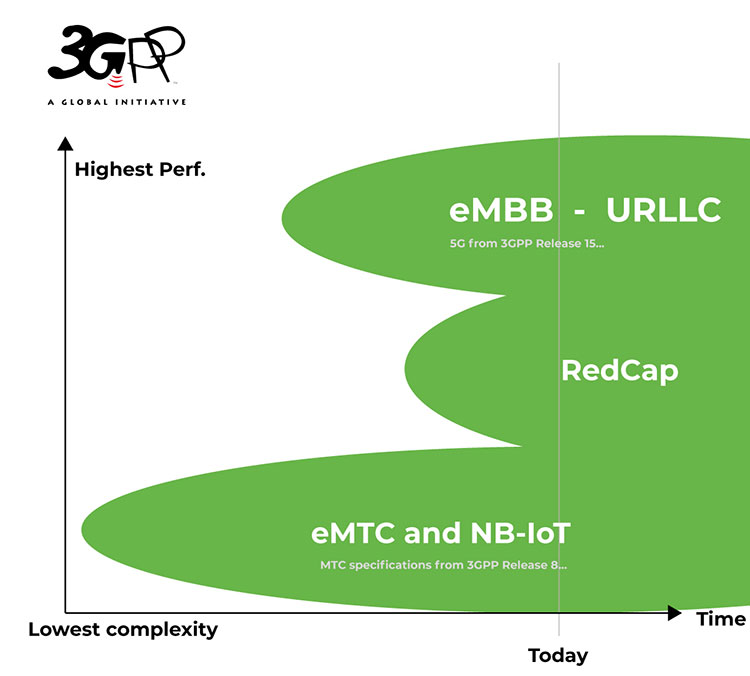
The 3GPP roadmap (see figure below) is continuously evolving to fulfill the larger 5G vision. In this initial 5G wave that began in 2018, 3GPP has completed three major releases (new releases every 1.5 to 2 years): 15, 16, and 17.
Release 17 is included in the ITU-R M.2150-1 recommendation which is the only standard for IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT (i.e. 5G RAN interface). 3GPP contributes its completed radio interface specifications to ITU-R WP5D via ATIS where they are discussed and approved for inclusion into the next version of the ITU-R M.2150 recommendation. The same procedure is likely for IMT 2030 RIT/SRIT (i.e. 6G RAN).
3GPP Release 18 and beyond (often referred to as 5G-Advanced or 5.5G) involve gradual technology improvements aimed at elevating 5G to the next level, creating a foundation for more demanding applications and a broader set of use cases. In addition to performance improvements and support for new applications, sustainability and intelligent network automation are also important building blocks in the broader 5G-Advanced vision (source: Ericsson).
The scope of 5G Advanced in Release 19 was approved at the December 2023 3GPP Plenary Meeting in Edinburgh, Scotland. Release 19 builds on Release 18 and focuses on enhancing 5G performance while expanding the capability of 5G across devices and deployments. In addition, it will establish the technical foundations for 6G and will include preliminary work on new 6G capabilities. Release 19 will be followed by Release 20, the first 3GPP release for 6G studies.
5G Advanced continues to push the spectral efficiency limits and coverage in both sub-7GHz and millimeter wave spectrum. In addition to continued enhancements to massive MIMO radios and mobility, 3GPP Release 19 provides advancements for new use cases such as XR and Non-Terrestrial Networks.
- Massive MIMO Radio – Release 18 introduced improvements to massive MIMO uplink and downlink throughput. Release 19 will boost capacity further by improving multi-user MIMO, which enables more UEs to share the same time and frequency resources.
Release 19 will also enable the cost-efficient realization of distributed transmitters and receivers, thus improving signal quality. This is an important step towards enabling fully distributed MIMO (D-MIMO) systems. Other enhancements include 5G beam management with UE-initiated measurement reporting, thus resulting in faster beam selection. - Mobility – 5G Advanced introduces a new handover procedure known as low-layer (i.e. L2) triggered mobility (LTM). In Release 18, LTM is supported between cells served by the same gNB. In Release 19, the LTM framework will be extended to support handover between cells served by different gNBs.
- XR and the Metaverse – Release 19 builds on the low latency and power saving features of Release 18 by enabling higher XR capacity by adding improved uplink and downlink scheduling using packet delay information.
- Non-Terrestrial Networks – 5G Advanced combines terrestrial and satellite communications under one standard for the first time. Release 19 will build on the enhancements introduced in Release 18 with a focus on increasing satellite downlink coverage, introducing UEs with higher output power and providing Redcap device support. It will also investigate whether additional support is required for regenerative payloads.
Current priorities for 5G-Advanced include:
- More capacity and better performance. Some estimates suggest that MIMO enhancements, better beam management, and full duplex technologies taken together with other advancements, including multi-band serving cell (MB-SC) and Extremely Large Antenna Array (ELAA) will deliver another 20% of efficiency improvements relative to today’s 5G. Enhanced uplink (UL) and multi-cell UL improvements could pave the way for greater data rate and latency improvements in the UL. For reference, Huawei defines 5G-Advanced as a site that can support at least 10 Gbps of cell capacity. ZTE is also targeting 10 Gbps+ with 5G-Advanced.
- Expanded coverage. In addition to MIMO and IAB coverage enhancements, 5G-Advanced includes Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) connectivity improvements, building on the NR/LTE-based NTN support that was introduced with Release 17.
- More intelligence. Releases 15-17 already include some AI/ML features. 5G-Advanced will offer AI/ML enhancements in the RAN (including the air interface) and the management layers. In addition, Intelligent RAN and AI-powered analytics will help operators to improve the performance and proactively address network issues before they become a problem.
- Energy savings. Release 18 includes a confluence of static and dynamic power-saving enhancements for the radios and the overall RAN. Also, the specification is targeting to define a base station energy consumption model with various KPIs to better evaluate transmission and reception consumption/savings.
- Flexible spectrum (FD, DSS, CA). NR is currently based on TDD or FDD spectrum. Full duplex (FD), a 5G-Advanced contender, improves spectrum utilization by allowing UL and DL to share the same spectrum (FD should improve capacity and latency, especially in the UL). Release 18 also includes DSS capacity enhancements (increasing PDCCH capacity by allowing NR PDCCH to be transmitted in symbols overlapping with LTE CRS). Other spectrum-related upgrades with 5G-Advanced include multi-carrier enhancements and NR support for dedicated spectrum bandwidths below 5 MHz.
- Critical IoT. 5G-Advanced includes multiple industrial and IoT related advancements. Release 17 included support for Time Sensitive Networking (TSN), which will be expanded in 5G-Advanced to support Deterministic Networking (DetNet).
- RedCap IoT. 5G NR-Light or Reduced Capability (RedCap) was introduced with 3GPP NR Release 17. 5G-Advanced will introduce lower-tier RedCap devices, seeking to find a better set of tradeoffs between cost, performance, and power consumption.
- Ambient IoT. Passive IoT, sometimes referred to as Ambient IoT, will allow devices/objects to connect without a power source.
- Sensing. Harmonized communication and sensing (HCS) is a Release 19 study item.
- Positioning. Positioning is already supported in Release 16/17, though 5G-Advanced is expected to improve positioning accuracy and power consumption (Nokia has said sub-10 cm positioning is doable). In addition, Release 18 will include support for RedCap devices.
Role of AI/ML in 5G Advanced:
AI/ML will become a key feature of 5G networks with numerous applications ranging from network planning and network operations optimization to full network automation. Another important application is the use of AI/ML to improve the performance and functionality of the 5G air interface.
3GPP studied the use of AI/ML in the air interface in Release 18 and defined three use cases: channel state feedback (CSF) information, beam management and positioning. Based on the conclusions of Release 18 studies, Release 19 will specify a general AI/ML framework, i.e. actual specifications to support the above three use cases as well as specific support for each individual use case. Release 19 will also explore new areas in the AI/ML air interface such as mobility improvement and AI/ML-related model training, model management and global 5G data collection.
AI/ML is another major focus for Qualcomm. The company has dedicated significant technical resources to develop full-scale demonstrations of the three Release 18 defined use cases. For example, it recently demonstrated CSF-based cross-node machine learning involving E2E optimization between devices and the network. This reduces device communication overheads resulting in improved capacity and throughput. Qualcomm has also demonstrated the use of AI/ML to improve beam prediction on its 28GHz massive MIMO test network and is heavily involved in positioning technologies. For example, it has showcased its outdoor precise positioning technology, which uses multi-cell roundtrip (RTT) and angle-of-arrival (AoA) based technologies, as well as its RF finger printing technology operating in an indoor industrial private network.
Over the next few months, 3GPP will continue exploring the applicability of AI/ML based solutions for other use cases such as load balancing between cells, mobility optimization and network energy savings. For example, there will be support for conditional Layer 2 mobility in Release 19 and a new study item targeting new use cases designed to improve coverage and capacity optimization, such as AI-assisted dynamic cell shaping.
Enhancing Device and Network Sustainability:
5G Advanced focuses on sustainability and introduces energy-saving features for devices and networks as well as exploring end-to-end energy saving opportunities that benefit devices. There are also improved features for RedCap and the study of ambient IoT as a new device type.
- Power-optimized devices – Releases 18 and 19 build on existing energy saving features, for example, a new low-power wakeup signal (LP-WUS). A low-complexity, power-optimized receiver is specified to monitor low-power wake-up signals from the network which only wakes-up the main radio when data is available at the device. This avoids the significant power consumption required to keep the main radio monitoring control signals from the network.
- Ambient IoT – enables new use cases enabled by very-low power devices that harvest energy from the ambient environment, for example, RF waves. Release 19 will investigate new architectures for ambient IoT devices and will include the development of a harmonized specification. Numerous use cases will be studied, including smart agriculture, industrial wireless sensor networks, smart logistics, warehousing, etc.
- Network energy savings – 5G Advanced reduces network energy consumption by dynamically adjusting the network’s operation based on feedback from the device, i.e. shutting down parts of the network when idle and transmitting less power depending on the overall traffic load or using more efficient antennas.

Dell’Oro’s Stefan Pongratz says “one fundamental aspect of 5G-Advanced will be to support more demanding consumer MBB applications. The days of exponential data traffic growth are clearly in the past; however, global mobile data traffic is still projected to increase threefold over the next five years, reaching 0.5 ZB/month by 2028 (mobile plus FWA). While operators are currently in a fairly good position from a capacity perspective, especially those not aggressively pursuing FWA, some of the technology improvements with 5G-Advanced can help to address capacity limitations in hotspot areas.”
Omdia (owned by Omdia) expects leading network service providers in Asia and Oceania are expected to launch 5G-Advanced between 2024 and 2025. They aim to leverage the new capabilities and features offered by 5G-Advanced to enhance their network infrastructure and offer innovative services to their customers. These advancements include enhanced performance metrics such as higher data rates, lower latency, improved reliability, and greater network efficiency.
During the next few years, 5G Advanced will continue to evolve within 3GPP while the specification of 6G officially starts to ramp up in parallel, leading to the ITU-R IMT 2030 standard.
Setting The Stage For 6G:
Although Release 19 will be the last release focused on 5G, it will also include some longer-term technologies that will become the foundation of 6G, thus setting the direction for Release 20. For example, Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC), which combines wireless communications with RF sensing, will enable a raft of new position-based use cases. Release 19 will study channel characteristics suitable for the sensing of various objects, including vehicles, UAVs and humans. Full duplex, another 6G technology, allows transmitters and receivers to operate simultaneously on the same frequency, potentially resulting in a doubling of network capacity. Release 19 will study sub-band full duplex, a type of full duplex, which will improve capacity and latency, particularly for the uplink. Release 19 will also include channel model studies for the upper mid-band spectrum (7-16GHz), which will be supported by “Giga-MIMO” in the 6G timeframe, in order to enable wide-area coverage in this higher band.
Whereas AI/ML is a key pillar of 5G Advanced, it will be a core foundational technology of 6G and will underpin the key features that will make 6G revolutionary. For example, 6G will start to move away from the traditional, model-driven approach of designing communication systems and transition towards a more data-driven design. Indeed, it is likely that the 6G air-interface will be designed to be AI-native from the outset, thus signalling a paradigm change in the way communication systems are designed. An AI-native air interface could offer many benefits. For example, it could refine existing communication protocols by continuously learning and improving them, thereby enabling the air interface to be customized dynamically to suit local radio environments.
References:
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
Nokia plans to investment €360 million in microelectronics & 5G Advanced/6G technology in Germany
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
ABI Research: 5G-Advanced (not yet defined by ITU-R) will include AI/ML and network energy savings
Draft new ITU-R recommendation (not yet approved): M.[IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND]
Nokia plans to investment €360 million in microelectronics & 5G Advanced/6G technology in Germany
Nokia plans to invest €360 million (US$391 million) on the development of energy-efficient software, hardware and high-performance microelectronics for use in future mobile communications systems based on future 5G-Advanced and 6G specs from 3GPP and ITU-R standards.
Nokia wrote that “3GPP Release 18 will mark another major evolution in 5G technology that will lead the industry into the 5G-Advanced era. 5G-Advanced is set to evolve 5G to its fullest, richest capabilities. It will create a foundation for more demanding applications and a wider range of use cases than ever before with a truly immersive user experience based on extended reality (XR) features. It will also introduce AI and ML enhancements across the RAN, Core, and network management layer for improved performance, network optimization, and energy efficiency.”

Source: Nokia
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Editors Note: 3GPP Release 18 is scheduled to be completed in June 2024
Source: 3GPP
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The project will focus on the integrated development of software, hardware and high-performance systems-on-chips based on a digital twin. These will be used in radio and optical products in future mobile communications systems based on the 5G-Advanced and 6G standards. Nokia is further expanding its extensive experience in chip design and strengthening the European value chain.
This development work will be carried out at Nokia’s Ulm and Nuremberg sites in Germany, and will be funded by Nokia, the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Climate Protection and the German states of Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria.
Another focus area is on the energy efficiency of the systems to support European climate targets under the Green Deal. Nokia is closely cooperating with research institutes and universities to achieve this objective.This cooperation will be strengthened by the long-term IPCEI investment and funding. The microelectronics systems developed as part of the project will help to make networks more energy-efficient and more powerful at the same time.
Nokia hopes that the project will strengthen Europe’s competitiveness, especially in the field of microelectronics for nascent technologies such as 6G and artificial intelligence.
Tommi Uitto, President of Mobile Networks at Nokia, said:
“This important funding will support our efforts to advance the telecommunications industry in Germany and in Europe, helping to drive innovation and strengthen competitiveness. In particular, it will help our research into microelectronics that will power future technologies such as 6G, artificial intelligence and the metaverse as well as develop networks that are more energy-efficient and powerful. Germany is an important market for Nokia, and we look forward to working with the government to produce cutting-edge technology that is ‘Made in Germany’.”
References:
https://www.nokia.com/about-us/newsroom/articles/5g-advanced-explained/
https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-18
Nokia exec talks up “5G Advanced” (3GPP release 18) before 5G standards/specs have been completed
Nokia and du (UAE) complete 5G-Advanced RedCap trial
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
ABI Research: 5G-Advanced (not yet defined by ITU-R) will include AI/ML and network energy savings
Nokia will manufacture broadband network electronics in U.S. for BEAD program
IEEE 5G/6G Innovation Testbed for developers, researchers and entrepreneurs
Courtesy of IEEE member David Witkowski (see his bio below the article):
David’s career began in the US Coast Guard where he led deployment and maintenance programs for mission-critical telecom, continuity of government, and data networking systems. After earning his B.Sc. in Electrical Engineering from University of California @ Davis, he held managerial and leadership roles for high technology companies ranging from Fortune 500 multi-nationals to early-stage startups.
David serves as Executive Director of the Civic Technology Program at Joint Venture Silicon Valley, Senior Advisor for Broadband at Monterey Bay Economic Partnership, and is a Fellow of the Radio Club of America and a Senior Member of the IEEE. He previously served as as Co-Chair of the GCTC Wireless SuperCluster at NIST, on the Board of Expert Advisors for the California Emerging Technology Fund.
David’s IEEE activities include:
-
Co-Chair of the Deployment Working Group at IEEE Future Networks (FNTC)
-
Life Member of the IEEE Microwave Theory and Techniques Society (MTT-S)
-
Member of the IEEE International Committee on Electromagnetic Safety (ICES)
-
Member of the IEEE Committee on Man and Radiation (COMAR)
Nokia and du (UAE) complete 5G-Advanced RedCap trial; future of RedCap?
Nokia and United Arab Emirates (UAE) telco du announced the conclusion of what it claimed to be UAE’s first 5G-Advanced 5G Reduced Capability (RedCap) trial over a commercial network. Nokia said that this recent trial showcased the readiness of du’s 5G network for innovative use cases in areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), wearables and Industry 4.0 to address 5G monetization challenges.
RedCap, sometimes referred to as (3GPP) 5G NR Light, is a reduced set of 5G capabilities intended for devices like wearables and low-cost hotspots that have low battery consumption, lower costs and lower bandwidth requirements. Introduced with 3GPP Release 17, 5G RedCap is designed for devices currently served by LTE CAT-4 but provides equivalent or better in performance with up to 150 Mbps theoretical maximum downlink throughput. This technology helps reduce the complexity, cost and size of 5G devices. The RedCap specification will be included in ITU-R M.2150-1.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The trial participants used MediaTek’s T300 series RedCap test equipment in du’s 5G Standalone (SA) Radio Access Network (RAN) built with Nokia’s AirScale radio products, leveraging the existing mid-band Spectrum. This will follow extending RedCap over low band frequencies, ensuring extreme coverage and connectivity. Notably, the low band in 600MHz, is a vital connectivity band currently under discussion at the World Radio Conference WRC-23 taking place in Dubai.
With RedCap devices expected to be commercially available from 2024, it will significantly augment du’s diversified use case portfolio to include cost-efficient 5G home wireless, wearables, video surveillance, and wireless industrial sensors.
5G devices commonly feature intricate hardware and energy-intensive capabilities, resulting in higher cost, size, and power consumption. RedCap technology is dedicated to streamlining 5G devices, specifically targeting compact IoT devices like wearables and health trackers, as well as ruggedized routers and sensors for environmental or condition-based monitoring. These devices exhibit lower demands for battery life and reduced bandwidth requirements. RedCap ensures they sustain performance while optimizing their power efficiency. Nokia has been instrumental in driving the evolution of RedCap IoT functionality in collaboration with the telecommunications industry.
Saleem Alblooshi, Chief Technology Officer at du, said: “This collaboration introduces the revolutionary 5G-Advanced RedCap functionalities, enabling seamless connectivity of RedCap devices to cutting-edge 5G networks. Nokia’s unparalleled innovation simplifies and pioneers the development of 5G devices, particularly wearables and small IoT devices, significantly enhancing LTE-CAT4 performance and optimizing energy efficiency. These remarkable technological advancements are pivotal in propelling Industry 4.0 revolution.”
Mikko Lavanti, Senior Vice President at Nokia MEA, said: “This new collaboration between du and Nokia represents not only a significant step forward in the monetization of 5G technology but also solidifies the UAE’s position as a pioneer in the evolution of 5G use cases for society and enterprises. As the collaboration progresses, both companies are poised to revolutionize the way we experience and interact with 5G technology, unlocking unprecedented possibilities for innovation and connectivity.”
Dr. Ho-Chi Hwang, General Manager of Wireless Communication System and Partnerships at MediaTek, said: “It’s essential to bring new capabilities of 5G to the UAE, and this trial is an important step in that direction. We are proud to have provided our RedCap devices to further develop the ecosystem for 5G monetization. We hope, by pioneering the technology in the Middle East and Africa region, MediaTek will be able to assure our customers of more innovative 5G products and services coming their way.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Future of RedCap:

Counterpoint Research expects that 5G RedCap modules will make up 18% of total cellular IoT module shipments by 2030—what it describes as “significant market potential, particularly in developing nations where the cost is key to wide technology adoption for digital transformation.”
“If we want to tackle some of these interesting business cases and really get the price point so the business can take off, then we need to provide the right types of options,” said Paul Harris, principal architect in the Office of the CTO at Viavi Solutions. “People don’t want to be paying for chipsets that are too performant in the wrong types of devices.” Harris also noted that standards work on RedCap continues, with a series of recommendations on reducing RedCap’s performance even further with support of just five megahertz of bandwidth, even lower data rates and reduced peak data rates as well as additional power savings in the form of Extended Discontinuous Reception (allowing longer periods during which a device can power off). While that work on “eRedCap” is still taking shape in Release 18 and additional features may be available to scale down RedCap further in Release 19. “It’s still kind of a moving target and probably will continue to be, but there will probably be different categories that get introduced of RedCap as it goes on,” he said. Harris goes on to offer up a potential vision of a RedCap market where there is a gradual progression into some parts of the market addressed with the initial Rel. 17 RedCap options, and that by Rel. 19, a scaled-back RedCap market could open up for even lower-complexity, lower data-rate devices that then leads to an explosion of 5G sensor devices.
“5G is absolutely the directional technology,” said Bill Stone, VP of technology development and planning at Verizon. “I do think it’s inevitable that we’ll be seeing all of IoT evolve over time, and it’s going to be starting as soon as next year. We’re going to see all of the IoT device community moving over to 5G, because that’s where—with 5G NR SA—we’re going to see the potential for much longer lifecycles [and] the ability to support that, to make commitments for longer-term support of IoT devices.”
References:
Standards leadership in action: How Nokia convinced the 5G world that less is more
Ericsson, Vodafone and Qualcomm: 1st Reduced Capability 5G data call in Europe
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/redcap
ITU-R M.2150-1 (5G RAN standard) will include 3GPP Release 17 enhancements; future revisions by 2025
T-Mobile and Google Cloud collaborate on 5G and edge compute
T-Mobile and Google Cloud announced today they are working together to combine the power of 5G and edge compute, giving enterprises more ways to embrace digital transformation. T-Mobile will connect the 5G Advanced Network Solutions (ANS) [1.] suite of public, private and hybrid 5G networks with Google Distributed Cloud Edge (GDC Edge) to help customers embrace next-generation 5G applications and use cases — like AR/VR experiences.
Note 1. 5G ANS is an end-to-end portfolio of deployable 5G solutions, comprised of 5G Connectivity, Edge Computing, and Industry Solutions – along with a partnership that simplifies creating, deploying and managing unique solutions to unique problems.

More companies are turning to edge computing as they focus on digital transformation. In fact, the global edge compute market size is expected to grow by 37.9% to $155.9 billion in 2030. And the combination of edge computing with the low latency, high speeds, and reliability of 5G will be key to promising use cases in industries like retail, manufacturing, logistics, and smart cities. GDC Edge customers across industries will be able to leverage T-Mobile’s 5G ANS easily to get the low latency, high speeds, and reliability they will need for any use case that requires data-intensive computing processes such as AR or computer vision.
For example, manufacturing companies could use computer vision technology to improve safety by monitoring equipment and automatically notifying support personnel if there are issues. And municipalities could leverage augmented reality to keep workers at a safe distance from dangerous situations by using machines to remotely perform hazardous tasks.
To demonstrate the promise of 5G ANS and GDC Edge in a retail setting, T-Mobile created a proof of concept at T-Mobile’s Tech Experience 5G Hub called the “magic mirror” with the support of Google Cloud. This interactive display leverages cloud-based processing and image rendering at the edge to make retail products “magically” come to life. Users simply hold a product in front of the mirror to make interactive videos or product details — such as ingredients or instructions — appear onscreen in near real-time.
“We’ve built the largest and fastest 5G network in the country. This partnership brings together the powerful combination of 5G and edge computing to unlock the expansion of technologies such as AR and VR from limited applications to large-scale adoption,” said Mishka Dehghan, Senior Vice President, Strategy, Product, and Solutions Engineering, T-Mobile Business Group. “From providing a shopping experience in a virtual reality environment to improving safety through connected sensors or computer vision technologies, T-Mobile’s 5G ANS combined with Google Cloud’s innovative edge compute technology can bring the connected world to businesses across the country.”
“Google Cloud is committed to helping telecommunication companies accelerate their growth, competitiveness, and digital journeys,” said Amol Phadke, General Manager, Global Telecom Industry, Google Cloud. “Google Distributed Cloud Edge and T-Mobile’s 5G ANS will help businesses deliver more value to their customers by unlocking new capabilities through 5G and edge technologies.”
T-Mobile is also working with Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services and Ericsson on advanced 5G solutions.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/business/t-mobile-and-google-cloud-join-5g-advanced-network-solutions
https://www.t-mobile.com/business/solutions/networking/5G-advanced-solutions
AT&T touts 5G advances; will deploy Standalone 5G when “the ecosystem is ready”- when will that be?
Backgrounder -5G SA Core Network:
5G SA core is the heart of a 5G network, controlling data and control plane operations. The 5G core aggregates data traffic, communicates with UE, delivers essential network services and provides extra layers of security, and all 3GPP defined 5G features and functions. There are no standards for implementation of 3GPP defined 5G SA core network architecture, which is said to be a service based architecture, recommended to be “cloud native.” Here are the key 3GPP 5G system specs:
- TS 22.261, “Service requirements for the 5G system”
- TS 23.501, “System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 23.502 “Procedures for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 32.240 “Charging management; Charging architecture and principles”
- TS 24.501 “Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3”
A 5G NSA network is a LTE network with a 5G NR, i.e. the 5G NR Access Network is connected to the 4G Core Network.
AT&T Yet to Deploy 5G SA Core Network but is “charging forward to advance 5G SA ecosystem readiness:
It’s been a long wait for AT&T’s 5G SA core network, which is required to realize ALL 5G functions defined by 3GPP, including network slicing, network virtualization, security, and edge computing (MEC).
- The U.S. mega network operator initially said they would launch 5G SA core network in 2020 but that never happened.
- On June 30, 2021, AT&T said their mobile network traffic will be managed using Microsoft Azure technologies. “The companies will start with AT&T’s 5G core, the software at the heart of the 5G network that connects mobile users and IoT devices with internet and other services.” Almost two years later, that hasn’t happened either!
- In an April 18, 2022 blog post on the company’s website, AT&T now says they are “Taking 5G to the Next Level with Standalone 5G.” AT&T has said that they “plan to deploy Standalone 5G when the ecosystem is ready, and AT&T is charging forward to advance 5G SA ecosystem readiness. Businesses and developers will be some of the first to take advantage of the new technologies standalone 5G enables as we continue to move from research & development to their deployment.”
However, AT&T did not provide a date or even a timeframe when its 5G SA core network would be deployed. Instead, the telco lauded several 5G advances they’ve recently made. Those include:
1. Completed the first 5G SA Uplink 2-carrier aggregation data call in the U.S.
Carrier aggregation (CA) means we are combining or “aggregating” different frequency bands to give you more bandwidth and capacity. For you, this means faster uplink transmission speeds. Think of this as adding more lanes in the network traffic highway.
The test was conducted in our labs with Nokia’s 5G AirScale portfolio and MediaTek’s 5G M80 mobile test platform. AT&T aggregated their low-band n5 and our mid-band n77 spectrum. Compared to the low-band n5 alone, AT&T realized a 100% increase in uplink throughput by aggregating the low-band n5 with 40MHz of AT&T’s mid-band n77. Taking it a step further, AT&T achieved a 250% increase aggregating 100MHz of n77. The bottom line: AT&T achieved incredible upload speeds of over 70 Mbps on n5 with 40MHz of n77 and over 120 Mbps on n5 with 100MHz of n77.
2. Using a two-layer uplink MIMO on time division duplex (TDD) in our mid-band n77. MIMO combines signals and data streams from multiple antennas (“vehicles”) to improve signal quality and data rates. This feature will not only improve uplink throughput but also enhance cell capacity and spectrum efficiency.
3. Last fall, AT&T completed a 5G SA four component carrier downlink call by combining two FDD carriers and two TDD carriers. These capabilities allow AT&T devices to aggregate our mid-band n77 in the C-Band and 3.45GHz spectrum ranges. Compared with low band and mmWave spectrum, mid-band n77 provides a good balance between coverage and speed. This follows the 5G SA three component carrier downlink feature that we introduced last year to 2022 AT&T Flagship devices which combines one frequency division duplex (FDD) carrier and two TDD carriers.
4. In the coming months, AT&T will enable 5G New Radio Dual Connectivity (NR-DC), aggregating our low and mid-band spectrum with our high-band mmWave spectrum on 5G SA. Our labs have achieved 5G NR-DC downlink throughput speeds of up to 5.3Gbps and uplink throughput speeds of up to 670Mbps. This technology will help provide high-speed mobile broadband for both downlink and uplink in stadiums, airports, and other high-density venues.
5. Here are some features that are on the horizon for 5G SA (how far away is the horizon?):
- Specialized Network Services – think network slicing, precision location, private routing, etc. – for tailored network solutions to meet specific user requirements;
- Non-terrestrial network solutions to supplement coverage in remote locations ; and
- Reduced capability 5G (RedCap) for a new generation of 5G capable wearables, industrial IoT or wireless sensors and other small form factor consumer devices.
In conclusion, AT&T’s Jason Sikes wrote, “The 5G SA ecosystem is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and capabilities being introduced to set the foundation for next generation applications and services.” Yet no information was provided on the status of AT&T’s 5G SA network running on Microsoft Azure cloud technology!

AT&T to run its mobility network on Microsoft’s Azure for Operators cloud, delivering cost-efficient 5G services at scale.
Image Credit: Microsoft
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In the U.S., T-Mobile launched 5G SA core network nationwide last year, while Verizon began shifting its own traffic onto its 5G SA core in 2022. More recently, Verizon officials have begun hinting at interest in selling SA-powered network slices to public safety customers and others.
At the close of 2022, Dell’Oro identified 39 MNOs (Mobile Network Operators) that have commercially launched 5G SA eMMB networks. “Reliance Jio, China Telecom-Macau, and Globe Telecom were new MNOs added to the list of 39 MNOs launching 5G SA eMMB networks in the fourth quarter of 2022. Reliance Jio has announced a very aggressive deployment schedule to cover most of India by the end of 2023. In addition, AT&T and Verizon plan large expansions to their 5G SA coverage in 2023, raising the projected Y/Y growth rate for the total MCN and MEC market for 2023 higher than 2022,” said Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/atandt-to-launch-standalone-5g-later-this-year/d/d-id/764109
https://about.att.com/blogs/2023/standalone-5g-innovations.html
https://about.att.com/story/2021/att_microsoft_azure.html
AT&T 5G SA Core Network to run on Microsoft Azure cloud platform
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network & MEC revenues to be > $50 billion by 2027
Huawei says 5.5G is necessary with fully converged cloud native core network
Huawei maintains that a new 5.5G core network is needed to address a plethora of new use cases and new opportunities. That despite of the very limited deployment of 3GPP’s 5G SA Core network architecture specs. The company is calling on partners to promote industry consensus and commercial deployments for the era of 5.5G, an evolution of 5G technology.
Yang Chaobin, senior vice-president of Huawei, said: “The rapid growth of 5G has led to new service requirements that are becoming more diverse and complex. Such changes demand stronger 5G capabilities.”
Yang said that as 6G is still in the early stages of research, 5.5G is a necessary and natural evolution of 5G, which has become an industry consensus.
According to GSA, 35 network operators in 20 countries have launched commercial public 5G SA networks. In addition to those, GSA identified 77 other operators that are currently investing in 5G SA for public networks (including those evaluating/testing, piloting, planning, or deploying).
In 2020, containers and micro-services were introduced as key components of cloud-native network design and migration path to 5G core networks with high degree of much needed automation. At this point, intent-driven algorithms are used to automate large-scale cloud-native 5G telecom networks.
Figure 1. Huawei at MWC 2023

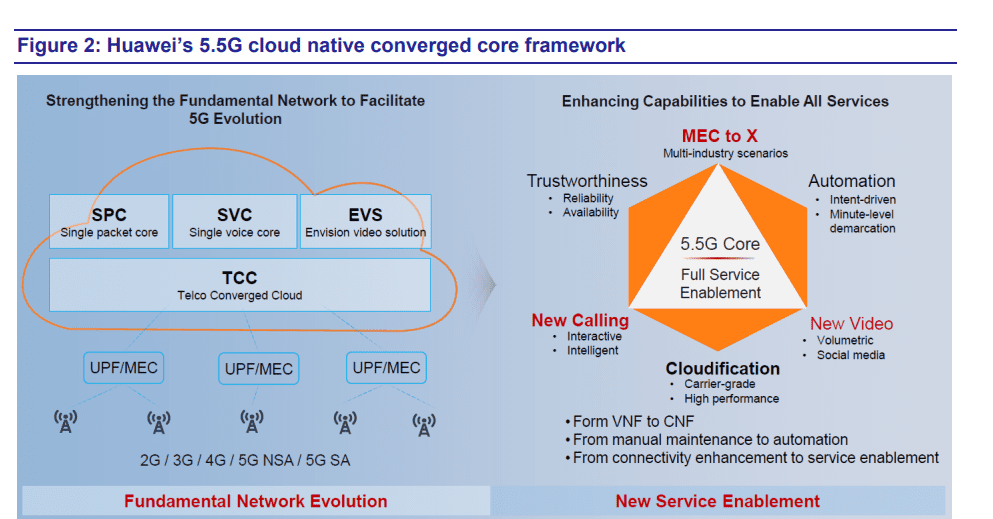
Figure 2. below illustrates Huawei’s complete 5.5G cloud-native converged core strategy that is based on strengthening the current networking building blocks that paved the way to where we are today, and continuously adding new capabilities and enhancing them to enable all services needed to address the plethora of new 5G use cases.
Source: Huawei
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Backgrounder on 5G Advanced:
3GPP initiated the 5G-Advanced project in early 2021 and started the formulation of Release 18 specs to enhance the existing mobile network capabilities. Case in point: UPF (User Plane Function) Mesh and MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) enhancements were introduced to enable 5G to cover more industry scenarios, which in the new 5.5G core platform, is addressed through the “MEC to X” concept to accelerate the digital transformation of industries.
In addition, the Rel. 18 NG-RTC (Next Generation Real-Time Communications) feature enhances the communication capability and enriches the communication services, including calling and video, or “New Calling” and “New Video” in 5.5G core (see Figure 2. above).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Huawei laid out five major characteristics of the 5.5G era – 10 Gbps experiences, full-scenario interconnection, integrated sensing and communication, autonomous networks and green information communications technology.
Yang called on the global telecom industry to jointly promote 5.5G development in four areas including setting clear roadmaps for industry standardization and a clear strategy for spectrum, which is fundamental to wireless networks.
Huawei and Saudi Arabian telecommunications operator Zain KSA signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) last month for the”5.5G City” joint innovation project.
Under the MoU, both parties will work together to promote technological innovation for 5.5G evolution and expand scalable offerings to individuals, enterprises and government customers. Additionally, they will strengthen the digital infrastructure and build a global 5.5G evolution pioneer network, providing a strong engine to achieve the national digitalization goals outlined in Saudi Vision 2030.
Abdulrahman Al-Mufadda, chief technology officer of Zain KSA, said, “Our commitment to driving digital transformation has been made possible by combining innovative technology investments with pioneering digital solutions across multiple fields, including cloud computing, fintech, business support and drone technologies.”
The cooperation came as 5G is now in the fast lane after three years of commercial use. By the end of 2022, global 5G users exceeded 1 billion, gigabit broadband users reached 100 million, and more than 20,000 industry applications were put into use, according to data compiled by Huawei.
Leading operators in China, South Korea, Switzerland, Finland and Kuwait have already achieved 5G user penetration rates of more than 30 percent with more than 30 percent of their traffic coming from 5G, Huawei said.
Network intelligence and connectivity insights provider Ookla’s latest 5G City Benchmark Report showed Huawei has played an important role in 5G network construction in all of the top 10 cities among the world’s 40 most 5G-enabled cities. Performance results in these 10 cities show 5G networks constructed by Huawei offer the best experience.
Last month, Huawei also revealed a collaboration with Botswana’s Debswana Diamond Co (Pty) Ltd on the world’s first 5G smart diamond mine project.
Debswana’s Head of Information Management Molemisi Nelson Sechaba said that the Huawei-enabled smart mine solution has been deployed at Debswana’s Jwaneng open-pit diamond mine. The project started operation in December 2021.
At present, Huawei’s 4G eLTE, an advanced version of 4G technology, provides stable connectivity for the Jwaneng mine, connecting more than 260 pieces of equipment, including drilling rigs, excavators, heavy trucks and pickup trucks. This enables interconnection between the mine’s production, safety and security systems, Sechaba said.
The Jwaneng mine is the world’s first 5G-oriented smart diamond mine, which means the hardware equipment such as base stations used in the mine’s digital transformation support network has upgraded to 5G, Huawei said.
Huawei claims they’ve seamlessly migrated their existing and dedicated core network platforms (e.g., SPC, SVC, EVS in Figure 2) as well as its telco converged cloud to a fully converged cloud-native 5.5G core that features full-service enablement. In other words, the company says the transition from virtual network functions (VNF) to cloud native network functions (CNF), from manual operation to automation and from connectivity provisioning and enhancement to full-service enablement has been completed.
–>That’s all in advance of 3GPP Release 18 specs on 5G Advanced (which won’t be frozen till March 2024)?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202303/20/WS6417b0a5a31057c47ebb55b2.html
Huawei’s blueprint to lay the foundation for 5.5G and the “intelligent world”
Virtual Network Function Orchestration (VNFO) Market Overview: VMs vs Containers
GSMA Intelligence: 5G connections to double over the next two years; 30 countries to launch 5G in 2023
GSMA Intelligence forecasts 5G connections are expected to double over the next two years, expedited by technological innovations and new 5G network deployments in more than 30 countries in 2023. Of the new networks to be deployed in 2023, it is expected that 15 will be 5G Standalone (SA) networks. As of January 2023, there were 229 commercial 5G networks globally and over 700 5G smartphone models available to users.
GSMA Intelligence, announced its latest 5G forecast during MWC Barcelona 2023, point to a significant period of growth in terms of mobile subscribers and enterprise adoption. Consumer connections surpassed one billion at the end of 2022 and will increase to around 1.5 billion this year – before reaching two billion by the end 2025.
India will lead the 5G expansion globally in 2023, with the expansion of services from Airtel and Jio in 2023 expected to be pivotal to the region’s ongoing adoption. GSMA Intelligence predicts there will be four 5G networks in India by the end of 2025, accounting for 145 million additional users. With operators such as Jio announcing ambitions to connect as many as 100 million homes across India to its 5G FWA network, the number of FWA users looks likely to grow substantially over the next few years, the report added.

Growth will also come from key markets within APAC and LATAM, such as Brazil and India, which have recently launched 5G networks. India will be especially significant, with the expansion of services from Airtel and Jio in 2023 expected to be pivotal to the region’s ongoing adoption. GSMA Intelligence predicts there will be four 5G networks in India by the end of 2025, accounting for 145 million additional users.
Many of the new 5G markets scheduled to launch networks in 2023 are in developing regions across Africa – including Ethiopia and Ghana – and Asia. Today, 5G adoption in the sub-Saharan region sits below 1% but will reach over 4% by 2025 and 16% in 2030, largely thanks to a concerted effort from industry and government organizations to provide connectivity to citizens.
“Until now, 5G adoption has been driven by relatively mature markets and consumer use cases like enhanced mobile broadband, but that’s changing. We’re now entering a second wave for 5G that will see the technology engage a diverse set of new markets and audiences,” said Peter Jarich, Head of GSMA Intelligence. “The extension to new use cases and markets will challenge the mobile ecosystem to prove that 5G truly is flexible enough to meet these diverse demands in a way that’s both inclusive and innovative.”
The Rise of 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA):
As of January 2023, more than 90 FWA broadband service providers (the vast majority of which are mobile operators) had launched commercial 5G-based fixed wireless services across over 48 countries. This means around 40% of 5G commercial mobile launches worldwide currently include an FWA offering.
In the U.S., T-Mobile added over half a million 5G FWA customers in Q4 2021 and Q1 2022 combined. By 2025, it expects to have eight million FWA subscribers, while Verizon is targeting five million FWA subscribers for the same period. The conventional wisdom holds that FWA is primarily useful as a rural service, targeted mostly at the previously unserved or underserved. Verizon says their FWA service is primarily urban and suburban service with target customers that are dissatisfied with terrestrial broadband services. Verizon has increasingly come to view FWA as an integral part of their broadband access offering everywhere that FiOS isn’t available.
Reliance Jio (India) announced ambitions to connect as many as 100 million homes across India to its 5G FWA network, the number of FWA users looks likely to grow substantially over the next few years.
While the majority of current 5G FWA deployments focus on the 3.5–3.8 GHz bands, several operators around the world are already using 5G mmWave spectrum as a capacity and performance booster to complement coverage provided by lower bands.
Only 7% of 5G launches have been in 5G mmWave spectrum so far but this looks set to change given 27% of spectrum allocations and 35% of trials are already using 5G mmWave bands. Furthermore, in 2023 alone, the industry will see ten more countries assigned 5G mmWave spectrum for use – a significant increase from the 22 countries who have been assigned it to date. Spain received the first European 5G mmWave spectrum allocation this year, resulting in Telefónica, Ericsson and Qualcomm launching its first commercial 5G mmWave network at MWC Barcelona 2023.
Enterprise IoT Driving Growth:
The figures from GSMA Intelligence also suggest that, for operators, the enterprise market will be the main driver of 5G revenue growth over the next decade. Revenues from business customers already represent around 30% of total revenues on average for major operators, with further potential as enterprise digitization scales. Edge computing and IoT technology presents further opportunities for 5G, with 12% of operators having already launched private wireless solutions – a figure that will grow with a wider range of expected IoT deployments in 2023.
Another major development for the enterprise will be the commercial availability of 5G Advanced (3GPP Release 18) in 2025. Focusing on uplink technology, 5G Advanced will improve speed, coverage, mobility and power efficiency – and support a new wave of business opportunities. GSMA’s Network Transformation survey showed half of operators expect to support 5G Advanced commercial networks within two years of its launch. While this is likely optimistic, it presents the ecosystem with a clear opportunity to execute on.
Editor’s Note:
GSMA’s 5G forecast is a direct contradiction to Omdia’s which expects weaker 5G growth in the near term. Which forecast do you believe?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Omdia forecasts weaker 5G market growth in near term, 4G to remain dominant
Huawei’s blueprint to lay the foundation for 5.5G and the “intelligent world”
According to Huawei, the intelligent world will be deeply integrated with the physical world. Everything, including personal entertainment, work, and industrial production, will be intelligently connected. This means that networks will have to evolve from ubiquitous Gbps to ubiquitous 10Gbps, connectivity and sensing will need to be integrated, and the ICT industry will have to shift its focus from energy consumption to energy efficiency. The evolution from 5G to 5.5G will be key to meeting these growing requirements.
At MWC 2023, Huawei unveiled its “GUIDE to the Intelligent World“ as a business blueprint to lay the foundation for 5.5G. Whatever happened to 5G Advanced and 3GPP Release 18? and ITU-R WP5D M.2150 recommendation?.
Following on from Huawei’s concept of “Striding Towards the 5.5G Era” that was proposed in July 2022, Huawei is highlighting the five major characteristics of the 5.5G era:
- 10 Gbps experiences
- Full-scenario interconnection
- Integrated sensing and communication
- L4 autonomous driving networks
- Green ICT
For Huawei, 5.5G represents a 10-fold improvement in performance over 5G in every metric. That means 10 Gbps headline connection speeds, 10 times the number of IoT connections – which translates to 100 billion in total – and reducing latency by a factor of 10. Networks also need to consume a tenth of the energy that they consume today on a per Terabyte basis, and they need to be 10x more intelligent, which means supporting level 4 autonomous driving, and making operations and maintenance (O&M) more efficient by a factor of 10.
With these capabilities in place, 5.5G networks will enable a boom in immersive interactive experiences, like VR gaming in 24K resolution, and glasses-free 3D video, predicts Huawei. It expects the installed user base of these services will grow 100-fold to 1 billion. On the enterprise side, the vendor expects the number of private cellular networks to increase from 10,000 today to 1 million by 2030.
Huawei says that leading global operators, standards organizations, and industry ecosystem partners are coming together to promote innovation and exploration for this 5.5G era, as it will create more new applications and business opportunities. This author disagrees- they are not coming together at all!
According to Ookla’s latest 5G City Benchmark Report, Huawei has played an important part in 5G network construction in all of the top 10 cities among the world’s 40 representative 5G-enabled cities. It’s important to note that 5G performance results in these 10 cities show that the 5G networks constructed by Huawei offer the best experience.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
David Wang, Huawei’s Executive Director of the Board, Chairman of the ICT Infrastructure Managing Board, and President of the Enterprise BG, said, “Huawei will deepen our roots in the enterprise market and continue our pursuit of innovation. We are ready to use leading technologies and dive deep into scenarios. Together with our partners, we will enable industry digitalization, help SMEs access intelligence, and promote sustainable development, creating new value together.”
Bob Chen, Vice President of Huawei Enterprise BG, delivered a keynote speech entitled “Digital Technology Leads the Way to the Intelligent World,” which outlined how digital technologies have impacted the development of the world’s economy, cultures, societies, and environment. He stated, “Archimedes, a great Greek physicist, said, ‘Give me a place to stand and I shall move the earth.’ Digital technology is the right place for us to help industries go digital. Huawei will focus on connectivity, computing, cloud, and other digital technologies. We will continue inspiring innovation to drive industry digital transformation. Together, let’s build a fully connected, intelligent world!”
Huawei said they would continue to work with customers to build next-generation network infrastructure to better serve all industries. Here are a few of their focus areas:
- Smart campus: Huawei redefines campus networks and launches the Next-Generation enterprise flagship core switch CloudEngine S16700, first enterprise-level Wi-Fi 7 AP AirEngine 8771-X1T, along with first 50G PON OLT and optical terminal product.
- Easy branch: Huawei launches the industry’s first simplified hyper-converged branch solution.
- Single OptiX: Huawei launches the industry’s first end-to-end optical service unit (OSU) product portfolio.
- Cloud WAN: Huawei defines a brand-new cloud WAN and launches the NetEngine 8000 series routers oriented to the all-service intelligent router platform in the cloud era.
- Data Center solution: Four industry-first products and product portfolios, unleashing the power of digital innovation
Storage and computing power have become one of the core strategic resources of enterprises. Huawei focuses on data center infrastructure innovation, leads the development of new data centers, helps enterprises cope with uncertain threats, ensures ultimate service experience, processes massive and diversified computing power, and brings data centers more green, more reliability, and more efficiency.
For large enterprises,Huawei launches the industry’s first multi-layer DC ransomware protection solution powered by network-storage collaboration, the industry’s first unified DC DR product portfolio featuring storage and optical connection coordination (SOCC),and CloudEngine 16800-X, which is the industry’s first DC switch designed for diversified computing power.
For SMEs, Huawei also launches OceanStor Dorado 2000 and OceanProtect X3000, which are the industry’s first entry-level storage combination based on the active-active architecture.
Juan De Dios Navarro Caballero, councillor of Alicante province, Spain, stated, “Huawei’s SDN-based CloudFabric Solution and All-Wireless Campus Network Solution enable network automation, intelligent O&M, and ubiquitous connectivity. Through these solutions, the government offices of Alicante province are now more efficient, and offer a better user experience for public services. The province has seen faster digital transformation along with digital economy development.”
Faith Burn, CIO of Eskom, a South African electric power company, shared the company’s digital transformation methodology and practical experience. She stressed that Eskom seeks to work with partners that can help realize the company’s digital vision, saying that, “It is very important to find capable partners to realize our digital vision. Eskom would like to collaborate with OEMs like Huawei to build advanced electricity ICT infrastructure to achieve comprehensive digitalization.”
Steven Zhu, President of Partner Development and Management of Huawei Enterprise BG, mentioned that “Huawei is committed to working with partners to complement each other, motivate partners to support customers proactively, and serve customers well together.”
In the future, Huawei says they will continue to invest and innovate, working alongside global customers and partners to deeply integrate ICT, accelerate digital transformation, promote digital economy development and speed up the realization of the intelligent world within industries, in order to create new value.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2023/2/mwc2023-5g-huawei%20-connectivity
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2023/2/mwc2023-industry-digital-transformation
https://telecoms.com/520240/huaweis-5-5g-vision-is-what-5g-should-have-been-all-along/