5G in China
China’s telecom industry rapid growth in 2025 eludes Nokia and Ericsson as sales collapse
According to a Chinese government update, “Telecommunications business volume and revenue grew steadily, mobile internet access traffic maintained rapid growth, and the construction of network infrastructure such as 5G, gigabit optical networks, and the Internet of Things was further promoted.”
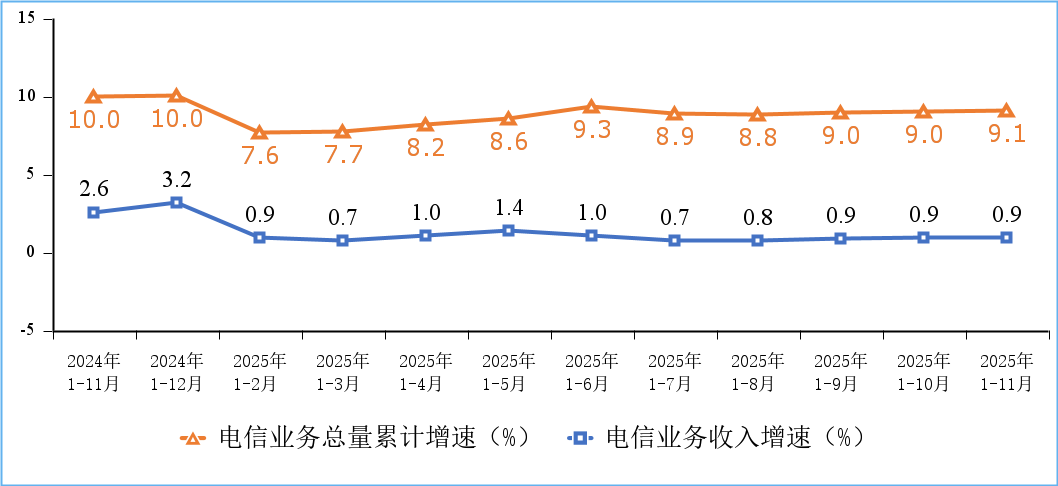
Figure 1. Cumulative growth rate of telecommunications service revenue and total telecommunications service volume
There were 4.83 million 5G base stations in service in China at the end of November 2025, an increase of 579,000 since late 2024 and 37.4% of the total number of mobile base stations in China. In one year, China claims to have added more 5G base stations than Europe has installed since the 5G technology was first put into service.
The total number of mobile phone users of the top four Chinese telcos (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, China Broadcasting Network) reached 1.828 billion, a net increase of 38.54 million from the end of last year. Among them, 5G mobile phone users reached 1.193 billion, a net increase of 179 million from the end of last year, accounting for 65.3% of all mobile phone users.
Meanwhile, the total number of fixed broadband internet access users of the three state owned telecom operators (China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom) reached 697 million, a net increase of 27.12 million from the end of last year. Among them, fixed broadband internet access users with access speeds of 100Mbps and above reached 664 million, accounting for 95.2% of the total users; fixed broadband internet access users with access speeds of 1000Mbps and above reached 239 million, a net increase of 32.52 million from the end of last year, accounting for 34.3% of the total users, an increase of 3.4 percentage points from the end of last year.
The construction of gigabit fiber optic broadband networks continues to advance. As of the end of November, the number of broadband internet access ports nationwide reached 1.25 billion, a net increase of 48.11 million compared to the end of last year. Among them, fiber optic access (FTTH/O) ports reached 1.21 billion, a net increase of 49.42 million compared to the end of last year, accounting for 96.8% of all broadband internet access ports. As of the end of November, the number of 10G PON ports with gigabit network service capabilities reached 31.34 million, a net increase of 3.133 million compared to the end of last year.
The penetration rate of gigabit and 5G users continued to increase across all regions. As of the end of November, the penetration rates of fixed broadband access users with speeds of 1000Mbps and above in the eastern, central, western, and northeastern regions were 34.6%, 33.8%, 35.8%, and 28.5%, respectively, representing increases of 3.4, 2.6, 4.1, and 4.9 percentage points compared to the end of last year; the penetration rates of 5G mobile phone users were 64.9%, 65.9%, 65.1%, and 65.9%, respectively, representing increases of 8.2, 8.7, 8.8, and 9.6 percentage points compared to the end of last year.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Light Reading reports that Ericsson and Nokia sales of networking equipment to China have collapsed.
Ericsson recently published earnings release for the final quarter of 2025 puts China revenues at just 3% of total sales last year. This would equate to revenues of 7.1 billion Swedish kronor (US$798 million). Based on a rounding range of 2.5% to 3.4%, it works out to be between SEK5.92 billion ($665 million) and SEK8.05 billion ($905 million) – down sharply compared with the SEK10.2 billion ($1.15 billion) Ericsson made in 2024, according to that year’s Ericsson annual report.
Nokia does not break out details of revenues from mainland China, instead lumping them together with the sales it generates in neighboring Hong Kong and Taiwan. But this “Greater China” business is in decline. Total annual revenues – which include Nokia’s sales of fixed, Internet Protocol and optical network products, as well as 5G – slumped from almost €2.2 billion ($2.6 billion) in 2019 to around €1.5 billion ($1.8 billion) in 2020, before creeping back up to nearly €1.6 billion ($1.9 billion) by 2022. Two years later, they had fallen to about €1.1 billion ($1.3 billion).
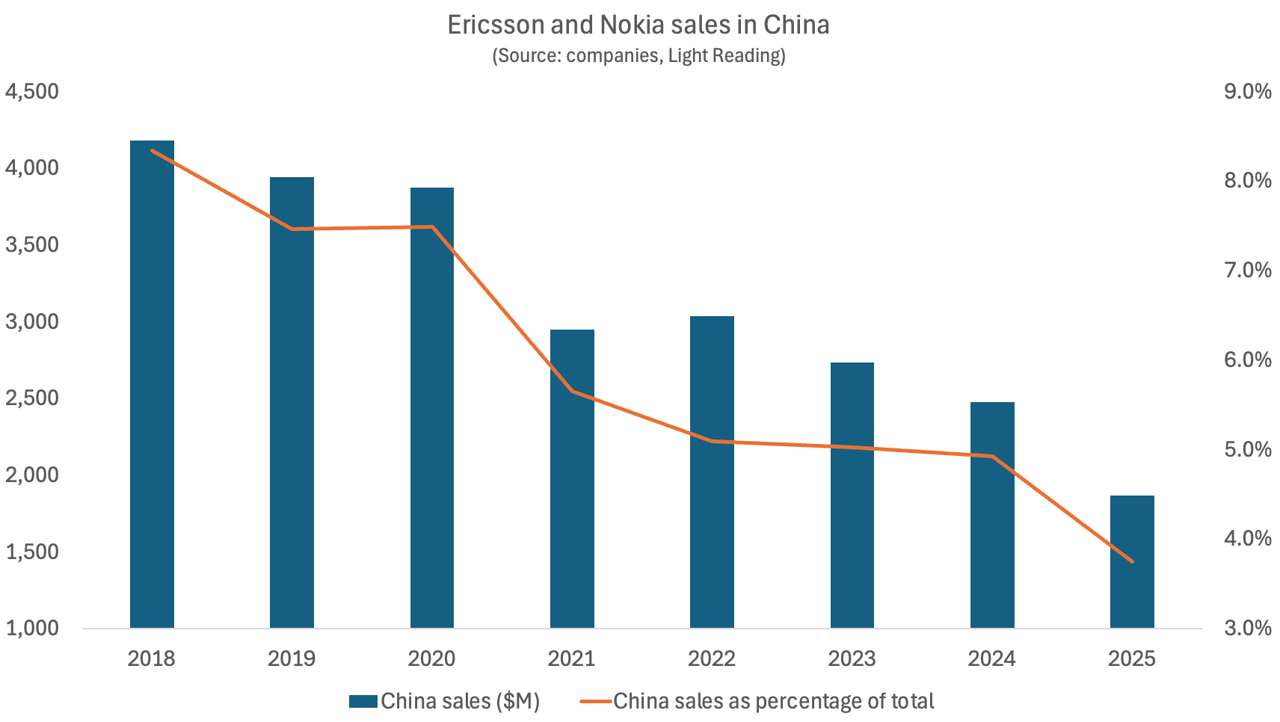
Bar Chart Credit: Light Reading
Nokia has recently indicated the complete disappearance of its China business. “Western suppliers, which is only us and Ericsson, have 3% market share now in China and it’s been coming down, and we are going to be excluded from China for national security reasons,” said Tommi Uitto, the former president of Nokia’s mobile networks business group, at a September press conference in Finland also attended by Justin Hotard, Nokia’s CEO. It implies China’s government is now treating the Nordic vendors in the same way Europe and the U.S. are banning Huawei and ZTE networking equipment.
Nokia revealed in its latest earnings update that Greater China revenues for 2025 had fallen by another 19%, to €913 million ($1.08 billion) – just 42% of what Nokia earned in the region seven years earlier. In the last few years, moreover, Nokia has cut more jobs in Greater China than in any other single region. While figures are not yet available for 2025, the Greater China headcount numbered 8,700 employees in 2024, down from 15,700 in 2019.
Ericsson has significantly reduced its China operations following greatly reduced 5G market share. In September 2021, the company consolidated three operator-specific customer units into a unified structure, impacting several hundred sales and delivery roles within its ~10,000-person local workforce. This followed the divestment of a Nanjing-based R&D center (approx. 650 employees), aligning with strategic pivots away from legacy 2G-4G technologies. The company’s total workforce in Northeast Asia plummeted from about 14,000 in mid-2021 to roughly 9,500 at the end of last year, according to Ericsson’s financial statements.
Exclusion from China would leave Ericsson and Nokia on the outside of the world’s most promising 6G market in 2030. That would intensify concern about a bifurcation of 6G into Western and Chinese variants of IMT 20230 RIT/SRIT standard and the 3GPP specified 6G core network.
References:
https://www.miit.gov.cn/gxsj/tjfx/txy/art/2025/art_7514154ec01c42ecbcb76057464652e4.html
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ericsson-and-nokia-see-their-sales-in-china-fall-off-a-cliff
China’s open source AI models to capture a larger share of 2026 global AI market
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
China ITU filing to put ~200K satellites in low earth orbit while FCC authorizes 7.5K additional Starlink LEO satellites
China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
At the 2024 Digital Technology Ecosystem Conference last week, China Telecom executives identified AI, 5G new calling and satellite-to-phone services as its handset priorities for 2025. The state-owned network operator, like other China telcos, is working with local manufacturers to build the devices it wants to sell through its channels.
China Telecom’s smartphone priorities align with its major corporate objectives. As China Telecom vice president Li Jun explained, devices are critical right across the business. “Terminals are an extension of the cloud network, a carrier of services, and a user interface,” he said.
China Telecom Vice President Li Jun
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
China Telecom Deputy General Manager Tang Ke, introduced the progress of China Telecom and its partners in AI and emerging terminal ecosystem cooperation. He stated that in 2024, China Telecom will achieve large-scale development of basic 5G services, with over 120 million new self-registered users annually and more than 140 models of phones supporting 5G messaging.
In terms of emerging businesses, leading domestic smartphone brands fully support direct satellite connection, with 20 models available and over 4 million units activated. Leading PC brands fully integrate Tianyi Cloud Computer, further enriching applications in work, education, life, and entertainment scenarios. Domestic phones fully support quantum secure calls, with over 50 million new self-registered users. Terminals fully support the upgrade to 800M, reaching over 100 million users. Besides phones to support direct-to-cell calling, it also hoped to develop low-cost positioning tech using Beidou and 5G location capabilities.
China Telecom continues to promote comprehensive AI upgrades of terminals, collaborating with partners to expand AI terminal categories and provide users with more diverse choices and higher-quality experiences. Tang Ke revealed that, at the main forum of the “2024 Digital Technology Ecosystem Conference,” China Telecom will release its first operator-customized AI phone.
Tang Ke emphasized that in the AI era, jointly building a collaborative and mutually promoting AI terminal ecosystem has become the inevitable path of industry development. Ecosystem participants must closely coordinate in technology, industry, and business to offer users the best AI experience. China Telecom will comprehensively advance technical collaboration, accelerating coordination from levels such as chips, large models, and intelligent agents, and promoting the construction of AI technology frameworks from both the device and cloud sides. The company will comprehensively push terminal AI upgrades, accelerating the AI development of wearables, healthcare, education, innovation, and industry terminals, based on key categories such as smartphones, cameras, cloud computers, and smart speakers.
Deputy Marketing Director Shao Yantao laid out the company’s device strategy for the year ahead. He said China Telecom’s business was based on networks, cloud-network integration and quantum security, with a focus on three technology directions – AI, 5G and satellites. With AI, it aims to carry out joint product development with OEM partners to build device-cloud capabilities and establish AI models. The state owned telco will pursue “domestic and foreign” projects in cloud-based AI mobile phones.
Besides smartphones, other AI-powered products next year would likely include door locks, speakers, glasses and watches, Shao said. The other big focus area is 5G new calling, based on new IMS DC (data channel) capabilities, with the aim of opening up new use cases like screen sharing and interactive games during a voice call.
China Telecom would develop its own open-source IMS DC SDK to support AI, payments, XR and other new functionality, Shao said. But he acknowledged the need to build cooperation across the industry ecosystem. The network operator and its partners would also collaborate on Voice over WiFI and 3CC carrier aggregation for 5G-Advanced devices, he added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) claims that China has built and activated over 4.1 million 5G base stations, with the 5G network continuously extending into rural areas, achieving “5G coverage in every township.” 5G has been integrated into 80 major categories of the national economy, with over 100,000 application cases accumulated. The breadth and depth of applications continue to expand, profoundly transforming lifestyles, production methods, and governance models.
The meeting emphasized the need to leverage the implementation of the “Sailing” Action Upgrade Plan for Large-scale 5G Applications as a means to vigorously promote the large-scale development of 5G applications, supporting new types of industrialization and the modernization of the information and communications industry, thereby laying a solid foundation for building a strong network nation and advancing Chinese-style modernization.
References:
https://www.c114.com.cn/news/22/c23811.html
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1279613.html
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1279469.html
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
China adds 20M “5G package” subscribers in July; 1H-2024 earnings gains outpace revenues for all 3 major China telcos
The number of 5G subscribers in China increased by a sizeable 20 million last month, according to new data from the country’s big three state owned network providers (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom). Of the three, China Mobile is still the only one to report actual customers using its 5G network; China Telecom and China Unicom are sticking to their 5G package subscribers metric, which essentially means customers signed up to a 5G plan, regardless of whether they use 5G network services (most continue to use 4G).
- China Mobile’s July net adds came in at 13.7 million, pushing its 5G customer base up to a colossal 528 million. China Mobile disclosed that it has 129 million customers using its 5G New Calling over high-definition video service reached 129 million, of which, smart application subscribers numbered 11.82 million.
- China Telecom added 3.1 million 5G package customers for a total of 340 million. They did not talk about 5G in their earnings report (more below).
- China Unicom added 2.9 million 5G package customers for a total of 279 million. China Unicom shared details of its 5G network build-out, pointing out that its 5G mid-band base stations numbered in excess of 1.31 million as of mid-year, while low-band sites reached 780,000.
For each of them, cloud and digital transformation (rather than 5G subs) drove topline growth, profit rose more than revenue and shareholder returns increased.
- China Mobile said net profit had improved 5.3% to RMB80.2 billion ($11.2 billion), outpacing revenue, which rose 3% to RMB546.7 billion ($76.6 billion).
- China Telecom, reported net earnings of 21.8 billion Chinese yuan (US3.1 billion), an 8.2% gain over last year, with revenue up 2.8% and service revenue 4.3% higher.
- China Unicom reported 11.3% higher net income of 13.8 billion ($1.93) on the back of a 2.9% lift in sales to RMB197.3 billion ($27.6 billion).
China Mobile says its digital transformation business grew 11% to RMB147.1 billion ($20.6 billion), accounting for 26% of all revenue. China Telecom reported digital industry sales of RMB73.7 billion ($10.3 billion), a 7% increase, and China Unicom said revenue grew 7% to RMB43.5 billion ($6.1 billion).

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo)
All three state owned telcos experienced double-digit growth in cloud services. China Telecom’s Tianyi Cloud grew revenue by 20% to RMB55 billion ($7.7 billion), while China Mobile Cloud hiked sales by 19% to RMB50 billion ($7 billion) and China Unicom grew 24% to RMB32 billion ($4.5 billion).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Silence is Golden?
There was a distinct lack of 5G commentary in China Telecom’s half year report; it is the last of the three to post numbers and did so alongside the publication of the market’s operational statistics for July. The telco shared its 5G package figures – it added almost 18 million in the first six months of 2024, incidentally – but made no other reference to the technology in a fairly wordy statement about its year-to-date performance. Instead, the operator focused on the progress of its digital transformation strategy, leaning heavily on the promise of artificial intelligence. Specifically, China Telecom is talking up what it terms AI+ – there’s always one – and the Xingchen large language model it launched at the back end of last year.
“The Company strengthened the integration and mutual promotion of capabilities in various fields, continuously enriched the Xingchen large model series product portfolio, empowered the intelligent transformation for thousands of industries, and supported enterprises to achieve costs reduction and efficiency enhancement,” it said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/china-added-20-million-5g-subs-last-month
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/cloud-digital-transformation-drive-chinese-telcos-h1-growth
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
ZTE reports H1-2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion (+2.9% YoY) and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion (+4.8% YoY)
China’s ZTE reported a 2.9% rise in total revenue to RMB62.5 billion ($8.76 billion), with net profit attributable to holders of ordinary shares of the Hong Kong listed company at RMB 5.73 billion, up 4.8% year-over-year (YoY). The biggest growth surge was in the corporate and government unit, which boosted revenue by 56% to RMB9.2 billion yuan ($1.29 billion), mainly through stronger server and storage sales. However, that was offset by a 68% hike in costs, depressing the gross margin by 5.7 points – a result of “changes in revenue mix,” the company said.
The company’s core carrier network equipment business declined 8.6% in the first half of 2024, holding back underlying earnings to 4.96 billion Chinese yuan (US$700 million) – a gain of just 1.1% over last year. The carrier unit, which accounted for 60% of the company’s total revenue, brought in RMB37 billion ($5.18 billion) in sales in H1, the company revealed in its stock exchange filing.
ZTE said demand from Chinese telecom operators had been constrained by “overall investment sentiments,” but it pointed to improved sales of indoor distribution, high-speed rail and metro networking equipment. ZTE’s consumer business, which includes mostly handsets and home routers, grew 14% to RMB16 billion ($2.24 billion). R&D spending remained flat at RMB12.7 billion ($1.78 billion).
_International_Software_Products.jpeg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
China’s domestic market accounted for 69% of total sales, roughly the same as last year. The biggest offshore growth region was Asia (excluding China), which grew 23%. ZTE said it is positioning itself as a “path-builder for the digital economy” and aimed to further expand its legacy connectivity business while growing its computing business. Its AI portfolio includes full-stack intelligent solutions, backed by key technologies such as high-speed networking, network computing and data processing.
ZTE is developing their own custom silicon. In the first half of 2024, the company continued to increase investment in advanced semiconductor process technologies, advanced architecture and seal packaging design, core intellectual properties and digitalized efficient development platform on the back of close to 30 years’ R&D build-up. We are an industry leader in terms of the ability to design the whole process of chip. On top of a solid foundation in the R&D of base-level technology for DICT chip, the Group has also constructed an ultra-efficient, green and intelligent full-stack computing network base pivoting on “data, computing and network” in line with developments in computing-network integration. The creation of a product regime meeting the core requirements of the diversified scenarios of “cloud, edge, terminal” has supported our ongoing leading position in terms of competitiveness.
ZTE has used its expertise in communication software and hardware development, engineering capabilities and industrialization to intensify its investment in computing power products and solutions. The company has launched a comprehensive suite of full-stack, full-scenario intelligent computing solutions, covering computing, networks, capabilities, intelligence and applications. These solutions include a full range of general computing servers, high-performance AI training servers, inference servers, liquid-cooled servers, distributed storage systems, high-end multi-control magnetic arrays, integrated training-inference machines and high-speed lossless switches.
In the terminal sector, ZTE has introduced the concept of “AI for All”, focusing on five core consumer scenarios: sports and health, audio and video entertainment, business and travel, home and education, and smart driving. The company has launched a full range of AI-driven terminal products, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and mobile internet devices, as part of its Full-Scenario Intelligent Ecosystem 3.0. This ecosystem promotes the integration of AI technology across mobile terminal devices, smart home devices, cloud computing and automotive electronics.
Moving forward, ZTE is dedicated to advancing its core technological innovations and accelerating its expansion into the “connectivity + computing + capability + intelligence” domain. The company will focus on strengthening its digital and intelligent infrastructure. By fostering open collaboration and pursuing diverse, mutually beneficial partnerships, ZTE aims to build a highly efficient and intelligent digital future with industry partners. The company said it expects: gradual adoption of 5G-Advanced, further rollout of 400G optical and construction of intelligent computing centers to drive the China’s telecom carrier market in the second half. Offshore, it will continue to focus on large national markets and big telcos for its wirelines and wireless product lines.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/zte-s-carrier-sales-slump-9-in-h1
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0816/2024081601602.pdf
ZTE reports H1 2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
Türk Telekom and ZTE trial 50G PON, but commercial deployment is not imminent
ZTE sees demand for fixed broadband and smart home solutions while 5G lags
China Unicom-Beijing and Huawei build “5.5G network” using 3 component carrier aggregation (3CC)
Huawei says it has deployed an “ultra large-scale 5.5G network” (there is no definition, 3GPP approved specs, or ITU-R recommendations/standards for 5.5G) operated by China Unicom in Beijing. The network uses three component carrier (3CC) aggregation to provide 70 percent coverage within Beijing’s 4th urban ring road. Huawei says China Unicom will offer comprehensive 5.5G service (again undefined) across stadiums, metro stations and tunnels, residential areas, scenic spots, business districts, and universities in key areas within the city’s 4th Ring Road and Beijing Municipal Administrative Center.
Editor’s Note: At the 5G Advanced Forum during MWC Shanghai 2023, Huawei’s President of ICT Products & Solutions, Yang Chaobin said, “In 2024, Huawei will launch a complete set of commercial 5.5G network equipment to be prepared for the commercial deployment of 5.5G.” Many believe that 5.5G is another name for 3GPP defined 5G Advanced, which is expected to bring new wireless technology innovations that improve speed, coverage, mobility, power efficiency, and sustainability. 3GPP Release 18 in 2024 is the beginning of 5G Advanced. The second and major release of 5G Advanced, Release 19, will be completed by the end of 2025. This release will focus on enhanced performance and the 5G system’s ability to meet commercial deployment needs.
In the Beijing Action Plan for Promoting 5G-A Technology Evolution and Application Innovation (2024-2026), Beijing Municipal Communications Administration hammered home the importance of Beijing’s role in pioneering 5.5G development. China Unicom Beijing is striving to do its part, with a large-scale 5.5G network demonstration at the beginning of 2024 followed by the ultra-large-scale commercial 5.5G network deployment of recent months, in helping Beijing become a “dual 10 Gbps” city that sets the bar for network construction, device development, and industry enablement. With the first version of 5.5G standards frozen in June 2024 and more than 20 commercial 5.5G devices now on the market, a mature 5.5G industry ecosystem is taking shape.

“Full 5.5G coverage” in Beijing’s core urban areas and the Beijing Municipal Administrative Center. Photo: Huawei
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In August 2022, China Unicom Beijing and Huawei commercialized the world’s largest 3.5 GHz 2CC network, which has brought 200 MHz 2CC coverage to more than 85% of Beijing’s urban area while providing comprehensive coverage for Beijing’s core areas and the Beijing Municipal Administrative Center. In 2023, this was further augmented when China Unicom Beijing and Huawei completed a 2.1 GHz band deployment targeting key urban scenarios. These deployments substantially improved the network experience of users in Beijing while laying a solid foundation for the future evolution to 5.5G, and this year’s 5.5G 3CC deployment paves the way for larger-scale 5.5G deployments in the coming years.
The ultra-large commercial 5.5G 3CC network consists of more than 4,000 base stations and covers well-known landmarks in Beijing, such as Wukesong, Capital Indoor Stadium, Workers’ Stadium, Beijing Railway Station, Guijie Street, Panjiayuan, and Beijing University of Technology. Featuring 5.5G capabilities, the network provides powerful support for services such as immersive video, UHD live streaming, and cloud gaming. In addition to consumer scenarios, China Unicom Beijing is proactively pursuing innovations in UHD shallow compression encoding, IoT, and XR split rendering, unlocking the full potential of 5.5G networks to enable various industries.
Yang Lifan, Deputy General Manager of China Unicom Beijing, remarked: “We have the world’s largest 200 MHz 5G network and it makes our 3CC carrier aggregation much easier. 5.5G 3CC coverage will be extended to match that of our current 200 MHz 5G network. With Huawei’s advanced technologies and our smart operations, we will provide users with a much better network experience.”
David Li, President of Huawei Wireless Network 5G<E TDD Product Line, said: “We are honored to mark a groundbreaking milestone in 5.5G network construction with China Unicom Beijing — large-scale commercial 5.5G. We will continue to innovate and provide more efficient, smarter, and greener network solutions, enabling users to enjoy a superior, smooth experience with 5.5G networks.”
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2024/7/5ga-beijing-3cc#
Huawei pushes 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) but there are no completed 3GPP specs or ITU-R standards!
https://blog.huawei.com/en/post/2023/11/14/5-5g-whats-in-a-number
5G Advanced offers opportunities for new revenue streams; 3GPP specs for 5G FWA?
Nokia, BT Group & Qualcomm achieve enhanced 5G SA downlink speeds using 5G Carrier Aggregation with 5 Component Carriers
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
Finland’s Elisa, Ericsson and Qualcomm test uplink carrier aggregation on 5G SA network
China’s mobile data consumption slumps; Apple’s market share shrinks-no longer among top 5 vendors
Mobile data demand is in a steep decline in China, the world’s largest 5G market by subscribers. China’s MIIT numbers released this week show per user data consumption (DOU) grew just 8.1% in the first half of the year. That compares to a 68% increase in 2019, the year that 5G licenses were issued. That fell to 13% in 2022 and 11% at end- 2023. Since then, there’s been a decrease in growth of nearly three percentage points in six months.
| Indicator name | unit | Cumulative from January to June | Year-on-year
Growth ( %) |
| Total volume of telecommunication business (at constant prices of the previous year) | 100 million yuan | 8992 | 11.1 |
| Operating income | 100 million yuan | 10712 | 2.8 |
| Including: Telecommunication business income | 100 million yuan | 8941 | 3.0 |
| Total call duration of fixed-line outgoing calls | 100 million minutes | 380 | -3.4 |
| Total mobile phone call duration | 100 million minutes | 10688 | -4.6 |
| Mobile SMS traffic | 100 million | 9407 | 0.5 |
| Mobile Internet access traffic | 100 million GB | 1604 | 12.6 |
| Average mobile Internet access traffic per household in the month (DOU) | GB/household · month | 18.15 | 8.1 |
| Note: 1. The duration of fixed-line outgoing calls and mobile phone calls includes the corresponding IP phone call duration.
2. Starting from February 2024, the 5G mobile Internet access traffic and the number of 5G mobile Internet users of China Radio and Television Network Group Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as China Radio and Television) will be included in the industry summary data, and the data for the same period last year will be adjusted synchronously. |
|||
“While China has rapidly rolled out 5G and continues to perform well vs other markets, there is a limit to the number of people in the market that will engage in advanced data services; the slowdown in traffic growth is an indication that we could be reaching that limit,” according to GSMA.
Commercial 5G standalone (SA) networks, now present in seven APAC countries (Australia, India, Japan, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, and Thailand), will help fuel this growth, alongside 5G Advanced, RedCap and AI, creating opportunities to launch new 5G applications and kick start a fresh round in 5G investments for enterprises and consumers.
The authors of the report, GSMA Intelligence, expect 5G to add almost $130 billion to the Asia Pacific economy in 2030, with the manufacturing industry forecast to benefit the most, driven by new 5G-enabed applications including smart factories, smart-grids, and IoT-enabled products. Financial services and public administration are also expected to be big beneficiaries, as they turn to 5G to digitally transform services and operations. To help support this growth the GSMA today launched the GSMA APAC Fintech Forum, a new community programme to unite the connected fintech and commerce sectors with Asia Pacific’s mobile network operators through new technologies.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Meanwhile, Apple’s smartphone market share in China shrank by two percentage points in the second quarter of 2024 and the company is no longer one of the top vendors, according to data from market research firm Canalys. The decline underscores the difficulties the U.S. tech giant faces in its third-largest market.
Huawei’s smartphone shipments surged 41 per cent year on year in the the quarter, bolstered by the launch of its new Pura 70 series in April. Chinese smartphone vendors held the top five spots in the second quarter.
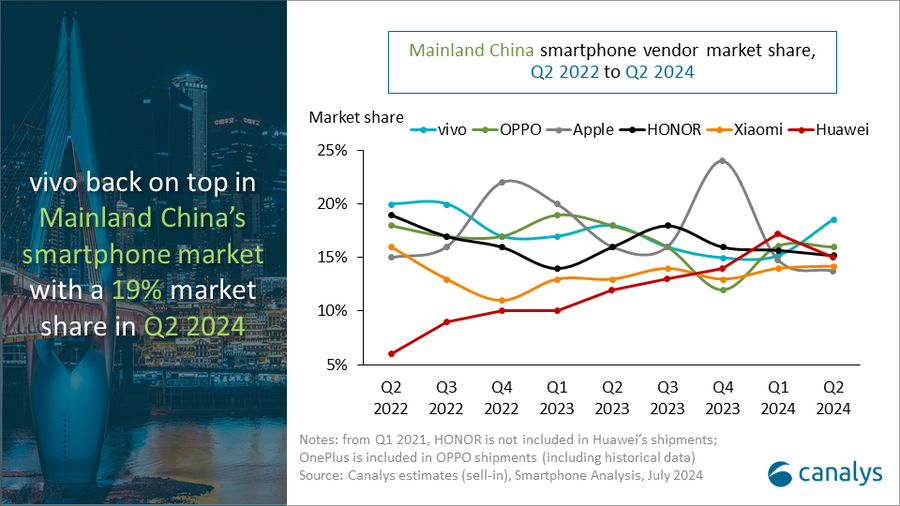
“It is the first quarter in history that domestic vendors dominate all the top five positions,” said Canalys Research Analyst Lucas Zhong. “Chinese vendors’ strategies for high-end products and their deep collaboration with local supply chains are starting to pay off in hardware and software features. HONOR’s latest Magic V3, which leverages GenAI, has significantly enhanced the user experience of foldable devices. Conversely, Apple is facing a bottleneck in mainland China. The vendor’s current channel strategy maintains a healthy inventory level and aims to stabilize retail prices and protect margins of channel partners. In the long term, the Chinese high-end market is ripe with opportunity. Local brands such as Huawei, HONOR, OPPO, and vivo are leading the way by incorporating technologies such as GenAI into products and services. Additionally, the localization of Apple’s Intelligence services in mainland China will be crucial in the next 12 months.”

People’s Republic of China (Mainland) smartphone shipments and annual growth
Canalys Smartphone Market Pulse: Q2 2024
|
Vendor |
Q2 2024 |
Q2 2024 |
Q2 2023 |
Q2 2023 |
Annual |
|
vivo |
13.1 |
19% |
11.4 |
18% |
15% |
|
OPPO |
11.3 |
16% |
11.4 |
18% |
-1% |
|
HONOR |
10.7 |
15% |
10.3 |
16% |
4% |
|
Huawei |
10.6 |
15% |
7.5 |
12% |
41% |
|
Xiaomi |
10.0 |
14% |
8.6 |
13% |
17% |
|
Others |
14.8 |
21% |
15.1 |
24% |
-2% |
|
Total |
70.5 |
100% |
64.3 |
100% |
10% |
|
Notes: from Q1 2021, HONOR is not included in Huawei’s shipments; OnePlus is included in OPPO shipments. |
|||||
References:
https://www.miit.gov.cn/gxsj/tjfx/txy/art/2024/art_e2f06366bb134479a40cf4cf86445b1e.html
https://canalys.com/newsroom/china-smartphone-market-Q2-2024
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/slowing-mobile-numbers-cast-doubt-on-gsma-s-buoyant-forecasts
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
China’s state sponsored 5G market is expected to add almost US$260 billion to its gross domestic product in 2030, with its 5G connections accounting for nearly a third of the worldwide total according to a recent GSMA report.
The report forecasts that more than half of Chinese mobile connections will be 5G by the end of 2024. 5G’s contribution to GDP in China is expected to reach almost $260 billion in 2030, which is 23% of the overall annual economic impact of mobile in China. Also by 2030, 5G connections in China will account for nearly a third of the global total, with 5G adoption in China reaching almost 90%, making it one of the leading markets globally.
The mobile industry contributed to 5.5% of China’s GDP last year, and in each of the coming years through 2030, nearly a quarter of that contribution will come from 5G – the highest echelon of current cellular technology – per the results of a study issued on Tuesday by the Group System for Mobile communications Association (GSMA).
Overall, the mobile market’s contribution to the Chinese economy will reach around US$1.1 trillion in 2030, GSMA said. Mats Granryd, Director General of the GSMA, said:
“It is great to see China, the world’s largest 5G market, commit so enthusiastically to the GSMA’s Open Gateway initiative to help drive the growth and maturity of the technology. As China surpasses 1 billion 5G connections this year, we expect to see further investment and potential in evolutions such as 5G-Advanced, 5G New Calling and 5G RedCap to improve user experience and unlock new revenue streams for operators.”

Photo credit: Shutterstock
GSMA’s Mobile Economy China 2024 report said the country’s entire mobile sector has so far provided a total of nearly 8 million jobs directly and indirectly, and generated US$110 billion in tax revenue in 2023 alone. According to that report:
- There are now 1.28 billion unique mobile subscribers in China – a penetration rate of 88%
- Mobile’s overall contribution to the Chinese economy in 2023 reached $970 billion, or 5.5% of GDP
- 5G is expected to reach 1.6bn connections in 2030, representing a third of the world’s total, and forecast to contribute $260 billion to China’s GDP
- An additional 290 million people in China now use mobile internet compared to eight years ago (2015), closing the country’s Usage Gap from 43% to just 16%
- Mobile data traffic in China is expected to quadruple by the end of the decade
China has the world’s most mobile phone users by a wide margin. As of the end of last year, there were 122.5 mobile phones for every 100 people, according to figures from the National Bureau of Statistics. The number of 5G base stations was nearly 3.38 million – a surge of 46% from a year earlier.
“China continues to set the pace for cutting-edge 5G technology standards,”the GSMA said, adding the country’s operators are “leading the way in the transition to 5G-advanced and 5G reduced capability networks. This is anticipated to kick-start a new round of 5G investment in 2024 and beyond.”
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
China Unicom & Huawei deploy 2.1 GHz 8T8R 5G network for high-speed railway in China
ABI Research: Telco transformation measured via patents and 3GPP contributions; 5G accelerating in China
Omdia: China’s 5G network co-sharing + cloud will create growth opportunities for Chinese service providers
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
ZTE, along with China Mobile’s Yunnan Branch, have created an accurate 3D model of the lineside infrastructure along the KunchuDali railway in China and used it to improve network performance. The companies introduced 5G-Advanced digital twin technology to build two core capabilities of digital site twinning and wireless channel twinning.
KunchuDali high-speed railway involves a large number of network planning challenges such as cross-bridge coverage, tunnel coverage, mountain-splitting area shielding, and abundant vegetation. It forms a vital segment of the China-Myanmar International Railway and the Trans-Asian Railway west line, connecting the key cities of Kunming, Chuxiong, Dali, and Lijiang in Yunnan Province. Serving as the backbone of the region’s transportation infrastructure, this route facilitates the daily movement of approximately 61,000 passengers, earning its reputation as the “golden tourism route.”
However, the railway’s construction and operation face formidable obstacles due to the rugged terrain characterized by fluctuating mountain ranges, perilous topography, and dense vegetation. Notably, a significant portion of the route traverses areas with a high concentration of bridges and tunnels, accounting for 64% of its total length. Moreover, many construction sites are situated in abnormal mountain zones, posing challenges to the efficiency and quality of surveying efforts.
China Mobile’s Yunnan Branch and ZTE introduced the 5G-Advanced digital twin technology to build two core capabilities of digital site twinning and wireless channel twinning. The 3D site twinning is achieved through UAV automatic flight control acquisition, thus implementing inspection survey of engineering parameters and AI identification of antenna assets, and guaranteeing engineering implementation quality with high efficiency and high quality.
- In June 2022, China Mobile unveiled a 6G network architecture which creates a virtual twin through digital means to realize a digital twin network architecture (DTN) with network closed-loop control and full lifecycle management; The service defines the end-to-end system to realize the full service system architecture (HSBA); In the group network, the Distributed Autonomous Network (DAN) with distributed, autonomous and self-contained features is implemented, which supports on-demand customization, plug and play and flexible deployment.
- ZTE’s RAN digital twin leverages digital twin, big data and artificial intelligence technologies, drastically enhancing network deployment and operation efficiency by minimizing resources and time needed for trial-and-error procedures of radio network deployment and optimization, making them more versatile, flexible and autonomous.
In addition, channel twinning is built in mountainous areas to achieve coverage prediction and optimization. The optimization elements required for mountainous areas, namely the azimuth, downtilt, power, and beam weights of antennas, are twinned and optimized beforehand. In this way, with the first-in-place construction of the pre-planning, the construction quality of the high-speed railway network is guaranteed faster and better, and the optimization period is shortened. Before the Spring Festival of 2024, the KunchuDali high-speed railway fully achieved the target of high-quality lines, with a coverage rate of 98.5% and a 5G download rate of more than 300Mbps. Compared with traditional planning and optimization methods, the KunchuDali high-speed railway saved more than RMB1.6 million and shortened the optimization period for nearly one month.
During the Spring Festival, China Mobile’s Yunnan Branch ensured an excellent internet experience for users with its high-quality high-speed railway network. The implementation of digital twin technology for high-speed railways enables efficient site surveys and coverage optimization to achieve higher efficiency and quality. This advancement fosters the deep integration of various industries with digital twin technology, paving the way for new industries, ecosystems, and operational modes. Furthermore, it lays a solid digital foundation for the future evolution towards 6G.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
According to Gartner, global digital twin revenues are expected to reach $183 billion by 2031. And when it comes to adoption, railway operators are at the forefront, using these virtual models to improve real-time asset management, reduce delays, and improve journey times.
In the UK, Transport for London (TfL) in 2022 announced plans to roll out a digital twin of the London Underground network so it can virtually monitor tracks and tunnels. Network Rail also offers a catalogue of training simulations built on digital twin technology.
According to an article in Mobility Innovators, bullet train operator JR East has deployed digital twins to monitor tracks, bridges and tunnels to enable predictive maintenance, while Hong Kong’s MTR (Mass Transit Railway) uses them to improve scheduling.
UAV automatic flight control acquisition implements 3D site twinning along the KunchuDali railway. Photo Credit: ZTE
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
ABOUT ZTE:
ZTE helps to connect the world with continuous innovation for a better future. The company provides innovative technologies and integrated solutions, and its portfolio spans all series of wireless, wireline, devices and professional telecommunications services. Serving over a quarter of the global population, ZTE is dedicated to creating a digital and intelligent ecosystem, and enabling connectivity and trust everywhere. ZTE is listed on both the Hong Kong and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges. www.zte.com.cn/global
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/china-mobile-zte-revolutionize-high-speed-railway-with-5g-a-digital-twin.html
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/solutions_latest/5g-advanced/digital_twin.html
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/china-mobile-zte-use-digital-twin-to-improve-lineside-5g
China Mobile unveils 6G architecture with a digital twin network (DTN) concept
Huawei pushes 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) but there are no completed 3GPP specs or ITU-R standards!
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
China Mobile increased revenue 7.7% to 1.009 trillion Chinese yuan (US$140 billion) in 2023, with earnings up 3.7%. China Mobile’s biggest growth drivers were cloud computing and storage, which grew 66% to RMB83 billion ($11.5 billion), and 5G enterprise, which hiked sales by 30% to RMB47.5 billion ($6.6 billion). It also revealed it had earned RMB5.4 billion ($750 million) in 5G private networking revenue, up 113%. Its “new business” segment, which covers international, investments and applications, expanded 28% to RMB49.3 billion ($6.9 billion).
China Mobile’s capital spending was RMB180.3 billion ($25 billion), a 2.6% decrease from 2022. It gave no guidance for 2024, but CAPEX will surely decrease in 2024 and coming years due to a recent change to retain existing 5G network equipment longer than previously planned.
China Mobile’s Board on Thursday voted to extend the depreciable life of its 5G assets from seven years to ten years, based on the belief that much of its 5G network equipment will continue to be deployed after the arrival of 6G (IMT 2030) at the end of this decade (or later). The state owned telco said it expects “that 5G network investments shall be reused in 6G network infrastructure to the maximum extent, and therefore it is expected that 5G/6G networks will coexist after commercialization of 6G and 5G equipment will have a relatively long life cycle.”
The immediate effect of this decision will be to cut a massive 18 billion yuan ($2.5 billion) out of China Mobile’s depreciation bill this year. It’s the first time any major telco has formally declared that not only is it reluctant to spend on new 6G equipment, but that it also intends to keep its 5G assets as long as possible. That sends a clear warning that in the aftermath of the 5G capex binge, telcos have little appetite for big technology bets without a clear ROI.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Meanwhile, China Unicom boosted net profit by 11.8% and topline revenue by 5.0%. Unicom said it had grown its cloud business by 42% to RMB51 billion ($7.1 billion), while its new computing and digital services business recorded RMB75 billion ($10.4 billion) in sales, up 13%.
“With 5G network coverage nearing completion, the Company’s investment focus is shifting from stable Connectivity and Communications (CC) business to high-growth Computing and Digital Smart Applications (CDSA) business. CAPEX was RMB73.9 billion in 2023. Network investment saw an inflection point.”
In 2023, Connectivity and Communications (CC) business, which encompasses mobile connectivity, broadband connectivity, TV connectivity, leased line connectivity, communications services as well as information services, achieved revenue of RMB244.6 billion. It contributed to three quarters of the service revenue of CC and CDSA combined. The Company’s connectivity scale further expanded, with the total number of CC subscribers exceeding one billion, representing an increase of about 140 million from the end of 2022.
China Unicom capital spending was flat at RMB73.9 billion ($10.3 billion), and it revealed it will slash CAPEX this year by RMB8.9 billion ($1.2 billion) or 12%.

References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/china-mobile-unicom-raise-red-flags-on-network-spend
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0321/2024032100246.pdf
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0319/2024031900241.pdf
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China Mobile verifies optimized 5G algorithm based on universal quantum computer
Omdia: China Mobile tops 2023 digital strategy benchmark as telcos develop new services
China Unicom & Huawei deploy 2.1 GHz 8T8R 5G network for high-speed railway in China
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China’s three state owned telecom operators have announced their subscriber totals for the month of December and for all of 2023. China’ Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) said the big three had a combined net increase of approximately 24.82M 5G package subscribers in China, boosting their combined 5G package subscriber base to nearly 1.373B.
As of the end of December, 5G package subscribers accounted for 80.2% and 78.1% of China Mobile’s and China Telecom’s total mobile subscriber bases, respectively.
C114.net reported that 3.377 million 5G base stations have been built, constituting 28.5 percent of the total mobile base stations. There are 23.02 million ports with gigabit network service capabilities. More than 80% of administrative villages nationwide now have 5G connectivity, telecoms portal.
The foundation of the Internet of Things (IoT) is constantly being consolidated, with mobile IoT terminal users accounting for 57.5% of the total number of mobile network terminal connections. Technological industry innovation and development, the commercial deployment of 5G customized base stations and 5G lightweight technology, and the launch of the world’s first satellite communication smartphone, 6G, quantum communication, artificial intelligence and other innovative capabilities have significantly improved.
- China Mobile ended last year with 794.5 million subscribers to its 5G package (contract), while its total mobile subscriber base reached 991 million.
- China Telecom had a total of 407.7 million mobile users, of which 318.66 million had signed up to a 5G package (up by 50.7 million during 2023).
- China Unicom’s 5G package subscriber total hit 259.6 million by the end of last year, though disclosure on total mobile subscribers has not been provided. China Unicom also reported that there were 8,563 “virtual 5G industry private network” subscriber for the month of December which was an increase of 554 month-on-month and up 4,758 since the end of 2022.
Mobile Subscriber Stats for China’s Three Main Carriers (Unit: Millions)
| Operator | December 2023 Month-end Total |
% of Combined Installed 5G Sub Base |
December 2023 Net Change |
Net Change Since Prior Year-End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China Mobile | 991.00 | 0.05 | 15.99 | |
| 5G Package Subs | 794.50 | 57.87% | 15.70 | 180.50 |
| China Telecom | 407.77 | 0.54 | 16.59 | |
| 5G Package Subs | 318.66 | 23.21% | 4.03 | 50.70 |
| China Unicom | Not Available | |||
| 5G Package Subs | 259.64 | 18.91% | 5.08 | 46.91 |
China’s fourth 5G telecom network operator, China Broadnet, saw its 5G user base surpass 20 mln on October 19, the company revealed at the 2023 World 5G Convention held in Zhengzhou from December 5-7. Since that time, however, China Broadnet has not publicly released any updated 5G subscriber statistics.
Broadnet officially launched 5G network services just 19 months ago, on June 27, 2022. Because Broadnet is not yet reporting its 5G subscriber totals on a regular, monthly basis, Marbridge is not yet integrating its totals with those of China’s three more established telecom operators above.
Cautionary Note:
The Chinese telecom operators specifically report numbers for 5G packages, rather than citing 5G service users or connections, as while customers may have signed up for a 5G service package offer, that doesn’t necessarily mean they have a 5G-enabled device that enables them to hook up to their network operator’s 5G network, or indeed that their service provider is offering 5G services in their area just yet.

In addition to the growing 5G market in China, the fixed broadband segment is also very large. China Mobile had a total of 298 million wireline broadband customers at the end of December 2023, and throughout the year it added a total of 26 million fixed customers. China Telecom had 190 million fixed broadband subscribers by the year end, having added a total of 9.26 million wireline broadband users in 2023. China Unicom’s operational statistics for the last month of 2023 did not provide a breakdown of broadband customers.
References:
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1253372.html




