Author: Alan Weissberger
Bharti Airtel conducts 5G SA trial in 700 MHz band with Nokia
Indian network operator Bharti Airtel on Thursday said it has conducted India’s first 5G SA network trial [1.] in the 700 MHz spectrum band in partnership with Nokia. The demonstration was conducted on the outskirts of Kolkata. It also marked the first 5G trial in the eastern India, the company said in a statement.
Note 1. No 5G commercial service can commence in India till the government auctions 5G spectrum which is scheduled for in the second half of 2022. However, it has been delayed time after time after time. Airtel has been allotted test spectrum in multiple bands by India’s Department of Telecommunications for the validation of 5G technology and use cases.
Using the 700 MHz band, Airtel and Nokia were able to achieve high speed wireless broadband network coverage of 40 Km between two 5G sites in real life conditions. Airtel used equipment from Nokia’s 5G portfolio, which included Nokia AirScale radios and Standalone (SA) core network. [Nokia provides a common core network which supports the 4G – EPC and a 5G Core.]
Randeep Singh Sekhon, CTO – Bharti Airtel said: “Back in 2012, Airtel launched India’s first 4G service in Kolkata. Today, we are delighted conduct India’s first 5G demo in the coveted 700 MHz band in the city to showcase the power of this technology standard. We believe that with the right pricing of 5G spectrum in the upcoming auctions, India can unlock the digital dividend and build a truly connected society with broadband for all.”
Naresh Asija, VP and Head of Bharti CT, Nokia, said: “5G deployment using 700Mhz spectrum is helping communications service providers across the world to cost-effectively provide mobile broadband in remote areas, where typically it is challenging for them to set up the network infrastructure. Nokia is at the forefront in the development of the global 5G ecosystem, and we look forward to supporting Airtel on its 5G journey.”
Airtel says they are “spearheading 5G in India.” Earlier this year Airtel demonstrated India’s first 5G experience over a live 4G network. It also demonstrated India’s first rural 5G trial as well as the first cloud gaming experience on 5G. As part of #5GforBusiness, Airtel has joined forces with leading global consulting and technology companies and brands to test 5G based solutions.
About Airtel:
Headquartered in India, Airtel is a global communications solutions provider with over 480 Mn customers in 17 countries across South Asia and Africa. The company ranks amongst the top three mobile operators globally and its networks cover over two billion people. Airtel is India’s largest integrated communications solutions provider and the second largest mobile operator in Africa. Airtel’s retail portfolio includes high speed 4G/4.5G mobile broadband, Airtel Xstream Fiber that promises speeds up to 1 Gbps with convergence across linear and on-demand entertainment, streaming services spanning music and video, digital payments and financial services. For enterprise customers, Airtel offers a gamut of solutions that includes secure connectivity, cloud and data centre services, cyber security, IoT, Ad Tech and cloud based communication.
For more details visit www.airtel.com
Nokia Contact:
Mohammed Shafeeq, Media Relations
Phone: +91 9167623398
E-mail: [email protected]
References:
Are China’s huge 5G numbers to be believed?
Disclosure:
Many experts believe you can not trust any economic numbers reported by China’s government. China has a long history of opaqueness when it comes to reporting economic statistics. Here’s a reference: https://www.heritage.org/international-economies/commentary/the-problem-false-chinese-economic-data
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Summary:
Xie Cun, Director of China’s Information and Communication Development Department of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), stated last week that China has built more than 1.15 million 5G base stations, accounting for more than 70% of the world.
Prefectural-level cities, more than 97% of counties and 40% of towns and towns have achieved 5G network coverage. China’s network operators report they have a total of 450 million 5G terminal users, accounting for 27% of all mobile subscribers in China and more than 80% of the world.
210 million 5G smartphones have been sold in China so far this year, up 69% over 2020 and representing nearly three-quarters of all handsets sold in China.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Analysis:
The overarching factor in China’s spectacular 5G statistics is the role of the national government. In addition to its direct control of the three state owned network operators [1.], the CCP has ensured – through its high-profile national plans, the supportive Chinese media, and the now-ubiquitous enterprise party committees – that the entire industry is in sync with its prolific 5G ambitions.
Note 1. China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom are together allocating 185 billion yuan ($29 billion) for 5G capex this year alone. 5G plans are available at ultra-low prices, with China Mobile’s entry-level package around $12 a month.
According to the China telecom operators’ numbers, the total number of ‘5G package’ subscribers is 667 million – more than 50% higher than the number of actual 5G users. That’s because there are a tremendous number of 4G subscribers buying the bigger 5G packages.

Light Reading’s Robert Clark wrote:
The operators and the MIIT do not disclose the kind of meaningful network rollout data used by operators in the rest of the world, like percentage of population covered.
So we know nothing about the actual reach of China’s giant 5G project. Most likely, the two giant networks – China Mobile’s and the shared China Telecom-China Unicom network – each covers exactly the same population.
Which leads to the second problem – the distortions of a top-down plan driven by bureaucratic dynamics rather than market needs.
Major cities have rushed to offer rent and tax rebates to speed up rollouts and, of course, to catch the eye of their Beijing bosses.
According to Light Reading’s count, a year ago the wealthy cities of Shanghai, Beijing and Shenzhen accounted for nearly a third of the total 5G rollout.
That is why the MIIT’s new five-year plan makes a point of demanding that 5G be extended to 80% of all rural administrative villages by 2025. Currently, 5G is available in exactly 0% of them.
The other problem in this approach is the built-in irrational exuberance. Since launching 5G, the telcos have worked tirelessly to build out a portfolio of enterprise use cases, as anticipated by the national 5G plans. China Mobile, for one, has developed 470 enterprise apps and nine industry platforms.
But the operators are now tapping out, acknowledging the futility of developing thousands of customized applications, most of which they now admit are “showroom-only.” That’s without getting into the complexities of telco generalists trying to sell into highly specialized segments.
At first look, the scale of China’s government mandated 5G project seems quite impressive. However, in reality it’s a story of fake numbers, rapid rollouts and low subscriber prices.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.finet.hk/newscenter/news_content/61944e4dbde0b33639732370
https://spectrum.ieee.org/how-america-can-prepare-to-live-in-chinas-5g-world
AT&T, Verizon Propose C Band Power Limits to Address FAA 5G Air Safety concerns
AT&T and Verizon said today that they would limit some of their 5G wireless services for six months while federal regulators review the signals’ effect on aircraft sensors, an effort to defuse a conflict about C band interference that has roiled both industries.
The cellphone carriers detailed the proposed limits Wednesday in a letter to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). The companies said they would lower the signals’ cell-tower power levels nationwide and impose stricter power caps near airports and helipads, according to a copy reviewed by The Wall Street Journal. This comes after, both companies agreed to push back their 5G C band rollouts by an additional month to January 5, 2022 after the FAA issued a Nov. 2 bulletin warning that action may be needed to address the potential interference caused by the 5G deployment.
“While we remain confident that 5G poses no risk to air safety, we are also sensitive to the Federal Aviation Administration‘s desire for additional analysis of this issue,” the companies said in the letter to FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel.
“Wireless carriers, including AT&T and Verizon, paid over $80 billion for C-band spectrum—and have committed to pay another $15 billion to satellite users for early access to those licenses—and made those investments in reliance on a set of technical ground rules that were expressly found by the FCC to protect other spectrum users.”
AT&T and Verizon said they had committed for six months to take “additional steps to minimize energy coming from 5G base stations – both nationwide and to an even greater degree around public airports and heliports,” and said that should address altimeter concerns.
Wireless industry officials have held frequent talks with FCC and FAA experts to discuss the interference claims and potential fixes, according to people familiar with the matter. An FCC spokesman said the agreed-upon limits “represent one of the most comprehensive efforts in the world to safeguard aviation technologies” and the agency will work with the FAA “so that 5G networks deploy both safely and swiftly.” Wireless groups argue that there have been no C-Band aviation safety issues in other countries using the spectrum.
Earlier this month, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) warned it could restrict U.S. airspace in bad weather if the networks were turned on as planned in December. The FAA warning came in the thick of cellphone carriers’ network upgrade projects. A spokesman for the FAA called the proposal “an important and encouraging step, and we are committed to continued constructive dialogue with all of the stakeholders.” The FAA believes that aviation and 5G service in the band telecom companies have planned to use can safely coexist, he said.
AT&T and Verizon said they would temporarily lower cell-tower power levels for their 5G wireless services nationwide.
Photo Credit: GEORGE FREY/AGENCE FRANCE-PRESSE/GETTY IMAGES
Wireless industry executives don’t expect the temporary limits to seriously impair the bandwidth they provide customers because networks already direct signals away from planes and airport tarmacs, according to another person familiar with the matter.
Still, the voluntary limits are a rare step for wireless companies that place a high value on the spectrum licenses they hold. U.S. carriers spent $81 billion to buy licenses for the 5G airwaves in question, known as the C-band, and spent $15 billion more to prepare them for service this winter.
The carriers earlier this month delayed their rollout plans until early January after FAA leaders raised concerns about the planned 5G service. Air-safety officials worried the new transmissions could confuse some radar altimeters, which aircraft use to measure their distance from the ground.
At an industry event last week, FAA Administrator Steve Dickson said conducting flights in a safe manner and tapping spectrum for 5G services can both occur. He said the question was how to “tailor both what we’re doing in aviation so that it dovetails with the use of this particular spectrum.” Mr. Dickson said another focus is the use of the spectrum in other parts of the world and how it differs compared with the U.S. “That’s what the discussions are that we’re having with the telecoms right now.”
U.S. wireless companies send 5G signals over lower frequencies than the altimeters, but air-safety officials worried that some especially sensitive sensors could still pick up cell-tower transmissions. Regulators in Canada and France have also imposed some temporary 5G limits.
The carriers’ letter said the mitigation measures would provide more time for technical analysis “without waiver of our legal rights associated with our substantial investments in these licenses.”
C-band limits are most relevant to AT&T and Verizon, which paid premiums to grab licenses for the new signals ready for use in December 2021. The companies still plan to launch their service, subject to the new limits, in January 2022. The proposed limits would extend to July 6, 2022 “unless credible evidence exists that real world interference would occur if the mitigations were relaxed.”
Rival carrier T-Mobile US Inc. is less vulnerable to delay because it spent a smaller amount for licenses that are eligible for use in December 2023. It also controls a swath of licenses suitable for 5G that aren’t subject to air-safety claims.
It’s not yet clear whether the proposal will be accepted by the FAA, which has warned pilots of the possibility that “interference from 5G transmitters and other technology could cause certain safety equipment to malfunction, requiring them to take mitigating action that could affect flight operations.” After July 6th, both carriers say they’ll set everything back to normal “unless credible evidence exists that real-world interference would occur if the mitigations were relaxed.”
“Our use of this spectrum will dramatically expand the reach and capabilities of the nation’s next-generation 5G networks, advancing US leadership, and bringing enormous benefits to consumers and the US economy,” Verizon and AT&T claimed in their joint letter sent to the FCC.
The federal agencies and the companies they oversee are meanwhile stuck in what New Street Research analyst Blair Levin called “a deep state game of chicken” guided by each regulator’s particular interest, with no clear path towards resolution.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/articles/at-t-verizon-propose-5g-limits-to-break-air-safety-standoff-11637778722
Analysis: FCC’s C band auction impact on U.S. wireless telcos
Dish Network as systems integrator; will use Rakuten Symphony’s observability framework in its 5G network
In a press release today, Dish Network said it would use Rakuten Symphony’s observability framework (OBF) in its planned yet delayed 5G network. The company said it would use the Japanese upstart’s technology to collect telemetry data from its network functions in order to support the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to make its operations more efficient.
Dish is adding Rakuten Symphony to its roster of modern telco infrastructure vendors that support Open RAN and cloud-native technologies as a provider of Operational Support Systems (OSS) services. Together, Dish’s roster of OSS vendors will aggregate service assurance, monitoring, customer experience and automation through a singular platform on the DISH 5G network.
The OBF will bring even greater visibility into the performance and operations of the network’s cloud-native functions with near real-time results. This collected data will be used to optimize networks through its Closed Loop Automation module, which executes procedures to provide automatic scaling and healing while minimizing manual work and reducing errors.
The agreement strengthens the operability of Dish’s cloud-native, Open RAN 5G network and lays the foundation for further collaboration in advancing OpenRAN and cloud-native network technologies. As noted previously, Dish’s cloud native 5G core network will be implemented by Amazon AWS
Rakuten Symphony – a new, independent division of the Japanese Internet company Rakuten developed specifically to sell open RAN technologies globally – joins a growing list of Dish 5G vendors that seems to expand almost every week.

Among those tools and services are service assurance solutions that were developed based on Rakuten’s experience in the Japanese market. Rakuten Symphony CEO Tareq Amin has described Japanese consumers as “quality-obsessed” and shared anecdotal stories about customers who experience a dropped call or otherwise sub-optimal network experience sharing their stories far and wide on social media. This led to the development of new service assurance tools that went from generalized customer experience measures to drilling down to “accurate empirical data” at an individual subscriber level. Amin also told RCR Wireless News that Rakuten Symphony’s goal is to be a “platform partner” rather than a vendor.
“We had gotten a lot of inquiries about the applicability of this approach to the U.S. market. So, we decided to expand in the U.S. I have formally started a few weeks ago,” Azita Arvani, GM of Rakuten Mobile Americas, told Light Reading in early 2020. The interest is mutual as Dish chairman Charlie Ergen said in February, “Rakuten is important in the sense that we’ve learned a lot from them.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Recently, Dish said it would use Cisco for routing, IBM for automation, Spirent for testing and Equinix for interconnections – announcements noteworthy considering Dish is mere weeks from its first market launch. The ability to automatically, virtually and in parallel test new 5G Standalone services, slices and software updates in the cloud is key to Dish Network’s network strategy and its differentiation, according to Marc Rouanne, Dish EVP and chief network officer for its wireless business. Rouanne said that the ability to rapidly test and certify network software and services has been part of Dish’s vision for its network.
Dish announced more than a year ago that it would use radio management software from both Mavenir and Altiostar, when Rakuten was a major investor in Altiostar [Note 1.]
–>So it seams that Dish Network’s 5G role will be that of a systems integrator, putting together the many outsourced parts of its 5G greenfield network. It remains to be seen what combination of vendors will supply the Open RAN portion of the 5G network and what development, if any, Dish’s engineers will do for it. And how will Dish’s 5G SA core network via AWS interface with those Open RAN vendors?
Note 1. Rakuten purchased Altiostar outright in August 2021 in a deal worth more than $1 billion. Rakuten’s purchase of Altiostar is part of the company’s broader effort to leverage its Japanese mobile network into a global business selling software, hardware and services to other network operators. The offering was initially dubbed Rakuten Mobile Platform (RMP), and then Rakuten Communications Platform (RCP), but the company in August named it Symphony and said the operation targeted an addressable market of up to $100 billion.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
While our colleague Craig Moffett of Moffett-Nathanson is highly skeptical, some analysts are optimistic about Dish’s 5G prospects. “We have been bullish on Dish on the view that they would have a lower cost for capacity than the incumbents,” wrote the financial analysts at New Street Research in a note to investors this week. We argued that Dish would be worth over $100 / share if they sold their capacity at prices below Verizon’s cost. If correct, this sets up an exciting opportunity for disruption.”
About DISH:
DISH Network Corporation is a connectivity company. Since 1980, it has served as a disruptive force, driving innovation and value on behalf of consumers. Through its subsidiaries, the company provides television entertainment and award-winning technology to millions of customers with its satellite DISH TV and streaming SLING TV services. In 2020, the company became a nationwide U.S. wireless carrier through the acquisition of Boost Mobile. DISH continues to innovate in wireless, building the nation’s first virtualized, O-RAN 5G broadband network. DISH Network Corporation (NASDAQ: DISH) is a Fortune 200 company.
For company information, visit about.dish.com.
About Rakuten Symphony:
Rakuten Symphony, a Rakuten Group organization with operations across Japan, Singapore, India, EMEA, and the United States, develops and brings to the global marketplace cloud-native, open RAN telco infrastructure platforms, services and solutions.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/open-ran/dish-network-officially-teams-up-with-rakuten/d/d-id/773703?
ZTE and Riedel jointly build customized Private 5G as a Service campus network
ZTE announced it has collaborated with Riedel Communications to deploy a customized, private 5G-as-a-Service on a campus network. The Germany media services company plans to work with ZTE on exploring the possible network services and infrastructure for serving large-scale events.
The 5G RAN and Stand Alone (SA) architecture is based on ZTE’s large-capacity Base Band Unit, 5G pad Remote Radio Unit and i5GC (Industrial 5G Core). For industry verticals, a private 5G networks with customized functions, precise SLAs, and reduced costs can be purchased on demand, ZTE said.

“In terms of the future, 5G is a topic that offers many new opportunities. Especially for our largescale events, we need flexible and high-performance systems that enable us to set up ad-hoc infrastructures. Riedel sees ZTE as a strong partner to drive forward these topics with smart technology and the right spirit” said Lutz Rathmann, Director Managed Technology Division.
“ZTE, as one of the global leaders in 5G, truly believes that 5G is driving the development of the verticals and the digital transformation of industries. Deploying a variety of 5G applications enables the move from traditional manufacturing to intelligent manufacturing while reducing costs and increasing efficiency and quality” said Yang Lin, Managing Director of ZTE Germany Representative Office. “In the cooperation, ZTE provides a campus network with a flexible architecture, which could be easily expanded as the size of campus or separated campus. The application platform and device can be also integrated in the campus network for different use cases.”
This cooperation is the first step for Riedel and ZTE to jointly explore the value of 5G in vertical industries. With the solid network foundation of 5G, it can be foreseen that subsequent open platforms and diversified applications based on 5G will innovate further in the future.
About ZTE:
ZTE is a provider of advanced telecommunications systems, mobile devices and enterprise technology solutions for consumers, operators, businesses and public sector customers. As part of ZTE’s strategy, the company is committed to providing customers with end-to-end integrated innovations to deliver excellence and value as the telecommunications and information technology sectors converge. ZTE sells its products and services in more than 160 countries.
About Riedel:
Riedel Communications designs, manufactures, and distributes pioneering real-time video, audio, data, and communications networks for broadcast, pro audio, event, sports, theater, and security applications. The company also provides rental services for radio and intercom systems, event IT solutions, fiber backbones, and wireless signal transmission systems that scale easily for events of any size, anywhere in the world. Riedel is headquartered in Wuppertal, Germany, and employs nearly 700 people in 25 locations throughout Europe, Australia, Asia, and the Americas.
Learn more about Riedel here
References:
Ericsson to acquire Vonage to create a global VoIP network and communication platform
Ericsson has agreed to buy VoIP network operator Vonage for $21 per share, for a total of $6.2 billion. The board of directors at Vonage approved the deal, which will enable Ericsson to expand its enterprise operations globally and build on its integration of Cradlepoint in September 2020.
Vonage reported revenues for the 12 months to end September of $1.4 billion, with an adjusted EBITDA margin of 14% and free cash flow of $109 million. The merger price represents a premium of 28% to Vonage’s closing share price on 19 November and 34% to the volume-weighted average share price for the three months to 19 November.
Vonage’s presence in the Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS) segment will provide Ericsson with access to a complementary and high-growth segment, the company said. The combination will also accelerate enterprise digitization and the development of advanced APIs made possible by 5G. Over the longer term, Ericsson intends to deliver services to the full ecosystem, including telecom operators, developers, and businesses, by creating a global platform for open network innovation, built on Ericsson and Vonage’s complementary solutions.
The cloud-based Vonage Communications Platform (VCP) serves over 120,000 customers and more than one million registered developers globally. The API (Application Programming Interface) platform within VCP allows developers to embed high quality communications – including messaging, voice and video – into applications and products, without back-end infrastructure or interfaces. Vonage also provides Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) and Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS) solutions as part of the Vonage Communications Platform.
VCP accounts for approximately 80% of Vonage’s current revenues and delivered revenue growth in excess of 20% in the three-year period to 2020, with adjusted EBITDA margins moving from -19% in 2018 to break-even in the 12-month period to 30 September 2021. Vonage’s management team projects annual growth of over 20% for VCP in the coming years.
Börje Ekholm, President and CEO of Ericsson, says: “The core of our strategy is to build leading mobile networks through technology leadership. This provides the foundation to build an enterprise business. The acquisition of Vonage is the next step in delivering on that strategic priority. Vonage gives us a platform to help our customers monetize the investments in the network, benefitting developers and businesses. Imagine putting the power and capabilities of 5G, the biggest global innovation platform, at the fingertips of developers. Then back it with Vonage’s advanced capabilities, in a world of 8 billion connected devices. Today we are making that possible.”
“Today Network APIs are an established market for messaging, voice and video, but with a significant potential to capitalize on new 4G and 5G capabilities. Vonage’s strong developer ecosystem will get access to 4G and 5G network APIs, exposed in a simple and globally unified way. This will allow them to develop new innovative global offerings. Communication Service Providers will be able to better monetize their investments in network infrastructure by creating new API driven revenues. Finally, businesses will benefit from the 5G performance, impacting operational performance, and share in new value coming from applications on top of the network.”
Rory Read, CEO of Vonage, says: “Ericsson and Vonage have a shared ambition to accelerate our long-term growth strategy. The convergence of the internet, mobility, the cloud and powerful 5G networks are forming the digital transformation and intelligent communications wave, which is driving a secular change in the way businesses operate. The combination of our two companies offers exciting opportunities for customers, partners, developers and team members to capture this next wave.”
“We believe joining Ericsson is in the best interests of our shareholders and is a testament to Vonage’s leadership position in business cloud communications, our innovative product portfolio, and outstanding team.”
References:
CEO and CFO presentation (pdf)
Two webcasts on November 22, 2021:
9:10 AM CET: Replay
3:30 PM CET: Replay
GSA: 5G Market Snapshot – 5G networks, 5G devices, 5G SA status
By end October 2021, GSA had identified 469 operators in 140 countries/territories were investing in 5G, including trials, acquisition of licenses, planning, network deployment and launches. (This number excludes nearly 200 additional companies awarded spectrum in the US CBRS PAL auction, which could potentially be used for 5G).
- Of those, a total of 182 operators in 73 countries/territories had launched one or more 3GPP-compliant 5G services
- 173 operators in 69 countries/territories had launched 5G mobile services
- 65 operators in 36 countries/territories had launched 3GPP-compliant 5G FWA services (36% of those with launched 5G services)
- Five operators had announced soft launches of their 5G networks that are not counted in the above launch figures.
- 97 operators are identified as investing in 5G standalone (including those evaluating/testing, piloting, planning, deploying as well as those that have launched 5G SA networks).
- GSA has catalogued 20 operators as having deployed/launched 5G SA in public networks
As for 5G endpoint devices:
The number of announced 5G devices continues to rise and has now reached 1115, an increase of 18.9% in the last quarter. Of these devices, 67.7% are understood to be commercially available. The number of commercial 5G devices has grown by 24.2% over the last three months passing 750 for the first time, to reach a total of 755 devices understood to be commercially available.
By end-October 2021, GSA had identified:
- twenty-two announced form factors.
- one hundred and sixty-five vendors who had announced available or forthcoming 5G devices.
- one thousand, one hundred and fifteen announced devices (including regional variants, but excluding operator-branded devices that are essentially re-badged versions of other phones), including 755 that are understood to be commercially available:
- five hundred and fifty phones (up 27 from September), at least 491 of which are now commercially available (up 32 in a month).
- one hundred and ninety FWA CPE devices (indoor and outdoor), at least of which 90 are now commercially available.
- one hundred and fifty-six modules.
- seventy-one industrial/enterprise routers/gateways/modems.
- forty-eight battery operated hotspots.
- twenty-five tablets.
- twenty laptops (notebooks).
- eleven in-vehicle routers/modems/hotspots.
- eight USB terminals/dongles/modems.
- thirty-six other devices (including drones, head-mounted displays, robots, TVs, cameras, femtocells/small cells, repeaters, vehicle OBUs, a snap-on dongle/adapter, a switch, a vending machine and an encoder).
- six hundred and twenty-seven announced devices with declared support for 5G standalone in sub-6 GHz bands, 434 of which are commercially available.
Not all devices are available immediately and specification details remain limited for some devices.
We can expect the availability of devices to continue to improve and for more information about announced devices to emerge as they reach the market. Based on vendors’ previous statements and recent rates of device release, we might expect to see the number of commercial devices surpassing the 820 mark by the end of Q4 2021. GSA will be tracking and reporting regularly on these 5G device launch announcements. Its GAMBoD database contains key details about device form factors, features and support for spectrum bands. Summary statistics are released in this regular monthly publication.
More information on 5G SA networks:
Operators are increasingly experimenting with and deploying 5G standalone (SA) networks. With a totally new, cloud-based, virtualized, microservices-based core infrastructure, some of the anticipated benefits of introducing 5G SA technologies include faster connection times (lower latency), support for massive numbers of devices, programmable systems enabling faster and more agile creation of services and network slices, with improved support for SLA management within those slices, and the advent of voice-over new radio (VoNR). Introduction of 5G SA is expected to facilitate simplification of architectures, improve security and reduce costs. 5G SA is expected to enable customization and open up new service and revenue opportunities tailored to enterprise, industrial and government customers.
GSA is tracking the emergence of the 5G SA system, including the availability of chipsets and devices for customers, plus the testing and then deployment of 5G SA networks by public mobile network operators as well as private network operators. This paper is the latest in an ongoing series of papers summarising market trends, drawing on the data collected in GSA’s various databases covering chipsets, devices, spectrum and networks.
Investment in 5G SA by public and private network operators
5G SA networks can be deployed in a variety of scenarios: as an overlay for a public 5G non-SA (NSA) network, as a greenfield 5G deployment for a public network operator without a separate LTE network, or as a private network deployment for an enterprise, utility, education, government or any other organization requiring its own private campus network.
GSA has identified 94 operators in 48 countries/territories worldwide that have been investing in public 5G SA networks (in the form of trials, planned or actual deployments). This equates to just over 20% of the 469 operators known to be investing in 5G licenses, trials or deployments of any type.
At least 19 operators in 15 countries/territories are now understood to have launched public 5G SA networks. A further four have deployed 5G SA technology but not yet launched services, or have only soft-launched them. In addition to these, at least 25 have been catalogued as deploying or piloting 5G standalone, 28 as planning to deploy the technology and 18 as being involved in evaluations/tests/trials.
A recent survey of European and North American mobile operators by Heavy Reading and EXFO (published October 2021) revealed that 49% of them plan to deploy 5G SA within a year and that a further 39% plan to deploy 5G SA within one or two years. Meanwhile, vendors are reporting the deployment of 5G core SA networks that are not announced publicly. So the active deployments and launches catalogued by GSA so far will be the first of many.
In addition to the investment in 5G SA for public mobile networks mentioned above, a number of organizations are testing, piloting or deploying 5G SA technologies for private networks. GSA has developed a new database tracking private mobile network licenses, trials and deployments. It has collated information about 626 organizations known to be deploying LTE or 5G private mobile networks, or known to have been granted a license suitable for the deployment of a private LTE or 5G network so far. Of those, 151 are known to be using 5G networks (excluding those labelled as 5G-ready) for private mobile network pilots or deployments. Of those, 27 (nearly 18% of them) are known to be working with 5G SA already, including manufacturers, academic organizations, commercial research institutes, construction, communications/IT services, rail and aviation organizations.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Addendum:
Despite the above 5G status report, many believe that 5G has been a failure. For example, Half-Baked Business Models…… from SDxCentral.
References:
https://gsacom.com/technology/5g/
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/half-baked-business-models-hamper-5gs-potential/2021/11/
Orange and Nokia demo 600Gb/sec transmission over a 914 km optical network; Nokia 25G PON
Nokia and Orange announced the completion of a network trial using the Nokia PSE-Vs, its fifth generation super coherent optics. With this field trial, Orange has successfully validated a planned upgrade of its long-haul backbone networks to support new high-bandwidth 400 Gb/sec services, and the ability to scale fiber capacity up to 600Gb/sec. This represents an increase in spectral efficiency by 50% compared to prior technologies on its long distance optical network.
The trial was performed in real-world conditions using Nokia PSE-Vs super coherent optics in production-ready optical transport hardware, just 16 months after the lab prototype trial done on Orange’s live network. Orange and Nokia demonstrated error-free performance at a data rate of 600Gb/sec over a 914 km network between Paris and Biarritz, under challenging live network conditions. The fiber network consisted of 13 spans of Orange’s existing network, through multiple cascaded reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexers (ROADM), using 100GHz WDM spectrum channels.
Jean-Luc Vuillemin, Vice President of International Networks and Services at Orange, said: “With the booming market bandwidth requirement and need for scalability and flexibility, it is important that Orange continues to support an ever-greater network scale and new high-bandwidth services across our terrestrial and subsea global footprint.
Validating super coherent optics with Nokia represents an important enabler for future-proof networks which will bring spectral efficiency and operational deployment flexibility to our customer solutions. Furthermore this technology will allow for power savings by nearly 50%, which is key to our objective of developing greener networks for our customers. ”
James Watt, Head of Optical Networks Division, Nokia, said: “We are delighted to work with Orange in continued support of their network upgrade plans. With the introduction of the PSE-Vs super coherent capabilities across our entire 1830 portfolio, Nokia enables spectrally-efficient transport at 600Gb/sec over real-world long haul networks, and 400Gbps services over ultra long haul networks spanning multiple 1000’s of kilometers.”

Nokia 1830 Photonic Service Interconnect (PSE)
The Nokia PSE-V
The Nokia PSE-V is the industry’s most advanced family of digital coherent optics (DCO), powering the next generation of Nokia high-performance, high-capacity transponders, packet-optical switches, disaggregated compact modular and subsea terminal platforms. The PSE-V Super Coherent DSP (PSE-Vs) implements the industry’s only 2nd generation probabilistic constellation shaping (PCS) with continuous baud rate adjustment, and supports higher wavelength capacities over longer distances – including support for 400G over any distance – over spectrally efficient 100GHz WDM channels while further reducing network costs and power consumption per bit.
Further resources:
• Web page: Nokia 1830 Photonic Service Interconnect (PSI)
• Web page: Nokia Photonic Service Engine (PSE) Coherent DSPs
• Web page: 400G Everywhere
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Earlier this week, Nokia and Bell Canada announced the first successful test of 25G PON fiber broadband technology in North America at Bell’s Advanced Technical Lab in Montréal, Québec.
The trial validates that current GPON and XGS-PON broadband technology and future 25G PON can work seamlessly together on the same fiber hardware, which is being deployed throughout the network today. 25G PON delivers huge symmetrical bandwidth capacity that will support new use cases such as premium enterprise service and 5G transport. Nokia’s 25G PON solution utilizes the world’s first implementation of 25G PON technology and includes Lightspan and ISAM access nodes, 25G/10G optical cards and fiber modems.
For the past decade, Bell has been rolling out fiber Internet service to homes and businesses across the country, a key component in the company’s focus on connecting Canadians in urban and rural areas alike with next-generation broadband networks. With this successful trial, Bell can be confident that its network will absorb the increased capacity of future technologies and connect Canadians for generations to come.
Stephen Howe, EVP & Chief Technology Officer, Bell, said:
“As part of Bell’s purpose to advance how Canadians connect with each other and the world, we embrace next-generation technologies such as 25G PON to ensure we remain at the forefront of broadband innovation. Our successful work with Nokia to deliver the first 25G PON trial in North America will help ensure we maximize the Bell fiber advantage for our customers in the years to come.”
Jeffrey Maddox, President of Nokia Canada, said: “Nokia innovations powered the fiber networks and the connectivity lifeline that carried Canadian homes and businesses through the pandemic. 25G PON innovations will drive the next generation of advances in our connected home experience.”
Bell and Nokia have closely collaborated over the years on many industry breakthroughs, such as the first Canadian trial of 5G mobile technology in 2016. Bell continues to work with Nokia to build and expand its 5G network across Canada.
References:
TIM Brasil, Ericsson, Qualcomm, Motorola test 5G SA for power distribution in LatAm
TIM Brasil has been carrying out a 5G Standalone (SA) pilot in Sao Paulo since August 2nd. It’s in partnership with energy distribution company Enel, reports Telesintese. The 5G SA tests in an electric substation in the neighborhood of Vila Olímpia are being conducted in the 3.5 GHz band and use Ericsson AIR 6449, AIR3227, and AIR 6488 antennas. Qualcomm provided a 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) gen 2 CPE with Snapdragon X62 5G Modem, while Motorola provided Edge, Moto G 5G and Moto G100 smartphones.
Sensors installed by Enel in the substation allow remote control of the structure and identify in real time if there are faults or maintenance needs. According to the companies, this is the first pilot to use 5G in electrical distribution in Latin America.

Photo Credit: Telesintese
As Leonardo Capdeville explained to Tele.Síntese , the 5G worked as a backhaul link for Qualcomm’s CPE, which radiated the WiFi signal through the power substation. Sensors installed by Enel in the substation allow remote control of the structure and identify in real time if there are failures or maintenance needs.
Another application tested is related to the field team. Enel technicians use smartphones connected directly to 5G. These feature augmented reality programs that allow instant access to substation data and detail how to perform maintenance just by pointing the camera at the equipment.
This was the first pilot to use 5G in electrical distribution in Latin America, according to the companies.
Currently, Enel uses systems that connect via 3G to its control centers. Such a connection is much slower, and results in response times in the seconds.
With 5G, observe Fernando Andrade, responsible for the Engineering and Construction area at the distributor, the response time is between 1 to 5 milliseconds, opening the way for a more intense use of the concept of “self healing” networks, that is, networks that establish routes for energy as problems in one of them are identified.
PROJECT WILL BE BIGGER WHEN 3.5 GHZ SIGNAL IS RELEASED:
According to the executives, the project should evolve. Enel liked the result, noted gains in efficiency and speed in handling incidents. In the city of São Paulo there are 120 power substations that could be connected, but the executive goes further: “We started with the substation because it is a relatively controlled environment, but it is possible to spread the technology to the equipment throughout the network ”, he observed.
Andrade envisions the use of 5G for commanding drones, capturing and analyzing images. It even suggests that, in the future, garbage trucks bring cameras and sensors that analyze energy networks, freeing inspectors for other tasks.
Capdeville, from TIM, points out that the current test is based on a provisional license from Anatel, but that the antenna installed in Vila Olímpia must remain and be used to serve the 5G consumer in general as soon as the 3.5 GHz spectrum is released in the city – the operator was one of the buyers of the track in the auction held by the regulatory agency at the beginning of the month .
The 5G network pilot is part of Enel’s Urban Futurability project, which will transform Vila Olímpia into a digital and sustainable neighborhood with an investment of R$125 million from the Research and Development program of the National Electric Energy Agency (Aneel).
TIM and Enel, both companies with Italian origins, already have a partnership for research and development of products and in different areas. Enel is one of the companies hired by TIM to supply energy from renewable sources. In this case, the built-in solar power plants distributor in Bahia serves the tele consumer units.
In addition, Enel X, the energy company’s innovation arm, has a contract with TIM to develop solutions for smart cities – such as smart grid applications.
References:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/tim-brasil-launches-5g-standalone-tests-with-enel–1404882
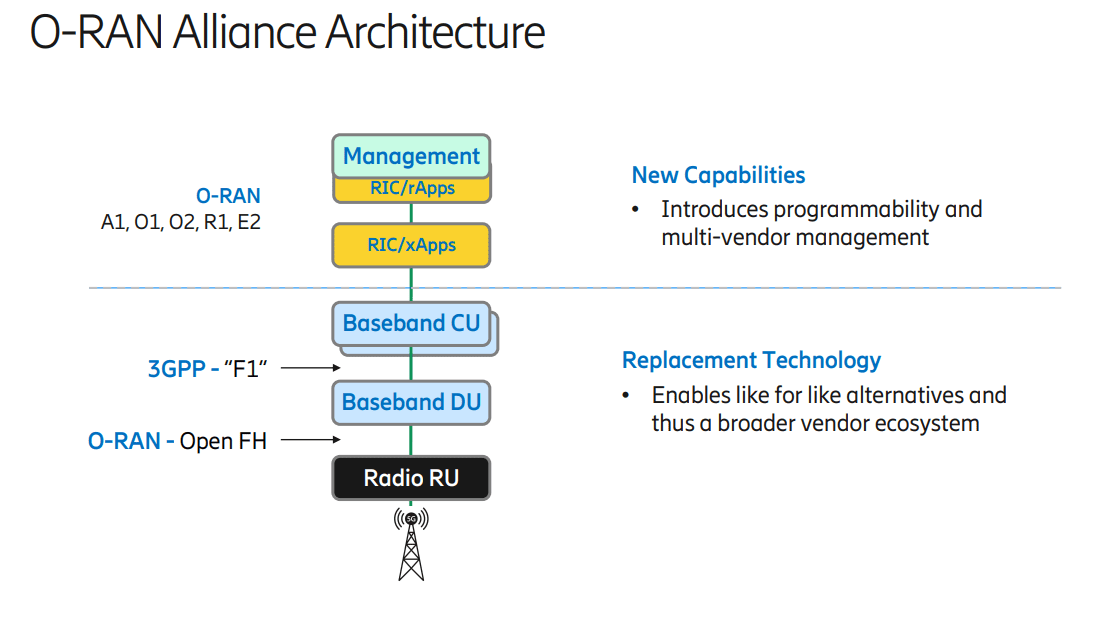
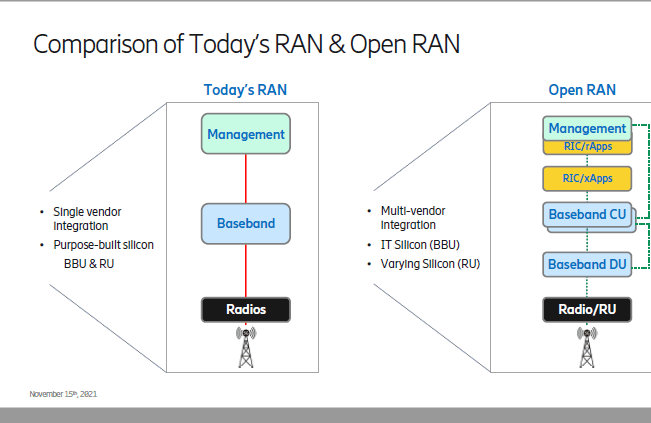
Ericsson expresses concerns about O-RAN Alliance and Open RAN performance vs. costs
In a letter to the FCC, Jared M. Carlson, Ericsson’s Vice President, Government Affairs and Public Policy expressed his company’s concern with the O-RAN Alliance. In particular, an August report of the European Commission could not determine whether the O-RAN Alliance was complying with various WTO criteria, including transparency and open procedures, and also noted a concern that any one of the five founding members could effectively veto any proposed specification.
Some O-RAN Alliance specifications are proceeding slowly, according to Ericsson. One reason why can be explained simply by the resources devoted to the group. For example, O-RAN front-haul meetings (a more mature O-RAN specification) sees about 60 members attending, with only about ten members actively contributing. In contrast, in a typical 3GPP RAN Plenary, there are approximately 600 members delivering 1000 contributions per quarter.
The lack of completed O-RAN specifications means that any such deployments require individual vendors to come to mutual agreements—a far cry from the “plug-and-play” vision of a complete set of Open RAN network interface standards. Light Reading referred to that months ago as another form of “vendor lock-in.”
Mike Murphy, CTO, Ericsson North America told the FCC that Ericsson has dedicated a number of resources to making O-RAN Alliance specifications successful, delivering about 1000 of 7000 total specifications,” the company told the FCC, citing Murphy’s presentation. “Indeed, without Ericsson’s contributions to the O-RAN Alliance, the timeline for more fully developed standards would likely be even further out in the future.”
Regarding security, Mr. Murphy noted that, again, Ericsson is one the top three contributors to the O-RAN Alliance Security working group. Yet there are no security specifications from the O-RAN Alliance Security group—there is only a set of requirements. He also noted that the performance of Open RAN does not compare to (vendor specific, purpose built) integrated RAN. Even if the so called 40% cost saving estimates were true on a per-unit cost basis, the two different types of RAN equipment would not deliver the same level of performance.
Furthermore, Ericsson’s own estimates have indicated that Open RAN is more expensive than integrated RAN given the need for more equipment to accomplish what purpose-built solutions can deliver and increased systems integration costs. That’s quite shocking considering that many upstarts (e.g. Rakuten, Inland Cellular, etc) have stated Open RAN is cheaper. For example, “Open RAN will allow for cost savings over proprietary architectures,” Open RAN vendor Mavenir declared in its own recent meeting with FCC officials. The company said open RAN equipment can reduce network providers’ operating expenses by 40% and total cost of ownership by 36%.
Ericsson isn’t the only 5G company cautioning the FCC on Open RAN. Nokia – another major 5G equipment vendor – made similar arguments in a recent presentation to the FCC. “While there are some vendors that only offer open RAN architecture and/or limited RAN products, Nokia is able to provide a choice of classical or open RAN depending on the desires of our customers,” Nokia explained. “To date, the vast majority of service providers have chosen classical RAN solutions, deferring investment in open RAN until further commercial maturity has been demonstrated.”
Nokia also took issue with the notion that open RAN equipment is dramatically cheaper than traditional, classic RAN equipment. “The draft cost catalog also demonstrates that there are not cost savings being offered through open RAN equipment estimates compared to integrated RAN estimates,” Nokia wrote to the FCC in April following the release of the agency’s initial, draft pricing catalogue.
Many telecom professionals, like John Strand, argue that open RAN is not yet mature. They contend that government mandates that would require the use of the technology – in a furtherance of geopolitical goals – would be misguided. “The US has clearly demonstrated that open and intense competition, not government mandates, is the most effective way to mobilize the telecom industry to enable unprecedented innovation and value creation,” Ericsson told the FCC. “The US led the world in 4G and the ‘app economy’ not by insisting on any particular network standard, but by creating an open, predictable and attractive investment climate for all industry stakeholders and allowing operators to select the best technology based on their needs.”
Mr. Murphy concluded that the Commission and the U.S. government more generally should continue to “keep their eyes on the prize.” Notably, ensuring that the U.S. continues to smooth the way for 5G deployments will continue to pay dividends for the U.S. economy, with over $500 Billion added to the U.S. economy from 5G-enabled business, is the critical job of the day. The key step the Commission can take is to continue to foster the deployment of 5G.
References:
https://ecfsapi.fcc.gov/file/1117953022367/Ericsson%20Open%20RAN%20ex%20parte%20Nov%2017%20FINAL.pdf
https://ecfsapi.fcc.gov/file/1117953022367/Ericsson%20O-RAN%20Update%20FINAL.pdf
https://www.lightreading.com/open-ran/ericsson-actually-open-ran-is-more-expensive/d/d-id/773617?
TIP OpenRAN and O-RAN Alliance liaison and collaboration for Open Radio Access Networks
Addendum -Tuesday 23 November 2021:
German study warns of security risks in Open RAN standards
Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN) based on the standards of the O-RAN Alliance carry significant security risks in their current form, according to a study commissioned by Germany’s Federal Office for Information Security (BSI). The analysis was carried out by the Barkhausen Institute, an independent research institution, in cooperation with the group Advancing Individual Networks in Dresden and the company Secunet Security Networks.
The implementation of Open RAN standards by the O-RAN Alliance is based on the 5G-RAN specifications developed by the 3GPP. Using a best / worst case scenarios analysis, the German study demonstrated that the Open RAN standards have not yet been sufficiently specified in terms of ‘security by design’, and in some cases carry security risks. The BSI called for the study’s findings to be taken into account in the further development of the Open RAN ecosystem, in order to support the rapid growth of the market with security from the start.
The open RAN project is supported by all three mobile operators in Germany – Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone and Telefonica – as well as the 1&1, which is building a fourth network in the country. The German government also recently awarded EUR 32 million in subsidies to support further development of the open RAN technology.
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/german-study-warns-of-security-risks-in-open-ran-standards–1405252