China Telecom
China ITU filing to put ~200K satellites in low earth orbit while FCC authorizes 7.5K additional Starlink LEO satellites
- Purpose: The planned systems are intended to provide global broadband connectivity, data relay, and positioning services, directly competing with U.S. efforts like SpaceX’s Starlink network.
- Filing Entities: The primary filings were submitted by the state-backed Institute of Radio Spectrum Utilization and Technological Innovation, along with other commercial and state-owned companies like China Mobile and Shanghai Spacecom.
- Status: These filings are an initial step in a long international regulatory process and serve as a claim to limited spectrum and orbital slots. They do not guarantee all satellites will ultimately be built or launched. The actual deployment will be a gradual process over many years.
- Context: The move is part of an escalating “space race” to dominate the LEO environment. Early filings are crucial for securing priority access to orbital resources and avoiding signal interference. The sheer scale of the Chinese proposal would, if realized, dwarf most other planned constellations.
- Regulations: Under ITU rules, operators must deploy a certain percentage of the satellites within seven years of the initial filing to retain their rights.
- Shanghai Yuanxin (Qianfan), currently China’s most advanced LEO satellite operator, has submitted a regulatory request for an additional 1,296 satellites.
- Telecommunications giant China Mobile is planning two separate constellations totaling 2,664 satellites.
- ChinaSat, the established state-owned satellite provider, is focusing on a 24-satellite medium-Earth orbit (MEO) system.
- GalaxySpace, a private satellite manufacturer based in Beijing, has applied for 187 satellites, and China Telecom has applied for 12.

Image Credit: Klaus Ohlenschlaeger/Alamy Stock Photo
“This gives SpaceX what they need for the next couple of years of operation. They’re launching a bit over 3,000 satellites a year, so 7,500 satellites being authorized is potentially enough for SpaceX to do what they want to do until late 2027,” said Tim Farrar, satellite analyst and president at TMF Associates.
SpaceX has plans for a larger D2D satellite constellation that would use the AWS-4 and H-block spectrum it is acquiring from EchoStar. It is awaiting FCC approval for the US$17 billion deal, but the spectrum is not expected to be transferred until the end of November 2027.
The FCC noted that the changes will allow the Starlink system to serve more customers and deliver “gigabit speed service.” Along with permission for another tranche of satellites, the FCC has set new parameters for frequency use and lower orbit altitudes. The modified authorizations will also apply to new satellites to be launched.
Starlink’s LEO satellite network competitors are Amazon Leo, OneWeb and AST Space Mobile.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
U.S. BEAD overhaul to benefit Starlink/SpaceX at the expense of fiber broadband providers
Huge significance of EchoStar’s AWS-4 spectrum sale to SpaceX
Telstra selects SpaceX’s Starlink to bring Satellite-to-Mobile text messaging to its customers in Australia
SpaceX launches first set of Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capabilities
SpaceX has majority of all satellites in orbit; Starlink achieves cash-flow breakeven
Amazon Leo (formerly Project Kuiper) unveils satellite broadband for enterprises; Competitive analysis with Starlink
NBN selects Amazon Project Kuiper over Starlink for LEO satellite internet service in Australia
GEO satellite internet from HughesNet and Viasat can’t compete with LEO Starlink in speed or latency
Amazon launches first Project Kuiper satellites in direct competition with SpaceX/Starlink
Vodafone and Amazon’s Project Kuiper to extend 4G/5G in Africa and Europe
China’s state owned telcos slash CAPEX to the lowest in decades!
China’s big three state-owned telecom operators are drastically slashing capital expenditures (CAPEX) before the next wave of heavy spending on 6G mobile network infrastructure beginning in 2030. Over a year ago, the IEEE Techblog reported the planned CAPEX reductions in this post.
- China Telecom expects its capital expenditure to decline by 11% to 83.6 billion yuan in 2025, returning to pre-5G expansion levels.
- China Mobile also plans to cut its capital expenditure by 8% in 2025, bringing spending close to 2012 levels.
- China Unicom, the smallest of the three, recorded the sharpest drop in spending.
Reasons for the Cuts:
- The 5G network infrastructure buildout has largely reached its peak, with China already having 3.5 million 5G base stations.
- The companies are preparing for the next major investment cycle, which is expected to focus on 6G and AI infrastructure.
- The CAPEX cuts are also being driven by government directives to improve market value and increase shareholder dividends.
- The companies are prioritizing investments in AI infrastructure and computational infrastructure.
- China Mobile’s Chairman Yang Jie stated that the next major investment cycle is expected to focus on 6G and is unlikely to begin before 2028.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
1. China Mobile, the largest wireless carrier in China with over 1 billion subscribers, slashed its annual capital expenditure by over 9% to 164 billion yuan in 2024. The company plans to cut another 8% this year to 151.2 billion yuan. That amount is approaching the 2012 level of 127.4 billion yuan, and is set to decline further in the years to come.
“The overall investment size in the next two to three years will continue to steadily fall,” Yang Jie, China Mobile’s chairman, told reporters in Hong Kong last Thursday. Asked what would trigger the next capital spending spree, Yang said: “From what I see now, the next investment peak will be on 6G” — but he expects that to kick off around 2028. Until then, the industry veteran expects “the proportion of investment to expand in the areas of computation and AI.”

China Mobile Chairman Yang Jie told reporters in Hong Kong on March 20 that the next telecom investment peak would be for 6G mobile network building. (Photo by Kenji Kawase)
Jefferies telecom analyst Edison Lee, said China Mobile’s capex figures were “lower than expected.” The ratio versus its revenue was 18% last year, marking the first dip below 20%, and he expects this proportion to further sink to 16% this year. “This is negative for equipment vendors such as ZTE,” Lee said, although it provides more room for returns to shareholders.
2. China Telecom (#2 in China) announced on Tuesday that its CAPEX for 2024 came to 93.51 billion yuan ($12.9 billion), 5% lower than the previous year. The forecast for this year is even lower, at 83.6 billion yuan, down 11% and lowering the amount to the level before the peak 5G network investment years of around 2020 to 2023. However, with soaring demand for AI computing, it plans a further hike in digital infrastructure spending. It will boost investment in cloud computing and data centers by 22% to RMB45.5 billion ($6.3 billion), making it the biggest single capex item, accounting for 38% of the total.
The company said it’s focused on four technology directions: network, cloud and cloud-network integration, AI and quantum security. It revealed it had deployed 70,000 5G-A base stations in 121 cities, with 5G RedCap coverage in more than 200 cities, and said it had signed up 2.4 million subs to its pioneering D2D mobile satellite service.
Chairman Ke Ruiwen told Nikkei Asia that “the general trend is heading downward.” He added that “before building the new large-scale network (apparently referring to 6G), the investment trend is going continue falling.” He said the company would continue to pursue its strategy focused on cloud and digital transformation.

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
3. China Unicom, the smallest of the three state owned telcos, also slashed its capital spending by 17% to 61.37 billion yuan in 2024, while planning a further reduction to 55 billion yuan this year. “Our investment emphasis has already shifted away from mobile broadband to computing network capabilities for internet data centers and cloud,” said Tang Yongbo, Unicom’s vice president. He also mentioned the impending heavy investment period when the 6G era arrives.
China Telecom and China Unicom have a “co-build, co-share” partnership for 5G investment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
All three Chinese network operators’ actual capital expenditure in 2024 were lower than the previous guidance they had provided, by an average of 5%. The sum of annual capital expenditure for the three Chinese telcos was 319 billion yuan for 2024, and the combined estimate for 2025 is 289.8 billion yuan. Including China Tower — a tower builder established in 2014 through a merger of the three telecom companies’ related businesses, and publicly listed in 2018 — the total capex last year was 351 billion yuan. This year’s projected amount of 322 billion yuan would be one of the lowest in decades.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/china-telecom-boosts-profit-cuts-capex
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
Dell’Oro: Global telecom CAPEX declined 10% YoY in 1st half of 2024
Omdia: Huawei increases global RAN market share due to China hegemony
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
According to a new research report from Goldman Sachs-China, the three major, state owned telecom operators (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom) are quietly becoming the core beneficiaries of China’s AI boom. One reason is that, thanks to their deployment of China’s most extensive cloud infrastructure, they can serve other cloud companies as well as provide their own cloud services to their end user customers. They also enjoy the cost and scale advantages of owning their own data centers and bandwidth. For some IaaS companies, data center and connectivity together account for as much as 60% of total expense, according to Goldman-China.
Goldman analysts believe that telecom operators’ cloud businesses have obvious cost advantages compared to other cloud companies. Those are the following:
- The big 3 Chinese network operators have built their own Data Centers (DCs) and so do not rely on external DC service providers. They even provide DC services to other cloud companies such as Alibaba, which makes the IDC expenses of their cloud business lower.
- The bandwidth cost of operator cloud business is significantly lower than that of other cloud companies because operators use their own network infrastructure, while other cloud companies need to pay operators for bandwidth and private network fees connecting different data centers.
- For the IaaS cloud business, if external DC and bandwidth are used, data center costs (DC services and bandwidth) will account for a considerable proportion of the total cost of the cloud company. Goldman cites QingCloud Technology as an example, its data center costs (including cabinets, bandwidth, etc.) account for 50%-60% of its total costs.
Looking ahead, the telcos are strongly placed to take advantage of the DeepSeek AI boom, thanks to their early embrace of DeepSeek and the government’s push to promote AI among the state-owned enterprises that account for about 30% of operator revenue, Goldman argues. The report states, “the state-owned enterprise background makes the deployment of AI/Deepseek by government agencies and state-owned enterprises more beneficial to telecom operators.”
In the past two weeks, China’s three major operators have begun to help important customers deploy DeepSeek models. China Mobile supports PetroChina in deploying a full-stack Deepseek model; China Telecom provides the same service to Sinopec; and China Unicom cooperates with the Foshan Municipal Bureau of Industry and Information Technology. More importantly, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council (SASAC) launched the “AI+” action plan on February 21 to encourage Chinese state-owned enterprises to accelerate the development and commercial application of AI. According to Goldman Sachs research, government-related customers account for about 30% of telecom operators’ cloud revenue. Therefore, the deployment of AI/DeepSeek by government agencies and state-owned enterprises will clearly benefit telecom operators.
Separately, China Mobile announced at Mobile World Congress 2025 in Barcelona that it is leveraging artificial intelligence to transform telecommunications networks and drive unprecedented data growth while positioning itself at the forefront of AI-Native network innovation. China Mobile Executive Vice President Li Huidi outlined the company’s ambitious “AI+NETWORK” strategy in a keynote address titled “AI+NETWORK, Pioneering the Digital-Intelligent Future” during the Global MBB Forum Top Talk Summit on Sunday.
.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Li Huidi, executive vice president of China Mobile, speaks at the Global MBB Forum Top Talk Summit at Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Spain, March 2, 2025. (Photo/China Mobile)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://wallstreetcn.com/articles/3741901 (Chinese)
https://www.telecoms.com/partner-content/china-mobile-unveils-ai-network-strategy-at-mwc
https://www.lightreading.com/ai-machine-learning/china-telcos-rush-to-embrace-deepseek
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
At the 2024 Digital Technology Ecosystem Conference last week, China Telecom executives identified AI, 5G new calling and satellite-to-phone services as its handset priorities for 2025. The state-owned network operator, like other China telcos, is working with local manufacturers to build the devices it wants to sell through its channels.
China Telecom’s smartphone priorities align with its major corporate objectives. As China Telecom vice president Li Jun explained, devices are critical right across the business. “Terminals are an extension of the cloud network, a carrier of services, and a user interface,” he said.
China Telecom Vice President Li Jun
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
China Telecom Deputy General Manager Tang Ke, introduced the progress of China Telecom and its partners in AI and emerging terminal ecosystem cooperation. He stated that in 2024, China Telecom will achieve large-scale development of basic 5G services, with over 120 million new self-registered users annually and more than 140 models of phones supporting 5G messaging.
In terms of emerging businesses, leading domestic smartphone brands fully support direct satellite connection, with 20 models available and over 4 million units activated. Leading PC brands fully integrate Tianyi Cloud Computer, further enriching applications in work, education, life, and entertainment scenarios. Domestic phones fully support quantum secure calls, with over 50 million new self-registered users. Terminals fully support the upgrade to 800M, reaching over 100 million users. Besides phones to support direct-to-cell calling, it also hoped to develop low-cost positioning tech using Beidou and 5G location capabilities.
China Telecom continues to promote comprehensive AI upgrades of terminals, collaborating with partners to expand AI terminal categories and provide users with more diverse choices and higher-quality experiences. Tang Ke revealed that, at the main forum of the “2024 Digital Technology Ecosystem Conference,” China Telecom will release its first operator-customized AI phone.
Tang Ke emphasized that in the AI era, jointly building a collaborative and mutually promoting AI terminal ecosystem has become the inevitable path of industry development. Ecosystem participants must closely coordinate in technology, industry, and business to offer users the best AI experience. China Telecom will comprehensively advance technical collaboration, accelerating coordination from levels such as chips, large models, and intelligent agents, and promoting the construction of AI technology frameworks from both the device and cloud sides. The company will comprehensively push terminal AI upgrades, accelerating the AI development of wearables, healthcare, education, innovation, and industry terminals, based on key categories such as smartphones, cameras, cloud computers, and smart speakers.
Deputy Marketing Director Shao Yantao laid out the company’s device strategy for the year ahead. He said China Telecom’s business was based on networks, cloud-network integration and quantum security, with a focus on three technology directions – AI, 5G and satellites. With AI, it aims to carry out joint product development with OEM partners to build device-cloud capabilities and establish AI models. The state owned telco will pursue “domestic and foreign” projects in cloud-based AI mobile phones.
Besides smartphones, other AI-powered products next year would likely include door locks, speakers, glasses and watches, Shao said. The other big focus area is 5G new calling, based on new IMS DC (data channel) capabilities, with the aim of opening up new use cases like screen sharing and interactive games during a voice call.
China Telecom would develop its own open-source IMS DC SDK to support AI, payments, XR and other new functionality, Shao said. But he acknowledged the need to build cooperation across the industry ecosystem. The network operator and its partners would also collaborate on Voice over WiFI and 3CC carrier aggregation for 5G-Advanced devices, he added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) claims that China has built and activated over 4.1 million 5G base stations, with the 5G network continuously extending into rural areas, achieving “5G coverage in every township.” 5G has been integrated into 80 major categories of the national economy, with over 100,000 application cases accumulated. The breadth and depth of applications continue to expand, profoundly transforming lifestyles, production methods, and governance models.
The meeting emphasized the need to leverage the implementation of the “Sailing” Action Upgrade Plan for Large-scale 5G Applications as a means to vigorously promote the large-scale development of 5G applications, supporting new types of industrialization and the modernization of the information and communications industry, thereby laying a solid foundation for building a strong network nation and advancing Chinese-style modernization.
References:
https://www.c114.com.cn/news/22/c23811.html
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1279613.html
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1279469.html
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
China adds 20M “5G package” subscribers in July; 1H-2024 earnings gains outpace revenues for all 3 major China telcos
The number of 5G subscribers in China increased by a sizeable 20 million last month, according to new data from the country’s big three state owned network providers (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom). Of the three, China Mobile is still the only one to report actual customers using its 5G network; China Telecom and China Unicom are sticking to their 5G package subscribers metric, which essentially means customers signed up to a 5G plan, regardless of whether they use 5G network services (most continue to use 4G).
- China Mobile’s July net adds came in at 13.7 million, pushing its 5G customer base up to a colossal 528 million. China Mobile disclosed that it has 129 million customers using its 5G New Calling over high-definition video service reached 129 million, of which, smart application subscribers numbered 11.82 million.
- China Telecom added 3.1 million 5G package customers for a total of 340 million. They did not talk about 5G in their earnings report (more below).
- China Unicom added 2.9 million 5G package customers for a total of 279 million. China Unicom shared details of its 5G network build-out, pointing out that its 5G mid-band base stations numbered in excess of 1.31 million as of mid-year, while low-band sites reached 780,000.
For each of them, cloud and digital transformation (rather than 5G subs) drove topline growth, profit rose more than revenue and shareholder returns increased.
- China Mobile said net profit had improved 5.3% to RMB80.2 billion ($11.2 billion), outpacing revenue, which rose 3% to RMB546.7 billion ($76.6 billion).
- China Telecom, reported net earnings of 21.8 billion Chinese yuan (US3.1 billion), an 8.2% gain over last year, with revenue up 2.8% and service revenue 4.3% higher.
- China Unicom reported 11.3% higher net income of 13.8 billion ($1.93) on the back of a 2.9% lift in sales to RMB197.3 billion ($27.6 billion).
China Mobile says its digital transformation business grew 11% to RMB147.1 billion ($20.6 billion), accounting for 26% of all revenue. China Telecom reported digital industry sales of RMB73.7 billion ($10.3 billion), a 7% increase, and China Unicom said revenue grew 7% to RMB43.5 billion ($6.1 billion).

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo)
All three state owned telcos experienced double-digit growth in cloud services. China Telecom’s Tianyi Cloud grew revenue by 20% to RMB55 billion ($7.7 billion), while China Mobile Cloud hiked sales by 19% to RMB50 billion ($7 billion) and China Unicom grew 24% to RMB32 billion ($4.5 billion).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Silence is Golden?
There was a distinct lack of 5G commentary in China Telecom’s half year report; it is the last of the three to post numbers and did so alongside the publication of the market’s operational statistics for July. The telco shared its 5G package figures – it added almost 18 million in the first six months of 2024, incidentally – but made no other reference to the technology in a fairly wordy statement about its year-to-date performance. Instead, the operator focused on the progress of its digital transformation strategy, leaning heavily on the promise of artificial intelligence. Specifically, China Telecom is talking up what it terms AI+ – there’s always one – and the Xingchen large language model it launched at the back end of last year.
“The Company strengthened the integration and mutual promotion of capabilities in various fields, continuously enriched the Xingchen large model series product portfolio, empowered the intelligent transformation for thousands of industries, and supported enterprises to achieve costs reduction and efficiency enhancement,” it said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/china-added-20-million-5g-subs-last-month
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/cloud-digital-transformation-drive-chinese-telcos-h1-growth
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
China Telecom, along with its partners [1.], says it has launched the world’s first live single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber optics transmission system with unidirectional capacity over 100T bps.
Note 1. ZTE, Yangtze Optical Fibre, Cable Joint Stock Limited Company and Huaxin Design Institute were also involved in the project, which was deployed over a transmission distance of 20km in the live network of the All-Optical Network Technology and Application in the Intelligent Computing Era seminar of the CCSA TC618/NGOF.
ZTE optical transport equipment was used for project, alongside some improvements in spectral efficiency, baud rate optimization, and amplification optimization technologies. The system extends 41 C-band 1.2T bps and 64 L-band 800G bps wavelengths, and archives unidirectional transmission capacity of over 100T bps and a transmission distance of 20km in the field network.
This demonstration completed the hollow-core fiber deployment and large-capacity transmission between China Telecom’s Hangzhou Intelligent Computing Center and Yiqiao IDC. As a key node of China Telecom’s intelligent computing power layout “2+3+7+M”, the Hangzhou Intelligent Computing Center has been deployed with the 1k GPUs computing power of the China Telecom Cloud. It also hails ‘breakthroughs in hollow-core fiber fusion splicing technologies,’ such as low-power discharge and mode field matching related to the demonstration.

To meet the requirements for distributed computing power with large bandwidth and low latency of optical networks, ZTE used its advanced high-speed optical transport equipment. Combined with improvements in spectral efficiency, baud rate optimization, and amplification optimization technologies, the system extends 41 C-band 1.2Tbit/s wavelengths and 64 L-band 800Gbit/s wavelengths. It achieves a unidirectional transmission capacity of over 100Tbit/s and a transmission distance of 20km in the field network.
The hollow-core fiber cable, independently developed by YOFC, is deployed in the field network with multiple waterproofing solutions. For instance, water-blocking glue and double-layer plastic caps are used at the cable ends to isolate the atmosphere, a pulling unit with a swivel is employed for cable deployment to minimize wear on the end caps, and a horizontal waterproof cable closure is utilized at the fusion splice point. Additionally, breakthroughs in hollow-core fiber fusion splicing technologies, such as low-power discharge and mode field matching, have achieved 0.05dB fusion splice loss between hollow-core fibers and 0.25dB fusion splice loss with 54dB return loss between hollow-core fibers and standard solid-core single-mode fibers.
China Telecom’s Zhejiang branch said: “We have always maintained the leading position in the field of basic transmission networks. By undertaking the national key R&D project, we have demonstrated and verified the hollow-core fiber and 1.2Tbit/s transport system in the field network, and can offer detailed engineering data and demonstration applications. In the future, we will further cooperate with the industry to conduct research on a larger scope, and provide practical scenarios for the interconnection of distributed intelligent computing centers.”
China Telecom says they will continue to expand the hollow-core optical cable environment and build a platform for testing and verifying new technologies and applications oriented towards intelligent computing scenarios. This effort aims to continuously promote technological innovation and application expansion in the telecommunications industry.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, China Telecom received four awards at the “Asia’s Best Managed Companies Poll 2024” by FinanceAsia, a reputable financial magazine in Asia:
⚫ “Best Investor Relations in China” – Gold Award
⚫ “Best Managed Company in China” – Silver Award
⚫ “Best Telecommunication Services Company” – Silver Award
⚫ “Best Large-Cap Company in China” – Bronze Award
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/fibre/china-telecoms-claims-a-world-s-first-hollow-core-fibre-demonstration
https://www.chinatelecom-h.com/en/media/news/p240730.pdf
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
China Telecom, ZTE jointly build spatiotemporal cognitive network for digital transformation
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
Two of China’s state-owned telcos have taken stakes in new LEO satellite companies.
- China Telecom has set up a new fully owned subsidiary, Tiantong Satellite Technology Co., registered in Shenzhen with 1 billion Chinese yuan (US$138 million) paid-in capital. China Telecom, which is currently the only operator with a mobile satellite license, operates three Tiantong Geo orbit satellites, launched between 2016 and 2021, covering China, the western Pacific and its neighbors.
- In April China Mobile took a 20% stake in a new RMB4 billion ($551 million) state-owned company, China Shikong Xinxi Co., registered in Xiongan. China Satellite Network Group, the company behind Starnet, China’s biggest LEOsat project, will own 55%, and aerospace contractor Norinco, a 25% shareholder.
China Telecom will shutter its legacy satellite subsidiary, established in 2009, and transfer the assets into the new company.
The other new business, China Shikong, lists its scope as satellite communication, satellite navigation and remote sensing services.
The two investments come as China Starnet is readying to launch its first satellites in the second half of the year. It is aiming to build a constellation of 13,000, with the first 1,300 going into operation over the next five years, local media has reported.

In addition to Starnet, two other mass constellations are planned – the state-owned G60 and a private operator, Shanghai Hongqing. Neither has set a timetable. They will be playing catch up with western operators like Starlink and OneWeb, which are already operating thousands of commercial satellites.
Since foreign operators are forbidden from selling into China, it is not yet clear how China is going to structure its LEO satellite industry and what role precisely the new operators are going to play.
References:
Chinese telcos tip cash into satellite (lightreading.com)
China Mobile launches LEO satellites to test 5G and 6G – Developing Telecoms
Very low-earth orbit satellite market set to reach new heights | TelecomTV
5G connectivity from space: Exolaunch contract with Sateliot for launch and deployment of LEO satellites
LEO operator Sateliot joins GSMA; global roaming agreements to extend NB-IoT coverage
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
Satellite 2024 conference: Are Satellite and Cellular Worlds Converging or Colliding?
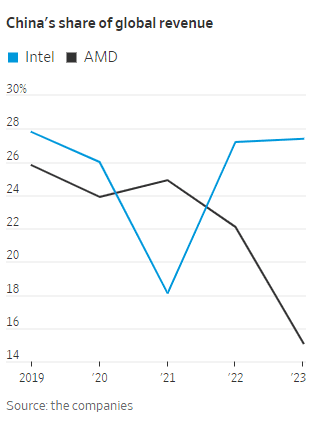
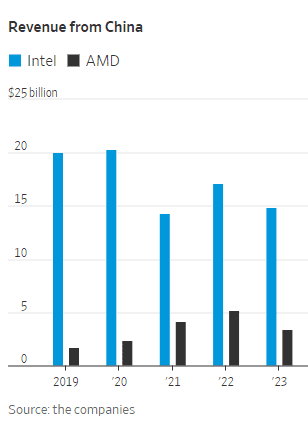
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s largest telecom firms were ordered earlier this year to phase out foreign computer chips from their networks by 2027. That news confirms and expands on reports from recent months. It was reported in the Saturday print edition of the Wall Street Journal (WSJ). The move will hit U.S. semiconductor processor companies Intel and Advanced Micro Devices. Asia Financial reported in late March that these retaliatory bans would cost the U.S. chip firms billions.
The deadline given by China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) aims to accelerate efforts by Beijing to halt the use of such core chips in its telecom infrastructure. The regulator ordered state-owned mobile operators to inspect their networks for the prevalence of non-Chinese semiconductors and draft timelines to replace them, the people said.
In the past, efforts to get the industry to wean itself off foreign semiconductors have been hindered by the lack of good domestically made chips. Chinese telecom carriers’ procurements show they are switching more to domestic alternatives, a move made possible in part because local chips’ quality has improved and their performance has become more stable, the people said.
Such an effort will hit Intel and AMD the hardest, they said. The two chip makers have in recent years provided the bulk of the core processors used in networking equipment in China and the world.
China’s MIIT, which oversees the regulation of the wireless, broadcasting and communication industries, didn’t respond to WSJ’s request for comment. China Mobile and China Telecom , the nation’s two biggest telecom carriers by revenue, also didn’t respond.
In March 2023, the Financial Times reported China is seeking to forbid the use of Intel and AMD chips, as well as Microsoft’s operating system, from government computers and servers in favor of local hardware and software. The latest purchasing rules represent China’s most significant step yet to build up domestic substitutes for foreign technology and echo moves in the US as tensions increase between the two countries. Among the 18 approved processors were chips from Huawei and state-backed group Phytium. Both are on Washington’s export blacklist. Chinese processor makers are using a mixture of chip architectures including Intel’s x86, Arm and homegrown ones, while operating systems are derived from open-source Linux software.
Beijing’s desire to wean China off American chips where there are homemade alternatives is the latest installment of a U.S.-China technology war that is splintering the global landscape for network equipment, semiconductors and the internet. American lawmakers have banned Chinese telecom equipment over national-security concerns and have restricted U.S. chip companies including AMD and Nvidia from selling their high-end artificial-intelligence chips to China.
China has also published procurement guidelines discouraging government agencies and state-owned companies from purchasing laptops and desktop computers containing Intel and AMD chips. Requirements released in March give the Chinese entities eight options for central processing units, or CPUs, they can choose from. AMD and Intel were listed as the last two options, behind six homegrown CPUs.
Computers with the Chinese chips installed are preapproved for state buyers. Those powered by Intel and AMD chips require a security evaluation with a government agency, which hasn’t certified any foreign CPUs to date. Making chips for PCs is a significant source of sales for the two companies.
China Mobile and China Telecom are also key customers of both chip makers in China, buying thousands of servers for their data centers in the country’s mushrooming cloud-computing market. These servers are also critical to telecommunications equipment working with base stations and storing mobile subscribers’ data, often viewed as the “brains” of the network. Intel and AMD have the lion’s share of the overall global market for CPUs used in servers, according to data from industry researcher TrendForce. In 2024, Intel will likely hold 71% of the market, while AMD will have 23%, TrendForce estimates. The researcher doesn’t break out China data.
China’s localization policies could diminish Intel and AMD’s sales in the country, one of the most important markets for semiconductor firms. China is Intel’s largest market, accounting for 27% of the company’s revenue last year, Intel said in its latest annual report in January. The U.S. is its second-largest market. Its customers also include global electronics makers that manufacture in China.
In the report, Intel highlighted the geopolitical risk it faced from elevated U.S.-China tensions and China’s localization push. “We could face increased competition as a result of China’s programs to promote a domestic semiconductor industry and supply chains,” the report said.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/china-telecom-intel-amd-chips-99ae99a9 (paywall)
https://www.ft.com/content/7bf0f79b-dea7-49fa-8253-f678d5acd64a
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China’s three state owned telecom operators have announced their subscriber totals for the month of December and for all of 2023. China’ Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) said the big three had a combined net increase of approximately 24.82M 5G package subscribers in China, boosting their combined 5G package subscriber base to nearly 1.373B.
As of the end of December, 5G package subscribers accounted for 80.2% and 78.1% of China Mobile’s and China Telecom’s total mobile subscriber bases, respectively.
C114.net reported that 3.377 million 5G base stations have been built, constituting 28.5 percent of the total mobile base stations. There are 23.02 million ports with gigabit network service capabilities. More than 80% of administrative villages nationwide now have 5G connectivity, telecoms portal.
The foundation of the Internet of Things (IoT) is constantly being consolidated, with mobile IoT terminal users accounting for 57.5% of the total number of mobile network terminal connections. Technological industry innovation and development, the commercial deployment of 5G customized base stations and 5G lightweight technology, and the launch of the world’s first satellite communication smartphone, 6G, quantum communication, artificial intelligence and other innovative capabilities have significantly improved.
- China Mobile ended last year with 794.5 million subscribers to its 5G package (contract), while its total mobile subscriber base reached 991 million.
- China Telecom had a total of 407.7 million mobile users, of which 318.66 million had signed up to a 5G package (up by 50.7 million during 2023).
- China Unicom’s 5G package subscriber total hit 259.6 million by the end of last year, though disclosure on total mobile subscribers has not been provided. China Unicom also reported that there were 8,563 “virtual 5G industry private network” subscriber for the month of December which was an increase of 554 month-on-month and up 4,758 since the end of 2022.
Mobile Subscriber Stats for China’s Three Main Carriers (Unit: Millions)
| Operator | December 2023 Month-end Total |
% of Combined Installed 5G Sub Base |
December 2023 Net Change |
Net Change Since Prior Year-End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China Mobile | 991.00 | 0.05 | 15.99 | |
| 5G Package Subs | 794.50 | 57.87% | 15.70 | 180.50 |
| China Telecom | 407.77 | 0.54 | 16.59 | |
| 5G Package Subs | 318.66 | 23.21% | 4.03 | 50.70 |
| China Unicom | Not Available | |||
| 5G Package Subs | 259.64 | 18.91% | 5.08 | 46.91 |
China’s fourth 5G telecom network operator, China Broadnet, saw its 5G user base surpass 20 mln on October 19, the company revealed at the 2023 World 5G Convention held in Zhengzhou from December 5-7. Since that time, however, China Broadnet has not publicly released any updated 5G subscriber statistics.
Broadnet officially launched 5G network services just 19 months ago, on June 27, 2022. Because Broadnet is not yet reporting its 5G subscriber totals on a regular, monthly basis, Marbridge is not yet integrating its totals with those of China’s three more established telecom operators above.
Cautionary Note:
The Chinese telecom operators specifically report numbers for 5G packages, rather than citing 5G service users or connections, as while customers may have signed up for a 5G service package offer, that doesn’t necessarily mean they have a 5G-enabled device that enables them to hook up to their network operator’s 5G network, or indeed that their service provider is offering 5G services in their area just yet.

In addition to the growing 5G market in China, the fixed broadband segment is also very large. China Mobile had a total of 298 million wireline broadband customers at the end of December 2023, and throughout the year it added a total of 26 million fixed customers. China Telecom had 190 million fixed broadband subscribers by the year end, having added a total of 9.26 million wireline broadband users in 2023. China Unicom’s operational statistics for the last month of 2023 did not provide a breakdown of broadband customers.
References:
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1253372.html
Nokia to exit TD Tech joint venture with Huawei due to U.S.-China tensions
According to a January 21,2024 article in the South China Morning Post, Nokia is set to exit its joint venture with Huawei in the telecommunications sector due to US-China tensions. Nokia has found new buyers for its majority stake in a Beijing-based joint venture with Huawei Technologies, after a proposed deal fell through last year following strong protest by the Chinese partner. The article states that Nokia will sell its majority stake in TD Tech [1.] to a group that will be jointly controlled by Huawei and a group of entities that include the government-owned Chengdu High-Tech Investment Group and Chengdu Gaoxin Jicui Technology Co, as well as venture capital firm Huagai, according to a disclosure published on Friday by the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR).

Huawei had a 14% share in the Chinese smartphone market in the third quarter 2023, putting it in fifth place behind its spin-off Honor and rivals Oppo, Vivo and Apple, data from market intelligence firm Counterpoint Research showed. According to Statista, Huawei had a 58% share of all 5G base stations in China as of the 3rd quarter 2023. Its closest competitor was ZTE with a market share of 31%. Nokia had only a 2% market share.