Telecom in India
India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for 5G equipment attracts Nokia & Ericsson
Nokia and Ericsson said India’s production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme [1.] for design-led 5G manufacturing will position India as a global manufacturing hub and allow them to deepen their manufacturing capabilities in the country.
Note 1. PLI is the sum of India government incentives that are directly linked to manufacturing performance. The more goods companies manufacture in India the better incentives they will get. The incentives are of diverse types: subsidies, monetary benefits, etc.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Nokia said it is exploring opportunities to manufacture more products in India in a cost-competitive manner to serve both the local and the global market. Nokia’s India spokesperson said the company was on track to fulfil its investment and production commitments under the existing PLI scheme for telecom equipment.
Swedish telecom equipment vendor Ericsson, in a separate statement, said 5G spectrum auction with 100% fiberization (backhaul) with public-private partnership (PPP) model by 2025 will help bridge the digital divide for an inclusive development of the nation in-line with the ‘Digital India’ vision.
“Design-led initiatives for 5G under the PLI scheme and 5% of USOF for R&D purposes will strengthen the ‘Make in India’ initiative, and contribute to making India a global manufacturing hub,” said Nitin Bansal, managing director for India at Ericsson.
Ericsson, along with Nokia, Akashastha Technologies, HFCL, Foxconn, Coral Telecom, VVDN Technologies, Dixon Technologies, Tejas Networks and GS India, were selected for the original PLI scheme. India’s Department of Telecommunications (DoT) approved 31 proposals in 2021 entailing investments of INR33.5 billion ($447.3 million) over the next four years.
“The scheme for design-led manufacturing to be launched for the 5G ecosystem as part of PLI will be a boost to the overall telecom and electronic sectors. It will also provide and promote research and development of technology and solutions and will enable affordable broadband and mobile communication,” says Sanjay Gupta, vice president and India managing director, NXP Semiconductors.
Some media reports suggest that it is possible that the funds for this scheme may come from the ongoing PLI scheme for the telecom sector.
The scheme is in keeping with the government’s keenness to position India as a telecom manufacturing destination with a growing emphasis on self-reliance and the domestic manufacturing ecosystem.
Chinese gear makers Huawei and ZTE are yet to receive trusted source approval from the National Cyber Security Coordinator (NCSC), which means the space is open to Indian manufacturers.
It’s possible that the government may mandate the Indian service providers to procure a certain percentage of their requirement from the Indian vendors only. The PLI scheme is timely, with the announcement that the 5G spectrum auction will be held in 2022.
Service providers are in the midst of conducting 5G trials, and will be investing heavily in 2022 to build networks. 5G capex is likely to increase significantly over the next few years – hopefully helping Indian manufacturers grab some share of the pie.

India creates 6G Technology Innovation Group without resolving crucial telecom issues
Having failed to hold the long promised 5G spectrum auction in 2021, India’s Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has authorized a 6G Technology Innovation Group (TIG) with the objective to co-create and participate in the development of the 6G technology ecosystem.
In a notification issued dated December 30, the Department mandated immediate deliverables by March 31, 2022 that included mapping of 6G activities and capabilities worldwide, and a white paper on India’s competencies. including research and pre-standardisation activities.
The new task groups are headed by Bhaskar Ramamurthy, director, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)-Chennai, Abhay Karandikar, director, IIT-Kanpur, Bharadwaj Amrutur, director, Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore, Kiran Kumar Kuchi, director, IIT-Hyderabad on multi platform for next generation networks, spectrum policy, multi-disciplinary innovative solutions, and devices respectively.
The 6G TIG task force includes members from the government, academia, industry associations, and TSDSI (Telecom Standards Development Society of India).
“With a strong emphasis on technology commercialization, the work will encompass the full lifecycle of research and development, manufacturing, pre-standardisation and market readiness,” the department said in its memorandum.
“This would be necessary to prepare India’s manufacturing and services ecosystem to capitalize on 6G opportunity,” DoT added.
Last month, the government formed an innovation group headed by K Rajaraman, secretary, DoT to create a vision to develop a 6G roadmap in the country.
Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea said that an early start into local 6G development will result in IP or intellectual property creation for the Indian telecom ecosystem. They said that there is a need for the Indian telecom industry and academia to join forces with the telecom department and contribute towards the 6G standard building in cooperation with 3GPP.
“…getting into the journey of 6G is absolutely the right time. India has the brainpower which contributes to the R&D. We should bring telcos, the academia, all the brain we have in our very high standard academic institutions and the Indian government together for the development of IPR for technologies…we can actually really start building 6G standards, and in these 6G standards, we cooperate with 3GPP,” Randeep Sekhon, CTO of Bharti AIrtel told ET.
…………………………………………………………….
India’s 5G efforts to date have been restricted to 5G NSA trials. The DoT awarded spectrum to the telcos for six months to conduct 5G trials and develop India-specific use cases. That time period was later extended for another six months at the telcos’ request. The big three India wireless service providers, Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea, have conducted several 5G tests over the last few months.
The Indian government has announced that the repeatedly postponed 5G spectrum auction will be held in the April-May 2022 timeframe. As per media reports, the target is to launch 5G on August 15th, India’s Independence Day.
Typically, India lags behind developed countries in the adoption of new technologies. The much delayed 5G auction launch in 2022 puts it way behind other countries.
This 6G initiative is truly remarkable since India has not sorted out any of the critical 5G and satellite internet issues it has faced. Those include:
- 5G spectrum auction with fair prices to participants.
- Acceptance of the 5Gi standard within ITU-R M.2150.
- Reliance Jio’s boast of developing and deploying indigenous (made in India) 5G technology.
- Indian telco cooperation with hyperscale cloud service providers for 5G core network, Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) and virtual RANs.
- Satellite internet services: Starlink was in the news for pre-booking clients even when it is yet to acquire required approvals from the DoT. The company has now suspended the sale of satellite services until it gets the license. Both SpaceX and OneWeb are likely to launch satellite services in the country in 2022.
- Spectrum allocation: A major controversy in this segment is the conflict between the three major telcos and satellite internet service providers regarding the spectrum. The telcos are asking for a level playing field with the satellite providers, which means that they should bid for spectrum, just like telcos. However, the satellite players disagree with this.
References:
https://smefutures.com/india-prepares-to-take-lead-in-6g-technology/
https://www.fiercewireless.com/wireless/indian-telecom-2022-faces-5g-auctions-satellite-competition
Reliance Jio trials connected robotics on its “indigenously developed” 5G network
Aayush Bhatnagar, SVP, of Reliance Jio said in a Linkedin post Friday:
Jio has successfully performed trials of Connected Robotics over its indigenously developed 5G RAN and 5G SA core network. This underlines the true potential of 5G Standalone networks in realizing real-life industrial use cases.
Jio 5G Robotics have implemented a wide canvas of services – from heavy lifting and logistics at manufacturing warehouses, to healthcare robots assisting medical staff – from remote ultrasound enablement to industrial automation robots.
This development opens up exciting possibilities for value creation in Industry 4.0, with direct relevance to businesses and the economy.
Jio’s Bhatnagar has said India’s top telco has undertaken use case trials such as Voice and Messaging over 5G NR (VoNR) using its own home grown 5G RAN and Core network, which it plans to export or license once its 5G technology is tested and deployed throughout India. Of course, that can’t happen till after the repeatedly delayed 5G spectrum auction (now scheduled for April or May 2022 if not delayed yet again).
Earlier this month, Jio reported it successfully trialed connected drones on its indigenous 5G network, the telco’s senior vice president Aayush Bhatnagar said. The trial involved a precision command and control of drones over 5G using a fleet management system running in the Cloud to perform tasks such as image recognition, track-and-trace, discrete payload pickup, and delivery, drone route sorties, video imagery, real-time drone control, and other applications, the executive added.
“5G-connected drones will enable future use cases across industries and enterprises,” Bhatnagar said. “At Jio, we have taken another major stride in “Making 5G real” – beyond speed tests and demos. Jio has successfully conducted trials of connected drones on its indigenous 5G network,” Bhatnagar said in a Linkedin post.
Jio has not disclosed all the other companies are helping to design, develop and test their indigenous 5G RAN and Core network. In July, Intel said that it is helping Reliance Jio make the transition from 4G to 5G as part of their 5G infrastructure deal. Intel and Jio are collaborating in the areas of 5G radio, core, cloud, edge and artificial intelligence.
“…our collaboration spans those areas, and it’s co-innovation. So, we have got our engineering and business unit teams working closely with Reliance Jio in those areas. And we are committed towards helping customers and partners like Reliance Jio to make the transition from 4G to 5G,” Prakash Mallya, vice president and Managing Director of sales, marketing and communications group at Intel told Economic Times.
Intel’s investment arm, Intel Capital, had in 2020 invested Rs 1,894.50 crore to buy a 0.39% equity stake in Jio Platforms.
While speaking at Reliance Industries Ltd’s 44th AGM, RIL Chairman Mukesh Ambani said that:
“Jio’s engineers have developed a 100 per cent home-grown and comprehensive 5G solution that is fully cloud native, software defined, and digitally managed. Jio’s ‘Made in India‘ solution is complete and globally competitive.”
Ambani also said that his company has achieved 1Gbps download speed on its 5G trial network.
As for Jio’s 5G competitors:
- Bharti Airtel previously said that it was collaborating with global consulting firm Accenture, along with Amazon Web Service (AWS), Cisco, Ericsson, Google Cloud, Nokia, Tata Consultancy, and unnamed others to demonstrate enterprise-grade use cases using high-speed, low-latency 5G networks.
- Airtel has been working on the 5 G-based solutions with Apollo Hospitals, Flipkart, and other manufacturing companies.
- Vodafone Idea (VI) has partnered with Nokia and Ericsson to work on several 5 G-powered applications, including enhanced mobile broadband (emBB), ultra-reliable low latency communications (uRLLC), multi-access edge computing (MEC), and AR/VR.
5G trials began earlier this year in May and in June:
- Jio reported achieving speeds over 1Gbps during the trial.
- Airtel also reported achieving over 1Gbps peak speed during its 5G network trial.
- VI claims to achieve a peak 5G speed of 3.7Gbps on the mmWave spectrum during the network trials in Pune.
Last month, India’s Department of Telecom (DoT) granted a six-month extension for 5G trials in India to telecom operators, including Jio, Airtel, and VI, upon their request. The telecom operators are currently conducting 5G trials in various parts of the country and have achieved tremendous results. However, the extension means that the 5G spectrum auction won’t happen anytime soon. So any 5G commercial launch is still a long way off in India.
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:6879954283375267840/
Vodafone Idea to use 5Gi (ITU M.2150-LMLC) in trials
Vodafone Idea (Vi) is working with a “few companies” to prepare for trials using India’s own 5G standard 5Gi, which is included in ITU-R M.2150 as 5G Radio Interface Technology (RIT) for LMLC- Low Mobility Large Cell. The third largest telco in India said that once the telecom equipment is ready, it will conduct trials using the 5G LMLC technology.
“We are already working with a few companies. As and when the product is ready, we will be keen and will be doing trials and deploy accordingly” Jagbir Singh, chief technology officer (CTO) of Vi said on Friday. He didn’t divulge details of the partners are.
5Gi is currently being evaluated by India’s Telecommunication Engineering Center (TEC) for commercial adoption in India. Experts believe that 5Gi is a better option for setting up rural connectivity as it is cost-effective, improves spectral efficiency, and reduces spectrum wastage of up to 11 per cent compared to its global counterpart — the 3GPP approved 5G standard. However, existing telecom operators and equipment vendors are not in favor of adopting the local standard as they say 5Gi is yet to show any of these performance gains at a commercial scale.
Vodafone Idea has partnered with L&T Smart World and Communications, Athornet, Vizzbee Robotics, Tweek labs, Athonet, Nokia and Erricson to provide enterprise solutions. Arvind Nevatia, Chief Enterprise Officer, Vodafone Idea, also said that Vi will be looking to partner with other enterprises now that they have been granted a six month extension on 5G trials.
Vi has been allocated 26 GHz and 3.5 GHz spectrum in the mmWave band by the DoT, for 5G network trials and use cases. Vi has achieved peak speeds in excess of 1.5 Gbps on 3.5 GHz, more than 4.2 Gbps on 26 GHz and up to 9.8 Gbps on backhaul spectrum of E-bands.
Indian telcos, network equipment and chipset vendors along with handset have opposed the incorporation of 5Gi as a national standard citing compatibility issues with 3GPP’s global 5G standard, which has already been adopted globally for commercial live networks. Telcos had urged the Department of Telecom (DoT) and the TEC to merge 5Gi with 3GPP’s global 5G NR spec to achieve scale and bring down costs, but that has not happened yet.
“We follow the 3gpp standards (they are specs- not standards– and have no official standing) for the core network…along with the firewalls. We are going to ensure whatever we do for our IT and network platform specific for the core data protection policy in coordination with 3GPP. Network slicing ensures data protection for each enterprise…all customers are equally protected in terms of security,” he added.
On Friday, Vodafone Idea (Vi) demonstrated some of the 5G technology solutions and use cases as a part of its ongoing 5G trials on government allocated 5G spectrum in Pune, Maharashtra and Gujarat. These tests come at a time when the three rivals -Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio. and Vi are trying to keep pace with each other in the race towards next generation technology.
Singh added that Vi has 30-35% fiber for backhaul for its wireless network, which it is increasing in urban areas. “5G will be a combination of fiber and E band.”
The company is now preparing to expand the scope of 5G trials and is in talks with its and is in talks with its existing customers and startups. Rival Airtel became the first telco to test 5G technology in the 700Mhz band on Thursday. The telco will be working with start-ups for more use cases.
“We were not aware that we will be getting an extension for trials till 3-4 weeks back. We were not doing that on a very high intensity basis, but now with the clarity we will restart the process of engagement,” Arvind Nevatia, Chief enterprise business officer, Vi.
The telco highlighted new revenue models, as a result of 5G. “What we are seeing is evolving models from fixed commission basis to subscription models whether it is in the consumer space or the SAAS space , a lot of new revenue models are emerging in the country…. ,” said Nevatia.
However, prices of 5G have been a contentious issue between the sector and the government. Chief regulatory officer P Balaji said the decision will be taken by the government, which is setting up the auction process process including consultation on prices with the regulator.
“We see Vodafone Idea as an active partner in the digital vision of the government and as India develops its own 5G plans , we will be happy to participate”, said Balaji.
The current base price of Rs 492 crore for a unit of 5G spectrum in the 3.3-3.6 GHz band has been deemed too expensive by all three Indian telcos.
Many experts believe that adoption of the ITU-R M.2150 5Gi standard in India by the government will enable India to leap-frog in the 5G space, with key innovations introduced by Indian entities accepted as part of global wireless standards for the first time. The nation stands to gain enormously both in achieving the required 5G penetration in rural and urban areas as well as in nurturing the nascent Indian R&D ecosystem to make global impact. TSDSI’s efforts are aligned with the national digital communication policy that promotes innovation, equipment design and manufacturing out of India for the world market. The TSDSI 5G standard also has the potential to make a significant impact in several countries with poor rural broadband wireless coverage. TSDSI remains committed to the development of globally harmonized 5G standards with substantial innovations to address hitherto neglected needs of countries such as India. TSDSI-RIT is a step in the right direction so that our indigenous technologies for rural coverage and connectivity find their rightful place in the 5G eco-system that will be deployed in India and elsewhere.
Bharti Airtel conducts 5G SA trial in 700 MHz band with Nokia
Indian network operator Bharti Airtel on Thursday said it has conducted India’s first 5G SA network trial [1.] in the 700 MHz spectrum band in partnership with Nokia. The demonstration was conducted on the outskirts of Kolkata. It also marked the first 5G trial in the eastern India, the company said in a statement.
Note 1. No 5G commercial service can commence in India till the government auctions 5G spectrum which is scheduled for in the second half of 2022. However, it has been delayed time after time after time. Airtel has been allotted test spectrum in multiple bands by India’s Department of Telecommunications for the validation of 5G technology and use cases.
Using the 700 MHz band, Airtel and Nokia were able to achieve high speed wireless broadband network coverage of 40 Km between two 5G sites in real life conditions. Airtel used equipment from Nokia’s 5G portfolio, which included Nokia AirScale radios and Standalone (SA) core network. [Nokia provides a common core network which supports the 4G – EPC and a 5G Core.]
Randeep Singh Sekhon, CTO – Bharti Airtel said: “Back in 2012, Airtel launched India’s first 4G service in Kolkata. Today, we are delighted conduct India’s first 5G demo in the coveted 700 MHz band in the city to showcase the power of this technology standard. We believe that with the right pricing of 5G spectrum in the upcoming auctions, India can unlock the digital dividend and build a truly connected society with broadband for all.”
Naresh Asija, VP and Head of Bharti CT, Nokia, said: “5G deployment using 700Mhz spectrum is helping communications service providers across the world to cost-effectively provide mobile broadband in remote areas, where typically it is challenging for them to set up the network infrastructure. Nokia is at the forefront in the development of the global 5G ecosystem, and we look forward to supporting Airtel on its 5G journey.”
Airtel says they are “spearheading 5G in India.” Earlier this year Airtel demonstrated India’s first 5G experience over a live 4G network. It also demonstrated India’s first rural 5G trial as well as the first cloud gaming experience on 5G. As part of #5GforBusiness, Airtel has joined forces with leading global consulting and technology companies and brands to test 5G based solutions.
About Airtel:
Headquartered in India, Airtel is a global communications solutions provider with over 480 Mn customers in 17 countries across South Asia and Africa. The company ranks amongst the top three mobile operators globally and its networks cover over two billion people. Airtel is India’s largest integrated communications solutions provider and the second largest mobile operator in Africa. Airtel’s retail portfolio includes high speed 4G/4.5G mobile broadband, Airtel Xstream Fiber that promises speeds up to 1 Gbps with convergence across linear and on-demand entertainment, streaming services spanning music and video, digital payments and financial services. For enterprise customers, Airtel offers a gamut of solutions that includes secure connectivity, cloud and data centre services, cyber security, IoT, Ad Tech and cloud based communication.
For more details visit www.airtel.com
Nokia Contact:
Mohammed Shafeeq, Media Relations
Phone: +91 9167623398
E-mail: [email protected]
References:
India’s 5G auction delayed again to April-May 2022 – Credibility Gap?
The long delayed auction for the 5G spectrum in India is now likely (???) to take place around April-May 2022, Telecommunications minister Ashwini Vaishnaw said on Thursday. While relief measures announced in September this year for telecom operators marked the first set of reforms, the government will bring out a series of further reforms and “telecom regulatory structure should change in coming 2-3 years”, Vaishnaw said at an event in India.
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (Trai) is working on the modalities of the auction. “Our estimate is by April-May. I think it will take time because Trai consultations are complex, diverse opinions are coming,” Vaishnaw said.
[Credibility gap: When he announced the government’s big-bang telecom reforms in September, Vaishnaw had said the auctions would be held in February.]
The telecom department has approached Trai for its recommendations on pricing, amount of 5G spectrum for sale and other modalities.
“The (India) government had budgeted for inflows of nearly Rs 54,000 crore from other communication services for the current year, presumably boosted by the expectation of fresh auction inflows,” according to Aditi Nayar, chief economist, Icra. “We now assess the inflows from the telecom sector into the government’s 2021-22 non tax revenues to be limited to Rs 28,000 crore, trailing the budgeted Rs 54,000 crore, which will modestly widen its fiscal deficit, “ she said.

Image Credit: Shutterstock
The government is targeting a fiscal deficit of 6.8 per cent of GDP in 2021-22, a big improvement over the previous year when the fiscal deficit shot up to 9.3 per cent in the Covid-affected economy. The DoT has sought the views of Trai across multiple bands such as 700Mhz, 800 Mhz, 900 Mhz, 1800 Mhz, 2100 Mhz, 2300 Mhz, 2500 Mhz bands as also 3,300-3,600 Mhz that were not put up for auctions in the last round.
On the timeline for 5G auctions, Vaishnaw noted that the Trai is undergoing consultations on the matter. “I think they will submit their report by February-mid is what we are thinking, maybe February-end, maximum to maximum March. Immediately after that, we will have the auctions,” he said.
References:
Starlink to explore collaboration with Indian telcos for broadband internet services
SpaceX subsidiary Starlink is planning to explore collaboration with telecom companies in India to expand broadband internet services in the country with a focus on rural areas, a top company official said on Friday. Starlink Country Director India Sanjay Bhargava told that discussions with broadband service providers will start once the 12 Phase-1 aspirational districts are identified by the Niti Aayog and the company will see the interest levels of the various players and the USOF (universal service obligation fund).
“I am hoping that we will get a time-bound 100 per cent broadband plan that can serve as a model for other districts but the devil is in the details and there may be many good reasons why one or more broadband providers do not want to collaborate, though to me that seems unlikely,” Bhargava said.
Starlink claims to have received over 5,000 pre-orders from India. The company is charging a deposit of $99 or Rs 7,350 per customer and claims to deliver data speeds in the range of 50-150 megabits per second in the beta stage.
Bhargava had earlier announced that the company will focus on 10 rural Lok Sabha constituencies to provide internet services for 80 per cent of the Starlink terminals shipped to India. “At Starlink, we can roll out fast if we have licensing approval and…the Starlink’s could move to other remote areas,” Bhargava said. In a social media post, Bhargava said the company wants to collaborate with all. “We want to collaborate with all and have others besides us licensed to provide satellite broadband so that satellite plus terrestrial together can provide 100 per cent broadband, especially in rural districts,” he said. There have been some reports of Starlink considering manufacturing of terminals to provide satellite broadband services in India, but Bhargava said the company is not actively thinking about making terminals for broadband locally.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Tech billionaire Elon Musk has said on Twitter that his aerospace company SpaceX may soon launch satellite-based internet service Starlink in India. Musk responded to a Twitter post that the company is exploring how the regulatory approval process in the country will work for Starlink. Musk said, “The regulatory approval process is being explored.”
Starlink recently shipped 100,000 terminals to customers. The objective of this project is to provide global broadband connectivity through a cluster of satellites. SpaceX began satellite launches in November 2019 and opened its $99 (Rs 7,223) per month beta program to select customers about a year later.
References:
Open RAN: A game-changer for mobile communications in India?
The author is a former Advisor, Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India
The mobile network comprises two domains: The Radio Access Network (RAN) and the Core Network. The RAN is the final link between the network and the phone. It includes an antenna on the tower plus the base station. Though it was possible for the operators to have one vendor for the core and a separate vendor for the RAN, the same was not done because of interoperability issues.
Open RAN is the hot topic now-a-days and most talked about technology, both in diplomatic and technical circles. This is a three year old technology and fifty operators in more than two fifty countries have deployed open RAN. First it was deployed in the network of Rakuten mobile, a Japanese telecom service provider. This technology makes RAN agnostic to vendors, programmable and converts it to plug & play type. Open RAN is at the epicentre of the digital transformation and plays a critical role in bringing more diversity to the 5G ecosystem. It is required for faster 5G rollout. Domestic (India) vendors may get the opportunity to supply the building blocks of RAN and so it is an initiative towards ‘self-reliant India.’
The RAN accounts for 60 per cent of capex/opex of mobile networks and so a lot of focus is there to reduce RAN costs. 5G signals have a shorter range than previous generation signals. As a result 5G networks require more base stations to provide the required coverage. So in 5G networks this percentage may be still higher.
Open RAN implementation reduces RAN costs. Instead of concentrating on making end-to-end open, opening the RAN ecosystem is given priority by the operators. The open RAN standards aim to undo the siloed nature of the RAN market where a handful of RAN vendors only offer equipment and software that is totally proprietary. Proprietary products are typically more expensive than their generic counterparts. Cellular networks have been evolving with various innovations. It has evolved from 1G to 5G. With these evolutions networks are evolving towards open networks having open interface and interoperability. Open RAN is a term used for industry wide standards for RAN interfaces that support interoperation between different vendor’s equipment and offer network flexibility at a lower cost. The main purpose of open RAN is to have an interoperability standard for RAN elements including non-proprietary hardware and software from different vendors. An open environment means an expanded ecosystem, with more vendors providing the building blocks. Open RAN helps the operators to overcome “Vendor lock in” introducing ‘best of breed’ network solutions.
There will be more innovations and more options for the operators. With a multi -vendor catalog of technologies, network operators have the flexibility to tailor the functionality of their RANs to the operators’ needs. They can add new services easily. Open RAN gives new equipment vendors the chance to enter the market with Commercial off the shelf (COTS) hardware. An influx of new vendors will spur competition. Cell site deployment will be faster. Third Party products can communicate with the main RAN vendor’s infrastructure. New features can be added more quickly for end users.
Current RAN technology is provided as a hardware and software integrated platform. The aim of open RAN is to create a multi supplier RAN solution that allows for the separation or disaggregation between hardware and software with open interface. Open RAN is about disaggregated RAN functionality built using open interface specifications between blocks. It can be implemented in vendor neutral hardware and software based on open interfaces and community developed standards.
In an open RAN environment, the RAN is disaggregated into three main building blocks:
- Radio Unit (RU)
- Distribution unit (DU)
- Centralized unit(CU)
The RU is where the radiofrequency signals are transmitted, received, amplified and digitized. It is located near or integrated into the antenna. The DU and CU are parts of the base station that send the digitized radio signal into the network. The DU is physically located at or near the RU whereas the CU can be located nearer the Core. DU is connected with RU on Optical Fiber cable. The concept of open RAN is opening the protocols and interfaces between these building blocks (radio, hardware and software) in the RAN.
Another feature of Open RAN is the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) which adds programmability to the RAN. For example, Artificial Intelligence can be introduced via the RIC to optimise the performance of the network in the vicinity of a cricket stadium on a match day. The RIC works by exposing an API (Application Programming Interface) which lets software talk to each other. There are two types of RIC: near-real time and non real time. Both perform logical functions for controlling and optimizing the elements and resources of open RAN. A near-real time RIC (response time on the order of 10’s of milliseconds) controls and optimizes elements and resources with data collection and communication. A non-real time RIC (response time greater than one second) uses AI and Machine Learning (ML) workflows that include model training, where the workflows learn how to better control and optimize the RAN elements and resources.
The O-RAN alliance has defined eleven different interfaces within the RAN including those for:
Front haul between RU and DU Mid haul between DU and CU Backhaul connecting the RAN to the Core (also called as transport network)
O-RAN alliance is a specification group defining next generation RAN infrastructures, empowered by principles of intelligence and openness. Openness allows smaller players in the RAN market to launch their own services. It was founded in 2018.
O-RAN alliance is a worldwide community of around two hundred mobile operators, vendors and research and academic institutions operating in the Radio Access Network industry. Its goals include to build mechanisms for enabling AI and ML for more efficient network management and orchestration. It supports its members in testing and implementation of their open RAN implementation. O-RAN conducts world wide plug tests to demonstrate the functionality as well as the multi vendor interoperability of open network equipment. O-RAN alliance develops, drives and enforces standards to ensure that equipment from multiple vendors interoperate with each other. It creates standards where none are available, for example Front haul and creates profiles for interoperability testing where standards are available.
Open RAN challenges:
1. Integration of equipment from multiple vendors
2. Since equipment is from different vendors, operators have to have multiple Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
3. Network latency may increase
4. Reliability and availability may be a challenge
5. Staff has to acquire multiple skill sets
6. Security Concerns
Open RAN offers a golden opportunity for software developers to become a global hub for offering RAN solutions. This technology leads to a great disruption to the traditional ecosystem and accelerates the adoption of more innovative technologies. The disaggregation of RAN has also added further advantages by enabling better network slicing and edge compute capabilities.
References:
https://www.telecomtv.com/content/open-ran/how-vran-can-be-a-game-changer-for-5g-40019/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/?q=Open%20RAN#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=Open%20RAN&gsc.page=1
Vodafone Idea to test 5G-based smart city solutions with Larsen & Toubro in Pune, India
India’s struggling telco Vodafone Idea is partnering with engineering and construction conglomerate Larsen & Toubro for a pilot project to test 5G-based smart city solutions, as part of its ongoing 5G trials on government-allocated spectrum.
In the pilot to be conducted in the city of Pune, the companies will collaborate to test and validate 5G use cases built on IoT and video AI technologies leveraging L&T’s Smart City platform, Fusion, to address the challenges of urbanization, safety and security, and offering smart solutions to the citizens.
Vi has deployed its 5G trial in a setup of end-to-end captive network of Cloud Core, new C1 – Vodafone Idea External generation Transport and Radio Access Network.

Abhijit Kishore, chief enterprise business officer at Vodafone Idea, said: “Telecommunications solutions are the backbone of building smart and sustainable cities. The advent of 5G technology opens whole new opportunities to address challenges of urban growth and provide end-to-end solutions to support sustainable creation of Smart Cities, in the future. Vodafone Idea is happy to partner with Larsen & Toubro to test 5G based Smart City solutions and utilize our mutual expertise to find solutions that can help shape cities of the future.”
“In this constantly-evolving world, we are seeing an exponential rise in demand for smarter and more intelligent solutions and L&T Smart World is committed towards leveraging the latest technological innovations in the IoT and Telecommunications areas to benefit society at large. We are excited to partner with Vodafone Idea to bring to the table our experience, of having successfully executed several smart solutions across Indian cities, to develop customized, IoT-driven 5G solutions for various industry and enterprise verticals”, said J. D. Patil, senior executive VP of Defense and smart technologies at L&T.
The partnership between Vodafone Idea and Larsen & Toubro will trial several 5G use cases that cover 5G services such as enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications (uRLLC) and Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC). The firms said that the partnership will help to analyze the performance requirements of smart city applications and business models in 5G, design and implement 5G-based “smart and safe city” applications and use data analytics tools to visualize and analyze the trial results.
Vodafone Idea (Vi) has been allocated 26 GHz and 3.5 GHz spectrum in the mmWave band by India’s Department of Telecom (DoT), for their 5G network trials and use cases. In its initial test results Vi has achieved peak speed in excess of 3.7 Gbps with very low latency on the mmWave spectrum band. These speeds were achieved with state-of-the-art equipment in 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) network using 5G NR compliant radios. The Indian telco has also achieved peak download speeds of up to 1.5 Gbps in a 3.5 GHz-band 5G trial network with its original equipment manufacturer (OEM) partners.
The high speed and low latency characteristics of 5G network may enable improved surveillance and video streaming/broadcast to permit the evolution of 5G smart cities and smart factories. Smart City and Industry 4.0 will hopefully accelerate with 5G deployment and usher in new era of Digital India.
As forVi’s two telco competitors:
- Bharti Airtel has recently demonstrated India’s first 5G rural trial using network equipment from Ericsson. It has also showcased 5G cloud gaming.
- India’s wireless network market leader Reliance Jio has trialed 5G VoNR, AI-multimedia chatbot, and immersive high-definition (HD) virtual reality.
The DoT had approved applications of Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel and Vodafone in May, and MTNL later for 5G trials. The permission has been granted for six-month trials with telecom gear makers Ericsson, Nokia, Samsung and C-DOT.
References:
https://www.vodafoneidea.com/media/press-releases
Vodafone Idea inks partnership to test 5G-based smart city solutions
https://www.businesstoday.in/industry/telecom/story/vodafone-idea-says-achieved-peak-5g-speed-of-over-37-gbps-in-pune-trials-307076-2021-09-19
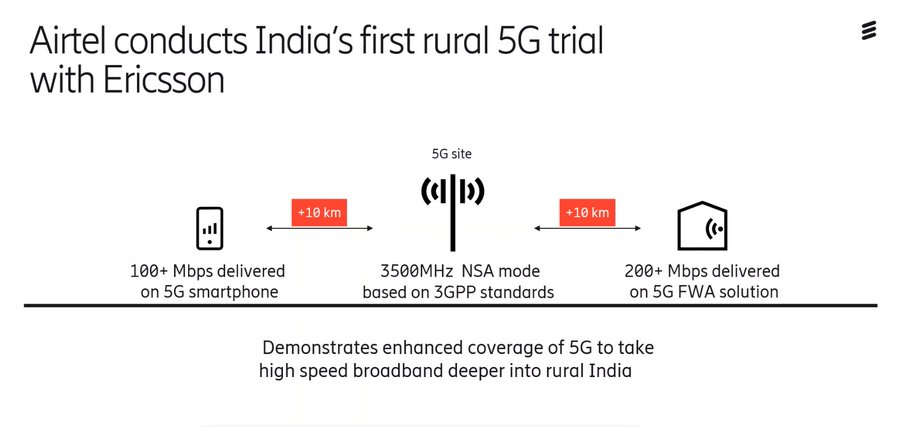
Bharti Airtel, Ericsson conduct India’s first rural 5G trial; Ericsson – India Q & A
On October 5th Bharti Airtel said it has conducted India’s first rural 5G trial with Swedish telecoms equipment maker Ericsson. The demonstration took place in Bhaipur Bramanan village on the outskirts of Delhi/NCR using 5G trial spectrum allocated by India’s Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
“The trial showcases the massive potential offered by 5G towards bridging the digital divide by enabling access to high speed broadband through solutions such as enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) services,” the companies said in a joint statement.
The trial demonstrated over 200Mbps throughput on 3GPP-compliant 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) device located more than 10km from the site.
The trial also showcased that a commercially available 3GPP-based 5G smartphone could connect to the test network and record over 100Mbps speeds at a distance of more than 10km from the site.
The 5G site was powered by Ericsson’s 3GPP-compliant 5G radio. The trial was carried out by utilizing the allocated mid-band trial spectrum in 3500MHz band and existing FDD spectrum band.
“Having demonstrated India’s first 5G network and also the first 5G cloud gaming experience, Airtel is proud to have also conducted the nation’s first 5G trial in a rural geography. 5G will be a transformational technology when it comes to delivering broadband coverage to the last mile through use cases like FWA and contribute to a more inclusive digital economy,” said Randeep Singh Sekhon, Airtel CTO.
“The technology milestone of extended coverage achieved by Ericsson and Airtel as part of the ongoing 5G trial in India is even more significant since it demonstrates how 5G can ‘connect the unconnected’ in India, enable faster 5G rollout and truly help India realize its ‘Digital India’ vision,” added Nunzio Mirtillo, Head of Ericsson South east Asia, Oceania and India.
According to an Ericsson study, on average, a 10% increase in the Mobile Broadband adoption ratio causes a 0.8% increase in GDP.
Airtel has previously demonstrated cloud gaming in a 5G environment, as part of its 5G trials in Gurgaon’s Manesar. It had used the mid-band spectrum provided by the DoT for this purpose. The Sunil Mittal-led telco has also been rallying to ensure that any new 5G handset sold in India must support all existing bands in India for 5G, including the mmWave bands.
Earlier this year, Airtel successfully demonstrated 5G services over a live 4G-LTE network in Hyderabad, marking an industry first. It is also conducting 5G trials in multiple cities across India and validating technologies and use cases through the trial spectrum allotted by the DoT . Airtel has partnered with Ericsson and Nokia for these trials.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Q and A with Nunzio Mirtillo, head of Ericsson (Southeast Asia, Oceania and India):
How has been the market performing for Ericsson this year?
We have been doing well in India and increasing our market share constantly. Over the past three/four years, we have been increasing our market share in India and we have kept our market share when the merger with Vodafone and Idea happened. When it comes to Bharti, we have increased market share substantially in the last few years, both on core and on radio, showing two things – one, our willingness to stay and increase our presence in India, and two, that we are competitive. Because you can be willing to do something but then you also need to be competitive in terms of technology, in terms of TCO and we have been showing that. And on top of that we have been delivering quite a good quality of service to our customers because that is ultimately what counts the most.
Have your telco partners been spending on network expansion aggressively?
We know the situation of Vodafone Idea, and I believe they have a great chance to do well in India and I think they will. And now with the latest from the government, I hope they will have a nice restart. When it comes to Jio we are not a relevant partner with Jio when it comes to the radio business, although we work with Jio. I think they have been also doing their job and their investment in a nice way. But Bharti has accelerated quite a lot in the last few years, and you can see the result in their market evaluation and also in terms of subscriber acquisition, ARPU increase, and we have been part of that journey, partnering with them as well. Showing that India is a market where if you do invest, you provide network quality and you have the right strategy and the right focus, the market is there. And if you do well, you will get the payback for that.
How do you see this whole 5G story panning out in the Indian market?
The sooner the better for the country actually. As everyone says in Q1, the spectrum will be made available from the government to the operators. So, I really hope so. India has been a bit sleepy for a while but then in the last three, four years it really did catch up quite a lot on 4G. So now the country should not lose momentum.
Secondly, the government should make available at least between 80 to 100 megahertz of 3.5GHz or the mid-band to the existing operators and also make sure that they auction millimeter wave spectrum which is a 400 megahertz which will be very much needed going forward to match the tremendous demand of mobile broadband that will be there in the future. And also, you also need to take care of the transport network, so we also need enough spectrum on the E band for connecting the 5G networks.
That’s what we believe and that’s the basic and India cannot, in my view, go below basic because there’s the Digital Highway for the country, it’s not only kind of business as such. It’s really a vital infrastructure for the future of India. And they also need to make sure that they deliver that spectrum at a reasonable price because otherwise they will impact from the start the ones that are supposed to invest.
I think they will be reasonable, because I have seen a lot of good things in India in the last few years with the tremendous push shown on Digital India, Make in India, and it’s all good programs.
References: