New Findings in Aryaka’s 2022 State of the WAN Report: Cloud Adoption, Hybrid Workplaces, Convergence of Network and Security with SASE
Overview:
Aryaka®, a leader in fully managed Cloud-First WAN solutions, today published its 2022 State of the WAN Report, offering a compendium of insights into global SD-WAN and SASE planning. 1,600 information technology (IT) enterprise decision makers across global enterprises answered the survey, the largest response to the survey since its inception.
Key trends identified in this year’s report include:
- A quarter of the respondents state they have closed 25-50% of their office sites, dovetailing into overall hybrid work initiatives where 75% state that at least a quarter of their employees will remain remote permanently post-pandemic.
- Accelerating digital transformation initiatives also impact legacy data centers, with 51% planning to eliminate their use within the next 24 months as they move to the cloud.
- The surveyed group says Microsoft Teams (58%) and Office 365 (55%) are among the most widely adopted SaaS applications, followed by Zoom and Google Docs (35%).
- A quarter of respondents expect budgets to grow by 25% or more in the next year, with a full three-quarters projecting at least a 10% growth. Investment appears to be accompanied via cost savings.
- A move to simplify, adopting a more cloud-centric and agile approach, is driving convergence. In the context of network and security, trends include the Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), with 64% deploying or planning to deploy over the next year. Over two-thirds will opt for a managed SASE to help address complexity and costs, but challenges include complexity at 40%, a single or dual-vendor approach at 39%, and developing a phased migration strategy at 33%. Observability and control should help with deployments, identified by over two-thirds as a top imperative.
- 29% state that they are already deploying what they consider to be a SASE architecture, with another 56% planning to deploy in the next 12-24 months.
- What capabilities do the respondence require? The top responses are SD-WAN at 34%, a Cloud Secure Web Gateway (SWG) at 30%, and Firewall as a Service (FWaaS) at 17%.
“This year’s Aryaka State of the WAN includes many valuable insights backing up trends we see in the industry. These include the effects of hybrid work, with 75% projecting a quarter of their employees to remain at least part-time remote, and cloud connectivity demands skyrocketing with 51% planning to move away from traditional data centers over the next two years. Both initiatives will require more sophisticated network-as-a-service (NaaS) solutions with integrated security offerings,” said Scott Raynovich founder and chief analyst of Futuriom.
“The sixth edition of the Global State of the WAN (SOTW) is one of the largest such surveys in the world,” said Shashi Kiran, CMO of Aryaka. “It packages an enormous number of insights from decisions makers from all over the world, drawn from CIOs, CISOs as well as network, security and cloud practitioners. The 2022 edition reveals new enterprise trends on workplaces, cloud adoption, convergence and several other areas putting a spotlight on the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic in the process. We hope this resource serves as a handy companion for enterprise architects engaged in planning their WAN, security and cloud infrastructure for years ahead.”
SD-WAN vendors have long touted the technology’s application- and policy-based routing capabilities as the antidote to network performance and complexity. However, customers are increasingly looking for ways to offload that complexity and consolidate services under a single roof. “There’s a fragmented value chain for SD-WAN, which we’ve seen before and now for SASE as well,” Kiran said.
Of those surveyed, 45% said they were considering a consolidated SASE architecture, up from 39% last year. However, enterprises’ desire for managed services doesn’t stop at SD-WAN or SASE. Respondents expressed a desire for managed last-mile and multi-cloud connectivity. “There is inherent complexity in all of these areas and having something that is managed and delivered as a service appears to be important,” Kiran said.
Year-on-Year Trends and Shifting Priorities:
In Aryaka’s 2021 State of the WAN Report, 21% indicated that half of their workforce would be working remote post-pandemic. This year that number increased by 11%, with 32% reporting that at least half of their workforce would be permanently remote.
Collaboration and Productivity suites have gained traction. The Microsoft suite has gained momentum, with Teams identified by respondents as the most deployed application, growing its footprint by over half, from 34% in 2021 to 58% this year. Conversely, Google Docs dropped from 41% last year to 35% today with Microsoft 365 now at 55%.
For China, basic connectivity concerns dropped noticeably from the last report, at 45% in 2021 to 30% today. In contrast, compliance and regulatory issues are now in the lead at 50%.
A renewed interest in ROI was reflected in this year’s report, with 36% of those responding having cost concerns, an increase of 16% compared to last year. Though budgets are expected to increase by 25%, both for networking and security, the focus on ROI implies that these increases must be spent judiciously.
IT professionals were less concerned vs previous years about the newness of the technology (28% vs 31% in 2021), and whether applications will perform properly (29% vs 36% in 2021), speaking to a greater confidence in application support. As change management takes priority, there is an increased focus on observability and control, increasing by 9% (69% vs 60% last year).
Aryaka 6th Annual State of the WAN 2022 – Four Themes:
1. Acceleration of Remote and Hybrid Work: The report looks at challenges in supporting the hybrid workforce, hybrid work trends, and investments planned to support this new environment. 75% state that at least a quarter of their employees will remain hybrid post-pandemic, aligned with the closure of physical facilities, with a quarter stating they have closed 25-50% of their office sites. Effectively managing worker movement between on-premises and remote requires dynamic bandwidth reallocation, identified by 61% as very important.
2. Application Performance and Consumption: In addition, the report dives into the diversity of applications in use and resulting challenges, how enterprises plan to address these, and potential concerns. As noted earlier, collaboration and productivity applications like Microsoft Teams and Office 365 experienced some of the strongest growth, but there was an overall uptick in SaaS application adoption including Zoom (35%), Salesforce (28%), and SAP/HANA (25%). Performance still must improve, with 42% identifying slow performance for remote and mobile users a key issue, followed by 37% calling out slow performance at the branch.
3. Managing Complexity and Managed Services Adoption: The report addresses what managed services enterprises expect, including SD-WAN and SASE implementation plans and budgets, as well as perceived barriers to adoption. This section also looks at MPLS migration. In evaluating managed services, enterprises continue to demand more from their providers, and are looking for a wider set of offers, an all-in-one SD-WAN and SASE that includes the WAN (45%), security (67%), application optimization (40%), last mile management (29%), and multi-cloud connectivity (27%). The movement to SD-WAN and SASE also follows the movement away from MPLS, with 46% planning to terminate some or all contracts over the next year. Enterprises are generally bullish on their budgets, with a quarter expecting it to grow by 25% or more, and a total of three quarters expecting at least 10% growth.
4. Networking and Security Convergence Including a SASE Architecture: SASE represents a promise of a converged Cloud-First architecture, but there are concerns on complexity and adoption. 42% state that lackluster application performance is a time sink, and 34% consider security to be a major priority. This path to SASE adoption includes setting a strategy (35%), phasing out of legacy VPNs (32%), as well as consolidating cloud security with zero-trust (29%).
Top desired capabilities include a SWG (47%), SD-WAN (36%), and FWaaS (28%). Implementation concerns identified earlier are balanced by expected advantages that include time and cost reduction (37%), as well as agility (33%), while decision-making is still mostly distributed across networking and security, 41% state it is now consolidated. Finally, over two-thirds plan to consume SASE as a managed offer.
What are the biggest challenges you’re facing with your WAN?
Total Responses 1,386
- High complexity/difficult to manage or maintain 37%
- Slow access to cloud services & SaaS applications 33%
- Slow performance of on-premises applications 32%
- Long deployment times to bring up new sites 29%
- Lack of adequate security 28%
- Poor voice or video quality 23%
- High cost 20%
- Lack of visibility 20%
*Respondents chose maximum three responses
–>The WAN continues to be a challenge, impacting manageability, performance, security, agility, and cost.
Study Methodology:
The Sixth Annual Global Aryaka 2022 State of the WAN study surveyed over 1600 enterprise decision makers and practitioners including CIOs, CTOs, as well as IT, network, and security managers. Respondents were based in the Americas, EMEA, and APAC, with their companies representing every vertical, led by technology, software, manufacturing, financial, and retail. The survey asked respondents about their networking and performance challenges, priorities, and their plans for 2022 and beyond.
Download the Report:
Download Aryaka’s 6th Annual State of the WAN Report here.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
MPLS to SD-WAN Migration (Source: Aryaka):
Aryaka’s fully managed SD-WAN and SASE solution leverages a flexible core architecture, FlexCoreTM, optimized for per-site and per-application performance requirements. It offers full per customer resource reservation, end-to-end, at a global level. The HybridWAN solution also leverages direct MPLS and public internet connectivity options.
Aryaka manages the last-mile internet link performance with patented technology to eliminate packet loss and deliver on superior latency and jitter performance. By leveraging a private global L2 network, Aryaka eliminates the issue of guaranteeing deterministic QoS when multiple service provider administrative domains are involved (which is almost always the case in a global network).
Aryaka customers rely on its architecture to deliver on better-than-MPLS performance at a global level and at reduced cost, either augmenting the existing MPLS infrastructure or replacing it altogether over time.
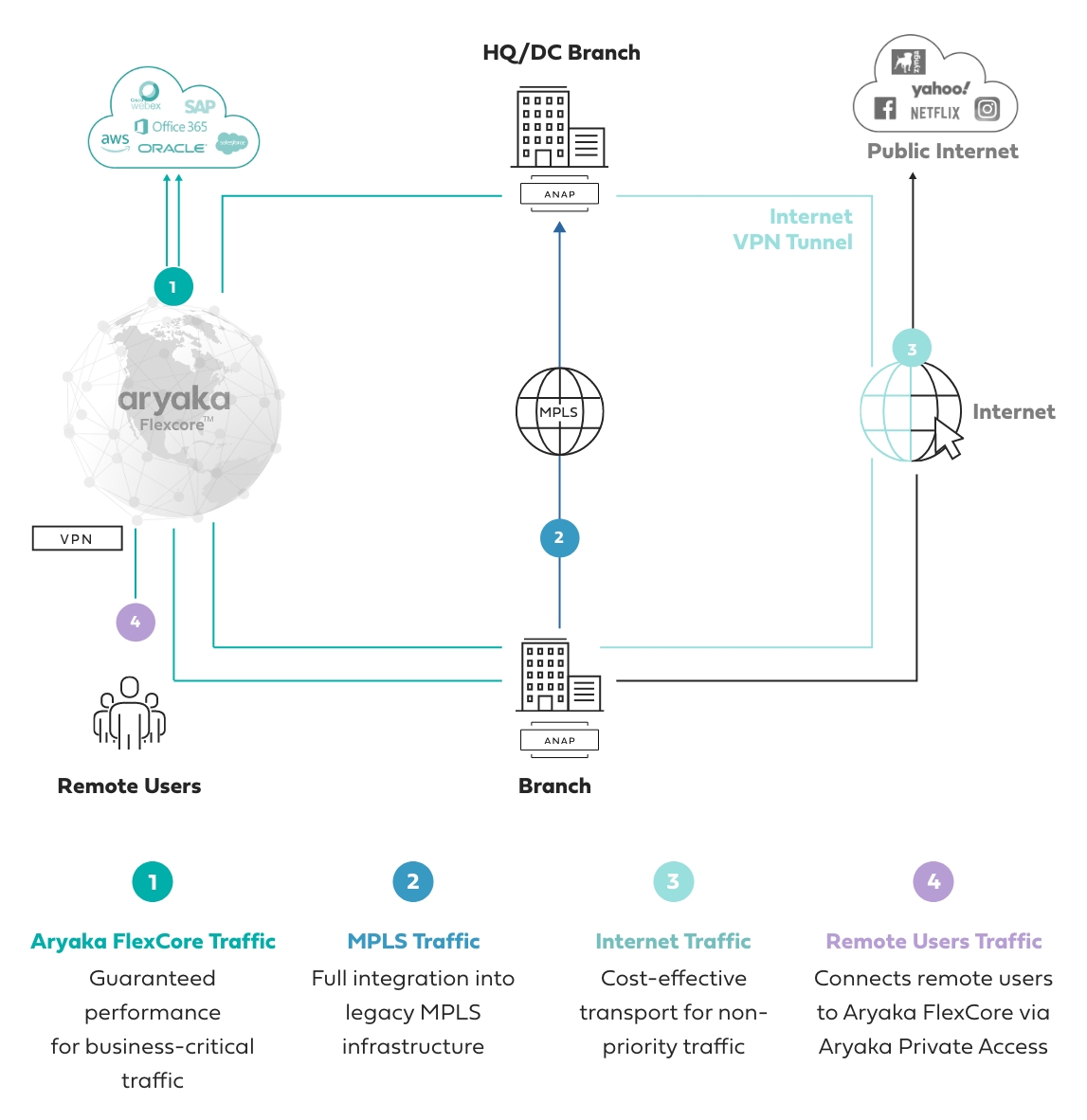
Source: Aryaka
References:
Shift from SDN to SD-WANs to SASE Explained; Network Virtualization’s important role
Dell’Oro: SD-WAN market grew 45% YoY; Frost & Sullivan: Fortinet wins SD-WAN leadership award
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
The slow uptake of 5G Standalone (SA) networks is decreasing the growth for the overall Mobile Core Network (MCN), which also includes IMS Core and 4G Core (EPC). Dell’Oro Group [1.] forecasts worldwide MCN 5-year growth will be at a 3% compounded annual growth rate (CAGR).
- 5G MCN, IMS Core, and Multi-Access Network Computing (MEC) will have positive growth rates for the forecast period while 4G MCN will experience negative growth.
- By 2026, 99% of the revenue for network functions will be from cloud native Container-based CNFs.
Via email, Dave wrote: The journey for network virtualization started in 2015 with ETSI NFV. We went from Physical Network Functions (PNFs) to Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) to cloud-ready VNFs, to Cloud- Native VNFs (CNF), to Container-Based Cloud-Native VNFs. Container-Based (CNF) enable microservices.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, the Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) recently wrote that only 99 operators in 50 countries are investing in 5G standalone (SA) core network, which includes those planning/testing and launched 5G SA networks.
The GSA said at least 20 network operators (Dell’Oro says 13) in 16 countries or territories are believed to have launched public 5G SA networks. Another five have deployed the technology, but not yet launched commercial services or have only soft-launched them. So only 20.6% of the 481 5G network operators (investing in 5G licenses, trials or deployments of any type) have deployed 5G and that percentage is lower if you go by Dell’Oro’s 13 5G SA network operators.
From GSA’s The Power of Standalone 5G – published 19th January 2022:
Importantly, the 5G standalone core is cloud-native and is designed as a service-based architecture, virtualizing all software network functions using edge computing and providing the full range of 5G features. Some of these are needed in the enterprise space for advanced uses such as smart factory automation, smart city applications, remote control of critical infrastructure and autonomous vehicle operation. However, 5G standalone does mean additional investment and can bring complexity in running multiple cores in the network.
This will be a potential source of new revenue for service providers, as digital transformation — with 5G standalone as a cornerstone — will enable them to deliver reliable low-latency communications and massive Internet of things (IoT) connectivity to customers in different industry sectors. The low latency and much higher capacity needed by those emerging service areas will only be feasible with standalone 5G and packet core network architecture.
In addition, the service-based architecture opens up the ability to slice the 5G network into customized virtual pieces that can be tailored to the needs of individual enterprises, while maximizing the network’s operational efficiency. Advanced uses for 5G NR aren’t backward- compatible with LTE infrastructure, so all operators will eventually need to get to standalone 5G.
Standalone 5G metrics:
- Volume: Gbps per month
- Speed: Mbps (peak), Mbps (guaranteed)
- Location: Network Slice, service per location
- Latency per service or location (dependent on URLLC in the 5G RAN and 5G Core)
- Reliability or packet loss
- Number of devices per square km
- Dynamic service-level agreements per location
- Full end-to-end encryption and authentication
Source: CCS Insight
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Note 1. Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, networks, and data center IT markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Feb 8, 2022 Update from Dave Bolan of Dell’Oro Group:
As of December 31, 2021 there were 21 known 5G SA eMBB networks commercially deployed.
|
5G SA eMBB Network Commercial Deployments |
|
|
Rain (South Africa) |
Launched in 2020 |
|
China Mobile |
|
|
China Telecom |
|
|
China Unicom |
|
|
T-Mobile (USA) AIS (Thailand) True (Thailand) |
|
|
China Mobile Hong Kong |
|
|
Vodafone (Germany) |
Launched in 2021 |
|
STC (Kuwait) |
|
|
Telefónica O2 (Germany) |
|
|
SingTel (Singapore) |
|
|
KT (Korea) |
|
|
M1 (Singapore) |
|
|
Vodafone (UK) |
|
|
Smart (Philippines) |
|
|
SoftBank (Japan) |
|
|
Rogers (Canada) |
|
|
Taiwan Mobile |
|
|
Telia (Finland) |
|
|
TPG Telecom (Australia) |
|
References:
Slow Uptake for 5G Standalone Drags on Mobile Core Network Growth, According to Dell’Oro Group
Why It’s Important: Rakuten Mobile, Intel and NEC collaborate on containerized 5G SA core network
T-Mobile US: 5G SA Core network to be deployed 3Q-2020; cites 5G coverage advantage
Heavy Reading: “The Journey to Cloud Native” – Will it be a long one?
Starlink’s huge ambition and deployment plan may clash with reality
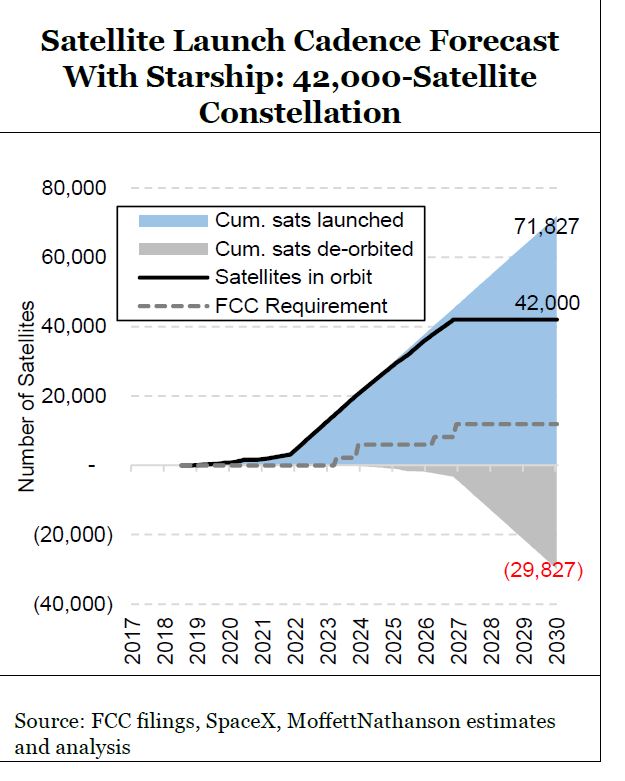
Starlink’s first mission of 2022 launched another 49 satellites into orbit, extending its grand total to nearly 2,000. But since completing its first orbital shell of about 1,600 satellites last May, “Starlink’s launch frequency has slowed dramatically with only four rocket launches over the past seven months, or roughly one every seven weeks,” explained Craig Moffett, principal analyst at MoffettNathanson in a note to clients. Craig wrote:
Starlink’s ambition is huge (a constellation of as many as 42,000 satellites). And the implied valuation for the still-private company is huge ($100B+ for all of SpaceX).
This “hugeness” has captured investors’ imaginations and no doubt hugeness itself is very much part of its appeal. But we haven’t yet seen investors come to grips with all of the implications of this bigness. We were struck by Elon Musk’s recent tweet conceding a “genuine risk of bankruptcy” – immediately dismissed by some as hyperbole – and it got us thinking about scale, and risk, in ways we really hadn’t considered before.
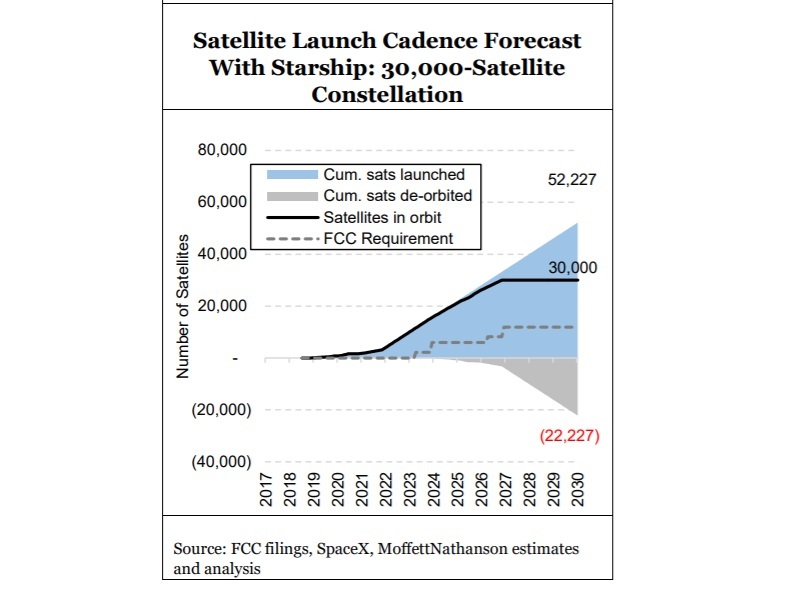
Moffett notes that the new Starlink V1.5 satellites are heavier, leading to fewer satellites per launch. “At a payload of 50 satellites per launch for Falcon 9 rockets – down from 60 per launch for V1.0 satellites – SpaceX would need to drastically increase launch frequency to once every seven days for five consecutive years just to launch the satellites required for their planned constellation of ~12,000 by their FCC deadline in 2027.”
In low-Earth orbit, satellites will drift back to Earth and burn up on re-entry. Assuming the satellites have an average lifespan of five years, the number of launches to simply replace expiring satellites will, by year five, be as large as the number of launches required over the next five years to grow the constellation. By the end of 2030, just nine years from now, they would have had to launch nearly 23,000 satellites in support of a 12,000 bird constellation. Assuming a Falcon 9 payload of 50 satellites, that would imply 48 launches each year – roughly one every seven days – just to sustain a constellation of 12,000 satellites even after the constellation is “finished.”
Privately held SpaceX (Starlink’s owner) will also need to strongly increase manufacturing capacity and manage tricky supply chain logistics to meet the needs for Starlink, as well as for SpaceX’s clients.
Based on $30 million per launch, Moffett estimates that it would cost about $15 billion to build a constellation of 30,000 satellites, with satellite replacement (production and launch) alone costing more than $3.6 billion per year. Please see chart below.
Starlink hopes to beef up its capabilities with Starship, a larger launch vehicle that’s had its share of problems, with an orbital test flight that could take place as soon as March. However, Craig suggests that Starship isn’t necessarily the answer to the problem, considering that new V2.0 satellites will be perhaps four times as massive as previous generation Starlink LEO satellites.
In November 2021, Elon Musk distributed a companywide email stating that a production crisis centered on the Starship rocket engine puts SpaceX on a path to “genuine risk of bankruptcy if we cannot achieve a Starship flight rate of at least once every two weeks next year.”
However, the costs will be very high. Moffett says the “sustenance” cost of the constellation, before considering any costs associated with overhead, engineering, ground facilities, network operations centers, or end-user support, installation, and/or maintenance, could tally $5B per year as per this chart:
Satellite projects are, by their very nature, huge. A defining characteristic of big infrastructure investments is that they demand that investors be confident about the success and payoffs from infrastructures that may take as much as a decade to build.
Moffett is concerned that investors [1.] have yet to “come to grips with all of the implications” of the audaciousness of the Starlink’s huge ambitions.
Note 1. It’s important to note that Starlink is part of SpaceX, which is still a privately owned company. As of October 2021, Barron’s said that “Elon Musk owns roughly 50% of SpaceX.” It is not known who or whom owns the other half of SpaceX
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.barrons.com/articles/elon-musk-net-worth-trillionaire-51634679420?tesla=y
NGMN Alliance: Green benchmark for mobile networks
The Next Generation Mobile Networks Alliance (NGMN Alliance) [1.] announced plans to create a new ‘green’ benchmark for mobile networks. The industry standard will be based initially on high-level sustainability indicators, with more detailed assessments to follow. It creates a new way to compare mobile networks, alongside service quality and user experience metrics.
Note 1. The NGMN Alliance (Next Generation Mobile Networks Alliance) is an open forum founded by world-leading mobile network operators. Its goal is to ensure that next generation network infrastructure, service platforms and devices will meet the requirements of operators and, ultimately, will satisfy end user demand and expectations.
NGMN seeks to incorporate the views of all interested stakeholders in the telecommunications industry and is open to three categories of participants (NGMN Partners): Mobile network operators (Members), vendors, software companies and many other leading industry players (Contributors), and research institutes contributing substantially to mid- to long-term innovation (Advisors).

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The new initiative is part of the alliance’s ‘Green Future Networks‘ program, set up in 2020 to help the mobile industry address the need to reduce carbon emissions while network traffic continues to grow. The project aims to improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions and increase the use of recyclable materials. The project will be guided by recommendations made in the NGMN 5G White Paper 2, which focuses on four main areas: on-board metering to control energy consumption; network energy efficiency; eco-design of equipment and products; and end-to-end services footprint.
The general objectives of this NGMN initiative are:
- to establish globally applicable KPIs and methodologies,
- to define a global evaluation methodology, and
- to define the data sources for the assessment and how such data are obtained
With the new benchmark, operators will have an incentive to work on sustainability, as well as a tool to verify and market their credentials to customers and public authorities.
The NGMN initiative plans to establish globally applicable KPIs and methodologies, defining data sources, data collection methods and a global evaluation methodology. Interested industry players are invited to join the project to help develop the new benchmark.
Arash Ashouriha, SVP Group Technology Innovation, Deutsche Telekom and Chairman of the NGMN Board states: ”Implementing concrete actions to mitigate climate action is a key priority for our industry. At Deutsche Telekom, our goal is to make sure that everyone can #takepart and connect over a green network. We are committed to ambitious net zero targets and are continuously optimizing our network to ensure the best quality for our customers while striving to systematically reduce the energy consumption. The Global Green Networks Benchmark from NGMN will certainly help the entire telco industry by providing transparency regarding the operator’s sustainability. In addition, it offers operators a unique opportunity to prove their sustainability credentials towards their customers and be recognized for the positive environmental and societal impact.”
Anita Döhler, CEO at NGMN, emphasizes: “There is a clear need for a Global Green Networks Benchmark. Being recognized for the operation of Green Networks will encourage Mobile Network Operators to engage even more in exploring innovative methods and solutions to implement their networks in an energy efficient manner and to increase the focus on reducing the E2E services’ environmental footprint, for instance, through improved eco-design of products and the implementation of new business models fostering a circular economy. Such efforts will also stimulate supplier innovation.”
NGMN invites interested industry players to join this new endeavor for the benefit of the global ecosystem.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
NGMN Defines Industry Standard for a “Global Green Networks Benchmark”
Heavy Reading: “The Journey to Cloud Native” – Will it be a long one?
To gauge how carriers are planning and implementing cloud-native technology, and in collaboration with Juniper, Nokia and Red Hat, Heavy Reading asked 92 global telco service providers about their plans for transition to cloud native. In their report, “The Journey to Cloud Native,” Heavy Reading analyzes the choices service providers are making along the road to cloud native and what challenges they are encountering along the way.
The migration to cloud native brings largescale shifts for the communications service providers (CSPs), including:
- The move to microservices
- Standardized access to these microservices via API exposure
- The integration of multiple operational layers and domains for application management
- Automation across the application lifecycle through the use of DevOps
These are profound changes to the application development and management environment of the CSPs, and will be tackled with dedicated internal resources and expanded partnerships with telecommunication equipment vendors (TEMs), integrators and hyper-scalers (Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Facebook, etc.).
Editor’s Note: There are no standards or implementation specs for “Cloud Native” 5G SA core network or anything else. Rakuten Symphony (Japan) and Reliance Jio (India) claim they are going to implement “Cloud Native” 5G SA core network themselves and sell the specifications and software to other service providers. Good luck! We think it will be a very long journey to cloud native for telecom network operators/5G SA core network service providers.
The prospect of cloud native:
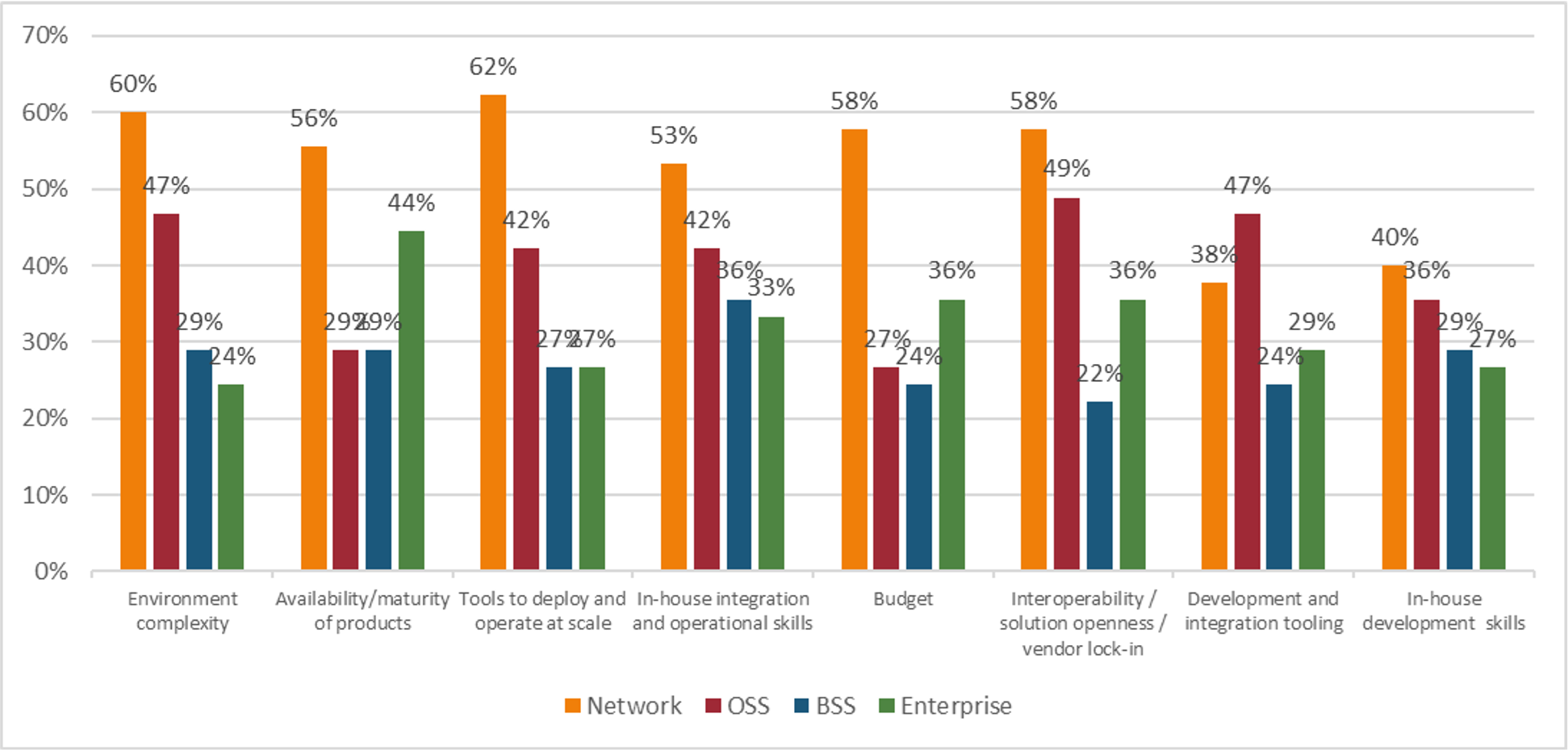
Heavy Reading queried the survey pool about where they were experiencing the greatest challenge in deploying cloud native: the network, operations support systems (OSS), business support systems (BSS), or the enterprise (see Figure 1). Heavy Reading established earlier in the survey that cloud native will be deployed first for network workloads. Respondents plan to transition workloads to the OSS business areas next, then BSS, and lastly, the enterprise.
In almost all cases, respondents ranked the challenges in that same order: first network, then OSS, BSS, and enterprise. The only challenges that were considered more severe in an area other than the network were “in-house development and integration skills” and “development and integration tooling,” where the OSS space was recognized as a greater challenge than the network. This is not surprising given that most Tier 1 carriers have dozens of OSS solutions in operation. They do much of any integration work between systems internally and some OSS systems are stand-alone – dedicated to siloed services.
Figure 1: The network space is seeing the most implementations and the most challenges N=92
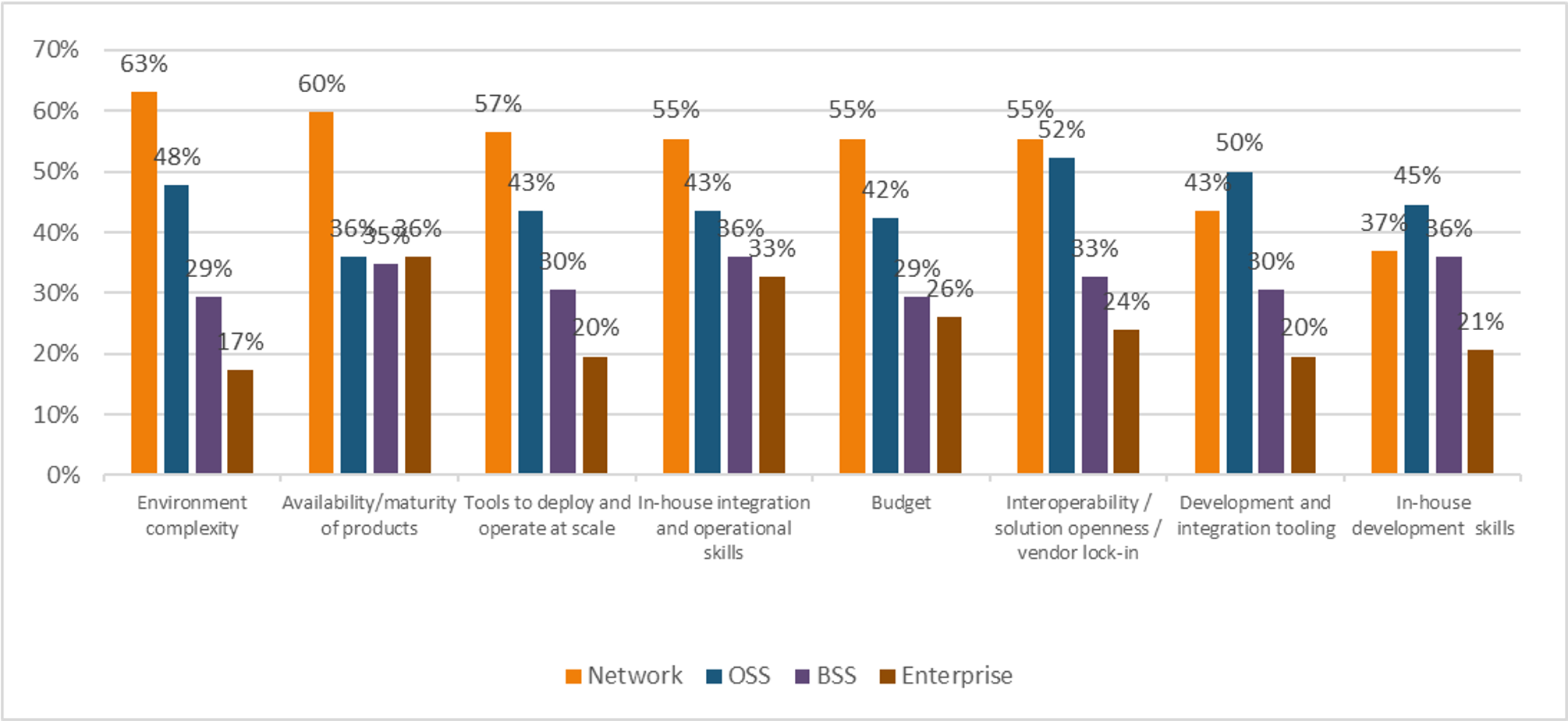
Q: In which business areas are you experiencing significant challenges to going cloud native? Check all that apply. Source: Heavy Reading
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Looking only at the survey results from respondents who have already deployed cloud native, (see figure 2), which is half of the respondent pool, there are significant differences compared to the rest of the survey base. In the network area, “tools to deploy and operate at scale” is a greater challenge by 11 percentage points compared to respondents planning to deploy cloud native in one to two years.
“Budget” in the OSS area plummets between those who have not yet deployed cloud native, (57% of respondents considering it a challenge), and those who have already deployed cloud native, (27% of the respondents finding it to be a concern).
Those who have already deployed cloud native also consider all of the challenges in the enterprise area to be greater than the survey base as a whole and all of the challenges in the BSS area to be less of a challenge. Their firsthand experience with implementing cloud native in the network area has opened their eyes to the challenges that await them in the enterprise space. However, they are more confident that they have the support needed, near term, for BSS tasks which include billing, revenue, and customer management.
n=45: only respondents that have already implemented Cloud Native
Source: Heavy Reading
Heavy Reading’s findings might be a good indication that CSPs today are committed to their journey to cloud native, but face daunting challenges that will require expanded partnerships with the cloud-native ecosystem, including platform vendors, ISVs (Independent Software Vendors), TEMs (Telecom Equipment Manufacturers???) and hyper-scalers.
To gain more in-depth details of service providers’ perspective on cloud-native migration, download and read the full report now.
— Jennifer Clark, Principal Analyst, Cloud Infrastructure and Edge Computing, Heavy Reading
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/new-report-highlights-cloud-native-migration-challenges/a/d-id/774623?
https://www.lightreading.com/lg_redirect.asp?piddl_lgid_docid=773720
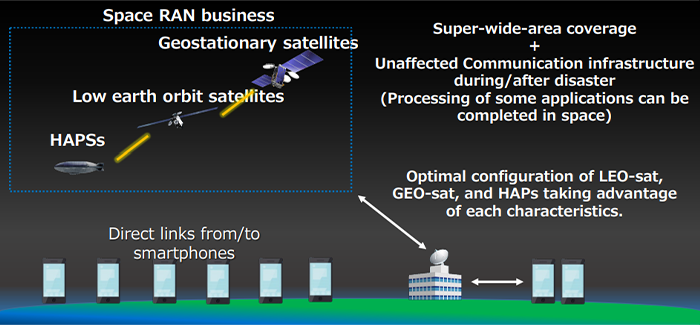
New partnership targets future global wireless-connectivity services combining satellites and HAPS
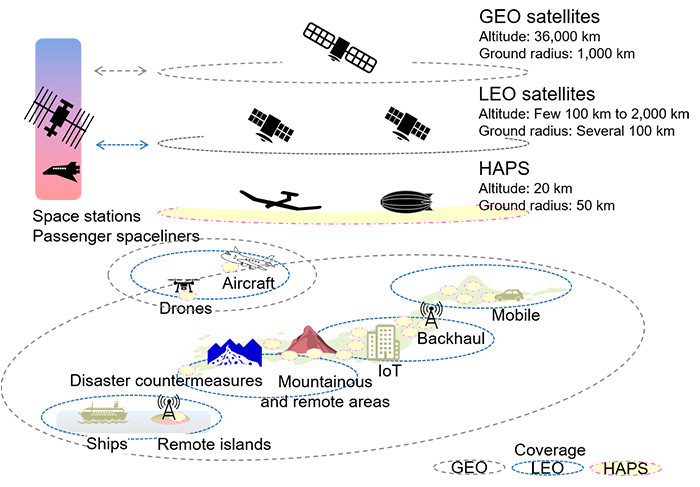
NTT, its mobile subsidiary DoCoMo, aircraft maker Airbus, and Japanese satcoms Sky Perfect JSAT Corporation are partnering to conduct a feasibility study on high altitude platform stations (HAPS). Deployed at altitudes of around 20 kilometers, they are essentially flying base stations that can provide coverage to a radius of around 50 kilometers.
Launched with a memorandum of understanding (MOU), the study will attempt to identify the early deployment requirements of a HAPS-based network. The collaboration will investigate the use of the Airbus Zephyr, the leading solar-powered, stratospheric unmanned aerial system (UAS), and the wireless communication networks of NTT, DOCOMO and SKY Perfect JSAT in order to test HAPS connectivity, identify practical applications, develop required technologies and ultimately launch space-based wireless broadband services.
Illustration of Airbus “Zephyr” HAPS aircraft:

In the global push to further advance 5G and eventually introduce 6G, initiatives are under way to expand coverage worldwide, including in the oceans and in the air. Such initiatives will include HAPS, which fly in the stratosphere about 20 km above the earth, and non-terrestrial network (NTN) technologies using geostationary-orbit (GEO) satellites and low Earth-orbit (LEO) satellites.
HAPS networks are deemed to be a relatively easy solution for air and sea connectivity and an effective platform for deploying disaster countermeasures and many industrial applications. The provision of space-based radio access network services using NTN technologies, collectively called Space RAN (radio access network), is expected to support worldwide mobile communications with ultra-wide coverage and improved disaster resistance as well enhanced 5G and 6G. In addition,
HAPS platforms can also interconnect to the nearest terrestrial network gateway and extend the reach of existing mobile services directly to end-user devices, providing service options including as rural, emergency and maritime connectivity.
With the signing of the MOU, the four companies will discuss and identify possible future developments necessary to unlock future HAPS-based connectivity services, lobby for standardization and institutionalization of HAPS operations, and explore business models for commercializing HAPS services.
Specific themes will include the applicability of HAPS for mobile connectivity on the ground and base station backhaul,1 the performance of various frequency bands in HAPS systems, the technological considerations for linking HAPS with satellites and ground base stations, and the establishment of a cooperative system to test a network combining NTN technology, satellites and HAPS.
As separately announced on November 15, 2021, DOCOMO and Airbus have successfully conducted a propagation test between the ground and a “Zephyr S” HAPS aircraft in the stratosphere, demonstrating the possibility of providing stable communication with such a configuration.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Nick Wood of Telecoms.com wrote:
If the group achieves its stated objectives, it will have succeeded where a few other big names have failed.
Google, which has a long and rich history of dabbling, had a go at HAPS in 2011. Project Loon as it was called, consisted of a fleet of stratospheric balloons with base stations dangling beneath them. It was spun out of Google’s ‘X’ lab into a standalone company in 2018 and launched its first commercial service in partnership with Telkom Kenya in 2020. However, Project Loon couldn’t drive the costs down low enough to turn it into a viable long-term business, and the whole enterprise ceased operations around this time last year. Alongside Project Loon, Google also flirted with drone-based connectivity. This one was called Project Titan, and it fared even worse than Loon. Test flights began in 2015, but amid rumours of funding issues and technical difficulties, the whole thing was canned in early 2016.
Meta (previously known as Facebook) also had a crack at HAPS. As part of its effort to connect the unconnected and sell their data to advertisers, in 2016 it showed off Aquila: a portable fleet of unmanned, solar-powered drones that would deliver service to rural areas. It gave up on the idea two years later after reaching the not-so-startling conclusion that it wasn’t particularly good at building aircraft.
Despite these high-profile failures, the aviation and telecoms industries are clearly not ready to give up on HAPS just yet. They even launched their own lobby group in February 2020, the HAPS Alliance. Last month it announced the successful test flight of Sunglider, an unmanned, solar-powered aircraft equipped with an LTE base station. Funnily enough, Airbus, DoCoMo and Sky Perfect JSAT are all members of the HAPS Alliance, which aims to create an ecosystem around the technology that will turn it into a sustainable business.
DoCoMo et al are undoubtedly aware of the unproven business case for this technology, and so spreading the risk across several experts – rather than going it alone like Google and Facebook – is probably better than the HAPS-hazard approach taken by those giants of Silicon Valley.
References:
https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2022/0117_00.html
https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2021/1115_00.html
NTT hopes to succeed where Google Loon and Facebook Aquila failed
ETSI Experiential Networked Intelligence – Release 2 Explained
ETSI has now completed Release 2 of its Experiential Networked Intelligence (ENI) specifications with the ETSI GS ENI 005 system architecture.
ETSI GS ENI 005 and associated documents will provide better insight into network operations – allowing more effective closed-loop decision making plus better lifecycle management. Through its use, network operators will be able to leverage acquired data and apply artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms to it. This will mean that operators will be able to respond much quicker to changing situations and gain far greater agility.
The services being delivered across their networks may thereby be rapidly adapted and the resources they have available correctly assigned in accordance with subscribers’ requirements, or any other alterations in circumstances (either operationally or commercially driven).
An industry specification group (ISG) focused on ENI was first established by ETSI five years ago. The organisations involved include many of the leading mobile operators worldwide – full list available here.
ETSI ENI Release 2 defines the key architectural requirements (GS ENI 002), and provides a more comprehensive array of potential use cases (GS ENI 001) and applicable proof of concept (PoC) specifications. To support this release, the ENI ISG has produced a series of reports. These cover data characterization, fault identification, the different types of AI mechanisms that can be employed (along with details of the associated bias and ethical implications), the constituent functional blocks needed for modular design implementations and how to assure their interoperability.
“ENI will have an important part to play in how next generation networks are managed, making them contextually aware and giving them greater inherent flexibility,” states Dr Raymond Forbes, Chair of the ETSI ENI ISG. “Use cases and PoCs are already enabling its validity to be demonstrated, and with ETSI ENI Release 2 we are providing a framework upon which operators and their technology partners can implement it into their infrastructure.”
ETSI’s ENI Release 2 includes the following specifications and reports:
-
- GS ENI 001 Use Cases
- GS ENI 002 Requirements
- GR ENI 004 Terminology
- GS ENI 005 System Architecture
- GR ENI 008 Intent Aware Network Autonomicity
- GR ENI 009 Data Mechanisms
- GR ENI 010 Evaluation of categories for AI application to Networks
- GR ENI 016 Functional Concepts for Modular System Operation
- GR ENI 017 Overview of Prominent Control Loop Architectures
- GR ENI 018 Artificial Intelligence Mechanisms for Modular Systems
From the Systems Architecture Spec:
The ENI System is an innovative, policy-based, model-driven functional architecture that improves operator experience. In addition to network automation, the ENI System assists decision-making of humans as well as machines, to enable a more maintainable and reliable system that provides context-aware services that more efficiently meet the needs of the business.
For example, the ENI System enables the network to change its behaviour (e.g. the set of services offered) in accordance with changes in context, including business goals, environmental conditions, and the varying needs of end-users.
This is achieved by using policy-driven closed control loops that use emerging technologies, such as big data analysis, analytics, and artificial intelligence mechanisms, to adjust the configuration and monitoring of networks and networked applications. It dynamically updates its acquired knowledge to understand the environment, including the needs of end-users and the goals of the operator, by learning from actions taken under its direction as well as those from other machines and humans (i.e. it is an experiential architecture).
It also ensures that automated decisions taken by the ENI System are correct and increase the reliability and stability, and lower the maintenance required, of the network and the applications that it supports. It improves and simplifies the management of network services through their visualization, and enables the discovery of otherwise hidden trends and interdependencies.
About ETSI:
ETSI provides members with an open and inclusive environment to support the development, ratification and testing of globally applicable standards for ICT systems and services across all sectors of industry and society. We are a non-profit body, with more than 950 member organizations worldwide, drawn from 64 countries and five continents. The members comprise a diversified pool of large and small private companies, research entities, academia, government, and public organizations. ETSI is officially recognized by the EU as a European Standards Organization (ESO). For more information, please visit us at https://www.etsi.org/
References:
Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) Market, Applications and ETSI MEC Standard-Part I
FCC Auction 110 rakes in $22.5 billion in gross proceeds for 3.45 GHz Service
The results of the FCC’s 3.45 GHz auction were announced today. On January 4, 2022, bidding in Auction 110—the auction of new flexible-use licenses in the 3.45–3.55 GHz band—concluded following the close of bidding in the assignment phase.1 Auction 110 raised a total of $22,418,284,236 in net bids and $22,513,601,811 in gross bids, with 23 bidders winning a total of 4,041 licenses.
With $22.5 billion in gross proceeds, Auction 110 was the third highest grossing auction in the FCC’s history.
The 3.45 GHz action makes available 100 megahertz of mid-band spectrum for commercial use across the contiguous United States. Licensees can use it for fixed or mobile uses.
Here are the big winners:
- AT&T: $9.1B
- Dish: $7.3B
- T-Mobile: $2.9B
AT&T won 1,624 licenses in the 3.45 GHz auction, and Dish, bidding under the name Weminuche LLC, won 1,232 licenses. US Cellular acquired 380 licenses, followed by Cherry Wireless LCC with 319. T-Mobile acquired 199 licenses. Meanwhile, Verizon bid =ZERO.
The remainder went to a relatively familiar list of private equity investors, including Grain Capital, Columbia Capital, and Charlie Townsend’s Bluewater Wireless. Here’s the complete list of bidders:
| Bidder | Bidding entity | Winning bids | Licenses won |
| AT&T | AT&T Auction Holdings, LLC | $9 billion | 1,624 |
| Dish Network | Weminuche L.L.C. | $7.3 billion | 1,232 |
| T-Mobile | T-Mobile License LLC | $2.9 billion | 199 |
| Columbia Capital | Three Forty-Five Spectrum, LLC | $1.4 billion | 18 |
| Uscellular | United States Cellular Corporation | $580 million | 380 |
| Whitewater Wireless II, L.P. | $428 million | 14 | |
| Grain Management | NewLevel III, L.P. 0 | $376 million | 8 |
| Moise Advisory | Cherry Wireless, LLC | $211 million | 319 |
| N Squared Wireless, LLC | $101.8 million | 55 | |
| Skylake Wireless II, LLC | $39 million | 57 | |
| Blue Ridge Wireless LLC | $8.9 million | 39 | |
| Agri-Valley Communications | Agri-Valley Communications | $8 million | 7 |
| LICT | LICT Wireless Broadband Company, LLC | $7.7 million | 24 |
| Viaero | NE Colorado Cellular, Inc. | $6.7 million | 18 |
| Nsight | Nsight Spectrum, LLC | $4.7 million | 6 |
| East Kentucky Network | East Kentucky Network, LLC | $4.4 million | 2 |
| Carolina West Wireless | Carolina West Wireless, Inc. | $3.8 million | 11 |
| PVT | PVT Networks, Inc. | $2 million | 6 |
| Chat Mobility | RSA 1 Limited Partnership | $1.7 million | 1 |
| Raptor Wireless LLC | $845,700 | 6 | |
| Horry Telephone | Horry Telephone | $88,060 | 12 |
| PocketiNet | PocketiNet Communications | $59,501 | 1 |
| Jones, Anthony L | $1,575 | 2 | |
| Bidder identity included where available. Source: FCC | |||
The results were pretty much as expected- Dish spent more than expected, and AT&T a bit less, but in rank order and in magnitude, the numbers were relatively close to expectations.

Credit: Getty Images
The “mid-band spectrum” that was auctioned off is considered crucial for mobile operators’ deployment of next generation of wireless service such as 5G, which promises to deliver much faster wireless service and a more responsive network. Mid-band spectrum provides more-balanced coverage and capacity due to its ability to cover a several-mile radius with 5G, despite needing more cell sites than lower-tiered spectrum bands. Its ability to connect more devices and offer real-time feedback is expected to spark a sea change in how we live and work, ushering in new advances like self-driving cars and advanced augmented reality experiences.
“Today’s 3.45 GHz auction results demonstrate that the Commission’s pivot to mid-band spectrum for 5G was the right move,” said FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel. “I am pleased to see that this auction also is creating opportunities for a wider variety of competitors, including small businesses and rural service providers. This is a direct result of the Commission’s efforts to structure this auction with diversity and competition front of mind.”
Craig Moffett wrote in a note to clients shortly after the auction results were announced by the FCC:
“After the almost $100B spent on the C-Band auction [1.], these numbers might sound almost quaint. Still, AT&T’s $9B translates to nearly a quarter turn of additional leverage. And for Dish Network, it is roughly two years of EBITDA, or two full turns. As always, spending money on spectrum is only the beginning. Now starts the spending on putting the new spectrum to work. The carriers did not pay up for this spectrum to allow it to languish in a fallow state, and the Towers will be natural beneficiaries of the deployment process over the coming years. Carrier plans for the C-Band suggest that spectrum will ultimately be deployed in a fairly broad-based manner, rather than just in more densely populated areas of the country, and a similar result seems likely for this spectrum, given its broadly similar propagation attributes.”
Note 1. The C-band auction broke records with its $81.2 billion in gross proceeds.
Analysts at New Street Research thought T-Mobile was going to win more spectrum than it did. They were predicting T-Mobile to spend in the range of $6.6 billion and Dish to spend about $5 billion. The FCC is planning for even more auctions in the future.
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-announces-winning-bidders-345-ghz-service-auction
https://www.fcc.gov/auction/110
FCC Auction 110 for mid-band 5G spectrum gets $21.9B in winning bids
https://www.cnet.com/tech/mobile/at-t-and-dish-big-winners-in-latest-5g-auction/
https://www.fiercewireless.com/wireless/att-dish-top-list-fccs-345-ghz-auction-winners
Chinese companies’ patents awarded in the U.S. increased ~10% while U.S. patent grants declined ~7% in 2021
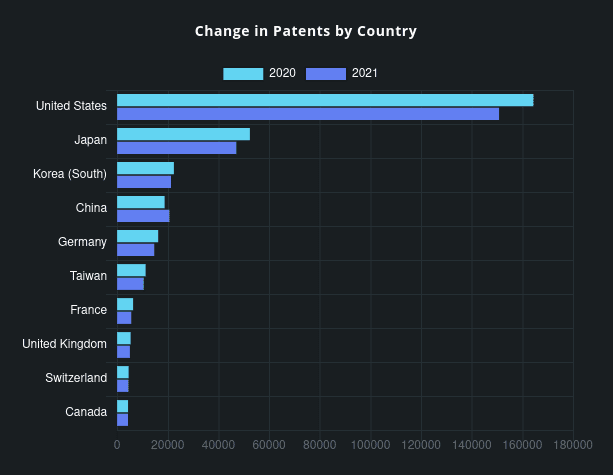
Chinese companies’ patents granted in the United States surged last year, even as total patent awards in the U.S. trended downward, according to a renowned U.S. patent service provider. Data from IFI Claims (more below) showed that Chinese companies’ patents earned in the U.S. increased ~10% to 20,679 in 2021, up from 18,792 in 2020.
The progress came as total U.S. patent grants declined about 7% from 2020 to 327,329 awards last year, the most precipitous drop in the past decade, said IFI Claims.
Several Chinese companies are now among the Top 50 in U.S. patent rankings, including world’s #1 chip maker Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC) at No 4, telecom giant Huawei at No 5, display maker BOE at No 11, tech heavyweight Oppo at No 49, while China’s Advanced New Technologies was ranked #43. Oppo was granted 719 patents in the U.S. last year, marking a surge of 33% year-on-year.
When it comes to total global patents held, China possesses 29% of the global 250 patent families – collections of patent applications covering the same or similar technical content – compared to the U.S. (24%) and Japan (19%), said IFI Claims.
A deeper analysis shows that the U.S. and Japanese portfolios are stronger and more mature. Nevertheless, it is clear that China has stimulated a research and development culture that is serious about intellectual property, said Mike Baycroft, CEO of IFI Claims Patent Services in a statement (see below).
The progress comes as Chinese companies increasingly strengthen their R&D push. Huawei, for instance, invested 141.9 billion yuan ($22.3 billion) in R&D in 2020, accounting for about 15.9% of its revenue.
Jason Ding, head of the intellectual property department at Huawei, said earlier that the company has become one of the world’s largest patent holders through investment in innovation.
Oppo is also beefing up its R&D push. Chen Mingyong, CEO of Oppo, said earlier that the company aims to be a tech pioneer by increasing R&D spending.
“We’ve been working hard for many years to ramp up our products,” Chen said. So far, Oppo has filed for patents in more than 40 countries and regions around the world as it accelerates efforts to expand its global business. As of Dec 31, 2021, Oppo had filed 75,000 patent applications globally, and its global number of authorized patents exceeds 34,000, the company said.
For more information, email: [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
IFI Claims Patent Services – China Surges, as Others Decline:
In a year that saw U.S. patent grants decrease anywhere from 8 to 12% among worldwide corporations, China-based companies stood out with an increase of 10 percent, going from 18,792 awards in 2020 to 20,679 during the past year. A total of four Chinese companies are now in the U.S. Top 50 including Huawei at #5, BOE at #11, Advanced New Technologies at #43, and Guangdong Oppo at #49. US company grants were down commensurate with the worldwide total decline, 8%.
“Last year saw the steepest decline in patent grants in the past decade. There could be many reasons for this – and clearly some are pandemic-related – but what we’re seeing is that corporations are still innovating at an impressive clip despite a challenging environment, particularly U.S. and Asia-based entities,” said Mike Baycroft, CEO of IFI CLAIMS Patent Services.
Consistent with the overall decline in U.S. patent activity from 2020 to 2021, all regions except China had a negative growth rate Year over Year (2021 vs 2020). That is depicted on this chart:
Source: IFI Claims Patent Services
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://mobile.chinadaily.net.cn/cn/html5/2022-01/14/content_013_61e07f4ced500fb050170922.htm
IPS Expands Long Haul Submarine Data Transmission Capacity with Ribbon’s 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100GbE) services
Ribbon Communications Inc, a global provider of real time communications software and IP Optical networking solutions to service providers, enterprises, and critical infrastructure sectors, today announced that Tokyo based IPS (a leading provider of international connectivity services for communications service providers), is using Ribbon’s Apollo Optical Networking solution to power 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100GbE) services delivered over both terrestrial and undersea cables from Manilla to Hong Kong and Singapore.
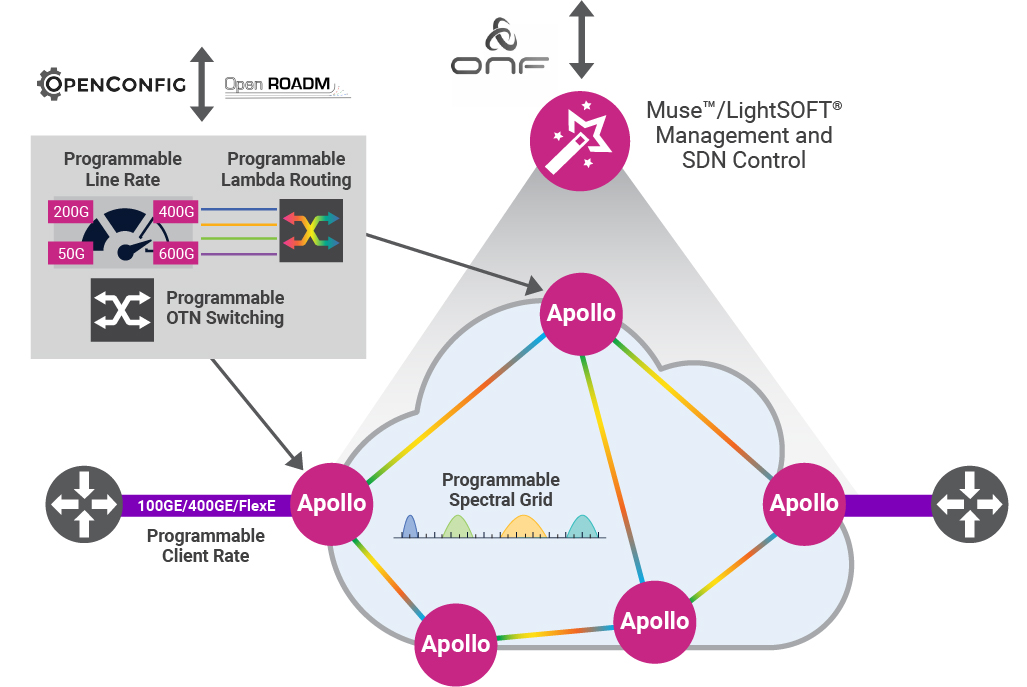
“Our ability to seamlessly deliver connectivity services to our customers over long distances is key to the success of our business,” said Koji Miyashita, President and CEO, IPS. “Ribbon’s Optical transport technology allowed us to maximize our available capacity and transmit world-class communications applications via our submarine services under the South China Sea.”
“Submarine applications must deliver extensive capacity and carry the highest level of communications services on each channel in order to realize cost efficiencies,” said Mickey Wilf, General Manager APAC and MEA Regions for Ribbon. “Our Apollo solution enables IPS to maximize capacity by leveraging dual wavelengths with programmable baud rate and modulation, in conjunction with flex grid technology.”
The solution deployed by IPS leverages Apollo’s high-performance programmable TM800 muxponder cards on Apollo 9600 series platforms to provide optimized long haul undersea connectivity for 100GbE services.
| 9504D | 9603 | 9608 | 9608D | 9624 | ||||
| Size | 1RU | 2RU | 5RU | 5RU | 15RU | |||
| Line Capacity | 1.6T | 2.4T | 6.4T | 6.4T | 19.2T | |||
| Photonics | CDC-F ROADMs, Fixed and Dynamic Amplifiers | |||||||
| Datasheet | Apollo 9504D | Apollo 9603 | Apollo 9608 | Apollo 9608D | Apollo 9624 | |||
| Image | Data Center |
 |
 |
Data Center |
 |
|||
About IPS:
IPS Inc. operates as a Carriers-of Carrier in the Philippines providing network services for local and international telecom companies, contact centers and data centers. It has international telecommunication lines connecting Manila with Hong Kong, Singapore, and many other countries. IPS is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.For more information visit ipsism.co.jp/en/.
About Ribbon:
Ribbon Communications (Nasdaq: RBBN) delivers communications software, IP and optical networking solutions to service providers, enterprises and critical infrastructure sectors globally. We engage deeply with our customers, helping them modernize their networks for improved competitive positioning and business outcomes in today’s smart, always-on and data-hungry world. Our innovative, end-to-end solutions portfolio delivers unparalleled scale, performance, and agility, including core to edge software-centric solutions, cloud-native offers, leading-edge security and analytics tools, along with IP and optical networking solutions for 5G. To learn more about Ribbon visit rbbn.com.
References:
https://ribboncommunications.com/products/service-provider-products/apollo-optical-systems