Month: October 2020
Connected Home IoT Technolgies and the EU TeamUp5G Project
by David Alejandro Urquiza Villalonga and Manuel José López Morales, researchers at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid
Introduction:
The concept of the “connected home” has gained a lot of attention in the last decade as a means to improve various aspects of life. Entertainment, security, energy and appliance control, and electronic health monitoring are just a few representative applications. Recently, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become increasingly important due to the COVID19 pandemic. With most employees working from home, remote access tools are booming because they connect people with their machines and assets. They enable people to remotely communicate with machines and perform virtual inspections, remote diagnostics as well as remote support.
Therefore, the development of a dynamic IoT environment that adapts to each individual’s needs is essential to provide an optimal productivity scenario. In this article, we describe an intelligent platform which interconnects several sensors and actuators using an IoT approach to collect and process big volumes of data. The IoT system, combined with a powerful artificial intelligence (AI) tool, learns the user’s behavior and offers improved new services according to their preferences [1] [2].
In this context, applications related to home security, remote health monitoring, climate control and lighting, entertainment, smart sleep, and intelligent shopping have been developed.
Challenges in IoT development and deployment:
There are several challenges to support massive IoT deployments providing connectivity for both cellular and non-cellular devices. New technologies with higher energy and spectral efficiency are required to enable smart device-to-device (D2D) communications with reduced connectivity costs [3]. The technical requirements to fulfill include:
• The interconnection of several sensors in an intelligent management platform according to a massive machine-type-communications (mMTC) approach. In this sense, new spectrum access techniques and energy-efficient technologies to support the operation of a large number of devices are required.
• Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) communication to support video streaming for entertainment, remote working, and online teaching.
• Scalability: this will become an issue mainly in relations to generic consumers as the number of devices in operation rises.
• Dense and durable off-grid power sources: it would make a difference if power could be broadcasted wirelessly to smartphones and sensors from a distance.
Popular current smart home devices:
Some of the most popular smart home devices include the intelligent wireless speaker “Google Home” with a connected voice management system that interacts with the Google Assistant helping with music, calendar, news, traffic, etc. On the other hand, Amazon has developed its own intelligent devices, namely “Amazon Echo” (with Alexa) and “Amazon Echo Plus,” which includes a smart home Zigbee hub for easy setup and control of compatible smart home devices.
Far-field speech recognition is included in the “Amazon Echo Spot,” which is designed with a smart alarm clock that can make video calls with a tiny 2.5-inch screen, or become a nursery camera. LifeSmart provides smart home solutions focusing on security, energy-saving, and bringing convenience to life with a complex network of automatic intercommunication devices that simplifies daily routines [4].
Renesas offers a wide variety of IoT solutions for security, comfiness, health, connectivity and others, for different sectors such as automotive, healthcare, industrial, and home appliances [5].
Supporting technologies for massive IoT deployment:
Nevertheless, many products offered by companies still provide IoT solutions that can be thought as of being in an infancy state. The underlying communication technologies have to increase their capabilities in order to overcome the challenging needs and provide an improvement to IoT solutions.
Therefore, new wireless communication technologies [including 5G (IMT 2020), WiFi 6 (IEEE 802.11ax), Bluetooth 5, etc.] will be combined with classical short range wireless technologies [such as ZigBee, NFC and others] and installed in homes and small business offices. Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technologies from cellular carriers are LTE-Cat M1 , narrow band IoT (NB-IoT) and LoRa/LoRaWAN.
Several studies reveal that higher frequencies are expected to be able to operate as complementary bands for the deployment of 5G networks with higher capacity. It is expected that millimeter wave (mmWave) ultra-dense small-cells supported by massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) will be able to offer the capabilities to interconnect multiple devices and to provide high-speed services even in indoor scenarios. These small-cells may be interconnected with each other and with the core network by means of a fiber optic connection or with a mmWave backhaul.
Editor’s Note: Some wireless communications professionals believe that a 5G fixed wireless network, using massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) systems at millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies, will be able to offer high throughput and low latency to support many WiFi connected home devices. Verizon’s 5G Home Internet is an example of this.
On the other hand, network densification is a promising technology to overcome many issues in mmWave systems such as blockage and short-range coverage that can significantly increase the capacity of the network. Therefore, Ultra-dense networks (UDN) compound by small cells (SCs) is also considered to have an important role in IoT connectivity.
In addition, a fundamental feature needed to support massive IoT is scalability on the device and the infrastructure sides which can be provided by 5G cellular networks. 5G systems will be able to offer connectivity to an extremely large number of low-cost, low-power, low-complexity devices, based on an evolution of the current LTE narrow band IoT (NB-IoT) [3].
New radio access technologies will also be required. For example, cognitive radio (CR) to allocate bandwidth dynamically and to handle high interference levels. In addition, the big data processing capabilities for the AI learning and prediction process is supported only by 5G networks.
TeamUp5G Project:
TeamUp5G [6] is a European Training Network (ETN) in the frame of the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Innovative Training Networks (MSCA ITN) of the European Commission’s Horizon 2020 framework. TeamUp5G’s EU funding adds up to 3.72 million Euros between 2019 and 2022.
TeamUp5G is currently working on the use cases, technical challenges, and solutions to facilitate the technical feasibility of ultra-dense small cell networks.
The research objectives of TeamUp5G are focused on solving three problems: (1) Interference Management, waveforms, and mMIMO, (2) Dynamic Spectrum Management and Optimisation, and (3) Energy Consumption Reduction. Among others, it can provide the technical solutions to make massive IoT Smart Home connectivity feasible. Some of their research results include [7] and [8].
Where in Europe is TeamUp5G:
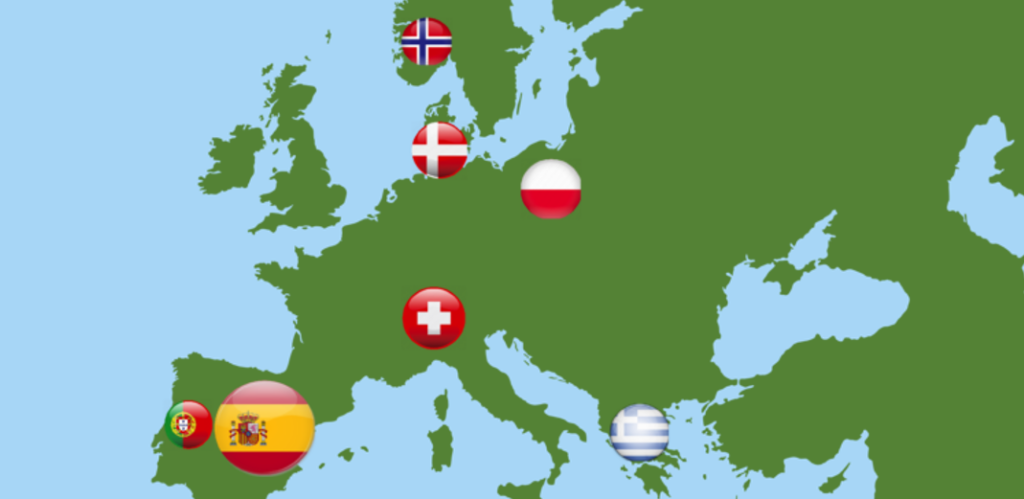
What Is the TeamUp5G Project:
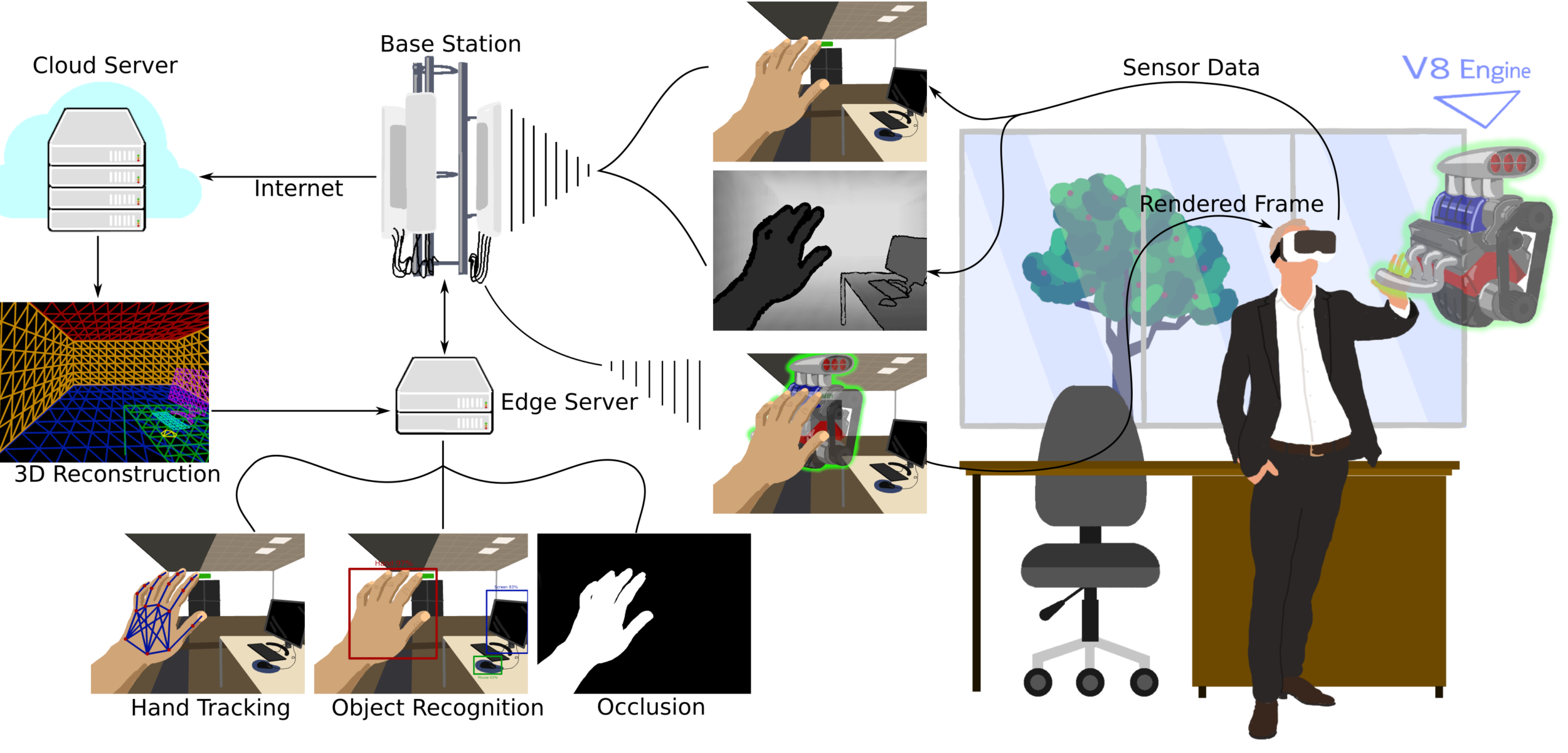
Image Credit: TeamUp5G Project
In reference [7], the authors study a cognitive radio system with energy harvesting capabilities (CR-EH) to improve the spectral and energy efficiency according to the green communication paradigm. A novel optimal sensing policy to maximize detection performance of available spectrum and to protect primary users from interference is developed. The proposed scheme is based on the efficient use of harvested energy to implement spectrum sensing operations. Offline and online scheduling policies are derived with an optimal formulation based on convex optimization theory and Dynamic Programming (DP) algorithm, respectively. In addition, two heuristic solutions with low complexity are also proposed to dynamically manage the use of spectrum with high levels of energy efficiency which is essential for IoT deployment.
In reference [8], the authors demonstrated how scenarios with stringent conditions such as high mobility, high frequency selective, low SNR and short-packet communications can benefit from the use of non-coherent mMIMO. Non-coherent mMIMO avoids the need of channel state information (CSI) to extract the benefits of mMIMO. This avoids the waste of resources due to the overhead created by the orthogonal signals, which is more severe in scenarios with stringent conditions. These types of scenarios are very common in Home IoT, since low battery powered devices will be the most common, such as a variety of domestic sensors and actuators. Furthermore, in short-packet communications, the use of CSI is proportionally greater due to shorter useful data as also happens in Home IoT, in which many devices send short bursts of data from time to time, thus benefiting from the use of non-coherent communications.
Thus, it has been shown that new interference management techniques, energy harvesting, and non-coherent communications can overcome some of the technical challenges inherent in IoT networks for Smart Home applications.
Conclusions:
In this article, we have covered some aspects considered in IoT Smart Home 5G. We have first made an introduction with the basics of the use of IoT in homes, aided by 5G technology and AI. Secondly, we have presented some already existing solutions from companies such as Google, Amazon, LifeSmart, and Renesas, which work over legacy networks and thus do not extract all the potential benefits of 5G IoT Smart Home. We have continued stating the main technical challenges in IoT deployment. We have defined some technologies that will support the use of IoT at homes, including massive multiple-input multiple-output, millimeter waves, ultra dense networks, small cells, and cognitive radio. We have talked about the TeamUp5G project which partly focuses on the research of new solutions that can make the massive deployment of IoT Smart Home feasible.
From the perspective of the authors, the following decade will see an increase in the appearance of products based on the referenced technologies, which will bring the concept of IoT Smart Home based on 5G closer to reality.
References:
[1] K. E. Skouby y P. Lynggaard, «Smart home and smart city solutions enabled by 5G, IoT, AAI and CoT services», en 2014 International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), nov. 2014, pp. 874-878, doi: 10.1109/IC3I.2014.7019822.
[2] H. Uddin et al., «IoT for 5G/B5G Applications in Smart Homes, Smart Cities, Wearables and Connected Cars», en 2019 IEEE 24th International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), sep. 2019, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/CAMAD.2019.8858455.
[3] S. Ahmadi, 5G NR: Architecture, Technology, Implementation, and Operation of 3GPP New Radio Standards. Academic Press, 2019.
[4] https://iot.ilifesmart.com/
[5] https://www.renesas.com/us/en/solutions.html
[6] https://teamup5g.webs.tsc.uc3m.es/
[7] D. A. Urquiza-Villalonga, J. Torres-Gómez, y M. J. Fernández-Getino-García, «Optimal Sensing Policy for Energy Harvesting Cognitive Radio Systems», IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 19, n.o 6, pp. 3826-3838, jun. 2020, doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2978818.
[8] M. J. Lopez-Morales, K. Chen-Hu and A. Garcia-Armada, “Differential Data-Aided Channel Estimation for Up-Link Massive SIMO-OFDM,” in IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, vol. 1, pp. 976-989, 2020, doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2020.3008634.
Vodafone and NEC Europe trial Open RAN technology with voice call
Vodafone and NEC Europe Ltd., a wholly owned subsidiary of NEC Corporation, in partnership with Altiostar, have jointly announced the first successful voice call made on an open virtual Radio Access Network (Open RAN) on Vodafone’s network in the Netherlands.
Open RAN technology holds promise and potential for next-generation wireless infrastructure. It’s being driven by innovation and open specifications from various consortiums (O-RAN, TIP Open RAN, and ONF). Today’s announcement demonstrates Vodafone’s strong commitment to sustaining its technological leadership, by bringing in such technological advances.
During the course of this trial, Vodafone and NEC intend to integrate solutions of leading Open RAN technology vendors, such as Altiostar [1.] and various other radio vendors, including NEC’s own 5G radio products, using commercial off the shelf (COTS) hardware from third parties, enabling Vodafone to transform its network to a software-based one suiting multiple deployment scenarios.
Note 1. It’s somewhat surprising that Altiostar was the only OpenRAN software vendor to be mentioned. Altiostar is part-owned by Rakuten and must therefore be near the front of the queue for its OpenRAN vendors. Rakuten has said it would make its Open RAN platform technology available to other operators. If successful, NEC and Altiostar will be involved in more deals as OpenRAN gathers momentum. Separately, there is the Rakuten-NEC 5G Core network (based on 3GPP 5G core “vision” specs) that Rakuten also wants to sell to global network operators.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

Image Credit: Rakuten Mobile
“We are proud to embark on this journey together with Vodafone that will transform mobile network economics, while deploying technology with greater flexibility, greater efficiencies, and more agility,” said Yogarajah Gopikrishna, GM at NEC Europe. “By integrating best of breed solutions, NEC, as an experienced Open RAN System Integrator, is committed to bring transformative change to the telecommunications space leveraging our long history and experience in mobile network solutions.”
“We are delighted to work together with NEC towards the first live Open RAN site,” said Ruud Koeyvoets, Vodafone Mobile Networks’ Director. “The introduction of the technology enables us to introduce new suppliers, such as Altiostar, giving us greater flexibility when rolling out our mobile network. We’re proud to be pioneering the development of Open RAN and will be monitoring the performance of this pilot.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Vodafone
VodafoneZiggo is a leading Dutch company that provides fixed, mobile and integrated communication and entertainment services to consumers and businesses. As of June 30, 2020 we have more than 5 million mobile, nearly 4 million TV, nearly 3.4 million fixed broadband internet and 2.4 million fixed telephony subscriptions. VodafoneZiggo is a joint venture by Liberty Global, the largest international TV and broadband internet company, and Vodafone Group, one of the world’s largest telecommunication companies.
About NEC Europe Ltd.
NEC Europe Ltd. is a wholly owned subsidiary of NEC Corporation, a leader in the integration of IT network technologies that benefit businesses and people around the world. NEC Europe Ltd. is building upon its heritage and reputation for innovation and quality by providing its expertise, solutions and services to a broad range of customers, from telecom operators to enterprises and the public sector. For additional information, please visit the NEC Europe Ltd. home page at:
http://uk.nec.com/
References:
https://www.nec.com/en/press/202010/global_20201019_04.html
Why It’s IMPORTANT: Telefonica, Rakuten MOU on Open RAN, 5G Core Network and OSS
ITU-R: Future Technology Trends for the evolution of IMT towards 2030 and beyond (including 6G)
Preface:
This author is truly astounded with all the buzz about 6G when neither 3GPP or ITU-R WP5D (or ITU-T) have completed their 5G specs. However, there is work progressing in ITU-R WP5D on the evolution of IMT in the next ten years with a report scheduled to be completed in June 2022.

……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Future Technology Trends for the evolution of IMT towards 2030 and beyond:
Considering the successful accomplishments by ITU-R for the evolution of IMT-2000, IMT‑Advanced and IMT-2020, similar actions are proposed for the evolution of IMT towards 2030 and beyond. The approach taken for IMT‑Advanced evolution towards IMT-2020 was to start with the work on the Report ITU-R M.2320 entitled “Future technology trends of terrestrial IMT systems” (approved in 2014) to develop the evolution for IMT-Advanced (aka “4G”).
At its 34th meeting (19-26 February 2020), ITU‑R Working Party (WP) 5D decided to start study on future technology trends for the future evolution of IMT. A preliminary draft new Report ITU-R M.[IMT.FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS] will be developed and will consider related information from various external organizations and country/regional research programs.
The scope of the new Report ITU-R M.[IMT.FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS] focuses on the following aspects:
“This Report provides a broad view of future technical aspects of terrestrial IMT systems considering the time frame up to 2030 and beyond. It includes information on technical and operational characteristics of terrestrial IMT systems, including the evolution of IMT through advances in technology and spectrally-efficient techniques, and their deployment.”
For the development of this report, WP 5D invites the views of External Organizations on future technology trends for terrestrial IMT systems, including but not limited to the motivation on driving factors such as new use cases, applications, capabilities, technology trends and enablers. These technical inputs are intended for the timeframe towards 2030 and beyond and are proposed to be significantly advanced and different from that of IMT-2020.
A few potential aspects of the new report (subject to change based on inputs from external organizations):
- Motivation on driving factors for future technology trends towards 2030 and beyond
- Driving factors in the design of future IMT technology
- Technology Trends and Enablers
- Technologies to enhance the radio interface
- Technologies to enhance radio network performance and precision
- Technologies for native AI based communication
- Technologies to enhance service coverage
- Technologies to enhance privacy and security
- Technologies for integrated sensing and communication
- Technologies for integrated terrestrial and non-terrestrial communications
- Technologies for integrated access and super sidelink communications
- Technologies to enhance adaptability and sustainability
- Technologies for efficient spectrum utilization
- Terminal technologies
- Technologies to support a wide range of new use cases and applications
- Summary and Conclusion
- Acronyms, Terminology, Abbreviations
WP 5D plans to complete this study at the 41st WP 5D meeting in June 2022.
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2020/Pages/default.aspx
Huawei Executive: “China’s 5G user experience is fake, dumb and poor”-is it a con game?
At the opening ceremony of the China International Information and Communication Exhibition on October 14th, Ding Yun, executive director of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd said that China’s 5G user experience has three problems of “fake, dumb, and poor.” In particular, some users have a 5G LOGO on their mobile phones, but they are not connected to the 5G network, cannot make 5G calls, or frequently switch signals, according to an article by Xia Xutian on the Sina Tech website.
How could a Huawei executive say such things about its home country which supposedly has very close ties, impact and influence on the world’s top telecom equipment supplier and #1 or #2 global smartphone vendor? See Comment and Analysis below for more on this.
While China has built the world’s largest 5G network, it has a gap in experience, coverage, and commercial closed-loop operation, Ding Yun said. For comparison purposes, that the 5G downlink rate in South Korea is more than 600 megabits while the average in China is only a bit more than 270 megabits. South Korea’s 5G user penetration at the end of September reached 25%, while China’s penetration level is only about 8%.
“Objectively speaking, I am also a 5G user. We have just completed the first phase of 5G construction today. It is indeed a great improvement over the 4G experience, but our network still has many problems. I use three words to sum it up: fake, dumb, bad/poor.”
Huawei’s Ryan Ding speaking at the China International Information and Communication Exhibition about 5G in China
Photo Credit: Huawei
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
What’s fake? In many cases the user’s smartphone has a 5G logo but no 5G coverage. The experience is still 4G, but the display is 5G. Those users are not connected to the 5G network and can’t make 5G calls.”
What is dumb? Some places in China have 5G signal coverage, but there is no 4G anchor station, so calls cannot be made. He said the anchor point of 4G happens to be on the edge of multiple cells. The frequent handover of 4G and 5G results in a very poor user experience.
Ding Yun noted that although the number of 5G users in China has reached 150 million, the matching rate of networks, mobile phones and packages of 5G users is still very low. Many users have bought 5G packages, but their mobile phones are still 4G. There are also many users who have 5G mobile phones, but there is no 5G network coverage in their geographical area.
Ding Yun pointed out that operations and maintenance costs are also an unavoidable issue for 5G. At present, the peak rate of 5G is 25 times that of 4G, but 5G equipment (especially mmWave if and when deployed in China) will greatly increase the power consumption of 5G base stations, which poses a huge challenge to the entire power supply system (not to mention the huge electricity costs incurred by the 5G network operator).
“We have conducted a survey on the power consumption of China’s network. About 32% of the sites have insufficient power, and in some places, the battery capacity is also insufficient,” he added.
Ding Yun urged 5G network operators to:
1] build out 5G business ecosystems through innovative and differentiated applications;
2] reduce expenditure and optimize the TCO of operators from an overall perspective; and
3] look towards the future and upgrade the current operating platform as soon as possible to face potential problems such as the bill storm that 5G will bring.
In response to the 3rd objective, Huawei is using big data to connect user data, operational data, and terminal data, so that the machine, network, and applications can provide a better match.
In conclusion Ding Yun suggested the following:
- To build the most successful 5G for thousands of industries, wireless network operators must first have a deep understanding of the industries they are targeting. Different industries have different specific requirements for 5G in terms of latency, reliability/availability, throughput, security, etc. Therefore, to develop 5G industry applications, we first need to clarify the boundaries of capabilities, consolidate the ability base to serve thousands of industries, implement a replicable business model, and actively promote ecological construction, especially the development of application ecology.
- As operators expand the construction of 5G industry applications from connection to connectivity + computing, and then to SLA (network) slicing, their corresponding business models will gradually shift from a direct sales model to a value sharing model that combines active integration and integration . Ultimately, the business model of 5G industry applications will develop in the direction of multi-path, closed-loop, and multi-win as operators choose their roles.
- Unify (5G and other) standards and develop ecology. (What 5G standards is he referring to? There are none at this time). The application development of the 5G industry is not only a matter for operators, but also requires the entire industry chain to “stretch it into one strand” and integrate the telecommunications industry with other industries to form industry standards. Only in this way can the development of 5G industry applications be accelerated.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Comment and Analysis:
Ding Yun’s remarks are a refreshing change from the usual self congratulatory speeches given by 5G network operators and equipment suppliers (like Huawei). We are astonished he can be so honest with the Chinese government and China Communist Party having so much control over telecommunications and other industries in China.
Here are a few copy/paste (and translated from Chinese to English) Sina reader comments:
“I have not found a demand for 5G in the current application (environment)”
“Haha, so embarrassing![[Yun Bei] [Yun Bei]](http://comment.sinaimg.cn/emoji/png/2018new_kuxiao_org.png)
![[Yun Bei] [Yun Bei]](http://comment.sinaimg.cn/emoji/png/2018new_kuxiao_org.png) “
“
“China’s 5G, got up early. Experience the night episode (where there is no 5G service to conserve electricity costs for carriers)”
“In Qingdao, there is basically no real 5G SA network. When only the SA mode is selected, the 5G signal is gone, and now the operator’s 5G speed limit is 500M bps”
“The conclusion is that I continue to use my 4G”
“The worst is a three-year contract with China Mobile”
“The three major operators are too hateful and must be punished.”
“China network operators are deliberately lowering the 4G signal, forcing everyone to use 5G. Just this dirty trick, give his grandma a whistle.”
“No 5G signal coverage.”
“Fake, dumb, and bad are synonymous with China’s three major network operators.”
“What is the conclusion? For 5G, it’s better to wait first, don’t worry about changing phones ![[Hee hee] [Hee hee]](http://comment.sinaimg.cn/emoji/png/2018new_xixi_org.png) , let alone changing pricing packages. It’s not very useful and costs money.
, let alone changing pricing packages. It’s not very useful and costs money.![[Yun Bei] [Yun Bei]](http://comment.sinaimg.cn/emoji/png/2018new_kuxiao_org.png) “
“
“The basic meaning is, the operator, burn me![[doge] [doge]](http://comment.sinaimg.cn/emoji/png/2018new_doge02_org.png) “
“
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Email from a very knowledgeable, anonymous Chinese 5G expert corroborates what Ding Yun said:
- China claims they have 100 millions of 5G end point devices now. Actually, those are mostly 4G handsets whose users were coerced to subscribe to a 5G package. The 3 major state owned network operators purposely lowered 4G-LTE speeds and forced subscribers change to the 5G package which only provides the previous 4G-LTE speeds.
- China claims they have deployed 40,000 5G NR base stations. But without URLLC (ultra high reliability, ultra low latency) enhancements to 5GNR (3GPP Release 16) and mMTC (massive machine to machine communications) standards, 5G NR is not complete. (3GPP has not set a date for the conclusion and evaluation of URLLC in the RAN performance testing which is supposed to be in the “frozen” 3GPP Release 16 set of specs)
- There are no mmWave 5G base stations at all in China.
- Currently China 5G base stations consume huge amounts of energy, so the 3 major 5G network operators shut them down at night to reduce electricity bills. Note the above readers comment, “Experience the night episode.”
- Former minister of China Ministry of Finance and seated deputy minister of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) recently publicly expressed concerns about China’s 5G development and investments. They said China had made bad 5G investments and that China has not yet balanced the 3G and 4G investments made by its network operators).
- What kind of joke is this?
References:
https://finance.sina.com.cn/tech/2020-10-15/doc-iiznezxr6037613.shtml
https://www.wsbtv.com/news/ap-explains-promise/KEKKYBDSVGE4W66CY24PMOYMJA/
FCC Chairman Pai Reviews 5G FAST plan and importance of the C-Band (3.7 GHz to 4.2 GHz) auction
Speaking at the Americas Spectrum Management Conference on October 12th, FCC Chairman Ajit Pai assessed the Commission’s 5G Fast Plan and highlighted the importance of this December’s C-Band auction for 5G spectrum.
Pai said the 5G Fast Plan, introduced in 2018, had three central planks: freeing up spectrum, promoting wireless infrastructure, and modernizing our regulations to encourage more fiber deployment. Pai said the FCC has been freeing up high-, mid-, and low-band spectrum for 5G:
High-band spectrum enables ultra-high-speed, gigabit-plus wireless connectivity. Last year, the FCC successfully concluded our nation’s first two auctions of millimeter-wave spectrum for 5G services, in the 28 GHz and 24 GHz bands, respectively. Earlier this year, we concluded bidding in an auction of the upper 37 GHz, 39 GHz, and 47 GHz spectrum bands. This was the largest auction in American history, releasing 3,400 megahertz of spectrum into the commercial marketplace.
All told, we’ve made available almost five gigahertz of high-band spectrum for commercial use though these auctions. To put that in perspective, that was more spectrum than was used before for terrestrial mobile broadband by all wireless service providers in the United States combined.
With respect to low-band spectrum, we’ve finished repurposing spectrum in the 600 MHz band, which was long used for broadcast television, for mobile broadband. To clear the 600 MHz band spectrum for wireless use, roughly half of our nation’s broadcast TV stations—nearly 1,000 total—had to change their transmission frequencies. This summer, we completed this enormous undertaking—known as the “repack.” Now, all of the valuable low-band airwaves sold in the ground-breaking broadcast incentive auction are available for wireless broadband service, and this spectrum is already being used to provide 5G service to areas where over 200 million Americans live.
Pai said the FCC has made the most headway on mid-band spectrum. Mid-band spectrum is appealing for 5G largely because of physics: it combines good geographic coverage with good capacity. The FCC chairman claims the commission has systematically identified mid-band airwaves that were being underused and set plans to put these airwaves to work for the American people.
The FCC also targeted rule changes to bring the 3.5 GHz band into commercial use. The rules for this band had not been optimized to encourage 5G deployment. But with the leadership of FCC Commissioner O’Rielly, new rules were promulgate to promote investment in the band. This August, the Commission successfully completed an auction of 70 megahertz of licensed spectrum in the 3.5 GHz band—the first-ever auction of mid-band spectrum for 5G. And we’ve completed the necessary technical work so that the band’s entire 150 megahertz is now available for commercial use.
Pai said the biggest move to free up mid-band spectrum for 5G is in the swath of spectrum from 3.7 GHz to 4.2 GHz—what is referred to as the C-band. This spectrum is mostly used by fixed-satellite companies to beam content to video and audio broadcasters, cable systems, and other content distributors. However, with advances in technology, these companies can now provide the same services using alternative technologies or considerably less spectrum.
This past February, the FCC voted to clear the lower 300 megahertz of the C-band and make 280 megahertz of this spectrum available for 5G through a public auction. All eligible space station operators currently using this spectrum have committed to an accelerated relocation to the upper 200 megahertz of the C-band—meaning that the lower 280 megahertz will become available for 5G two to four years earlier than otherwise would have been the case. The FCC will begin the auction of the lower 280 megahertz of the C-band on December 8th.
And just a couple weeks ago, at our September meeting, the Commission proposed to make the 3.45-3.55 GHz band available for innovative commercial operations while accommodating limited remaining operations by federal incumbents. This action follows through on the White House and the Defense Department’s August announcement that this 100 megahertz of contiguous mid-band spectrum should be made available for 5G as quickly as possible. I am optimistic that we will be able to auction the 3.45 GHz band next year.
The bottom line of all these mid-band efforts is this: With the aforementioned auctions of the C-band, the 3.5 GHz band, and a 2021 auction of the 3.45 GHz band, the FCC is on a path to have a contiguous 530-megahertz swath—from 3.45 to 3.98 GHz—of mid-band spectrum available for 5G.

GSA: “Global regulators have sought to open up access to the C-band, which has become (initially at least) the most important spectrum band for 5G.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Pai asserts that he has presided over the most aggressive FCC in history when it comes to spectrum. He claims that the FCC has been similarly productive on the other two planks of 5G FAST PLAN: promoting wireless infrastructure and modernizing our regulations to encourage more fiber deployment.
For example, the number of new cell sites in the United States has skyrocketed. We added fewer than 7,000 cell sites from 2013 to 2016, but added over 87,000 from 2016 to 2019, with an increase of over 46,000 in 2019 alone. He said that the FCC is focused on the integrity of the communications supply chain—the process by which products and services are manufactured, distributed, sold, and ultimately integrated into our communications networks.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Comment and Analysis on the C-band auction:
Analysts at Morgan Stanley Research raised their C-band mid-point auction forecasts from $23.5 billion in proceeds to about $26 billion, with their high-end estimates at $35.2 billion. The firm cited a relatively low turnout in the Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) 3.5 GHz auction as a catalyst, as well as improved macro environment and supportive credit markets. The lower-than-expected turnout by big carriers in the CBRS auction indicates they’re likely saving their gun powder for the big C-band auction, which offers more unencumbered mid-band spectrum for 5G.
Former FCC Chairman Tom Wheeler said, “One of the challenges the FCC faces is that the allocation of spectrum was first made from analog assumptions that have been rewritten as a result of digital technology.” Consider the transition from analog to digital TV, where an analog TV signal took up 6MHz of spectrum and required guard bands on either side to avoid interference, four or five digital signals can fit into that one channel.
“I went through it with the [Department of Defense], with the satellite companies, and the fact of the matter is that one of the big regulatory challenges is that nobody wants to give up the nice secure position that they have based on analog assumptions,” said Wheeler. “I think you also have to pay serious consideration, but I found that claims of interference were the first refuge of people who didn’t like the threat of competition or anything else.”
“As we look at C-Band, it brings forward some use cases that could increase the size of the 5G opportunity for us,” Verizon CFO Matt Ellis said during a recent investor event. While Verizon has purchased billions of dollars worth of unused millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum for 5G, such spectrum isn’t suitable for covering large geographic areas because transmissions in such bands can only travel a few thousand feet in the best of conditions and requires line of sight communications (no trees, walls, buildings between cell site and mmWave end point subscriber),
Indeed, analyst Craig Moffett forecasts that Verizon will need to spend as much as $20B on spectrum in order to keep pace with T-Mobile, which currently enjoys a huge spectrum advantage by virtue of their 2.5 GHz spectrum. He says that even if Verizon acquires C-Band spectrum, its propagation shortcomings relative to T-Mobile’s 2.5 GHz spectrum suggest that Verizon will still be disadvantaged in either coverage or cost.
Craig believes that AT&T won’t be able to keep pace with Verizon’s bidding at the C-band auction. The New York Post reported that a sale of all of DirecTV (owned by AT&T) might yield less than what Verizon is expected to spend in the upcoming C-Band auction alone. Without a large block of mid-band spectrum to compete with T-Mobile and Verizon, AT&T’s Mobility segment could fall behind for a generation. Satellite-TV provider Dish Network, which is building out a 5G network, isn’t participating in the auction, according to several sources.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-establishes-bidding-procedures-december-c-band-auction-0
https://www.fcc.gov/news-events/blog/2020/07/15/need-speed
https://nypost.com/2020/10/06/att-pushes-ahead-with-auction-of-directv-despite-lowball-bids/
https://www.tvtechnology.com/news/fcc-issues-c-band-auctions-draft-procedures
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20200106/spectrum/gsa-c-band-is-most-important-spectrum-band-for-5g
Apple announces 3 new 5G iPhone 12 models, but what version of 5G, what frequencies and which carrier networks?
Apple today unveiled its new 5G capable iPhone 12 set today, but other than Verizon’s Ultra-Wideband (5G mmWave) the company’s presentations and press releases did not identify which carrier networks (see Addendum below) or frequencies are supported. Or when, if ever, the new new 5G iPhones would work on any 5G SA Core networks (vs 5G NSA which requires a LTE anchor) or with network slicing (which requires a 5G core network). However, the company said it has tested its 5G devices on 100 5G carrier networks in 30 regions, including mmWave in the U.S. (presumably for Verizon’s Ultra-Wideband network).
Apple said its new 5G iPhones will offer a “superior 5G user experience.” The company wrote in a press release:
iPhone 12 Pro and iPhone 12 Pro Max deliver an advanced 5G experience on a global scale, engineered with a seamless integration of world-class hardware and world-class software. 5G on iPhone boasts improved speeds for faster downloads and uploads, higher quality video streaming, more responsive gaming, real-time interactivity in apps, FaceTime in high definition, and much more. Customers will also be able to enjoy a secure, fast connection, reducing the need to connect to public Wi-Fi hotspots.Featuring the most 5G bands on any smartphone, iPhone 12 Pro models offer the broadest 5G coverage worldwide.1 Models in the US support millimeter wave, the higher frequency version of 5G, allowing iPhone 12 Pro models to reach speeds up to 4Gbps, even in densely populated areas. iPhone 12 Pro models also feature Smart Data mode, which extends battery life by intelligently assessing 5G needs and balancing data usage, speed, and power in real time.
Apple CEO Tim Cook sought to explain why 5G technology would improve iPhone users’ experience. He later called on Verizon CEO to give a “razzle-dazzle” pitch on that U.S. carrier’s mmWave and now nationwide 5G network.
Photo Credit: Brooks Kraft/Apple
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Verizon’s CEO Gets Center Stage:
Tim Cook introduced Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg who announced that Apple’s new iPhone 12 sets would operate on Verizon’s Ultra Wideband (5G mmWave) network- the world’s fastest, he claimed. Vestberg used this soapbox talk opportunity to announce the launch of Verizon’s nationwide 5G service using Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS).
Perhaps in a nod to Verizon’s Ultra Wideband network, a lady from Apple said its new “smart data mode” would ensure that its customers stay on a 4G LTE network most of the time to reduce power consumption, but that would be auto switched to a 5G connection when they need faster download speeds.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Comment and Analysis:

Analyst Forecasts and Opinions:
Analysts surveyed by FactSet, on average, predict iPhone revenue will rise 15% to $160 billion in the fiscal year that began Oct. 1. That is about $6 billion shy of the record set in fiscal 2018, when the $1,000 iPhone X helped bolster sales even as shipments failed to reach a new high.
Katy Huberty, a veteran Apple analyst for Morgan Stanley, last week predicted the company could ship as many as 240 million iPhones this year, helped by customers who haven’t upgraded in several years and excitement for 5G. That would set a record, beating the 231 million devices sold in fiscal 2015. Sales at that level could send the company’s shares up 37% from Monday’s close to a market value of almost $2.9 trillion, she said. “We expect this fall’s launch to be the most significant iPhone event in years,” she wrote in a note to investment bank clients.
“Now we have an iPhone that is capable of exploiting the benefits of the 5G wireless network, but we have an underdeveloped network,” said Tom Forte, a D.A. Davidson research analyst. “It could take a couple [of] years for that to happen. There are large parts of the country that may never have it,” he said. While Apple’s smartphone rivals Samsung and Google have already introduced phones able to connect to 5G, Forte said the challenge for Apple now is to manage people’s expectations. “When people get the new iPhone and can’t use the high-speed network, there is real potential for high levels of disappointment there,” he added.
Dan Morgan, a portfolio manager at Synovus Trust and longtime Apple investor, said iPhone sales peaked about five years ago. Every update since then has been more of a ripple than a wave, he said, noting that he does not expect the iPhone 12 to set any sales records. With so many working from home and using Wi-Fi as their main connection to the Internet, Morgan said a 5G connection may not be as attractive to those seeking faster speeds. “If you really wanted to watch a Netflix movie or play a game, maybe you can just go and use your Wi-Fi instead right now,” he said.
Colleague Craig Moffett of MoffettNathanson wrote in an email, “It’s striking to me that Apple is acting as though the network is the application. That’s a real departure for them, and it risks being a disappointment if consumers expect that there will be genuinely differentiated things they’ll be able to do with their new devices. That said, we have to be careful about being overly focused on the U.S. market. In China and Korea and a handful of other markets, the network is at least a little bit further along.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Starting Oct. 16, AT&T customers can pre-order iPhone 12 Pro and iPhone 12 at www.att.com with online and in-store availability starting Oct. 23. AT&T customers will be able to order iPhone 12 Pro Max and iPhone 12 mini beginning on November 6, with availability on November 13.“Today ushers in a new era for the world’s best smartphone with the arrival of 5G on the iPhone 12 lineup and we’re excited to work alongside AT&T to introduce a powerful 5G experience to iPhone users,” said Greg Joswiak, Apple’s senior vice president of Worldwide Marketing. “With the seamless integration of world-class hardware and world-class software on iPhone 12 models combined with AT&T’s expansive 5G network, we’re able to provide customers with an advanced 5G experience that offers improved speeds for fast downloads and uploads, higher quality video streaming, and much more.”
References:
https://www.apple.com/newsroom/2020/10/apple-introduces-iphone-12-pro-and-iphone-12-pro-max-with-5g/
https://www.apple.com/apple-events/october-2020/
https://about.att.com/story/2020/apple_iphone.html
https://www.cnn.com/2020/10/12/tech/apple-iphone-12-5g-experience/index.html
https://www.apple.com/iphone-12/specs/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/category/dynamic-spectrum-sharing/
Nokia Report: 5G will add $8T to global GDP by 2030; Barriers to Adoption & Catalysts Noted
In a just released 5G Readiness report commissioned by Nokia, market research firm Sapio surveyed 1,628 technology purchasing decision-makers in eight markets and across six industry sectors to get a broad sense of how professionals believe 5G is going to affect their business.
- The markets (and participants) surveyed were as follows: Australia (203), Finland (200), Germany (203), Japan (203), Saudi Arabia (202), South Korea (200), UK (207), US (210).
- The sectors were: energy and utilities (208 responses), mining (119), manufacturing (455), public sector (271), healthcare (445), transportation (130). Respondents from companies of less than 250 employees were only permitted for energy and utilities and mining companies.
The grand summary of this extensive survey and extrapolating exercise is that Nokia now forecasts 5G will add $8 trillion to global GDP by 2030. A key message is that a lot of technological progress over the next decade will depend on 5G. That remains to be seen, especially in light of the lack of standards for the non radio aspects of 5G and the ultimate number of 5G Radio Interface Technologies to be included in the 2nd version of IMT 2020.SPECS, sometime in 2021.
On average, whilst the importance of 5G adoption is well understood, a significant investment gap remains. 86% of decision makers said they have some kind of strategy for 5G, and over a third fear being outpaced by the competition should they not invest in 5G in the next 3 years. However, only 15% are currently investing in its implementation, and over a quarter (29%) of businesses are not planning any 5G investment in the next 5 years.

Image Credit: Nokia
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The report breaks down the findings by country and also looks at specific events like the COVID-19 pandemic. How literally to take all these extrapolations from a company with a vested interest in driving the market is down to the individual, but at the very least it provides a good snapshot of industry expectations. Here are a few survey results:
- 43% of global technology decision makers have increased their overall investment in their strategic technology planning. This represents a 27% net increase in the number of budgets that have increased.
- In the U.S., additional costs (44%), disrupted timelines (42%) and the emergence of new technology gaps (38%) have been the most prevalent impacts of COVID-19 on technology road maps.
- 41% have C-Level sponsor for 5G implementation in their organization. 25% don’t have any 5G championing from management (23%).
- Businesses are more likely to feel that their industry is middling in terms of 5G adoption, with 20% setting a high benchmark.
- 43% of technology decision makers have a long term 5G strategy. Just over 1 in 10 have no strategy whatsoever (11%)
- Over a third fear being outpaced by the competition should they not invest in 5G, while 27% feel whatever their 5G investment they will still be successful.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
5G Investment Plans (SOURCE: Nokia):

Barriers to 5G adoption:
The gap between enterprise awareness of 5G’s benefits and current levels of adoption suggests there are notable barriers to implementation. The research identified five principal barriers to 5G adoption for:
- Ecosystem availability: Limited availability of key infrastructure outside urban centers was cited by 28% of decision-makers.
- Education and understanding: 17% said a key barrier is that decision-makers within their business do not understand 5G, while 14% said they don’t know enough about it themselves.
- Awareness: Over a fifth of technology buyers (22%) said that 5G implementation is not a current priority for their business.
- Cost and complexity: 15% said they were not confident their company would be able to implement the necessary technologies.
- Security: Over a third (34%) said that they are concerned about the security of 5G.
Quotes:
“As organizations across the world move faster towards deployment of 5G enabled technologies, those who wish to be the first to leverage its potential cannot afford to lose more time,” said Gabriela Styf Sjöman, Chief Strategy Officer at Nokia. “To capture the tremendous opportunities of 5G, organizations must start or intensify their planning now and accelerate business model innovation to remain competitive in a rapidly digitalizing global economy. Beyond investment in the technology itself, this will require digitalizing operations, processes and ways of working to capture the full potential of 5G.
“5G adoption is categorically shown to fuel business success. Organizations that have integrated 5G stand to benefit from advantages that go way beyond faster, more efficient and reliable network services. As 5G enables businesses to transform, it will also accelerate wider technological and economic trends, with unimaginable possibilities for global economies and societies.
“The cities, hospitals and factories of the future depend on 5G and the unparalleled ability it offers to move, process and store vast volumes of data. Moreover, the biggest challenges we face as a society – from climate change to the pandemic – can be better tackled through at-scale use of the data and technologies that 5G will unleash.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
5G Catalysts:
The report identifies three key catalysts for change in order to bring about improved understanding, confidence and ultimately adoption of 5G. These are: improved regulation, collaboration and willingness to innovate.
- A third of technology buyers said that government investment in infrastructure or subsidies to drive down costs would encourage them to invest more in 5G. Enterprises will not adopt 5G unless the supply from network operators is presented and priced appropriately, which in turn relies on governments and regulators making 5G spectrum in low, mid and high bands available and affordable.
- The lack of understanding that exists within some businesses around 5G must be directly addressed. Companies and consumers alike need more information about the technology and how it can both improve operations and solve real world problems, ranging from enterprise use cases to telehealth to green technology.
- As companies better understand 5G, they must boldly move to overhaul their operations to accommodate it, for example, exploring how they could use 5G to streamline and more effectively monitor their mobile workforce, fleet or supply chain.
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/5g/readiness-report/
https://www.nokia.com/networks/5g/readiness-report/about-this-report/
https://onestore.nokia.com/asset/210070?_ga=2.168806049.1042908821.1602549124-1767387886.1601396220
Nokia report says 5G could add $8 trillion to global GDP by 2030
ABI Research: Open RAN radio units to exceed $47 billion by 2026
ABI Research expects the total CAPEX spent on Open RAN radio units (RUs) for public outdoor networks, including both macro and small cells will reach US$40.7 billion in 2026. Cumulative unit shipments will reach 9.9 million during the same year. Meanwhile, the total revenue of Open RAN radios for indoor enterprise networks will reach as much as US$6.7 billion in 2026, with cumulative unit shipments expected to reach 29.4 million. The Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) market is rapidly expanding and is expected to exceed the traditional RAN market for the first time around 2027-2028.
“The Open RAN opportunity invites various stakeholders to bring their best in class technologies and hardware/software components to contribute to building a flexible, secure, agile, and multi-vendor interoperable network solution,” said Jiancao Hou, Senior Analyst at ABI Research. “In addition, trade wars and the global pandemic of COVID-19 have resulted in tremendous restrictions on the telecom supply chain and disrupt the evolution of new technologies. These effects will accelerate the development of Open RAN and open networks.”
Rakuten Mobile, a greenfield network operator in Japan, set a prime example to deploy this new approach. Moreover, many other operators are also quite active in the field, namely Dish Network in the U.S., Vodafone, Telefonica, Deutsche Telekom, Orange, and Turkcell in the EU and other geological regions. The Open RAN supply chain is also expanding with Altiostar, Mavenir, and Parallel Wireless leading the charge while new entrants are announced every week.
“ABI Research expects greenfield installations, as well as private enterprise networks and public consumer networks, in rural/uncovered areas to drive the deployment of Open RAN throughout the entire forecast period,” Hou points out. Open RAN can introduce many advantages to the enterprise market, including infrastructure reconfigurability, network sustainability, and deployment cost efficiency. On the other hand, these small and easily manageable network use cases will likely lower the entry barrier for Open RAN. Simultaneously they help network operators and their ecosystem partners clearly understand the approach and suppliers’ maturity level, therefore paving the way for a broader market. Besides, “ABI Research sees new entrants will lead the early deployment for Open RAN, but they will be increasingly challenged by tier-one vendors and system integrators for both public cellular implementations and enterprise deployment,” Hou concludes.
These findings are from ABI Research’s Open RAN market data report. This report is part of the company’s 5G & Mobile Network Infrastructure research service, which includes research, data, and analyst insights. Market Data spreadsheets are composed of in-depth data, market share analysis, and highly segmented, service-specific forecasts to provide detailed insight where opportunities lie.
Earlier this week, the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) saw fit to recap its recent achievements regarding OpenRAN; read more about them here.
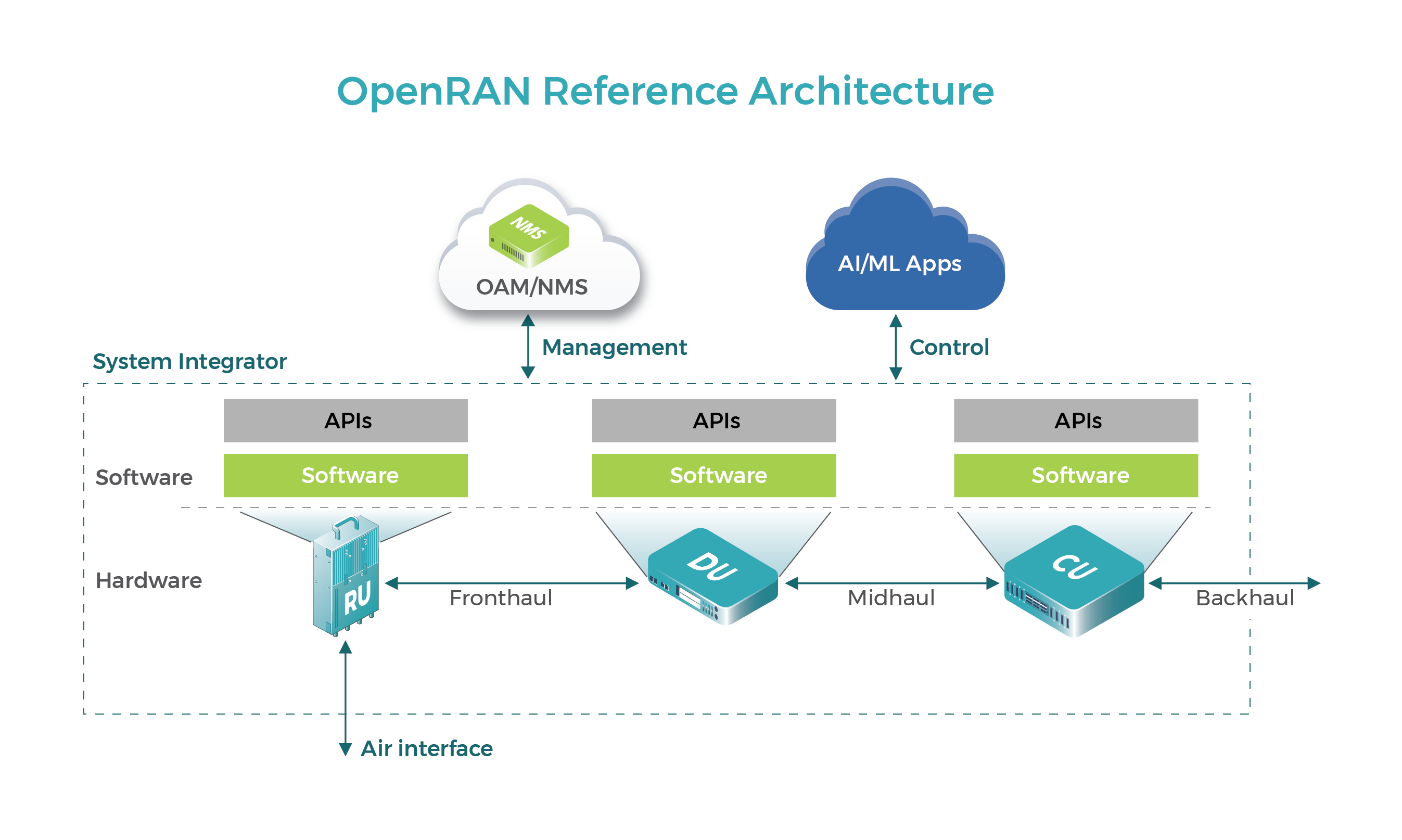
Image Credit: Telecom Infra Project
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About ABI Research
ABI Research provides strategic guidance to visionaries, delivering actionable intelligence on the transformative technologies that are dramatically reshaping industries, economies, and workforces across the world. ABI Research’s global team of analysts publish groundbreaking studies often years ahead of other technology advisory firms, empowering our clients to stay ahead of their markets and their competitors.
References:
https://www.abiresearch.com/press/open-ran-radio-units-soar-more-us47-billion-2026/
U.S. DoD: $600 Million for 5G Experimentation and Testing at 5 sites
On October 8th, the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) announced $600 million in awards for 5G experimentation and testing at five U.S. military test sites, representing the largest full-scale 5G tests for dual-use applications in the world. Each installation will partner military Services, industry leaders, and academic experts to advance the Department’s 5G capabilities.
Projects will include: piloting 5G-enabled augmented/virtual reality for mission planning and training, testing 5G-enabled Smart Warehouses, and evaluating 5G technologies to enhance distributed command and control.
DoD identified these test sites for their 5G testbeds: Hill Air Force Base, Utah; Joint Base Lewis-McChord (JBLM), Washington; Marine Corps Logistics Base Albany, Georgia; Naval Base, San Diego, California; and Nellis Air Force Base, Las Vegas, Nevada.
Those military bases were selected for their ability to provide streamlined access to spectrum bands and mature fiber and wireless infrastructure, support new or improved infrastructure requirements, and conduct controlled experimentation with dynamic spectrum sharing.
The telecom companies and vendors involved include AT&T, Ericsson, Nokia, GE Research, Federated Wireless, Shared Spectrum Company, Keybridge Wireless LLC, General Dynamics Mission Systems, Scientific Research Corp, KPMG, Deloitte, Vectrus Mission Solutions Corporation, Booz-Allen Hamilton, Oceus Networks, and GBL Systems (GBL’s Samsung-based 5G testbed will utilize mid-band spectrum).
Research and Engineering Acting Under Secretary of Defense Michael Kratsios said:
“The Department of Defense is at the forefront of cutting edge 5G testing and experimentation, which will strengthen our nation’s warfighting capabilities as well as US economic competitiveness in this critical field. Through these test sites, the department is leveraging its unique authorities to pursue bold innovation at a scale and scope unmatched anywhere else in the world.”
“Importantly, today’s announcement demonstrates the department’s commitment to exploring the vast potential applications and dual-use opportunities that can be built upon next-generation networks.”
Joseph Evans, the DoD’s director of 5G, said the testbeds should be working in a year. Evans told reporters:
“Each of the experiments has some aspect that’s really new and exciting to us. In addition, it also provides an opportunity for industry to experiment and mature their technologies along those parallel tracks.”
“We’re basically trying to make our forces more survivable by taking command and control functions that have long been housed in single buildings and spread them out and make them make them mobile. So [we’re] really trying to change the way our forces are deployed in the field.”
The tests and projects to be performed at each base are detailed in the press release, which concludes with this statement:
5G communications technology is a foundational enabler for all U.S. defense modernization programs, and vital to U.S. national and economic security.
DoD’s efforts focus on large-scale experimentation and prototyping of dual-use 5G technology that will provide high speeds and quicker response times, connect many more wireless devices than current wireless technology, and enable leap-ahead capabilities for the U.S. military.
Today’s announcement builds on DoD’s previously-announced 5G prototyping efforts and is part of a 5G development roadmap guided by the Department of Defense 5G Strategy. It represents the first tranche of awards on 5G experimentation and testing, with additional sites to be announced in the future.
Last month, AT&T Communications announced that the USAF will test 5G and an array of networking-as-a-service (NaaS) capabilities at three AFBs. In May this year, the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (OUSD) for Research and Engineering (R&E) and the US Air Force Warfare Center (USAFWC) at Nellis AFB, Nevada partnered to build a 5G cellular network.
The DoD is also in the process of choosing vendors for 5G experiments at seven more bases. According to Evans, the first solicitation release and industry day for the Navy and Marines Corps bases in that tranche will come in mid-October using the Navy’s Information Warfare Research Project consortium. The Air Force and Army solicitations are expected to be rolled out through December through the National Spectrum Consortium, Evans said.
Comment and Analysis:
Ultra high reliability/availability will be required for any 5G military/DoD application, but it remains to be seen if that feature can be realized considering the current status of IMT 2020.SPECS and 3GPP Release 16 (URLLC in the RAN and URLLC in the Core work items).
Also, military grade equipment and devices must have air-tight security and “hardened” hardware to correctly operate during different environmental conditions. That will make the equipment to be developed much more expensive than commercial 5G products.
References:
Swisscom achieves 50 Gbps on a fixed PON connection – a world first!
Swisscom has achieved transmission speeds of 50 Gbps in a real PON (Passive Optical Network) environment test – a world first, according to the company. Swisscom has upgraded existing OLT (Optical Line Termination) hardware with a 50 Gbps PON Line Card prototype to reach a download speed of 50 Gbps and an upload speed of 25 Gbps on a fixed network.
The PON technology can be ready to market and deployed in around two years, according to Swisscom. It can be an option for business customers initially. Progressive network virtualization will enable companies to use the bandwidth they need on a flexible basis in line with their requirements.
The 10 Gbps service is expected to be sufficient for the residential mass market for several years yet, the company said. The 50 Gbps option allows for flexible deployment using existing fibre-optic infrastructure.
Markus Reber, Head of Swisscom Networks, said: “There is no question that the bandwidth need will continue to increase over the coming years. That’s why, here at Swisscom, we are already considering how our technology needs to develop to ensure that Switzerland continues to be ready to take advantage of the latest digital services with the best possible experience in the future. The results of testing based on PON technology and architecture clearly demonstrate that we have some powerful options available.”
“In my opinion, PON with 50 Gbit/s will be an option for the business customer market initially. Progressive network virtualisation will enable companies to use the bandwidth they need on a flexible basis in line with their requirements, for instance. In contrast, the 10 Gbit/s already available in the residential mass market should be more than enough for several years to come. However, the 50 Gbit/s option offers even more opportunities, as it allows the existing fibre optic infrastructure to be deployed in a more versatile way. As an example, the technology will soon facilitate access to mobile communication masts, particularly for 5G, as the same network can be used as the one already built to connect households. With a transmission speed of 50 Gbit/s, there is ample bandwidth available.”
The technology also will support fiber optic access to mobile communication masts, particularly for 5G, since the same network can be used as the one already built to connect households.
Swisscom says that “over the coming years, the development of digital applications will result in a similar growth in bandwidth need as seen in recent years, when it increased more than tenfold within a decade. Swisscom is therefore investing in network expansion on an ongoing basis, deploying the latest innovative technologies to do so and safeguarding Switzerland’s high degree of digital competitiveness.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In April 2020, market research powerhouse Omdia (owned by Informa) forecast that In the 2018-2025 timeframe, the PON market will see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% to be worth $8.4 billion by 2025. “This market remains in an upswing as operators continue to expand and upgrade their fiber-based access networks for both residential and non-residential subscribers and applications,” states the Omdia team in their report (published prior to the global impact of COVID-19, it should be noted).
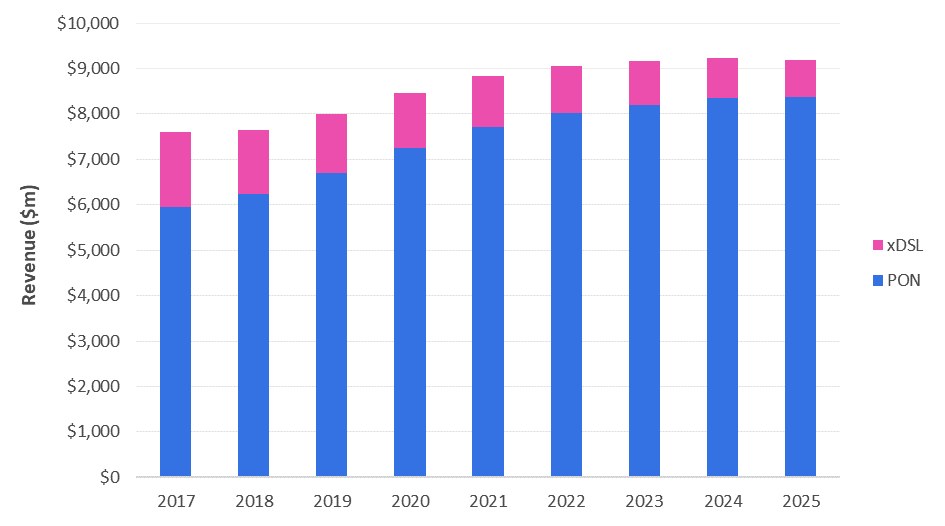
Omdia: PON and xDSL/Gfast equipment market by major segment, 2017–2025
Growth in the PON market will be driven by increasing demand for next-generation PON equipment, including 10G GPON, 10G EPON, NG-PON2 and 25G/50G PON, according to Omdia: By 2021, most GPON OLT (optical line terminal) shipments are expected to be 10G.
Omdia expects demand for NG-PON2 equipment (which is expensive because it includes tunable lasers) is expected to be limited, with significant deployments anticipated only by one major operator, Verizon.
In Western Europe, PON investments are only just starting: That market is set for a CAGR of 16.5% to be worth $1.6 billion in 2025.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.swisscom.ch/en/about/news/2020/10/08-weltpremiere.html
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/swisscom-reaches-50-gbps-in-real-network-environment–1357116
http://www.broadbandworldnews.com/document.asp?doc_id=758638



