MediaTek
MediaTek will use TSMC to make its Dimensity SoC’s in 2024
Taiwan’s MediaTek, one of the few 5G merchant semiconductor vendors, has successfully developed its first chip using TSMC’s leading-edge 3nm technology, taping out MediaTek’s flagship Dimensity system-on-chip (SoC) with volume production expected in 2024. MediaTek joins Apple as an early adopter of TSMC’s 3-nanometer tech, a rare joint statement by a chip developer and chip manufacturer.
This marks a significant milestone in the long-standing strategic partnership between MediaTek and TSMC, with both companies taking full advantage of their strengths in chip design and manufacturing to jointly create flagship SoCs with high performance and low power features, empowering global end devices.
“We are committed to our vision of using the world’s most advanced technology to create cutting edge products that improve our lives in meaningful ways,” said Joe Chen, President of MediaTek. “TSMC’s consistent and high-quality manufacturing capabilities enable MediaTek to fully demonstrate its superior design in flagship chipsets, offering the highest performance and quality solutions to our global customers and enhancing the user experience in the flagship market.”
“This collaboration between MediaTek and TSMC on MediaTek’s Dimensity SoC means the power of industry’s most advanced semiconductor process technology can be as accessible as the smartphone in your pocket,” said Dr. Cliff Hou, Senior Vice President of Europe and Asia Sales at TSMC. “Throughout the years, we have worked closely with MediaTek to bring numerous significant innovations to the market and are honored to continue our partnership into the 3nm generation and beyond.”

Image Credit: AP
TSMC’s 3nm process technology provides enhanced performance, power, and yield, in addition to complete platform support for both high performance computing and mobile applications. Compared with TSMC’s N5 process, TSMC’s 3nm technology currently offers as much as 18% speed improvement at same power, or 32% power reduction at same speed, and approximately 60% increase in logic density.
MediaTek’s Dimensity SoCs, built with industry-leading process technology, are designed to meet the ever-increasing user experience requirements for mobile computing, high-speed connectivity, artificial intelligence, and multimedia. MediaTek’s first flagship chipset using TSMC’s 3nm process is expected to empower smartphones, tablets, intelligent cars and various other devices starting in the second half of 2024.
References:
Mediatek Dimensity 6000 series with lower power consumption for affordable 5G devices
Samsung-Mediatek 5G uplink trial with 3 transmit antennas
Ericsson and MediaTek set new 5G uplink speed record using Uplink Carrier Aggregation
MediaTek Introduces Global Ecosystem of Wi-Fi 7 Products at CES 2023
MediaTek to expand chipset portfolio to include WiFi7, smart homes, STBs, telematics and IoT
Nokia, China Mobile, MediaTek speed record of ~3 Gbps in 3CC carrier aggregation trial
Bullitt Group & Motorola Mobility unveil satellite-to-mobile messaging service device
Nokia, China Mobile, MediaTek speed record of ~3 Gbps in 3CC carrier aggregation trial
Nokia, China Mobile [1.] and MediaTek have announced a speed record in a test of the world’s first 3 Components (3CC) Carrier Aggregation (CA) technology in Shanghai. The converged 700 MHz/2.6 GHz network reached a peak downlink speed rate of 2.94 Gbps. The trial used Nokia’s AirScale 5G baseband and MediaTek’s Dimensity 9000 5G mobile platform on China Mobile’s 5G SA network. The tests will continue, using China Mobile’s network in Shanghai.
Note 1. China Mobile was banned from the U.S. in 2019.
Nokia said it is the first time the n28 (700MHz band; 30MHz) and n41 (2.6GHz band; 100+60MHz) frequency bands have been successfully combined to reach 190 MHz bandwidth (n28 + n41) with carrier aggregation technology.
CA combines frequency bands for higher data rates and increased coverage, delivering superior network capacity by maximizing the spectral efficiency of 5G networks. The combination of 5G FDD and TDD bands, supplemented by carrier aggregation, can give full play to the advantages of spectrum synergy, greatly reducing the cost of network construction while improving network coverage and user experience. The result is faster data speeds, increased coverage area, and better indoor performance.
The combination of 5G FDD and TDD bands, supplemented by carrier aggregation, augment the advantages of spectrum synergy, cutting the cost of network construction and improving network coverage and service to users.
Nokia has been a partner for over 20 years of China Mobile, which is expanding its network with the convergence of the 700 MHz and 2.6 GHz bands.

JS Pan, General Manager, Wireless Communication Technology at MediaTek, said: “Through this tripartite collaboration we have successfully demonstrated the technical advantages of DL 3CC CA using FDD+TDD. Smartphones powered by the new Dimensity 9000 flagship 5G mobile platform, and forthcoming Dimensity 5G mobile platforms, will be able to take advantage of this cutting-edge 5G connectivity feature, and MediaTek will continue to work closely with industry partners to set new milestones for 5G development.”
Ding Haiyu, Vice President of the Research Institute of China Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.), said: “China Mobile has been fully promoting the evolution and development of 5G technology. CMRI emphasizes that new technology verification provides a technical basis for the improvement of network performance and services, and forms a technical cornerstone for future network planning. China Mobile is also committed to building a 5G multi-frequency collaborative network; This 3CC CA verification can provide users with better throughput and user experience, and provide good technical foundations for new services. China Mobile is willing to work with all vendors to contribute to the 5G evolution.”
Mark Atkinson, SVP, Radio Access Networks PLM at Nokia said: “Nokia has put a strong focus on leading in 5G Carrier Aggregation. This new speed record, using commercially available hardware and software, highlights how Nokia’s pioneering approach continues to drive important innovation in the market. 5G Carrier Aggregation is a critical technology for mobile operators around the world to maximize the impact of their spectrum holdings and deliver enhanced coverage and capacity to subscribers. Nokia will keep pushing the boundaries of 5G to deliver industry-leading performance.”
Resources:
Nokia AirScale
Nokia 5G RAN
Nokia 5G Core
Nokia achieves first 5G carrier aggregation call in standalone architecture with Taiwan Mobile
Spectrum Explained
References:
MediaTek Announces Filogic Connectivity Family for WiFi 6/6E
Taiwan based MediaTek (one of only two 5G merchant silicon vendors) unveiled its new Filogic connectivity chip sets with the introduction of the Filogic 830 Wi-Fi 6/6E system-on-chip (SoC) and Filogic 630 Wi-Fi 6E network interface card (NIC) products. MediaTek said its new Filogic series of Wi-Fi 6/6E chipsets provide reliable connectivity, high computation functionalities and a rich set of features in highly integrated, power-efficient designs.
MediaTek Filogic Wi-Fi 6/6E products are certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance and deliver unbeatable performance in a wide range of applications.
- Home, business or enterprise router and repeater devices
- Service provider broadband equipment or retail devices
- Wi-Fi Alliance EasyMeshTM certified
- Home automation bridges and IoT
- Consumer devices and applications such as laptops, TVs, IP cameras, wireless storage, audio and more

MediaTek Filogic 830
Filogic 830 packs a wide variety of features into a compact, ultra-low power 12nm SoC, allowing customers to design differentiated solutions for routers, access points and mesh systems. The SoC integrates four Arm Cortex-A53 processors operating at up to 2GHz per core for up to +18,000 DMIPs processing power, dual 4×4 Wi-Fi 6/6E for up to 6Gbps connectivity, two 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces and a host of peripheral interfaces. Filogic 830’s built-in hardware acceleration engines for Wi-Fi offloading and networking enable faster and more reliable connectivity. In addition, the chipset also supports MediaTek FastPath™ technology for low latency applications such as gaming and AR/VR.

MediaTek Filogic 630
Filogic 630 is a Wi-Fi 6/6E NIC solution that supports dual-band, dual-concurrent 2×2 2.4GHz and 3×3 5GHz or 6GHz for up to 3Gbps. The chipset supports a unique 3T3R 5/6GHz system with internal front-end modules (FEMs) which provide equivalent or better range than competing 2T2R solutions with external FEMs. This highly integrated design helps lower bill of materials (BOM) cost, while allowing for sleeker designs with its small RF frontend area. Filogic’s 630’s third antenna enables superior transmit beamforming capability as well as diversity gains. Filogic 630 supports interfaces such as PCIe, which allows it to be combined with Filogic 830 for tri-band connectivity solutions for broadband gateways, enterprise access points and retail routers with even higher speeds and bandwidth capacity.
“The MediaTek Filogic series ushers in a new era of smart Wi-Fi solutions with extreme speeds, low latency and superb power efficiency for seamless, always connected experiences,” said Alan Hsu, Corporate Vice President & General Manager, Intelligent Connectivity at MediaTek. “These new chipsets provide best-in-class features with highly integrated designs for the next generation of premium broadband, enterprise and retail Wi-Fi solutions.”
MediaTek has the broadest Wi-Fi portfolio and is the No. 1 Wi-Fi supplier across broadband, retail routers, consumer electronics devices and gaming. MediaTek’s Wi-Fi portfolio powers hundreds of millions of devices every year. Over the years, MediaTek has worked closely with the Wi-Fi Alliance to ensure MediaTek’s connectivity portfolio supports the latest Wi-Fi features. In January 2021, MediaTek was selected to be on the test bed for Wi-Fi 6E, the latest certification from Wi-Fi Alliance® for Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 6™ devices with 6GHz support.
Wi-Fi 6E offers a number of advantages over previous Wi-Fi generations, including lower latency and additional capacity and speed. Devices using Wi-Fi 6 connections in 6GHz are designed to make use of wide 160 MHz channels and uncongested bandwidth in 6GHz to deliver multi-gigabit, low latency Wi-
About MediaTek Inc.
MediaTek Incorporated (TWSE: 2454) is a global fabless semiconductor company that enables nearly 2 billion connected devices a year. We are a market leader in developing innovative systems-on-chip (SoC) for mobile device, home entertainment, connectivity and IoT products. Our dedication to innovation has positioned us as a driving market force in several key technology areas, including highly power-efficient mobile technologies, automotive solutions and a broad range of advanced multimedia products such as smartphones, tablets, digital televisions, 5G, Voice Assistant Devices (VAD) and wearables. MediaTek empowers and inspires people to expand their horizons and achieve their goals through smart technology, more easily and efficiently than ever before. We work with the brands you love to make great technology accessible to everyone, and it drives everything we do. Visit www.mediatek.com for more information.
References:
https://www.mediatek.com/products/connectivity-and-networking/mediatek-filogic-wifi-6
Ericsson & MediaTek near 500 Mbps upload in mmWave carrier aggregation tests
Ericsson announced a new upload speed record with 5G on mmWave spectrum – double the current upload speeds and the fastest recorded to date.
In a four-component carrier uplink aggregation tests with MediaTek, a peak throughput rate of 495 Mbps was achieved. This included 425 Mbps on 5G New Radio (5G RAN) test and a 70 Mbps on 4G-LTE test.
The demo performed in June used pre-commercial software on a device containing a MediaTek M80 5G chipset. The lab tests used Ericsson RAN Compute baseband 6648 with the AIR 5331 millimeter wave radio. Four carriers of 100 MHz each in the 39 GHz band were used for non-standalone 5G, along with 20 MHz in the 1,900 MHz band for LTE (more in Tech Details below).
Ericsson said the test of uplink carrier aggregation is the first of its kind, as the industry previously focused more on boosting download speeds. The increased adoption in the past year of home working and schooling has driven the use of applications like videoconferencing that require also fast upload speeds.
Upload speed dictates how quickly data is sent from the computer or handheld device to the internet. This includes uploading files, such as photos and videos to social media or collaborative worksites. Upload speeds are also crucial to the image and sound quality of video conferencing. Strong uplink means less or even none of those frozen screens, or broken audio, when using apps like Skype or Microsoft Teams. Similarly, faster uplink improves voice over internet protocol (VoIP) calls and online gaming experience.
Hannes Ekström, Head of Product Line 5G RAN at Ericsson, said: “We continue to build on our previous successes, breaking our own record in upload speed. With a peak rate of close to 500 Mbps, we’ve demonstrated in this latest milestone with MediaTek how unprecedented data speeds can be delivered in uplink using mmWave and carrier aggregation. This means our customers can enhance their 5G offerings with higher uplink data rates, vastly improving user experience.”
JS Pan, General Manager of Wireless Communication System and Partnership at MediaTek, said: “This world’s first demonstration of an industry-leading mmWave uplink technology in partnership with Ericsson, shows MediaTek is again establishing 5G milestones and pushing the envelope of its capabilities. 5G mmWave connectivity helps boost network coverage and capacity, faster performance, and introduces more diverse use cases.”
This latest technology milestone follows a single user multiple input multiple output (SU-MIMO demo in April 2021 when Ericsson delivered a single user uplink data rate of 315 Mbps, 15-20 times faster than current typical uplink speed.
Tech details:
Ericsson and MediaTek integrated four component carrier, each of 100 MHz, in the uplink using non-standalone architecture (aggregating 8x100MHz in the downlink and 4×100 MHz in the uplink). The integration carried out in a lab setting resulted in a throughput of 495 Mbps (425 Mbps in 5G plus 70 Mbps in 4G), doubling the current uplink speed on the market.
The test was done using the 39 GHz spectrum of NR (400 MHz) and combining it with a single carrier of LTE 1900 MHz spectrum (20 MHz). The whole bandwidth was then aggregated using the LTE and NR links, realizing a total throughput of close to 500 Mbps.
RELATED LINKS
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2021/7/ericsson-and-mediatek-achieve-mmwave-uplink-record
Counterpoint Research: Mediatek is world’s #1 smartphone chipset vendor
Christmas day surprise! Taiwanese fabless chipmaker Mediatek has overtaken Qualcomm and is now the #1 smartphone chipset vendor with a 31% market share in Q3 2020. Mediatek was helped by its growth in regions like India and China, and a strong performance in the $150-200 price smartphone category, according to estimates from market research firm Counterpoint Technology Market Research.
In terms of market share, MediaTek led the chipset market at the first position, followed by Qualcomm (29%), HiSilicon (12%), Samsung (12%), Apple (12%), and UNISOC (4%) respectively.
Qualcomm was the biggest 5G chipset vendor in Q3 2020. Its silicon powered 39% of the 5G phones sold worldwide. The demand for 5G smartphones doubled in Q3 2020 – 17% of all smartphones sold in Q3 2020 were 5G. This impressive growth trajectory is going to continue, more so with Apple launching its 5G line-up. One-third of all smartphones shipped in Q4 2020 are expected to be 5G enabled. There is still a chance Qualcomm will regain the top position in Q4 2020.
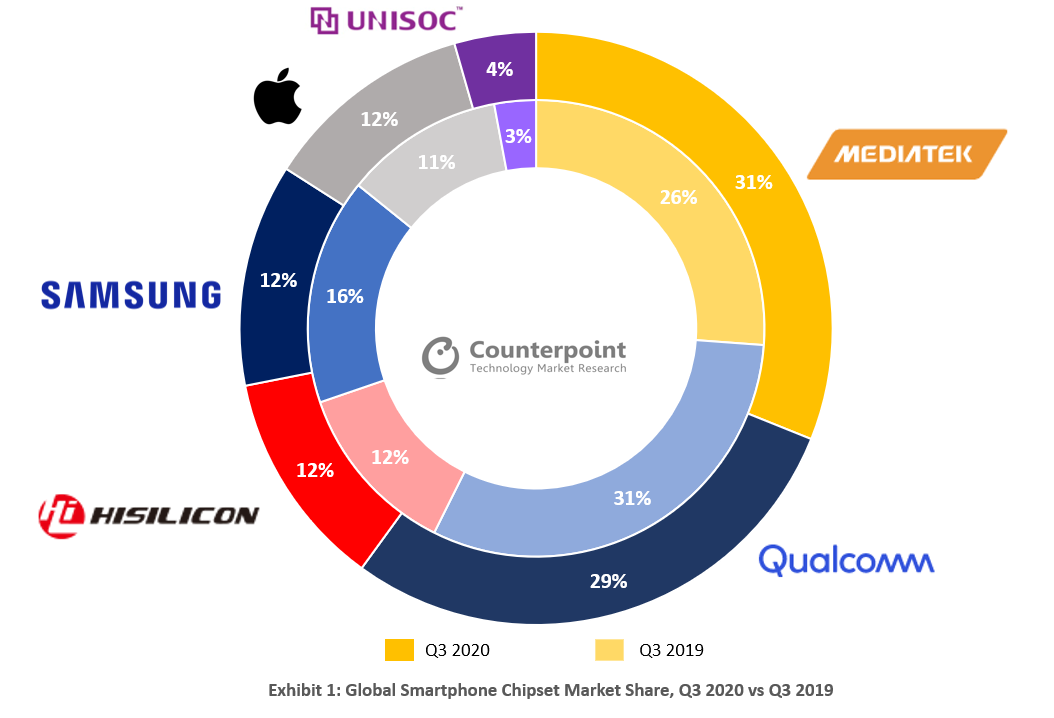
Source: Counterpoint Research
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
MediaTek’s Research Director Dale Gai said:
“MediaTek’s strong market share gain in Q3 2020 happened due to three reasons – strong performance in the mid-end smartphone price segment ($100-$250) and emerging markets like LATAM and MEA, the U.S. ban on Huawei and finally wins in leading OEMs like Samsung, Xiaomi and Honor. The share of MediaTek chipsets in Xiaomi smartphones has increased by more than three times since the same period last year.’
“MediaTek was also able to leverage the gap created due to the U.S. ban on Huawei. Affordable MediaTek chips fabricated by TSMC became the first option for many OEMs to quickly fill the gap left by Huawei’s absence. Huawei had also previously purchased a significant amount of chipsets ahead of the ban.”
“On the other hand, Qualcomm also posted strong share gains (from a year ago) in the high-end segment in Q3 2020, again thanks to HiSilicon’s supply issues. However, Qualcomm faced competition from MediaTek in the mid-end segment. We believe both will continue to compete intensively through aggressive pricing, and mainstream 5G SoC products into 2021.”
Counterpoint Research Analyst Ankit Malhotra said:
“Qualcomm and MediaTek have both reshuffled their portfolios, and consumer focus has played a key role here. Last year, MediaTek launched a new gaming-based G-series, while Dimensity chipsets have helped in bringing 5G to affordable categories. The world’s cheapest 5G device, the realme V3, is powered by MediaTek.”
Commenting on the outlook for chipset vendors, Malhotra added, “The immediate focus of chipset vendors will be to bring 5G to the masses, which will then unlock the potential of consumer 5G use cases like cloud gaming, which in turn will lead to higher demand for higher clocked GPUs and more powerful processors. Qualcomm and MediaTek will continue to contend for the top position.”

Source: Counterpoint Research
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Counterpoint Research:
Counterpoint Technology Market Research is a global research firm specializing in Technology products in the TMT industry. It services major technology firms and financial firms with a mix of monthly reports, customized projects and detailed analysis of the mobile and technology markets. Its key analysts are experts in the industry with an average tenure of 13 years in the high-tech industry.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, MediaTek 5G silicon will be used in future notebook PCs with Intel inside.
MediaTek’s T700 5G modem, which will be used to bring 5G connectivity to Intel-powered PCs, completed 5G standalone (SA) calls in real world test scenarios. Additionally, Intel has progressed on system integration, validation and developing platform optimizations for a superior user experience and is readying co-engineering support for its OEM partners. MediaTek and Intel are both committed to delivering a superior user experience.
“Our partnership with Intel is a natural extension of our growing 5G mobile business, and is an incredible market opportunity for MediaTek to move into the PC market,” said MediaTek President Joe Chen. “With Intel’s deep expertise in the PC space and our groundbreaking 5G modem technology, we will redefine the laptop experience and bring consumers the best 5G experiences.”
“A successful partnership is measured by execution, and we’re excited to see the rapid progress we are making with MediaTek on our 5G modem solution with customer sampling starting later this quarter. Building on our 4G/LTE leadership in PCs, 5G is poised to further transform the way we connect, compute and communicate. Intel is committed to enhancing those capabilities on the world’s best PCs,” said Chris Walker, Intel corporate vice president and general manager of Mobile Client Platforms.
References:
MediaTek Becomes Biggest Smartphone Chipset Vendor for First Time in Q3 2020
Analysis: Intel and MediaTek partnership to make 5G PCs; Qualcomm competition?
Summary:
Intel and MediaTek are partnering to make cellular-connected personal computers. Intel will “define” a 5G PC system spec (“Intel will define a 5G solution specification focused on deployment in key laptop segments”) while MediaTek will develop the 5G cellular chip for those PCs. The first products are targeting availability in early 2021. Dell and HP are expected to be among the first OEMs to deliver laptops enabled with Intel and MediaTek’s 5G solution.
Intel also will help make sure the 5G chip works properly and will help computer makers integrate their processor into PCs (“Intel will also provide optimization and validation across the platform and lend system integration and co-engineering support to further enable its OEM partners.”).
The partnership is also expected to increase the global presence for MediaTek’s 5G modems, which are mainly sold to Chinese smartphone makers. The 5G PC chip is based in part on MediaTek’s Helio M70 5G modem, introduced earlier this year. From the Intel announcement:
“5G is poised to unleash a new level of computing and connectivity that will transform the way we interact with the world. This partnership with MediaTek brings together industry leaders with deep engineering, system integration and connectivity expertise to deliver 5G experiences on the next generation of the world’s best PCs.”
–Gregory Bryant, Intel executive vice president and general manager of the Client Computing Group
The partnership helps MediaTek break into a bigger U.S. market and prevents Intel from being shut out of 5G-connected PCs. It also helps Intel defends one of its most important markets: computers. It has long made the majority of chips that go into PCs, but rival Qualcomm has been gaining market traction with its Snapdragon SoCs that were originally designed for smartphones. Qualcomm’s SoCs generally provide better battery life and connectivity that are not traditionally found in computers.

Image courtesy of Intel
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The two companies are also working with Fibocom on the development of M.2 modules optimized for integration with Intel client platforms. As the first module vendor for this solution, Fibocom will provide operator certification and regulatory support, as well as lead 5G M.2 module manufacturing, sales and distribution.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Analysis:
Intel earlier this year introduced its Project Athena initiative, a multiple-company, multiple-year effort to make PCs more like computers. Devices are meant to wake instantly, sport brighter screens for outdoor use and have battery life that lasts all day. Project Athena laptops also need to be able to complete a biometric login process in a second or less after a laptop lid is opened, and Athena gets an additional second to connect to Wi-Fi. The first devices are due this year, but they’re not cellular-enabled. For that, users have to turn to Qualcomm-powered PCs.
Last year, Qualcomm unveiled its first processor designed specifically for computers, called the Snapdragon 8cx Compute Platform. Qualcomm partnered with Lenovo to introduce its the Snapdragon 8cx 5G compute platform in late May this year. “Consumers can expect more to come from Lenovo and Qualcomm in early 2020,” the Qualcomm said. The chip is powerful but also power efficient, giving users multiple days of battery life on a single charge.
Many PC makers have started using Qualcomm chips. That includes the Samsung’s Galaxy Book S, which was unveiled in August and runs on the 8cx. The ultrathin, ultralight laptop has a 13.3-inch touchscreen and sports 23 hours of battery life. It also has built-in LTE.
Intel, on the other hand, struggled to make a cost competitive 5G chip for Apple’s iPhones and was losing lots of money on that project. it exited the cellular modem business After Apple and Qualcomm reached a multiyear chip supply agreement in April, Intel exited the 5G smartphone modem business. This past July, Apple and Intel jointly announced that Apple planned to buy Intel’s smartphone modem business for $1 billion. The deal likely gives Apple access to some of Intel’s work on 5G technology mostly from the latter’s acquisition of Infineon cellular division.
There are only four companies in the world making 5G chips: Qualcomm, MediaTek, Samsung and Huawei while only the first two sell into the merchant semiconductor market. Samsung and Huawei largely only use their 5G chips in their own devices (though a new phone from Vivo will use Samsung’s Exynos 5G modem).
MediaTek predominantly supplies modems to Asian (mostly China) handset makers. Its first 5G modem chip/chip set won’t work on any of the 5G networks that have been deployed in the U.S.
Intel and MediaTek now hope their efforts will be enough to fend off Qualcomm and attract PC makers. Other spin offs are also possible, depending on the success of this initial effort.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Qualcomm Competition or 5G Monopoly?
Qualcomm has supplied 5G modems for the vast majority of 5G smartphones sold this year. Intel wouldn’t partner with Qualcomm, a company it views as its chief rival in the semiconductor business. Michael Chertoff, former Head of U.S. Homeland Security penned an oped in yesterday’s Wall Street Journal that Qualcomm’s Monopoly Imperils National Security. He wrote:
A monoculture technology system likewise poses substantial risks. If there is some critical flaw in the single system on which the U.S. is dependent, its failure would be catastrophic. These technical vulnerabilities are especially risky in security-sensitive industries such as telecommunications. American reliance on a single chip provider creates an inviting target for adversaries, who would need to find and exploit only one vulnerability to execute a destructive cyberattack.
In the Pentagon’s view, maintaining the company’s economic health is also essential because it is a critical player in the competition with China to develop 5G technology. To be sure, it’s important to support the viability of U.S. firms that can compete with China on 5G, but this hardly justifies the risks of a mono-culture in the defense-industrial base.
Further, the argument mistakenly links two national-security issues in an artificial way. Qualcomm doesn’t need protection in the wireless chipset market to strengthen its competitive edge in the 5G race. To the contrary, it has every incentive to develop leading 5G technologies even in the absence of protection in the chip market.
In the technology race against China, the U.S. should prefer to let competition drive innovation rather than support exclusive national champions. Apart from the economic inefficiency, a single-source national champion creates an unacceptable risk to American security—artificially concentrating vulnerability in a single point. The government’s argument in support of Qualcomm isn’t prudent, and if courts accept it, the result would be a self-inflicted wound to U.S. national interests. We need competition and multiple providers, not a potentially vulnerable technological monoculture.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://newsroom.intel.com/news/intel-mediatek-partner-deliver-5g-pc/
https://www.cnet.com/news/intel-mediatek-partners-to-make-5g-chips-for-pcs/
https://www.lightreading.com/mobile/5g/intel-partners-with-mediatek-for-5g-pc-chips/d/d-id/755933?
JEDEC Forum: AI/ML for IoT; LP-WANs & Mediatek’s SoC Solutions – Part I.
Introduction:
Several new ideas, concepts and forecasts were made at JEDEC’s Mobile & IOT Forum on March 26, 2018 in Santa Clara, CA. In particular:
- Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning/Deep Learning will have a huge, positive impact on control of IoT devices (2 presentations summarized);
- 3GPP specified NB-IoT is a strong contender among the many Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs) for IoT;
- New and different IT requirements at the network edge are needed to provide the low latency needed for real time control of IoT devices;
- MIPI Alliance specifications for Mobile and IoT were presented and MIPI’s role explained.
In this first of a two part event summary we provide highlights of the first two keynote speeches at the conference. In part II, we’ll look at more aspects of AI, MIPI, and the new IT requirements for the intelligent network edge as suggested by Lenovo.
Discussion of Selected Keynote Presentations:
- Signs of Intelligent Life: AI Simplifies IoT
In his opening keynote presentation, Stephen Lum of Samsung said that some IoT industry vertical device volumes have seen an explosion of demand due to the introduction of Artificial Intelligence into their usage model. The connection and control of those devices is driving tremendous data traffic volumes into the cloud where the AI/ML/DL actually takes place. For example, the Amazon Echo and Google Home connected device control has all voice recognition, language understanding, AI/ML/DL done in cloud resident data center compute servers owned and programmed by Amazon and Google, respectively. Autonomous vehicles will also have AI/ML/DL done in the cloud but likely at the network edge to provide ultra-low latency.
Stephen stated that a simple thesis of deep learning is that the more data used to train neural networks, the smarter the AI becomes. Some of his other cogent data points were the following:
- New AI chips are being designed to efficiently process deep neural networks.
- Solid state memory needs to keep pace with processors to prevent bottlenecks. See bullet points below for UFS.
- Scalability becomes more critical as consumers adopt new services.
- Universal Flash Storage (UFS) is a high performance, scalable interface for storage at the edge of the network.
- UFS combines the key features of eMMC (embedded Multi-Media Controller) and SSDs (Solid State Drives).
- UFS Card brings benefits to a removable storage form factor.
The diverse needs of three IoT industry verticals were said to be as follows:
- Wearables (e.g. smart watches, fitness trackers, etc): Low power, Low density, Specialized form factors.
- Smart Home (AKA Connected Home): Low cost, Low to mid density, Low to high bandwidth –depending on the device to be analyzed and/or controlled, 2-5 years longevity.
- Automotive (more than just autonomous vehicles): High bandwidth, High density, Very high reliability, 7-10 years longevity.
Summary:
- Artificial Intelligence is enabling more innovative real-time services to be delivered to consumers.
- AI in the Cloud simplifies edge devices, encourages their adoption with low cost of entry.
- Autonomous vehicles, cannot be Cloud dependent, will become AI servers on wheels.
- JEDEC has enabled tremendous advances in memory while expediting quick adoption and provides a firm foundation for memory-related ecosystems
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- Opening a New Era of IoT -Opportunities and Solutions
Note: I related best to this presentation at it was the only one dealing exclusively with the network aspects of IoT.
Harrison Hsieh of Mediatek said at the beginning of his excellent presentation that we should look at the network required for IoT based on whether the devices/ end points were indoors or outdoors.
Let’s first look at an IoT indoor application presented by Mr. Hsieh:
Challenges of Smart Home (e.g. kitchen management, living room control, home heating/cooling/climate control, entertainment device control, security/surveillance, etc.):
- Uncovered Zone: Bad connection, No signal, Dead end
- Different Protocols (and wiring or wireless): Kitchen, Living room, Lighting, Climate control, Surveillance
Whole home IoT coverage requires Adaptive Networking which includes: Easy Setup/Configuration, Network Healing (after failure detection), Fast Roaming, Beam/Frequency Band Steering, Smart QoS, and Solid Security.
According to MediaTek, the IoT home system should be: Easy to Use, Have a unified protocol, be intuitive to install, have a single ecosystem with a user friendly interface (e.g. plug and play).
Harrison said that MediaTek’s Human to Machine interface solutions will focus on Hands-Free Voice Controlled Applications which are intuitive to configure and control diverse devices. We strongly agree!
Next, the outdoor IoT applications face many challenges today, including:
a.] Complicated Technologies:
• Unlicensed Wireless (e.g. LoRa WAN, Sigfox, etc)
• Proprietary Technologies (too many)
• Complex Deployment
b.] Limitation of Signal Coverage:
• Low Penetration Capability (trees, buildings/walls, etc)
• Limited Range with Single Base Station
c.] High Power Consumption:
• Legacy Technologies
• Not Dedicated or purpose built for outdoor IoT design (except for SIgfox and LoRA WAN, maybe LTE Category M/M1?)
Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs) for IoT [1.] need a dedicated solution, which Mediatek believes is 3GPP’s NB-IoT. They think it’s the clear winner when compared to other LTE standards, including LTE Category M/M1 which many carriers are using today for IoT applications.
In particular, LTE NB-IoT R14 [2] was said to offer the following attributes:
- System Bandwidth of 200kHz
- Down Link Peak Rate of 127kbps
- Up Link Peak Rate of 18kbps(ST) / 158kbps(MT)
- Link Budget (power consumption) of 164 dB
- Low Memory Requirement (especially compared to other LTE standards)
- Half Duplex mode
- Battery life measured in years rather than days or weeks
Other advantages of LTE NB-IoT R14 include:
- Location Accuracy (UTDOA/OTDOA)
- Mobility Enhancement (Cell Reselection)
- High Data Rate (Supports FOTA or firmware updates over the air)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Note 1. Market for LPWANs:
LPWANs will be the world’s fastest-growing connectivity technology through 2025, supporting 4 billion IoT devices by that date, according to market tracker ABI Research.
“We expect to have more than 100 million NB-IoT connections on our network by 2020,” said Xiaotian Chen, general manager of China Unicom’s IoT group, said in a Cisco press statement.
China Mobile reported at MWC 2018 that it has launched NB-IoT networks in 346 cities using chipsets from five companies — Huawei, Mediatek, Qualcomm, RDA, and ZTE. The carrier has approved for use on its network 15 NB-IoT modules using the chips, according to a report from TechInsights analysts at the MWC 2018 event.
China Telecom, gave an update on its aggressive deployments of NB-IoT at a U.S. the MWC Americas event last September.
In the U.S., T-Mobile, Sprint and Verizon plan to deploy NB-IoT with T-Mobile’s offering planned for 2018 with the others to follow.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Note 2. 3GPP’s LTE NB-IoT R14 briefly explained:
In 3GPP LTE Release 13, Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) was specified for providing wide-area connectivity for massive machine-type communications for IoT.
In 3GPP LTE Release 14, NB-IoT was further developed to deliver an enhanced user experience in selected areas through the addition of features such as increased positioning accuracy, increased peak data rates, the introduction of a lower device power class, improved non-anchor carrier operation, multicast, and authorization of coverage enhancements.
According to MediaTek, 3GPP Release 14 imbues essential features for NB-IoT mobile applications such as:
- Location accuracy via just modem (UTDOA/OTDOA)
- Mobility enhancements from seamless cell re-selection
- Push-to-talk voice messaging services
- Higher efficiency by lowering power consumption for wearables
- Supports massive industrial or city-wide deployments with multicast
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Summary of Mediatek’s IoT LPWAN Solution:
• Global Oriented NB-IoT Solution:
– Support NB1 (Rel.13) & NB2 (Rel.14) Global Bands (450Mhz – 2.1Ghz)
– Latest NB2 Modem Technology (Position allocation/Higher Data Rate/Cell Reselection)
• Highly Integration with Low Power Design:
– Leading SoC integrated design with Small form factor
– Rich I/Os for various application
– Optimized low power design in One-time battery
• Comprehensive Product Portfolio:
– Combination with MediaTek Connectivity technologies
– Integrated and matured Software offerings
In closing, Harrison predicted that the IT user interface will change from keyboard to voice (it already has for this author on his smart phone and tablet) while NB-IOT market will “take off in 2019-2020” timeframe.
Mediatek’s System on a Chip (SoC) connectivity solutions are targeted at the home, on the move (mobile) and in the cloud.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Part II. of this event summary was published on March 29, 2018 at https://techblog.comsoc.org/2018/03/29/ai-deep-learning-new-it-requirements-for-edge-computing-mipi-alliance-for-mobile-and-iot/
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://labs.mediatek.com/en/blog/IoT-tech-comparison-and-vision
MediaTek targets “huge” NB-IoT opportunity – Mobile World Live
https://www.eetimes.com/document.asp?doc_id=1333023
https://www.nickhunn.com/13-companies-announce-nb-iot-chips/
https://www.eetimes.com/document.asp?doc_id=1332311
https://www.link-labs.com/blog/overview-of-narrowband-iot