ABI Research
ABI Research: 5G Network Slicing Market Slows; T-Mobile says “it’s time to unleash Network Slicing”
5G network slicing [1.] use cases are still few and far between, mainly because so few 5G telcos have deployed the 5G SA core network which is mandatory for ALL 3GPP defined 5G features and functions, such as network slicing and 5G security.
ABI’s 5G network slicing and cloud packet core market data report found that growing ecosystem complexity and ongoing challenges with cloud-native tooling adoption have placed increased pressure on new service innovation, like 5G network slicing. ABI expects the 5G network slicing market to be worth US$19.5bn in value by 2028. Considering existing market activities, a growing force behind 5G slicing uptake is enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and fixed wireless access (FWA). To that end, there is growing market activity and commercial engagements from network equipment vendors (NEVs) Ericsson, Huawei, Nokia, and ZTE, among other vendors. ABI regards these market engagements as representing a good foundation for the industry to match 5G slicing technology to high-value use cases, such as enhanced machine-type communication and ultra-reliable low-latency communications.
Note 1. A network slice provides specified network capabilities and characteristics – or multiple, isolated virtual networks – to fit a user’s needs. Although multiple network slices run on a single physical network, network slice users are sometimes (depending upon the access level of the individual) authenticated for only one network level, enabling data and security isolation and a much higher degree of security. Individuals can be sanctioned for more than network level. Each slice spans multiple connected components that form a network, components that include physical computing, storage and networking infrastructure. These are virtualized, and protocols are set in place to create a specific network slice for each user or application. This means that varying types of 5G traffic, such as video streaming, industrial automation and mission-critical applications, all can be accommodated on the same network, yet each has its own dedicated resources and performance guarantees.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“5G Slicing continues to promise new value creation in the industry. However, as reflected in multiple ABI Research’s market intelligence reports, a solid software and cloud-native foundation must be in place for that promise to materialize. That, in turn, is a prerequisite for a wider diffusion of 5G core adoption, an architecture that provides native support for 5G slicing,” explains Don Alusha, Senior Analyst at ABI Research.

Image Credit: Viavi Solutions
From a network architecture perspective, ABI said two modalities are emerging to deploy 5G slicing. The first one is to share the whole infrastructure spanning radio access network (RAN), core, physical devices and physical servers. This, said the analyst, constitutes a unified resource pool, the basis of which can be used to instantiate multiple logical connectivity transmissions.
A second approach is to provide hardware-based logical slices by slicing the physical equipment. The analyst cautions that this is a time-consuming, resource-intensive endeavor, but said it may be the best option for mission-critical services. It requires slicing the physical transmission network and oftentimes a dedicated user plane.
“Horizontal integration for cross-domain interoperability is critical going forward. Equally important is vertical integration for 5G slicing lifecycle management of multi-vendor deployments. There is ongoing market activity for the 5G core network penetration and maturity of 5G slice management functions. To that end, enterprises will seek to create and reserve slices statically and on-demand. They also want to efficiently integrate with cloud providers through open and programmable Application Program Interfaces (APIs) to enable hybrid cloud/cellular slice adoption. NEVs and other suppliers (e.g., Amdocs, Netcracker, etc.) offer solutions enabling CSPs to create fully automated and programmatic slicing capability over access, transport, and core network domains,” Alusha concludes.
These findings are from ABI Research’s 5G Network Slicing and Cloud Packet Core market data report. This report is part of the company’s 5G Core & Edge Networks research service, which includes research, data, and analyst insights. Market Data spreadsheets comprise deep data, market share analysis, and highly segmented, service-specific forecasts to provide detailed insight into where opportunities lie.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
T-Mobile US, the only U.S. carrier that has deployed 5G SA core network, has recently shared details of what it claims is “first use of 5G network slicing for remote video production on a commercial network,” which took place during Red Bull’s cliff diving event in Boston, MA. This customized slice gave the broadcast team supercharged wireless uplink speeds so they could easily and quickly transfer high-resolution content from cameras and a video drone circling the event to the Red Bull production team in near real-time over T-Mobile 5G. The uplink speed was up to 276 Mbps!
T-Mobile says they can also use network slicing for specific application types for enterprise customers across the U.S. Earlier this month they launched a first-of-its-kind network slicing beta for developers who are working to supercharge their video calling applications with the power of 5G SA. With a customized network slice, developers can sign up to test video calling applications that require consistent uplink and downlink speeds along with increased reliability. In the weeks since, we’ve seen tremendous interest from the developer community with dozens of companies large and small signing up to join the likes of Dialpad, Google, Webex by Cisco, Zoom and more.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Vodafone recently worked with Ericsson to provision network slices optimized for cloud gaming. In January, Samsung and KDDI announced the successful demonstration of Service Level Agreements (SLA) assurance network slicing in a field trial conducted in Tokyo, Japan. Yet there’s hardly a flood of real-world use cases (see References below).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.abiresearch.com/market-research/product/market-data/MD-SLIC/
https://www.computerweekly.com/news/366550353/5G-network-slicing-value-hits-19bn-but-growth-stalls
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/network/its-time-to-unleash-network-slicing
https://www.viavisolutions.com/en-us/5g-network-slicing
Network Slicing and 5G: Why it’s important, ITU-T SG 13 work, related IEEE ComSoc paper abstracts/overviews
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
Ericsson, Intel and Microsoft demo 5G network slicing on a Windows laptop in Sweden
Ericsson and Nokia demonstrate 5G Network Slicing on Google Pixel 6 Pro phones running Android 13 mobile OS
Nokia and Safaricom complete Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial
Is 5G network slicing dead before arrival? Replaced by private 5G?
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
GSA 5G SA Core Network Update Report
SatCom market services, ITU-R WP 4B, 3GPP Release 18 and ABI Research Market Forecasts
Satellite Communications (SatCom) market services will include fixed broadband Internet access, satellite Internet of Things (IoT), and Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) mobile (satellite-to-cell services). These services will experience growth due to more satellite players launching networks in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), alongside an increasing interest in terrestrial and satellite network convergence.
The market is expanding rapidly and major players are quickly recognizing its potential. While satellite networks are experiencing rapid changes due to innovations in small satellites and nanosatellites, Software-Defined Networking (SDN) applications, High Throughput Satellites (HTS), and inter-satellite links, terminals on the ground continue to see growth, with Very Small Aperture Terminals (VSAT) SatCom solutions maintaining dominance in the market.
According to Research & Markets, the SATCOM equipment market is valued at $22.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $38.7 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 11.3% from 2023 to 2028. Based on frequency, the multiband frequency is projected to register the highest during the forecast period 2023-2028.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
ITU-R Working Party 4B (WP 4B) is responsible for recommendations related to: Systems, air interfaces, performance and availability objectives for FSS, BSS and MSS, including IP-based applications and satellite news gathering.
WP 4B has a working document which is a preliminary draft new Report ITU-R M.[SAT IOT] – Technical and operational aspects of satellite Internet of Things (IoT) applications, a work plan and working document on Work plan for development of a preliminary draft new Report ITU-R M.[DEVELOPMENT AND TECHNOLOGY TRENDS FOR THE SATELLITE COMPONENT OF INTERNATIONAL MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATIONS]. WP5D last meeting was July 2023, but the following meeting won’t be till April 29 to May 5, 2024!
Yet the real SatCom air interface specifications work is being done by 3GPP, under the umbrella term of NTN:
3GPP Release 17 introduced new network topologies that are based on High-Altitude Platforms (HAPs) and LEO and Geostationary Orbit (GEO) satellites. Crucially, these laid out the foundation for satellite IoT and NTN mobile as Release 17 extended the cellular IoT protocols, LTE-M and Narrowband (NB)-IoT for satellites. This enabled two new standards for satellite networks, IoT-NTN and New Radio-NTN (NR-NTN). SatCom with individual mobile devices will close gaps in the terrestrial cellular networks to provide global connectivity. It will target issues like unreachability and service continuity in underserved regions and improve network resilience around the world.
The discussion items in the upcoming 3GPP Release 18 are expected to enhance NTN Mobile and Satellite IoT as key satellite enabled services. While Release 17 established the standards for IoT-NTN and NR-NTN, Release 18 will evolve both those specifications for IoT and satellite-to-mobile broadband connectivity. For NR-NTN, there are plans to run NR-NTN on Radio Frequency (RF) spectrum above 10 Gigahertz (GHz) to serve the aerospace and maritime industry, alongside businesses and buildings (with building-mounted devices). Release 18 is also expected to include enhancements in satellite backhaul, specifically the dedication of more spectrum for Mobile Satellite Services (MSS), with approximately 80 Megahertz (MHz) of uplink in the L-band and downlink in the S-band.
At the same time, improvements targeted toward Fixed Satellite Services (FSS) will be brought about by Release 18 as well, with the consideration of more bands in the Ka frequency bands for downlink (17.7 – 20.2 GHz) and uplink (27.5 – 30 GHz). While the specifics of 3GPP Release 18 are still in development, 3GPP has already established the boundaries of Release 18 that will benefit the SatCom market. Furthermore, with the recent mergers of Eutelsat and OneWeb in 2022 and Viasat and Inmarsat in 2023, in addition to the launch of Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity and Security by Satellite (IRIS2), a project endorsed by the European Union (EU) in 2022 to enhance connectivity throughout the EU, more partnerships and agreements are expected to arise ahead of the official launch of 3GPP Release 18 in 2024.
ABI Research says that 3GPP Release 18 aims to unlock new capabilities toward the evolution of 5G-Advanced and establish new regulatory requirements, along with new bands, while optimizing satellite access performance. The market research firm forecasts the market value for worldwide SatCom to be US$94.9 billion by 2027 (MD-SATCC-102). The growth of NTN mobile, in addition to broadband, will drive the market moving forward, with special mention of NTN mobile revenue likely to shoot from 0.2% of the total revenue in 2023 to 8.8% of the overall SatCom revenue by 2027. ABI Research recognizes that greater value has been placed on the protocols, such as 3GPP Release 18 and beyond, that will develop and nurture the SatCom space.
Strategic partnerships between terrestrial and NTN operators, solution providers/Communication Service Providers (CSPs), and wireless end-user equipment vendors are currently on the rise and will be critical in expanding the ecosystem and market toward 2027. For instance, MediaTek and Qualcomm have partnered with Inmarsat and Iridium, respectively, to target the NTN mobile market.
Meanwhile, AST SpaceMobile has agreements with AT&T, Rakuten Mobile, and several other mobile network operators. Where satellite IoT is concerned, CSPs like Deutsche Telekom have established partnerships with Intelsat and Skylo, whereas Telefónica and Sateliot are working together to trial satellite IoT connectivity. While partnerships are a good indicator of SatCom’s market potential, it is important that operators consider differentiated and unique product offerings for clients.
The value proposition that SatCom players can offer their target market will be essential for this process. Some examples might include integrated end-to-end IoT solutions for maritime, offshore connectivity, or end-to-end NTN mobile solutions that marry NTN hardware and software for satellite connectivity. Nonetheless, the creation of new value added services will benefit from 3GPP Release 18, in addition to driving the overall momentum and agenda of the Satellite Communications market.
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg4/rwp4b/Pages/default.aspx
ABI Research’s Highlights & Developments in the SatCom NTN Market (PT-2740)
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/global-satellite-communication-satcom-equipment-214500758.html
https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-18
Samsung announces 5G NTN modem technology for Exynos chip set; Omnispace and Ligado Networks MoU
GSMA- ESA to collaborate on on new satellite and terrestrial network technologies
ABI Research and CCS Insight: Strong growth for satellite to mobile device connectivity (messaging and broadband internet access)
China Mobile Partners With ZTE for World’s First 5G Non Terrestrial Network Field Trial
ITU-R M.2150-1 (5G RAN standard) will include 3GPP Release 17 enhancements; future revisions by 2025
ABI Research and CCS Insight: Strong growth for satellite to mobile device connectivity (messaging and broadband internet access)

CCS Insight believes that these enhanced satellite networks have the capability to grow to deliver voice and data services as the constellations evolve. It adds that network operators will be able to offer these satellite services as add-ons to existing subscription packages, catering to the growing demand for ubiquitous connectivity.
As demand for enhanced global connectivity continues to rise, the analyst forecasts that 15% of global mobile subscribers are expected to own a smartphone that supports satellite messaging by 2027 and an additional 10% will benefit from satellite plans provided by their operator. By capitalizing on revenue streams generated through operators and supplementary services, CCCS believes that the direct-to-device satellite market is poised to amass $18bn in revenue by 2027. This market it said represented a “vast opportunity”, with an audience of more than 4.8 billion people who could access satellite services through a compatible smartphone. It calculated that as many as 493 million people worldwide lack any kind of mobile network coverage.
“Bringing satellite capabilities to mass-market smartphones marks a milestone in the telecom industry,” said Luke Pearce, senior analyst at CCS Insight. “This development creates exciting opportunities for consumers, manufacturers and operators and promises to help bridge the digital divide. The projected growth in revenue and subscribers highlights the potential this integration holds for expanding connectivity options – we’re witnessing the start of a new era where satellite services become an integral part of everyday smartphones.”
CCS Insight’s free report, Direct Satellite-to-Device Mobile Services, shares unique insight into the market for satellite-connected phones and unpacks its developing dynamics.
AST SpaceMobile achieves 4G LTE download speeds >10 Mbps during test in Hawaii
FCC Grants Experimental License to AST SpaceMobile for BlueWalker 3 Satellite using Spectrum from AT&T
ABI Research: Network-as-a-Service market to be over $150 billion by 2030
Global technology market intelligence firm ABI Research expects the Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) [1.] market to expand significantly, reaching over $150 billion by 2030.
Note 1. NaaS is a secure, cost-effective subscription-based model that lets businesses of all sizes consume network infrastructure on-demand and as needed. It offers scale-up or scale-down flexibility that many businesses require to stay competitive in today’s unpredictable data traffic environment.
Networks have been commoditized over the last few years and the cost of connectivity has fallen. Value has shifted from network infrastructure to the services built on top of the network. Enterprises need scalable solutions that offer cloud-native agility, multi-cloud accessibility, and services that can dynamically fluctuate to support digital transformation. This has led to significant interest in the NaaS market, according to ABI Research.
Image Credit: Verizon
The firm’s blog promoting their NaaS report notes that telecom operators currently lack business models that allow them to build on their physical connectivity advantages to gain control of the NaaS market.
“Telcos must seize the opportunity to dominate the NaaS market, as revenue generated from connectivity provision will continue to decline. However, their investment strategy, business, operational, and ‘go-to-market’ models are not ready to deliver a competitive NaaS solution, explains Reece Hayden, Distributed & Edge Computing Analyst at ABI Research. “The market is immature and highly fragmented, but telco market revenue will exceed US$75 billion by 2030 if they act now and transform technology, culture, and structure to better align with the requirements of the NaaS market.”
Currently, telcos face NaaS competition from two key players. Interconnection providers (e.g., Megaport and Packet Fabric) have built their agile solutions from the ground up, focusing energy on virtualization and software specialization. At the same time, cloud infrastructure providers (e.g., Amazon AWS, Google GCP, and Microsoft Azure) continue to offer cloud-specific NaaS solutions.
“Telecom operators remain in the best position to lead the market as long as they recognize their service/innovation limitations, invest/restructure successfully, and focus their messaging appropriately,” according to Hayden.
Telcos must look to transform three areas. First, telcos must virtualize network infrastructure to deliver cloud-native services and continue to invest heavily to integrate automation (AIOps) throughout network services, including paying attention to 5G slice-as-a-service and other ‘value-add services’ which are critical to monetization.
Second, telecom operators must restructure business and operating models with a look toward openness and partnerships across the industry and reduce internal fragmentation to drive cross-business service continuity.
Third, telcos must look to develop a problem-solving culture and realign their ‘go-to-market’ strategy to better position themselves within the NaaS market. This involves developing vertical and enterprise size-specific sales strategies and establishing consultative processes that educate enterprises to bridge the ever-present gap between awareness and understanding. Telco executives should focus more on service provision and up/reskilling their workforce.
NaaS adoption will rapidly grow over the next eight years. ABI Research expects that by 2030, just under 90% of enterprises will have migrated at least 25% of their global network infrastructure to be consumed within a NaaS model. However, this process will not be organic, suppliers will have to drive education and consultative practices, as significant skepticism within SMEs and MNCs pervades the market. “To drive short-run sales, suppliers must educate and tailor their sales strategy to focus on first adopters (startups and SMEs) and specific verticals,” Hayden recommends.
The outlook in the NaaS market is hugely positive for telcos, especially given the rising demand from startups and SMEs. “But a lot still needs to be done to bridge technological, cultural, and structural gaps,” Hayden concludes. “Although it seems like an expensive and risky uphill battle, developing NaaS will be crucial to the long-term upside. But, if telcos miss this opportunity and drop the ball, interconnection providers and hyperscalers will be waiting and willing to catch it.”
These findings are from ABI Research’s Network-as-a Service: Business, Operational, and Technological Strategies for Telco Digital Service Transformation application analysis report. This report is part of the company’s Distributed and Edge Computing research service, which includes research, data, and ABI Insights. Based on extensive primary interviews, Application Analysis reports present an in-depth analysis of key market trends and factors for a specific application, which could focus on an individual market or geography.
ABI’s NaaS report does not include IT equipment and software vendors like Cisco, Dell Technologies, and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), which have been bolstering their own NaaS hardware and software stacks while established sales channels into most enterprises.
About ABI Research:
ABI Research is a global technology intelligence firm delivering actionable research and strategic guidance to technology leaders, innovators, and decision makers around the world. Our research focuses on the transformative technologies that are dramatically reshaping industries, economies, and workforces today.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/network-service-explained
ABI Research: Open RAN radio units to exceed $47 billion by 2026
ABI Research expects the total CAPEX spent on Open RAN radio units (RUs) for public outdoor networks, including both macro and small cells will reach US$40.7 billion in 2026. Cumulative unit shipments will reach 9.9 million during the same year. Meanwhile, the total revenue of Open RAN radios for indoor enterprise networks will reach as much as US$6.7 billion in 2026, with cumulative unit shipments expected to reach 29.4 million. The Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) market is rapidly expanding and is expected to exceed the traditional RAN market for the first time around 2027-2028.
“The Open RAN opportunity invites various stakeholders to bring their best in class technologies and hardware/software components to contribute to building a flexible, secure, agile, and multi-vendor interoperable network solution,” said Jiancao Hou, Senior Analyst at ABI Research. “In addition, trade wars and the global pandemic of COVID-19 have resulted in tremendous restrictions on the telecom supply chain and disrupt the evolution of new technologies. These effects will accelerate the development of Open RAN and open networks.”
Rakuten Mobile, a greenfield network operator in Japan, set a prime example to deploy this new approach. Moreover, many other operators are also quite active in the field, namely Dish Network in the U.S., Vodafone, Telefonica, Deutsche Telekom, Orange, and Turkcell in the EU and other geological regions. The Open RAN supply chain is also expanding with Altiostar, Mavenir, and Parallel Wireless leading the charge while new entrants are announced every week.
“ABI Research expects greenfield installations, as well as private enterprise networks and public consumer networks, in rural/uncovered areas to drive the deployment of Open RAN throughout the entire forecast period,” Hou points out. Open RAN can introduce many advantages to the enterprise market, including infrastructure reconfigurability, network sustainability, and deployment cost efficiency. On the other hand, these small and easily manageable network use cases will likely lower the entry barrier for Open RAN. Simultaneously they help network operators and their ecosystem partners clearly understand the approach and suppliers’ maturity level, therefore paving the way for a broader market. Besides, “ABI Research sees new entrants will lead the early deployment for Open RAN, but they will be increasingly challenged by tier-one vendors and system integrators for both public cellular implementations and enterprise deployment,” Hou concludes.
These findings are from ABI Research’s Open RAN market data report. This report is part of the company’s 5G & Mobile Network Infrastructure research service, which includes research, data, and analyst insights. Market Data spreadsheets are composed of in-depth data, market share analysis, and highly segmented, service-specific forecasts to provide detailed insight where opportunities lie.
Earlier this week, the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) saw fit to recap its recent achievements regarding OpenRAN; read more about them here.
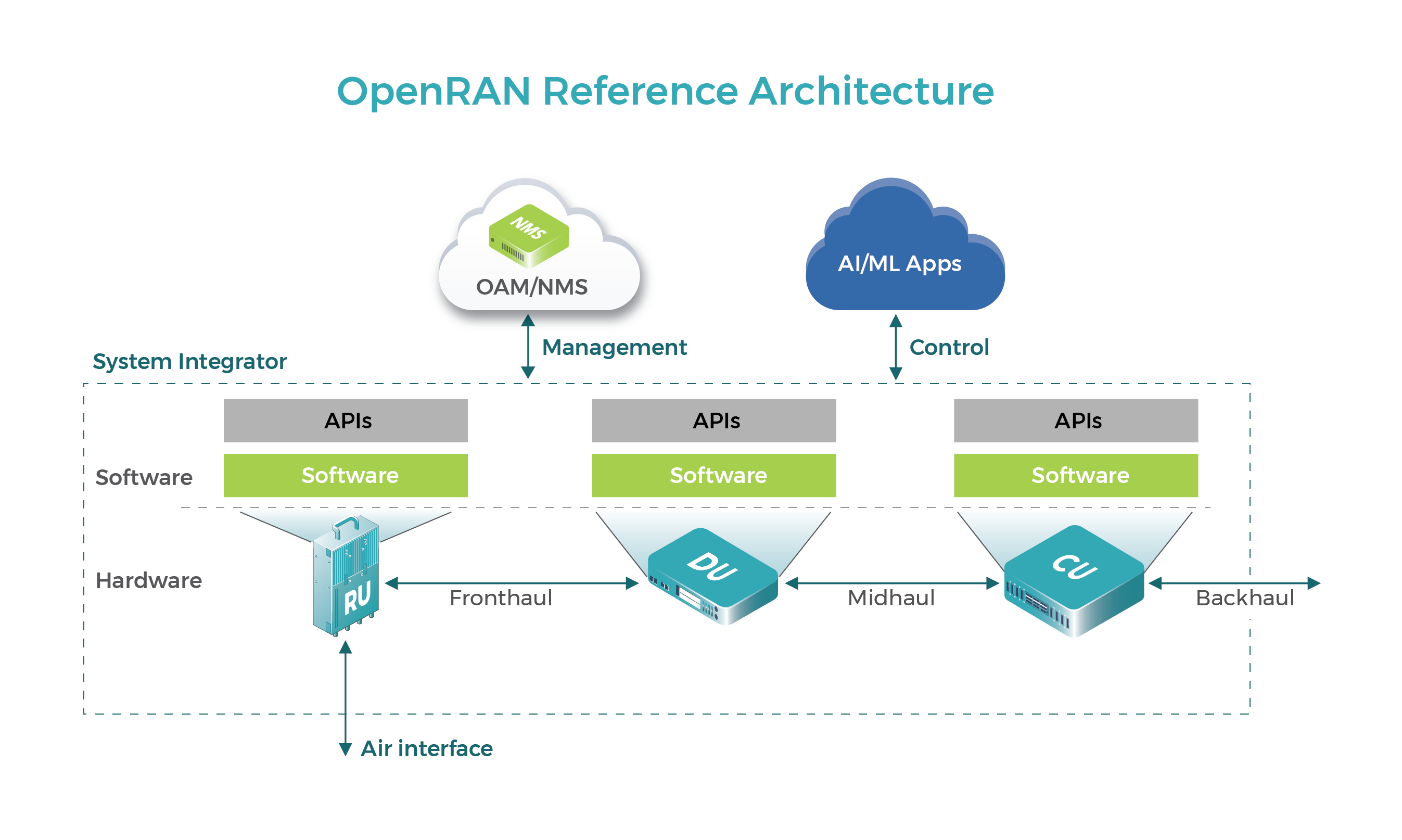
Image Credit: Telecom Infra Project
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About ABI Research
ABI Research provides strategic guidance to visionaries, delivering actionable intelligence on the transformative technologies that are dramatically reshaping industries, economies, and workforces across the world. ABI Research’s global team of analysts publish groundbreaking studies often years ahead of other technology advisory firms, empowering our clients to stay ahead of their markets and their competitors.
References:
https://www.abiresearch.com/press/open-ran-radio-units-soar-more-us47-billion-2026/


