SKT with Global Telcos to Expand Metaverse Platform in US, Europe and Southeast Asia
On February 27 at MWC Barcelona 2023, South Korean network operator SK Telecom (SKT) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Deutsche Telekom and T-Mobile US to jointly explore opportunities for expanding its metaverse platform ifland into Germany and the U.S.

Image Credit: SKT
The three companies will begin to conduct market tests in the U.S. and Germany in the second quarter of this year, with the main goal of the trials being to try “more diverse metaverse services in Europe and the U.S.”
SKT, Deutsche Telekom and T-Mobile US will also produce content tailored to local preferences, and will jointly promote the metaverse offering.
The ifland platform is also set to be made available to more countries in South East Asia, and the telco has agreed a partnership with its Malaysian partner CelcomDigi to boost its ifland user numbers in the country and develop new business models. It will also be made available to all 11 subsidiaries of Axiata operating in the ASEAN (Association of South-east Asian Nations) and South Asian regions, including Malaysia, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Cambodia, Bangladesh and Nepal.
SKT and Axiata also plan to develop “metaverse platform-related business models” and create business opportunities based on artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the competitiveness of these models.
By expanding its metaverse service into the Southeast Asian market, where Korean culture such as K-content is gaining popularity, SKT expects to expand ifland’s services and develop new business opportunities.
“As we advance into the global market with our metaverse platform ifland, major telecommunications companies in each country and region play an important role as our partners,” said Ryu Young-sang, CEO of SKT. “Going forward, we will continue to work closely with diverse global companies to expand the scope of our metaverse service.”
“The collaboration between the leading Malaysian telecoms operator serving more than 20 million customers and global ICT leader SKT will set the stage for the nation’s metaverse development, and drive growth and digitalisation within the digital economy,” said Datuk Idham Nawawi, CEO of CelcomDigi. “We look forward to working together on leveraging innovative technologies and practices particularly in virtual spaces to develop and deliver a wider range of innovative solutions for our customers and Malaysian businesses.”
“Axiata is deeply committed to leveraging emerging technologies towards the inclusive advancement of Societies and Economies across Asia,” said Dr Hans Wijayasuriya, CEO of Axiata. “We are proud to partner with SKT and the ifland platform and consider the partnership a significant component of our participation in the metaverse going forward.”
SKT pointed out that each of the three operator partners has more than 100 million customers, giving it a solid foundation on which to expand the international impact of ifland. The company’s CEO, Ryu Young-sang, pointed out that partnering with major telcos “in each country and region” plays a key role in advancing ifland’s influence, so it plans to continue working closely with global companies to broaden the scope of the service.
SKT’s metaverse platform launched in June 2021 and after an initial collaboration with Deutsche Telekom, it aggressively moved to global expansion across North America, Europe, the Middle East and Asia in November 2022.
References:
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?idx=1560
SK Telecom launches its metaverse platform ‘ifland’ in 49 countries and regions
NTT Docomo will use its wireless technology to enter the metaverse
Cloud RAN with Google Distributed Cloud Edge; Strategy: host network functions of other vendors on Google Cloud
At MWC 2023 Barcelona, Google Cloud announced that they can now run the radio access network (RAN) functions as software on Google Distributed Cloud Edge, providing communications service providers (CSPs- AKA telcos) with a common and agile operating model that extends from the core of the network to the edge, for a high degree of programmability, flexibility, and low operating expenses. CSPs have already embraced open architecture, open-source software, disaggregation, automation, cloud, AI and machine learning, and new operational models, to name a few. The journey started in the last decade with Network Functions Virtualization, primarily with value added services and then deeper with core network applications, and in the past few years, that evolved into a push towards cloud-native. With significant progress in the core, the time for Cloud RAN is now, according to Google. However, whether for industry or region-specific compliance reasons, data sovereignty needs, or latency or local data-processing requirements, most of the network functions deployed in a mobile or wireline network may have to follow a hybrid deployment model where network functions are placed flexibly in a combination of both on-premises and cloud regions. RAN, which is traditionally implemented with proprietary hardware, falls into that camp as well.
In 2021,the company launched Google Distributed Cloud Edge (GDC Edge), an on-premises offering that extends a consistent operating model from our public Google Cloud regions to the customer’s premises. For CSPs, this hybrid approach makes it possible to modernize the network, while enabling easy development, fast innovation, efficient scale and operational efficiency; all while simultaneously helping to reduce technology risk and operational costs. GDC Edge became generally available in 2022.

Google Cloud does not plan to develop its own private wireless networking services to sell to enterprise customers, nor does the company plan to develop its own networking software functions, according to Gabriele Di Piazza, an executive with Google Cloud who spoke at MWC 2023 in Barcelona. Instead, Google Cloud would like to host the networking software functions of other vendors like Ericsson and Mavenir in its cloud. It would also like to resell private networking services from operators and others.
Rather than develop its own cloud native 5G SA core network or other cloud networking software (like Microsoft and AWS are doing), Google Cloud wants to “avoid partner conflict,” Di Piazza said. Google has been building its telecom cloud story around its Anthos platform. That platform is directly competing against the likes of AWS and Microsoft for telecom customers. According to a number of analysts, AWS appears to enjoy an early lead in the telecom industry – but its rivals, like Google, are looking for ways to gain a competitive advantage. One of Google’s competitive arguments is that it doesn’t have aspirations to sell network functions. Therefore, according to Di Piazza, the company can remain a trusted, unbiased partner.

Image Credit: Google Cloud
Last year, the executive said that moving to a cloud-native architecture is mandatory, not optional for telcos, adding that telecom operators are facing lots of challenges right now due to declining revenue growth, exploding data consumption and increasing capital requirements for 5G. Cloud-native networks have significant challenges. For example, there is a lack of standardization among the various open-source groups and there’s fragmentation among parts of the cloud-native ecosystem, particularly among OSS vendors, cloud providers and startups.
In recent years, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Oracle and other cloud computing service providers have been working to develop products and services that are specifically designed to allow telecom network operator’s to run their network functions inside a third-party cloud environment. For example, AT&T and Dish Network are running their 5G SA core networks on Microsoft Azure and AWS, respectively.
Matt Beal, a senior VP of software development for Oracle Communications, said his company offers both a substantial cloud computing service as well as a lengthy list of network functions. He maintains that Oracle is a better partner for telecom network operators because of it. Beal said Oracle has long offered a wide range of networking functions, from policy control to network slice management, that can be run inside its cloud or inside the cloud of other companies. He said that, because Oracle developed those functions itself, the company has more experience in running them in a cloud environment compared with a company that hasn’t done that kind of work. Beal’s inference is that network operators ought to partner with the best and most experienced companies in the market. That position runs directly counter to Google’s competitive stance on the topic. “When you know how these things work in real life … you can optimize your cloud to run these workloads,” he said.
While a number of other telecom network operators have put things like customer support or IT into the cloud, they have been reluctant to release critical network functions like policy control to a cloud service provider.
References:
https://cloud.google.com/solutions/telecommunications
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/telecommunications
GSMA Intelligence: 5G connections to double over the next two years; 30 countries to launch 5G in 2023
GSMA Intelligence forecasts 5G connections are expected to double over the next two years, expedited by technological innovations and new 5G network deployments in more than 30 countries in 2023. Of the new networks to be deployed in 2023, it is expected that 15 will be 5G Standalone (SA) networks. As of January 2023, there were 229 commercial 5G networks globally and over 700 5G smartphone models available to users.
GSMA Intelligence, announced its latest 5G forecast during MWC Barcelona 2023, point to a significant period of growth in terms of mobile subscribers and enterprise adoption. Consumer connections surpassed one billion at the end of 2022 and will increase to around 1.5 billion this year – before reaching two billion by the end 2025.
India will lead the 5G expansion globally in 2023, with the expansion of services from Airtel and Jio in 2023 expected to be pivotal to the region’s ongoing adoption. GSMA Intelligence predicts there will be four 5G networks in India by the end of 2025, accounting for 145 million additional users. With operators such as Jio announcing ambitions to connect as many as 100 million homes across India to its 5G FWA network, the number of FWA users looks likely to grow substantially over the next few years, the report added.

Growth will also come from key markets within APAC and LATAM, such as Brazil and India, which have recently launched 5G networks. India will be especially significant, with the expansion of services from Airtel and Jio in 2023 expected to be pivotal to the region’s ongoing adoption. GSMA Intelligence predicts there will be four 5G networks in India by the end of 2025, accounting for 145 million additional users.
Many of the new 5G markets scheduled to launch networks in 2023 are in developing regions across Africa – including Ethiopia and Ghana – and Asia. Today, 5G adoption in the sub-Saharan region sits below 1% but will reach over 4% by 2025 and 16% in 2030, largely thanks to a concerted effort from industry and government organizations to provide connectivity to citizens.
“Until now, 5G adoption has been driven by relatively mature markets and consumer use cases like enhanced mobile broadband, but that’s changing. We’re now entering a second wave for 5G that will see the technology engage a diverse set of new markets and audiences,” said Peter Jarich, Head of GSMA Intelligence. “The extension to new use cases and markets will challenge the mobile ecosystem to prove that 5G truly is flexible enough to meet these diverse demands in a way that’s both inclusive and innovative.”
The Rise of 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA):
As of January 2023, more than 90 FWA broadband service providers (the vast majority of which are mobile operators) had launched commercial 5G-based fixed wireless services across over 48 countries. This means around 40% of 5G commercial mobile launches worldwide currently include an FWA offering.
In the U.S., T-Mobile added over half a million 5G FWA customers in Q4 2021 and Q1 2022 combined. By 2025, it expects to have eight million FWA subscribers, while Verizon is targeting five million FWA subscribers for the same period. The conventional wisdom holds that FWA is primarily useful as a rural service, targeted mostly at the previously unserved or underserved. Verizon says their FWA service is primarily urban and suburban service with target customers that are dissatisfied with terrestrial broadband services. Verizon has increasingly come to view FWA as an integral part of their broadband access offering everywhere that FiOS isn’t available.
Reliance Jio (India) announced ambitions to connect as many as 100 million homes across India to its 5G FWA network, the number of FWA users looks likely to grow substantially over the next few years.
While the majority of current 5G FWA deployments focus on the 3.5–3.8 GHz bands, several operators around the world are already using 5G mmWave spectrum as a capacity and performance booster to complement coverage provided by lower bands.
Only 7% of 5G launches have been in 5G mmWave spectrum so far but this looks set to change given 27% of spectrum allocations and 35% of trials are already using 5G mmWave bands. Furthermore, in 2023 alone, the industry will see ten more countries assigned 5G mmWave spectrum for use – a significant increase from the 22 countries who have been assigned it to date. Spain received the first European 5G mmWave spectrum allocation this year, resulting in Telefónica, Ericsson and Qualcomm launching its first commercial 5G mmWave network at MWC Barcelona 2023.
Enterprise IoT Driving Growth:
The figures from GSMA Intelligence also suggest that, for operators, the enterprise market will be the main driver of 5G revenue growth over the next decade. Revenues from business customers already represent around 30% of total revenues on average for major operators, with further potential as enterprise digitization scales. Edge computing and IoT technology presents further opportunities for 5G, with 12% of operators having already launched private wireless solutions – a figure that will grow with a wider range of expected IoT deployments in 2023.
Another major development for the enterprise will be the commercial availability of 5G Advanced (3GPP Release 18) in 2025. Focusing on uplink technology, 5G Advanced will improve speed, coverage, mobility and power efficiency – and support a new wave of business opportunities. GSMA’s Network Transformation survey showed half of operators expect to support 5G Advanced commercial networks within two years of its launch. While this is likely optimistic, it presents the ecosystem with a clear opportunity to execute on.
Editor’s Note:
GSMA’s 5G forecast is a direct contradiction to Omdia’s which expects weaker 5G growth in the near term. Which forecast do you believe?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Omdia forecasts weaker 5G market growth in near term, 4G to remain dominant
Huawei’s blueprint to lay the foundation for 5.5G and the “intelligent world”
According to Huawei, the intelligent world will be deeply integrated with the physical world. Everything, including personal entertainment, work, and industrial production, will be intelligently connected. This means that networks will have to evolve from ubiquitous Gbps to ubiquitous 10Gbps, connectivity and sensing will need to be integrated, and the ICT industry will have to shift its focus from energy consumption to energy efficiency. The evolution from 5G to 5.5G will be key to meeting these growing requirements.
At MWC 2023, Huawei unveiled its “GUIDE to the Intelligent World“ as a business blueprint to lay the foundation for 5.5G. Whatever happened to 5G Advanced and 3GPP Release 18? and ITU-R WP5D M.2150 recommendation?.
Following on from Huawei’s concept of “Striding Towards the 5.5G Era” that was proposed in July 2022, Huawei is highlighting the five major characteristics of the 5.5G era:
- 10 Gbps experiences
- Full-scenario interconnection
- Integrated sensing and communication
- L4 autonomous driving networks
- Green ICT
For Huawei, 5.5G represents a 10-fold improvement in performance over 5G in every metric. That means 10 Gbps headline connection speeds, 10 times the number of IoT connections – which translates to 100 billion in total – and reducing latency by a factor of 10. Networks also need to consume a tenth of the energy that they consume today on a per Terabyte basis, and they need to be 10x more intelligent, which means supporting level 4 autonomous driving, and making operations and maintenance (O&M) more efficient by a factor of 10.
With these capabilities in place, 5.5G networks will enable a boom in immersive interactive experiences, like VR gaming in 24K resolution, and glasses-free 3D video, predicts Huawei. It expects the installed user base of these services will grow 100-fold to 1 billion. On the enterprise side, the vendor expects the number of private cellular networks to increase from 10,000 today to 1 million by 2030.
Huawei says that leading global operators, standards organizations, and industry ecosystem partners are coming together to promote innovation and exploration for this 5.5G era, as it will create more new applications and business opportunities. This author disagrees- they are not coming together at all!
According to Ookla’s latest 5G City Benchmark Report, Huawei has played an important part in 5G network construction in all of the top 10 cities among the world’s 40 representative 5G-enabled cities. It’s important to note that 5G performance results in these 10 cities show that the 5G networks constructed by Huawei offer the best experience.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
David Wang, Huawei’s Executive Director of the Board, Chairman of the ICT Infrastructure Managing Board, and President of the Enterprise BG, said, “Huawei will deepen our roots in the enterprise market and continue our pursuit of innovation. We are ready to use leading technologies and dive deep into scenarios. Together with our partners, we will enable industry digitalization, help SMEs access intelligence, and promote sustainable development, creating new value together.”
Bob Chen, Vice President of Huawei Enterprise BG, delivered a keynote speech entitled “Digital Technology Leads the Way to the Intelligent World,” which outlined how digital technologies have impacted the development of the world’s economy, cultures, societies, and environment. He stated, “Archimedes, a great Greek physicist, said, ‘Give me a place to stand and I shall move the earth.’ Digital technology is the right place for us to help industries go digital. Huawei will focus on connectivity, computing, cloud, and other digital technologies. We will continue inspiring innovation to drive industry digital transformation. Together, let’s build a fully connected, intelligent world!”
Huawei said they would continue to work with customers to build next-generation network infrastructure to better serve all industries. Here are a few of their focus areas:
- Smart campus: Huawei redefines campus networks and launches the Next-Generation enterprise flagship core switch CloudEngine S16700, first enterprise-level Wi-Fi 7 AP AirEngine 8771-X1T, along with first 50G PON OLT and optical terminal product.
- Easy branch: Huawei launches the industry’s first simplified hyper-converged branch solution.
- Single OptiX: Huawei launches the industry’s first end-to-end optical service unit (OSU) product portfolio.
- Cloud WAN: Huawei defines a brand-new cloud WAN and launches the NetEngine 8000 series routers oriented to the all-service intelligent router platform in the cloud era.
- Data Center solution: Four industry-first products and product portfolios, unleashing the power of digital innovation
Storage and computing power have become one of the core strategic resources of enterprises. Huawei focuses on data center infrastructure innovation, leads the development of new data centers, helps enterprises cope with uncertain threats, ensures ultimate service experience, processes massive and diversified computing power, and brings data centers more green, more reliability, and more efficiency.
For large enterprises,Huawei launches the industry’s first multi-layer DC ransomware protection solution powered by network-storage collaboration, the industry’s first unified DC DR product portfolio featuring storage and optical connection coordination (SOCC),and CloudEngine 16800-X, which is the industry’s first DC switch designed for diversified computing power.
For SMEs, Huawei also launches OceanStor Dorado 2000 and OceanProtect X3000, which are the industry’s first entry-level storage combination based on the active-active architecture.
Juan De Dios Navarro Caballero, councillor of Alicante province, Spain, stated, “Huawei’s SDN-based CloudFabric Solution and All-Wireless Campus Network Solution enable network automation, intelligent O&M, and ubiquitous connectivity. Through these solutions, the government offices of Alicante province are now more efficient, and offer a better user experience for public services. The province has seen faster digital transformation along with digital economy development.”
Faith Burn, CIO of Eskom, a South African electric power company, shared the company’s digital transformation methodology and practical experience. She stressed that Eskom seeks to work with partners that can help realize the company’s digital vision, saying that, “It is very important to find capable partners to realize our digital vision. Eskom would like to collaborate with OEMs like Huawei to build advanced electricity ICT infrastructure to achieve comprehensive digitalization.”
Steven Zhu, President of Partner Development and Management of Huawei Enterprise BG, mentioned that “Huawei is committed to working with partners to complement each other, motivate partners to support customers proactively, and serve customers well together.”
In the future, Huawei says they will continue to invest and innovate, working alongside global customers and partners to deeply integrate ICT, accelerate digital transformation, promote digital economy development and speed up the realization of the intelligent world within industries, in order to create new value.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2023/2/mwc2023-5g-huawei%20-connectivity
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2023/2/mwc2023-industry-digital-transformation
https://telecoms.com/520240/huaweis-5-5g-vision-is-what-5g-should-have-been-all-along/
Microsoft announces Azure Operator Nexus; Enea to deliver subscriber data management and traffic management in 4G & 5G
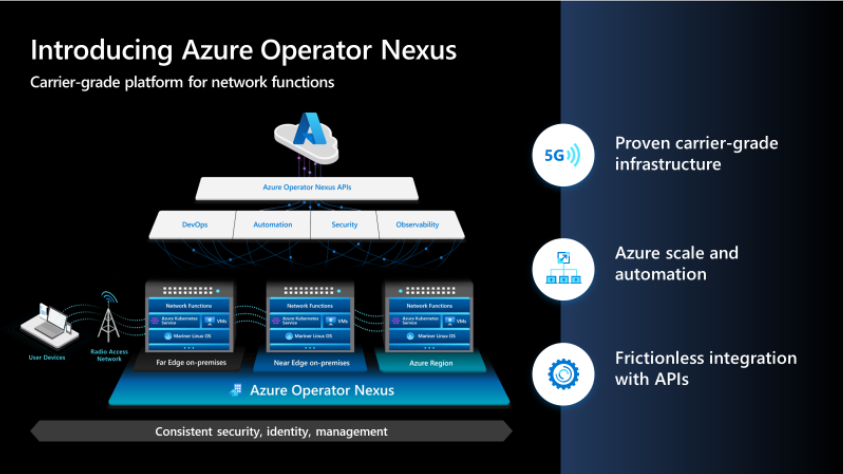
Microsoft launched its brand new next-gen hybrid cloud platform – Azure Operator Nexus – for network operators today. Azure Operator Nexus is an expansion of the Azure Operator Distributed Services private preview. Azure Operator Nexus is a hybrid, carrier-grade cloud platform designed for the specific needs of the operator in running network functions such as packet core, virtualized radio access networks (vRAN), subscriber data management, and billing policy. Azure Operator Nexus is a first-party Microsoft product that builds on the functionality of its predecessor, adding essential features of key Microsoft technologies such as Mariner Linux, Hybrid AKS, and Arc while continuing to leverage Microsoft Services for security, lifecycle management, Observability, DevOps and automation.
Azure Operator Nexus has already been released to our flagship customer, AT&T, and the results have been incredibly positive. Now, we’re selectively working with operators for potential deployments around the world. In this blog post, we provide an overview of the service from design and development to deployment and also discuss benefits the customers can expect, including research and analysis into the total cost of ownership (TCO).
Overview:
Microsoft Azure Operator Nexus leverages cloud technology to modernize and monetize operator network investments to deliver benefits such as:
- Lower overall TCO
- Greater operations efficiency and resiliency through AI and automation
- Improved security for highly-distributed, software-based networks
Azure Operator Nexus is a purpose-built service for hosting carrier-grade network functions. The service is specifically designed to bring carrier-grade performance and resiliency to traditional cloud infrastructures. Azure Operator Nexus delivers operator mobile core and vRAN network functions securely in on-premises (far-edge, near-edge, core datacenters) and on-Azure regions. This delivers a rich Azure experience, including visibility into logging, monitoring, and alerting for infrastructure components and workloads. Operators will have a consistent environment across both on-premises and Azure regions, allowing network function workloads to move seamlessly from one location to another based on application needs and economics.
Whether deployed on-premises or in Azure infrastructure, network functions may access an identical set of platform capabilities. On-premises, the service uses a curated hardware BOM of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS)-based servers, network switches, dedicated storage arrays, and terminal servers. Both deployment models are Linux-based, in alignment with network function needs, telecommunications industry trends, and relevant open-source communities. Additionally, the service supports both virtualized network functions (VNFs) and containerized network functions (CNFs).
The Azure Operator Nexus is based on the experience of a large telecommunications operator that has spent the past seven years virtualizing more than 75 percent of its network and overcoming the scale challenges of network-function virtualization. From this deep networking and virtualization experience, Operator Nexus was designed to:
- Provide the network function runtime that allows the fast-packet processing required to meet the carrier-grade-network demands of network functions supporting tens of millions of subscribers. Examples of requirements the platform delivers include optimized container support, flexible, fine-grained VM sizing, NUMA alignment to avoid UPI performance penalties, Huge Pages, CPU pinning, CPU isolation, Multiple Network Attachments, SR-IOV & OVS/DPDK host coexistence, SR-IOV trusted mode capabilities and complex scheduling support across failure domains.
- Ensure the quality, resiliency, and security required by network-function workloads through robust test automation.
- Deliver lifecycle automation to manage cloud instances and workloads from their creation through minor updates and configuration changes, and even major uplifts such as VMs and Kubernetes upgrades. This is accomplished via a unified and declarative framework driving low operational cost, high-quality performance, and minimal impact on mission-critical running network workloads.
In addition to the performance-enhancing features, Azure Operator Nexus also includes a fully integrated solution of software-defined networking (SDN), low latency storage, and an integrated packet broker. The connectivity between the Operator premises and Azure leverages Express Route Local capabilities to address the transfer of large volumes of operational data in a cost-effective manner.
One of the key benefits of a hybrid cloud infrastructure is its ability to provide harmonized observability for both infrastructure and applications. This means one can easily monitor and troubleshoot any issues that may arise, ensuring systems are running smoothly and efficiently. The platform collects logs, metrics, and traces from network function virtualization infrastructure (NFVI) and network functions (NFs). It also offers a rich analytical, AI/ML-based toolset to develop descriptive and prescriptive analytics. Our goal with this observability architecture is to securely bring all operator data into a single data lake where it can be processed to provide a global-network view and harvested for operational and business insights.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Stockholm Sweden based Enea is amongst the first to join the program. They will deliver subscriber data management and traffic management in 4G and 5G for the new platform.
The introduction of Enea’s Telecom product portfolio will further enhance mobile operators’ ability to unlock the potential of 5G and provide more choice in pre-validated solutions to ensure a faster time to deployment for solutions. Enea’s telecom products include the Stratum Network Data layer, 5G Service Engine, Subscription Manager and Policy Manager, providing a range of subscriber data management, authorization and traffic management capabilities for both 4G & 5G mobile environments.
Azure Operator Nexus program provides an API layer to automate and manage network functions. The Enea network functions will integrate and validate at both the API interoperability level and the automated deployment level to provide telecom operators the option to build, host and operate these containerized functions as part of a network in a cloud or hybrid cloud environment. As pre-validated services, the Enea network functions will be available in the Azure Marketplace.
“The integration with Microsoft Azure Operator Nexus demonstrates Enea’s commitment to multi-vendor telecom architecture, software-based solution and open interoperability.”, said Osvaldo Aldao, Vice President of Product Management at Enea. Further adding, “The addition of our Stratum network data layer as an open 5G UDR & UDSF will provide the data management foundation to drive a fully cloud native architecture with Azure Operator Nexus”.
“Enea joining the Microsoft Azure Operator Nexus Ready Program enables both network function expertise and deployment experience from their extensive portfolio”, said Ross Ortega, Vice President – Azure for Operators, “Enea’s pre-validated functions in the Azure Marketplace will be an essential building block for operator networks.”
References:
Microsoft Azure for Operators:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/solutions/industries/telecommunications/#overview
Enea software portfolio:
Network Data Layer: https://www.enea.com/solutions/4g-5g-network-data-layer/
5G Applications https://www.enea.com/solutions/data-management-applications/
Traffic Management – https://www.enea.com/solutions/traffic-management/4g-5g-user-plane-dual-mode-services/
About Enea:
Enea is a world-leading specialist in software for telecom and cybersecurity. The company’s cloud-native solutions connect, optimize, and secure services for mobile subscribers, enterprises, and the Internet of Things. More than 100 communication service providers and 4.5 billion people rely on Enea technologies every day.
Enea has strengthened its product portfolio and global market position by integrating a number of acquisitions, including Qosmos, Openwave Mobility, Aptilo Networks, and AdaptiveMobile Security.
Contact: Stephanie Huf, Chief Marketing Officer [email protected]
GSMA announces Open Gateway with 21 carriers, Microsoft Azure and AWS
Today, GSMA (the association representing the world’s major mobile operators) announced a new initiative called Open Gateway, a framework to provide universal, open-source-based APIs into carrier networks for developers to access and use a variety of mobile network services.
GSMA Open Gateway is a framework of common network Application Programmable Interfaces (APIs) designed to provide universal access to operator networks for developers. Launched with the support of 21 mobile network operators, the move represents a paradigm shift in the way the telecoms industry designs and delivers services in an API economy world. GSMA Open Gateway will help developers and cloud providers enhance and deploy services more quickly across operator networks via single points of access to the world’s largest connectivity platform.
Applications like location or identity verification and carrier billing, previously would have been more complicated or more expensive (if not impossible) to integrate and use. The plan is to be able to kick off more development using APIs in applications like immersive mixed-reality experiences and web3 applications that will in turn give more 5G business to the 21 mobile carriers that are part of Open Gateway.
The 21 carriers that have signed up for Open Gateway are: America Movil, AT&T, Axiata, Bharti Airtel, China Mobile, Deutsche Telekom, e& Group, KDDI, KT, Liberty Global, MTN, Orange, Singtel, Swisscom, STC, Telefónica, Telenor, Telstra, TIM, Verizon and Vodafone. These carriers have signed a memorandum of understanding, and the plan is to build and work on these APIs by way of CAMARA, an open source project co-developed by the Linux Foundation and the GSMA for this purpose: to help developers access “enhanced” network capabilities.
The carriers have invested billions in new networking technology, but they don’t really have a lot of usage on those networks. This move is being driven in part by them trying to kick-start activity on them.
GSMA Open Gateway APIs are defined, developed and published in CAMARA, the open source project for developers to access enhanced network capabilities, driven by the Linux Foundation in collaboration with the GSMA. Working in CAMARA, APIs between telcos and developers can be delivered quickly, using developer-friendly tools and software code. However, no details were provided about which services we might see rolled out first.
José María Álvarez-Pallete López, GSMA Board Chairman and Chairman & CEO of Telefónica, said: “GSMA Open Gateway will enable single points of access to ultra-broadband networks and provide a catalyst for immersive technologies and Web3 – giving them the ability to fulfill their potential and reach critical mass. Telcos have come a long way in developing a global platform to connect everyone and everything. And now, by federating open network APIs and applying the roaming concept of interoperability, mobile operators and cloud services will be truly integrated to enable a new world of opportunity. Collaboration amongst telecom operators and cloud providers is crucial in this new digital ecosystem.”
“By applying the concept of interconnection for operators to the API economy developers can utilise technology once, for services such as identity, cybersecurity or billing, but with the potential to be integrated with every operator worldwide. This is a profound change in the way we design and deliver services,” said Mats Granryd, Director General of GSMA. “In 1987, representatives from 13 countries worked together to harmonise mobile voice services and enable roaming, and I believe that 35 years on, GSMA Open Gateway has the potential to deliver a similar impact for digital services.”
GSMA Open Gateway will help developers and cloud providers enhance and deploy services more quickly via single points of access to operator networks. This is achieved via common, northbound service APIs that simply expose mobile operators’ network capabilities within a consistent, interoperable and federated framework.
Ishwar Parulkar, Chief Technologist for the Telco Industry at Amazon Web Services (AWS), said: “GSMA Open Gateway is a significant step in enriching the cloud developer experience. Developers using AWS’s more than 200 services will also be able to leverage APIs from telco operators. This allows the developer community to create new applications, and for telcos to open up new models of consumption and monetisation for their networks. We believe this will help accelerate innovation in the telecom industry.”
Erik Ekudden, CTO & SVP, Ericsson, said: “Together with Vonage, we enable operators to take their advanced mobile network capabilities to developers via easy-to-use APIs. The QoD API that we are demonstrating at MWC Barcelona 2023 – live on the networks of Orange, Telefónica and Vodafone – shows how GSMA Open Gateway APIs are highly scalable across operators and with different app developers. This places 5G as an innovation platform at the heart of digital transformation and we are excited to be part of the GSMA Open Gateway initiative.”
“At Microsoft, we are focused on extending a distributed computing fabric from the cloud to the edge, together with our operator partners,” said Satya Nadella, Chairman and CEO, Microsoft. “We look forward to bringing the GSMA Open Gateway initiative to Microsoft Azure, to empower developers and help operators monetise the value of their 5G investments.”
The GSMA Open Gateway initiative launches with eight universal network APIs, including SIM Swap, QoD, Device Status (Connected or Roaming Status), Number Verify, Edge Site Selection and Routing, Number Verification (SMS 2FA), Carrier Billing – Check Out and Device Location (Verify Location). The initiative plans to launch further APIs throughout 2023.
Examples of services supported by the introduction of GSMA Open Gateway include Edge Site Selection and Routing to support autonomous vehicles and Verify Location for fleet management and incident reporting; SIM Swap to combat financial crime and QoD for drones, robotics, eXtended Reality (XR) and immersive online gaming.
The GSMA Open Gateway demonstrations available to see at MWC Barcelona 2023 include:
- At the GSMA Pavilion, Axiata is showcasing its first ever immersive music concert on the Axiata Digital Concert Platform, powered by Dialog and Axiata Digital Labs’ Axonect, designed in association with GSMA Open Gateway APIs for Number Verification (SMS 2FA), Device Location and Carrier Billing.
- At MWC’s startup showcase, 4YFN, Deutsche Telekom (DT) will announce details of its developer marketplaces and Early Adopter Programmes for CAMARA APIs in association with GSMA Open Gateway. In addition, DT will be demonstrating applications of APIs, including QoD, alongside Matsuko and Orange in Hall 3 on stand 3M31.
- The 5G Future Forum (5GFF) will take collaboration to the next level across three operator networks – Rogers, Verizon and Vodafone. Musicians from around the world will jam over 5G, using Mobile Edge Compute (MEC) and the GSMA Open Gateway’s Edge Site Selection API. See the show on Wednesday, 1st March at 12pm in Theatre 1, Hall 6.
- At the GSMA Pavilion, KDDI, Telefónica, Mawari and Sturfee will showcase a revolution in online shopping with the 5G MEC powered XR Digital Twin Store. This allows shoppers in a physical store, and online shoppers in its Digital Twin, to share an immersive retail experience together. This project will explore opportunities based on the GSMA Open Gateway QoD API.
- On stand 4A60 in Hall 4, KT will be showing a demonstration of B2B use cases – built on the GSMA Open Gateway APIs for Edge Site Selection and Routing – with MEC. Titled ‘5G Connectivity & Cloud Federation’ this demonstration enables enterprise customers to receive the best service experience anywhere in the world by discovering optimal edge resources.
- Orange, Telefónica, Vodafone, Vonage and Ericsson are showing how user experience in mobile cloud gaming – and interactive high definition video applications – can be significantly enhanced by leveraging advanced network functionality through global network APIs. Application developers from Blacknut, Zoom and Vonage utilised the GSMA Open Gateway QoD API to add innovative features and enhance the mobile experience.
- Singtel, AIS, Summit Tech and Bridge Alliance will be showing their live broadcast demonstration at the GSMA Pavilion, leveraging 5G and MEC to provide a hyper-personalised view in 8K resolution. Participants are able to interact in real-time within live events across different country networks.
- Demonstrations at Telefónica’s booth will show GSMA Open Gateway API availability in Telefónica Kernel, in collaboration with Microsoft. Microsoft will also be announced as a partner in Telefónica’s Early Adopter Programme for developers and experience creators, which also features AWS, Google and Vonage.
- In addition, at its booth, Microsoft will present a solution for developers to build network-aware applications through a unified interface across operator networks.
Over the next 12 months the initiative will support engagement via Early Adopter Programmes for developers and it will promote GSMA Open Gateway APIs via significant developer channels, including Microsoft events such as Ignite and Build; and AWS’ re:Invent.
References:
Nvidia Survey Reveals How Telcos Plan to Use AI; Quantifying ROI is a Challenge
A Nvidia sponsored survey of more than 400 telecommunications industry professionals from around the world found a cautious tone in how they plan to define and execute on their AI strategies. Virtually every telco is already engaged with AI in some way, although mostly at an early stage. NVIDIA’s first “State of AI in Telecommunications” survey consisted of questions covering a range of AI topics, infrastructure spending, top use cases, biggest challenges and deployment models. The survey was conducted over eight weeks between mid-November 2022 and mid-January 2023.
Amid skepticism about the money-making potential of 5G, telecoms see efficiencies driven by AI as the most likely path for returns on investment. 93% of those responding to questions about undertaking AI projects at their own companies appear to be substantially underinvesting in AI as a percentage of annual capital spending.
Some 50% of respondents reported spending less than $1 million last year on AI projects; a year earlier, 60% of respondents said they spent less than $1 million on AI. Just 3% of respondents spent over $50 million on AI in 2022.
The reasons cited for such cautious spending? Some 44% of respondents reported an inability to adequately quantify return on investment, which illustrates a mismatch between aspirations and the reality in introducing AI-driven solutions. 34% cited an insufficient number of data scientists as the second-biggest challenge.
The biggest telco objectives for AI are to: optimize operations (60%), lower costs (44%) and enhance customer engagement (35%). Respondents cited use cases ranging from cell site planning and truck-route optimization to recommendation engines.
Just over a third of respondents said they had been using AI for more than six months. 31% said they’re still weighing different options, 18% reported being still in a trial phase and only 5% said they had no AI plans at all. Most industry execs say they see AI technologies will positively impact their business – 65% agreed AI was important to their company’s success, and 59% said it would become a source of competitive advantage.
Operators are spending a fraction of their capex budgets on AI projects – last year half said they spent less than $1 million on AI. At the top end, 2% spent more than $50 million in 2021, with that number rising to 3% in 2022.
The latest AI Index compiled by Stanford University puts telcos at the forefront of AI deployment. Using its own data and that from a McKinsey study, it found that the highest level of AI adoption is in product or service development by hi-tech companies and telcos (45%), followed by AI in service operations (45%).
The biggest single application in any industry was natural language text understanding deployed by 34% of hi-tech and telco firms, with 28% implementing AI-based computer vision and 25% using virtual agents.
- Moving from proof of concept to production/scale 47%
- Economic uncertainty 46%
- Infrasctructure upgrades 46%
- Market differentiation 34%
- Change in priority of data science 20%
- 92% will either increase or maintain their AI spend in 2023.
References:
https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2023/02/21/telco-survey-ai/
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/lp/industries/telecommunications/state-of-ai-in-telecom-survey-report/
https://aiindex.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/2022-AI-Index-Report_Master.pdf
Allied Market Research: Global AI in telecom market forecast to reach $38.8 by 2031 with CAGR of 41.4% (from 2022 to 2031)
Global AI in Telecommunication Market at CAGR ~ 40% through 2026 – 2027
The case for and against AI in telecommunications; record quarter for AI venture funding and M&A deals
SK Telecom inspects cell towers for safety using drones and AI
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
Nokia launches anyRAN to drive CloudRAN partnerships for mobile network operators and enterprises
Overview:
On the eve of MWC 2023 in Barcelona, Nokia today announced that it has signed go-to-market agreements with the world’s leading cloud infrastructure and server providers giving mobile network operators and enterprises flexibility in their choice of hardware, cloud infrastructure, and data center solutions for running Cloud RAN. To support this Nokia has also announced the launch of anyRAN, a new concept to help mobile operators and enterprises extend their options for building and evolving their radio access networks. Nokia’s approach supports the evolution of today’s purpose-built networks to Cloud RAN and hybrid solutions, ensuring performance consistency across all network environments.
anyRAN was introduced by Nokia’s President of Mobile Networks Tommi Uitto at the Intercontinental Hotel in Barcelona, Spain.

Image Credit: Nokia
The Collaborative Advantage: Nokia launches anyRAN:
Nokia anyRAN is designed to help mobile operators and enterprises extend their options for building and evolving their radio access networks. The software can run on any partner’s Cloud and Server infrastructure in addition to Nokia AirScale base stations and Nokia AirFrame servers. This approach removes the complexity from deployments by allowing a mix of purpose-built, hybrid, and fully Cloud-based RAN solutions, enabling deep multi-level disaggregation at the Cloud Infrastructure layer and data center (server) hardware layer. Close collaboration with partners also ensures performance consistency of Cloud RAN with Nokia’s field-proven purpose-built RAN.
Future-ready performance: Cloud RAN SmartNIC for anyRAN:
Underpinning these high-performance solutions is the Nokia Cloud RAN SmartNIC, a Layer 1 (fronthaul) In-Line acceleration card that integrates seamlessly with all leading Cloud or server infrastructures. L1 acceleration needs specialized silicon with extreme computing capacity, which is beyond the capabilities of general-purpose processors. Nokia Cloud RAN SmartNIC uses dedicated and optimized silicon technology, which is more energy efficient and provides higher performance. Nokia and its partners have already successfully performed end-to-end 5G data calls (Layer 3 calls) in multi-vendor setups powered by Nokia’s solution.
Nokia 5G Cloud RAN:
While Nokia’s AnyRAN solution offers deep multi-level vertical disaggregation, Nokia also continues to serve the mobile operator and enterprise market with its optimized Nokia AirFrame OpenEdge server family. Benefitting from the SmartNIC, the enhanced AirFrame Open Edge server delivers a 50 percent performance boost compared to the system shown at Mobile World Congress 2022. Nokia’s solutions offer network performance consistency between purpose-built AirScale baseband and Cloud RAN and secures the best possible feature performance parity, with the fastest time-to-market for cloud/hybrid networks.
Sue Rudd, Director Networks and Service Platforms at TechInsights: “As service providers evolve on the path towards disaggregated RAN, Nokia’s anyRAN offers them a solution with standard O-RAN fronthaul and 3GPP midhaul interfaces under seamless control that can operate across multiple Cloud partner data centers. Combined with acceleration from a new Layer 1 SMARTNIC and a ‘host neutral’ Container as a Service (CaaS) layer for DU and CU processing, this flexible open approach will allow operators to leverage Nokia’s powerful new ecosystem of platform and cloud partners to deliver very cost effective, high performance Cloud RAN service.”
Tommi Uitto, President of Mobile Networks at Nokia: “The strength of our industry partnerships and the launch of anyRAN unlocks more choice and higher performance in Cloud RAN for our mobile network operator and enterprise customers. Server-based Cloud RAN will have to co-exist with purpose-built RAN in the short-to-medium term which calls for performance consistency and service continuity between the two. Together with our leading industry partners, we have made huge progress towards this goal by driving consistent performance across any partner’s Cloud Infrastructure or server hardware. Our collaborative approach to Cloud RAN means we can drive efficiency, innovation, openness, and scale by jointly delivering competitive advantage to organizations embracing Cloud RAN.”
Mobile World Congress 2023:
At MWC 2023 in Barcelona, Nokia will showcase anyRAN as well as the future-ready SmartNIC solution, its enhanced AirFrame Open Edge server as well as the progress made in Cloud RAN with its best-in-class partners. Additional demonstrations will also be included on our partner’s stands. Please visit Hall 3 to see our industry-leading technology solutions.
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/mobile-networks/anyran/
Comcast selects Nokia’s 5G SA Core software to support its mobile connectivity efforts
Resources and additional information:
Nokia AirScale Cloud RAN
Nokia anyRAN
Cloud RAN: A Guide to Acceleration Options
In-Line architecture: bringing efficiency and performance to Cloud RAN
Ericsson to lay off 8,500 employees as part of cost cutting plan
After warning in January that profit margins at its RAN business would worsen, telecom equipment maker Ericsson will lay off 8,500 employees globally as part of its plan to cut costs, according to a memo sent to employees and seen by Reuters.
“The way headcount reductions will be managed will differ depending on local country practice,” Chief Executive Borje Ekholm wrote in the memo. “In several countries the headcount reductions have already been communicated this week,” he said. “It is our obligation to take this cost out to remain competitive,” Ekholm said in the memo. “Our biggest enemy right now may be complacency.”
While technology companies such as Microsoft, Meta and Alphabet have laid off thousands of employees citing economic conditions, Ericsson’s move would be the largest layoff to hit the telecoms industry.
On Monday, the company, which employs more than 105,000 worldwide, announced plans to cut about 1,400 jobs in Sweden. While Ericsson did not disclose which geography would be most affected, analysts had predicted that North America would likely be most affected and growing markets such as India the least.
The company said in December it would cut costs by 9 billion crowns ($880 million) by the end of 2023 as demand slows.
“Our aim is to manage the process in every country with fairness, respect, professionalism and in line with local labor legislation,” Ericsson said in a statement.
“We are also working on our service delivery, supply, real estate and IT. We have already started to implement and accelerate various initiatives to help us reach” the cost-cutting goal, Ericsson said.
Many telecom companies had beefed up their inventories during the height of the pandemic which is now leading to slowing orders for telecom equipment makers like Ericsson and Nokia.
References:
https://www.reuters.com/business/media-telecom/ericsson-lay-off-8500-employees-memo-2023-02-24/
https://apnews.com/article/technology-stockholm-covid-business-07bda439ac93836817a00d0d54892d0a
Ericsson Mobility Report: 5G monetization depends on network performance
High Tech Layoffs Explained: The End of the Free Money Party
HPE acquires private cellular network provider Athonet (Italy) to strengthen HPE Aruba’s networking portfolio
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) today announced the expansion of its connected edge-to-cloud offering with the acquisition of Athonet, a private cellular network technology provider that delivers mobile core networks to enterprises and communication service providers. Combined with the HPE telco and Aruba networking portfolios, Athonet will put HPE at the forefront of a growing market that is predicted by IDC to increase to more than $1.6 billion1 by 2026.
Based in Vicenza, Italy, Athonet has more than 15 years of experience delivering 4G and 5G mobile core solutions to customers and partners globally. Athonet is an award-winning technology pioneer with more than 450 successful customer deployments in various industries, including leading mobile operators, hospitals, airports, transportation ports, utilities, government and public safety organizations.
With enterprises facing complex connectivity challenges across large and remote sites, private 5G offers high levels of coverage, reliability and mobility across campus and industrial environments. It also augments the cost-effective, high-capacity connectivity provided by Wi-Fi. The incorporation of Athonet’s technology will allow HPE to deliver private networking capabilities directly to enterprises as part of HPE’s Aruba networking portfolio, while also enabling communications service providers (CSPs) to quickly deploy private 5G networks for their customers.

“Telco customers are looking for simpler ways to deploy private 5G networks to meet growing customer expectations at the connected edge,” said Tom Craig, global vice president and general manager, Communications Technology Group at HPE. “At the same time, enterprise customers are demanding a customized 5G experience with low-latency, segregated resources, extended range and security across campus and industrial environments that complement their existing wireless networks. With the acquisition of Athonet, HPE now has one of the most complete private 5G and Wi-Fi portfolios for CSP and enterprise customers – and we will offer it as a service through HPE GreenLake.”
HPE expands private 5G solutions for both telcos and the enterprise:
HPE will integrate Athonet’s technology into its existing CSP and Aruba networking enterprise offerings to create a private networking portfolio that accelerates digital transformation from edge-to-cloud. The networking portfolio will provide the following benefits:
- Enhanced private networks that combine the high capacity of Wi-Fi with the coverage and mobility of 5G
- Accelerated private 5G deployments that improve agility and innovation to help telco B2B teams and enterprise customers
- New enterprise revenue streams for telcos with differentiated services leveraging 5G and Wi-Fi
- Alignment of costs to revenues with consumption-based models for enterprises and telcos through HPE GreenLake, reducing the risk of entering new markets
- Management of operational complexity and cost efficiency with 5G orchestration and zero-touch automation to deliver new workloads from edge-to-cloud
With 5G investments running into the billions of dollars, CSPs are looking for simple ways to meet customer needs and drive new B2B revenue by deploying both edge compute and private 5G networks. The addition of Athonet’s software to HPE’s telco portfolio enhances one of the broadest communications portfolios in the market, which serves a base of more than 300 customers across 160 countries and connects more than one billion mobile devices worldwide. Building on its existing private 5G solutions, HPE’s enhanced offering for CSPs will support private 4G and 5G networks and include telco-grade orchestration and automation capabilities. These capabilities will help launch new B2B services that meet growing customer expectations for the connected edge.
“Athonet was founded to provide customers with private 4G and 5G solutions that deliver carrier-grade reliability and performance to suit their increasing and more challenging connectivity needs,” said Gianluca Verin, CEO and co-founder of Athonet. “We are excited to join HPE and combine our highly skilled teams as we expand our joint service provider offerings for the rapidly growing private 5G market and build on HPE’s strategy to be the leading edge-to-cloud solutions provider.”
Private 5G offers enterprises new capabilities that are ultra-secure, easy to deploy and manage, ready for highly specialized applications such as robotics and industrial IoT, data networks and pipelines, and security systems facilitation. The acquisition of Athonet strengthens Aruba’s connected edge portfolio, providing the unique and highly sought-after ability to deliver fully integrated Wi-Fi and private 5G networks. Integration with Aruba Central will enable network managers to administer Wi-Fi and private 5G through a single pane of glass and bring to bear the power of AI-powered insights, workflow automation, and robust security.
HPE GreenLake, HPE’s edge-to-cloud platform, will offer Athonet private 5G offerings, combining all costs for Wi-Fi and private 5G into one single monthly subscription with no capital expenditure. Flexible consumption options, including HPE’s networking as a service, mean private 5G networks can be deployed with reduced risk, little upfront investment and scaled according to demand.
HPE portfolio integration and availability:
HPE will integrate Athonet’s solutions with its existing telco software assets and plans to make them available to customers some time following the close of the transaction. HPE will also integrate the solutions with the Aruba networking portfolio in the near future. The transaction is expected to close at the beginning of the third quarter of HPE’s 2023 fiscal year, subject to regulatory approvals and other customary closing conditions.
About Hewlett Packard Enterprise:
Hewlett Packard Enterprise is the global edge-to-cloud company that helps organizations accelerate outcomes by unlocking value from all of their data, everywhere. Built on decades of reimagining the future and innovating to advance the way people live and work, HPE delivers unique, open and intelligent technology solutions as a service. With offerings spanning Cloud Services, Compute, High Performance Computing & AI, Intelligent Edge, Software, and Storage, HPE provides a consistent experience across all clouds and edges, helping customers develop new business models, engage in new ways, and increase operational performance. For more information, visit: www.hpe.com
Media Contacts for U.S. & Canada:
Ben Stricker [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Analysis from Channel Futures:
While HPE already offers a 5G cloud-native software core, Athonet gives deeper in-house capabilities to more quickly and directly deploy private 5G networks.
“Given HPE’s Wi-Fi and security assets – like Aruba – I’d say this makes a clear play to simplify management for key enterprise digital assets. And this is the kind of issue that enterprises are often bringing up to us,” Omdia chief analyst of enterprise services Camille Mendler told Channel Futures. (Omdia and Channel Futures share a parent company, Informa.)
Patrick Filkins, IDC‘s research manager for IoT and telecom network infrastructure, said Athonet can give HPE customers an improved option for deploying a private 5G network together with Wi-Fi. Filkins said that integrated portfolio could well serve an enterprise that has already done the heavy legwork of building a Wi-Fi network.
“This is a very complicated task, and one the enterprise itself controls. They don’t want to start from scratch or be forced to have someone else tinkering in their systems, so this acquisition will hopefully provide some assurance to enterprise customers that the vendors will help ensure their customers can repurpose work they’ve already done to integrate a new network technology, and hopefully new use cases,” Filkins said.
Filkins said the acquisition will immediately improve the HPE 5G core and gradually work its way into Aruba portfolio improvements. For example, HPE will integrate Athonet into the Aruba Central network management platform.
“Specifically, we expect HPE/Aruba to over time release follow-on solutions which help enterprises manage the two technologies seamlessly. Enterprises are not interested in deploying both 5G and Wi-Fi networks in a silo. They want a combined solution that can help tackle the integration and management issues from a single pane. This means you’ll see HPE’s telco and Aruba teams working together more closely over time,” Filkins said.
Mendler said one might see a U.S. equivalent in Celona, despite Athonet’s age (founded 2004) compared to that of Celona (founded in 2019). Filkins added that although many vendors provide private and public LTE/5G cores in the U.S., most run their headquarters abroad. He pointed to Cisco and Microsoft-acquired Mavenir, Affirmed Networks and MetaSwitch as 5G core providers in the U.S.
“However, from a competitive standpoint, Athonet competes globally against Nokia, Ericsson, Mavenir, Microsoft Azure, Cisco, etc., among others,” Filkins told Channel Futures. He described Athonet as “no slouch” in the wireless market. He calls the company’s customer base deep, though consisting of smaller customers. HPE said in an announcement that Athonet has performed 450 customer deployments in various verticals. Athonet’s customers include SpaceX, which uses a private cellular network in Antarctica.
Filkins called the Athonet technology offerings “relatively advanced for 5G.” For example, the cloud-native 5G core meets almost all of 3GPP‘s listed functions. He also said Athonet’s core augments HPE’s 5G core offerings.
“The cloud-native part means it can be deployed fully on-site, fully in the cloud, or in a hybrid format. This should cover any scenario the customer wants. [Athonet] has specialized in selling mobile core software to enterprises, and smaller, regional operations for years. It knows the needs of the enterprise well,” Filkins said.
Athonet CEO and co-founder Gianluca Verin said his team looks forward to joining HPE. Moreover, he said he wants to enhance HPE’s goal of being “the leading edge-to-cloud solutions provider.” Verin worked in support and solution engineer positions at Ericsson for eight years before starting Athonet.
HPE’s GreenLake edge-to-cloud services platform will host the private 5G service. HPE executives have said GreenLake as-a-service consumption model will “simplify” enterprises’ entrance into 5G and lower risk.
“I think this is an important step HPE is taking. For the most part, private 5G and Wi-Fi networks have been offered as point solutions, but HPE/Aruba intend to do the ‘under-the-hood’ work to make them as integrated as possible, which is what enterprise customers want,” Filkins said.
In December, HPE said 80% of its top 100 customers have adopted the GreenLake platform. The vendor is also equipping Aruba partners to deliver its network-as-a-service offering.
When HPE unveiled a private 5G offering one year ago, an executive said HPE preferred to go to market though system integrators, telcos and service providers rather than straight to the enterprise. HPE’s telco business serves 300 customers across the world, the company said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References: