fiber optics
Lumen launches Multi-Cloud Gateway (MCGW) and expands metro fiber network after selling consumer FTTH business to AT&T
Lumen Technologies has announced a new Multi-Cloud Gateway (MCGW) and expanded its metro fiber optic network across 16 major U.S. markets, delivering up to 400G b/sec connectivity to support high-speed AI data processing. This initiative provides a software-defined, self-service platform for secure, private, and flexible connections between enterprise data centers and cloud providers.
Lumen says the new MCGW product and expanded fiber footprint will simplify how data moves across hybrid environments by bringing both centralized multi-cloud routing and high-capacity private metro connectivity. The result will be a more consistent, controllable networking foundation for AI and other modern workloads. This expansion is part of a broader strategy where Lumen plans to reach 58 million fiber miles by 2031 to meet the soaring demand for AI-ready infrastructure.
“Moving data across hybrid environments is a lot like managing air traffic – you need clear routes, predictable timing, and the ability to adjust when conditions change. Most legacy networks weren’t built for that level of coordination,” said Jim Fowler, Lumen chief technology and product officer. “With our expanded network fabric, Lumen gives enterprises a way to move data securely, effortlessly, and consistently across clouds, data centers, and edge locations, designed to reduce the complexity that hold AI-driven operations back.”
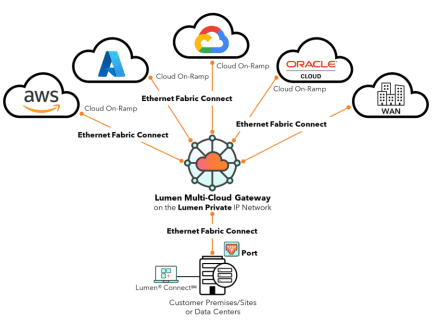
Multi-Cloud Gateway: Multi-Cloud Gateway (MCGW) is a core element of Lumen’s shift to cloud-based telecom. Built as a software-defined, self-service routing layer on Lumen’s global fiber network, MCGW provides private, high-capacity connectivity among enterprises, hyperscalers and emerging cloud platforms. It turns traditional telecom interconnection into a programmable cloud fabric, allowing customers to dynamically connect cloud-to-cloud and cloud-to-enterprise environments, optimize traffic for performance and cost, and support advanced use cases such as AI workload distribution and real-time data exchange. By unifying connectivity, routing and policy, MCGW is designed to reduce operational complexity, speed time to service and lower total cost of ownership.
Lumen Multi-Cloud Gateway:
Image credit: Lumen Technologies
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Metro Ethernet & IP Services: Expanded high-capacity, dedicated connectivity across 16 U.S. markets, delivering up to 100Gbps between regional data centers, campuses, and edge locations and up to 400Gbps at key cloud data centers in those markets. This enables fast, secure movement of massive datasets for AI training, analytics, replication, and disaster recovery.
Recently upgraded markets include Northern Virginia; Atlanta; Chicago; Columbus; Dallas; Denver; Kansas City; Las Vegas; Los Angeles; Minneapolis; New York City; Phoenix; Portland; San Antonio; San Jose; and Seattle.
“AI is reshaping network design, pushing enterprises to move from experimentation to execution with architectures that reduce latency, cost variability, and operational complexity,” said Courtney Munroe, Vice President, Worldwide Telecommunications Research at IDC. “As workloads become more distributed and performance sensitive, organizations are rethinking how they connect edge sites, data centers, and multiple clouds, and Lumen’s network fabric shows how programmable networks can deliver more consistent data movement.”
The business impact is immediate and practical for industries scaling their AI ambitions:Financial Services: Keep risk, payments, and fraud workloads synchronized across multiple clouds with centralized policy control for lower latency and more predictable performance.
- Retail: Improve business agility by accelerating data movement across cloud and enterprise environments, so analytics keep pace with changing demand.
- Healthcare: Maintain data separation, support telehealth services, imaging and analytics, disaster recovery, and manage research workloads across institutions and resource centers.
- Manufacturing: Connect regional facilities and cloud environments to enable real-time analytics and predictive maintenance.
- Multi-Cloud Gateway (MCGW): Launched and available as of February 17, 2026, as a software-defined, self-service routing layer.
- Metro Network Expansion: Currently live across 16 major U.S. markets (including New York, Chicago, and Los Angeles), offering up to 400 Gbps at key cloud data centers.
- Internet On-Demand: Expanded in late 2025 to over 10 million new business locations, providing “cloud-like” connectivity scalability within minutes.
- Wavelength RapidRoutes: Available for deployment in just 20 business days, significantly faster than industry standard turn-up times.
- Microsoft: Chosen to expand Microsoft’s network capacity to support surging demand for Azure AI services. Microsoft utilizes Lumen’s Private Connectivity Fabric (PCF) for custom network architecture between data centers.
- Google Cloud: Partnered to modernize Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) offerings. This allows Lumen-managed SD-WAN and security services to be hosted directly in Google Cloud regions.
- Palantir Technologies: A multi-year alliance formed in October 2025 to combine Lumen’s connectivity fabric with Palantir’s Foundry and AI Platform (AIP), enabling enterprises to deploy AI faster in multi-cloud environments.
- Other Hyperscalers: Lumen has secured approximately $8.5 billion in private connectivity deals with companies including Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Meta to support their AI model training.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
On February 2nd, Lumen announced that it completed the sale of its Mass Markets fiber-to-the-home business in 11 states, including Quantum Fiber, to AT&T for $5.75 billion in cash. The sale includes substantially all of the related consumer fiber access network and customer relationships in those 11 states, which serve more than 1 million fiber customers and reaches more than 4 million enabled fiber locations. The completed transaction is another strategic milestone in Lumen’s transformation into the leading enterprise digital networking services company built for the multi-cloud, AI-driven economy rather than for consumer fiber access.
As part of the completed transaction, Lumen will retain assets that will continue to serve as the foundation of its enterprise transformation, including all national, regional, state, and metro level fiber backbone network infrastructure, central offices and associated real estate. In addition, Lumen is retaining and caring for its copper-based consumer services, which continue to provide a strong ongoing financial contribution to Lumen. The enterprise and wholesale fiber customers will remain with Lumen in all geographies.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Lumen Technologies:
Lumen is unleashing the world’s digital potential. We ignite business growth by connecting people, data, and applications – quickly, securely, and effortlessly. As the trusted network for AI, Lumen uses the scale of our network to help companies realize AI’s full potential. From metro connectivity to long-haul data transport to our edge cloud, security, managed service, and digital platform capabilities, we meet our customers’ needs today and as they build for tomorrow.
When networks shift from constraint to enabler, organizations can move faster, scale with confidence, and unlock greater innovation. To learn more about these products and availability timelines, visit Multi-Cloud Gateway and Connectivity Services.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://assets.lumen.com/is/content/Lumen/lumen-multi-cloud-gateway-data-sheet
Lumen: “We’re Building the Backbone for the AI Economy” – NaaS platform to be available to more customers
Lumen deploys 400G on a routed optical network to meet AI & cloud bandwidth demands
Lumen and Ciena Transmit 1.2 Tbps Wavelength Service Across 3,050 Kilometers
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
Lumen Technologies to connect Prometheus Hyperscale’s energy efficient AI data centers
Microsoft choses Lumen’s fiber based Private Connectivity Fabric℠ to expand Microsoft Cloud network capacity in the AI era
Lumen, Google and Microsoft create ExaSwitch™ – a new on-demand, optical networking ecosystem
ACSI report: AT&T, Lumen and Google Fiber top ranked in fiber network customer satisfaction
Fiber Optic Boost: Corning and Meta in multiyear $6 billion deal to accelerate U.S data center buildout
Corning Incorporated and Meta Platforms, Inc. (previously known as Facebook) have entered a multiyear agreement valued at up to $6 billion. This strategic collaboration aims to accelerate the deployment of cutting-edge data center infrastructure within the U.S. to bolster Meta’s advanced applications, technologies, and ambitious artificial intelligence initiatives. The agreement specifies that Corning will furnish Meta with its latest advancements in optical fiber, cable, and comprehensive connectivity solutions. As part of this commitment, Corning plans to significantly scale its manufacturing capabilities across its North Carolina facilities.
A key element of this expansion is a substantial capacity increase at its fiber optic cable manufacturing plant in Hickory NC, for which Meta will serve as the foundational anchor customer. The construction and operation of these data centers — critical infrastructure that supports our technologies and moves us toward personalized superintelligence — necessitate robust server and hardware systems designed to facilitate information transfer and connectivity with minimal latency. Fiber optic cabling is a cornerstone component for enabling this high-speed, near real-time connectivity, powering applications from sophisticated wearable technology like the Ray-Ban Meta AI glasses to the global connectivity services utilized by billions of individuals and enterprises.
“This long-term partnership with Meta reflects Corning’s commitment to develop, innovate, and manufacture the critical technologies that power next-generation data centers here in the U.S.,” said Wendell P. Weeks, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Corning Incorporated. “The investment will expand our manufacturing footprint in North Carolina, support an increase in Corning’s employment levels in the state by 15 to 20 percent, and help sustain a highly skilled workforce of more than 5,000 — including the scientists, engineers, and production teams at two of the world’s largest optical fiber and cable manufacturing facilities. Together with Meta, we’re strengthening domestic supply chains and helping ensure that advanced data centers are built using U.S. innovation and advanced manufacturing.”
Meta is expanding its commitment to build industry-leading data centers in the U.S. and to source advanced technology made domestically. Here are two quotes from them:
- “Building the most advanced data centers in the U.S. requires world-class partners and American manufacturing,” said Joel Kaplan, Chief Global Affairs Officer at Meta. “We’re proud to partner with Corning – a company with deep expertise in optical connectivity and commitment to domestic manufacturing – for the high-performance fiber optic cables our AI infrastructure needs. This collaboration will help create good-paying, skilled U.S. jobs, strengthen local economies, and help secure the U.S. lead in the global AI race.”
- “As digital tools and generative AI continue to transform our economy — in fields like healthcare, finance, agriculture, and more — the demand for fiber connectivity will continue to grow. By supporting American companies like Corning and building and operating data centers in America, we’re helping ensure that our nation maintains its competitive edge in the digital economy and the global race for AI leadership.”
Key elements of the agreement:
- Multiyear, up to $6 billion commitment.
- Corning to supply latest generation optical fiber, cable and connectivity products designed to meet the density and scale demands of advanced AI data centers.
- New optical cable manufacturing facility in Hickory, North Carolina, in addition to expanded production capacity across Corning’s North Carolina operations.
- Agreement supports Corning’s projected employment growth in North Carolina by 15 to 20 percent, sustaining a skilled workforce of more than 5,000 employees in the state, including thousands of jobs tied to two of the world’s largest optical fiber and cable manufacturing facilities.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Comment and Analysis:
Corning’s “up to $6 billion” Meta agreement is essentially a long‑term, anchor‑tenant bet that AI‑era data centers will be fundamentally more fiber‑intensive than legacy cloud resident data centers, with Corning positioning itself as the default U.S. optical plant for Meta’s buildout through ~2030. In practice, this deal is a long‑term take‑or‑pay style capacity lock that de‑risks Corning’s capex while giving Meta priority access to scarce, high‑performance data‑center‑grade fiber and cabling.
AI data centers are becoming the new FTTH in the sense that hyperscale AI buildouts are now the primary structural driver of incremental fiber demand, design innovation, and capex prioritization—but with far higher fiber intensity per site and far tighter performance constraints than residential access ever imposed.
Why “AI Data Centers are the new FTTH” for fiber optic vendors:
For fiber‑optic vendors, AI data centers now play the role that FTTH did in the 2005–2015 cycle: the anchor use case that justifies new glass, cable, and connectivity capacity.
-
AI‑optimized data centers need 2–4× more fiber cabling than traditional hyperscalers, and in some designs more than 10×, driven by massively parallel GPU fabrics and east–west traffic.
-
U.S. hyperscale capacity is expected to triple by 2029, forcing roughly a 2× increase in fiber route miles and a 2.3× increase in total fiber miles, a demand shock comparable to or larger than the early FTTH boom but concentrated in fewer, much larger customers.
-
This is already reshaping product roadmaps toward ultra‑high‑fiber‑count (UHFC) cable, bend‑insensitive fiber, and very‑small‑form‑factor connectors to handle hundreds to thousands of fibers per rack and per duct.
In other words, where FTTH once dictated volume and economies of scale, AI data centers now dictate density, performance, and margin mix.
Carrier‑infrastructure: from access to fabric:
From a carrier perspective, the “new FTTH” analogy is about what drives long‑haul and metro planning: instead of last‑mile penetration, it’s AI fabric connectivity and east–west inter‑DC routes.
-
Each new hyperscale/AI data center is modeled to require on the order of 135 new fiber route miles just to reach three core network interconnection points, plus additional miles for new long‑haul routes and capacity upgrades.
-
An FBA‑commissioned study projects U.S. data centers alone will need on the order of 214 million additional fiber miles by 2029, nearly doubling the installed base from ~160M to ~373M fiber miles; that is the new “build everywhere” narrative operators once used for FTTH.
-
Carriers now plan backbone routes, ILAs, and regional rings around dense clusters of AI campuses, treating them as primary traffic gravity wells rather than as just a handful of peering sites at the edge of a consumer broadband network.
The strategic shift: FTTH made the access network fiber‑rich; AI makes the entire cloud and transport fabric fiber‑hungry.
Strategic implications:
-
AI is now the dominant incremental fiber use case: residential fiber adds subscribers; AI adds orders of magnitude more fibers per site and per route.
-
Network economics are moving from passing more homes to feeding more GPUs: route miles, fiber counts, and connector density are being dimensioned to training clusters and inference fabrics, not household penetration curves.
-
Policy and investment narratives should treat AI inter‑DC and campus fiber as “national infrastructure” on par with last‑mile FTTH, given the scale of projected doubling in route miles and more than doubling in fiber miles by 2029.
In summary, the next decade of fiber innovation and capex will be written less in curb‑side PON and more in ultra‑dense, AI‑centric data centers with internal fiber optical fabrics and interconnects.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Meta Announces Up to $6 Billion Agreement With Corning to Support US Manufacturing
Big tech spending on AI data centers and infrastructure vs the fiber optic buildout during the dot-com boom (& bust)
Analysis: Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia network equipment for AI data centers
Networking chips and modules for AI data centers: Infiniband, Ultra Ethernet, Optical Connections
Will billions of dollars big tech is spending on Gen AI data centers produce a decent ROI?
Superclusters of Nvidia GPU/AI chips combined with end-to-end network platforms to create next generation data centers
Lumen Technologies to connect Prometheus Hyperscale’s energy efficient AI data centers
Proposed solutions to high energy consumption of Generative AI LLMs: optimized hardware, new algorithms, green data centers
Hyper Scale Mega Data Centers: Time is NOW for Fiber Optics to the Compute Server
Fiber Optic Networks & Subsea Cable Systems as the foundation for AI and Cloud services
Introduction:
A foundational enabler of global AI infrastructure and cloud service expansion are the fiber-optic networks interconnecting data centers worldwide. These high-capacity optical systems form the invisible backbone of modern digital society, facilitating everything from real-time financial transactions and mission-critical enterprise traffic to defense systems, entertainment, and personal communications. Access to cloud-based AI platforms—and the data-driven intelligence they deliver—depends on efficient, low-latency connectivity to data centers. As AI workloads proliferate across industries and continents, the unifying role of optical fiber becomes paramount, ensuring equitable global access to advanced digital capabilities.
A core prerequisite for scaling AI and cloud services is the mesh of high-capacity fiber-optic networks that interconnect data centers globally. These networks silently underpin digital society, carrying the data that powers financial markets, mission-critical enterprise applications, national security, entertainment platforms, and everyday human communication.
Cloud-based AI services only become meaningful when users, enterprises, and machines can reach them with low latency, high reliability, and predictable performance. In this context, the unifying role of fiber is increasingly strategic, as it determines who can participate in the AI economy and at what scale.
Subsea (fiber) cable systems as digital unifier:
The massive capacity and spectral efficiency of optical fiber have driven its deployment from access networks to backbone routes and across the world’s oceans. Today, more than 570 subsea cables carry over 99% of international traffic, effectively stitching together a single global fabric for AI and cloud connectivity.
New subsea systems highlight how infrastructure investments are closing regional gaps rather than just adding raw terabits: the Medusa submarine cable system will help narrow the digital divide between Europe and North Africa, the Bangladesh Private Cable System (BPCS) will establish the country’s first private subsea on-ramps to global cloud and AI ecosystems, and a new Jakarta–Singapore route by PT Solusi Sinergi Digital Tbk (Surge) is set to increase data center interconnectivity while expanding affordable broadband to tens of millions of Indonesians.
As multiple new subsea cable system build outs enter planning and deployment, global bandwidth growth is expected to remain strong, extending the reach of AI and cloud platforms to more geographies, users, and industries.
From PoPs to data centers:
The traffic matrix of the AI era looks very different from that of legacy telecom networks. Instead of primarily connecting PoPs, carrier hotels, and central offices, modern optical networks are being engineered around dense, high-capacity flows between data centers.
More than 11,000 data centers, including over one thousand hyperscale facilities, now form the core nodes of the global digital infrastructure, generating on the order of thousands of petabytes of WAN traffic daily. Subsea bandwidth demand is expected to grow at roughly 30% per year as AI and cloud services scale, placing new design pressure on how subsea and terrestrial backhaul networks are engineered end-to-end.
Unifying subsea and terrestrial backhaul:
This shift is driving a deliberate architectural pivot: instead of treating subsea and terrestrial backhaul as separate domains, leading operators and cloud providers are moving toward unified, end-to-end design philosophies. Traffic no longer “terminates” at a cable landing station or central office; it flows optically and logically from data center to data center across continents.
By optimizing subsea and terrestrial segments as a single system, operators can simplify their networks, reduce CapEx and OpEx, and unlock higher effective capacity. Approaches such as optical pass-through at cable landing sites reduce cost, footprint, and power, while spectrum expansion into C+L bands can deliver a twofold or greater increase in per-fiber capacity, significantly lowering the cost of backhauling subsea traffic to inland data centers.

An ever-increasing number of data centers powering AI services is driving significant bandwidth growth over subsea fiber optic cables. Image Credit: Nokia
Unified optical platforms for the AI supercycle:
Realizing this vision at scale requires platforms that unify roles traditionally split across multiple, specialized systems. For Nokia’s customers, this means leveraging the 1830 Global Express (GX) compact modular portfolio as a single, DCI-optimized solution for transponders, open optical line systems (OLS), and submarine line terminal equipment (SLTE) across both subsea and terrestrial applications.
High-performance coherent transponders on the 1830 GX support 800 Gigabit Ethernet across trans-oceanic distances, using techniques such as Probabilistic Constellation Shaping, Nyquist filtering, and continuous baud rate tuning to push performance toward the Shannon limit. The integrated OLS delivers the full suite of SLTE capabilities, including ROADM-based wavelength switching and spectrum management, ASE or CW idler insertion, and optical channel monitoring, while C+L operation on terrestrial backhaul provides step-function increases in capacity per fiber and reduces the cost of leased backhaul infrastructure.

Photo Credit: Nokia
Operational simplicity and resilience:
Beyond raw capacity, unified platforms enable operators to rationalize operations. Using a common hardware and software stack across subsea and terrestrial domains simplifies planning, training, sparing, deployment, and lifecycle management.
Capabilities such as constant-power ILAs for stable end-to-end DC-to-DC transport, integrated OTDR for proactive fiber monitoring and fault localization, and a rich set of optical protection schemes for service protection and restoration help operators build networks that are not only faster and denser, but also more resilient and easier to run.
What’s next: pluggables and sensing:
The industry is now entering a phase where innovation in optics is tightly coupled to AI and automation. At PTC 2026 in Honolulu, discussions will highlight how pluggable coherent optics and fiber sensing are being introduced into subsea environments to further collapse layers and enhance awareness.
ICE-X 800G coherent pluggables are already enabling 400G, 600G, and 800G per wavelength over regional subsea spans exceeding 4,000 km, and future advances in chromatic dispersion tolerance are expected to extend the thin transponder layer paradigm to trans-Atlantic routes. In parallel, operators are exploring fiber sensing, powered by machine learning and advanced coherent techniques, to transform existing fiber assets into distributed sensors capable of supporting security, integrity monitoring, and new data-driven services.
Connectivity for all:
“Advancing connectivity for the AI supercycle” is more than a tagline; it captures two simultaneous imperatives: scaling networks for performance, efficiency, and sustainability while extending those networks to every region and community. As described herein, fiber optics connectivity is becoming the strategic control point for value creation in the age of large-scale AI.
Nokia’s Role in Subsea Fiber Optic Networks:
Nokia has invested for more than 15 years in helping subsea operators and their customers design, deploy, and operate end-to-end SLTE and terrestrial optical networks, backed by global services and multi-country program support. Following its unification with Infinera, Nokia has emerged as the number-two global vendor of subsea optical transport equipment, earning the confidence of a large majority of operators involved in the latest wave of Asia-Pacific subsea builds. These partnerships position Nokia to help the industry scale and unify networks for the AI supercycle—and to ensure that the benefits of AI-era connectivity reach as many people, countries, and enterprises as possible.
Nokia’s 1830 Global Express (GX) supports high-performance coherent transponders for transmission of high-speed data connections such as 800 Gigabit Ethernet (800GE) across trans-oceanic distances, leveraging features such as Probabilistic Constellation Shaping (PCS), Nyquist filtering and continuous baud rate adjustment to maximize optical reach and fiber capacity up to the Shannon Limit. The 1830 GX OLS supports all needed SLTE functions including ROADM-based wavelength switching and spectrum management, insertion of ASE spectrum or continuous-wave (CW) idler channels, and optical channel monitor.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.nokia.com/blog/the-unifying-role-of-subsea-fiber-networks/
https://www.nokia.com/optical-networks/1830-global-express/
Subsea cable systems: the new high-capacity, high-resilience backbone of the AI-driven global network
FCC updates subsea cable regulations; repeals 98 “outdated” broadcast rules and regulations
Automating Fiber Testing in the Last Mile: An Experiment from the Field
Automating Fiber Testing in the Last Mile: An Experiment from the Field
By Said Yakhyoev with Sridhar Talari & Ajay Thakur
The December 23, 2025 IEEE ComSoc Tech Blog post on AI-driven data center buildouts [1.] highlights the urgent need to scale optical fiber and related equipment[1]. While much of the industry focus is on manufacturing capacity and high-density components inside data centers, a different bottleneck is emerging downstream— a sprawling last-mile network that demands testing, activation, and long-term maintenance. The AI-driven fiber demand coincided with the historic federal broadband programs to bring fiber to the premises for millions of customers[2]. This not only adds near-term pressure on fiber supply chains, but also creates a longer-term operational challenge: efficiently servicing hundreds of thousands of new fiber endpoints in the field.
As standard-setting bodies and vendors are introducing optimized products and automation inside data centers, similar future-proofing is needed in the last-mile outside plant. This post presents an example of such innovation from a field perspective, based on hands-on experimentation with a robotic tool designed to automate fiber testing inside existing Fiber Distribution Hubs (FDHs).
While central office copper terminating DSLAMs—and Optical Line Terminals (OLTs) in Passive Optical Networks (PONs)—aggregate subscribers and automate testing and provisioning, FDHs function as passive patch panels[3] that deliberately omit electronics to reduce cost. Between an OLT and the subscriber, the passive distribution network remains fixed. As a result, accessing individual ports at a local FDH—and anything downstream of it—remains a manual process. In active networks, DSLAMs and OLTs can electronically manage thousands of subscribers efficiently, but during construction this manual access is a bottleneck. There are likely tens of thousands of FDHs deployed nationwide.
Consider this problem from a technician’s perspective: suburban and urban Fiber to the Home (FTTH) networks are often deployed using a hub-and-spoke architecture centered around FDHs. These cabinets carry between 144 and 432 ports serving customers in a neighborhood, and each line must be tested bidirectionally[4]. In practice, this typically requires two technicians: one stationed at the FDH to move the test equipment between ports, and another at the customer location or terminal.
Testing becomes difficult during inclement weather. Counterintuitively, the technician stationed at the hub—often standing still for long periods—is more exposed than technicians moving between poles in vehicles. In addition to discomfort, there is a real economic penalty: either a skilled technician is tied up performing repetitive port switching, or an additional helper must be assigned. Above all, dependence on both favorable weather and helper availability makes testing schedules unpredictable and slows network completion.
To mitigate this bottleneck, we developed and tested Machine2 (M2)—a compact, gantry-style robotic tool that remotely connects an optical test probe inside an FDH, allowing a single technician to perform bidirectional testing independently.
M2 was designed to retrofit into a commonly deployed 288-port Clearfield FDH used in rural and small-town networks. The available space in front of the patch panel—approximately 9.5 × 28 × 4 inches—constrained the design to a flat Cartesian mechanism capable of navigating between ports and inserting a standard SC connector. Despite the simple design, integrating M2 into an unmodified FDH in the field proved more challenging than expected. Several real-world constraints shaped the redesign.
 |
 |
| FDH cabinet. Space to fit an automated switch | M2 installed for dry-run testing |
Space and geometry constraints: The patch panel occupies roughly 80% of the available volume, leaving only a narrow strip for motors, electronics, and cable routing. This forced compromises in pulley placement, leadscrew length, and motor orientation, limiting motion and requiring multiple iterations. The same constraints also limited battery size, making energy efficiency a primary design concern.
Port aiming: The patch panel is composed of cassettes with loosely constrained SC connectors. Small variations in connector position led to unreliable insertions. After repeated attempts, small misalignments accumulated, rendering the system ineffective without corrective feedback.
Communications reliability: A specialized cellular modem intended for IoT applications performed poorly for command-and-control. Message latency ranged from 1.5 seconds to over 12 seconds – and in some cases minutes – making real-time control impractical. In rural areas of Connecticut and Vermont, cellular coverage was also inconsistent or absent. Thus, the effort was abandoned between 2022 and 2024.
When the project resumed, an unexpected solution emerged. A low-cost consumer mobile hotspot proved more reliable than the specialized modem when cellular signal was available, providing predictable latency and stable Wi-Fi connectivity inside the FDH—even with the all-metal cabinet door closed and locked.
To further reduce latency, we explored using the fiber under test itself as a communication channel, a kind of temporary orderwire. When a two-piece Optical Loss Test Set (OLTS) is connected across an intact fiber, the devices indicate link readiness via an LED. By tapping this status signal, M2 can infer when a technician at the far end disconnects the meter and automatically connects to the next port. While this cue-based mode is limited, it enables near-zero-latency coordination and rapid testing of multiple ports without spoken or typed commands, which proved effective for common field workflows.
A second breakthrough came from addressing port aiming with vision. Standard computer-vision techniques such as edge detection were sufficient to micro-adjust the probe position at individual ports. To detect and avoid dust caps, M2 also uses a lightweight edge-ML[5] model trained to recognize caps under varying illumination. Using only 30 positive and 30 negative training images, the model correctly detected caps in over 80% of cases.
In our experience, lightweight vision models proved sufficient for practical field tasks, suggesting that accessibility—not sophistication—may drive adoption of automation in outside-plant environments.
What building M2 revealed:
- Overcoming communications issues led to an intriguing idea: optical background communication, where modulated laser light subtly changes ambient illumination inside the FDH that a camera can detect and extract instructions.
- M2 also proved useful beyond testing. For example, in a verify-as-you-splice workflow, M2 can lase a specific fiber as confirmation before splicing. Interactive port illumination and detection allow a single technician to troubleshoot complex situations.
The comparison below is illustrative and reflects observed workflows rather than controlled benchmarking.
Illustrative comparison of testing workflows in our experience
| Human helper (remote) | M2 | |
| Connect next port | 1–1.5 s | 2.5–4 s |
| Connect random / distant port | 8–24 s | ~11–30 s |
| Ease of deployment | Requires flat ground, fair weather, ground-level FDH | ~15 min setup; requires software familiarity |
| Functionality | Highly adaptable | Limited to 2–3 functions |
| Economics | Inefficient for small networks | Well-suited for small and medium networks |
| Independence factor | Low; requires two people | High; largely weather-independent |
| Best use | Variable builds, high adaptability | Repetitive builds, independent workflows |
Early insights for OSP vendors and standards
Building M2 revealed two broader lessons relevant to operators and vendors. First, there are now practical opportunities for automation to enter outside-plant workflows following developments in the power industry and datacenters[6]. Second, infrastructure design choices can facilitate this transition.
More spacious or reconfigurable FDH cabinets would simplify retrofitting active devices. Standardized attachment points on cabinets, terminals and pluggable components would allow mechanized or automated fiber management, reducing the risk of damage in dense installations.
Fiducial marks are among the lowest-cost adaptations. QR marks conveying dimensions and part architecture would help machines determine part orientation and position easily. Although these are common in the industry, it may be time to adopt them more broadly in telecom infrastructure maintenance.
Aerial terminals may benefit the most from machine-friendly design. Standardized port spacing and swing-out or hinged caps would significantly simplify autonomous or remotely assisted connections. Such cooperative interfaces could enable standoff connections without requiring a technician to climb a pole, improving safety and reducing access costs. Retrofitting aerial infrastructure to make it robot-friendly has been recommended[7] by the power industry and is also needed in the broadband utilities.
Conclusion
A growing gap is emerging between rapidly evolving data-center infrastructure and the more traditional telecom networks downstream. As fiber density increases, testing, activation, and maintenance of last-mile networks are likely to become bottlenecks. One way ISPs and vendors can future-proof outside-plant infrastructure is by proactively incorporating automation- and robot-friendly design features. M2 is one practical example that helps inform how such transitions might begin.
Short video clip from our early field trial in Massachusetts:
https://youtube.com/shorts/MiDoQd_S6Kw
References:
[1] IEEE ComSoc Technology blog post, Dec 23 2025, How will fiber and equipment vendors meet the increased demand for fiber optics in 2026 due to AI data center buildouts? ↩
[2] U.S. Dept. of Commerce Office of Inspector General, “NTIA Broadband Programs: Semiannual Status Report,” Washington, DC, USA, Rep. no. OIG-25-031-I, Sept. 24, 2025. ↩
[3] for an overview of an FTTH architecture see: Fiber Optic Association (FOA), FTTH Network Design Considerations and Fiber Optic Association (FOA), FTTH and PON Applications ↩
[4] Corning Optical Communications, “Corning Recommended Fiber Optic Test Guidelines,” Hickory, NC, USA, Application Engineering Note LAN-1561-AEN, Feb. 2020. ↩
[5] Refer to tools available for easy to use edge computing by Edge Impulse. ↩
[6] See state of the art indoor optical switches like ROME from NTT-AT and G5 from Telescent. ↩
[7] Andrew Phillips, “Autonomous overhead transmission line inspection robot (TI) development and demonstration,” IEEE PES General Meeting, 2014. ↩
About the Author:
Said Yakhyoev is a fiber optic technician with LightStep LLC in Colorado and a developer of the experimental Machine2 (M2) platform for automating fiber testing in outside-plant networks.
The author acknowledges the use of AI-assisted tools for language refinement and formatting.
How will fiber and equipment vendors meet the increased demand for fiber optics in 2026 due to AI data center buildouts?
Fiber optic vendors are employing a mix of manufacturing expansion, technological innovation in high-density and next-generation fibers, and strategic supply chain alignment to meet the anticipated surge in demand from AI and data centers in 2026. The demand is so high that at least one major fiber manufacturer, whose name was not explicitly disclosed in news reports, has already sold all its fiber inventory through 2026. Major fiber optic vendors by category are:
- Fiber & Cable Manufacturing: Corning, Prysmian Group, Sumitomo Electric, Fujikura, CommScope, Sterlite Technologies (STL), Yangtze Optical Fibre & Cable (YOFC)
- Optical Transport/Networking: Nokia, Ciena (gaining share), Cisco, Fujitsu, Huawei, Infinera (now part of Nokia)
- Optical Components/Transceivers: Coherent Corporation, Lumentum, Broadcom, Innolight, Accelink
Major focus areas of selected vendors:
- Corning: Leading in fiber cable quality and innovation
- Nokia & Ciena: Strong in optical transport and network solutions, gaining market share
- Cisco & Huawei: Significant players in optical transceivers, catching up to leaders
- CommScope, Clearfield, STL: Preparing for huge demand surges
John McGirr, SVP and general manager for Corning Optical Fiber & Cable, said, “The surge in hyperscale and AI network loads has significantly increased our expectations for fiber demand. Enterprise sales grew 58% year-over-year in Q3 2025, driven by continued strong adoption of Corning’s Gen AI products, largely due to AI network growth demands. The 72-GPU nodes, such as (Nvidia’s) Blackwell, require 16 times more fiber than traditional cloud switch racks. We see no signs of AI network growth slowing down especially as operators scale up (increase computational power by adding more resources within the existing backend AI network node) and scale out (increase the number of nodes to accommodate increasing demand) their networks.”
Rahul Puri, CEO of the Optical Networking Business at STL, said, “AI-focused data centers require significantly more fiber — about 36x more fiber than traditional CPU-based racks — to handle the massive data volumes and high-speed connectivity required by GPU clusters.” Puri predicts that cumulative hyperscale data capacity will increase by three times in the next few years alone. “The U.S. will need to add 213.3 million more fiber miles by 2029, more than doubling its current amount from 159.6 million fiber miles to 372.9 million miles. Our roadmap is shaped directly with the world’s leading cloud, AI and data center operators,”” Puri added.
CommScope’s VP of Technology John Chamberlain and VP of Hyperscale Cloud Erik Gronvall noted that the company has expanded its fiber manufacturing capacity in recent years to meet increased demand. “We are also innovating to reduce the amount of time it takes to deploy AI clusters,” said Chamberlain and Grovall.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Fiber Vendor Strategies:
Capacity Increase: Vendors like Corning and CommScope are investing in increasing their production capacity for fiber optic cables and the necessary preforms (raw material for fiber). This includes expanding existing facilities to help alleviate the current supply chain tightness and long lead times.
Technological Innovation in Fiber Design: To support the extreme bandwidth and low-latency needs of AI, vendors are focusing on advanced fiber technologies.
-
- Higher Fiber Counts: Companies are launching cables with extremely high fiber counts (e.g., 1,728+ strands) and higher density options to pack more capacity into existing infrastructure.
- Next-Generation Fibers: Research is ongoing in areas like hollow-core fiber (which uses air or a vacuum to transmit light faster and with less loss) and multicore fiber (multiple cores in one strand to increase capacity). These technologies, while not yet mainstream for 2026, are part of the long-term strategy.
- Bend-Insensitive Fiber: Innovations in bend-insensitive and ultra-high fiber count cables are improving durability and easing deployment in complex data center environments.
Pre-connectorized and Modular Solutions: To counter a persistent skilled labor shortage and speed up deployment, vendors are pushing factory-terminated, plug-and-play fiber systems and modular platforms (like Siemon’s LightStack). These solutions require less on-site expertise and reduce installation time.
Strategic Partnerships and Supply Chain Alignment: Vendors are forming strategic collaborations with hyperscalers and network operators (like the agreement between Corning and Lumen) to align manufacturing platforms with future demand and ensure supply. They are also working to optimize supply chains and, in some cases, regionalize manufacturing to reduce lead times.
Structured Cabling and Photonics: There is a renewed focus on structured cabling architectures, as recommended by some AI platform providers, to ensure predictable, low-latency performance and simpler long-term management. The industry is also exploring integrated photonics to address the power and thermal challenges of future systems.
Focus on AI-Specific Demands: Vendors recognize that AI data centers require up to five times more connectivity than traditional hyperscaler topologies and network architectures. Their strategies are specifically tailored to high-volume, intra-bay, inter-bay, and middle-mile fiber connections to link distributed data center clusters into a single, unified AI computing environment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Ciena and Nokia:
- Ramping up Production: Ciena is accelerating the production of 800G ZR+ optical pluggables, with plans to ship a large volume in 2026 to major cloud providers who are currently testing the technology.
- New Architectures: The company is developing new interconnect solutions under the “Scaleacross” architecture designed to support growing AI workloads by significantly increasing capacity and density within the data center.
- Increased Forecasts: Driven by record orders from hyperscalers, Ciena has raised its revenue guidance for fiscal 2026 to a range of $5.7 billion to $6.1 billion, a significant increase that analysts tie directly to AI-driven demand.
- Strategic Positioning: Ciena emphasizes that the network will be the primary limiter of AI performance by 2026, positioning its high-speed fiber solutions as critical for moving massive amounts of data between compute nodes efficiently.
- Major U.S. Investment: Nokia announced a $4 billion investment in U.S. R&D and manufacturing capabilities for “AI-ready” network technologies, including optical and data center networking, to ensure robust domestic supply.
- Strategic Reorganization: Effective at the start of 2026, Nokia will reorganize into two primary segments, one of which is “Network Infrastructure” (including optical networks), which it sees as the center of the “AI supercycle.”
- Industry Collaboration: Nokia has deepened its commitment to the Open Compute Project (OCP) at the Platinum level, aiming to collaborate on open, interoperable AI networking innovations that optimize space, cost, and power efficiency with standards-driven technology.
- Advocacy for Network Modernization: Nokia’s research highlights that current networks are insufficient for future AI growth, advocating for substantial investment and cross-industry collaboration to modernize digital infrastructure to handle the uplink-heavy, distributed data flows generated by AI.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/major-fiber-vendors-strategize-huge-demand-ai-2026
https://www.fierce-network.com/premium/research/1410126?pk=FN-Research-Commscope-111925-listing
NTT to launch 25 Gps FTTH service in Tokyo starting March 2026
AI wireless and fiber optic network technologies; IMT 2030 “native AI” concept
AI infrastructure investments drive demand for Ciena’s products including 800G coherent optics
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
Lumen and Ciena Transmit 1.2 Tbps Wavelength Service Across 3,050 Kilometers
Co-Packaged Optics to play an important role in data center switches
Coherent Optics: Synergistic for telecom, Data Center Interconnect (DCI) and inter-satellite Networks
Hyper Scale Mega Data Centers: Time is NOW for Fiber Optics to the Compute Server
Microsoft acquires Lumenisity – hollow core fiber high speed/low latency leader
China Mobile to deploy 400G QPSK by the end of 2023
Verizon to build new, long-haul, high-capacity fiber pathways to connect AWS data centers
Verizon Business has announced a new Verizon AI Connect deal with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to provide resilient high-capacity, low-latency network infrastructure essential for the next wave of AI innovation. As part of the deal, Verizon will build new, long-haul, high-capacity fiber pathways to connect AWS data center locations. This will enable AWS to continue to deliver and scale its secure, reliable, and high-performance cloud services for customers building and deploying advanced AI applications at scale.
These new fiber segments mark a significant commitment in Verizon’s network buildout, to enable the AI ecosystem to intelligently deliver the exponential data growth driven by generative AI. The Verizon AI Connect solution will provide AWS with resilient network paths that will enhance the performance and reliability of AI workloads underpinned by Verizon’s award-winning network. The Verizon-AWS collaboration also encompasses joint development of private mobile edge computing solutions that provide secure, dedicated connectivity for enterprise customers. These existing collaborations have delivered significant value across multiple industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to retail and entertainment, by combining Verizon’s powerful network infrastructure with AWS’s comprehensive cloud services.

“AI will be essential to the future of business and society, driving innovation that demands a network to match,” said Scott Lawrence, SVP and Chief Product Officer, Verizon Business. “This deal with Amazon demonstrates our continued commitment to meet the growing demands of AI workloads for the businesses and developers building our future.”
“The next wave of innovation will be driven by generative AI, which requires a combination of secure, scalable cloud infrastructure and flexible, high-performance networking,” said Prasad Kalyanaraman, vice president, AWS Infrastructure Services. “By working with Verizon, AWS will enable high-performance network connections that ensure customers across every industry can build and deliver compelling, secure, and reliable AI applications at scale. This collaboration builds on our long-standing commitment to provide customers with the most secure, powerful, and efficient cloud infrastructure available today.”
This initiative strengthens Verizon’s long-standing strategic relationship with AWS. The companies have already established several key engagements, including Verizon’s adoption of AWS as a preferred strategic public cloud provider for its digital transformation initiatives. Previous engagements have targeted use cases across sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail and media, pairing Verizon’s network capabilities with AWS’s cloud stack. It should be noted, however, that AWS also uses other major carriers and dark fiber providers, such as Lumen Technologies, Zayo, AT&T, and others, to ensure a highly redundant and diverse global inter-data center network.
This deal highlights how telecommunications companies are becoming critical enablers of the AI-driven economy by investing in the foundational fiber optic infrastructure required for large-scale AI processing.
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-business-and-aws-new-fiber-deal
Verizon transports 1.2 terabytes per second of data across a single wavelength
Verizon, AWS and Bloomberg media work on 4K video streaming over 5G with MEC
Amazon AWS and Verizon Business Expand 5G Collaboration with Private MEC Solution
Lumen deploys 400G on a routed optical network to meet AI & cloud bandwidth demands
Verizon’s commercial agreement with Eaton Fiber to accelerate fiber/mobile convergence
Verizon has announced a commercial fiber agreement with Eaton Fiber LLC [1.], an affiliate of Tillman Global Holdings, that will enable Verizon to sell fiber-based services outside its current wireline footprint and beyond the areas it will gain via its pending acquisition of Frontier Communications. It’s another important step to accelerate Verizon’s broadband and mobility convergence strategy, which has also been embraced by AT&T and T-MobileUS.
Note 1. “Eaton Fiber is a wholesale-only FTTP network provider powering ISPs with fast, frictionless access to future-ready fiber. Our open-access platform makes it easy for ISPs to expand across key U.S. markets—without building or managing the network. Our open-access platform makes it easy for ISPs to expand across key U.S. markets – without building or managing the network. You bring the service. We deliver the speed,” Eaton Fiber states on its website.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Eaton Fiber will fund and build the network and take care of network maintenance and installation, while Verizon will be responsible for sales and marketing and end-user customer service. The agreement will expand Verizon’s premium broadband offering, complementing the company’s ongoing fiber builds and planned acquisition of Frontier. The agreement is expected to bring ultra-fast, high-capacity fiber service to homes and customers in markets outside of Verizon’s and Frontier’s current fiber-to-the-home footprint.

Image Credit: Eaton Fiber
“Our strategy is clear: lead the market in premium mobility and broadband convergence, and fiber is the foundation of that leadership,” said Sowmyanarayan Sampath, Executive Vice President for Verizon and CEO for Verizon Consumer. “This agreement allows us to rapidly enter new markets, accelerate deployment speed and ensure we maintain the necessary flexibility to capture growth opportunities across the country.”
“We are pleased to partner with a world-class provider in Verizon,” Sanjiv Ahuja, Founder, Chairman, and CEO of Tillman Global Holdings. “Marking a significant expansion of Tillman’s fiber deployments, this announcement underscores our shared commitment to expanding next-generation infrastructure nationwide.”
Missing from the press release: Verizon did not say where Eaton Fiber has built networks, where it intends to build, or how many homes and businesses Verizon eventually will be able to serve off of Eaton’s platform. Verizon also neglected to say when it will start to offer services via Eaton Fiber’s networks. It’s also not clear if Verizon is considered an anchor tenant or will represent one of multiple tenants that will sell services over Eaton Fiber’s network.
Tillman Fiber, builds and operates symmetrical gigabit-capable services over fiber-to-the-premises networks. The company was founded in 2021, and its backers include Tillman Global Holdings and Northleaf Capital Partners. In July, Tillman Fiber launched fiber networks serving parts of Northport, Kissimmee and Deltona and Hernando County in Florida. T-MobileUS is offering services on that network as part of a broader fiber Internet strategy that’s also underpinned by partnerships and acquisitions of Lumos, Metronet and US Internet.
Both Tillman Fiber and Eaton Fiber note on their respective websites that their fiber networks use an open access model that sells wholesale access to other Internet service providers (ISPs).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
New Street Research David Barden remarked in a research note (registration required) that Eaton Fiber has not yet revealed its leadership. But given that Verizon referenced Frontier in today’s announcement, he wondered if Veronica Bloodworth, a former AT&T exec who has been serving as Frontier’s EVP and chief network officer since 2021, or Vishal Dixit, Frontier’s EVP of strategy and wholesale, “could be on a short list.” Barden also suggested that today’s announcement with Eaton Fiber is more about intent rather than specifics. “Given that this agreement was seen as worthy of a press release, especially within a month of Dan Schulman taking over the reins of the company, this release is also very likely about ambition as well,” Barden wrote.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Verizon’s new agreement with Eaton Fiber is proceeding as the company approaches the finalization of its $20 billion acquisition of Frontier Communications.
The integration of Frontier’s assets is expected to boost Verizon’s fiber network, increasing its reach to serve about 25 million premises throughout 31 states and Washington, D.C.. In addition to constructing 500,000 new FiOS locations this year, Verizon has set a strategic goal of achieving over 30 million fiber passings by 2028 and is exploring an eventual expansion to 35-40 million homes and businesses.
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-expanding-broadband-new-strategic-fiber-agreement
https://www.lightreading.com/broadband/verizon-taps-into-eaton-fiber-to-broaden-fiber-reach
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-acquisition-starry
Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
UK’s CityFibre launches 5.5Gbit/s wholesale broadband service- 3 times faster than BT Openreach
CityFibre, the UK’s largest independent full fiber optic platform, has unveiled a new 5.5Gbit/s wholesale broadband internet service based on 10Gbit/s XGS-PON technology that has already been rolled out across 85% of the company’s network. CityFibre claims its new product is more than three times faster than the highest rate available service from its much larger rival, Openreach (the network access arm of BT). and available at a much lower wholesale cost, CityFibre’s 5.5Gb symmetrical product will enable partners to offer a range of Multi-Gig speed tiers to customers, improving margins whilst providing a valuable customer retention tool for the long term.
Highlights:
- CityFibre’s new 5500/5500Mbps service offers >3x faster downloads, >45x faster uploads than BT Openreach’s fastest full fibre service which is 1800/120Mbps and is delivered over its GPON network.
- CityFibre’s upgraded XGS-PON network provides numerous benefits over GPON technology, including network cost savings, reduced power consumption, improved performance, and enhanced efficiency.
- CityFibre’s launch of its new Multi-Gig products enables the UK to keep pace with countries including France, the Netherlands, New Zealand and the United States of America where consumers are already making the most of affordable Multi-Gig services.

Photo Credit: CityFibre
Greg Mesch, CEO of CityFibre, said: “The UK’s full fibre future is here, thanks to CityFibre’s powerful, 10Gb XGS-PON network. Our ISP partners are already connecting customers with speeds over 2Gb and exceeding expectations when it comes to quality and reliability, but our next generation of full fibre will set a new standard for what’s possible.
“CityFibre started out to challenge the incumbents and bring choice and competition to the UK market. This is another huge step-forward, giving ISPs more power and flexibility than ever before and bringing affordable Multi-Gig speeds and an unrivalled experience to millions of UK consumers.”
Even faster multi-gig services will be launched in 2026 the company promises.
CityFibre’s network now passes more than 4.3 million premises, which the company says means it is more than halfway along its journey towards its “rollout milestone” of 8 million premises. Actual service take-up, however, has reached just 518,000, an increase of around 181,000 customers on its previous total. During the year covered by the earnings statement, CityFibre announced a partnership with Sky that will see the UK’s second-largest broadband provider launch services on CityFibre’s network later this year.
References:
https://cityfibre.com/news/cityfibre-unveils-new-5-5gb-wholesale-product-its-fastest-ever
Nokia and CityFibre sign 10 year agreement to build 10Gb/second UK broadband network
Dell’Oro: Broadband access equipment sales to increase in 2025 led by XGS-PON deployments
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Frontier Communications fiber growth accelerates in Q1 2025
AT&T grows fiber revenue 19%, 261K net fiber adds and 29.5M locations passed by its fiber optic network
Google Fiber planning 20 Gig symmetrical service via Nokia’s 25G-PON system
STELLAR Broadband offers 10 Gigabit Symmetrical Fiber Internet Access in Hudsonville, Michigan
Frontier Communications fiber growth accelerates in Q1 2025
Frontier Communications reported record fiber subscriber net adds in Q1-2025. However, the “fiber first” carrier had a loss of $0.26 per share, compared to break-even earnings per share a year ago. The telco posted revenues of $1.51 billion for the quarter ended March 2025, compared to year-ago revenues of $1.46 billion.
“We had the strongest start to a year yet, led by continued strength in our fiber business,” said Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier. “Consumers, business owners and technology companies are increasingly relying on fiber to power networks and connect to the digital economy – and that trend is shining through in our results. The team delivered 19% growth in fiber broadband customers and 24% growth in fiber broadband revenues this quarter, which taken together drove record first-quarter growth in both revenue and Adjusted EBITDA.”
Jeffery continued, “We also hit a milestone in the first quarter, growing our fiber network to reach more than 8 million passings. We started this turnaround journey with a goal of 10 million fiber passings and four years later, I’m proud to say that we’re nearly there. As we scale our network, we’re expanding access for millions of Americans and building a legacy that will continue to endure long after our planned combination with Verizon.”
First-Quarter 2025 Highlights
- Added 321,000 fiber passings to reach 8.1 million total locations passed with fiber
- Added 107,000 fiber broadband customers, resulting in fiber broadband customer growth of 19.3% year-over-year
- Consumer fiber broadband ARPU of $68.21 increased 4.7% year-over-year
- Revenue of $1.51 billion increased 3.4% year-over-year as growth in fiber-based products was partly offset by declines in copper-based products
- Operating income of $76 million and net loss of $64 million
- Adjusted EBITDA of $583 million increased 6.6% year-over-year driven by revenue growth and lower content expense, partially offset by higher customer acquisition costs1
- Cash capital expenditures of $757 million plus $16 million of vendor financing payments resulted in total cash capital investment of $773 million2
- Generated net cash from operations of $519 million
Frontier added 103,000 residential fiber broadband customers in Q1 2025, beating the 95,000 expected by MoffettNathanson (see graph below). Frontier’s residential fiber additions in the quarter were just shy of the record 104,000 it added in Q3-2024. The fiber facilities based carrier gained a record 59,000 net broadband customers in the period, which included losses of legacy copper subscribers.
Frontier built another 321,000 fiber passings in Q1-2025, pushing its total past the 8 million mark. Alongside subscriber growth, Frontier’s consumer fiber broadband average revenue per unit (ARPU) also climbed – to $68.21, up 4.7% versus the year-ago period.
Frontier said the “vast majority” of new fiber subs are now taking multi-gigabit speeds. A specific number wasn’t shared, but back in Q2 2024 more than 60% of new Frontier fiber customers took speeds of 1 Gbit/s or more.
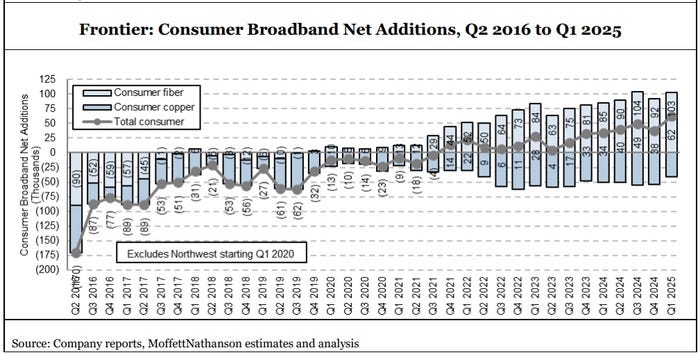
CEO Jeffery said Frontier is sticking with its plan to build fiber to 1.3 million locations in 2025. The current pace puts Frontier on a path to reach its 10 million fiber passing goal around the third quarter of 2026, New Street Research analyst Jonathan Chaplin said in a research note.
Jeffery said Frontier’s “fiber build machine” is capable of going faster, but he stressed that the current pace gives the company the time it needs to also sell, service and support fiber broadband as it builds. “The whole company needs to be in balance. We want more customers and higher ARPU, and we’ve demonstrated that it’s doable,” Jeffery said.
He attributed ARPU growth to multiple factors, including customers taking higher-level speed tiers and subscribing to additional, premium services. Frontier estimates that more than 50% of new customers take some type of add-on, including whole-home Wi-Fi and YouTube TV.
Jeffery said Frontier is seeing good adoption of “Unbreakable Wi-Fi,” a $25 per month add-on that flips to 4G cellular backup (with 130 gigabytes of data per billing cycle) when the primary fiber connection is down. Those customers can also opt for a battery backup that provides up to four hours of backup power.
Frontier’s Q1 results come as it moves ahead with its proposed acquisition by Verizon which is currently expected to close by the first quarter of 2026. Jeffery would only say that the deal process is going smoothly at the state and federal levels.
“My job is now very much to deliver this asset in the best possible shape it can be to its future owner, Verizon,” he said. “I’m delighted to say that that’s really been evident in our first quarter results.”
References:
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250429128668/en/Frontier-Reports-First-Quarter-2025-Results
Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
Frontier Communications recovering from unknown cyberattack!
Building out Frontier Communications fiber network via $1.05 B securitized debt offering
Frontier Communications fiber build-out boom continues: record number of fiber subscribers added in the 1st quarter of 2023
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
AT&T grows fiber revenue 19%, 261K net fiber adds and 29.5M locations passed by its fiber optic network
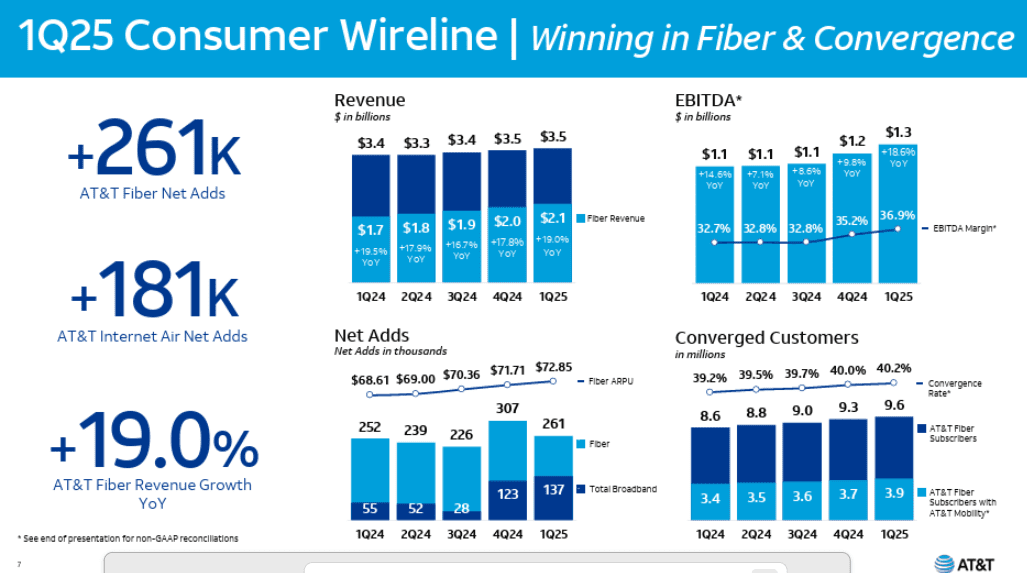
In the 1st quarter of 2025, AT&T’s fiber business showed strong performance, with fiber revenue growing by 19% year-over-year and 261,000 net fiber subscribers added. This growth helped drive overall wireline revenue and operating income, with fiber revenue contributing significantly to the 9.6% broadband revenue increase. AT&T’s fiber strategy is a key part of its broader plan for growth, including 5G wireless, and is expected to continue contributing to strong financial results. At the end of the 1Q2025, AT&T said that 29.5 million locations were passed with its fiber network. The company expects to surpass 30 million by midyear, months ahead of its original target. Consumer fiber broadband revenue was $2.1 billion in the quarter, up 19% year-over-year, as more customers upgraded to faster service tiers. Executives noted that more than 40% of AT&T Fiber households now also subscribe to AT&T wireless, part of a deliberate strategy to drive “converged” customer relationships.
AT&T continues to lead the Fiber-to-the-Home market, and has reportedly been in talks to acquire Lumen Technologies’ consumer fiber business in a deal valued at more than $5.5 billion, according to Bloomberg and Reuters
CFO Pascal Duroche on the 1Q2025 earnings call:
“We delivered 261,000 AT&T Fiber net adds, up from 252,000 in the first quarter of last year. This was driven by growth in our consumer locations served with fiber, which reached 23,800,000 at the end of 1Q and growing contribution of net adds in regions served with Giga Power Fiber. We love the return profile of fiber and the lift it provides our mobility business only makes investing in fiber more attractive. AT and T Internet Air net adds were 181,000 in the quarter, which is a significant improvement from a year ago, driven by broader availability across our distribution channels. Our combined success with these two services helped us deliver 137,000 total broadband net adds in the quarter.
This marks our seventh straight quarter of overall broadband subscriber growth and second consecutive quarter with more than 100,000 broadband net adds. We grew Consumer Wireline revenue by 5.1% versus the prior year. This was driven by fiber revenue growth of 19%, reflecting subscriber gains and solid fiber ARPU growth of 6.2%. Consumer wireline EBITDA grew 18.6% for the quarter. Our first quarter results benefited from vendor settlements that positively impacted our total wireline operating expenses by approximately $100,000,000 Roughly $55,000,000 of the impact was in Consumer Wireline with the rest in Business Wireline.”
AT&T is investing heavily in its fiber network which is reflected in the increase in its capital expenditures (CAPEX) which are expected to remain in the $22 billion range annually from 2025 through 2027.

AT&T logo on a building in Pasadena, California, U.S., January 24, 2018. REUTERS/Mario Anzuoni/File Photo Purchase Licensing Rights
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“Where we have fiber, we win,” said CEO John Stankey. “This dynamic continues to drive growth, shown by our increasing rate of convergence, customer penetration and significant wireless share gains within our fiber footprint.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/1q-earnings.html