5G
Performance analysis of big 3 U.S. mobile operators; 5G is disappointing customers
Speedtest Intelligence® from Ookla reveals T-Mobile was the fastest mobile operator in the United States during Q1 2021 with a Speed Score™ of 50.21 on modern chipsets. AT&T was second and Verizon Wireless third.
Note that this is the first quarter Ookla is reporting on the country as a whole, rather than using competitive geographies. Ookla says that expanding its focus to include rural areas will show drops in performance, decreasing speed and increasing latency when compared with prior reports.
In Q1 2021, T-Mobile had the fastest median 5G network download speed in the U.S. at 82.35 Mbps. AT&T was second at 76.60 Mbps and Verizon Wireless third at 67.24 Mbps. For a complete view of commercially available 5G deployments in the U.S. to-date, visit the Ookla 5G Map™.
Ookla discovered that during Q1 2021 that T-Mobile subscribers with 5G-capable devices were connected to a 5G service 65.4% of the time. 5G “time spent” on Verizon Wireless’ network was at 36.2% and at 31% on AT&T’s network.
In measuring each operator’s ability to provide consistent speeds, Ookla found that T-Mobile had the highest Consistency Score™ in the U.S. during Q1 2021, with 84.8% of results showing at least 5 Mbps download and 1 Mbps upload speeds. AT&T was second and Verizon Wireless third. All three U.S. mobile carriers were above 80% in terms of consistency.
Here’s the current status of Worldwide median 5G Speeds as of Q3-2022:

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Earlier this week a new report from becnhmarking company Rootmetrics found that T-Mobile US is leading in 5G availability across U.S. cities. Rootmetrics found that AT&T’s 5G provides the best performance, and AT&T and Verizon both won high marks for 5G reliability.
“While we’ve seen strong and improving 5G availability and speeds from the carriers in many cities, it’s important to keep in mind that with the major U.S. networks utilizing different types of spectrum for 5G, the 5G availability and speeds that consumers experience can vary a great deal for different carriers across or even within different markets,” Rootmetrics concluded.
Rootmetrics tested 5G networks in 45 cities across the U.S. between January and March of this year. It recorded at least some 5G availability from all three carriers in nearly all of them. T-Mobile US was the only carrier with a 5G network presence in all 45 of the cities, AT&T had 5G service in 44 out of the 45, and Rootmetrics saw 5G availability for Verizon in 43 out of the 45 cities.
The availability of T-Mobile’s 5G was one common theme across both testing reports. Rootmetrics’ testing, conducted in the first half of 2021, said that T-Mobile had 5G availability in all 45 of the markets it tested and showed the highest percentages of 5G availability in the most markets: More than 55% availability in 30 markets, with the lowest tested market being Sarasota, FL, where Rootmetrics’ testing showed T-Mo 5G available for a device to connect to only about 19% of the time.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Light Reading’s Mike Dano writes that “AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile offer unlimited 5G disappointment.” In a subhead titled, “T-Muddle” Dano writes:
In 2019, T-Mobile boasted that “5G speed will be up to 10x faster, compared to LTE.” But when it first launched its 5G network on its lowband 600MHz spectrum, speeds were only 20% faster than its LTE network. Then, after T-Mobile closed its acquisition of Sprint’s 2.5GHz midband spectrum, it quickly began offering 5G speeds up to 1Gbit/s. The operator even debuted a new 5G lexicon for its offerings: “5G Ultra Capacity” refers to its speedy 2.5GHz network, while “Extended Range 5G” refers to its slower 600MHz network.
So it would stand to reason that customers might want to see which flavor of T-Mobile 5G they can access, right? A quick check of T-Mobile’s coverage map reveals none of these details. The operator only offers a generic “5G” coverage layer that does not provide details about whether it’s 600MHz or 2.5GHz. One is slightly faster than LTE while the other provides average speeds of 300Mbit/s. Prospective T-Mobile customers are left in the dark.
T-Mobile isn’t the only operator seemingly content to hide behind 5G obfuscation. AT&T has debuted no fewer than three different 5G brands – 5G+, 5Ge and 5G – yet it does not offer any details to prospective customers about how it might charge for those offerings. The operator’s pricing plans mention only “5G” and do not specify whether that means 5G+, 5Ge or 5G, or all three.
Regarding Verizon’s 5G pricing plans, Dano stated:
The operator offers a truly dizzying array of 5G plans and pricing options – one observer described Verizon’s pricing plans as “a series of nesting dolls.”
In 5G, Verizon is reserving its faster “Ultra Wideband” technology only for its expensive unlimited plans. Customers on its cheapest Start Unlimited plan can either pay $10 extra for 5G specifically, or they can spend that same $10 to upgrade to a more expensive unlimited plan that offers 5G as well as other goodies, such as more mobile hotspot data. Why the two different upgrade options? “We always like to give customers choices,” explained a Verizon spokesperson.
But what that really means is that customers are simply left to fend for themselves. They’re left to pick from among a dizzying number of pricing options, all promising “unlimited” data, but all limiting that data in various ways. Customers are left to figure out why messages from iPhones to Android phones won’t show delivery receipts. They’re left to discover why they’re still receiving robocalls, and what they might need to do to block them. They’re left to uncover what kind of 5G they can get and whether it’s any different from 4G.
In conclusion, Dano says that “AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile continue to be very interested in outdoing one another in their 5G pricing schemes and big, new network claims.” However, they’re not succeeding in pleasing their customers who remain frustrated and disappointed.
Cartoon courtesy of long time IEEE contributor Geoff Thompson:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.speedtest.net/global-index/united-states#market-analysis
https://rootmetrics.com/en-US/content/5g-in-the-us-1H-2021
Lumen Technologies and T-Mobile collaborate on edge compute for enterprise customers
Following this week’s Verizon-AWS announcement on Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), T-Mobile US has entered the mobile edge computing business using wireline carrier Lumen Technologies (formerly CenturyLink) as its initial preferred vendor.
T-Mobile US has taken a decidedly different MEC approach compared to its two domestic rivals (Verizon and AT&T). The U.S.’s #2 wireless network operator effectively views the edge as a latter opportunity that doesn’t merit a large initial investment. Its edge computing initiatives are exclusively focused on businesses and government agencies that fall under Lumen’s enterprise unit and T-Mobile for business.
“By pairing America’s largest and fastest 5G network with Lumen’s enterprise solutions, we can break down industry barriers and deliver unparalleled network reach to enterprise and government organizations looking to optimize their applications across networks,” Mike Katz, EVP for T-Mobile for Business, said in a prepared statement. “With our leading 5G network, Lumen and T-Mobile have the opportunity to accelerate business innovation in an era where the network is more critical than ever,” Katz added,

Enterprise applications will likely benefit from Lumen’s hundreds of thousands of fiber connected enterprise locations paired with T-Mobile’s “largest and fastest 5G network.”
“The Lumen platform, with 60 plus planned edge market nodes distributed on our high-capacity global fiber network enables application designs with latency of 5 milliseconds or less between the workload and the endpoint device,” wrote David Shacochis, VP of enterprise technology and field CTO at Lumen.
“Lumen’s fiber reach and edge computing resources can augment business solutions for T-Mobile customers, and private wireless solutions can augment business solutions for Lumen customers,” Shacochis added.
“The companies envision starting with metropolitan areas where they are already well connected, and expanding their joint go-to-market over time,” Shacochis wrote, adding that more details about commercial availability and services will be shared throughout 2021.
These efforts aim to address the pressing needs of enterprises to transform their networks to meet the data-intensive challenges across a variety of industries and use cases. Both companies will also continue to drive innovation in this space through T-Mobile’s labs and Tech Experience Center and the Lumen Edge Experience Center.
“Our relationship with T-Mobile aims to introduce a powerful trifecta – access to national 5G wireless and fiber connectivity, managed services across a range of technologies and edge computing resources,” said Shaun Andrews, executive vice president and chief marketing officer for Lumen Technologies. “T-Mobile’s expansive 5G footprint coupled with our extensive edge computing platform would provide enterprise developers with the best of both worlds to power the next wave of digital business.”
- For a current list of Lumen live and planned edge locations, visit: https://www.lumen.com/en-us/solutions/edge-computing.html#edge-computing-map
- The Lumen low latency network is comprised of approximately 450,000 global route miles of fiber and more than 180,000 on-net buildings, seamlessly connected to:
- 2,200 public and private third-party data centers in North America, Europe & Middle East, Latin America, and Asia Pacific
- Leading public cloud service providers including Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute & Azure Government, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud
T-Mobile’s partnership with Lumen is likely just the beginning. “As in all things with 5G, I think a lot of our efforts have to be done through partnerships,” said John Saw, EVP of advanced and emerging technologies at T-Mobile. Apparently, the network operator will form partnerships with many of the big vendors in the space, including hyperscalers (Google, Amazon, Microsoft), and other specialized mobile edge computing vendors.
Similarly, Shacochis said Lumen is also “open to and looking at” other partnerships in the wireless space. Lumen executives outlined a plan to offer edge compute services in August 2019. The company deployed its first block of edge nodes and obtained its first customer in Q3-2020, before formally launching its edge platform in December 2020.
Building on cloud partnerships with Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS), Lumen bolstered its edge capabilities through additional deals with VMware and IBM.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/lumen-lands-t-mobiles-first-5g-edge-contract/2021/04/
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/lumen-strikes-edge-compute-deal-t-mobile
https://www.sdxcentral.com/edge/definitions/multi-access-edge-computing-vendors/
IBM and Verizon Business Collaborate on 5G, Edge Computing and AI Solutions for Enterprise Customers
Work from Home Reality Impacts Market for New Networking Technologies
SOURCE: Bigleaf Networks
Introduction:
Hype around next generation wireless standards (e.g. WiFi6/IEEE 802.11ax, 5G: ITU-R IMT 2020.SPECS/3GPP Release 16) has become a distraction, according to Bigleaf Networks founder and CEO, Joel Mulkey. Marketers are promoting these new technologies which sacrifice reliability to push faster speeds that are mostly useless in the new work from home era.
Mulkey and Bigleaf Vice President of Product, Jonathan Petkevich, looked into the reality behind the marketing hype around 5G and WiFi 6, as well as other networking trends such as satellite networks and artificial intelligence, in a wide-ranging panel discussion hosted for the company’s customers, partners, and agents.
As IT leaders look to regain their footing in 2021, many tech conversations that were trending at the beginning of 2020 picked up where they left off, while other trends emerged. Below are selected highlights from Mulkey and Petkevich’s conversation:
The Work From Home Reality:
“If you look at some of the Stay-At-Home mandates that have happened over the course of 2020, we estimate that about 85 million people are working from home, and that’s a big shift towards where we were at the start of 2020,” said Mulkey. “Starting at about the mid-March timeframe, 88% of organizations asked employees or required employees to work from home. About 57% of the US workforce started to work from home on a regular basis. So that was a big shift towards most people working in the office, with a few people working remotely in regional or local areas. And a lot of organizations have been talking about how they’re switching to a more long-term remote work-from-home strategy.”
Adapting to this new work from home reality meant frantically moving technology to the cloud. Part of that shift meant IT and network infrastructure teams needed to revamp their networks to support the connection reliability and application performance required in this kind of new normal.
“You need to have a healthy path between the device you’re using and the cloud server, otherwise you’re not going to have a usable experience,” said Mulkey. “One of the things we’re seeing companies running into is a sudden realization that quality of connectivity is really important.”
The Danger of WiFi 6:
According to Gartner, WiFi (IEEE 802.11) is the primary high performance network technology that companies will use through 2024. Today, roughly 96% of organizations use some form of wireless technology with many of those companies looking to move to faster versions of those networking capabilities in the next couple of years. Mulkey and Petkevich say the hype is hurting companies.
“Ensuring that you have technology that’s built on the latest standards makes sense,” said Petkevich. “I don’t know that 5G or WiFi 6 are drastically changing how a business operates day-to-day. There’s a little bit of over-hype around the speed and performance and some of the promise that’s with both of these.”
“WiFi 6 is a bit misplaced in our industry’s priorities and 5G is a marketing mess,” said Mulkey. “WiFi 6 is good for really dense, high bandwidth needs. So if you have an office with 1,000 people in a small area or you’re trying to provide WiFi offload in a stadium, WiFi 6 has technologies that will help you out. But if you’re a normal person and you’ve got a house with a couple of kids and you need to make sure your WiFi doesn’t drop-out when you’re on Zoom calls, I don’t see WiFi 6 moving the needle there. In fact, I think it’s harmful. The WiFi industry has become so focused on a story of faster, faster, faster, that the pace of innovation comes at the sacrifice of reliability. What you really need is stable WiFi connectivity that doesn’t drop out, that deals really well with roaming, that has some more intelligence to the quality of connectivity rather than prioritizing speed.”
5G Hype and Rural America:
“Now, 5G is interesting because there’s some really promising stuff there,” continued Mulkey. “Imagine if you didn’t even need WiFi, you just had always-on connectivity from all your devices at say, 100 megabits a second. That was the vision cast for it. The problem is, it’s almost all hype. What you need for the really high speeds is millimeter wave connectivity, which is really only going to be available in dense urban areas. So the folks that absolutely need good 5G today in rural areas or suburban areas without good landline connectivity, are probably not gonna get that millimeter wave behavior, surely not in rural areas.”
“We really have most of the benefits, if not all of them, with 4G today, so the evolution from a 4G to 5G in these longer distance connections is minimal to nothing,” added Mulkey. “It’s just a marketing term slapped on 4G. Now, 4G has gotten better since your phone first said 4G on it, but you’re not going to magically be able to stream 3D Star Wars style holograms because your phone has a 5G icon on it. That may come some day, but it won’t be 2021.”
Satellites:
Those who have the toughest time with WAN internet connectivity are those in rural areas or suburban areas that have been abandoned by the telecom and cable operators. An area Mulkey and Petkevich see low Earth orbit satellite networks moving beyond hype.
“The issue with traditional satellites is latency,” said Petkevich. “Starlink fixes that. So it’ll be interesting to see that play out in 2021.”
Artificial Intelligence in the Network:
44% of IT decision-makers believe that AI and machine learning can help companies optimize their network performance, and more than 50% identify AI as a priority investment needed to deliver their ideal network and make things work for them.
“There are two main ways that AI is in use today. You have a consumer-facing flavor — Siri on my iPhone, or the way that Google can find me images of apples; and then you have the hidden AI that nobody knows about — the instantaneous response of a Google search, where they’ve built smart technology that would fall under the definitions of AI to make sure that your request for Google gets to the right server from the right path and gets back to you as efficiently and effectively as possible,” said Mulkey. “Those technologies are available today. The challenge is they’re not available to the everyday person. This is an area where we, ourselves, have dedicated people and resources to figure out, ‘How can we make our network behave in an autonomous manner far better than it could if there were just people controlling it?'”
“There’s a kind of a misconception that when we talk about AI, the first thought is all the wonderful movies that have come out over the years,” quipped Petkevich. “Where we are today is there’s a lot of innovation going on to make this more tangible and more practical for businesses to use on the smaller scale, and not reserve it for the large enterprises of the world, and make it more generally available. This is definitely an area where a technology is moving beyond its hype.”
About Bigleaf Networks:
Bigleaf Networks is the intelligent networking service that optimizes Internet and Cloud performance by dynamically choosing the best connection based on real-time usage and diagnostics. Inspired by the natural architecture of leaves, the Bigleaf Cloud-first SD-WAN platform leverages redundant connections for optimal traffic re-routing, failover and load-balancing. The company is dedicated to providing a better Internet experience and ensuring peace of mind with simple implementation, friendly support and powerful technology. Founded in 2012, Bigleaf Networks is investor-backed, with service across North America.

Bigleaf combines a simple on-site installation, intelligent hands-off operations, and redundancy at every level to turn commodity broadband connections into a worry-free, Enterprise-grade connection to your applications.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Tutorial on Advanced Antenna Systems (AAS) for 5G Networks
Editor’s Note:
Rec. ITU‑R M.2101 uses the term AAS to mean Advanced Antenna System(s), while 3GPP uses the term AAS to mean Active Antenna System (s).
Definition:
Advanced antenna systems (AAS) is the general term used to describe antenna systems utilizing techniques aiming at improving performance and spectral efficiency of radiocommunication transceivers taking advantage of antenna array theory and practice.
These techniques include adaptive beamforming, multiple input multiple output (MIMO), and space division multiple access (SDMA) among other ones. These multi-antenna techniques are generally applicable to any frequency band or radio application and can be implemented using passive or active antennas.
In higher frequency bands, such as those around the millimetric wave bands, active advanced antenna systems are the prevalent technology choice.
- Smart antennas
- Adaptive beamforming
- Phased arrays
- Spatial multiplexing and MIMO
- Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA)
- Active and passive antennas
- Antenna Array Theory
Basic concepts:
Multiple antennas can be arranged in space in specific configurations to form a highly directive pattern. These arrangements are referred to as “arrays.” In an array antenna, the fields from the individual elements add constructively in some directions and destructively (cancel) in others thus creating an overall array radiation pattern different from that of the individual elements.
The major advantage of antenna arrays over a single antenna element is their electronic scanning capability; that is, the major lobe can be steered toward any direction by changing the phase of the excitation current at each array element (phased array antennas). Furthermore, by also controlling the magnitude of the excitation current, a large variety of radiation patterns and sidelobe level characteristics can be produced. Adaptive antennas (also called “smart antennas” in mobile communication applications) go a step further than phased arrays and can direct their main lobe (with increased gain) in a desired direction (e.g., a mobile user in a cellular communication system) and nulls in the directions of interference or jammers.
AAS enables state-of-the-art beamforming and MIMO techniques that are powerful tools for improving end-user experience, capacity and coverage. As a result, AAS significantly enhances network performance in both uplink and downlink. Finding the most suitable AAS variants to achieve performance gains and cost efficiency in a specific network deployment requires an understanding of the characteristics of both AAS and of multi-antenna features.
Multi-antenna techniques
Multi-antenna techniques, here referred to as AAS features, include beamforming and MIMO. Such features are already used with conventional systems in today’s LTE networks. Applying AAS features to an AAS radio results in significant performance gains because of the higher degrees of freedom provided by the larger number of radio chains, also referred to as Massive MIMO.
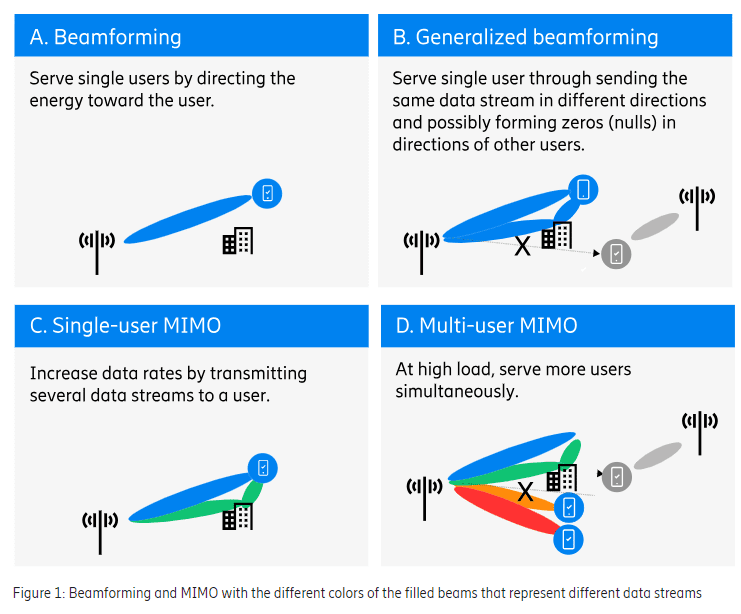
Beamforming
When transmitting, beamforming is the ability to direct radio energy through the radio channel toward a specific receiver, as shown in the top left quadrant of Figure 1. By adjusting the phase and amplitude of the transmitted signals, constructive addition of the corresponding signals at the UE receiver can be achieved, which increases the received signal strength and thus the end-user throughput. Similarly, when receiving, beamforming is the ability to collect the signal energy from a specific transmitter. The beams formed by an AAS are constantly adapted to the surroundings to give high performance in both UL and DL.
Although often very effective, transmitting energy in only one direction does not always provide an optimum solution. In multi-path scenarios, where the radio channel comprises multiple propagation paths from transmitter to receiver through diffraction around corners and reflections against buildings or other objects, it is beneficial to send the same data stream in several different paths (direction and/or polarization) with phases and amplitudes controlled in a way that they add constructively at the receiver. This is referred to as generalized beamforming, as shown in the upper right quadrant of Figure 1. As part of generalized beamforming, it is also possible to reduce interference to other UEs, which is known as null forming. This is achieved by controlling the transmitted signals in a way that they cancel each other out at the interfered UEs.
MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) techniques:
Spatial multiplexing, here referred to as MIMO, is the ability to transmit multiple data streams, using the same time and frequency resource, where each data stream can be beamformed. The purpose of MIMO is to increase throughput. MIMO builds on the basic principle that when the received signal quality is high, it is better to receive multiple streams of data with reduced power per stream, than one stream with full power. The potential is large when the received signal quality is high and the streams do not interfere with each other. The potential diminishes when the mutual interference between streams increases. MIMO works in both UL and DL, but for simplicity the description below will be based on the DL.
Single-user MIMO (SU-MIMO) is the ability to transmit one or multiple data streams, called layers, from one transmitting array to a single user. SU-MIMO can thereby increase the throughput for that user and increase the capacity of the network. The number of layers that can be supported, called the rank, depends on the radio channel. To distinguish between DL layers, a UE needs to have at least as many receiver antennas as there are layers.
SU-MIMO can be achieved by sending different layers on different polarizations in the same direction. SU-MIMO can also be achieved in a multi path environment, where there are many radio propagation paths of similar strength between the AAS and the UE, by sending different layers on different propagation paths, as shown in the bottom left quadrant of Figure 1.
In multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO), which is shown in the bottom right quadrant of Figure 1. above, the AAS simultaneously sends different layers in separate beams to different users using the same time and frequency resource, thereby increasing the network capacity. In order to use MU-MIMO, the system needs to find two or more users that need to transmit or receive data at the very same time. Also, for efficient MU-MIMO, the interference between the users should be kept low. This can be achieved by using generalized beamforming with null forming such that when a layer is sent to one user, nulls are formed in the directions of the other simultaneous users.
The achievable capacity gains from MU-MIMO depend on receiving each layer with good signal-to-interference-and-noise-ratio (SINR). As with SU-MIMO, the total DL power is shared between the different layers, and therefore the power (and thus SINR) for each user is reduced as the number of simultaneous MU-MIMO users increases. As the number of users grows, the SINR will further deteriorate due to mutual interference between the users. The wireless network capacity (the number of devices that can use a wireless network at the same time and the bandwidth consumed) typically improves as the number of MIMO layers increases, to a point at which power sharing and interference between users result in diminishing gains, and eventually losses.
It should be noted that the practical benefits of many layers in MU-MIMO are limited by the fact that in today’s real networks, even with a high number of simultaneous connected users, there tends not to be many users who want to receive data simultaneously. This is due to the bursty (chatty) nature of data transmission to most users. Since the AAS and the transport network must be dimensioned for the maximum number of layers, the MNO needs to consider how many layers are required in their networks. In typical MBB deployments with the current 64T64R AAS variants, the vast majority of the DL and UL capacity gains can be achieved with up to 8 layers.
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/white-papers/advanced-antenna-systems-for-5g-networks
Executive Summary: IMT-2020.SPECS defined, submission status, and 3GPP’s RIT submissions
Introduction – IMT-2020.SPECS:
The forthcoming ITU-R recommendation “IMT-2020.SPECS” identifies the terrestrial radio interface technologies of International Mobile Telecommunications-2020 (IMT-2020) and provides the detailed radio interface specifications.
IMPORTANT: This new ITU-R standard will NOT include IMT 2020 non-radio aspects, such as 5G Core Network, Signaling, Network Slicing, Virtualization, Network Management/Maintenance, Security/Privacy, Fault Detection/Recovery, Codecs, Interworking, etc.
This new recommendation was developed by ITU-R WP5D (aka 5D) over the last five years. It consists of IMT 2020 (5G) Radio Interface Technologies (RIT) and Sets of Radio Interface Technologies (SRIT).
The final IMT-2020.SPECS is expected to be approved in late November 2020 at the ITU-R SG 5 (parent of WP 5D) meeting. Here’s the related ITU-R meeting schedule for the remainder of 2020:
|
WP 5D |
36 |
5 October 20 |
16 October 20 |
Geneva |
10 day meeting |
|
WP 5D |
36bis |
17 November 20 |
19 November 20 |
Geneva |
Focused WP 5D meeting on the technology aspects and related administrative activities for finalization of Step 8 of the IMT-2020 process for draft new Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT-2020.SPECS] |
|
SG 5 |
23 November 20 |
24 November 20 |
Geneva |
Anticipated dates |
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT submission status:
IMT 2020 RIT submissions from 3GPP/China/Korea [1.], TSDSI [2], DECT/ETSI, and Nufront are all being considered by 5D. The latter two submissions have defined their own version of 5G New Radio (NR) as they do NOT use 3GPP’s 5G NR.
Note 1. ATIS found the China and Korea IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT submissions to be technically identical to 3GPPs. Please see IMT-2020 Consensus Building and Decision by 5D for more detail.
Note 2. The TSDSI submission uses 3GPP’s 5GNR but also ADDS functional capability to support Low Mobility Large Cell (LMLC).
->Hence, there are potentially three different 5G NRs (as the basis for the respective RIT submissions) that may be standardized in IMT-2020.SPECS if the DECT/ETSI and Nufront submissions achieve final approval from WP5D. 5D requested additional work for both DECT/ETSI and Nufront RIT submissions before they can be progressed to the next step at 5D’s October 2020 meeting. Those submissions will NOT be included in the first IMT-2020.SPECS recommendation 5D will send to ITU-R SG5 in late November 2020. If 5D subsequently approves them, they will be included in a revision of IMT-2020.SPECS in 2021.
At its July virtual meeting, 5D determined that the IMT-2020 candidate technology submission proposals from DECT/ETSI and Nufront will require additional evaluation to conclude their respective final assessment through Steps 6 and 7 of the current process. They will, therefore, on an exceptional basis continue in the process, rewinding to Step 4 in order to consider additional material.
– Candidate SRIT submission from ETSI (TC DECT) and DECT Forum (Acknowledgement of submission under Step 3 of the IMT-2020 process in IMT‑2020/17(Rev.1)).
– Candidate RIT submission from Nufront (Acknowledgement of submission under Step 3 of the IMT-2020 process in IMT-2020/18(Rev.1)).
The process extension for these two candidate technology submissions will not impact the schedule for the first release of Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT-2020.SPECS] and the inclusion of the identified Proponent submissions identified below (IMT-2020 RIT/SRIT Submissions being progressed by 5D) that will proceed into Step 8. If these two proponent submission satisfy 5D requirements, they might then be included in a 2021 revision of IMT-2020.SPECS, but they won’t be in the initial recommendation expected to be approved at the end of 2020.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Sidebar: DECT-2020 NR
The “DECT-2020 NR” Radio Interface Technology (RIT) is designed to provide a slim but powerful technology foundation for wireless applications deployed in various use cases and markets. It utilizes the frequency bands below 6 GHz identified for International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT) in the ITU Radio Regulations.
The DECT-2020 radio technology includes, but is not limited to: Cordless Telephony, Audio Streaming Applications, Professional Audio Applications, consumer and industrial applications of Internet of Things (IoT) such as industry and building automation and monitoring, and in general solutions for local area deployments for Ultra-Reliable Low Latency (URLLC) and massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC) as envisioned by ITU-R for IMT-2020.
–>ETSI supports this DECT RIT mainly because of its URLLC capabilities, according to an email received from ETSI.
DECT-2020 NR is claimed by its sponsor to be a technology foundation is targeted for local area wireless applications, which can be deployed anywhere by anyone at any time. The technology supports autonomous and automatic operation with minimal maintenance effort. Where applicable, interworking functions to wide area networks (WAN). e.g. PLMN, satellite, fibre, and internet protocols foster the vision of a network of networks. DECT-2020 NR can be used as foundation for: Very reliable Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint Wireless Links provisioning (e.g. cable replacement solutions); Local Area Wireless Access Networks following a star topology as in classical DECT deployment supporting URLLC use cases, and Self-Organizing Local Area Wireless Access Networks following a mesh network topology, which enables to support mMTC use cases.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
5D has approved the 3GPP and TSDSI RIT/SRIT submissions to be progressed to the next step at their recent e-Meeting which ended July 9, 2020. From the July 13, 2020 DRAFT NEW REPORT ITU-R M.[IMT-2020.OUTCOME]:
1.] Summary of the evaluations received for the candidate RIT submission (Document IMT-2020/14) from 3GPP Proponent:
There were ten relevant evaluation reports received for the candidate 3GPP RIT submission. The relevant received evaluation reports confirmed that the candidate 3GPP RIT proposal in IMT-2020/14 fulfils the minimum requirements for the five test environments comprising the three usage scenarios.
2.] The evaluated candidate RIT proposal (Document IMT-2020/19(Rev.1)) from TSDSI is assessed by ITU-R as satisfactorily fulfilling the minimum requirements for the five test environments comprising the three usage scenarios. Thus, this TSDSI RIT proposal is ‘a qualifying RIT’ and therefore will go forward for further consideration in Step 7.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
IMT-2020 RIT/SRIT Submissions being progressed by 5D:
Each of the following IMT-2020 candidate technology submission proposals will be accepted for inclusion in the standardization phase described in Step 8.
– IMT-2020/13 – Acknowledgement of candidate SRIT submission from 3GPP proponent under step 3 of the IMT-2020 process.
– IMT-2020/14 – Acknowledgement of candidate RIT submission from 3GPP proponent under step 3 of the IMT-2020 process.
– IMT-2020/15 – Acknowledgement of candidate RIT submission from China (People’s Republic of) under step 3 of the IMT-2020 process.
– IMT-2020/16 – Acknowledgement of candidate RIT submission from Korea (Republic of) under Step 3 of the IMT-2020 process
– IMT-2020/19(Rev.1) – Acknowledgement of candidate RIT submission from TSDSI under step 3 of the IMT-2020 process.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
However, there is still confusion (at least for this author) as to whether the China and Korea submissions (which were stated to be technically identical to 3GPP submissions) will ultimately be included in IMT-2020.SPECs as independent/separate text or merged with the 3GPP RIT/SRIT submissions. That may be decided at the October or November 2020 5D meetings.
–>If they are all included as separate texts, it will pose a version change challenge with 3 technically identical sets of IMT 2020 RIT/SRITs with each proponent able to revise the spec at any time, independent of the others.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Overview of IMT-2020.SPECS:
The radio interface specifications in IMT-2020.SPECS detail the feature and parameters of IMT-2020. This Recommendation indicates that IMT-2020 enables worldwide compatibility, international roaming, and access to the services under all three usage scenarios, including enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), massive machine type communications (mMTC) and ultra-reliable and low latency communications (URLLC).
The capabilities of IMT-2020 include:
– very high peak data rate;
– very high and guaranteed user experienced data rate;
– quite low air interface latency;
– quite high mobility while providing satisfactory quality of service;
– enabling massive connection in very high density scenario;
– very high energy efficiency for network and device side;
– greatly enhanced spectral efficiency;
– significantly larger area traffic capacity;
– high spectrum and bandwidth flexibility;
– ultra high reliability and good resilience capability;
– enhanced security and privacy.
These features enable IMT-2020 to address evolving user and industry needs. The capabilities of IMT-2020 systems are being continuously enhanced in line with user and industry trends, and consistent with technology developments.
IMT-2020 Frequencies and Arrangements:
It’s vitally important to recognize that the frequencies to be used by IMT-2020 RITs, including five sets of mmWave bands, will NOT be in IMT-2020.SPECS. Instead, they will be included in a revision of ITU-R M.1036 Recommendation (see below). At their July 2020 meeting, 5D could not reach consensus on the draft revision of M.1036, because the Russian Federation expressed concerns about the current version of the revision. Hence, this work item was carried over to 5D’s October 2020 meeting.
The highly touted and ultra hyped mmWave frequency arrangements (five such frequency arrangements were recommended by WRC 19) have yet to be added to the M.1036 revision. Frequency arrangements in the bands: 24.25-27.5 GHz, 37-43.5 GHz, 45.5-47 GHz, 47.2-48.2GHz, and 66-71 GHz will all use unpaired frequency arrangement with Time Division Duplexing (TDD) used to separate transmit and receive channels for full duplex communications.
Related ITU-R References:
– Recommendation ITU-R M.1036 Frequency arrangements for implementation of the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) in the bands identified for IMT in the Radio Regulations
– Recommendation ITU-R M.2083 IMT vision -Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT-2020 and beyond
– Recommendation ITU-R M.1822 Framework for services supported by IMT
– Report ITU-R M.2320 Future technology trends of terrestrial IMT systems
– Report ITU-R M.2370 IMT traffic estimates for the years 2020-2030
– Report ITU-R M.2376 Technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 6 GHz
Report ITU-R M.2411 Requirements, evaluation criteria and submission templates for the development of IMT-2020
– Report ITU-R M.2410 Requirements related to technical performance for IMT-2020 radio interface(s)
– Report ITU-R M.2412 Guidelines for evaluation of radio interface technologies for IMT-2020
– Resolution ITU-R 56 Naming for International Mobile Telecommunications
– Resolution ITU-R 65 Principles for the process of development of IMT for 2020 and beyond
– Document IMT-2020/1 IMT-2020 Background 2020
– Document IMT-2020/2(Rev.2) Submission and evaluation process and consensus building for IMT-2020
– Document IMT-2020/20 Process and the use of Global Core Specification (GCS), references, and related certifications in conjunction with Recommendation ITU‑R M.IMT-[2020.SPECS]
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
IMT-2020 Independent Evaluation Groups:
Under Step 4 of IMT-2020 process, candidate RITs or SRITs were evaluated by Independent Evaluation Groups (IEG) that registered with the ITU-R in conformance with the process. In this step, the candidate RITs or SRITs were assessed based on Reports ITU-R M.2411 and ITU-R M.2412.
The IEGs utilized the defined ITU-R evaluation methodology and criteria established in the relevant ITU-R Reports covering IMT-2020. ITU-R concluded that the IEGs had fulfilled their role in the process and that the inclusion of views from organizations external to the ITU‑R.
Considering the requirements, evaluation criteria and submission templates for the development of IMT-2020 included in Report ITU-R M.2411, the minimum requirements related to technical performance for IMT‑2020 radio interface(s) in Report ITU-R M.2410, and the guidelines for evaluation of radio interface technologies for IMT‑2020 are included in Report ITU‑R M.2412, the conclusions have been reached for each of the IMT-2020 RIT/SRITs submitted by 3GPP, China, Korea, TSDSI (India), DECT/ETSI, and Nufront. Those detailed conclusions are beyond the scope of this article.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Overview of 3GPP’s radio interface technologies (E-UTRA/LTE and 5G NR):
The IMT-2020 RIT/SRIT specifications known as “5G” have been developed by 3GPP and consist of LTE and 5G NR Releases 15, 16, and beyond.
In 3GPP terminology, the term Evolved-UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) is also used to signify the LTE radio interface. 5G is a Set of Radio Interface Technologies (RITs) consisting of E-UTRA/LTE as one component RIT and (5G) NR as the other component RIT. Both components are designed for operation in IMT defined spectrum.
5G fulfills all technical performance requirements in all five selected IMT-2020 test environments : Indoor Hotspot – enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Dense Urban – eMBB, Rural – eMBB, Urban Macro – Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) and Urban Macro – massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC).
5G also fulfills the service and the spectrum requirements. Both component RITs, NR and E-UTRA/LTE, utilize the frequency bands below 6 GHz identified for International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT) in the ITU Radio Regulations. In addition, the NR component RIT can also utilize the frequency bands above 6 GHz, i.e., above 24.25 GHz, identified for IMT in the ITU Radio Regulations. The complete set of standards for the terrestrial radio interface of IMT-2020 identified as 5G includes not only the key characteristics of IMT-2020 but also the additional capabilities of 5G both of which are continuing to be enhanced.
ITU-R WP5D’s conclusion on 3GPP’s 5G SRIT and 5G RIT is shown in the table below:
|
Radio Interface Technologies: |
NAME: (3GPP 5G:1 SRIT) |
|
Proponents (submission in): |
3GPP Proponent (IMT-2020/13)2 |
|
Determination whether the RIT or SRIT meets the requirements of Res. ITU‑R 65, resolves 6 e) and f), for the five test environments comprising the three usage scenarios |
YES |
|
Inclusion in the standardization phase described in Step 8 |
YES |
|
Radio Interface Technologies: |
NAME: (3GPP 5G:3 RIT) |
|
Proponents (submission in): |
3GPP Proponent (IMT-2020/14) China (People’s Republic of) (IMT-2020/15) Korea (Republic of) (IMT-2020/16) |
|
Determination whether the RIT or SRIT meets the requirements of Res. ITU‑R 65, resolves 6 e) and f), for the five test environments comprising the three usage scenarios |
YES |
|
Inclusion in the standardization phase described in Step 8 |
YES |
1 Developed by 3GPP as 5G, Release 15 and beyond (as indicated in Documents 5D/1215 and 5D/1216)
2 The NB-IoT part of IMT-2020/15 (China) candidate technology proposal is technically identical to the specifications for the NB-IoT part of IMT-2020/13 (3GPP SRIT).
3 Developed by 3GPP as 5G, Release 15 and beyond (as indicated in Documents 5D/1215 and 5D/1217)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The 3GPP 5G System (5GS) also includes specifications for its non-radio aspects, such as the core network elements (the Enhanced Packet Core (EPC) Network and 5G Core (5GC) Network), security, codecs, network management, etc.
–>These non-radio specifications are not included in the so-called “Global Core Specifications (GCS)” of IMT-2020.
Support of Industry Verticals:
The E-UTRA/LTE and 5G NR component RITs from 3GPP support a diverse set of mobile broadband (eMBB) services and other so-called industry “verticals,” including URLLC, Industrial IoT, Automotive/V2X, Private Networks (NPN), and others. NR RIT supports in-band coexistence with NB-IoT and eMTC. For optimal support of specific verticals, the 5G NR RIT has been designed, or enhanced, with certain key features, or set of features.
A short summary of relevant NR RIT capabilities for a few industry verticals is provided below.
Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications (URLLC) and Industrial IoT (IIoT):
For support of Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications services, some of the main features supported by the 5G NR RIT are:
• Logical Channel Priority (LCP) restrictions
• Packet duplication with DC or CA
• New QCI table for block error rate 10*-5
• Physical layer short transmission time interval (TTI)
From 3GPP Rel-16 onwards, URLLC and Industrial IoT use cases are further facilitated by:
• NR PDCP duplication enhancements,
• Prioritization/multiplexing enhancements,
• NR Time Sensitive Communications (TSC) related enhancements,e.g. Ethernet header compression, and
• Precise time information delivery
Factory Automation and “Industry 4.0”:
5G URLLC in Release 16 (RAN and 5G core) was said to improve link reliability by as much as 99.9999%. These types of applications are best served by a coordinated multi-point (CoMP) approach that leverages multiple transmission and reception (multi-TRP) architecture to provide redundant communication paths with some degree of spatial diversity.
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications:
From 3GPP Rel-16, NR RIT includes support of Vehicle-to-everything (V2X), mainly by means of NR sidelink communication over the PC5 interface, partly leveraging what was defined for E-UTRA V2X sidelink communication.
Sidelink transmission and reception over the PC5 interface are supported when the UE is inside NG-RAN coverage, irrespective of which RRC state the UE is in, and when the UE is outside NG-RAN coverage.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
IMT-2020 Consensus Building and Decision by 5D:
– IMT-2020/15 (China) candidate technology proposal is technically identical to the IMT‑2020/14 (3GPP RIT) candidate technology proposal and NB-IoT part of IMT‑2020/13 (3GPP SRIT) candidate technology proposal;
– IMT-2020/16 (Korea) candidate technology proposal is technically identical to the IMT‑2020/14 (3GPP RIT) candidate technology proposal;
Additionally, consensus building has been performed with the objective of achieving global harmonization and having the potential for wide industry support for the radio interfaces that are developed for IMT‑2020. (?????)
As a result of the consensus building in ITU-R among the seven technology proposals, the following groupings are agreed by ITU-R:
– The SRIT proposed in IMT-2020/13 including NB-IoT part to which China (People’s Republic of) (NB-IoT part of IMT-2020/15) is technically identical, is identified in ITU as “3GPP 5G SRIT”1, developed by the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), for Step 7 and subsequent IMT-2020 development.
– The RITs proposed in IMT-2020/14, NR part of IMT-2020/15 and IMT-2020/16 are grouped into the technology identified in ITU as “3GPP 5G RIT”, developed by the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), for Step 7 and subsequent IMT-2020 development.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Future plans for the IMT process:
IMT is an on-going process of development and updates within ITU-R WP 5D.
In 2021, ITU-R will define the schedule for future general revisions of the Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT-2020.SPECS], to accommodate any future new, improved, or updated IMT-2020 candidate technology proposals beyond the first release, utilizing the same baseline IMT ‘revision and update process’ currently in place, as applied to IMT 2020.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Future IEEE Techblog posts on 3GPP Rel 16 and IMT 2020.SPECS:
This author has been in dialog with 3GPP leaders via the 3GPP Marketing Communications Manager to accurately assess 3GPP Rel 16 completed work items related to 5G (both radio and non-radio aspects).
In particular, we are very much interested in the 3GPP Rel 16 URLLC specification, performance simulation(s), and performance testing (not yet started). Only after independent performance testing will we know if the URLLC test implementation meets the required performance parameters specified by 3GPP and/or Minimum requirements related to technical performance for IMT-2020 radio interface(s) [ITU M.2410].
The IEEE Techblog Editorial Team is soliciting guest blog posts related to 3GPP Rel 16 and/or issues with IMT-2020.SPECS as well as other topics listed here.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
5G Specifications (3GPP), 5G Radio Standard (IMT 2020) and Standard Essential Patents
https://techblog.comsoc.org/?q=IMT%202020#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=IMT%202020&gsc.page=1
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2020/Pages/submission-eval.aspx
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=9114983
5G Specifications (3GPP), 5G Radio Standard (IMT 2020) and Standard Essential Patents
by Yigang Cai, PhD
Introduction:
On July 3, 2020, 3GPP (the organization that generates all the specifications for cellular networks) announced that its Release 16 (R16) specification was frozen, and thereby declared the completion of the first evolution of “5G New Radio (NR).” As 3GPP’s specs have “no official standing,” they must be transposed by SDOs, like ITU, ETSI, ATIS, TSDSI (India), etc. The international standard for 5G Radio aspects is known as IMT 2020.specs, which includes the Radio Interface Technology (RIT) and Set of Radio Interface Technologies (SRIT) from various proponents, including 3GPP (IMT-2020/14, and /IMT-2020/13, respectively).
3GPP R16 is the first technical specification in the history of 3GPP that was reviewed and finalized through an e-meeting (due to the COVID-19 travel and meeting restrictions). The declared R16 completion was the result of collaboration and coordination amongst many global companies, government agencies and telecom regulators.
From the 3GPP website: “Rel-16 is now officially Frozen. Rel-15 and Rel-16 constitute the basis for 5G and this is a great achievement and recommended that delegates hold a personal celebration for this.”
The complete R16 spec not only enhances the functions of 5G, but also allows 5G to enter a new digital ecosystem. It takes into account factors such as cost and efficiency, so that the basic investment in wireless communications infrastructure can play a greater role and further help the digital transformation of the social economy. Let’s examine 3GPP’s 5G NR in the context of R15 and R16:
- “5G NR” in R15 was frozen in 2018. It strived to produce a “usable” specification for Physical (PHY) layer transmit/receive in 5G trials/pilots and early (pre-IMT 2020 standard) 5G networks.
- In contrast, “5G NR” in R16 will achieve an “easy to use” and more robust 5G transmit/receive capability.
3GPP R16 is a major release for the project as noted in an earlier IEEE Techblog post. It brings the specification organization’s ITU-R WP 5D submission “IMT-2020 Radio Interface Technology/Set of Radio Interface Technologies (RIT/SRIT)” to a more complete 5G system; what 3GPP calls “5G Phase 2.”
3GPP R16 is supposed to enhance Ultra-Reliable (UR) Low Latency Communications (URLLC), support V2V (vehicle-to-vehicle) and V2I (vehicle-to-roadside unit) direct connection communications, and support 5GS Enhanced Vertical and LAN Services as reported in the earlier IEEE Techblog article. Please refer to References below for further information.
URLLC is 1 of 3 use cases for 5G/IMT 2020. It is intended for mission critical, precise, accurate, always ON/never down, real time communications that require low latency in the 5G access and core networks.
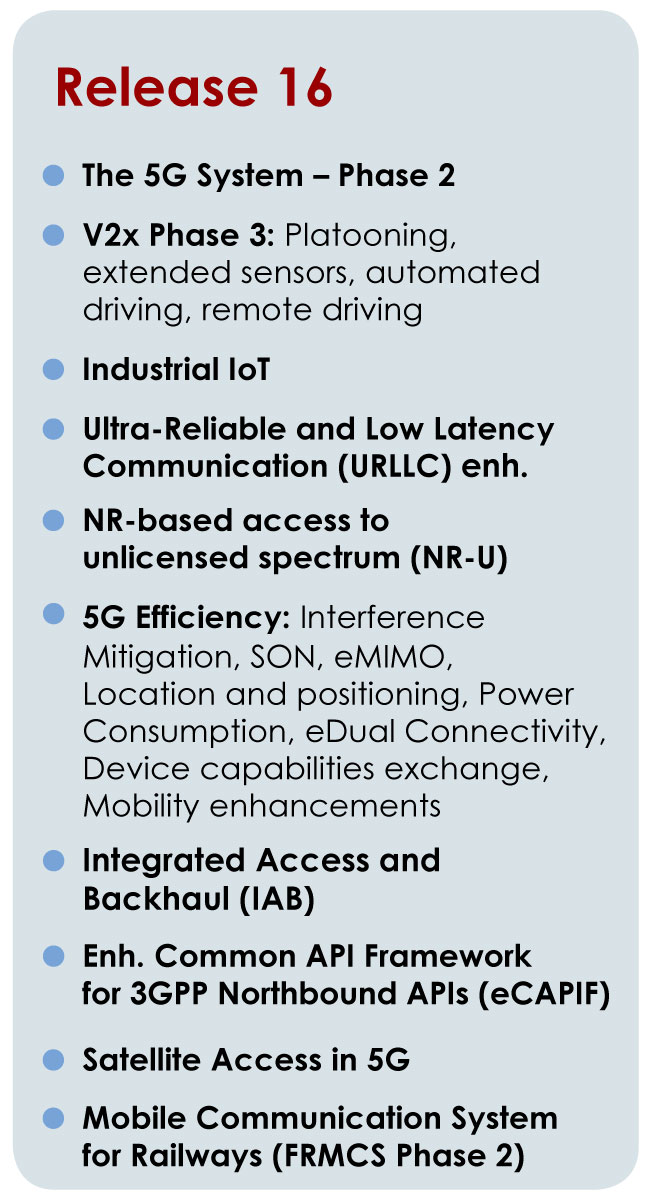
SOURCE: 3GPP
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Editor’s Note: ONLY the 3GPP “5G Radio Aspects” are included in the forthcoming ITU-R IMT 2020.SPEC (RIT/SRIT) recommendation, which is expected to be approved in late November 2020 by ITU-R SG D. All the non-radio aspects, such as 5G Core Network, network slicing, network management, privacy and security, etc. will NOT be part of IMT 2020. However, those declared R16 completed work items are likely to be transposed by ETSI into international standards.
From 3GPP: “5G non-radio specs in R16 are handled by 3GPP Working Groups. None of the work is done in the SDOs – 3GPP does all of the work. See the 3GPP Work Plan at to see how the work is split between groups.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Perspective on 5G Standard Essential Patents (SEPs):
The announcement of the 3GPP R16 freeze also means the “War of SEPs (Standard Essential Patents [1.]),” i.e. those patents that are related to 5G NR standards/specifications might come to the end of a critical stage. However, it’s likely that a new SEP war will start soon. But that is a subject for another day.
Note 1. A standard essential patent (SEP) is a patent that claims an invention that must be used to comply with a technical standard or specification to be standardized by an accredited standards development organization (SDO).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
During 5G NR specification development, industries and companies have competed in a 5G patent race and generated thousands of SEPs. A recent study, published in the IEEE Techblog, found that Huawei was the undisputed leader in 5G SEPs. Some companies tried to convince the world they are leading the SEP war. However, the news and hype about published SEPs has often misled the public.
From this author’s standards and patent experiences, there are some facts of 5G SEPs which have been neglected in the SEP war:
- There is no one-to-one mapping between declared SEP and 5G standards feature. In fact, one standards contribution (e.g., WID, CR, WF or others in 3GPP) may be declared with one or multiple SEPs, or one SEP is declared in multiple contributions. SEP number declared does not match standards features.
- Many of SEP relevant standards contributions are not taken or baselined by standards bodies in standards specifications. Someone can do statistics what percentages (overall and/or per contributing company) of SEP relevant standards are agreed or approved in standards bodies.
- Some declared SEPs, including filed and published patents, may not be granted, or may even be rejected, after standards contributions are baselined.
- One standards contribution may be co-authored/co-signed with multiple companies, it is very likely multiple companies filed multiple patents for the same standards contribution.
There is no doubt SEPs can accelerate 5G standards development and enhance standards feature quality. But, the war of SEPs also brings some confusions in 5G technology development, implementation, deployment and applications.
First of all, the patent war lead to industries creating numerous patents which actually may not be “essential.” We all understand that a considerable percentage of those patents have no real value, i.e. they are not implementable or deployable and so not at all profitable.
Companies try to earn IPR revenues from SEPs and spend enormous efforts and finances focusing on creation of SEPs (for example, giving over the half of total IPR budget to SEP generation) because they probably believe licensing of granted SEPs can bring IPR revenue much quick. However, simple number of declared SEPs is much less important than innovation of critical 5G features and functions.
The 5G SEP war we have recently experienced concentrates on patent number; not patent quality. In fact, a feature critical invention can be much better and heavier than dozens of banal and non-essential SEPs which have been seen almost every aspect.
Conclusions:
Industry success relies on innovations, such as technique innovation, cultural innovation, and business innovation. There is no single high-tech company that has succeeded by starting numerous DEPs. Relying on licensing of granted patents cannot produce a great company. It does not mean patent productivities not important. Inventions in 5G should create more useful and reliable features, products, applications and capability to meet commerce and consumer needs (unfortunately, we have not seen many consumer-related 5G features so far).
5G and “5G Beyond” or “6G” (?) SEPs can strive for implementable and economic inventions, including investment and cost saving, energy saving and green communications. Innovations should drive ecosystem end-to-end solutions and use cases. Currently there are hundreds of 5G use cases that have been identified. Unfortunately, many of them (like the IoT use cases) can also be realized by existing 4G/LTE or enhanced WiFi.
Closing Note on URLLC (Ultra Reliable, ultra Low latency Communications):
URLLC is one of three use cases defined by ITU for the IMT 2020 standard and “5G” networks worldwide. It is included for both the 5G RAN and 5G Core Network in 3GPP Release 16. From a 3GPP report on URLLC:
“New 3GPP R16 URLCC use cases with higher requirements include: Factory automation Transport Industry, including the remote driving use case, and Electrical Power Distribution. A 3GPP “Study on Physical layer enhancements for NR ultra-reliable and low latency communication (URLLC)” concludes that it is beneficial to support a set of enhancements to URLLC, and further establishes detailed recommendations as given in Section 9.2 in TR 38.824.”
However, URLLC 5G NR enhancements for the RAN is currently only 53% complete (as per the 3GPP Work Plan for Release 16). That’s because no performance testing has been done yet to validate if the URLLC enhancement to 5G NR will meet 3GPP’s targeted performance requirements. We have been told by 3GPP marketing manager Kevin Flynn that such URLLC performance testing will be completed in three to six months, however there is no official 3GPP target completion date set at the time this article was published (July 10, 2020).
For URLLC to be successful, we first need standardized URLLC requirements (such as 1 millisecond synchronization accuracy, 0.5-to-1 millisecond air interface (in the RAN) latency, <5 milliseconds end-to-end latency (including the 5G Core Network), and six 9’s reliability) to be achieved on paper as clearly specified 5G NR enhancements. Then the performance parameters must be verified/validated in duplicable performance tests (by independent testing agencies) and reliably implemented in both 5G endpoint and network products. Only then can new 5G system and use cases (e.g. mission critical and/or low latency applications. autonomous vehicles, etc) achieve economic benefits and gains.
Along with the IEEE Techblog Editorial Team, I’ve been carefully researching and studying all aspects of URLLC in 3GPP Release 16 and hope to provide you with a co-authored article which will provide more clarity on that topic. Stay tuned!
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Yigang Cai:
Yigang Cai, PhD is an IEEE Fellow (2018) and former Senior Research Scientist at Bell Labs. As a long time IEEE volunteer, Yigang served as IEEE ComSoc director of North American Region (NAR) (2012-2013), ComSoc global coordinator of Distinguished Lecturer Tour (DLT) (2010-2011), and ComSoc Chicago chapter chairman (2003-2006).
Dr. Cai is one of most prolific telecommunications industry inventors. He received the Bell Labs Inventor Award three times (2008, 2010 and 2011), and was honored with a first-ever lifetime Alcatel-Lucent “Distinguished Inventor Award” (2013) with his inventive accomplishments and patent contributions throughout his career with the company. Yigang has filed a total of 1000+ patents globally, of which 665 are granted patents (including 193 U.S. granted patents).
Many of his inventions in wireless networks have been built into products and systems of 2G/3G/4G and 5G, and deployed worldwide. He is one of the pioneers and leaders in developing the principles and components of Machine Type Communications (MTC). Dr. Cai generated many 5G inventions, including 5G New Radio (NR), 5G end-to-end architectures and use cases (both Access Networks and Core Networks), Network Slicing, MEC, 5G Machine Type Communications (MTC), and Device-to-Device Communications.
Yigang worked with Verizon Wireless to incorporate his work on Core Network MTC architecture, into 3GPP specifications. He was the first inventor in the area of radio interface physical resource sharing [between LTE and eMTC (Category M, or CatM)]. Dr. Cai filed dozens of patents related to that subject matter. Feature software with those pending patents were developed and delivered to Verizon (2016) and AT&T networks in 2017 (over 40,000 base stations), and twenty some other operators worldwide.
Together with ComSocSCV Chair Emeritus Alan J Weissberger, Yigang published an IEEE Global Communications Newsletter (GCN) article on Substantial Progress in ComSoc North American Region which appeared in the December 2013 issue of IEEE Communications magazine.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Editor’s Addendum : 3GPP R16 5G work items related to IMT 2020.specs and 5G Non-Radio Aspects:
The two ATIS contributions from 3GPP on the latter’s IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT (based on 3GPP documents PCG45_07 and PCG45_08), were submitted to ITU-R WP5D on 21 May 2020. They were discussed and accepted at the 5D meeting which ended 9 July 2020. There were no other 3GPP/ATIS contributions related to IMT 2020 at that 5D meeting, which was the deadline for submission of material for inclusion in ITU-R Rec. M.[IMT 2020.SPECS].
Therefore, we do not know what the disposition will be of any other 5G radio related work items in 3GPP R16 that were completed after 21 May 2020. In particular, the state of 3GPP’s 5GNR enhancements for URLLC.
We understand that the 5G NON-RADIO aspects of R16, e.g. 5G architecture, 5G core, network slicing, network management, security, etc. will NOT be sent to ITU-T. Rather, they will likely be transposed and standardized by ETSI.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2020/03/25/3gpp-delays-release-16-and-17-by-3-months/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2019/10/06/3gpp-release-16-update-5g-phase-2-including-urllc-to-be-completed-in-june-2020/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2020/03/24/5g-patent-war-are-nokias-3000-5g-patent-declarations-legit/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2020/06/24/greyb-study-huawei-undisputed-leader-in-5g-standard-essential-patents-seps/
https://www.nokia.com/about-us/news/releases/2020/03/24/nokia-announces-over-3000-5g-patent-declarations/
https://telecoms.com/503274/5g-patent-chest-beating-is-an-unhelpful-distraction/
https://www.wsj.com/articles/qualcomm-5g-security-and-patent-wars-11576096074
https://www.statista.com/chart/20095/companies-with-most-5g-patent-families-and-patent-families-applications/
https://www.iplytics.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/5G-patent-study_TU-Berlin_IPlytics-2020.pdf
https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2019/10/5g-patent-leadership
https://www.kidonip.com/news/iplytics-patent-counting-fallacy/
https://www.epo.org/news-events/news/2020/20200312.html
https://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/GanttChart-Level-2.htm
https://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/WiSpec–830074.htm
Executive Summary: IMT-2020.SPECS defined, submission status, and 3GPP’s RIT submissions
Busting a Myth: 3GPP Roadmap to true 5G (IMT 2020) vs AT&T “standards-based 5G” in Austin, TX
Rakuten Mobile, Inc. and NEC to jointly develop the containerized standalone (SA) 5G core network
Japanese upstart carrier Rakuten Mobile, Inc. and NEC Corporation today announced that they have reached an agreement to jointly develop the containerized standalone (SA) 5G core network (5GC) to be utilized in Rakuten Mobile’s fully virtualized cloud native 5G network.
Based on the agreement, Rakuten Mobile and NEC will jointly develop the containerized SA 5G mobile core to be made available on the Rakuten Communications Platform (RCP), Rakuten Mobile’s fully virtualized and containerized cloud-native mobile network platform. The two companies will collaborate to build a Japan-made, highly reliable 5GC, based on the 5GC software source code developed by NEC. Subsequent to the launch of its non-standalone (NSA) 5G service in 2020, Rakuten Mobile aims to provide its SA 5G service in Japan in 2021.
The containerized 5GC will also play a key role in the global expansion of RCP, a platform aimed at offering solutions and services for the deployment of virtualized networks at speed and low cost by telecom companies and enterprises around the world, tailored for their unique needs. The 5GC will be offered as an application on the RCP Marketplace, allowing customers to quickly and easily “click, purchase and deploy” a fully virtualized SA 5G core network solution.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Editor’s Note: The two companies don’t state what spec they’re using for their container based SA 5G Core Network.
–Please see Tareq Amin’s Comment below.
The only standards work we know of related to SA 5G Core Network is in 3GPP (5GCN), but it’s based on a NFV enabled network cloud and a service based architecture, rather than containers.
We suggest that NEC contribute this spec to both 3GPP and ITU-T (for IMT 2020 non-radio aspects). However, neither ITU-R or ITU-T has any serious ongoing work related to the 5G Core Network at this point in time.
The 3GPP specified 5G core network covers both wire-line and wireless access. Key characteristics:
Control plane is separated from the data plane and implemented in a virtualized environment
Fully distributed network architecture with single level of hierarchy
GW to GW interface to support seamless mobility between 5G-GW
Traffic of the same flow can be delivered over multiple RITs
From the latest 3GPP Release 16 – TS.23501 5G Systems Architecture-V16.4.0 (2020-03):
The 5G System architecture is defined to support data connectivity and services enabling deployments to use techniques such as e.g. Network Function Virtualization and Software Defined Networking. The 5G System architecture shall leverage service-based interactions between Control Plane (CP) Network Functions where identified. Some key principles and concept are to:
– Separate the User Plane (UP) functions from the Control Plane (CP) functions, allowing independent scalability, evolution and flexible deployments e.g. centralized location or distributed (remote) location.
– Modularize the function design, e.g. to enable flexible and efficient network slicing.
– Wherever applicable, define procedures (i.e. the set of interactions between network functions) as services, so that their re-use is possible.
– Enable each Network Function and its Network Function Services to interact with other NF and its Network Function Services directly or indirectly via a Service Communication Proxy if required. The architecture does not preclude the use of another intermediate function to help route Control Plane messages (e.g. like a DRA).
– Minimize dependencies between the Access Network (AN) and the Core Network (CN). The architecture is defined with a converged core network with a common AN – CN interface which integrates different Access Types e.g. 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
– Support a unified authentication framework.
– Support “stateless” NFs, where the “compute” resource is decoupled from the “storage” resource.
– Support capability exposure.
– Support concurrent access to local and centralized services. To support low latency services and access to local data networks, UP functions can be deployed close to the Access Network.
ITU-T SG13 is working on IMT 2020 non-radio aspects, but are heavily dependent on 3GPP documents to be liased in order to drive their future standards work in that area. Unfortunately that has not happened.
Please see Comment in box underneath this article for GSMA Feb 2020 document on SA 5G Core option 2 guidelines for implementation.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“We are very excited to collaborate with NEC on the development of our standalone 5G core network,” commented Tareq Amin, Representative Director, Executive Vice President and CTO of Rakuten Mobile. “Our partnership with NEC represents a joint collaboration to build an open, secure and highly scalable 4G and 5G cloud native converged core, that will also become a key feature of the highly competitive services we will offer to global customers through the Rakuten Communications Platform.”
“NEC is proud to be the 5GC development partner for Rakuten Mobile’s advanced, fully virtualized, cloud-native network. Following the BSS/OSS for the 4G network and 5G radio equipment that we have already begun offering, we look forward to providing a high-quality, highly reliable 5GC and contributing to Rakuten Mobile’s 5G services,” said Atsuo Kawamura, Executive Vice President and President of the Network Services Business Unit, NEC.
Through the joint development of the SA 5GC, Rakuten Mobile and NEC aim to drive innovation in global mobile technology and provide high quality 5G network technology to customers both in Japan and around the world.
Rakuten Mobile CTO Tareq Amin clarification comments; via edited email to this author:
NEC/Rakuten 5GC is 3GPP standardized software for network service and a de facto standard container basis infrastructure (“infrastructure agnostic”). It is a forward looking approach, but not proprietary.
1. 3GPP standardized software for network service:
NEC/Rakuten 5GC openness are realized by implementation of “Open Interface” defined in 3GPP specifications (TS 23.501, 502, 503 and related stage 3 specifications).
2. Containerization/Cloud native:
3GPP 5GC specification requires cloud native 5G core (5GC) architecture as the general concept (service based architecture). It should be distributed, stateless, and scalable. However, an explicit reference model is out of scope for the 3GPP specification. Therefore NEC 5GC cloud native architecture is based on above mentioned 3GPP concept as well as ETSI NFV treats “container” and “cloud native”, which NEC is also actively investigating to apply its product.
3. Reference To Open RAN in the press release:
This has no relationship to 5G Core, but only an indication that our Radio Access Network (RAN) architecture is O-RAN Compliant.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Press Release:
Forward Reference:
Rakuten Communications Platform (RCP) defacto standard for 5G core and OpenRAN?
About Rakuten Mobile
Rakuten Mobile, Inc. is a Rakuten Group company responsible for mobile communications, including mobile network operator (MNO) and mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) businesses, as well as ICT and energy. Through continuous innovation and the deployment of advanced technology, Rakuten Mobile aims to redefine expectations in the mobile communications industry in order to provide appealing and convenient services that respond to diverse customer needs.
About NEC Corporation
NEC Corporation has established itself as a leader in the integration of IT and network technologies while promoting the brand statement of “Orchestrating a brighter world.” NEC enables businesses and communities to adapt to rapid changes taking place in both society and the market as it provides for the social values of safety, security, fairness and efficiency to promote a more sustainable world where everyone has the chance to reach their full potential.
more information, visit NEC at http://www.nec.com.
Contacts:
Rakuten, Inc. Corporate Communications Department
[email protected]
NEC Corporation Corporate Communications Division
[email protected]
3GPP delays Release 16 and 17 Freeze by 3 months; IMT 2020 impact unclear
3GPP stated on its website that the timeline for the completion of two of their upcoming releases that include 5G specifications will be delayed.
A shift of the Release 16 timeline was approved at the 3GPP March 20th TSG#87 plenary e-meetings.
- Rel-16 Stage 3 freeze now June 2020 (shifted by 3 months)
- Rel-16 ASN.1 and OpenAPI specification freeze will also be complete in June 2020 (stays as planned)
Freezing stage 3 of a 3GPP release essentially means no further functions can be added to the spec. ASN.1 refers to abstract syntax notation object identifiers maintained by ETSI.
3GPP SA Plenary Chairman Georg Mayer wrote in an email to this author:
“Whilst 3GPP shifted the R16 stage 3 freeze by three months, we kept the code freeze in June.
It is from my perspective incorrect to say that we shifted R16 by three months. Just the stage 3 freeze and the code freeze are now coinciding. This was also clearly stated in the approved discussion papers in all groups. Those are the source of information people should go to when they look for guidance.”
3GPP RAN Chairman Belasz Bertenyi wrote in an email to this author:
“The Release-16 ASN.1 and OpenAPI code freeze timeline is kept unchanged, and is still targeting June 2020.”
…………………………………………………………………………….
New 3GPP Release Timeline:
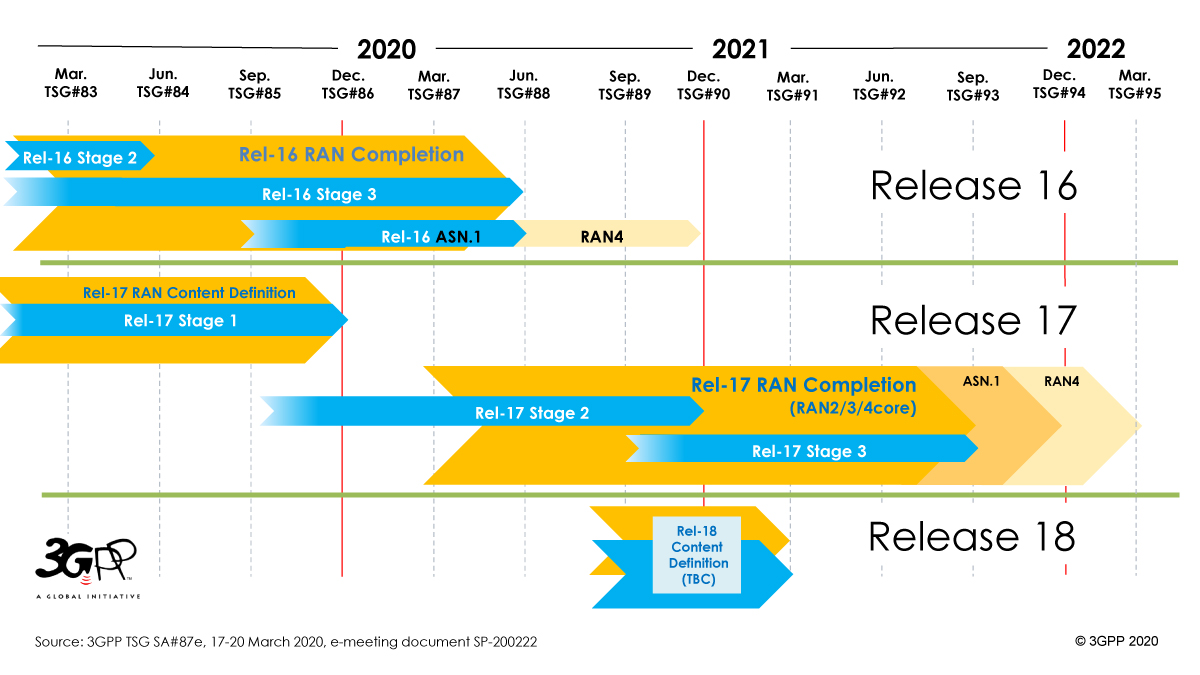
The “Release 16 Description: Summary of Rel-16 Work Items” (TR21.916) is now in production, with the Work Plan manager adding summary notes about each of the Features that it will bring, to the 3GPP system. As the Release approaches its Freeze date and completion (June 2020) – TR21.916 will start to expand and fill with useful detail about the main purpose and state of each feature.
The schedule for Release 17 is to be shifted by three months, such that the freezing of stage 3 will take place in September 2021. [Release 17 is to include further 5G system enhancements such as 5G wearables and faster network performance.] The specification freeze for Release 17 ASN.1 and OpenAPI is now scheduled for December 2021.
……………………………………………………………………………………………
The move had been expected after 3GPP announced it would cancel its face-to-face meetings in February and March due to concerns about the spreading coronavirus.
While 3GPP’s face-to-face meetings have been canceled through May, the organization has scheduled online meetings to continue its work despite the pandemic and will hopefully be able to keep their specifications on schedule going forward.
However, the impact of 3GPP’s Release 16 delay will surely push back the roll-out of true 5G deployments. It remains to be seen if the much touted but not yet completed Enhancement of Ultra-Reliable (UR) Low Latency Communications (URLLC) in 3GPP Release 16 will be submitted to ITU-R WP5D at their June 2020 meeting for inclusion in the IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT standard.
This author suspects ITU-R WP 5D leaders are looking at how to adjust their meeting plans in light of the global pandemic. Their next meeting is scheduled for June 23 to July 1, 2020 in Geneva.
Balasz says that “whatever the IMT 2020 schedule, 3GPP is continuously committed to make sure its IMT 2020 submissions will arrive in time and with high specification quality.”
………………………………………………………………………………………….
Reference:
https://www.3gpp.org/specifications/releases
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
15 April 2020 Update:
VERY IMPORTANT to note that unless it’s delayed till 2021, ITU-R IMT 2020 standard will NOT specify ultra low latency/ultra high reliability cause those capabilities are in 3GPP Rel 16 which won’t be frozen till July 3rd when their next meeting ends. ITU-R WP5D meeting ends July 1st. Hence, it will not be possible for 3GPP to submit 5G portions of Rel 16 till after WP5D’s July 1st meeting which will be too late to be included in the 1st version of IMT 2020 scheduled for late November 2020. The alternative is for WP 5D to delay their IMT 2020 completion schedule at their June-July 2020 meeting so we’ll watch that 5D meeting very closely to keep readers informed.
Background on Release 16:
- See the full Release 16 Description – TR21.916 (Available at Release freeze)
- RAN Rel-16 progress and Rel-17 potential work areas (July 18, 2019)
- Early progress on Rel-16 bands for 5G (April 2, 2019)
- “Working towards full 5G in Rel-16″…See a webinar presentation (July 3, 2018)
- Preparing the ground for IMT-2020
- SA1 completes its study into 5G requirements
Details of the features and work items under each 3GPP Release are kept in the corresponding, on-line, list of features and study items.
Strategy Analytics: Huawei 1st among top 5 contributors to 3GPP 5G specs
Even though there are more than 600 member companies participating in 3GPP, their 5G specification process is actually led by only a few leading telecom companies. New research from Strategy Analytics analyzes the contributions to 3GPP 5G specifications (Release 15 and Release 16) and finds that 13 companies contributed more than 78% 5G related papers and led 77% of the 5G related Work Items and Study Items.
The Strategy Analytics report “Who Are the Leading Players in 5G Standardization? An Assessment for 3GPP 5G Activities” is available to clients and registered guests here . The report assesses the 13 leading companies’ contributions to 3GPP 5G standards for the period of Releases 15 and 16 so far, based on the following criteria:
- Volume of 5G related papers, including submitted papers, approved/agreed papers and the ratio of approved/agreed papers to total submissions in all Technical Specification Groups (TSGs) and Working Groups (WGs)
- Chairmanship positions, i.e. Chairman and Vice Chairmen for all TSGs and WGs
- Rapporteurs of 5G related Work Items (WIs) / Study Items (SIs) in all TSGs and WGs
The results indicate that the top 5 companies in 3GPP 5G specification activities are Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, Qualcomm and China Mobile.
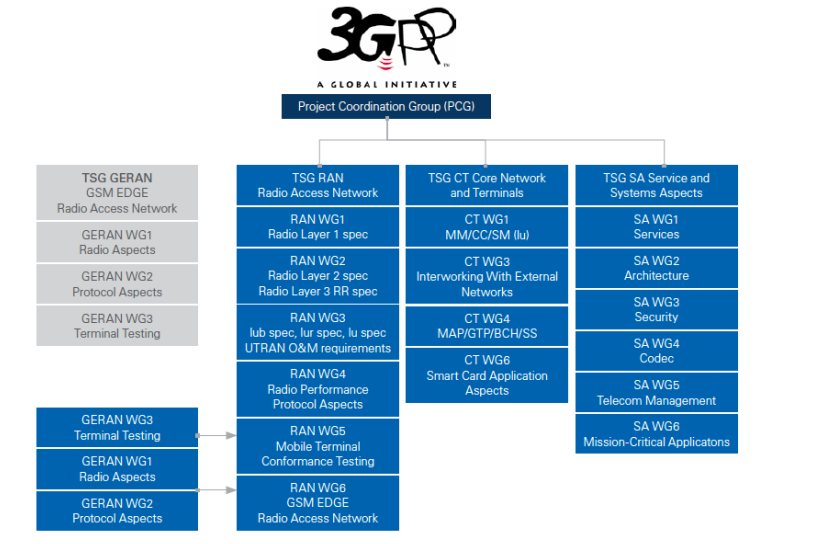
Guang Yang , Director at Strategy Analytics, noted, “3GPP plays the central role in the ecosystem of global 5G standardization. By analyzing the contributions of industry players to 3GPP 5G standards, we can get an idea of different companies’ positions in 5G innovation as well as their influence in the global mobile industry. So we looked at 3GPP organization and work procedures to assess each company’s influence from multiple aspects.”
Sue Rudd , Director Networks and Service Platforms service, added, “According to our assessment, leading infrastructure vendors – Huawei , Ericsson and Nokia – made more significant contributions to 5G standards than other studied companies. Huawei leads in terms of overall contributions to the end-to-end 5G standards, while Ericsson leads in TSG/WG chairmanship and Nokia in approved/agreed ratio of 5G contribution papers .”
Phil Kendall , Executive Director at Strategy Analytics, added, “It is important to remember that the true nature of the standardization process is actually one of industry collaboration rather than competition. 3GPP standardization continues to be a dynamic process. It is expected that emerging players and new market requirements will increasingly impact priorities for 3GPP Release 17 standards.”
3GPP Timeline:
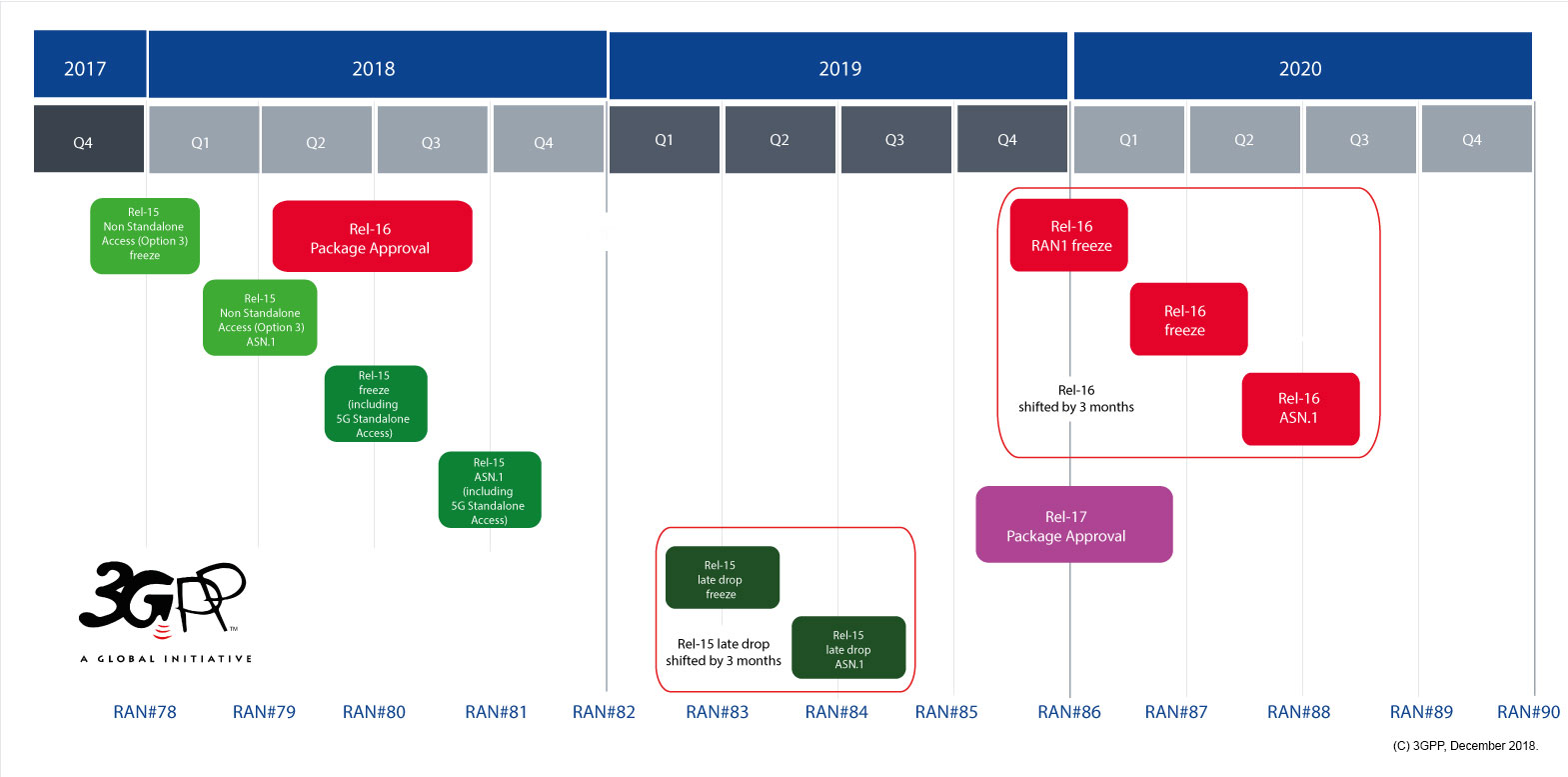
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
Mike Dano of Lightreading says “Huawei being the biggest contributor to the 3GPP’s 5G specs will undoubtedly worry U.S. lawmakers and regulators, who for years have argued the company poses a security threat to the nation. Huawei denies those allegations.”
“We must have a vocal presence at the standards bodies that are defining the rules for 5G. We have been woefully absent and need to make participation a priority,” wrote Mike Rogers in a recent opinion column. Rogers is a former US representative who co-authored the 2012 US government report initially outlining the security threats posed by Chinese equipment vendors like Huawei and ZTE.
“We need to work with our allies to staunch the spread of Huawei and other Chinese companies owned by the state. We need to better communicate what Chinese dominance of 5G means. This is something we have not successfully done, as shown by Britain deciding to allow Huawei into certain elements of the 5G network,” Rogers added.
Rogers now chairs the “5G Action Now” 501(c)4 advocacy organization, which has been working with the now-disbanded C-Band Alliance to speed up the C-Band spectrum auction in the US for 5G.
Indeed, legislation introduced early this year would require the Trump administration to develop a strategy to “promote United States leadership at international standards-setting bodies for equipment, systems, software, and virtually-defined networks relevant to 5th and future generation mobile telecommunications systems and infrastructure, taking into account the different processes followed by the various international standard-setting bodies.” That legislation passed the House and is now headed to the Senate.
Companies’ 3GPP contributions to the 5G specs [1.] don’t necessarily translate into revenues. For that, companies must patent their inventions.
Note 1. 3GPP specs vs 5G standards:
3GPP 5G specs in Release 15 and 16 have and will continue to be input to ITU-R WP 5D, but only some of those contributions will be in IMT 2020 which is currently restricted to the Radio Interface Technologies (RITs) or sets of RITs (SRITs). Other essential 5G specs like signaling, 5G packet core, 5G network management, etc will be standardized by SDOs (like ETSI) but the real work is done in 3GPP. Also note that IMT 2020 will have several NON 3GPP RITs from ETSI/DECT Forum and India (TSDSI).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
According to one study, Huawei leads in that respect also. IPlytics recently reported that the Chinese firm has far and away the most “declared 5G families” of patents, and the most filed since 2012.
However, it’s worth noting that UK law firm Bird & Bird argues that the reliance on such patent calculations isn’t very insightful, and that different methodologies yield different results.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Gartner: Market Guide for 3GPP “5G New Radio (NR)” Infrastructure
Editor’s Note:
Most mobile 5G deployments to date are based on 3GPP Release 15 “5G NR” or “NR”in the data plane and Non Stand Alone (NSA), with LTE for everything else (i.e. control plane/signalling, mobile packet core, network management, etc). 3GPP Release 16 will hopefully add ultra low latency, ultra high reliability to the 5G NR data plane. Equally important will be the 5G systems architecture-phase 2 that will be specified in Release 16. That spec includes a 5G mobile packet core (5GC) which is a forklift upgrade from the 4G-LTE Evolved Packet Core (EPC). It remains to be seen which ITU study group will standardized 5GC when 3GPP Release 16 is completed in late June 2020.
From the paper titled Narrowband Internet of Things 5G Performance published in 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall):
5G NR supports new frequency bands ranging all the way up to 52.6 GHz. These new frequency bands make large system bandwidths available that are needed to improve the mobile broadband data rates beyond what LTE can offer.
NR also supports a reduced latency by means of reduced transmission time intervals and shortened device processing times compared to LTE. To provide high reliability, NR supports low code rates and a high level of redundancy.
In the initial phase of the transition from 4G to 5G, NR is expected to be a complement to both LTE and NB-IoT, providing enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) and critical IoT services. The past industrial practice suggests that the mobile network operators will stepwise re-farm parts of its LTE spectrum for enabling NR. Since NR supports a new range of frequency bands, an attractive alternative approach is to deploy NR in a set of new rather than existing bands. 3GPP Release 15 allows NR to connect to the EPC to support a seamless transition from LTE to NR.
The NR traffic volumes will eventually motivate a full refarming of the LTE MBB spectrum to NR. The longevity of NB-IoT devices is however expected to make NB-IoT a natural component within the 5G echo-system. For this reason, NR supports reservation of radio resources to enable LTE operation including NB-IoT, within an NR carrier. This allows NB-IoT to add NR in-band operation to its list of supported deployment options. Since both NR and NB-IoT employ an OFDM based modulation with support for 15-kHz subcarrier numerology, in the downlink (DL) true interference-free orthogonality can be achieved without configuration of guard-bands between the two systems.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
From Gartner report published Dec 16, 2019:
By Peter Liu, Sylvain Fabre, Kosei Takiishi
Introduction:
As communications service providers move forward with 5G commercialization, New Radio infrastructure investment is prioritized and crucial for 5G rollout success. We analyze the market direction and the product strategies of equipment vendors to help guide product managers in CSPs.
By 2021, investments in 5G NR network infrastructure will account for 19% of the total wireless infrastructure revenue of communications service providers (CSPs), elevated from 6% in 2019.
-
Support for new subcarrier spacing
-
Massive multiple input/multiple output (MIMO)/beamforming
-
Enhanced scheduling by hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ)
-
Cyclic-prefix orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (CP-OFDM) and discrete fourier transform spread orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (DFTS-OFDM)
-
Bandwidth part (BWP) and carrier aggregation (CA)
-
New Radio spectrum
-
Optimized orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)
-
Adaptive beamforming
-
Massive MIMO
-
Spectrum sharing
-
Unified design across frequencies
Key Findings:
-
The deployment of 5G New Radio (NR) products will accelerate in 2020, through high total cost of ownership (TCO), absence of “killer application,” unmatured millimeter wave ecosystem and inexpensive device availability that prevent rapid growth in capital investment.
-
Most of current commercial 5G sub-6 gigahertz (GHz) communications service providers (CSPs) also start building their multiband strategy which is in line with their business strategy; for example, sub-1GHz for coverage enhancement and millimeter wave for capacity.
-
Initial 5G deployment was based on non-stand-alone (NSA) architecture which couples the Long Term Evolution (LTE) with 5G NR radio layers to accelerate time to market and reduce cost. This coexistence will last for many years, though specific CSPs may move toward stand-alone (SA) deployment as early as 2020.
-
Open radio access network (RAN) and virtualized RAN (vRAN) have seen an increase in attention after Rakuten Mobile announced its commercial adoption in LTE. However, fragmented standards, incumbent vendor support, technology immaturity and poor fiber availability continue to hamper its success.
Market Description
-
Baseband unit capacity
-
Portfolio broadness
-
Deployment feasibility
-
Technology evolution


Recommendations for 5G Communications Service Providers (CSPs):
-
Build a step-wise 5G NR implementation strategy by initially focusing on best use of existing infrastructure investment, then simplifying the deployment in order to reduce the time to market and minimize risk.
-
Develop spectrum strategies based on business focus, frequencies available as well as ecosystem maturity. Choose the vendors that have preferred radio spectrum support with combinations of spectrum reframing and sharing.
-
Select the 5G NR solution by accessing a vendor’s capabilities of interworking with existing 4G/LTE networks and its ability to provide a high degree of continuity and seamless experience for users. In addition, explore a seamless software upgrade path to enable 5G SA evolution.
-
Build an end-to-end understanding of the Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) impact on network, operations, performance and procurement by conducting a proof of concept (POC)/pilot.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Acronym Key and Glossary Terms
| 2G |
second generation
|
| 3G |
third generation
|
| 3GPP |
Third Generation Partnership Project
|
| 4G |
fourth generation
|
| 5G |
fifth generation
|
| AAU |
Active Antenna Unit
|
| AI |
artificial intelligence
|
| AR |
augmented reality
|
| ASIC |
application-specific integrated circuit
|
| BBU |
baseband unit
|
| BWP |
bandwidth part
|
| C-RAN |
cloud radio access network
|
| CA |
carrier aggregation
|
| capex |
capital expenditure
|
| CBRS |
Citizens Broadband Radio Service
|
| CoMP |
coordinated multipoint
|
| CP-OFDM |
cyclic-prefix orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
|
| CPE |
customer premises equipment
|
| CSP |
communications service provider
|
| CU |
centralized unit
|
| DAFE |
Digital/Analog Front End
|
| DFTS-OFDM |
discrete fourier transform spread orthogonal frequency-division multiple access
|
| DIS |
digital indoor system
|
| DL |
downlink
|
| DU |
distributed unit
|
| eCPRI |
enhanced Common Public Radio Interface
|
| eMBB |
enhanced mobile broadband
|
| EPC |
Evolved Packet Core
|
| FDD |
frequency division duplex
|
| FH |
fronthaul
|
| FWA |
fixed wireless access
|
| Gbps |
gigabits per second
|
| GHz |
gigahertz
|
| gNB |
Next Generation Node B
|
| HARQ |
hybrid automatic repeat request
|
| I&O |
infrastructure and operations
|
| IBW |
instantaneous bandwidth (ZTE)
|
| IC |
integrated circuit
|
| ICT |
information and communication technology
|
| IMT-2020 |
International Mobile Telecommunications-2020
|
| IoT |
Internet of Things
|
| ITU-R |
International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Sector
|
| LAA |
Licensed Assisted Access
|
| LTE |
Long Term Evolution
|
| LTE-V |
LTE Vehicle
|
| MAA |
Multiple Input/Multiple Output Adaptive Antenna
|
| MHz |
megahertz
|
| ML |
machine learning
|
| MIMO |
multiple input/multiple output
|
| mMTC |
Massive Machine Type Communications
|
| mmWave |
millimeter wave (frequencies above 24GHz)
|
| MOCN |
multioperator core network
|
| MORAN |
multicarrier radio access network
|
| MOS |
Multi-Operator Servers (Mavenir)
|
| NFV |
network function virtualization
|
| NR |
New Radio
|
| NSA |
non-stand-alone
|
| O-RAN |
Open Radio Access Network
|
| OBW |
occupied bandwidth
|
| OEM |
original equipment manufacturer
|
| OFDM |
orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
|
| opex |
operating expenditure
|
| POC |
proof of concept
|
| PRB |
physical resource blocks
|
| QAM |
quadrature amplitude modulation
|
| R&D |
research and development
|
| RAN |
radio access network
|
| RAT |
Radio Access Technology
|
| RIC |
RAN Intelligent Controller (Nokia)
|
| RF |
radio frequency
|
| RFIC |
Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit
|
| RRU |
remote radio unit
|
| RU |
radio unit
|
| SA |
stand-alone
|
| SDN |
software-defined network
|
| SDR |
software-defined radio
|
| SON |
self-organizing network
|
| Sub-1GHz |
Low-band frequencies are those at 600MHz, 800MHz, and 900MHz.
|
| Sub-6GHz |
Frequencies under 6GHz but above the low-band frequencies (2.5GHz, 3.5GHz, and 3.7GHz to 4.2GHz).
|
| SUL |
Supplementary Uplink
|
| TCO |
total cost of ownership
|
| TD-LTE |
Time Division-Long Term Evolution
|
| TDD |
time division duplex
|
| TRX |
Transceiver/Receiver
|
| UBR |
Ultra Broadband RRU (ZTE)
|
| UL |
uplink
|
| URLLC |
ultrareliable and low-latency communications
|
| VR |
virtual reality
|
| vRAN |
virtualized radio access network
|
| WG2 |
Work Group 2
|
| WG3 |
Work Group 3
|
-
Gartner surveys
-
CSP and vendor briefings, plus discussions
-
Associated Gartner research
-
Gartner market forecasts
-
Gartner client discussions
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
References- related Gartner posts:
Gartner: Telecom at the Edge + Distributed Cloud in 3 Stages
Gartner Group Innovation & Insight: Cutting Through the 5G Hype