Uncategorized
Semtech LoRa® PHY technology enables Amazon Sidewalk to expand while supporting fixed and mobile IoT endpoints
Introduction:
Semtech Corporation, a leading provider of high-performance semiconductor, Internet of Things (IoT) systems and cloud connectivity service solutions, is the creator and primary owner of the intellectual property (IP) for LoRa® technology, providing the Physical layer chips (PHY transceivers) used in LoRaWAN – the very popular Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) for IoT endpoints.
The Camarillo, CA based company last week announced that LoRa® technology will continue to serve as the core radio modulation for Amazon Sidewalk across all markets in this year’s Sidewalk international expansion. Sidewalk’s global expansion officially begins in Canada and Mexico with further expansion to other international regions is scheduled for later in 2026. The network is projected to expand to over 30 new countries by year’s end.
Amazon Sidewalk is increasingly viewed as a commercial success in terms of infrastructure deployment and technical capability, transitioning from a niche smart home feature to a broad, LoRa-based Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN). While it faced initial skepticism regarding privacy and adoption, the network now boasts massive, passive coverage of over 95% of the U.S. population and is undergoing rapid international expansion.
Architectural role of LoRa in Sidewalk:

LoRa is the de facto wireless platform of LPWANs for IoT. Semtech’s LoRa chipsets connect sensors to the Cloud and enable real-time communication of data and analytics that can be utilized to enhance efficiency and productivity. LoRa devices enable smart IoT applications that solve some of the biggest challenges facing our planet: energy management, natural resource reduction, pollution control, and infrastructure efficiency.
Amazon Sidewalk aggregates spectrum in unlicensed bands and combines multiple physical layers, with Semtech’s LoRa modulation providing the long‑range, low‑power tier for neighborhood‑scale coverage beyond home Wi‑Fi and short‑range Personal Area Networks (PANs). By using ONLY LoRa as the core wide‑area PHY, Sidewalk evolves from a home‑centric LAN into a geographically distributed WAN that can support both fixed and mobile IoT endpoints across dense residential environments.
Network scale and coverage:
Sidewalk already covers roughly 95% of the U.S. population, making it one of the largest license‑free, consumer‑facing LPWA deployments, and the 2026 roadmap extends the footprint into Canada and Mexico first, followed by additional international markets later in the year. This expansion effectively turns Sidewalk into a multi‑continent overlay network, leveraging existing consumer premises equipment and LoRa‑enabled endpoints to provide persistent connectivity without requiring dedicated operator‑grade RAN build‑outs.
Technology differentiation vs other LPWAN options:
NB-IoT (included in ITU-R M.2150 IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT standard) holds the largest LPWAN share at roughly 54%–58% of total LPWAN connections, due to massive adoption in China which accounts for approximately 84% of all global NB-IoT connections. Outside of China, LoRaWAN is the clear market leader with a 41% share of connections. As of late 2025, there are over 125 million LoRaWAN end devices deployed globally, growing at a 25% annual rate. It is the preferred choice for private IoT networks, specifically in smart buildings, agriculture, and industrial asset tracking.
LoRa’s combination of long range, ultra‑low power operation, and mature ecosystem (silicon, gateways, and cloud stacks) gives Sidewalk a differentiated profile relative to alternatives such as narrowband cellular IoT and other unlicensed LPWAN modulation methods. For Amazon, anchoring Sidewalk on LoRa reduces RF and protocol fragmentation on the end‑device side while preserving flexibility to layer higher‑level Sidewalk services and security on top of the underlying LoRa/LoRaWAN protocol stack.
Market and ecosystem context:
Amazon Sidewalk now sits alongside large industrial and enterprise LoRaWAN networks, reinforcing LoRa’s position as the leading low‑power wide‑area connectivity technology in unlicensed spectrum. The LoRaWAN IoT connectivity market is forecast to grow from about 10.7 billion USD in 2025 to 44.8 billion USD by 2030 (33.1% CAGR), while LoRaWAN deployments have surpassed 125 million devices globally with a 25% CAGR, signaling a robust runway for Sidewalk‑class Massive IoT use cases.
Implications for device and service design:
For device OEMs and service providers, Amazon’s decision effectively de‑risks LoRa as a long‑term connectivity bet for consumer and prosumer IoT, given Sidewalk’s trajectory to tens of millions of active devices worldwide. Vendors integrating LoRa‑based designs can now target both traditional LoRaWAN operator networks and the Sidewalk ecosystem, enabling common hardware platforms to support smart home, safety, environmental monitoring, and asset‑tracking applications at neighborhood and city scale.
LoRa Enables Sidewalk’s Technical Evolution:
Chirp spread spectrum (CSS) modulation in LoRa technology provides the technical foundation enabling Amazon Sidewalk’s new capabilities:
- Enhanced Network Density: LoRa multi-spreading factor capability optimizes longer range and shorter time-on-air, supporting higher device concentrations in urban environments while maintaining reliable connectivity.
- Location-Based Services: Unique location accuracy service that combines the power of Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and GPS enables a new class of location aware devices that don’t need expensive cellular solutions for asset tracking applications.
- Hub-Less Deployments: Utilized for both out-of-band-diagnostics as well as signaling radio for battery-powered cameras, LoRa lowers the need for hubs/repeaters, reducing infrastructure complexity for consumers while extending effective coverage areas.
Proven Heritage of LoRa in Massive IoT Networks:
Semtech’s LoRa technology has been deployed by more than 170 major mobile network operators globally, with over 500 million connected devices across smart cities, utilities, logistics, unmanned aircraft systems, and industrial applications. This proven deployment heritage provides the technical foundation and ecosystem maturity required for Amazon Sidewalk’s global expansion.
The technology’s long-range capability, extending connectivity up to several kilometers from Sidewalk bridge devices, combined with its ability to penetrate buildings and operate in dense urban environments makes it uniquely suited for neighborhood-scale networks. LoRa provides free, long-range connectivity that consumers can rely on for years of battery-powered operation.
Building on CES 2026 Momentum:
Ring showcased its expanded product portfolio using LoRa at CES 2026, introducing comprehensive sensor families for security, safety and home automation. These products join the growing network of devices powered on Sidewalk, including water leak and freeze detection sensors, wearable devices and environmental monitoring solutions, all leveraging the connectivity advantages of LoRa.
The Sidewalk network’s architecture—combining LoRa for long-range communication with Bluetooth Low Energy for device setup—creates a robust, resilient IoT infrastructure that can scale to support millions of devices while maintaining the ultra-low power consumption critical for battery-operated sensors and cameras.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Semtech:
Semtech Corporation (Nasdaq: SMTC) is a leading provider of high-performance semiconductor, IoT systems and cloud connectivity service solutions dedicated to delivering high-quality technology solutions that enable a smarter, more connected and sustainable planet. Our global teams are committed to empowering solution architects and application developers to develop breakthrough products for the infrastructure, industrial and consumer markets.
Amazon’s Sidewalk Low Power WAN is a dud, despite four announced partnerships
From LPWAN to Hybrid Networks: Satellite and NTN as Enablers of Enterprise IoT – Part 2
Enterprise IoT and the Transformation of UK Telecom Business Models – Part 1
Empowering Low-Power Wide-Area Networks to Meet the IoT Challenge
NTT’s IoT Services for Sustainability supported by new LoRaWAN low power network
IoT for Smart Cities: LoRa with Semtech Silicon as a leading LPWAN
LoRa Alliance and OMS Group integrate smart metering standards which may result in massive scale for IoT
LoRaWAN gains momentum: NEC LoRaWAN server + New Zealand nationwide network
LoRaWAN and Sigfox lead LPWANs; Interoperability via Compression
New LoRaWAN™ network for IoT in Saudi Arabia from Actility and machinestalk
LPWAN to Application standardization within the IETF
Taara Lightbridge Pro: an ultra reliable wireless optical communications system for 5G mobile backhaul
Google moonshot factory X graduate Taara [1.] is launching Lightbridge Pro, a wireless optical communications system designed to deliver 99.999% (“five nines”) carrier-grade uptime for 20 Gbps backhaul, addressing weather-related reliability issues in Free Space Optical Communication (FSOC).
Lightbridge Pro is designed for seamless integration into carrier-grade networks, including mobile backhaul and mission-critical infrastructure. By integrating intelligent optical switching directly into the hardware, it automatically reroutes traffic to fiber or RF backups during, for example, heavy fog or rain.
Note 1. Tara says that for the last eight years, they have been developing novel technology that uses beams of light to deliver high-speed, secure connectivity where fiber and wireless can’t – bringing abundant access to everyone, everywhere.

“As demand for data soars, existing connectivity solutions are reaching their limits. What if we could harness the power of light to deliver a better, faster, more efficient connection, without the need for cables?” Mahesh Krishnaswamy, Founder and CEO.
Key Features and Impact:
Carrier-Grade Reliability: Lightbridge Pro is purpose-built for high-availability requirements of 5G mobile backhaul,, and city-wide network providers.
Intelligent Switching: The system ensures seamless, near-instantaneous, switching between optical and backup connections (like RF) to maintain continuity.
Performance: It delivers up to 20 Gbps full-duplex capacity, bridging gaps where fiber installation is too costly or difficult.
Global Application: Already deployed in over 20 countries, the technology is used in dense urban, rural, and disaster recovery scenarios.
Operational Efficiency: The system includes comprehensive Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, and Security (FCAPS) management, suitable for integration with existing Operations and Business Support Systems (OSS/BSS).
Deployment and Use Cases: Tara’s platform is aimed at large-scale network operators and mission-critical communications, particularly in dense urban environments or rough terrain where laying fiber is not economically viable.
Current Partners: Taara Lightbridge is already deployed in more than 20 countries, from dense urban cores to remote terrain to disaster recovery scenarios. Carriers already using Taara’s technology include Airtel, T-Mobile, SoftBank, Digicel, and Liquid Intelligent Technologies. T-Mobile previously deployed Taara units for high-capacity backhaul at Coachella and the Albuquerque Balloon Festival.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Taara is showcasing these new solutions at Mobile World Congress (MWC) Barcelona 2026 where the start-up will also be announcing a new photonics-based wireless optical system designed for even greater density and scalability.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Editor’s Analysis:
Taara’s Lightbridge Pro looks like a serious, carrier-minded evolution of free-space optics (FSO) for 5G backhaul, but its real value will hinge on how well the “five nines” claim holds up under diverse atmospheric and operational conditions in the field.
Risks and open questions:
-
SLA realism: “Five nines” across mixed optical/RF paths is a strong claim; operators will want multi-year availability data by climate region, plus clear modeling of residual outage during extreme events where both optical and RF paths can degrade.
-
Operational complexity: Even with integrated switching and FCAPS, adding a new transport technology introduces planning, monitoring, and skillset overhead versus staying on homogeneous fiber/microwave.
-
Regulatory and spectrum: Where RF is the backup, spectrum licensing, interference management, and coordination with existing microwave/E‑band layers will affect total cost and deployment speed, and those aspects are not detailed in the product material.
Overall assessment:
For 5G mobile backhaul, Lightbridge Pro is best viewed as a targeted tool for high-value, hard-to-fiber routes, and for rapid-capacity or temporary deployments, rather than a universal replacement for fiber or microwave. If Taara’s integrated protection switching performs as advertised at scale, it meaningfully advances FSO from “interesting niche” to a credible part of a multi-layer transport strategy for carriers and city-scale operators.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.taaraconnect.com/post/introducing-lightbridge-pro#
https://www.taaraconnect.com/product/lightbridge-pro
https://www.taaraconnect.com/about
Google X spin-out Taara and Digicomm International partner to offer high speed wireless communications
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Networks +15% in 2025; Ookla: Global Reality Check on 5G SA and 5G Advanced in 2026
Palo Alto Networks and Google Cloud expand partnership with advanced AI infrastructure and cloud security
Google’s Project Suncatcher: a moonshot project to power ML/AI compute from space
Google Cloud announces TalayLink subsea cable and new connectivity hubs in Thailand and Australia
India 5G subscribers top 400 Million with rapid adoption continuing without 5Gi
With over 400 million 5G subscribers, India now ranks #2 globally (China is #1 [1.]). What’s even more remarkable is the speed of adoption after 5G spectrum auctions were repeatedly delayed. Jyotiraditya Scindia, India’s union minister for communications and development of the North Eastern Region, said the country is “setting new global benchmarks in scale, speed and digital transformation.”
According to figures cited by the minister, the country’s 5G subscriber base now exceeds that of other major markets, including the United States with around 350 million users, the European Union with 200 million, and Japan with 190 million. China remains the global leader, with more than 1.2 billion 5G connections.
Note 1. China has over 1.2 billion 5G subscribers as of late 2025, representing over 60% of all mobile connections in the country, driven by massive infrastructure rollout and strong adoption across major operators like China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom, making it the global leader in 5G penetration.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Bharti Airtel and Reliance Jio Infocomm spearheaded the launch, becoming the first carriers to operationalize 5G networks and achieving significant subscriber acquisition, with each surpassing the 50 million user milestone within their initial year of service [1]. Vodafone Idea subsequently entered the 5G market with launches in specific cities during 2025.
State-owned telecom provider BSNL is projected to launch 5G services within the current year [1]. This deployment is slated to exclusively utilize India’s indigenously developed telecom technology stack, a collaborative effort involving the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT), Tejas Networks, and Tata Consultancy Services (TCS).
As of the close of 2025, the national 5G infrastructure comprised 518,854 operational base stations, marking a substantial increase from approximately 464,990 recorded at the start of the year [1]. The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) reported the deployment of 4,112 new 5G base transceiver stations (BTS) in December 2025 alone, contributing to the year-end cumulative total
- Infrastructure Growth: Rapid BTS deployment, exceeding 4,100 new installations in December 2025 alone, demonstrates intense network densification, with coverage now reaching most districts.
- Vodafone Idea’s Entry: Vi, after initial delays, commenced its phased 5G service introduction in select cities during 2025.
- BSNL’s Indigenous Strategy: The state-owned operator is slated to launch 5G using India’s homegrown stack (C-DOT, Tejas, TCS), showcasing self-reliance in telecom technology.
- Market Dynamics: The rapid expansion aims to unlock enterprise and consumer use cases, positioning India as a significant global 5G player, despite ongoing discussions about monetization and infrastructure investment.
Technical & Deployment Highlights:
- Architecture: A mix of 5G SA (Jio) and 5G NSA (Airtel) is prevalent, with SA offering lower latency and true 5G capabilities.
- Spectrum: Operators utilize various bands, including sub-6 GHz (3.3 GHz, 26 GHz) for broad coverage and capacity.
- Deployment Pace: Driven by ministerial targets, operators installed BTS at an accelerated pace, focusing initially on high-revenue urban centers.
This author deeply regrets that the Telecommunications Standards Development Society India (TSDSI)’s 5Gi RIT specification, included as part of the ITU-R M.2150 IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT standard, was not implemented in India. On January 25, 2022, TSDSI told the Telecommunication Engineering Center (TEC) under the DoT not to proceed with the adoption of 5Gi as a national 5G standard. TSDSI added that it “does not intend to further update 5Gi specifications.”
References:
OpenSignal: real world 5G deployment in India, market status & what happened to 5Gi?
Nokia Executive: India to Have Fastest 5G Rollout in the World; 5Gi/LMLC Missing!
LightCounting & TÉRAL RESEARCH: India RAN market is buoyant with 5G rolling out at a fast pace
Nokia’s Bell Labs to use adapted 4G and 5G access technologies for Indian space missions
Reliance Jio in talks with Tesla to deploy private 5G network for the latter’s manufacturing plant in India
Communications Minister: India to be major telecom technology exporter in 3 years with its 4G/5G technology stack
India to set up 100 labs for developing 5G apps, business models and use-cases
Adani Group to launch private 5G network services in India this year
Adani Group planning to enter India’s long delayed 5G spectrum auction
At long last: India enters 5G era as carriers spend $ billions but don’t support 5Gi
5G in India to be launched in 2023; air traffic safety a concern; 5G for agricultural monitoring to be very useful
Bharti Airtel to launch 5G services in India this August; Reliance Jio to follow
5G Made in India: Bharti Airtel and Tata Group partner to implement 5G in India
India government wants “home-grown” 5G; BSNL and MTNL will emerge as healthy
5G in India dependent on fiber backhaul investments
Hindu businessline: Indian telcos deployed 33,000 5G base stations in 2022
Arm Holdings unveils “Physical AI” business unit to focus on robotics and automotive
- Cloud and AI: Focused on data center and AI infrastructure solutions.
- Edge: Encompassing mobile devices, personal computing, and related technologies.
- Physical AI: Integrating its automotive business with robotics initiatives.
- Market Opportunity: Acknowledged the significant growth potential in robotics, from industrial automation to humanoid robots, driven by AI advancements.
- Synergy with Automotive: Combined robotics and automotive within the unit due to shared technical needs, such as power efficiency, safety, and sensor technology.
- Strategic Reorganization: Positioned Physical AI as a third core business line, alongside Cloud & AI and Edge (mobile/PC), to better focus resources and expertise.
- Customer Demand: Responding to existing customers (like automakers and robotics firms such as Boston Dynamics) who are integrating more AI into physical devices.
- Enhancing Real-World Impact: Aims to deliver solutions that fundamentally improve labor, productivity, and potentially GDP, moving AI from data centers to physical interactions
2026 Consumer Electronics Show Preview: smartphones, AI in devices/appliances and advanced semiconductor chips
Marvell shrinking share of the RAN custom silicon market & acquisition of XConn Technologies for AI data center connectivity
Groq and Nvidia in non-exclusive AI Inference technology licensing agreement; top Groq execs joining Nvidia
The Internet of Things (IoT) explained along with ARM’s role in making it happen!
Sebastian Barros: Using telecom networks for weather sensing requires a strategic telco shift from connectivity providers to ecosystem orchestrators
Telecom networks for weather sensing can be facilitated by using existing microwave links and 4G/5G signals as virtual sensors, detecting changes in signal strength and timing caused by rain, humidity, and temperature, effectively turning vast infrastructure into a dense, real-time atmospheric monitoring system for improved forecasting and disaster alerts, notes Sebastian Barros on Substack. By analyzing signal attenuation, telecom networks create high-resolution weather maps, complementing traditional methods like radar. Yet very few network operators or vendors have attempted to use telecommunications infrastructure for dense atmospheric sensing. The data exists but is rarely activated, processed, or disclosed.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) [1.] based atmospheric estimation, rain attenuation on microwave links, and radio refractivity effects have been studied for more than 20 years. The physics is well understood and already embedded in network planning and synchronization systems. There are eight million radio sites span cities, roads, ports, factories, and borders. Every site has power, compute, backhaul, antennas, timing, and regulatory protection. Today, the network only provides connectivity. Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) starts to change that. It repurposes radio waves for radar-like sensing, including presence detection, velocity, Doppler shift, and range.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Note 1. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is the umbrella term for satellite constellations like the U.S.’s GPS, Russia’s GLONASS, the EU’s Galileo, and China’s BeiDou, which provide global positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) services. GNSS receivers use signals from these orbiting satellites to calculate precise locations on Earth, offering increased accuracy and reliability compared to relying on a single system, enabling applications from smartphone navigation to autonomous vehicles and precision agriculture.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Receiver: Your end point receiving device (phone, car navigation, etc.) picks up signals from several of these satellites.
- Calculation: By measuring the time it takes for signals to arrive from at least four satellites, the receiver performs complex calculations (trilateration) to pinpoint your exact position.
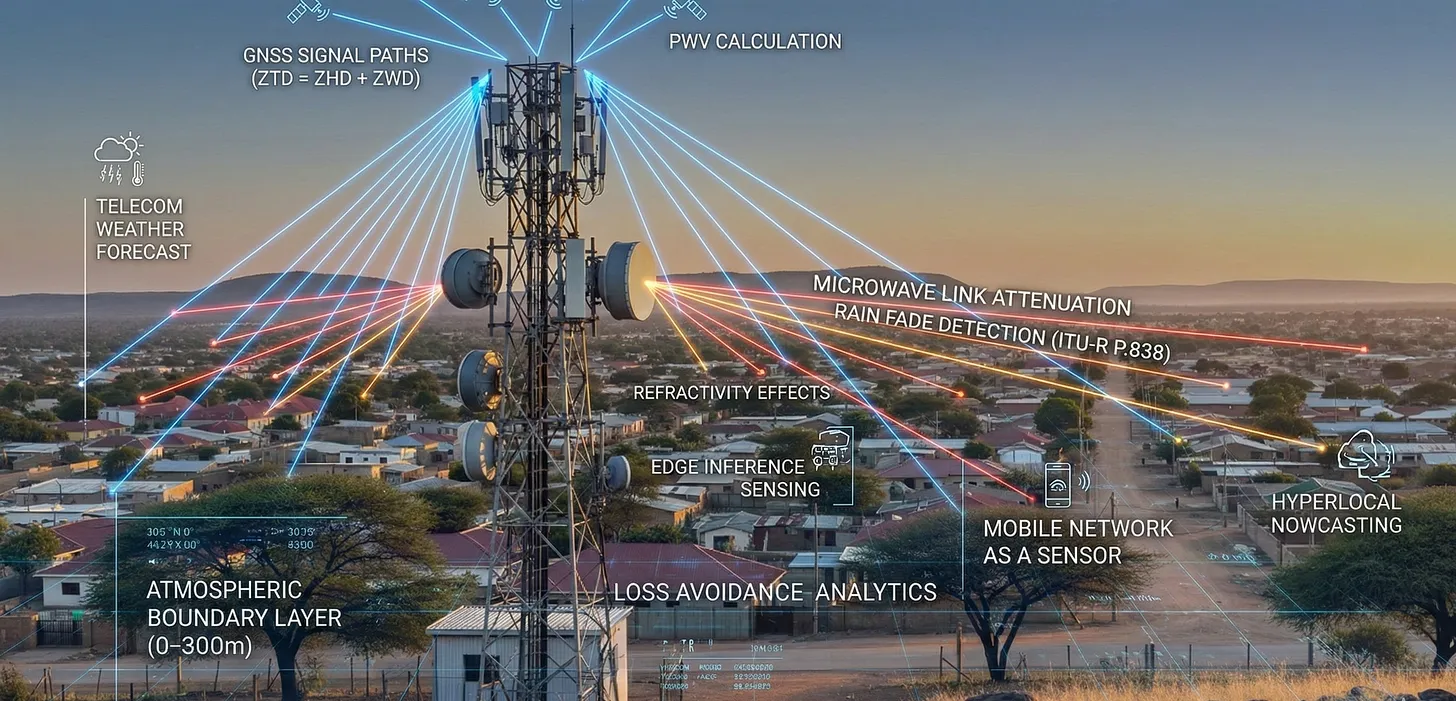
Telecom networks can expose not just connectivity but structured awareness: object motion, crowd flow, anomalies, risks, and environmental state. In real time, across every continent. The infrastructure already exists. What’s missing is the architecture and the will to build the sensing layer on top of it. With dense, real-time sensing already in place, telecom can expose environmental intelligence through Open Gateway APIs, just as it exposes location or quality today. No new hardware. No new towers. Just activation, inference at the edge, and exposure.

- Data Siloing: The data produced by ISAC currently remains locked within the physical (PHY) and Media Access Control (MAC) layers of the network. It is primarily used for internal network optimization and is not exposed to external applications or platforms.
- Lack of Abstraction and APIs: There are no standard abstraction layers or Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that would allow external systems (e.g., weather services, autonomous navigation systems, urban infrastructure management) to access and interpret the raw sensing data.
- Absence of Data Fusion Standards: There is no standard methodology to fuse the output from ISAC with data from other sensing modalities (e.g., vision, audio, thermal sensors). This prevents the creation of a comprehensive, multimodal sensing mesh.
- Missing Marketplace: The lack of standardized access and integration means there is no marketplace for this valuable data, which stifles innovation and collaboration across different industries that could benefit from real-world awareness information.
References:
https://sebastianbarros.substack.com/p/telecom-built-the-worlds-best-weather
https://sebastianbarros.substack.com/p/telco-network-as-a-sensor-is-a-huge
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7413260481743769600/
https://www.euspa.europa.eu/eu-space-programme/galileo/what-gnss
2025 Year End Review: Integration of Telecom and ICT; What to Expect in 2026
Smart electromagnetic surfaces/RIS: an optimal low-cost design for integrated communications, sensing and powering
Deutsche Telekom: successful completion of the 6G-TakeOff project with “3D networks”
Smart electromagnetic surfaces/RIS: an optimal low-cost design for integrated communications, sensing and powering
Researchers at Xidian University in China have pioneered a smart electromagnetic surface that converts ambient electromagnetic waves into electrical power, marking a potential leap in stealth and wireless technologies. This meta-surface innovation merges advanced electromagnetic engineering with communication principles, enabling self-powered systems for demanding applications. The self-sustaining electronic system integrates wireless information transfer and energy harvesting and has the potential to upend the dynamics of electronic warfare.
The surface facilitates simultaneous energy harvesting and data transmission, drawing power from radar or environmental signals without traditional batteries. Xidian’s team highlights its role in “electromagnetic cooperative stealth,” where networked platforms collaboratively minimize radar cross-sections and sensor detectability. Prototypes demonstrate viability for real-time wave manipulation, building on metasurface designs that dynamically adjust phase and amplitude.
The researchers said this included investigating “electromagnetic cooperative stealth,” where multiple entities work together to reduce their visibility to radar and electromagnetic sensors. In electronic warfare, the technology flips the script on radar threats: stealth aircraft could harvest enemy beams for propulsion or comms, reducing logistical vulnerabilities. This cooperative approach extends to multi-asset formations, enhancing collective invisibility across spectra.
Early tests align with broader Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS), a two-dimensional reflecting surface. RIS advancements facilitate beam steering up to ±45° with low side lobes. According to a paper published in the IEEE Internet of Things magazine last year, RIS could also be used in anti-jamming technology, unmanned aerial vehicle communication and radio surveillance – all of which are difficult to do using older optimization tools.
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces can also be configured to create intentional radio “dead zones” to mitigate interference and reduce the risk of eavesdropping, according to German electronics manufacturer Rohde & Schwarz. The European Space Agency has further highlighted RIS as a candidate technology for satellite-to-ground communications, where controllable reflection and redirection of signals could help route links around physical obstacles.

For telecommunications, the surface promises 6G breakthroughs like integrated sensing and powering satellites or base stations. China’s lead here could accelerate reconfigurable networks, improving coverage in non-line-of-sight scenarios. Ongoing refinements target complex interactions for higher precision. By including sensing, communication and power into one hardware platform, the device could allow for a range of advanced applications while reducing eavesdropping and interference.
“Ultimately, it is expected to have a broad impact on 6G communications, the Internet of Things, intelligent stealth and other related fields,” the team said in a paper published in the peer-reviewed journal National Science Review last month. Many scientists say that a key area for next-generation wireless communications will be the transmission channel.
Researchers from Fudan University, the University of Sydney and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization note that, when combined with artificial intelligence (AI), this technology could significantly enhance the security of air-to-ground Internet of Things (IoT) links.
In their latest publication, the Xidian University team describes RIS as a “powerful solution” for future wireless networks, citing its low cost, high programmability and ease of deployment. However, for 6G systems, RIS must support both communication and sensing on a unified hardware platform by integrating data transmission and radar-like functionality to lower cost and optimize spectrum and hardware resource utilization.
Addressing this requirement will demand architectures that can jointly manipulate both scattered electromagnetic waves and actively radiated signals. The researchers propose that an electromagnetic all-in-one radiation–scattering RIS architecture could provide a viable path to meeting this dual-control challenge. “This achieves significant savings in physical space and cost while ensuring multifunctionality across diverse application scenarios,” the team said. The RIS system could also work in a receiver mode to harvest wireless energy to be used to power the meta-surface itself or charge other electronic devices, the paper added.
It could be used for line-of-sight wireless communication, where there is a direct, unobstructed path between a transmitter and receiver, as well as non-line-of-sight wireless communication, in which there is no direct visual link due to physical barriers like buildings.
The proposed RIS “stands out as the optimal low-cost design” for integrated communication and sensing. “In the future, this architecture could enable the development of environment-adaptive integrated sensing and communication systems, micro base stations and relay integrated systems, as well as self-powered sensing systems,” the team said.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10907868
Nokia sees new types of 6G connected devices facilitated by a “3 layer technology stack”
Electromagnetic Signal & Information Theory (ESIT): From Fundamentals to Standardization-Part I.
Electromagnetic Signal and Information Theory (ESIT): From Fundamentals to Standardization-Part II.
IMT Vision – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond
ITU-R WP5D: Studies on technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 100 GHz
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
Excerpts of ITU-R preliminary draft new Report: FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS OF TERRESTRIAL IMT SYSTEMS TOWARDS 2030 AND BEYOND
Juniper Research: Global 6G Connections to be 290M in 1st 2 years of service, but network interference problem looms large
Groq and Nvidia in non-exclusive AI Inference technology licensing agreement; top Groq execs joining Nvidia
AI chip startup Groq [1.] today announced that it has entered into a non-exclusive licensing agreement with Nvidia for Groq’s AI inference technology [2.]. The agreement reflects a shared focus on expanding access to high-performance, low cost inference. As part of this agreement, Jonathan Ross, Groq’s Founder, Sunny Madra, Groq’s President, and other members of the Groq team will join Nvidia to help advance and scale the licensed technology. Groq will continue to operate as an independent company with Simon Edwards stepping into the role of Chief Executive Officer. GroqCloud will continue to operate without interruption. It remains to be seen how Groq’s new collaboration with Nvidia will effect its recent partnership with IBM.
Note 1. Founded in 2016, Groq specializes in what is known as inference, where artificial intelligence (AI) models that have already been trained respond to requests from users. While Nvidia dominates the market for training AI models (see Note 2.), it faces much more competition in inference, where traditional rivals such as Advanced Micro Devices have aimed to challenge it as well as startups such as Groq and Cerebras Systems.
Note 2. Training AI models (used by Nvidia GPUs) involves teaching a model to learn patterns from large amounts of data, while AI “inferencing” refers to using that trained model to generate outputs. Both processes demand massive computing power from AI chips.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Groq has achieved a significant financial milestone, elevating its post-money valuation to $6.9 billion from $2.8 billion following a successful $750 million funding round in September. The company distinguishes itself in the competitive AI chip landscape by employing a unique architectural approach that does not rely on external high-bandwidth memory (HBM) chips. This design choice, leveraging on-chip static random-access memory (SRAM), mitigates the supply chain constraints currently impacting the global HBM market.
The LPU (Language Processing Unit) architecture, while enhancing inference speed for applications like chatbots, currently presents limitations regarding the maximum size of AI models that can be efficiently served. Groq’s primary competitor utilizing a similar architectural philosophy is Cerebras Systems, which has reportedly commenced preparations for an initial public offering (IPO) as early as next year. Both companies have strategically secured substantial contracts in the Middle Eastern market.
Nvidia’s investments in AI firms span the entire AI ecosystem, ranging from large language model developers such as OpenAI and xAI to “neoclouds” like Lambda and CoreWeave, which specialize in AI services and compete with its Big Tech customers. Nvidia has also invested in chipmakers Intel and Enfabrica. The company made a failed attempt around 2020 to acquire British chip architecture designer Arm Ltd. Nvidia’s wide-ranging investments — many of them in its own customers — have led to accusations that it’s involved in circular financing schemes reminiscent of the dot-com bubble. The company has vehemently denied those claims.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
This deal follows a familiar pattern in recent years where the world’s biggest technology firms pay large sums in deals with promising startups to take their technology and talent but stop short of formally acquiring the target.
- A great example of that was Meta which in June invested ~$14.3 billion in Scale AI for a 49% stake in the company. That move valued the startup at around $29 billion. As part of that deal, 28 year old Alexandr Wang resigned as CEO of Scale AI to become Meta’s first-ever Chief AI Officer. He will remain on Scale AI’s board of directors. Wang’s team at the new “superintelligence” lab is tasked with building advanced AI systems that can surpass human-level intelligence.
- In a similar but smaller scale deal, Microsoft agreed to pay AI startup Inflection about $650 million in cash in an unusual arrangement that would allow Microsoft to use Inflection’s models and hire most of the startup’s staff including its co-founders, a person familiar with the matter told Reuters. The high-profile AI startup’s models will be available on Microsoft’s Azure cloud service, the source said. Inflection is using the licensing fee to pay Greylock, Dragoneer and some other investors, the source added, saying the investors will get a return of 1.5 times what they invested.
Bernstein analyst Stacy Rasgon wrote in a note to clients on Wednesday after Groq’s announcement:
“The Nvidia-Groq deal appears strategic in nature for Nvidia as they leverage their increasingly powerful balance sheet to maintain dominance in key areas…..Antitrust would seem to be the primary risk here, though structuring the deal as a non-exclusive license may keep the fiction of competition alive (even as Groq’s leadership and, we would presume, technical talent move over to Nvidia). Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang’s “relationship with the Trump administration appears among the strongest of the key U.S. tech companies.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang recently dedicated a significant portion of his 2025 GTC 2025 conference keynote speech to emphasize that Nvidia intends to maintain its market dominance as the AI sector increasingly transitions its focus from model training to inference workloads. Huang delivered two major GTC keynotes in 2025: The primary annual conference held in San Jose, California, in March 2025 and a second GTC in Washington, D.C., in October 2025. At these events, he emphasized the rise of “reasoning AI” and “agentic AI” as the drivers for an unprecedented 100x surge in demand for inference computing in just a couple of years. Huang announced that the new Blackwell system, designed as a “thinking machine” for reasoning, was in full production and optimized for both training and large-scale inference workloads.
Huang shared a vision of moving from traditional data centers to “AI factories“—ultra-high-performance computing environments designed specifically to generate intelligence at scale, positioning investment in Nvidia’s infrastructure as an economic necessity.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.arm.com/glossary/ai-inference
IBM and Groq Partner to Accelerate Enterprise AI Inference Capabilities
Sovereign AI infrastructure for telecom companies: implementation and challenges
AI wireless and fiber optic network technologies; IMT 2030 “native AI” concept
Custom AI Chips: Powering the next wave of Intelligent Computing
OpenAI and Broadcom in $10B deal to make custom AI chips
Reuters & Bloomberg: OpenAI to design “inference AI” chip with Broadcom and TSMC
Analysis: OpenAI and Deutsche Telekom launch multi-year AI collaboration
Expose: AI is more than a bubble; it’s a data center debt bomb
Will the wave of AI generated user-to/from-network traffic increase spectacularly as Cisco and Nokia predict?
Ookla: FWA Speed Test Results for big 3 U.S. Carriers & Wireless Connectivity Performance at Busy Airports
Ookla just released two new reports based on Speedtest Intelligence data, revealing critical shifts in how Americans connect to the Internet- from their homes and from the country’s 50 busiest airports.
Key findings from the first report:
- T-Mobile, AT&T and Verizon — adding 1.04 million new subscribers in Q3 2025 bringing the total number of FWA customers to 14.7 million, which is slightly more than 12.5% of the 117.4 million U.S. households with broadband, according to the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2024 American Community Survey.
- T-Mobile, Verizon and AT&T all experienced declines in both their median download and upload speeds during Q2 2025 and Q3 2025.
- T-Mobile is the FWA speed leader with median download speed of 209.06 Mbps for Q3 2025, which is approximately double that of AT&T’s median download speed of 104.63 Mbps in the same quarter.
- AT&T and T-Mobile customers in the 10th percentile of users are experiencing speed declines during peak hours in the late afternoon and evening. Verizon subscribers in the 10th percentile don’t have the same sorts of declines, indicating the operator’s enforcement of speed caps may be helping it deliver a more consistent experience to those customers.
- AT&T Internet Air’s latency is higher than its peers but it’s improving. AT&T’s median multi-server latency is ~ 67 milliseconds, “consistently higher” than Verizon (54 ms) and T-Mobile (50 ms) but a notable improvement from 78 ms in Q3 2024.
Separately, the analysts at New Street Research estimated AT&T, T-Mobile and Verizon can currently support up to 32 million FWA customers and they have already added nearly 50% of that number. Operators could potentially increase that load to 36 million following the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC) upper C-Band auction.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Ookla’s second report analyzes cellular and Wi-Fi performance across the top 50 U.S. airports by passengers. Key findings:
- Cellular network providers had a faster median download speed than Wi-Fi in most airports and more than twice as fast on average. The overall median download speed for cellular was 219.24 Mbps. Note that 5G/4G splits were not explicitly examined.
- Verizon was fastest in the most airports comparing among all mobile providers and airport Wi-Fi including ties.
- Airport Wi-Fi was faster than mobile networks in just over one-third of head-to-head comparisons (including ties), and faster than all mobile providers in five airports.
- Older Wi-Fi technologies may be holding back internet speed in airports with 72.9% of Speedtest samples on Wi-Fi 5 and older generation versus 46.0% in the U.S. overall.

Wi-Fi was faster than any mobile provider in these five airports:
- Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International
- San Francisco International
- Orlando International
- Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International
- Baltimore/Washington International (tie)
Wi-Fi is better by the Bay:
As shown in Wi-Fi’s fastest five airports, Oakland International and Norman Y. Mineta San José International made that list. Rounding out the Bay Area airportstrio, the Wi-Fi speed in San Francisco International comfortably topped the mobile providers.
| Airport | AT&T | T-Mobile | Verizon | Airport Wi-Fi |
| Oakland International | 229.70 | 28.58 | 103.90 | 194.23 |
| Norman Y. Mineta San José International | 103.83 | 211.40 | 251.06 | 176.59 |
| San Francisco International (SFO) | 67.07 | 92.91 | 100.56 | 169.51 |
SFO was the only airport in Ookla’s analysis with Speedtest samples using the 6 GHz band. This was on Wi-Fi 6E – too soon to expect Wi-Fi 7 in airports – with a median download speed of 364.74 Mbps (also remarkable were the median upload speed of 426.04 Mbps and an 8 ms multi-server latency).
References:
https://www.ookla.com/articles/u-s-fwa-report-december-2025
https://www.ookla.com/articles/cellular-faster-than-wi-fi-in-us-airports
Ookla: Global performance of Apple’s in-house designed C1 modem in iPhone 16e
Ookla: Uneven 5G deployment in Europe, 5G SA remains sluggish; Ofcom: 28% of UK connections on 5G with only 2% 5G SA
Ookla: Europe severely lagging in 5G SA deployments and performance
Highlights of Ookla’s 1st Half 2024 U.S. Connectivity Report
Ookla: T-Mobile and Verizon lead in U.S. 5G FWA
Ookla Q2-2023 Mobile Network Operator Speed Tests: T-Mobile is #1 in U.S. in all categories!
Highlights of ITU Global Connectivity Report 2025 and the Baku Action Plan
The ITU Global Connectivity Report 2025, released at the conclusion of the World Telecommunication Development Conference (WTDC-25) in Baku, Azerbaijan, delivers a comprehensive assessment of how global connectivity has evolved from a scarce asset in 1994 into a foundational layer of the digital economy and everyday life, with close to 6 billion users projected to be online by 2025. Its analytical framework is anchored in the policy objective of achieving universal and meaningful connectivity (UMC), structured across six interdependent dimensions: Quality, Availability, Affordability, Devices, Skills, and Security.
The report underscores the socio‑economic gains associated with large‑scale digital transformation, including enhanced productivity, innovation, and service delivery across sectors. At the same time, it emphasizes that progress is constrained by persistent digital divides along income, gender, age, and geographic lines, as well as by escalating exposure to online harms, misinformation, and non‑trivial environmental externalities from ICT infrastructure and usage.
It suggests the era of easy, organic network expansion is over. While 74% of the world is now online, the curve is flattening, and the remaining deficits are structural rather than merely about access.
With an estimated 2.2 billion people still offline, ITU Member States (194) agreed this week on the Baku Action Plan—a four-year roadmap to 2029 designed to close these persistent divides.
The report provides detailed analysis of structural barriers to universal and meaningful connectivity (UMC), notably high connectivity and device costs, gaps in digital skills, and constrained access to appropriate end‑user devices. It translates this analysis into evidence‑based policy guidance focused on regulatory coherence, targeted affordability interventions, and demand‑side enablers to ensure that connectivity translates into effective and inclusive digital usage.
From a network engineering and infrastructure perspective, the report highlights the critical role of resilient, high‑capacity backbones, including submarine cable systems and satellite constellations, as strategic layers of the global connectivity fabric. It stresses the need for coordinated investment, robust redundancy and security models, and integrated planning across terrestrial, subsea, and space‑based networks to support UMC objectives.
The report identifies high service and device costs, insufficient digital skills, and limited device availability as key barriers, and provides evidence‑based policy guidance on regulatory coherence, affordability, and demand‑side enablers. It emphasizes the importance of resilient infrastructure such as submarine cables and satellites, along with stronger national data ecosystems, to support inclusive connectivity strategies and informed digital policy‑making.
Finally, the report calls for strengthening national data ecosystems—covering data collection, governance, sharing, and analytics—as a prerequisite for effective digital inclusion strategies and evidence‑driven policy‑making. It positions mature data capabilities and coherent digital governance frameworks as key enablers for monitoring progress across the six UMC dimensions and for calibrating telecom and ICT policy in line with evolving market and technology dynamics.
References:
https://www.itu.int/itu-d/reports/statistics/global-connectivity-report-2025/
ITU’s Facts and Figures 2025 report: steady progress in Internet connectivity, but gaps in quality and affordability
ITU-R WP 5D reports on: IMT-2030 (“6G”) Minimum Technology Performance Requirements; Evaluation Criteria & Methodology
ITU-R report: Applications of IMT for specific societal, industrial and enterprise usages
https://www.itu.int/itu-d/reports/statistics/global-connectivity-report-2022/
VC4 Advances OSS Transformation with an Efficient and Reliable AI enabled Network Inventory System
By Juhi Rani assisted by IEEE Techblog editors Ajay Lotan Thakur and Sridhar Talari Rajagopal
Introduction:
This year, 2025, VC4 [a Netherlands Head Office (H/O) based Operational Support System (OSS) software provider] has brought sharp industry focus to a challenge that many experience in telecom. Many operators/carriers still struggle with broken, unreliable, and disconnected inventory systems. While many companies are demoing AI, intent-based orchestration, and autonomous networks, VC4’s newly branded offering, Service2Create (or S2C as it’s known to some), is refreshingly grounded. Also as we have learnt very quickly, bad data into AI is a “no-no”. None of the orchestration and autonomous networks, will work accurately if your OSS is built on flawed data. The age-old saying “Garbage in, Garbage out” comes to mind.
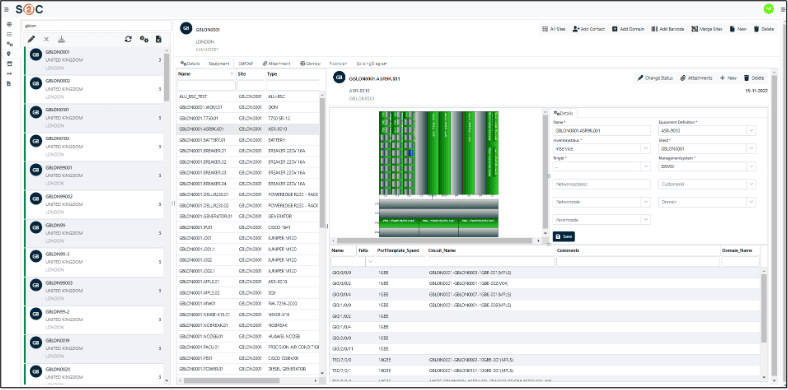
VC4’s platform, Service2Create (S2C), is a next-generation OSS inventory system that supports the evolving needs of telecom operators looking to embrace AI, automate workflows, and run leaner, smarter operations. Service2Create is built from over two decades of experience of inventory management solutions – IMS. By focusing on inventory accuracy and network transparency, S2C gives operators a foundation they can trust.
Inventory: The Most Underestimated Barrier to Transformation
In a post from TM Forum, we observed that operators across the world are making huge investments in digital transformation but many are slowed by a problem closer to the ground: the inability to know what exactly is deployed in the network, where it is, and how it’s interconnected.
VC4 calls this the “silent blocker” to OSS evolution.
Poor mis-aligned inventory undermines everything. It breaks service activations, triggers unnecessary truck rolls, causes billing mismatches, and frustrates assurance teams. Field engineers often discover real-world conditions that don’t match what’s in the system, while planners and support teams struggle to keep up. The problem doesn’t just stop with network data.
In many cases, customer records were also out of date or incomplete… and unknown inventory can also be a factor. Details like line types, distance from the central office, or whether loading coils were present often didn’t match reality. For years, this was one of the biggest issues for operators. Customer databases and network systems rarely aligned, and updates often took weeks or months. Engineers had to double-check every record before activating a service, which slowed delivery and increased errors. It was a widespread problem across the industry and one that many operators have been trying to fix ever since.
Over time, some operators tried to close this gap with data audits and manual reconciliation projects, but those fixes never lasted long. Networks change every day, and by the time a cleanup was finished, the data was already out of sync again.
Modern inventory systems take a different approach by keeping network and customer data connected in real time. They:
- Continuously sync with live network data so records stay accurate.
- Automatically validate what’s in the field against what’s stored in the system.
- Update both customer and network records when new services are provisioned.
In short, we’re talking about network auto-discovery and reconciliation, something that Service2Create does exceptionally well. This also applies for unknown records, duplicate records and records with naming inconsistencies/variances.
It is achieved through continuous network discovery that maps physical and logical assets, correlates them against live service models, and runs automated reconciliation to detect discrepancies such as unknown elements, duplicates, or naming mismatches. Operators can review and validate these findings, ensuring that the inventory always reflects the true, real-time network state. A more detailed explanation can be found in the VC4 Auto Discovery & Reconciliation guide which can be downloaded for free.
Service2Create: Unified, Reconciled, and AI-Ready
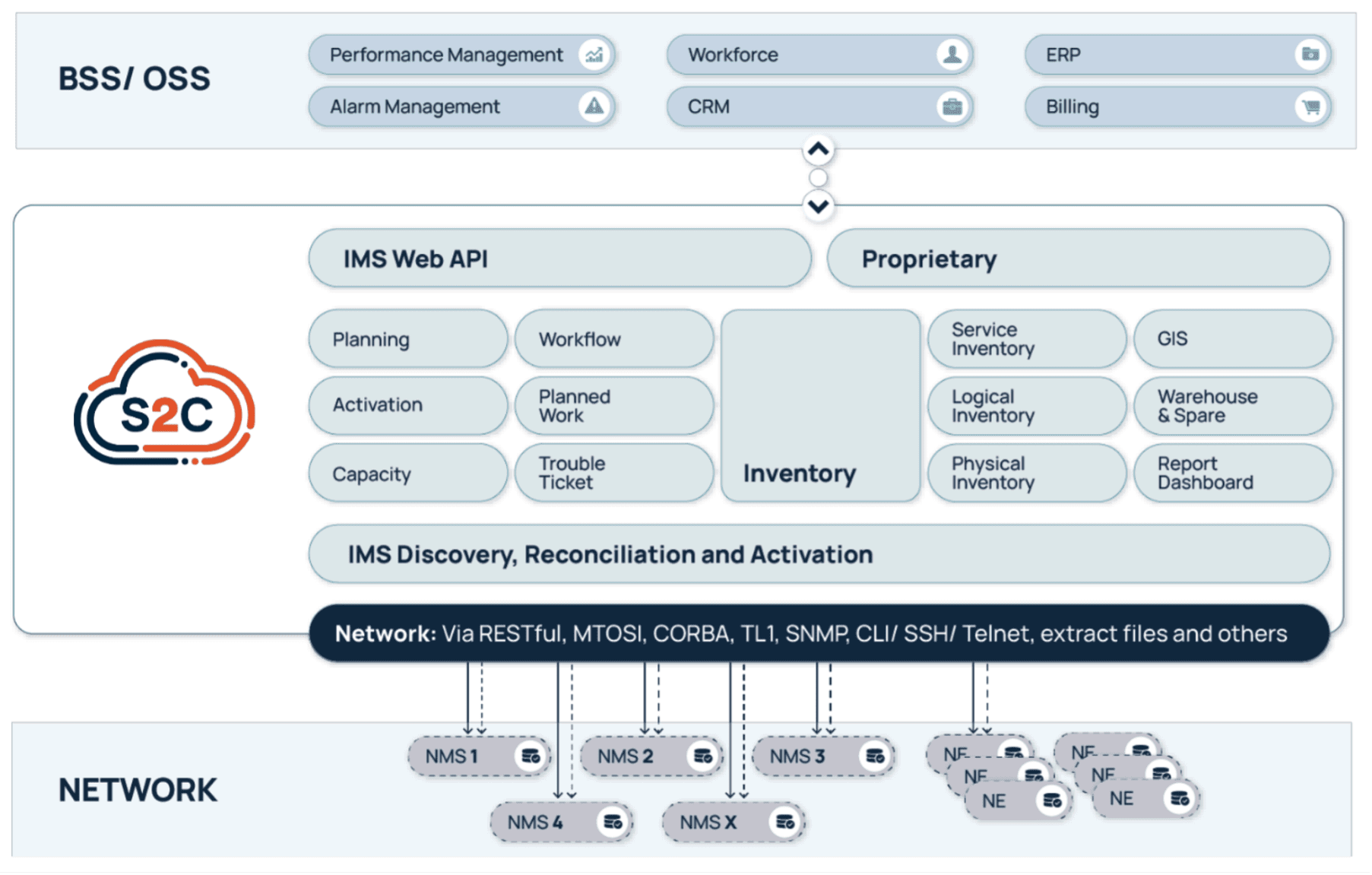
Service2Create is designed to reflect the actual, current state of the network across physical, logical, service and virtual layers. Whether operators are managing fiber rollout, mobile backhaul, IP/MPLS cores, or smart grids, S2C creates a common source of truth. It models infrastructure end-to-end, automates data reconciliation using discovery, and integrates with orchestration platforms and ticketing tools.
To make the difference clearer here is the table below shows how Service2Create compares with the older inventory systems still used by many operators. Traditional tools depend on manual updates and disconnected data sources, while Service2Create keeps everything synchronized and validated in real time.
Comparison between legacy inventory tools and Service2Create (S2C)
| Feature | Legacy OSS Tools | VC4 Service2Create (S2C) |
|---|---|---|
| Data reconciliation | Manual or periodic | Automated and continuous |
| Inventory accuracy | Often incomplete or outdated | Real-time and verified |
| Integration effort | Heavy customization needed | Standard API-based integration |
| Update cycle | It takes days or weeks | Completed in hours |
| AI readiness | Low, needs data cleanup | High, with consistent and normalized data |
What makes it AI-ready isn’t just compatibility with new tools, it’s data integrity. VC4 understands that AI and automation only perform well when they’re fed accurate, reliable, and real-time data. Without that, AI is flying blind.
Built-in Geographic Information System (GIS) capabilities help visualize the network in geographic context, while no/low-code workflows and APIs support rapid onboarding and customization. More than software, S2C behaves like a data discipline framework for telecom operations.
Service2Create gives operators a current, trusted view of their network, improving accuracy and reducing the time it takes to keep systems aligned.
AI is Reshaping OSS… But only if the Data is Right
AI is driving the next wave of OSS transformation from automated fault resolution and dynamic provisioning to predictive maintenance and AI-guided assurance. But it’s increasingly clear: AI doesn’t replace the need for accuracy; it demands it.
In 2025, one common thread across operators and developers was this: telcos want AI to reduce costs, shorten response times, and simplify networks. According to a GSMA analysis, many operators continue to struggle as their AI systems depend on fragmented and incomplete datasets, which reduces overall model accuracy.
VC4’s message is cutting through: AI is only as useful as the data that feeds it. Service2Create ensures the inventory is trustworthy, reconciled daily with the live network, and structured in a way AI tools can consume. It’s the difference between automating chaos and enabling meaningful, autonomous decisions.
Service2Create has been adopted with operators across Europe and Asia. In national fiber networks, it’s used to coordinate thousands of kilometers of rollout and maintenance. In mixed fixed-mobile environments, it synchronizes legacy copper, modern fiber, and 5G transport into one unified model.
Designed for Operational Reality
VC4 didn’t build Service2Create for greenfield labs or ideal conditions. The platform is designed for real-world operations: brownfield networks, legacy system integrations, and hybrid IT environments. Its microservices-based architecture and API-first design make it modular and scalable, while its no/low-code capabilities allow operators to adapt it without long customization cycles. See the diagram below.
S2C is deployable in the cloud or on-premises and integrates smoothly with Operational Support System / Business Support System (OSS/BSS) ecosystems including assurance, CRM, and orchestration. The result? Operators don’t have to rip and replace their stack – they can evolve it, anchored on a more reliable inventory core.
What Industry Analysts are Saying
In 2025, telco and IT industry experts are also emphasizing that AI’s failure to deliver consistent ROI in telecom is often due to unreliable base systems. One IDC analyst summed it up: “AI isn’t failing because the models are bad, it’s failing because operators still don’t know what’s in their own networks.”
A senior architect from a Tier 1 European CSP added, “We paused a closed-loop automation rollout because our service model was based on inventory we couldn’t trust. VC4 was the first vendor we saw this year that has addressed this directly and built a product around solving it.”
This year the takeaway is clear: clean inventory isn’t a nice-to-have. It’s step one.
Looking Ahead: AI-Driven Operations Powered by Trusted Inventory
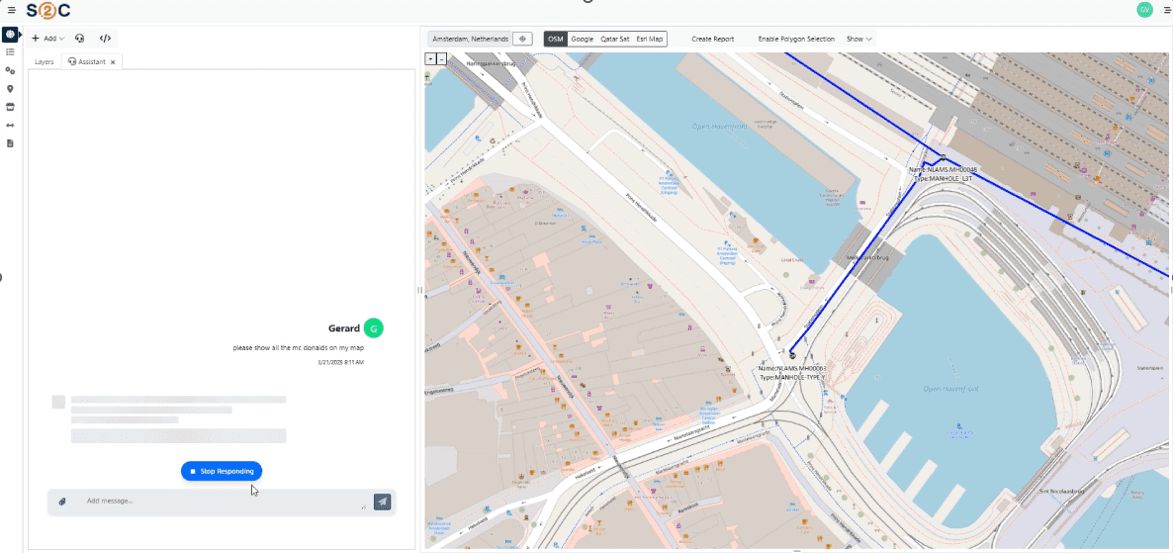
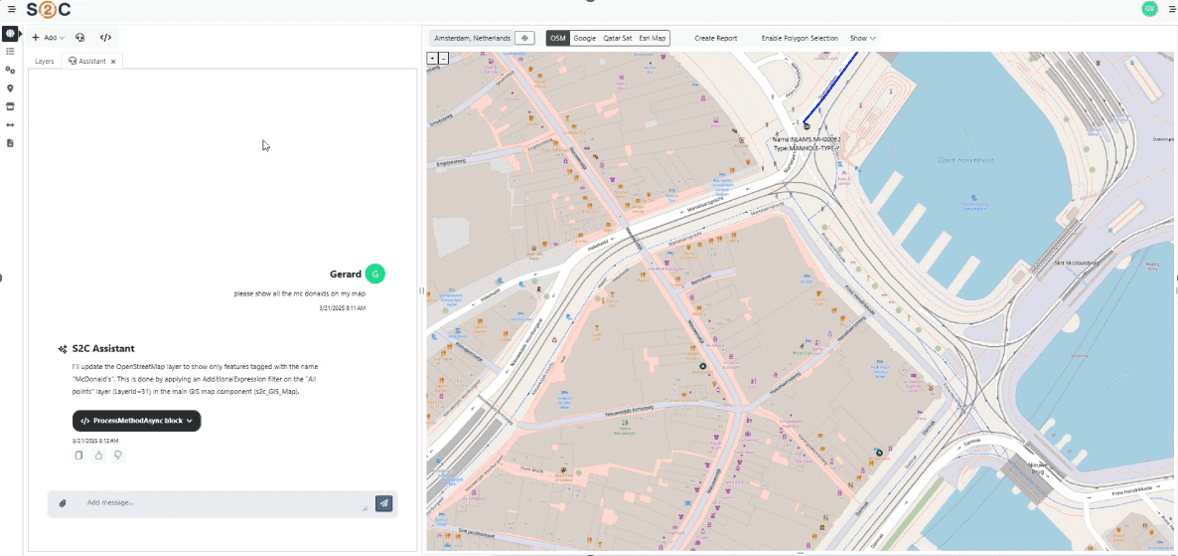
VC4 is continuing to enhance Service2Create with capabilities that support AI-led operations. Currently, S2C is enhanced with AI-powered natural language interfaces through Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers. This creates a revolutionary way for users to access their data and makes it also easier for them to do so. Simply ask for what you need, in plain language, and receive instant, accurate results from your systems of record.
The S2C platform now offers multiple synchronized access methods:
- Natural Language Interface
- Ask questions in plain language: “Show me network capacity issues in Amsterdam”
- AI translates requests into precise system queries
- No training required – productive from day one
- Direct API Access via MCP
- Programmatic access using Language Integrated Query (LINQ) expressions
- Perfect for integrations and automated workflows
- Industry-standard authentication (IDP)
- S2C Visual Platform
- Full-featured GUI for power users
- Parameterized deeplinks for instant component access
- Low/no-code configuration capabilities
- Hybrid Workflows
-
- Start with AI chat, graduate to power tools
- AI generates deeplinks to relevant S2C dashboards
Export to Excel/CSV for offline analysis
-
What It All Comes Down To
Digital transformation sounds exciting on a conference stage, but in the trenches of telecom operations, it starts with simpler questions. Do you know what’s on your network? Can you trust the data? Can your systems work together?
That’s what Service2Create is built for. It helps operators take control of their infrastructure, giving them the confidence to automate when ready and the clarity to troubleshoot when needed.
VC4’s approach isn’t flashy. It’s focused. And that’s what makes it so effective – a direction supported by coverage from Subseacables.net, which reported on VC4’s partnership with AFR-IX, to automate and modernize network operations across the Mediterranean.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About the Author:
Juhi Rani is an SEO specialist at VC4 B.V. in the Netherlands. She has successfully directed and supervised teams, evaluated employee skills and knowledge, identified areas of improvement, and provided constructive feedback to increase productivity and maintain quality standards.
Juhi earned a B. Tech degree in Electronics and Communications Engineering from RTU in Jaipur, India in 2015.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ajay Lotan Thakur and Sridhar Talari Rajagopal are esteemed members of the IEEE Techblog Editorial Team. Read more about them here.