SoftBank to be 1st to launch 5G network service in Japan
SoftBank has announced it will launch 5G services on March 27th in Japan – the first network operator to launch 5G services, according to Japan Times.

SoftBank plans to charge an additional monthly fee of JPY 1,000 (approximately USD 9) for access to its 5G service. However, as a service launch promotion, customers will have free access to SoftBank’s 5G service for the first 2 years, under a sales campaign that runs until August.
SoftBank plans to initially provide its 5G service in Tokyo, Osaka, Chiba, Aichi, Hiroshima, Ishikawa and Fukuoka prefectures, starting 31 March. The operator intends to deploy more than 10,000 base stations by end-March 2023.
SoftBank will start selling two 5G-enabled smartphone models on March 27th and add two more later this year. Sharp and Sony recently unveiled their first 5G smartphone models. SoftBank plans to provide 5G smartphones from Sharp, China’s ZTE, Oppo and LG. Sharp unveiled its first 5G smartphone model, the Aquos R5G, on 17 February. The Android phone will be available in Japan this spring and its price will be similar to existing high-end smartphones, Sharp said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
Rivals NTT Docomo Inc. and KDDI Corp. are expected to reveal their own 5G plans soon.
While the launch of 5G in Japan will ramp up domestic competition, Rakuten Inc.’s foray into the market as the nation’s fourth big carrier will stir things up further.
Earlier this week, Rakuten announced it would undercut its rivals with a 4G service on April 8 that only costs ¥2,980 a month for unlimited data usage.
The plan is about half the price charged by the top three mobile phone carriers, but Rakuten’s coverage is limited by comparison. Rakuten also said the first year of its 4G service would be free for the first 3 million subscribers.
SoftBank’s 4G plan costs ¥6,500 a month for up to 50GB of data, with a ¥1,000 discount for the first year. SoftBank, however, has recently lowered prices — ostensibly to head off Rakuten’s aggressive charge — and is laying the groundwork for getting customers to shift to 5G without any added financial catches.
Rakuten will reportedly launch a 5G network in June. This new age carrier had previously announced plans to launch 4G services starting April, and then upgrade to 5G in summer as it gradually expands the network. It aims to have nationwide Japan coverage by March 2021.
Pre-standard 5G networks have already been deployed in the United States, South Korea, China and parts of Europe.
References:
https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2020/03/05/business/tech/softbank-5g-japan-first/
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/softbank-to-launch-5g-service-in-japan-on-27-march–1329354
AT&T deploys XGS-PON to power FTTH nets
AT&T has enhanced its fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) “last mile” network by deploying XGS-PON [1.] technology which will be live in 40 markets. AT&T will start out providing 1 gigabit download speeds before eventually boosting them to 10 gigabits per second in both directions as it upgrades from GPON networks. The company said it has deployed XGS-PON in “a few thousand locations” noted that it has employed multiple vendors in the process. It’s part of AT&T’s road map to virtualize network access functions within its last mile network.
NOTE 1. XGS-PON is a fixed wavelength symmetrical 10 Gbps passive optical network technology.
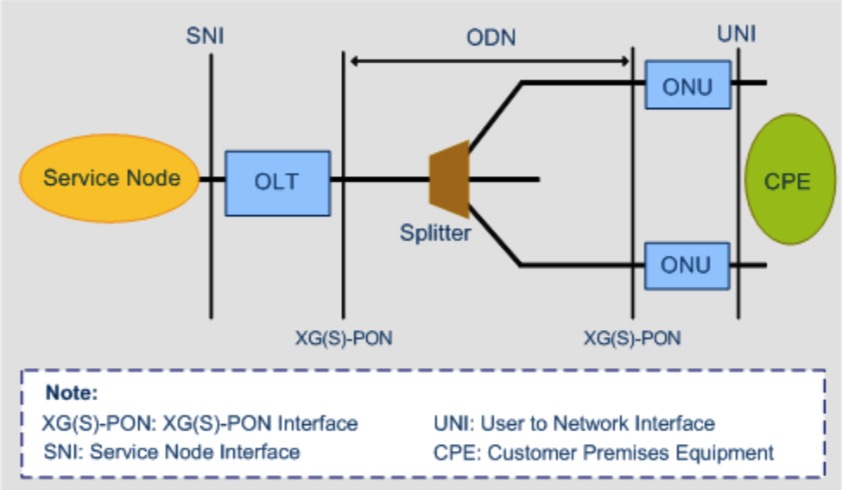
The “X” in XGS represents the number 10, and the letter “S” stands for symmetrical, XGS-PON = 10 Gigabit Symmetrical PON. An earlier, non-symmetrical 10 Gigabit PON version (XG-PON) was limited to 2.5 Gbps in the upstream direction.
PON technology originated in the 1990’s and has continued to develop through multiple iterations with differing wavelengths, speeds and components emerging as the technology has improved. The common denominator of all fiber optic PON networks remains the unpowered or passive state of the fiber and its splitting or combining components, i.e. no active elements such as optical amplifiers, which would require power, are present in the network. With streaming, high definition, 5G and other emerging technologies continually pushing bandwidth demands, the development of XGS-PON and other standards has proven to be essential.
Simultaneous upstream and downstream transmission over the same fiber is made possible through wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). This technology allows one XGS-PON wavelength or color of light transmission for upstream and another for downstream.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Two years ago, AT&T completed trials of 10 Gbps XGS-PON by using Open Source Access Manager Hardware Abstraction (OSAM-HA) software in Atlanta and Dallas. OSAM-HA was released into the Open Networking Foundation (ONF) in 2017 as VOLTHA.
- OSAM, which used the Open Networking Automation Platform (ONAP) platform that AT&T helped develop, is a vendor-agnostic operational suite for managing consumer and business broadband access network elements and capabilities. ONAP has undergone several major releases over the past few years.
- ONF’s Virtual OLT Hardware Abstraction (VOLTHA) open source software project, which is a component of ONF’s SDN Enabled Broadband Access (SEBA) platform, abstracts a PON network to make it manageable as if it were a standard OpenFlow switch.
- SEBA describes how to assemble a collection of open source components to build a virtualized PON network to deliver residential broadband and mobile backhaul. SEBA uses a disaggregated white-box approach for building next generation access networks by using open source.
“AT&T continues to work with open communities such as ONF, ONAP, and OCP (Open Compute Project) to drive innovation, time-to-market, and cost improvements as we build next generation networks,” the company said in a March 4th statement in regard to a request for more information on the deployments in the 40-plus cities.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Conventional wisdom in the fiber broadband industry suggests NG-PON2 is the platform most providers will eventually adopt, with XGS-PON as an interim step to get there.
Verizon seems to be leapfrogging that approach. For what it’s worth regarding conventional wisdom, the AT&T spokesperson tells Telecompetitor, that “AT&T is not currently planning to use NG-PON2 at this time.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
AT&T Fiber Begins Transition to Next Generation XGS-PON FTTH
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/at-t-tees-up-1-gig-xgs-pon-speeds-over-40-cities
https://www.viavisolutions.com/en-us/xgs-pon
http://www.tarluz.com/ftth/specification-differences-among-gpon-xg-pon-and-xgs-pon/
AT&T deploys XGS-PON to power FTTH nets
AT&T has enhanced its fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) “last mile” network by deploying XGS-PON [1.] technology which will be live in 40 markets. AT&T will start out providing 1 gigabit download speeds before eventually boosting them to 10 gigabits per second in both directions as it upgrades from GPON networks. The company said it has deployed XGS-PON in “a few thousand locations” noted that it has employed multiple vendors in the process. It’s part of AT&T’s road map to virtualize network access functions within its last mile network.
NOTE 1. XGS-PON is a fixed wavelength symmetrical 10 Gbps passive optical network technology.

The “X” in XGS represents the number 10, and the letter “S” stands for symmetrical, XGS-PON = 10 Gigabit Symmetrical PON. An earlier, non-symmetrical 10 Gigabit PON version (XG-PON) was limited to 2.5 Gbps in the upstream direction.
PON technology originated in the 1990’s and has continued to develop through multiple iterations with differing wavelengths, speeds and components emerging as the technology has improved. The common denominator of all fiber optic PON networks remains the unpowered or passive state of the fiber and its splitting or combining components, i.e. no active elements such as optical amplifiers, which would require power, are present in the network. With streaming, high definition, 5G and other emerging technologies continually pushing bandwidth demands, the development of XGS-PON and other standards has proven to be essential.
Simultaneous upstream and downstream transmission over the same fiber is made possible through wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). This technology allows one XGS-PON wavelength or color of light transmission for upstream and another for downstream.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Two years ago, AT&T completed trials of 10 Gbps XGS-PON by using Open Source Access Manager Hardware Abstraction (OSAM-HA) software in Atlanta and Dallas. OSAM-HA was released into the Open Networking Foundation (ONF) in 2017 as VOLTHA.
- OSAM, which used the Open Networking Automation Platform (ONAP) platform that AT&T helped develop, is a vendor-agnostic operational suite for managing consumer and business broadband access network elements and capabilities. ONAP has undergone several major releases over the past few years.
- ONF’s Virtual OLT Hardware Abstraction (VOLTHA) open source software project, which is a component of ONF’s SDN Enabled Broadband Access (SEBA) platform, abstracts a PON network to make it manageable as if it were a standard OpenFlow switch.
- SEBA describes how to assemble a collection of open source components to build a virtualized PON network to deliver residential broadband and mobile backhaul. SEBA uses a disaggregated white-box approach for building next generation access networks by using open source.
“AT&T continues to work with open communities such as ONF, ONAP, and OCP (Open Compute Project) to drive innovation, time-to-market, and cost improvements as we build next generation networks,” the company said in a March 4th statement in regard to a request for more information on the deployments in the 40-plus cities.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Conventional wisdom in the fiber broadband industry suggests NG-PON2 is the platform most providers will eventually adopt, with XGS-PON as an interim step to get there.
Verizon seems to be leapfrogging that approach. For what it’s worth regarding conventional wisdom, the AT&T spokesperson tells Telecompetitor, that “AT&T is not currently planning to use NG-PON2 at this time.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
AT&T Fiber Begins Transition to Next Generation XGS-PON FTTH
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/at-t-tees-up-1-gig-xgs-pon-speeds-over-40-cities
https://www.viavisolutions.com/en-us/xgs-pon
http://www.tarluz.com/ftth/specification-differences-among-gpon-xg-pon-and-xgs-pon/
5G Technology and It’s Future in Mobile Communications
by Jacob Wolinski. Excerpts of article posted at: https://www.valuewalk.com/2020/03/5g-tech-market/
Introduction:
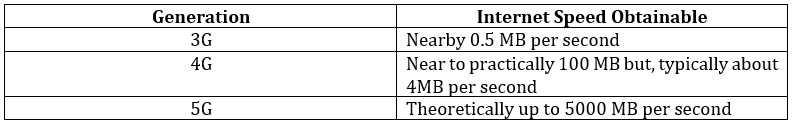
It is evident that 3G and 4G network mobile phones have been an immense driver in the steep surge of internet use on mobile phones, across the world, and the continuing growth of the network.
The next generation of a telecom network is 5G, which operates at higher radio frequencies. This also offers the chance for much quicker internet speeds: –
In this table, it clearly claims the uprising about 5G is that it will change the world. This is because the capability and capacity of the 5G technology have the tendency to transform existing technologies in incredible ways.
Various Studies on 5G Technology:
Here is the list of various studies over 5G technology that came up when the revolution was going to happen. They are as follows:
Impact on Various Industries:
5G will employ an enormous influence mainly in the automotive, healthcare, and IoT sectors in the near future, and will dramatically change lives. 5G technology will, however, take time to have an analogous effect on other industries.
5G will Generate New Revenue Streams:
It has been observed that the 5G network has the possibility to unlock up to $12.3 trillion of revenue, crosswise a broad range of telecom industries.
5G Technology Will Create New Growth and Jobs:
It is predictable that by the year 2035, the output from the global value chain of 5G (network operators) will be superior to what the entire mobile value chain is at present. In terms of contribution to global GDP, research predicts that contribution of 5G between the years of 2020 and 2035 will equal the size of India’s economy in recent times and will also see 5G supporting 22 million jobs globally.
5G will Drive Innovation of New Genres of Products and Services
5G technology has the potential to give rise to new industries, along with having an impact on existing businesses in terms of the products and services. Research indicates positive outlooks on 5G’s technology towards ensuring security and reliability.
In fact, while 5G evolves into a more tangible network, there will be much happening depending on investments that are being made in 5G infrastructure, related applications, products as well as services.
In the new term, a broad agreement is that initial deployments of 5G will be driven by enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB). However, eMBB alone will not be able to create substantial revenue from 5G for network operators. Yet, past migrations from one generation of mobile technology to the next invariably meant consumers might pay almost similar amounts while data speeds increased, and call-data payments grew due to falling unit network cost.
For wide-spread and transformative impact along with tangible business benefits, the 5th generation of wireless network technologies will need to expand its scope. Thus, the possibilities of 5G technology are immense in the coming years.
Features of 5G Technology:
In the essential aspect, 5G technology caters to a lot of possibilities to explore new ways to manage networks. In this, a term referred to as network slicing comes up, which empowers a single physical network that supports many virtual networks with assorted performance and features. Picking an instance, one network slice can deliver high-speed mobile broadband on the same infrastructure, above which another slice might result in lower consumption of network over the speed of the connection, which is in 5G.
In fact, 5G technology also makes it possible to use the same infrastructure in offering various services to different users and industry-sectors. After seeing such tremendous outcome, it is evident that 5G technology will, therefore, open lucrative scopes for more new business models in the future than the current environment where network providers offer the same services, yet the only variation is in regards to pricing and the bill plans.
Enhancements for Future Mobile Broadband:
The established reliable 5G technology continues to work on multiple fronts to improve its performance and efficiency further, counting improved coverage, capacity, potential, mobility, power, and more. These enhancements will further benefit not only core mobile broadband services and smartphone connectivity, but also the prolonged use cases that 5G NR is bringing with Release 16 and more.
Another critical area of research is continued towards advancements in multiple antenna MIMO technology. There has been a proper working on enhancements that can deliver more optimized downlink and uplink massive MIMO operations, along with reduced signaling, lower latency, and expanded support for multiple transmission points.
Besides, there has also been a proper focusing on further reduction of device power consumption with features like enhanced C-DRX, which is known as connected mode discontinuous reception and 2-step RACH (simplified random-access procedure). With this, improving mobility is another core research area for multi-network access systems with enhancements for minimizing network interruptions, thus allowing for quicker activation of proper connection, and supporting more seamless dual connectivity.
2020 – Is the Year of Real 5G?
At present, 5G is leading in the telecom industry. A lot of operators all over the world are preparing or already commercially launching new services for the customers to connect to next-generation mobile networks with 5G technology.
Most of the early deployments in 5G technology are based on especially RAT (Radio Access Technology) upgrades, that uses the existing frequency spectrum and legacy core network. This results in delivering a fraction of the technology’s potential. Though 5G expectations were set very high where the data rates grew up to 1 Gb/s downlink, the end-users often get surprised when they experience better improvement in comparison to existing 4G technology.
Upgrades of these core networks, which include edge computing, virtualization (VNF and SDN technologies), and network slicing, will let them forming new platforms for 5G tech market growth. While some mobile operators in the line are still analyzing potential deployment strategies, and others are already advanced in upgrading their infrastructure of networks using 5G.
In the case of point, Verizon introduced CAPEX efficiencies since implementing its Intelligent Edge Network with unified transport and the single network core. It has completed 60% of a unified framework for various networks by Q4 20191. Another major market player in the US telecom industry, AT&T, in collaboration with Microsoft’s Azure Cloud, has virtualized 75% of its primary network functions with software by the end of the year, consenting them to cut $1.5 billion in costs in the year 2020.
Potential of 5G Technology:
The potential use of 5G technology has been subjected to the assumption for moderately some time. It is supposed that 5G has the potential to change many industries and can take further in smart cities, autonomous vehicles, smart industry 4.0, and more. It is a great thanks to the new features and enhancements found in 5G technology in the present year, where mobile operators can potentially see more returns on their significant investments. The improvements in mobile broadband that includes power consumption can thus allow device vendors to produce cheaper handsets, thereby raising the number of users and helping mobile operators spend less on device subsidies.
The Expanding 5G Tech Market Snapshot:
As per a study conducted by Market Research Future, the global level market of 5G technology is expanding year by year. The real growth period is detected to be between 2020 to 2025, in which the 5G tech market will be developing more than present at a compound annual growth rate of 70.83%. Even the market can achieve a valuation of USD 700 Bn by 2025-end, by examining massive opportunities knocking the door in the present time.
The final report of the 5G tech market is picked from https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/5g-technology-market-2988.
The market, as per the study, is gaining a quick mileage. A developing solution to the network, along with cost-effective and feasible options, is making the market vulnerable to attain more worth than before in the future. When looking at regional prospects, North America is becoming the ruler and is at the forefront in the adoption of 5G technology at a rapid pace. This region is commanding more than two-thirds of the global market share. The reasons depicting such a rise in the 5G tech market here is attributed to the swelling popularity of consumer electronic devices with applications that depend on a high-speed network. Thus, the statistics presented that North America’s regional market is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 71.0% throughout the growth period.
Followed by North America, the Asia-Pacific region is also likely to emerge as the second-largest market for 5G technology by the year 2025. The region shows the potential of reaching a valuation of USD 17.55 at 74.60% CAGR.
Gartner: Enterprise Data Network Services Market Moves to Transformational Technologies
Market Overview
Gartner forecasts that the market for enterprise data networking services in 2020 will be $157.5 billion, broadly unchanged from 2019 (see “Forecast: Enterprise Communications Services, Worldwide, 2017-2023, 4Q19 Update”).
The number of global NSPs included in this Gartner research has increased as more providers have met our revised inclusion criteria. In addition to large global providers, enterprises are increasingly willing to consider smaller providers, including managed service providers with little or no network infrastructure of their own (such as those featured in the “Market Guide for Managed SD-WAN Services”). Alternatively, enterprises may choose a combination of multiple regional providers.
Sourcing Trends
Providers are increasingly focused on providing the managed service platform (e.g., managed SD-WAN and NFV/vCPE); however, they are also more open to “bring your own access” and other flexible sourcing approaches for the network transport components.
The global network service market continues to move toward a more software-driven, as-a-service model, with increasing levels of visibility and self-service via portals and APIs available to enterprise customers.
However, this means providers are reluctant to allow deviations from their standard offerings, because that will require deployment of a custom solution at a higher cost that could rapidly become obsolete in this fast-moving market.
Operational Trends
The network buying discussion is gradually moving away from technologies toward outcomes and service levels. Providers continue to improve their SLAs with more-realistic objectives and more-meaningful penalties for failing to meet those objectives, increasingly including the right to cancel the service in the event of chronic breach. Installation lead times — a pain point for many enterprises with global networks — are starting to be covered by standard SLAs, and providers are striving to improve delivery times, although they remain frustrated by third-party/local access providers. The increasing speeds of cellular services are making this technology more useful as a rapid deployment (interim) solution. In addition, it provides a truly diverse backup option. However, the hype around 5G cellular replacing fixed connectivity should be treated with caution, due to maturity issues — especially coverage limitations.
Electronic quoting and ordering are increasingly widespread, with electronic bonding between the global providers and their local access providers. Self-service ordaining and/or provisioning, as well as the increased visibility of the service being delivered via portals continue to gain momentum. This is blurring the lines between managed services and self-management, to create a spectrum of co-management possibilities.
However, global networks are also becoming more complex, because transport becomes a hybrid of MPLS, internet and Ethernet; cloud endpoints are added; and SD-WAN and NFV technology are added. In addition, the internet, especially using broadband or cellular access, is an inherently less predictable service than MPLS. Visibility capabilities, sometimes referred to as performance analytics, can help by enabling enterprises see the actual performance of their applications.
Thanks to the continual investment in enhancing the customer experience, customer satisfaction with global NSPs is improving.
Network Architectures
New global network proposals are predominantly for managed SD-WAN services based on a hybrid mix of MPLS and internet transport, with different applications using the most appropriate link type. Most providers support a small portfolio of SD-WAN vendors, because the market is more fragmented and differentiated than the router market it is replacing. Some providers offer network-based SD-WAN gateways, allowing traffic to use the internet for access, but use the providers’ higher-quality, long-haul backbones.
Enterprises’ adoption of cloud IT service delivery remains key to transforming their WAN architectures. Fortunately for enterprises, global NSPs have deployed a range of capabilities to address enterprises’ cloud connectivity needs (see “Five Key Factors to Prepare Your WAN for Multicloud Connectivity”).
The providers in this research offer carrier-based cloud interconnect from their MPLS and Ethernet networks to leading CSPs, such as Amazon, Microsoft and Google. Most offer connection to additional cloud providers as well. The key differentiators are the specific cloud providers and the cities connected, and the ability to add virtualized services (e.g., security) into the cloud connection points.
Managed SD-WAN services typically offer the option of local internet access (split tunneling) from every site, which is especially useful for access to SaaS applications, such as Microsoft Office 365. Perimeter security can be provided on-site or as a cloud-based service. An option for managed SD-WAN services is for the provider to deploy network-based SD-WAN gateways to facilitate interconnection between SD-WAN and non-SD-WAN networks, improve scalability and avoid the need for traffic to traverse long distances over the internet. Alternatively enhanced internet backbone services may be available to improve the performance of cloud service access over the internet and to improve end-to-end performance, when using the internet as a transport link.
An increasing number of global WANs incorporate managed application visibility and/or WAN optimization, with some providers now offering application-level visibility by default. SD-WAN services, which operate based on application-level policies, also typically offer inherently higher levels of application visibility.
Network functions, such as edge routing, SD-WAN, security, WAN optimization and visibility, can be delivered as on-site appliances. However, many providers prefer to offer these as VNFs, running in NFV service nodes in their POPs or in uCPEs, which are essentially industry-standard servers, deployed at the customers locations, supporting one or more virtual functions. This makes it easy to rapidly change the functions deployed in the network and is also usually consumed on an “as a service” basis with a monthly subscription fee for each function.
Ethernet WAN services (virtual private line and virtual private LAN services) remain more niche. They are principally used for data center interconnection; high-performance connections, including extranets (such as trading networks); or for sites that are geographically close (i.e., Metro Ethernet). Different combinations of these services can be used to obtain different service levels appropriate to each enterprise location.
Providers are starting to offer NoD services, where bandwidth can be adjusted via a portal or APIs. Some of these services support multiple services (e.g., MPLS and internet) on a single access line, and also allow dynamic control of cloud connectivity.
Access Options
WAN access is evolving, with traditional leased-line access, such as T1 or E1 lines, no longer proposed in new deals, except when no other form of access is available, such as in rural locations or some emerging markets.
Pricing for these legacy service types is typically increasing, and, in some cases, the services are reaching the end of their life.
Traditional access lines have largely been replaced by optical Ethernet access at 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps or 10 Gbps. The scale economics of Ethernet access are very good, with each tenfold increase in speed, typically increasing cost by only two to three times. As a result, in developed markets, enterprises now tend to purchase access lines with much higher speeds than they initially require, with the port capacity limited to their current needs. This allows them to easily and quickly upgrade capacity in response to changing requirements.
For smaller, less critical or remote locations, broadband (increasingly, “superfast broadband,” such as very-high-speed DSL [VDSL], cable modem or passive optical network [PON]) is the access technology of choice, despite having no SLAs or poorer SLAs than Ethernet access. When enterprises require large numbers of broadband connections, they can sometimes find that they are able to get better pricing than that offered by global service providers by sourcing broadband access directly or from aggregators. Many providers now support “bring your own broadband.” This refers to the service provider delivering managed services over broadband sourced by the enterprise.
Finally, cellular connectivity (4G) and, in the future, 5G, is increasingly being used for backup, rapid deployment or temporary locations, although it does not offer SLAs. As with broadband, enterprises may be able to get attractive deals for data-only mobile services themselves, which will then be managed by their global provider.
Managed Services
Most global WANs are delivered on a managed service basis, with the on-site devices, such as routers, security appliances and WAN optimizers, provided and managed by the service provider. Transport links are usually sourced from the managed service provider, but might also be sourced by the enterprise, who would then give the managed service provider operational responsibility for them. Although more U.S.-headquartered multinationals are moving to managed network services, a significant number still manage their networks in-house and only source transport links from their global providers.
As more network functions, such as SD-WAN application policies or NoD bandwidth, are controllable via the providers’ portals and APIs, networks are moving more to a co-managed reality. In this case, responsibilities for various network management functions are divided between the provider and the enterprise.
Pricing Trends
Downward pressure on global network service prices is relentless (e.g., global MPLS services are undergoing unit price declines averaging 10% per year, although with strong regional variance). Gartner has produced research summarizing and predicting pricing trends for different services and geographies (see “Network Service Price Trends: What You Need to Know to Save Money on Your Next Contract Negotiation”). The response from providers varies, with some focusing on extending their own networks, while others are relying heavily on network-to-network interface (NNI) connections to partners to improve their regional coverage. Most providers are increasingly using carrier-neutral communications hubs, such as those operated by Equinix, to allow them to cost-effectively interconnect with multiple access, backbone and cloud providers.
These hubs, particularly when combined with NFV and/or SD-WAN, have dramatically reduced the level of investment required to be competitive in the global network service market. This has allowed smaller providers, including some of the more recent entrants to this Magic Quadrant, to offer solutions competitive with those of the largest providers. However, maintaining a consistent set of service features and user experiences across these different elements remains a challenge.
Change Underway:
The network service market is undergoing a major transformation, with new generations of software-based network technologies enabling new services and new business models that are less focused on large-scale infrastructure. To reflect these trends, this Magic Quadrant focuses on transformational technologies and/or approaches that address the future needs of end users, as well as today’s market.
Gartner defines the global network service market as the provision of fixed corporate networking services with worldwide coverage.
Current global network services evaluated in this Magic Quadrant include:
- WAN Transport Services — These include Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) service, Ethernet services and internet services, such as dedicated internet access (DIA), broadband and cellular.
- Carrier-Based Cloud Interconnect (CBCI) — This is a direct connection between a service provider’s enterprise network services, such as MPLS and/or Ethernet services, and the private connection option of one or more cloud service providers (CSPs). CBCI can be established directly between the network service provider (NSP) and the cloud provider or via a cloud exchange, such as Equinix Cloud Exchange.
- Managed WAN Services — These include managed software-defined WAN (SD-WAN). Although a minority of enterprises are renewing their managed router networks, most new managed global network deployments in 2019 were managed SD-WAN networks using a mix of MPLS and internet transport. This is a trend Gartner expects to continue. An option for managed SD-WAN services is for the provider to deploy network-based SD-WAN gateways to facilitate interconnection between SD-WAN and non-SD-WAN networks, improve scalability and avoid the need for traffic to traverse long distances over the internet.
Emerging global network services that will be evaluated include:
- Network On Demand (NoD) — NoD services from NSPs enable enterprises to make real-time changes to access/port bandwidth, change the WAN service types delivered over a network port and, in some cases, add and remove endpoints (e.g., connections to cloud providers). This occurs under software control, via the provider’s web portal or APIs.
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV) — NFV is an architecture to deliver multiple network functions, including routing, firewall, SD-WAN, WAN optimization, visibility and voice as software, termed virtual network functions (VNFs). NFV enables enterprises to rapidly (in minutes) deploy network functionality to locations where it is required. This functionality is the replacement for purpose-built hardware devices, such as routers, security devices or WAN optimizers. NFV can be implemented on universal customer premises equipment (uCPE; see below) or in NFV service nodes, located in the provider’s network, or in colocation facilities. NFV enables network functions to be activated on demand (and deactivated when no longer required) and consumed on an “as a service” basis. This can improve the agility and cost-effectiveness of the enterprise WAN.
- Virtual Customer Premises Equipment (vCPE) — This is the use of industry-standard x86 devices (uCPE), rather than function-specific appliances, to deliver enterprise network edge functions, including WAN edge routing, SD-WAN, WAN optimization, visibility and security functions (e.g., firewalls).
In addition, it is highly desirable for providers to offer related network services, including managed WAN optimization, managed application visibility, and managed, network-related security services. Integrators, virtual operators and carriers may be included, but only if they will bid for stand-alone WAN deals and provide and manage offerings that include the WAN connectivity.
During the past 12 months, Gartner has seen continued changes in enterprise requirements and buying criteria for global networks. Enterprises are placing an ever-growing emphasis on their need for greater agility and especially enabling their organization’s adoption of cloud services and the Internet of Things (IoT). They are increasingly willing to consider smaller providers and innovative services, particularly those that can be consumed on an as-a-service basis. Therefore, they are placing less emphasis on supplier size, network scale and the availability of large numbers of provider staff to deliver customized capabilities.
NSPs are taking advantage of the marketplaces created by carrier hubs, such as those provided by Equinix and Digital Reality. This enables them to source access that’s distance-insensitive, at the national or even regional level, reducing the need to deploy large numbers of network points of presence (POPs). POPs are increasingly acting as gateways between access and backbone network services of various types, and cloud providers. In addition, they are serving as locations where virtualized network services, such as security, can be applied.
Internet services, including broadband, DIA and cellular, are growing in importance as transport options, alongside the continued use of MPLS and Ethernet services. New services such as managed SD-WAN, NoD services, NFV and vCPE, which transform the enterprise networking market, are being deployed to improve the agility of providers’ network solutions. Many of these services require a platform-based approach to delivering services, increasing the trend to move away from customized solutions, toward standard, off-the-shelf managed services, consumed on an as-a-service basis.
We are seeing a distinct split in providers’ attitudes toward NFV and vCPE. Some providers are “doubling down” on the technology, making it their default edge device offering. Others are still focusing on appliances at the network edge, frequently accompanied by network-based NFV, especially for services such as security.
Although delivering against a strong technological roadmap is important, it is equally important that services be delivered with good operational performance to implement and sustain them.
The inclusion and exclusion criteria for this year’s Magic Quadrant (see Figure 1), although similar to prior years, have been adjusted to reflect these trends.
Figure 1. Magic Quadrant for Network Services

Source: Gartner (February 2020)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Digital business initiatives are placing increasing demands on the enterprise network, increasing the needs for bandwidth (between 20% and 30% annually), reliability and performance. Video, live and stored, is driving significant increases in bandwidth, whereas IoT typically requires greater reliability.
A growing proportion of enterprise applications are being delivered as cloud services — infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and SaaS. This requires incorporation of cloud endpoints into the network and a burgeoning need for data center-to-cloud and cloud-to-cloud connectivity.
Above all, digital business requires that enterprise networks become significantly more agile, to allow the rapid accommodation of new endpoints, new applications and new network capabilities. However, enterprises continually need to do all of this, while optimizing their WAN expenditure.
To address these requirements service providers are deploying a range of new networking technologies. SD-WAN is now the default offering for new network deployments and major refreshes, while the virtualization of network edge functions, using NFV and vCPE, is gradually becoming more common. CBCI is also mainstream, complemented by emerging NoD services.
Growing use of the internet as a network transport option, together with cloud endpoints, is resulting in performance uncertainty, and is driving significant demand for application visibility services.
Fortunately, enterprises can choose from a wide selection of solution providers, most operating across multiple geographies. This breadth is allowing enterprises to choose between one, two or many providers to find the best solution for their specific needs. These decisions will be based on geographic requirements, the specific service required and the preferred sourcing approach (i.e., the enterprise’s desire to manage multiple networks from multiple providers). Competition continues to drive down unit prices for global networking services. However, in a market in which there are no meaningful price lists, enterprises still need to use competitive procurement practices and strong negotiations to obtain the best prices.
India’s Tumultuous Telecom Market: Government vs the Telcos
by MG Arun, India Today
Ten years after the Indian telecom was rattled by the 2G spectrum scam and the Supreme Court cancelled 122 licences issued by the UPA government in 2008, the sector is witnessing another upheaval. This time, the apex court has stepped in to ensure that telcos Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea and Tata Teleservices pay up over Rs 1 lakh crore in revenue share the government claims they owe in return for acquiring licences and spectrum. The three companies are widely referred to as the ‘incumbent’ players, since the other major operator, Reliance Jio, entered the market only in 2016. According to the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), which issues the licences, the three incumbents owe the government Rs 35,600 crore, Rs 53,038 crore and about Rs 14,000 crore, respectively.
On February 17, three days after the Supreme Court pulled up telcos for not abiding by its January 16 order to clear the dues, Vodafone Idea made a Rs 2,500 crore part-payment to the DoT, with the assurance that it will pay another Rs 1,000 crore by February 21. Bharti Airtel said it had paid Rs 10,000 crore to the DoT while Tata Teleservices paid Rs 2,197 crore.
While the telcos have sought relief from the hefty payments, Vodafone Idea‘s case is particularly complicated, with the court rejecting its plea that the DoT be directed not to invoke the company’s bank guarantees-reportedly about Rs 2,500 crore-to recover dues. “I hope good sense prevails over the government that if it encashes the guarantees, the banks will pay, but the company will go down,” Vodafone Idea’s counsel Mukul Rohatgi told a TV channel.
Industry observers say if Vodafone Idea shuts down, the consequences will be drastic. “It will be a terrible thing for the economy, the banking system, the telecom industry and its customers, suppliers and digital partners,” says a telecom official, requesting anonymity. “Unlike airlines, where the supply breach caused by the closure of, say, Jet Airways could be filled by other players, in telecom, capacity cannot be replaced, including the enormous physical infrastructure. In such cases, the executive should wield its powers and step in to save the operator.”
The industry expects the government to allow it an extended moratorium to make the payments, to redefine Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR), or even waive interest and penalties, and to stick to the principal amount to be paid. The incumbents and the DoT have been waging a legal battle for around 15 years. The crisis points to ambiguities in policy, which have not only caused confusion, but also left loopholes for telcos to exploit. The government’s handling of the telecom sector has also come under question. What was a sunrise industry now sees players, except Reliance Jio, battling for survival. It all threatens to end in a duopoly that could send tariffs skyrocketing.
TROUBLED HISTORY
The telecom sector was liberalised under the National Telecom Policy, 1994, paving the way for the entry of private players. For a fixed fee, licences were issued in various categories-unified licence, which allowed a firm to offer both wireless and wireline services; licences to Internet Service Providers (ISPs); and licences to provide passive infrastructure, such as towers and fibre. In 1999, the NDA government gave licensees the option to migrate to the revenue-sharing fee model.
As per the model, telecom operators were to share a percentage of their AGR with the government as annual licence fee and spectrum usage charges. The licence fee was pegged at 8 per cent of AGR while the spectrum usage charges were fixed at 3-5 per cent. According to Clause 19.1 of the Draft Licence Agreement, gross revenue included installation charges, revenue on account of interest, dividend, value-added services and so on. Calculated on this basis, AGR excluded certain charges, such as the Interconnection Usage Charge (IUC) and roaming revenues that are passed on to other operators.
While the DoT says it is following the definition of AGR as per the licence agreement, industry sources claim the definition of AGR in the licence conditions underwent revisions regarding the applicable rates for licence fee and spectrum usage charge. While operators wanted to be charged on the basis of their core business, involving use of the spectrum allotted, the DoT said the definition of AGR includes other items, such as dividend, interest, capital gains on sales of assets and securities and gains from foreign exchange fluctuations. In 2001, the Association of Basic Telecom Operators submitted to the government that non-operational income should not be included while computing AGR. However, in 2002-2003, the DoT demanded revenue share as per the Draft Licence Agreement, following which operators approached the Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT).
A long-drawn-out legal battle followed. Around the same time, the telcos stopped paying their revenue share on the disputed part of the AGR. Operators argued that taxes and levies in India were among the highest in the world and appealed to the government not to press for payment of AGR-based dues. The industry’s contention is that it pays the government Rs 30 for every Rs 100 earned, in the form of levies and taxes. GST is at 18 per cent, and the industry has been demanding that the licence fee be reduced to 3 per cent, and the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) charge to 3 per cent from the current 5 per cent. USOF was created in 2002 to expand internet and mobile connectivity in rural areas. In August 2019, the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) alleged that half the funds raised by USOF between 2002-03 and 2018-19 remained unutilised.
In 2015, the TDSAT ruled that AGR includes all receipts except capital receipts and revenue from non-core sources. But on October 24, 2019, the Supreme Court set aside that order and upheld the DoT’s definition of AGR. The incumbents approached the court for a review, but the plea was rejected on January 16 this year. However, the Supreme Court agreed, on January 21, to take up a modification plea filed by the telcos, seeking to negotiate a ‘sustainable payment schedule’. This followed the Union cabinet’s decision on November 20, 2019, that telcos be given a two-year moratorium on payments.
However, on February 14 this year, the Supreme Court slammed the telcos over unpaid dues and warned of contempt proceedings if they did not pay up by March 17. “The companies have violated the order passed by this court in pith and substance,” said the court. “In spite of the dismissal of the review application, they have not deposited any amount so far.” Following the Supreme Court rap, the DoT asked the telcos to pay the AGR dues by the end of day on February 14.
As per reports, the original disputed amount of about Rs 23,000 crore snowballed to the present figure of close to Rs 1.5 lakh crore as the DoT contended that the entire dues accumulated over the past 15 years be paid with interest and penalty.
The Supreme Court was of the view that telecom players benefited immensely from the DoT’s formula of AGR calculation. In its October 24, 2019, order, the court said the “revenue-sharing package turned out to be very beneficial to the telecom service providers, which is evident from the continuing rise in the gross revenue”. Gross revenues earned by telecom service providers stood at Rs 4,855 crore in 2004, Rs 89,108 crore by 2007, and subsequently touched Rs 2,37,676 crore in 2015, said the court.
SIGNALS TURN RED
“The industry is reeling from the Supreme Court decision on AGR. It has further aggravated the already precarious financial position of operators,” says Rajan Mathews, director general of COAI. “The ball is now firmly in the government’s court to fix the vexatious AGR problem, by either eliminating it altogether or redefining it along the lines recommended by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India and the industry, as well as reduce the licence fee and spectrum usage charge to 3 per cent and 1 per cent, respectively. We believe AGR is an anachronism in a day when operators have paid for spectrum and licences upfront.”
As of January, TRAI pegs Reliance Jio as the largest telecom player, with 369 million mobile subscribers, followed by Vodafone Idea (336 million) and Bharti Airtel (327 million). ‘The increase in Jio’s subscriber base is largely at the cost of the fall in Vodafone Idea‘s subscriber base,’ says a report by India Ratings and Research. While a Vodafone Idea spokesperson refused to comment, company sources said the board had assessed the company could pay up Rs 3,500 crore without delay, of which Rs 2,500 crore was paid on February 17. Vodafone Idea‘s assessment of its dues to the government is “significantly different” from the government’s claim, the source says. For part payments of dues, the company can dip into its cash reserves without affecting its working capital needs. Also, the Indian subsidiary can ask the parent Vodafone Plc to pitch in with Rs 8,000 crore, the source says. The proposed sale of Indus Towers, a telecom infrastructure firm jointly promoted by the Bharti Group and Vodafone Group, would also help.
In a February 17 letter to member (finance), DoT, Bharti Airtel director-legal Vidyut Gulati said that of the Rs 10,000 crore paid, Rs 9,500 crore was on behalf of Bharti Airtel and Rs 500 crore on behalf of its subsidiary, Bharti Hexacom. ‘We are in the process of completing the self-assessment exercise expeditiously and will duly make the balance payment upon completion of the same, before the next hearing in the Supreme Court,’ says the letter, which india today has seen. While a Bharti Airtel spokesperson declined comment on the AGR matter, a mail sent to Tata Teleservices went unanswered till the time of going to press.
The Supreme Court’s October 2019 directive hit the incumbent telcos hard. The year-to-date losses for Vodafone Idea, Bharti Airtel and Tata Teleservices in FY2019-20 stand at Rs 62,233.8 crore, Rs 26,946 crore and Rs 2,840 crore, respectively. Vodafone Plc has already spent over $17 billion (around Rs 1.2 lakh crore) to buy out Hutch and Essar’s stake in Vodafone Essar between 2007 and 2012, and injected several billions of dollars more to acquire spectrum and build infrastructure. Effective December 1, 2019, Reliance Jio, Vodafone Idea and Bharti Airtel announced tariff hikes, for the first time in five years. According to India Ratings and Research: ‘The average revenue per user (ARPU) reported by telcos has started showing signs of recovery in the last two-three quarters. The recent tariff hikes are likely to support the increase in ARPU over the next few quarters.’
Even if Vodafone Idea tides over the AGR crisis by, say, delayed annual payments over the long term, its weak balance sheet makes it vulnerable, as per an SBI Caps note, to incremental regulatory changes. In a three-player market, that could be a reason for TRAI to go soft on it. ‘But the moment Indian telecom shapes up as a duopoly, the regulator may start perceiving telcos differently. Price hikes, pricing power, spectrum pricing-all…may see the regulator taking a tougher stand,’ the note says. While some analysts foresee a Reliance Jio–Bharti Airtel duopoly and higher tariffs, Vodafone Idea is looking to stay in the fight. “There is hope of some relief in terms of staggered payments [of dues],” says a company official. But the options seem to be running out for the British telco that had entered India betting on its high growth potential.
Telstra’s 5G network expands to 32 Australian cities; CEO Andrew Penn: “mmW to supercharge 5G”
Telstra has rolled out 5G network coverage to selected areas in 32 major and regional cities. It aims to deliver 5G into 35 cities by mid-year. “More than 4 million people pass through our 5G footprint,” said Telstra CEO Andrew Penn.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
We’re busy rolling out 5G, and our coverage is growing day-by-day. Right now, we’re in 32 cities and regional centres across Australia – more than any other network. If you’re in an area without 5G Coverage, your device automatically swaps to 4G or 3G depending on the available signal.
This map shows where we have 5G coverage at 13 February 2020.

……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Telstra CEO Andrew Penn said internal testing of the 5G mmWave technology had begun and work was underway to roll out trial mobile sites in selected areas ahead of an expected auction of mmWave spectrum in 2021. 26 GHz will be the first mmWave band to be used for mobile services in Australia.
“mmWave will supercharge 5G. Its higher capacity and the potential to deliver even faster speeds as well as lower latency will help power the next generation of devices and innovations,” Penn said.
Telstra customers’ early access to its mmWave 5G network will initially be in selected areas. It will be made possible through ACMA 26 GHz scientific licenses that can be used for trials ahead of the spectrum auction early next year. 26GHz is set to become one of the most prevalent spectrum bands for mmWave 5G in the world, including Europe and Asia.
Telstra and technology partners Ericsson and Qualcomm Technologies recently tested live mobile base station in a commercial network using the 26GHz band.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Telstra earlier said its mobile footprint is more than 2.5 million square kilometers, at least 1 million square kilometers more than any other mobile network in Australia. Telstra has built more than 237 new mobile sites and upgraded 267 in the second half of 2019.
Average download speeds have increased from 200 megabits to 304 megabits per second now. Telstra also recorded about 1.9 gigabit in the live network. Data usage on 5G network has increased more than 28x in the first half of the year.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Telstra has expanded narrowband (NB-) IoT coverage (included in the not yet completed IMT 2020 specs) to nearly 4 million square kilometers from over 3.5 million. LTE CatM1 IoT coverage is around 3 million square kilometers.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
GSMA: New Telco Edge Cloud Platform Project has 9 Telcos Participating
GSMA announced a new initiative to develop a common telco edge cloud platform for network operators. China Unicom, Deutsche Telekom, EE, KDDI, Orange, Singtel, SK Telecom, Telefonica and TIM are participating in the project. It will make local network operator assets made available to developers and software vendors to bring their services closer to enterprise customers.
The inter-operable platform will be developed in 2020. The operators have agreed to work together to develop the edge compute architectural framework and reference platform, and the GSMA has launched an Operator Platform Project to support the initiative. Initially, the platform will be deployed across multiple markets in Europe, before expanding to other parts of the world.
Operators will offer through the platform edge compute, storage and connectivity to their customers. The GSMA said the open platform will ensure data protection and sovereignty mechanisms, while offering carrier-grade reliability, security and trustworthiness. It will leverage existing technology where possible, such as aggregation platforms like MobiledgeX, or the interconnection mechanisms developed as part of the GSMA MultiOperator MEC experience.
Telco Edge Cloud will:
- Be open and inclusive
- Provide data protection and sovereignty mechanisms
- Offer carrier-grade reliability, security, trustworthiness
- Leverage existing technology solutions; as appropriate, including, but not limited to, aggregation platform solutions such as MobiledgeX, or the interconnection mechanisms developed as part of the GSMA MultiOperator MEC experience.
“Operators are very well placed to provide capabilities such as low latency through their network assets,” said Alex Sinclair, CTO at GSMA. “It is essential for enterprises to be able to reach all of their customers from the edge of any network. Based on the GSMA Operator Platform Specification, Telco Edge Cloud will provide enterprise developers and aggregators with a consistent way to reach connected customers.”
“Edge cloud will build a unified network edge ecosystem, providing diversified and customised products and services, and multiple platform capabilities. It will also realise more extensive boundary-crossing cooperation to meet the requirements of digital transformation of various vertical industries,” said Xiongyan Tang, the Chief Scientist of China Unicom Network Technology Research Institute and the Chief Architect of China Unicom Intelligent Network Center, China Unicom.
“Edge Cloud has an exciting potential to enable and enhance many innovative experiences for our customers. I welcome this operator initiative to take ownership of the edge opportunity by joining forces to deliver our capabilities in a federated edge service,” said Claudia Nemat, Board Member Technology & Innovation at Deutsche Telekom. “Leveraging MobiledgeX as platform partner and aggregator in the federation puts operators on the best track to create scale, bring in the developer community and make a market impact.”
“Edge Cloud is a promising opportunity to enable the development of services that need low latency connection and to meet various service demands from enterprise customers. The innovation of telecommunication services will be accelerated by the enhancement of service quality and the customer experience in real-time applications such as cloud XR and cloud gaming,” said Yoshiaki Uchida, Member of the Board, Executive Vice President, Executive Director, Technology Sector at KDDI.
“To address the edge-cloud computing market, operators need to work very closely together to create an interoperable platform and to monetise their extremely valuable assets,” said Mari-Noëlle Jégo-Laveissière, Deputy Chief Executive Officer, Chief Technology and Global Innovation Officer, Orange. “We, at Orange, believe that it is a must-have to unleash new business opportunities enabled by both edge computing and 5G. That’s why we are proud to support the GSMA Telco Edge Cloud initiative.”
“We believe that a cross-border edge cloud platform which serves bandwidth needs and lower latency requirements, is what’s needed at this time as it allows organisations with multi-market operations to deploy and manage time-critical applications closer to where the data is collected. We look forward to collaborating with GSMA and the other telcos on this exciting initiative,” said Mark Chong, Group CTO of Singtel.
“Edge Cloud is a key enabler to unlock the full potential of emerging applications such as AR/VR, cloud robots, and smart factory with improved QoS, real-time intelligence, security and data privacy. In order to provide a seamless global MEC experience to our customers, it is critical that mobile operators around the world come together and join forces,” says Dr. Kang-Won Lee, Vice President and Head of Cloud Labs at SK Telecom. “SK Telecom is excited to collaborate with global partners, bringing our edge cloud experience and tech leadership to the team to realise the vision of mobile edge cloud.”
“The market needs an Edge Cloud that meets the enterprise demands to service their customers. Telecom operators are in an extremely good position to provide a trusted and open Edge Cloud, so enterprises can maximise their service offering and business opportunities being as close as needed to their customers,” said Enrique Blanco, Group CTO, Telefonica.
“Edge Cloud is a fundamental asset for the new requirements of many business segments and customers,” said Elisabetta Romano, Chief Innovation & Partnership Officer, TIM. “Edge Cloud will be a formidable enabler to transform the network from a “bit pipe” to an effective digital business platform, thanks to flexible computing capacity and low access latency to computing resources.”
Geoff Hollingworth, CMO of MobiledgeX, told RCR Wireless News that he has been very close to the company’s collaboration with the GSMA/operator initiative. He said that the goal of the program is to build an operator edge platform that presents a solution “as homogenous as possible” to the enterprise market, in the same way that the mobile industry has presented global messaging and data solutions.
“They want to fast-track that in the industry, as much as possible into the real world,” he said. Enterprises, Hollingworth went on, need easy access to high-performance, cloud-native computing close to where they need that data processed, whether it’s in a country where their products are manufactured or perhaps where they are used, or both. He said there is more than one model for providing that, such as a form of aggregated networks where local operators are paid for being part of it and running workloads locally, or via something similar to roaming agreements between operators for so-called “east-west interfaces” that allow access to local edge computing resources. He expects both to be explored in the GSMA initiative.
“It’s purely a question of agreeing to roll out in a way that actually meets the needs of the real customers,” he added. MobiledgeX, Hollingworth said, has been in conversations with operators around the world as it seeks to build its own edge computing platform footprint, and he said it has a good handle on just what enterprise customers and application developers need and brings that knowledge to the table as part of its participation in the GSMA Operator Platform Project.
Edge use cases, he went on, always begin with one thing in common: a large volume of data that is very information-rich, that needs to be interpreted in real-time, probably by artificial intelligence; and then resulting insights need to be transmitted both locally to make an immediate change, and to a larger big-data engine for longer-term processing. MobiledgeX sees that such data streams are often coming from video cameras being used as IoT sensors and requiring vast, fast image processing capabilities. Even in the case of lower-data-intensive IoT sensor capabilities, Hollingworth said, those capabilities are increasingly being built into products and solutions that enterprises are buying—but they’re not being turned up, even if the companies would like to use them, because the enterprises can’t cope with the volume of information that would result. Globally available, easily accessed edge computing resources could change that.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The GSMA Operator Platform Project:
The GSMA’s Operator Platform Project intends to develop a framework for operators to expose and monetise their network capabilities. Operators will offer through the Operator Platform edge compute, storage and connectivity to their customers leveraging:
- their existing relationships with enterprises who already have use cases requiring edge,
- their vast local footprint/real estate,
- an inimitable position for stringent security and data privacy, residency, sovereignty and
- the organisational competence from the experience of providing highly reliable (five nines) services over a distributed and capillary network environment.
Cloud capabilities will be treated as a subset of edge.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About the GSMA:
The GSMA represents the interests of mobile operators worldwide, uniting nearly 750 operators with almost 300 companies in the broader mobile ecosystem, including handset and device makers, software companies, equipment providers and internet companies, as well as organisations in adjacent industry sectors. The GSMA also produces industry-leading events such as Mobile World Congress, Mobile World Congress Shanghai, Mobile World Congress Americas and the Mobile 360 Series of conferences.
For more information, please visit the GSMA corporate website at www.gsma.com. Follow the GSMA on Twitter: @GSMA.
Media Contacts:
For the GSMA
GSMA Press Office
[email protected]
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
SKT Forms Global Alliance with 9 Telcos on 5G Mobile Edge Computing
SK Telecom Co., South Korea’s largest mobile carrier, said Sunday it has formed an international alliance with nine telecommunication firms to develop 5G mobile edge computing (MEC) technologies and services.
SK Telecom said Telecom Edge Cloud TF was established with nine other companies at a GSMA meeting in London last week. Its members include Deutsche Telekom AG of Germany, KDDI Corp. of Japan and EE Ltd. of Britain. The TF aims to have global commercialization of 5G MEC by sharing each member’s technology and service know-how.
MEC is a key technology in delivering ultra-low latency data communication in 5G networks that allows companies to offer better solutions in cloud gaming, smart factory and autonomous driving. It aims to minimize latency by providing a “shortcut” — which can be completed by installing small-scale data centers at 5G base stations — for data transmission.
SK Telecom has been one of the active players in the mobile industry to develop 5G MEC solutions. In January, the company formed Global MEC TF with five Asian telecommunication firms to develop 5G MEC technologies and services.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Telecom Operators Collaborate to Build the Telco Edge Cloud Platform with GSMA Support
Nine operators join forces on global edge computing, with GSMA’s support
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/10-things-you-should-know-telco-edge-compute-philip-laidler
https://mobiledgex.com/assets/resources/stl/what-edge-developers-want-from-telcos-now—final.pdf
ITU-R WP5D Feb 2020 Meeting Report Excerpts: Technology Aspects WG (IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT)
by Hu Wang, Chair, ITU-R WP 5D Working Group Technology Aspects (edited for clarity by Alan J Weissberger)
NOTE that all documents referenced in this meeting report are ONLY available to those that have an ITU TIES account.
Introduction and Overview:
The WP 5D Technology Aspects WG met two times during the 34th meeting of ITU-R Working Party (WP) 5D in Geneva, Switzerland. The meeting concluded on February 26, 2020.
Main activities of Technology Aspects WG during this meeting were to:
-
review evaluation reports of Independent Evaluation Groups for the candidate technologies; complete evaluation report summaries (IMT-2020/ZZZ) and complete the Step 4 of the Evaluation Process;
-
continue working on a new Report ITU-R M.[IMT-2020.OUTCOME];
-
continue working on a new Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT-2020.SPECS];
-
continue working on the revision of Recommendation ITU-R M.1457-14 (LTE);
-
continue working on synchronization of multiple IMT TDD networks;
-
start the work on two new subjects [IMT TERRESTRIAL BROADBAND REMOTE COVERAGE] and [IMT.FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS].
During this meeting, WG Technology Aspects established five Sub-Working Groups (SWGs):
– SWG Coordination (Chair: Mr. Yoshio HONDA),
– SWG Evaluation (Acting Chair: Mr. Yoshio HONDA),
– SWG IMT Specifications (Chair: Mr. Yoshinori ISHIKAWA),
– SWG Out of band emissions (Chair: Mr. Uwe LÖWENSTEIN),
– SWG Radio Aspects (Chair: Mr. Marc GRANT)

Evaluation of IMT-2020 candidate technology submissions:
This 34th WP 5D meeting is a milestone of the IMT-2020 submission and evaluation process: Step 4 – Evaluation of candidate RITs or SRITs by independent evaluation groups.
Twelve Independent Evaluation Groups (IEGs) submitted to this meeting twenty-seven evaluation reports of all the candidate technology submissions. The meeting reviewed these evaluation reports, with participations of the IEGs, the proponents of candidate technology submissions and other participants. The Step 4 was completed with all the evaluation reports recorded.
Evaluation report summaries are captured in the respective documents (5D/TEMP/112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 125 and 126). The meeting also developed an overall summary – Summary of Step 4 of the IMT-2020 Process for Evaluation of IMT-2020 Candidate Technology Submissions (5D/TEMP/124), which also captures different views raised during the discussion at the meeting.
An addendum to the Circular Letter 5/LCCE/59 was developed to convey the completion of Step 4.
The meeting also made progress on the work of Document M.[IMT-2020.OUTCOME]. It was agreed to upgrade the working document to a preliminary draft new Report (5D/TEMP/111).
IMT-2020.SPECS
The work of M.[IMT‑2020.SPECS] continued at this meeting based on received contributions. The working document and the work plan were revised accordingly (5D/TEMP/41 and 40).
A draft liaison statement to potential GCS Proponents to request the inputs to 35th meeting was developed. It was noted that confirmation of the potential GCS Proponents can only be done after WP 5D takes a decision for Steps 6 & 7 on IMT-2020 RIT/SRIT at its 35th meeting.
Work items in SWG Radio Aspects
The meeting made progress on the work of Synchronization of multiple IMT-2020 TDD networks and the working document was updated (5D/TEMP/93).
A new working document is created to study terrestrial IMT for remote sparsely populated areas providing high data rate coverage – M.[IMT TERRESTRIAL BROADBAND REMOTE COVERAGE] (5D/TEMP/101).
The meeting also agreed to start work on future technology trends, and a work plan was developed (5D/TEMP/96).
Objective for the 35th WP 5D meeting:
The key objectives of WG Technology Aspects for the 35th WP 5D meeting are as follows:
i) complete the work of Step 6 and Step 7 of the IMT-2020 submission and evaluation process; finalize the document M.[IMT-2020.OUTCOME];
ii) continue work on M.[IMT‑2020.SPECS];
iii) finalize the revision of Recommendation ITU-R M.1457-14;
iv) continue work on synchronization of multiple IMT-2020 TDD networks;
v) continue work on M.[IMT TERRESTRIAL BROADBAND REMOTE COVERAGE] and M.[IMT.FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS].
TIP OpenRAN and O-RAN Alliance liaison and collaboration for Open Radio Access Networks
Overview:
The Telecom Infra Project (TIP) OpenRAN project and the O-RAN Alliance today announced a liaison agreement to ensure their alignment in developing interoperable, disaggregated and open Radio Access Network (RAN) solutions.
Since their inception, the overlapping efforts of the two consortiums led to a lot of questions about duplication of work, different specs and interface for the same functions as well as different IP licensing policies. The two groups are calling this liaison arrangement as a “new level of collaboration” for open RAN, rather than a merger. The press release stated:
With this liaison agreement O-RAN and TIP are now reaching a new level of collaboration for open RAN. The liaison allows for sharing information, referencing specifications and conducting joint testing and integration efforts.
The O-RAN Alliance was formed in February 2018 when the x-RAN Forum merged with the C-RAN Alliance. The group is focused on the development of open, intelligent, virtualized and interoperable RAN specifications. The Alliance has already created 31 specifications, with 37 demonstrations of the technology at past MWC events, global plugfests, and more than 1 000 000 lines of code released in partnership with the Linux Foundation. Operators have begun to announce network implementations.
O-RAN Alliance’s mission and focus complements TIP’s mission of deploying end-to-end disaggregated telecom infrastructure in varying environments.
TIP said it’s seen a rapid increase in demand for advanced OpenRAN trials and deployments.
- Following on the heels of its TIP Summit announcement in November 2019, Vodafone launched trials in Mozambique and the Democratic Republic of the Congo and is progressing with trials in the UK and Ireland.
- In Indonesia, Indosat Ooredoo and Smartfren will conduct the first OpenRAN field trials in the APAC region. Smartfren has also conducted and completed the first OpenRAN lab trial in the region.
- In Malaysia, Edotco, the tower arm of Axiata group, is collaborating with Celcom Axiata in conducting lab trials with the path to field trials. Following their announcement of TIP OpenRAN deployment in the UAE, Etisalat is starting trials of OpenRAN systems in other regions. In North America, Sprint completed its RFI evaluation and will begin trials of OpenRAN 5G NR technologies in its TIP Community Lab.
…………………………………………………………………………………….
Evenstar Program to feed into OpenRAN:
Vodafone, Deutsche Telekom, Mavenir, Parallel Wireless, MTI, AceAxis, Facebook Connectivity and additional partners have unveiled the Evenstar RRU (Remote Radio Units). The Evenstar program will focus on building general-purpose RAN reference designs for 4G/5G networks in the Open RAN ecosystem that are aligned with 3GPP and O-RAN specifications.
The Evenstar program will contribute to the OpenRAN ecosystem by focusing on building general-purpose RAN reference designs for 4G and 5G networks that are aligned with 3GPP and O-RAN specifications and will help accelerate the adoption of TIP OpenRAN Project Group Solutions.
By decoupling the RRU hardware, Central Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit (DU) software, mobile network operators will have the ability to select best-of-breed components and the flexibility to deploy solutions from an increasing number of technology partners, TIP said. The intention of the Evenstar program is to contribute the proposed solution into TIP’s OpenRAN Project Group to help accelerate adoption.
…………………………………………………………………………………….
Quotes:
“This new collaboration framework between O-RAN and TIP, two major initiatives in the area of open networking, will support our mission to re-shape the RAN industry towards open and intelligent mobile network infrastructure,” said Alex Jinsung Choi, COO of the O-RAN Alliance and SVP Strategy & Technology Innovation, Deutsche Telekom.
“Alignment on O-RAN interoperability efforts will help the industry to speed up the delivery of commercial open RAN solutions. The establishment of the first joint O-RAN Open Test and Integration Center (OTIC) with the TIP Community Lab in Berlin is a concrete step to facilitate this multi-community approach.”
“TIP’s OpenRAN solutions are an important element of our work to accelerate innovation across all elements of the network including Access, Transport, Core & Services. Across the TIP community, we are seeing increasing demand and have achieved meaningful progress with OpenRAN deployments around the world,” said Attilio Zani, Executive Director, Telecom Infra Project.
“With this collaboration framework in place, TIP and O-RAN will work together to develop interoperable 5G RAN solutions. One of our first outputs will be the release of the OpenRAN 5GNR NR Base Station Platform requirements document with normative references to the O-RAN specifications.”
“Our hope, longer term, is that this forms the ability to accelerate the solutions that are in the marketplace and drives greater adoption of Open RAN technologies across the world,” Zani added.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
About O-RAN Alliance:
O-RAN Alliance is a world-wide community of more than 160 mobile operators, vendors, and research & academic institutions operating in the Radio Access Network (RAN) industry. As the RAN is an essential part of any mobile network, O-RAN Alliance’s mission is to re-shape the industry towards more intelligent, open, virtualized and fully interoperable mobile networks. The new O-RAN standards will enable a more competitive and vibrant RAN supplier ecosystem with faster innovation to improve user experience. O-RAN-compliant mobile networks will at the same time improve the efficiency of RAN deployments as well as operations by the mobile operators. To achieve this, O-RAN Alliance publishes new RAN specifications, releases open software for the RAN, and supports its members in integration and testing of their implementations.
For a short video describing O-RAN’s progress, see www.o-ran.org/videos
For more information please visit www.o-ran.org
About Telecom Infra Project:
TIP is a collaborative telecom community that is evolving the infrastructure that underpins global connectivity. TIP’s mission is to accelerate the pace of innovation in next generation telecom networks, through the design, build, test and deployment of standards-based, open and disaggregated end-to-end solutions. Over the past four years, TIP has driven substantial innovation across all elements of the network including Access, Transport, Core & Services, while spanning urban through to rural market use cases. To date, it has 13 Community Labs which test, validate and integrate solutions, embarked on field trials in Africa, Latin America, Middle East and Europe. The recently launched TIP Exchange hosts 45 products from 28 member companies.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
Vodafone Moves to O-RAN:
One of those early-adopter operators of the O-RAN Alliance specs is Vodafone. In November 2019, Vodafone’s head of network strategy and architecture Santiago Tenorio announced at the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) Summit in Amsterdam that Vodafone would issue a request for quotes (RFQ) for open RAN technology for its entire European footprint.
“That’s significantly more than 100,000 sites, and all the technologies are to tender — 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G,” said Tenorio. “We’ve invited the incumbent suppliers in Europe of course, but we’ve also invited the open RAN suppliers.” He didn’t sound too optimistic about the incumbent suppliers. Apparently, they hadn’t even responded to a Vodafone request for information about open 5G new radio equipment.
Mostafa Essa, an AI and data analytics distinguished engineer with Vodafone, told FierceWireless: “If you use a specific vendor for the RAN and ask him to carry some new features for something you are needing that is impacting your customers, they have to go back to their R&D and build up features,” said Essa. “Then we’ll test and give feedback. Right now, by using the open RAN concept, you can build up whatever you want whenever you want. It’s not connected to vendors’ roadmaps,” he added.
Vodafone has been conducting field trials in some of its markets in Europe, including Spain, Italy and in a rural area north of London. Vodafone used Parallel Wireless for its first open RAN tests, which it conducted in Turkey and Africa.
Essa continued: “We have a lot of instability, which is to be expected in trials. Right now, we are in the building phase. When you roll out this technology, sometimes you can get a lot of dropped calls and so on. But it’s the same as working with the vendors…..who are building systems with their own closed-source software.”
References:
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180227005673/en/xRAN-Forum-Merges-C-RAN-Alliance-Form-ORAN
https://www.fiercewireless.com/operators/vodafone-leads-early-adopter-phase-o-ran
https://www.fiercewireless.com/wireless/tip-o-ran-alliance-reach-liaison-agreement