China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
Introduction:
According to the Wall Street Journal, the U.S. maintains its early lead in AI technology with Silicon Valley home to the most popular AI models and the most powerful AI chips (from Santa Clara based Nvidia and AMD). However, China has shown a willingness to spend whatever it takes to take the lead in AI models and silicon.
The rising popularity of DeepSeek, the Chinese AI startup, has buoyed Beijing’s hopes that it can become more self-sufficient. Huawei has published several papers this year detailing how its researchers used its homegrown AI chips to build large language models without relying on American technology.
“China is obviously making progress in hardening its AI and computing ecosystem,” said Michael Frank, founder of think tank Seldon Strategies.
AI Silicon:
Morgan Stanley analysts forecast that China will have 82% of AI chips from domestic makers by 2027, up from 34% in 2024. China’s government has played an important role, funding new chip initiatives and other projects. In July, the local government in Shenzhen, where Huawei is based, said it was raising around $700 million to invest in strengthening an “independent and controllable” semiconductor supply chain.
During a meeting with President Xi Jinping in February, Huawei Chief Executive Officer Ren Zhengfei told Xi about “Project Spare Tire,” an effort by Huawei and 2,000 other enterprises to help China’s semiconductor sector achieve a self-sufficiency rate of 70% by 2028, according to people familiar with the meeting.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
AI Models:
Prodded by Beijing, Chinese financial institutions, state-owned companies and government agencies have rushed to deploy Chinese-made AI models, including DeepSeek [1.] and Alibaba’s Qwen. That has fueled demand for homegrown AI technologies and fostered domestic supply chains.
Note 1. DeepSeek’s V3 large language model matched many performance benchmarks of rival AI programs developed in the U.S. at a fraction of the cost. DeepSeek’s open-weight models have been integrated into many hospitals in China for various medical applications.
In recent weeks, a flurry of Chinese companies have flooded the market with open-source AI models, many of which are claiming to surpass DeepSeek’s performance in certain use cases. Open source models are freely accessible for modification and deployment.
The Chinese government is actively supporting AI development through funding and policy initiatives, including promoting the use of Chinese-made AI models in various sectors.
Meanwhile, OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman said his company had pushed back the release of its open-source AI model indefinitely for further safety testing.
AI Research:
China has taken a commanding lead in the exploding field of artificial intelligence (AI) research, despite U.S. restrictions on exporting key computing chips to its rival, finds a new report.
The analysis of the proprietary Dimensions database, released yesterday, finds that the number of AI-related research papers has grown from less than 8500 published in 2000 to more than 57,000 in 2024. In 2000, China-based scholars produced just 671 AI papers, but in 2024 their 23,695 AI-related publications topped the combined output of the United States (6378), the United Kingdom (2747), and the European Union (10,055).
“U.S. influence in AI research is declining, with China now dominating,” Daniel Hook, CEO of Digital Science, which owns the Dimensions database, writes in the report DeepSeek and the New Geopolitics of AI: China’s ascent to research pre-eminence in AI.
In 2024, China’s researchers filed 35,423 AI-related patent applications, more than 13 times the 2678 patents filed in total by the U.S., the U.K., Canada, Japan, and South Korea.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/how-china-is-girding-for-an-ai-battle-with-the-u-s-5b23af51
Huawei launches CloudMatrix 384 AI System to rival Nvidia’s most advanced AI system
U.S. export controls on Nvidia H20 AI chips enables Huawei’s 910C GPU to be favored by AI tech giants in China
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
Gen AI eroding critical thinking skills; AI threatens more telecom job losses
Softbank developing autonomous AI agents; an AI model that can predict and capture human cognition
AI spending is surging; companies accelerate AI adoption, but job cuts loom large
Big Tech and VCs invest hundreds of billions in AI while salaries of AI experts reach the stratosphere
ZTE’s AI infrastructure and AI-powered terminals revealed at MWC Shanghai
Deloitte and TM Forum : How AI could revitalize the ailing telecom industry?
Ericsson completes Aduna joint venture with 12 telcos to drive network API adoption
Today, Ericsson announced the completion of the equity investments by twelve global communication service providers (CSPs) into its subsidiary Aduna, formally establishing Aduna as a 50:50 joint venture. Aduna was created to combine and sell aggregated network Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) globally. It has been operational since the deal signed on 11 September 2024. Aduna is now owned by AT&T, Bharti Airtel, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, KDDI, Orange, Reliance Jio, Singtel, Telefonica, Telstra, T-Mobile, Verizon and Vodafone.
The network APIs, based on the CAMARA open source project of the GSMA and Linux Foundation, are designed to enable network operators to offer services such as service level assurance, fraud prevention and authentication programmatically to application developers, similar to how those same application developers can easily spin up cloud compute instances on cloud providers like Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure. For telcos and other network operators, network APIs promise the potential to leverage 5G networks for new business models and revenue streams.
The Aduna ecosystem includes additional CSPs worldwide, as well as major developer platform companies, global system integration (GSI) companies, communication platform-as-a-service (CPaaS) companies, and independent software vendor (ISV) companies. To date these include: e& (in UAE -formerly Etisalat), Bouygues Telecom, Free, CelcomDigi, Softbank, NTT DOCOMO, Google Cloud, Vonage, Sinch, Infobip, Enstream, Bridge Alliance, Syniverse, JT Global, Microsoft, Wipro and Tech Mahindra – each playing a vital role in advancing the reach and impact of network APIs worldwide.
Former Vonage COO Anthony Bartolo, became Aduna CEO this past January. He said in a statement:
“The closing of the transaction is another important step for Aduna. In just ten months we have built an impressive ecosystem comprising the biggest names in telecoms and the wider ICT industry. The closing provides renewed motivation for Aduna to accelerate the adoption of network APIs by developers on a global scale. This includes encouraging more telecom operators to join the new company, further driving the industry and developer experience.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
A Febuary 2024 McKinsey article stated:
Network APIs are the interlocking puzzle pieces that connect applications to one another and to telecom networks. As such, they are critical to companies seamlessly tapping into 5G’s powerful capabilities for hundreds of potential use cases, such as credit card fraud prevention, glitch-free videoconferencing, metaverse interactions, and entertainment. If developers have access to the right network APIs, enterprises can create 5G-driven applications that leverage features like speed on demand, low-latency connections, speed tiering, and edge compute discovery.
In addition to enhancing today’s use cases, network APIs can lay the foundation for entirely new ones. Remotely operated equipment, semi-autonomous vehicles in production environments, augmented reality gaming, and other use cases could create substantial value in a broad range of industries. By enabling these innovations, telecom operators can position themselves as essential partners to enterprises seeking to accelerate their digital transformations.
Over the next five to seven years, we estimate the network API market could unlock around $100 billion to $300 billion in connectivity- and edge-computing-related revenue for operators while generating an additional $10 billion to $30 billion from APIs themselves. But telcos won’t be the only ones vying for this lucrative pool. In fact, with the market structure currently in place, they would cede as much as two-thirds of the value creation to other players in the ecosystem, such as cloud providers and API aggregators—repeating the industry’s frustrating experience of the past two decades.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
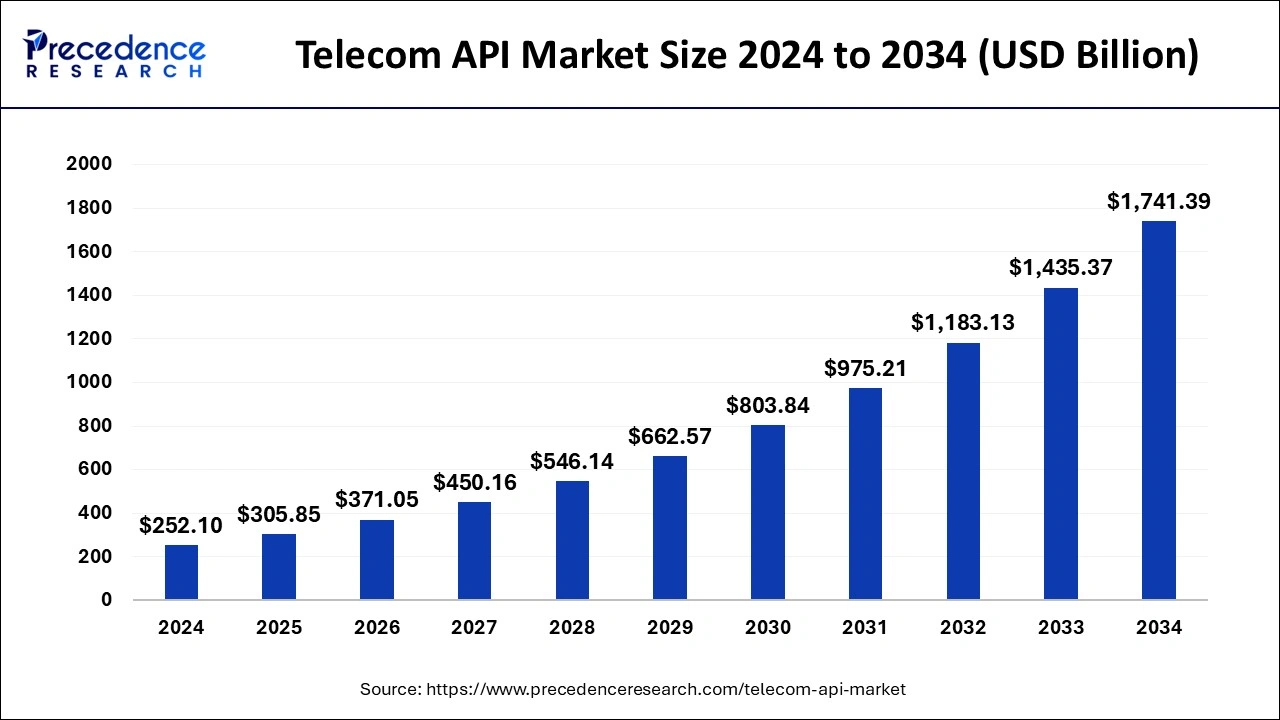
Telecom API Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034 by Precedence Research:
The global telecom API market size was estimated at USD 252.10 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 1741.39 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 21.32% from 2025 to 2034.
Aduna Global can potentially scale network APIs across regions, and maybe even globally, Leonard Lee, executive analyst at neXt Curve, told Fierce Network. Aduna can potentially help deliver trust and regulatory clients that network APIs need for widespread adoption. Aduna itself won’t directly offer services Aduna partners such as JT Global, Vonage and AWS already offer fraud prevention services that leverage relevant security and authentication-related network APIs, Lee said.
“You won’t likely see Aduna Global offer a fraud prevention service,” he added. “You need to look at Vonage, Infobip, Tech Mahindra and the like to offer these solutions that will likely be accessible to developers through APIs.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/press-releases/2025/7/ericsson-announces-completion-of-aduna-transaction
New venture to sell Network Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) on a global scale
https://www.precedenceresearch.com/telecom-api-market
Telefónica and Nokia partner to boost use of 5G SA network APIs
Countdown to Q-day: How modern-day Quantum and AI collusion could lead to The Death of Encryption
By Omkar Ashok Bhalekar with Ajay Lotan Thakur
Behind the quiet corridors of research laboratories and the whir of supercomputer data centers, a stealth revolution is gathering force, one with the potential to reshape the very building blocks of cybersecurity. At its heart are qubits, the building blocks of quantum computing, and the accelerant force of generative AI. Combined, they form a double-edged sword capable of breaking today’s encryption and opening the door to an era of both vast opportunity and unprecedented danger.
Modern Cryptography is Fragile
Modern-day computer security relies on the un-sinking complexity of certain mathematical problems. RSA encryption, introduced for the first time in 1977 by Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman, relies on the principle that factorization of a 2048-bit number into primes is computationally impossible for ordinary computers (RSA paper, 1978). Also, Diffie-Hellman key exchange, which was described by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman in 1976, offers key exchange in a secure manner over an insecure channel based on the discrete logarithm problem (Diffie-Hellman paper, 1976). Elliptic-Curve Cryptography (ECC) was described in 1985 independently by Victor Miller and Neal Koblitz, based on the hardness of elliptic curve discrete logarithms, and remains resistant to brute-force attacks but with smaller key sizes for the same level of security (Koblitz ECC paper, 1987).
But quantum computing flips the script. Thanks to algorithms like Shor’s Algorithm, a sufficiently powerful quantum computer could factor large numbers exponentially faster than regular computers rendering RSA and ECC utterly useless. Meanwhile, Grover’s Algorithm provides symmetric key systems like AES with a quadratic boost.
What would take millennia or centuries to classical computers, quantum computers could boil down to days or even hours with the right scale. In fact, experts reckon that cracking RSA-2048 using Shor’s Algorithm could take just 20 million physical qubits which is a number that’s diminishing each year.
Generative AI adds fuel to the fire
While quantum computing threatens to undermine encryption itself, generative AI is playing an equally insidious but no less revolutionary role. By mass-producing activities such as the development of malware, phishing emails, and synthetic identities, generative AI models, large language models, and diffusion-based visual synthesizers, for example, are lowering the bar on sophisticated cyberattacks.
Even worse, generative AI can be applied to model and experiment with vulnerabilities in implementations of cryptography, including post-quantum cryptography. It can be employed to assist with training reinforcement learning agents that optimize attacks against side channels or profile quantum circuits to uncover new behaviors.
With quantum computing on the horizon, generative AI is both a sophisticated research tool and a player to watch when it comes to weaponization. On the one hand, security researchers utilize generative AI to produce, examine, and predict vulnerabilities in cryptography systems to inform the development of post-quantum-resistant algorithms. Meanwhile, it is exploited by malicious individuals for their ability to automate the production of complex attack vectors like advanced malware, phishing attacks, and synthetic identities radically reducing the barrier to conducting high impact cyberattacks. This dual-use application of generative AI radically shortens the timeline for adversaries to take advantage of breached or transitional cryptographic infrastructures, practically bridging the window of opportunity for defenders to deploy effective quantum-safe security solutions.
Real-World Implications
The impact of busted cryptography is real, and it puts at risk the foundations of everyday life:
1. Online Banking (TLS/HTTPS)
When you use your bank’s web site, the “https” in the address bar signifies encrypted communication over TLS (Transport Layer Security). Most TLS implementations rely on RSA or ECC keys to securely exchange session keys. A quantum attack would decrypt those exchanges, allowing an attacker to decrypt all internet traffic, including sensitive banking data.
2. Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies use ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) for signing transactions. If quantum computers can crack ECDSA, a hacker would be able to forge signatures and steal digital assets. In fact, scientists have already performed simulations in which a quantum computer might be able to extract private keys from public blockchain data, enabling theft or rewriting the history of transactions.
3. Government Secrets and Intelligence Archives
National security agencies all over the world rely heavily on encryption algorithms such as RSA and AES to protect sensitive information, including secret messages, intelligence briefs, and critical infrastructure data. Of these, AES-256 is one that is secure even in the presence of quantum computing since it is a symmetric-key cipher that enjoys quantum resistance simply because Grover’s algorithm can only give a quadratic speedup against it, brute-force attacks remain gigantic in terms of resources and time. Conversely, asymmetric cryptographic algorithms like RSA and ECC, which underpin the majority of public key infrastructures, are fundamentally vulnerable to quantum attacks that can solve the hard mathematical problems they rely on for security.
Such a disparity offers a huge security gap. Information obtained today, even though it is in such excellent safekeeping now, might not be so in the future when sufficiently powerful quantum computers will be accessible, a scenario that is sometimes referred to as the “harvest now, decrypt later” threat. Both intelligence agencies and adversaries could be quietly hoarding and storing encrypted communications, confident that quantum technology will soon have the capability to decrypt this stockpile of sensitive information. The Snowden disclosures placed this threat in the limelight by revealing that the NSA catches and keeps vast amounts of global internet traffic, such as diplomatic cables, military orders, and personal communications. These repositories of encrypted data, unreadable as they stand now, are an unseen vulnerability; when Q-Day which is the onset of available, practical quantum computers that can defeat RSA and ECC, come around, confidentiality of decades’ worth of sensitive communications can be irretrievably lost.
Such a compromise would have apocalyptic consequences for national security and geopolitical stability, exposing classified negotiations, intelligence operations, and war plans to adversaries. Such a specter has compelled governments and security entities to accelerate the transition to post-quantum cryptography standards and explore quantum-resistant encryption schemes in an effort to safeguard the confidentiality and integrity of information in the era of quantum computing.
Arms Race Toward Post-Quantum Cryptography
In response, organizations like NIST are leading the development of post-quantum cryptographic standards, selecting algorithms believed to be quantum resistant. But migration is glacial. Implementing backfitting systems with new cryptographic foundations into billions of devices and services is a logistical nightmare. This is not a process of merely software updates but of hardware upgrades, re-certifications, interoperability testing, and compatibility testing with worldwide networks and critical infrastructure systems, all within a mode of minimizing downtime and security vulnerabilities.
Building such a large quantum computer that can factor RSA-2048 is an enormous task. It would require millions of logical qubits with very low error rates, it’s estimated. Today’s high-end quantum boxes have less than 100 operational qubits, and their error rates are too high to support complicated processes over a long period of time. However, with continued development of quantum correction methods, materials research, and qubit coherence times, specialists warn that effective quantum decryption capability may appear more quickly than the majority of organizations are prepared to deal with.
This convergence time frame, when old and new environments coexist, is where danger is most present. Attackers can use generative AI to look for these hybrid environments in which legacy encryption is employed, by botching the identification of old crypto implementations, producing targeted exploits en masse, and choreographing multi-step attacks that overwhelm conventional security monitoring and patching mechanisms.
Preparing for the Convergence
In order to be able to defend against this coming storm, the security strategy must evolve:
- Inventory Cryptographic Assets: Firms must take stock of where and how encryption is being used across their environments.
- Adopt Crypto-Agility: System needs to be designed so it can easily switch between encryption algorithms without full redesign.
- Quantum Test Threats: Use AI tools to stress-test quantum-like threats in encryption schemes.
Adopt PQC and Zero-Trust Models: Shift towards quantum-resistant cryptography and architectures with breach as the new default state.
In Summary
Quantum computing is not only a looming threat, it is a countdown to a new cryptographic arms race. Generative AI has already reshaped the cyber threat landscape, and in conjunction with quantum power, it is a force multiplier. It is a two-front challenge that requires more than incremental adjustment; it requires a change of cybersecurity paradigm.
Panic will not help us. Preparation will.
Abbreviations
RSA – Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman
ECC – Elliptic-Curve Cryptography
AES – Advanced Encryption Standard
TLS – Transport Layer Security
HTTPS – Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
ECDSA – Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm
NSA – National Security Agency
NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology
PQC – Post-Quantum Cryptography
References
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.07603
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/382853518_CryptoGenSec_A_Hybrid_Generative_AI_Algorithm_for_Dynamic_Cryptographic_Cyber_Defence
- https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5185525
- https://www.classiq.io/insights/shors-algorithm-explained
- https://www.theguardian.com/world/interactive/2013/nov/01/snowden-nsa-files-surveillance-revelations-decoded
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.00691
- https://secureframe.com/blog/generative-ai-cybersecurity
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/news/365531559/How-hackers-can-abuse-ChatGPT-to-create-malware
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.07228
- https://www.technologyreview.com/2019/05/30/65724/how-a-quantum-computer-could-break-2048-bit-rsa-encryption-in-8-hours/
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.10377
- https://thequantuminsider.com/2025/05/24/google-researcher-lowers-quantum-bar-to-crack-rsa-encryption/
- https://csrc.nist.gov/projects/post-quantum-cryptography
***Google’s Gemini is used in this post to paraphrase some sentences to add more context. ***
About Author:
Omkar Bhalekar is a senior network engineer and technology enthusiast specializing in Data center architecture, Manufacturing infrastructure, and Sustainable solutions with extensive experience in designing resilient industrial networks and building smart factories and AI data centers with scalable networks. He is also the author of the Book Autonomous and Predictive Networks: The future of Networking in the Age of AI and co-author of Quantum Ops – Bridging Quantum Computing & IT Operations. Omkar writes to simplify complex technical topics for engineers, researchers, and industry leaders.
Huawei launches CloudMatrix 384 AI System to rival Nvidia’s most advanced AI system
On Saturday, Huawei Technologies displayed an advanced AI computing system in China, as the Chinese technology giant seeks to capture market share in the country’s growing artificial intelligence sector. Huawei’s CloudMatrix 384 system made its first public debut at the World Artificial Intelligence Conference (WAIC), a three-day event in Shanghai where companies showcase their latest AI innovations, drawing a large crowd to the company’s booth.
The Huawei CloudMatrix 384 is a high-density AI computing system featuring 384 Huawei Ascend 910C chips, designed to rival Nvidia’s GB200 NVL72 (more below). The AI system employs a “supernode” architecture with high-speed internal chip interconnects. The system is built with optical links for low-latency, high-bandwidth communication. Huawei has also integrated the CloudMatrix 384 into its cloud platform. The system has drawn close attention from the global AI community since Huawei first announced it in April.
The CloudMatrix 384 resides on the super-node Ascend platform and uses high-speed bus interconnection capability, resulting in low latency linkage between 384 Ascend NPUs. Huawei says that “compared to traditional AI clusters that often stack servers, storage, network technology, and other resources, Huawei CloudMatrix has a super-organized setup. As a result, it also reduces the chance of facing failures at times of large-scale training.

Huawei staff at its WAIC booth declined to comment when asked to introduce the CloudMatrix 384 system. A spokesperson for Huawei did not respond to questions. However, Huawei says that “early reports revealed that the CloudMatrix 384 can offer 300 PFLOPs of dense BF16 computing. That’s double of Nvidia GB200 NVL72 AI tech system. It also excels in terms of memory capacity (3.6x) and bandwidth (2.1x).” Indeed, industry analysts view the CloudMatrix 384 as a direct competitor to Nvidia’s GB200 NVL72, the U.S. GPU chipmaker’s most advanced system-level product currently available in the market.
One industry expert has said the CloudMatrix 384 system rivals Nvidia’s most advanced offerings. Dylan Patel, founder of semiconductor research group SemiAnalysis, said in an April article that Huawei now had AI system capabilities that could beat Nvidia’s AI system. The CloudMatrix 384 incorporates 384 of Huawei’s latest 910C chips and outperforms Nvidia’s GB200 NVL72 on some metrics, which uses 72 B200 chips, according to SemiAnalysis. The performance stems from Huawei’s system design capabilities, which compensate for weaker individual chip performance through the use of more chips and system-level innovations, SemiAnalysis said.
Huawei has become widely regarded as China’s most promising domestic supplier of chips essential for AI development, even though the company faces U.S. export restrictions. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang told Bloomberg in May that Huawei had been “moving quite fast” and named the CloudMatrix as an example.
Huawei says the system uses “supernode” architecture that allows the chips to interconnect at super-high speeds and in June, Huawei Cloud CEO Zhang Pingan said the CloudMatrix 384 system was operational on Huawei’s cloud platform.
According to Huawei, the Ascend AI chip-based CloudMatrix 384 with three important benefits:
- Ultra-large bandwidth
- Ultra-Low Latency
- Ultra-Strong Performance
These three perks can help enterprises achieve better AI training as well as stable reasoning performance for models. They could further retain long-term reliability.
References:
https://www.huaweicentral.com/huawei-launches-cloudmatrix-384-ai-chip-cluster-against-nvidia-nvl72/
https://semianalysis.com/2025/04/16/huawei-ai-cloudmatrix-384-chinas-answer-to-nvidia-gb200-nvl72/
U.S. export controls on Nvidia H20 AI chips enables Huawei’s 910C GPU to be favored by AI tech giants in China
Huawei’s “FOUR NEW strategy” for carriers to be successful in AI era
FT: Nvidia invested $1bn in AI start-ups in 2024
Intel to spin off its Networking & Edge Group into a stand-alone business
As originally reported by CRN, Intel revealed its plan to spin off its Network and Edge Group in a memo addressed to customers and said it will seek outside investment for the business unit. Intel will be an anchor investor in the stand-alone business. The memo, seen by CRN, was authored by Sachin Katti, who has led the Network and Edge Group, abbreviated as NEX, since early 2023. He was given the extra role of chief technology and AI officer by Intel CEO Lip-Bu Tan in April to lead the chipmaker’s AI strategy. An Intel spokesperson confirmed the contents of the memo to CRN.
“We plan to establish key elements of our Networking and Communications business as a stand-alone company and we have begun the process of identifying strategic investors,” the representative said in a statement. “Like Altera, we will remain an anchor investor enabling us to benefit from future upside as we position the business for future growth,” the spokesperson added.
The NEX spin-off plan was announced to Intel customers and employees the same day the semiconductor giant revealed more changes under Tan’s leadership, including a 15% workforce reduction and a more conservative approach to its foundry business. “We are laser-focused on strengthening our core product portfolio and our AI roadmap to better serve customers,” Tan said in a statement.

In Katti’s memo, he said Intel “internally announced” on Thursday its plan to “establish its NEX business as a stand-alone company.” This will result in a “new, independent entity focused exclusively on delivering leading silicon solutions for critical communications, enterprise networking and ethernet connectivity infrastructure,” he added.
Katti did not give a timeline for when Intel could spin off NEX, which has been mainly focused on networking and communications products after the company moved its edge computing business to the Client Computing Group last September. Intel also shifted its integrated photonics solutions to the Data Center Group that same month. Similar to other businesses Intel has spun off, the company plans to maintain a stake in the stand-alone NEX company as it seeks out other investors, according to Katti. “While Intel will remain an anchor investor in the new company, we have begun the process of identifying additional strategic and capital partners to support the growth and development of the new company,” he wrote.
Katti said the move is “rooted in our commitment to serving” Intel’s customers better and promised that there will be “no change in service or the support” they rely on. He added that it will also help NEX “expand into new segments more effectively. Backed by Intel, this new, independent company will be positioned to accelerate its customer-facing strategy and product road map by innovating faster and investing in new offerings.”
Katti said he expects the transition to be “seamless” for Intel’s customers. “What we expect to change is our ability to operate with greater focus, speed and flexibility—all to better meet your needs,” he wrote.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Intel was rumored to be looking for a buyer for its Network and Edge group in May. This business produced $5.8 billion in revenue in 2024.
This strategy seems similar to the company’s decision to spin off RealSense, its former stereoscopic imaging technology business, earlier this month. Intel decided to spin RealSense out during former CEO Pat Gelsinger’s tenure and the company struck out on its own with $50 million in venture funding.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Shortly after Tan became Intel’s CEO in March, the leader made clear that he would seek to spin off businesses he considers not core to its strategy. Then in May, Reuters reported that the company was exploring a sale of the NEX business unit as part of that plan.
While Tan didn’t reference Intel’s decision to spin off NEX in the company’s Thursday earnings call, he discussed other actions it has taken to monetize “non-core assets,” including the sale of a portion of Intel’s stake in Mobileye earlier this month.
The company is also expected to complete its majority stake sale of the Altera programmable chip business to private equity firm Silver Lake by late September, according to Tan. Silver Lake will gain a 51 percent stake in the business while Intel will own the remaining 49%. “I will evaluate other opportunities as we continue to sharpen our focus around our core business and strategy,” Tan said on the earnings call.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In 2019, Apple acquired the majority of Intel’s smartphone modem business for $1 billion. This deal included approximately 2,200 Intel employees, intellectual property, equipment, leases, and over 17,000 wireless technology patents. The acquisition allowed Apple to accelerate its development of 5G modem technology for its iPhones, reducing reliance on third-party suppliers like Qualcomm. Intel, in turn, refocused its 5G efforts on areas like network infrastructure, PCs, and IoT devices
References:
https://www.crn.com/news/networking/2025/intel-reveals-plan-to-spin-off-networking-business-in-memo
https://techcrunch.com/2025/07/25/intel-is-spinning-off-its-network-and-edge-group/
https://www.lightreading.com/semiconductors/intel-sale-of-networks-sounds-like-an-ericsson-problem
CES 2025: Intel announces edge compute processors with AI inferencing capabilities
Massive layoffs and cost cutting will decimate Intel’s already tiny 5G network business
Nokia utilizes Intel technology to drive greater 5G SA core network energy savings
Nokia selects Intel’s Justin Hotard as new CEO to increase growth in IP networking and data center connections
T-Mobile’s growth trajectory increases: 5G FWA, Metronet acquisition and MVNO deals with Charter & Comcast
T-Mobile US is having a banner year. The “uncarrier” has again increased its annual earnings outlook, supported by the acquisition of fiber network operator Metronet and strong mobile customer growth in Q2. After gaining another 1.73 million postpaid customers in the quarter, T-Mobile now expects total postpaid net additions this year of 6.1-6.4 million, up from its previous guidance of 5.5-6.0 million. Postpaid customer growth strengthened compared to the first quarter and included 830,000 new phone customers and 902,000 other devices, while churn was little changed at 0.90 percent. Prepaid growth was more muted, with just 39,000 net additions. T-Mobile counted 132.778 million mobile customers at the end of June, up by around 1.9 million from a year ago. 5G broadband customers rose by 454,000 in the three months to 7.308 million.
In the three months to June, the company posted service revenues up 6% year-on-year to $17.4 billion, and core adjusted EBITDA (after leases) also was up 6% to $8.5 billion. The net profit rose 10 percent to a record $3.2 billion, and adjusted free cash flow increased 4% to $4.6 billion. Cash CAPEX rose 17.5 percent to $2.4 billion in Q2 and is still expected to reach $9.5 billion over the full year. The company also spent $2.5 billion buying back its own shares in Q2.
“T-Mobile crushed our own growth records with the best-ever total postpaid and postpaid phone nets in a Q2 in our history,” said Mike Sievert, CEO of T-Mobile. “T-Mobile is now America’s Best Network. When you combine that with the incredible value that we have always been famous for, it should surprise no one that customers are switching to the Un-carrier at a record pace. These durable advantages enabled us to once again translate customer growth into financial growth, with the industry’s best service revenue growth by a wide mile and record Q2 Adjusted Free Cash Flow.”

The new forecast includes the expected close of the Metronet acquisition on July 24th (today). The Metronet deal – crafted as a joint venture with KKR – will expand T-Mobile’s fiber reach by about 2 million homes across 17 states. It follows the completion of the deal with EQT to buy fiber operator Lumos.
T-Mobile plans to close the UScellular buyout and “become one team” on August 1st. “The combination gives us an expected 50% or more increase in capacity, in the combined footprint, and our site coverage will expand by a third from 9,000 to 12,000 sites,” CEO Mike Sievert said, noting that this will be in addition to 4,000 greenfield sites planned for this year, of which 1,000 have already been “lit up” to date.
T-Mobile stands at a critical juncture in its history, as it prepares to absorb more wireless and fiber assets, build a fiber network access business and enter a new market with the launch of T-Satellite in collaboration with Elon Musk’s Starlink. T-Mobile has already launched T-Mobile Fiber Home Internet and has forecast 100,000 fiber net customer adds in the second half of 2025 following the Lumos and Metronet deals. Sievert also reiterated that T-Mobile would continue to “keep an open mind” about any further fiber M&A.
T-Mobile is now the market’s fifth-largest ISP. Currently, the operator’s goals are to reach 12 million fixed wireless access subscribers by 2028 and to pass 12 million to 15 million households with fiber by the end of 2030, through both the fiber joint ventures and wholesale partnerships.
COO Srini Gopalan said on the earnings call, “We’re positioned to be a scale player in broadband,” claiming that the combined FWA and fiber targets would be equivalent to 40 million to 45 million homes passed as a broadband player, “and that’s before we go make other investments. As we’ve said before, we’re very open to looking at investments in fiber,” he added.
Separately, Charter Communications and Comcast announced Tuesday that they’ve cut a multi-year MVNO agreement with T-Mobile focused on their respective business customers. As the telecom industry growth rate is very low (real growth rate is barely positive), this additional source of revenue will be most welcome by the uncarrier. T-Mobile is expected to generate $850 million in incremental after tax income from its MVNO deals with Charter and Comcast. This revenue is included in the company’s updated guidance, but that guidance excludes the planned acquisition of UScellular assets.
T-Mobile Recognized as Network Leader by Third Parties:
- Ookla awarded T-Mobile as the only carrier in the country to win back-to-back Best Mobile Network awards in the largest, most-comprehensive tests of their kind, each leveraging half a billion real world data points on millions of devices measuring speed and experience
- Recognized by Opensignal for best Overall Experience for the fourth consecutive year and blew away the competition in best download speeds, nearly 200% faster than the nearest competitor, and upload speeds, approximately 65% faster than the nearest competitor
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/fttx/t-mobile-readies-for-the-next-stage-after-a-record-breaking-q2
Evercore: T-Mobile’s fiber business to boost revenue and achieve 40% penetration rate after 2 years
T-Mobile posts impressive wireless growth stats in 2Q-2024; fiber optic network acquisition binge to complement its FWA business
T-Mobile to acquire UScellular’s wireless operations in $4.4 billion deal
T-Mobile & EQT Joint Venture (JV) to acquire Lumos and build out T-Mobile Fiber footprint
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
ITU-R WP5D IMT 2030 Submission & Evaluation Guidelines vs 6G specs in 3GPP Release 20 & 21
Like previous generations of international mobile telecommunications (IMT) recommendations, ITU-R defines the 6G terrestrial radio access network requirements while 3GPP develops the standardized technology specifications that will be the project’s candidate to the ITU-R process. The target date for “Technology proposals for IMT-2030 RIT/SRITs” has been defined by ITU-R to be early 2029, and resulting specifications (i.e. full system definition) are to be submitted by mid-2030 at the latest. 3GPP contributions to ITU-R WP 5D are made via ATIS – its North American partner standards organization. That is effectively how IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT became standardized in ITU-R M.2150 (5G RIT/SRITs).
At it’s July 2025 meeting in Japan, ITU-R WP 5D generated an outline of a working document that, when completed, will specify the requirements, evaluation criteria and submission templates for the development of IMT-2030 recommendation(s) sometime in 2030. The structure of this working document is based on Report ITU-R M.2411, and the sections and contents of each section are to be further discussed. This meeting also discussed 16 contributions on evaluation guidelines for IMT-2030 and that working document was updated
Meanwhile, 3GPP has concluded that two 3GPP Releases are needed to specify 6G: Release 20 for Studies and Release 21 for the normative work that will produce 6G specs. Technical studies on the 6G radio interface and 6G core network architecture within the RAN and SA Working Group to start in June 2025. Release 21 will be the official start of normative 6G work.

Juan Montojo, Qualcomm’s vice president of technical standards, told Light Reading that all of today’s 3GPP 6G contributors are committed. “I can say I’m very confident that every player that comes to the 3GPP is a full believer in the value of having a single, global standard,” he told Light Reading. “I’ve not seen any exception, or any [other] indication.” 3GPP Release 20 lays an important foundation for 6G, said Montojo in a blog post.
Huawei had way more delegates attending 3GPP 5G sessions than any other company which raised concerns that the company might exert undue influence on the development of 3GPP 5G specs to its advantage. However, it has now become much harder for companies from a particular region to dominate proceedings, according to Montojo. “There are very recent decisions where working group officials cannot all come from the same region,” he explained. The system has also been changed so that companies with operations in multiple geographies, such as Huawei and Qualcomm, cannot claim to be from any region except that of their headquarters, Montojo said.
Future 6G Patents:
While the standardization process remains open to new entrants, the likelihood is that 6G’s ultimate patent owners will be drawn heavily from the ranks of today’s 5G network equipment vendors, chipmakers and smartphone companies that actively participate at 3GPP and ITU-R meetings. Several independent assessments forecast that Qualcomm and Huawei will likely remain at or near the top for the forthcoming 6G related patents,. In January, a LexisNexis study ranked Huawei first in 5G based on patent ownership and standards contributions. A separate LexisNexis ranking called the Patent Asset Index, which attempted to score organizations based on the value of their patents, gave the top spot to Qualcomm. In 2024, patent licensing accounted for only 14% of Qualcomm’s revenues but ~39% of its pre-tax earnings.
- Huawei (China): Huawei holds a significant share of 5G patents and is actively developing 6G technology, according to Williams IP Law. They are also a strong contributor to 5G technical standards.
- Qualcomm (US): Qualcomm is evolving its research from 4G and 5G towards 6G, holding a notable percentage of global 5G patents. They are also a major player in software-defined network solutions for 6G.
- Samsung (South Korea): Samsung is a prominent player in 5G patent ownership and is leading efforts in 6G standardization, including chairing the ITU-R 6G Vision Group. They are also investing heavily in terahertz communication technologies for 6G.
- Ericsson (Sweden): Ericsson is recognized for its strong 5G patent portfolio and contributions to technical standards. They are actively engaged in 6G research and development, including collaborations and investments in areas like network compute fabric and trustworthy systems.
- Nokia (Finland): Nokia is another key player in 5G patent ownership and a significant contributor to 5G technical standards. They identified key technologies for 6G early on and are actively testing and setting 6G standards through collaborations and research labs.
Higher Spectrum Bands for 6G:
Much of the industry’s recent attention has been captured by the upper 6GHz band and the 7GHz to 15GHz range. Unfortunately, signals do not travel as far or penetrate walls and other obstacles as effectively in these higher bands. To compensate, 6G’s active antenna systems are set to include four times as many elements as today’s most advanced 5G technologies, according to Montojo.
“It is part of the requirement in 3GPP to reduce the site grid of the existing C-band,” he said. “You would not want to require a densification beyond the levels that we currently have but can actually guarantee reuse of the site grid of the C-band into these higher bands.” Some analysts, however, remain dubious. A so-called massive MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) radio loaded with an even bigger number of antennas is likely to be expensive, meaning the deployment of 6G for mass-market mobile services in higher spectrum bands might not be economically viable.
6G Core Network (3GPP only- no ITU involvement):
“The best-case scenario, and I would say default scenario, is that 6G radio will be connected to 6G core as basically the standards-based approach,” said Montojo. “What 6G core will be is TBD, but there is a lot of desire from the operator community to have a 6G core that is an evolved 5G core with some level, to be defined, of backwards compatibility.”
Here’s an AI generated speculation on the 6G core network to be specified by 3GPP in Release 21:
- AI and Machine Learning (ML) will be fundamental to the 6G core, moving beyond supplementary roles to become an inherent part of the network’s design and operation.
- Every network function may be AI-powered, enabling advanced decision-making, predictive maintenance, and real-time optimization.
- 6G core will be designed to support the full lifecycle of AI components, including data collection, model training, validation, deployment, and performance monitoring.
- Network slicing will evolve further in 6G, enabling even more flexible, customized, and isolated network slices tailored to the diverse requirements of emerging applications.
- The 6G core will likely leverage a streamlined, unified, and future-proof exposure framework, potentially building on the 3GPP Common API Framework (CAPIF), to enable new value creation and monetization opportunities through network service exposure to third parties.
- The 6G core will be designed with a strong focus on energy efficiency and sustainability, considering the growing demands and environmental impact of network operations.
- It will need to be resilient to handle high mobility conditions of devices across various networks and administrative domains, including terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) like satellites & drones.
- Security and trustworthiness will be paramount, requiring a strong emphasis on authentication, data privacy, integrity, and operational resilience.
- The 6G core will likely incorporate quantum-safe cryptography to address the threat of quantum computing.
- While many in the industry favor an evolutionary path building upon the 5G core, some in the Chinese telecom ecosystem have advocated for a completely new 6G core network architecture.
- This suggests a potential for divergence in the early stages of 6G development, with discussions and debates within 3GPP shaping the ultimate architectural choices.
In summary, the 6G core network to be specified by 3GPP is anticipated to be a highly intelligent, flexible, and efficient platform, deeply integrated with AI/ML, supporting diverse services through enhanced network slicing and exposure, while addressing critical challenges in security, sustainability, and global connectivity.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-20
The SA1 road to 6G: https://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/sa1-6g-road
Introduction to 3GPP Release 19 and 6G Planning – Contains an introduction to the preparation for 6G in 3GPP: https://atis.org/webinars/introduction-to-3gpp-release-19-and-6g-planning/
Advancing 5G towards 6G, TSDSI Workshops (Jan 2023): https://www.3gpp.org/news-events/partner-news/tsdsi-workshops
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/qualcomm-is-optimistic-geopolitics-won-t-tear-6g-apart
ITU-R WP 5D reports on: IMT-2030 (“6G”) Minimum Technology Performance Requirements; Evaluation Criteria & Methodology
Highlights of 3GPP Stage 1 Workshop on IMT 2030 (6G) Use Cases
ITU-R: IMT-2030 (6G) Backgrounder and Envisioned Capabilities
ITU-R WP5D invites IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
IMT-2030 Technical Performance Requirements (TPR) from ITU-R WP5D
Draft new ITU-R recommendation (not yet approved): M.[IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND]
IMT Vision – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond
Gen AI eroding critical thinking skills; AI threatens more telecom job losses
Two alarming research studies this year have drawn attention to the damage that Gen AI agents like ChatGPT are doing to our brains:
The first study, published in February, by Microsoft and Carnegie Mellon University, surveyed 319 knowledge workers and concluded that “while GenAI can improve worker efficiency, it can inhibit critical engagement with work and can potentially lead to long-term overreliance on the tool and diminished skills for independent problem-solving.”
An MIT study divided participants into three essay-writing groups. One group had access to Gen AI and another to Internet search engines while the third group had access to neither. This “brain” group, as MIT’s researchers called it, outperformed the others on measures of cognitive ability. By contrast, participants in the group using a Gen AI large language model (LLM) did the worst. “Brain connectivity systematically scaled down with the amount of external support,” said the report’s authors.
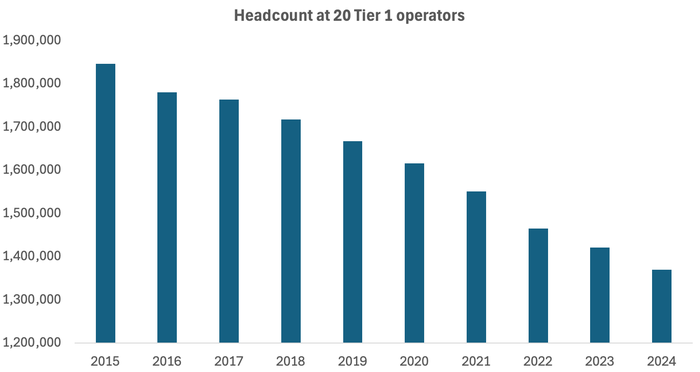
Across the 20 companies regularly tracked by Light Reading, headcount fell by 51,700 last year. Since 2015, it has dropped by more than 476,600, more than a quarter of the previous total.
Source: Light Reading
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Doing More with Less:
- In 2015, Verizon generated sales of $131.6 billion with a workforce of 177,700 employees. Last year, it made $134.8 billion with fewer than 100,000. Revenues per employee, accordingly, have risen from about $741,000 to more than $1.35 million over this period.
- AT&T made nearly $868,000 per employee last year, compared with less than $522,000 in 2015.
- Deutsche Telekom, buoyed by its T-Mobile US business, has grown its revenue per employee from about $356,000 to more than $677,000 over the same time period.
- Orange’s revenue per employee has risen from $298,000 to $368,000.
Significant workforce reductions have happened at all those companies, especially AT&T which finished last year with 141,000 employees – about half the number it had in 2015!
Not to be outdone, headcount at network equipment companies are also shrinking. Ericsson, Europe’s biggest 5G vendor, cut 6,000 jobs or 6% of its workforce last year and has slashed 13,000 jobs since 2023. Nokia’s headcount fell from 86,700 in 2023 to 75,600 at the end of last year. The latest message from Börje Ekholm, Ericsson’s CEO, is that AI will help the company operate with an even smaller workforce in future. “We also see and expect big benefits from the use of AI, and that is one reason why we expect restructuring costs to remain elevated during the year,” he said on this week’s earnings call with analysts.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Other Voices:
Light Reading’s Iain Morris wrote, “An erosion of brainpower and ceding of tasks to AI would entail a loss of control as people are taken out of the mix. If AI can substitute for a junior coder, as experts say it can, the entry-level job for programming will vanish with inevitable consequences for the entire profession. And as AI assumes responsibility for the jobs once done by humans, a shrinking pool of individuals will understand how networks function.
“If you can’t understand how the AI is making that decision, and why it is making that decision, we could end up with scenarios where when something goes wrong, we simply just can’t understand it,” said Nik Willetts, the CEO of a standards group called the TM Forum, during a recent conversation with Light Reading. “It is a bit of an extreme to just assume no one understands how it works,” he added. “It is a risk, though.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
AI spending is surging; companies accelerate AI adoption, but job cuts loom large
Verizon and AT&T cut 5,100 more jobs with a combined 214,350 fewer employees than 2015
Big Tech post strong earnings and revenue growth, but cuts jobs along with Telecom Vendors
Nokia (like Ericsson) announces fresh wave of job cuts; Ericsson lays off 240 more in China
Deutsche Telekom exec: AI poses massive challenges for telecom industry
Lack of wireless network operator consolidation & EU over-regulation weakened mobile network infrastructure investments
by John Strand of Strand Consult
Over-regulation in the European Union (EU) has had a negative impact on mobile network operator’s investment in both fixed and mobile infrastructure. Years ago, the EU identified a €100 billion investment gap in telecommunications. By 2025, this gap has reportedly doubled to €200 billion. Why did that happen?
The EU telecom market has a large number of operators, many of whom lack the subscriber base to generate sufficient returns on capital to justify large infrastructure investments. In contrast, countries like the US and China have a smaller number of larger operators, allowing for greater economies of scale and more investment per operator.
Regulatory Complexity and Costly Landscape: Overregulation and fragmented national rules create a complex and costly environment that stifles innovation and adds uncertainty for telecom companies, says the ECIPE. This impacts the ability to attract investment, according to the European Investment Bank.

Mobile operators around the world would like to merge four mobile networks in their respective nations into three. This would improve the business case for investment by eliminating duplicative administrations, improving spectrum synergies, and upgrading customers to better networks. Strand Consult has studied mobile industry consolidation since 2000 with the groundbreaking case of South Korea merging five operators into three and being first in the world to launch 3G. South Korea has remained at the forefront of mobile industry innovation, investment, and rollout ever since.
Unfortunately, during the period 2014 to 2024 European Union Vice President for Competition Margrethe Vestager had a crude view on in market consolidation. She did not understand that market consolidation could have a positive impact on the wireless infrastructure that citizens have access to.
The result is that this proceeding appears to overlook that critical lever—making it unlikely to achieve its core goal of boosting private-sector investment in broadband, fiber, and next-generation networks like 5G and 6G. While reducing compliance and reporting burdens is welcome, if the overarching regulatory model remains flawed, the fundamental barriers to investment will persist.
If you look at countries such as the United States, India and Brazil, the in-market consolidation has had a positive impact on the infrastructure to which citizens have access. Today, in a country like India, there is better 5G infrastructure than there is in large parts of Europe.
There is no requirement that EU Competition authorities justify their merger decisions empirically. Only occasionally are official post-mortems issued examining whether their decision was right. Generally, such reports conclude that prices remain low. However, in a world in which mobile prices are flat or falling anyway, a merger rejection is not needed to ensure competitive prices. Competing voice technologies like WhatsApp and Telegram drive down mobile prices, as do the competitive wireless offerings by fixed line providers.
Notably few, if any, competition authorities have studied how the length of merger review impacts network investment. When companies request permission to merge, it’s as if time stops. Operators must hold back on critical capital decisions while authorities assess the merger request.
In the United Kingdom, some analysts have blamed poor mobile coverage on new restrictions placed on Huawei and ZTE. This is nonsense. Operators across the EU have switched and upgraded to trusted equipment vendors without impacting coverage. See TDC Denmark, Telenor and Telia in Norway, T-Mobile in the Netherlands (Odido), and Proximus in Belgium.
The UK has had two recent mobile merger attempts: O2/Hutchison (2015-2016), which Vestager blocked in May 2016. The parties sued the Commission and won in 2020. However, the EC appealed and won in 2023. By that point, the issue was moot as the UK had left the Union. Most competition authorities don’t care that their review of transactions can take years, but markets do. Few companies can afford to tie up so much capital for so long, and fewer still can afford to challenge such decisions when they are unfavorable. Hence the Draghi report is on to something.
Vodafone and Hutchison have tried to merge since June 2023. Upon leaving the EU, UK merger decisions were restored to local authorities. The UK Competition and Markets Authority issued a favorable decision last year.
Slow merger review process is almost as bad as a merger rejection. Before firms announce a merger, they have done their internal due diligence, perhaps over 12-18 months. Once submitted, a merger review can take 12 to 24 months. If approved, the merger can take another 18 to 24 months to implement. This process can take from 36-66 months from start to finish. This period of planning, submission, review, merger, and implementation puts network investment on hold. The numbers speak for themselves just look at Ookla´s numbers for the UK.
T-Mobile – Sprint Merger:
In US, it’s a wonder that the merger of #3 T-Mobile and operator #4 Sprint happened at all. Depending on the asset and transfer, telecom merger review can include the Department of Justice, the Federal Communications Commission, the Attorneys General of the 50 states and other gatekeepers, all of whom want to extract concessions from the transaction. While there are fewer authorities in the case of Vodafone and Hutchison, it still takes time.
With the Sprint acquisition, T-Mobile wanted to create an operator to compete at scale with AT&T and Verizon. Today the merger is an unqualified success; customers have gained access to a better network, while T-Mobile today has grown the muscle to compete head on with AT&T and Verizon.
The military needs to get access to 5G SA:
In the telecommunications industry, there has been talk for many years about how mobile companies can gain access to new sources of revenue. 5G and not least 5G SA and 5G private networks have received a lot of attention. Conversely, there has not been much talk about what communication solutions the defense system needs in the future.
The war in Ukraine and shifting geopolitical realities have dramatically changed perspectives in recent years. There is now a fundamentally different understanding of why and how defense investments must be made. We live in a world in which Russia has invaded Ukraine; China counts Russia, North Korea, and Iran as allies; and these countries support Russia’s invasion of Ukraine
All countries across NATO are in the process of modernizing the defense systems, gigantic sums will be invested in new and advanced equipment. The shopping list is very long, on the other hand, all these new defense solutions have in common that they need access to modern communication solutions.
Modern militaries cannot function without secure, advanced, and integrated communications. 5G SA is the go-to solution for its speed, security, and adaptability. When it comes to the limited rollout of 5G SA in Europe, it has major implications for NATO´s access to access to a single national network free from untrusted vendors like Huawei and ZTE.
At the same time NATO does not use equipment from countries like China, Russia, North Korea, or Iran. Indeed, NATO’s procurement rules prohibit its contracting with communist countries. NATO would not purchase Chinese fighter jets from Chengdu Aircraft Corporation and Shenyang Aircraft Corporation, nor Huawei network equipment. The rationale is that ill-advised to acquire critical supplies from one’s adversary.
One of NATO´s key problems in Europe is a large number of operators have chosen to use equipment from suppliers like Huawei and ZTE there are unlikely to meet the security requirements from NATO. The qualification review and exercise which will be undertaken among the 32 NATO countries and many other nations around the world aligned with NATO, countries like Japan, the Philippines, and others. Countries which consider China a military partner (Pakistan, Belarus, and Cambodia) use Huawei and ZTE equipment.
The European Commission wants to transform telecom regulation in Europe:
The EU will have a public consultation regarding The Digital Networks Act (DNA). It is EU’s initiative to modernize telecom regulation by harmonizing rules, spurring infrastructure investment, and cutting red tape. It seeks to streamline spectrum licensing, network authorizations, and reporting across member states, while promoting sustainability and consumer protection. These are worthy aims—but past experience suggests the European Commission lacks the resolve, or the “DNA,” to turn vision into action. While Strand Consult supports the effort to bring telecom policy into the 21st century, the proposals arrive too little, too late to inspire investors, entrepreneurs, or citizens. Outside of standout digital performers like Denmark, Europe’s digital sector has long trailed the U.S., South Korea, Norway, and Switzerland by most competitive benchmarks.
At Strand Consult, we are concerned that the EU’s ongoing regulatory reforms will once again fail to address the fundamental challenges. Years ago, the EU identified a €100 billion investment gap in telecommunications. By 2025, this gap has reportedly doubled to €200 billion.
The EU’s record on AI is similarly illustrative. In 2018, the EU announced its ambition to lead in AI. However, by 2023, it had passed legislation that imposed significant constraints on AI development. In 2025, despite limited presence in the global AI landscape, the EU reiterated its ambition to lead, this time with an “AI Continent Action Plan.”
These historical examples suggest that the European Commission excels at producing regulations that slow technological development and deter investment. There are few—if any—notable technology firms that owe their success to EU regulatory frameworks. In contrast, we see a steady decline in key sectors like telecommunications and hardware, driven by regulatory missteps.
The European Commission has now pledged to transform telecom regulation in Europe. It may be too little, too late to address the deep-rooted challenges the EU itself has acknowledged and in part, created.
The bottom line is that The European figures from Ookla speak for themselves. The problem that they have uncovered is a problem that many of us have talked about a lot for many years.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Consolidation would renew European telecoms, says digital industry chief
https://www.eib.org/files/publications/thematic/accelerating_the_5g_transition_in_europe_en.pdf
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
John Strand is the CEO of Strand Consult. He founded Strand Consult in 1995. Strand Consult is an independent telecom consultancy known for its expert knowledge and many reports which help mobile operators and their shareholders navigate an increasing complex world. It has 170 mobile operators from around the world on its client list.
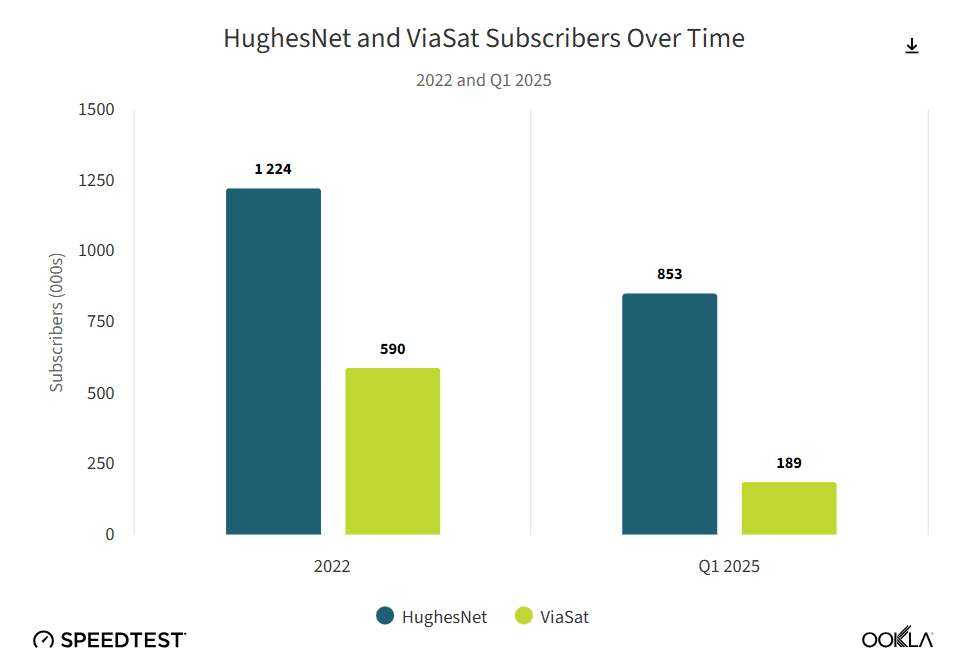
GEO satellite internet from HughesNet and Viasat can’t compete with LEO Starlink in speed or latency
GEO satellite internet providers provide reliable connectivity across large land masses, but their distance from Earth presents challenges to delivering low-latency and high-speed satellite Internet services. HughesNet and Viasat operate stationary satellites 22,000 miles above Earth, whereas LEO satellite operators such as Starlink have satellites orbiting a mere 340 miles above Earth. GEO satellites are also less ubiquitous than LEO satellites – GEO operators have fewer satellites in their constellations.
According to Ookla, GEO satellite providers HughesNet and Viasat can’t compete with Starlink when it comes to latency and download speeds. HughesNet and Viasat are best-known for providing consistent coverage across large land masses. But because they operate in geostationary orbit rather than low-Earth orbit (LEO) and because they have fewer satellites in their constellations, they struggle with speed limitations and latency, making it difficult for them to compete with LEO providers such as SpaceX’s Starlink.
HughesNet and Viasat have three satellites each in their fleet delivering fixed broadband service. Viasat plans to launch its Viasat-3 F2 satellite later this year and the Viasat-3 F3 in 2026. In addition, it owns a fleet of satellites from the company’s Inmarsat acquisition in May 2023 which are primarily used in maritime and mission-critical applications.
The challenges facing these GEO satellite providers have become more pronounced over the past few years, particularly as Starlink has moved aggressively into the U.S. market with promotions such as its recent offer to provide free equipment to new customers in states where it has excess capacity.
“HughesNet and Viasat are losing subscribers at a rapid rate thanks to competition from LEO satellite provider Starlink with its lower latency and faster download speeds,” according to Sue Marek, editorial director and analyst with Ookla.
Ookla’s Key Takeaways:
- HughesNet saw its median multi-server latency improve from 1019 milliseconds (ms) in Q1 2022 to 683 ms in Q1 2025. Viasat’s median latency increased slightly over that time period from 676 ms in Q1 2022 to 684 ms in Q1 2025. But neither are remotely close to matching Starlink with its median latency of just 45 ms in Q1 2025.
- HughesNet more than doubled its median download speeds from 20.87 Mbps in Q1 2022 to 47.79 Mbps in Q1 2025 while Viasat increased its median download speeds from 25.18 Mbps to 49.12 Mbps during that same time period.
- Upload speeds are another area where GEO satellite constellations struggle to compete with Starlink and other low-Earth orbit systems. HughesNet has increased its median upload speeds from 2.87 Mbps in Q1 2022 to 4.44 Mbps in Q1 2025 but that is still far lower than Starlink, which has a median upload speed of 14.84 Mbps in Q1 2025. Viasat saw its median upload speeds decline over that same time period from 3.06 Mbps in Q1 2022 to 1.08 Mbps in Q1 2025.
- HughesNet and Viasat are losing subscribers at a rapid rate thanks to competition from LEO satellite provider Starlink with its lower latency and faster download speeds.
Meanwhile, Starlink has nearly 8,000 satellites in low earth orbit (LEO) as part of its mega-constellation, according to Space.com. Starlink’s median download speeds, according to data from Ookla’s Speedtest users, almost doubled from 53.95 Mbit/s in Q3 2022 to 104.71 Mbit/s in Q1 2025. These latest average download speeds are also nearly twice that of HughesNet and Viasat.
In addition to network performance, Starlink has made strides in the U.S. market with promotions and distribution of free equipment to “new customers in states where it has excess capacity,” said Marek. In May, Starlink offered its Standard Kit, priced at $349, for free to consumers in select areas who agree to a one-year service commitment. But, “high demand” areas would still need to pay a one-time, upfront “demand surcharge” of $100, the company said.
Starlink is making headway teaming up with terrestrial service providers on direct-to-device (D2D) services, which connect smartphones and mobile devices directly to satellite networks in areas of spotty wireless service. Canada’s Rogers Communications launched a beta D2D service this week that initially supports text messaging via Starlink LEO satellites. The Canadian operator is also working with Lynk Global in a multi-vendor approach to D2D. Starlink announced this week that it has over 500,000 customers across Canada.
T-Mobile’s D2D service, T-Satellite with Starlink, will be commercially available later this month and will include SMS texting, MMS, picture messaging and short audio clips. In October, T-Satellite will add a data service to its Starlink-based satellite offering.
However, T-Mobile announced it would bump up the launch of T-Satellite to areas impacted by the recent flooding in central Texas. During a number of recent natural disasters, Starlink has offered free services and/or satellite equipment kits to affected communities.
Starlink is providing Mini Kits, which support 50 gigabyte and unlimited roaming data subscriptions, for search and rescue efforts in central Texas, in addition to one month of free service to customers in the areas impacted by recent flooding. In January, the satellite operator offered about a month of free service to new customers and a one-month service credit to existing customers in areas affected by the Los Angeles wildfires.
Starlink could be facing increasing competition from Project Kuiper, Amazon’s LEO satellite broadband service, as it ramps up deployment of a planned LEO constellation of over 3,000 satellites. However, Project Kuiper has fallen far behind schedule in meeting the FCC’s deadline of having more than 1,600 LEO satellites in orbit by the summer of 2026. Since its initial launch in April, Amazon only has a total of 78 satellites in orbit, according to CNBC. Meanwhile, Starlink has launched over 2,300 satellites in the past year alone.
References:
https://www.ookla.com/articles/hughesnet-viasat-performance-2025
https://www.space.com/space-exploration/launches-spacecraft/spacex-starlink-15-2-b1093-vsfs-ocisly
KDDI unveils AU Starlink direct-to-cell satellite service
Telstra selects SpaceX’s Starlink to bring Satellite-to-Mobile text messaging to its customers in Australia
One NZ launches commercial Satellite TXT service using Starlink LEO satellites
SpaceX launches first set of Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capabilities
FCC: More competition for Starlink; freeing up spectrum for satellite broadband service
U.S. BEAD overhaul to benefit Starlink/SpaceX at the expense of fiber broadband providers
Starlink’s Direct to Cell service for existing LTE phones “wherever you can see the sky”
ABI Research and CCS Insight: Strong growth for satellite to mobile device connectivity (messaging and broadband internet access)
AST SpaceMobile completes 1st ever LEO satellite voice call using AT&T spectrum and unmodified Samsung and Apple smartphones
PCMag Study: Starlink speed and latency top satellite Internet from Hughes and Viasat’s Exede