Month: July 2023
Telecom TV Poll: How to maximize cloud-native opportunities?
The adoption of cloud-native methodologies, processes and tools has been a challenge for communications service providers (CSPs), aka telcos or network operators.
- Telcos are embracing cloud-native processes and tools
- It’s part of their evolution towards being digital service providers
- But the cloud-native journey is still in its early stages
- Real cultural change is needed if telcos are to capitalise fully on the cloud-native opportunities
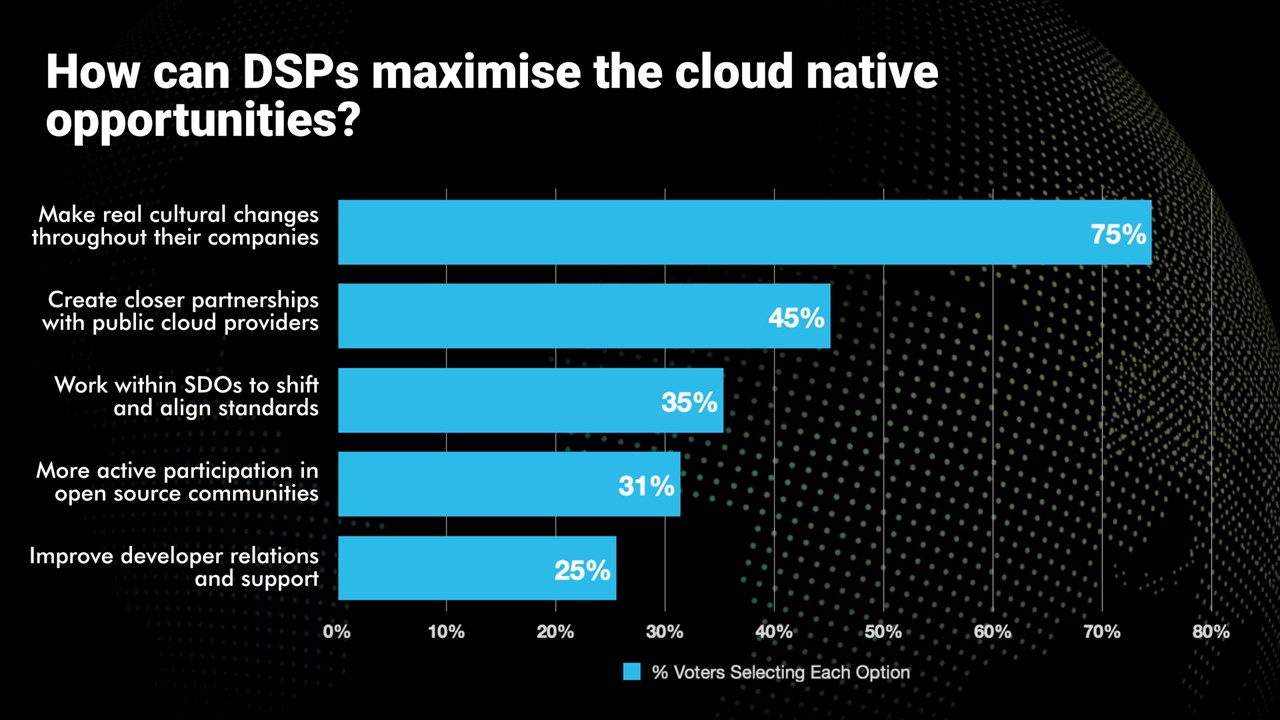
Alongside a a session, Why cloud native is essential to delivering the automation, agility and innovation needed to support new services, at Telco TV’s DSP Leaders World Forum event in Windsor, UK, a poll was taken. The following question was asked, “How can Digital Service Providers maximize the cloud-native opportunities?” Respondents were able to select all the options they deemed relevant. Here are the results:
Please check out the upcoming Cloud Native Telco Summit session on cloud-native application development to see what the industry experts have to say.
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
Huawei Connect 2022: It’s Cloud Native everything!
Mediatek Dimensity 6000 series with lower power consumption for affordable 5G devices
MediaTek [1.] today officially launched its new Dimensity 6000 series along with a chipset designed to enhance the next generation of mainstream 5G devices. The Dimensity 6100+ SoC delivers premium features—including exceptional power efficiency, vivid displays, high frame rates, AI-powered camera technologies, leading low power consumption, and reliable Sub-6 5G connectivity—at an accessible price point.
The ‘Enhanced’ 5G modem on the chip supports 3GPP Release 16, with up to 140 MHz 2CC 5G Carrier Aggregation (more details below). The SoC also uses MediaTek’s UltraSave 3.0+ technology that the company claims “significantly reduces 5G power consumption” by up to 20% when compared to other available solutions in the market.
Note 1. Taiwan based Mediatek is one of 3 fabless semiconductor companies making and selling 5G baseband silicon. The other 2 are Qualcomm and Unisoc (China). In addition, Huawei and Samsung make 5G chips which are embedded in their 5G endpoint products, but not sold on the merchant semiconductor market.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“As developing markets continue rolling out 5G networks at a rapid pace and operators in developed markets work to finish transitioning consumers from 4G LTE to 5G, there has never been a more vital need for chipsets that cater to the growing number of mainstream mobile devices that feature next-generation connectivity,” said CH Chen, Deputy General Manager of MediaTek’s Wireless Communications Business Unit. “The MediaTek Dimensity 6000 series makes it possible for device makers to stay ahead of the curve with impressive upgrades that boost performance, increase power efficiency and reduce material costs,” Chen added.
The Dimensity 6100+ integrates an enhanced 5G modem supporting 3GPP Release 16 with up to 140MHz 2CC 5G Carrier Aggregation, significantly reducing power consumption contributed by MediaTek UltraSave 3.0+ technology. This chip features two Arm Cortex-A76 big cores and six Arm Cortex-A55 efficiency cores, offering notable enhancements, including support for AI-powered cameras, 10-bit displays, outstanding UX and GPU performance, and rich peripheral features.
Other key features of the Dimensity 6100+ chipset include:
- Up to 108MP Non-ZSL camera support.
- Up to 2K 30fps video capture.
- UltraSave 3.0+ technology offers 20% reduced 5G power consumption compared to competitive solutions.
- Powerful camera features including AI-bokeh for stunning portraits and selfies; working with Arcsoft, MediaTek is also bringing AI-color technology to mainstream devices so users can showcase their creativity.
- Premium 10-bit display support: Reproduces more than one billion colors for vibrant images and videos, along with support for 90Hz to 120Hz frame rates for a smooth user experience.
 MediaTek’s broad 5G portfolio expands across different price tiers to make great mobile experiences more accessible. The Dimensity 9000 series is designed for flagship smartphones and tablets; the Dimensity 8000 family is geared for premium mobile devices; and the Dimensity 7000 lineup expands the company’s range of high-tech devices. The new Dimensity 6000 series will now democratize higher-end features to mainstream 5G devices.
MediaTek’s broad 5G portfolio expands across different price tiers to make great mobile experiences more accessible. The Dimensity 9000 series is designed for flagship smartphones and tablets; the Dimensity 8000 family is geared for premium mobile devices; and the Dimensity 7000 lineup expands the company’s range of high-tech devices. The new Dimensity 6000 series will now democratize higher-end features to mainstream 5G devices.
The first smartphones featuring the Dimensity 6100+ chipset will be available in the third quarter of 2023.
References:
https://i.mediatek.com/mediatek-5g
Samsung-Mediatek 5G uplink trial with 3 transmit antennas
Ericsson and MediaTek set new 5G uplink speed record using Uplink Carrier Aggregation
MediaTek Introduces Global Ecosystem of Wi-Fi 7 Products at CES 2023
MediaTek to expand chipset portfolio to include WiFi7, smart homes, STBs, telematics and IoT
Nokia, China Mobile, MediaTek speed record of ~3 Gbps in 3CC carrier aggregation trial
Altice Launches Optimum 8 Gig Fiber Symmetric Internet Service
Altice USA’s Optimum is the latest provider to trot out a symmetrical 8-gig fiber tier, which Altice said is now available to more than 1.7 million residents and businesses across the company’s fiber footprint. By year end, Optimum 8 Gig Fiber will be available to nearly 3 million passings and will expand as the Company’s fiber network build continues.
This launch represents the largest deployment of 8 Gig internet speeds in the country and cements Optimum as the nation’s largest 8 Gig internet provider, delivering the fastest Fiber Internet available in its serviceable footprint that is four times faster than Verizon, 60% faster than Frontier, and 32 times faster than T-Mobile 5G Home Internet.
Reliability
“After launching 2 and 5 Gig symmetrical Fiber Internet speeds last year, Optimum is pleased to have invested even further in our network and infrastructure to bring next level 8 Gig symmetrical internet speeds to our fiber footprint,” said Leroy Williams, Chief Growth Officer, Optimum. “Optimum is now the nation’s largest 8 Gig Fiber Internet provider, and availability will continue to increase as we deploy fiber to more homes and businesses as we solidify our position as the connectivity provider of choice across all the communities we serve. We look forward to bringing these reliable and faster speeds, along with an enhanced customer experience, to meet our customers’ growing data needs today and into the future.”
Backed by Optimum’s 100% Fiber Internet network with 99.9% network reliability, Optimum’s 8 Gig Fiber Internet offers 8 Gig symmetrical upload and download speeds to support the most data-intensive applications such as AR/VR, gaming, graphic design, and video production, all while providing increased bandwidth that can simultaneously connect 100+ devices to the internet at once. The service is delivered directly into the home via the Optimum Fiber Gateway to enable fast, reliable WiFi in the home or business, with extenders available for extra coverage.
“Optimum’s Fiber is deployed using XGS-PON, an advanced technology that enables multi-gigabit symmetrical speeds and that is superior to the legacy GPON standard used by many other fiber providers,” said Pragash Pillai, Chief Technology and Information Officer, Optimum. “As we continue to bring faster, more reliable service to customers through this state-of-the-art technology, the strength of Optimum’s Fiber network goes unmatched.”
Optimum continues to be a leader in the deployment of multi-gigabit internet speeds across the nation, having launched 2 and 5 Gig internet service across its fiber footprint in the New York tri-state area last year, and now adding an additional 8 Gig speed tier to more homes and businesses on its 100% Fiber Internet Network.
An Altice rep told Fierce the 8-gig offering is currently live in all markets where multi-gig speeds are available, which is “predominantly” in the New York tri-state area. Consumers can check the Optimum website to see if they’re eligible for the service. “In addition to multi-gig, up to 1 gig speeds are available in more than 90% of the Optimum footprint,” the rep told Fierce.
8-gig speeds come after Altice last year released 2-gig and 5-gig tiers across New York, New Jersey and Connecticut. Altice said “nearly 3 million passings” will have access to 8-gig fiber by year-end, and that number will increase as Altice ramps up its fiber expansion.
For more information on Optimum’s multi-gig speed tiers and other fiber offerings, prospective customers can visit Optimum.com/8Gig. Existing customers can call 1.866.347.4784 to upgrade.
About Optimum:
Optimum is a brand of Altice USA, one of the largest broadband communications and video services providers in the United States, delivering broadband, video, and mobile services to nearly 5 million residential and business customers across 21 states. The company operates a4, an advanced advertising and data business, which provides audience-based, multiscreen advertising solutions to local, regional and national businesses and advertising clients. Altice USA also offers hyper-local, national, international and business news through its News 12, Cheddar News and i24NEWS networks.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Other 8-gig Network Providers:
Windstream’s Kinetic has also gotten into the 8-gig game, as a spokesperson recently told Fierce it will make 8-gig speeds available to 400,000 households across its 18-state footprint. Others that have rolled out 8-gig tiers include C Spire, Google Fiber, Lumen Technologies and TDS Telecom. Google Fiber is particularly stepping up its speeds, as it’s seeking testers for its nascent 20-gig product.
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/broadband/altice-usa-unveils-8-gig-optimum-fiber-tier
GSA: 5G Device Ecosystem June 2023 Summary
Highlights:
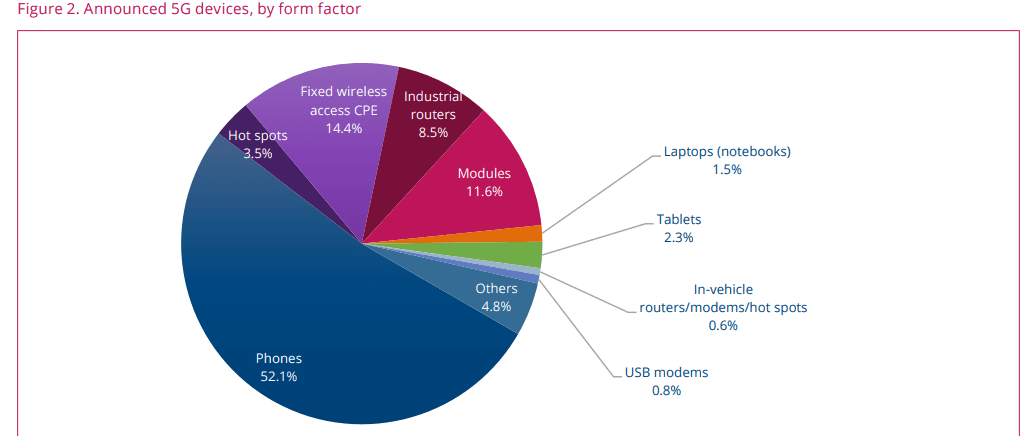
- The number of announced 5G devices rose by 1.2% between April and May 2023, reaching a total of 1,965 devices. Of these, 1,579 are understood to be commercially available, representing 80.4% of all announced 5G devices. This is an increase of 48.7% in the number of commercial 5G devices since the end of May 2022. Highlights this edition include:
- 233 manufacturers with announced available or forthcoming 5G devices
1,965 announced devices, of which at least 1,579 are understood to be commercially available
Not all devices are available immediately and specification details remain limited for some. We expect devices to continue to become more widely available and for more information about announced devices to emerge as they reach the market. - The number of commercially available devices has been growing steadily since the start of the year and should continue in this manner. GSA will continue to track and report on 5G device launches during the coming year. Its GAMBoD database contains important details about device form factors, features and support for spectrum bands. Summary statistics are released in this regular monthly publication.
By the end of May 2023, GSA had identified:
• 26 announced form factors
• 233 manufacturers with announced available or forthcoming 5G devices
• 1,965 announced devices, including regional variants, but excluding operator-branded devices that are essentially rebadged
versions of other phones. Of these, at least 1,579 are understood to be commercially available:
• 1,024 phones (up 15 from April 2023), at least 942 of which are now commercially available (up 14 from April 2023)
• 283 fixed wireless access customer-premises equipment (CPE) devices for indoor and outdoor uses, at least 183 of which are
now commercially available
• 227 modules
• 167 industrial or enterprise routers, gateways or modems
• 68 battery-operated hot spots
• 46 tablets
• 29 laptops or notebooks
• 12 in-vehicle routers, modems or hot spots
• 15 USB terminals, dongles or modems
• 94 other devices, including drones, head-mounted displays, robots, TVs, cameras, femtocells/small cells, repeaters, vehicle
on-board units, keypads, a snap-on dongle/adapter, a switch, a vending machine and an encoder
• 1,063 announced devices with declared support for 5G standalone in sub-6 GHz bands, 864 of which are commercially available.
- Not all devices are available immediately and specification details remain limited for some. We expect devices to continue to become more widely available and for more information about announced devices to emerge as they reach the market.
- The number of commercially available devices has been growing steadily since the start of the year and should continue in this manner.
- GSA will continue to track and report on 5G device launches during the coming year. Its GAMBoD database contains important details about device form factors, features and support for spectrum bands. Summary statistics are released in this regular monthly publication.
References:
GSA FWA Report: 38 commercially launched 5G FWA networks in the EU; Speeds revealed
GSA: 200 global operators offer 5G services; only 20 (Dell’Oro says 13) have deployed 5G SA core network
GSA: 5G Market Snapshot – 5G networks, 5G devices, 5G SA status
Draft new ITU-R recommendation (not yet approved): M.[IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND]
Introduction:
At its 44th meeting in June 2023, ITU-R WP 5D finalized development of a draft new Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND] on “Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond.” This draft recommendation is expected to be approved by year end 2023.
With the evolution of information and communications technologies, IMT-2030 is expected to support enriched and immersive experience, enhanced ubiquitous coverage, and enable new forms of collaboration. Furthermore, IMT-2030 is envisaged to support expanded and new usage scenarios compared to those of IMT-2020, while providing enhanced and new capabilities.
The objective of this Recommendation is to provide guidelines on the framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT-2030 (aka “6G”).
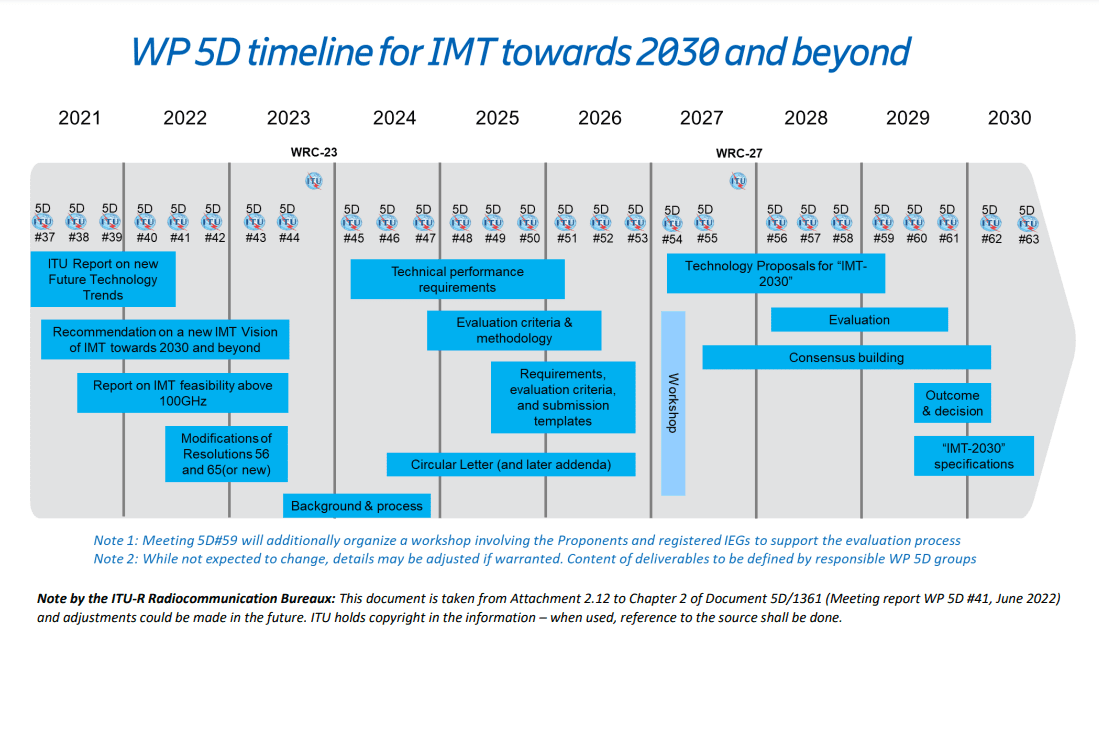
In the next three years starting from 2024, ITU-R WP 5D will focus on the study of detailed technical performance requirements and the evaluation criteria and methodologies, paving the way for the technology proposal evaluation in the last phase of the IMT-2030 cycle, i.e. from 2027 to 2030.
Relationship between ITU-R (WP 5D) and 3GPP:
ITU-R WP 5D establishes the overall research and development direction, key performance indicators, as well as the standardization, commercialization, and spectrum roadmap for the new generation of IMT through a Framework Recommendation. It then moves on to defining the technical performance requirements to achieve the Framework.
After that, 3GPP develops detailed technical specifications that meet the requirements defined by the ITU-R recommendations and submits their specs to ITU-R WP5D (via ATIS) as a candidate radio interface technology. 5D then evaluates whether the 3GPP defined technology meets the requirements of the ITU-R (for 5G and presumably for 6G too). If it passes the evaluation process, it is approved as ITU-R Recommendation.
Figure 1. below shows these relationships:

Figure 1. Relationship between ITU-R and 3GPP
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Motivation and societal considerations:
The motivation for the development of IMT-2030 is to continue to build an inclusive information society and to support the UN’s sustainable development goals (SDGs). To this end, IMT-2030 is expected to be an important enabler for achieving the following goals, among others:
– Inclusivity: Bridging digital divides, to the maximum extent feasible, by ensuring access to meaningful connectivity to everyone.
– Ubiquitous connectivity: To connect unconnected, IMT-2030 is expected to include affordable connectivity and, at minimum, basic broadband services with extended coverage, including sparsely populated areas.
– Sustainability: Sustainability refers to the principle of ensuring that today’s actions do not limit the range of economic, social, and environmental options to future generations. IMT-2030 is envisaged to be built on energy efficiency, low power consumption technologies, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and use of resources under the circular economy model, in order to address climate change and contribute towards the achievement of current and future sustainable development goals.
– Innovation: Fostering innovation with technologies that facilitate connectivity, productivity and the efficient management of resources. These technological advances will improve user experience and positively transform economies and lives everywhere.
– Enhanced security, privacy and resilience: The future IMT system is expected to be secure and privacy-preserving by design. It is expected to have the ability to continue operating during and quickly recover from a disruptive event, whether natural or man-made. Making security, privacy and resilience key considerations in the design, deployment and operation of IMT-2030 systems is fundamental to achieving broader societal and economic goals.
– Standardization and interoperability: To achieve wide industry support for IMT 2030, future IMT systems are expected to be designed from the start to use transparently and member-inclusively standardized and interoperable interfaces, ensuring that different parts of the network, whether from the same or different vendors, work together as a fully functional system.
– Interworking: IMT-2030 is expected to support service continuity and provide flexibility to users via close interworking with non-terrestrial network implementations, existing IMT systems and other non-IMT access systems. IMT-2030 is also expected to support smooth migration from existing IMT systems, where including support of connectivity to IMT-2020 and potentially IMT-Advanced devices will be advantageous for inclusivity.
User and application trends:
Applications and services enabled by IMT-2030 are expected to connect humans, machines and various other things together. With the advances in human-machine interfaces, interactive and high-resolution video systems such as extended reality (XR) displays, haptic sensors and actuators, and/or multi-sensory (auditory, visual, haptic or gesture) interfaces, IMT-2030 is expected to offer humans immersive experiences that are virtually generated or happening remotely. On the other hand, machines are envisaged to be intelligent, autonomous, responsive, and precise due to advances in machine perception, robotics, and artificial intelligence (AI). In the physical world, humans and machines are expected to continuously interact with each other, working with a digital world that extends the real world by using a large number of advanced sensors and AI. Such a digital world not only replicates but also affects the real world by providing virtual experiences to humans, and computation and control to machines.
IMT-2030 is expected to integrate sensing and AI-related capabilities into communication and serve as a fundamental infrastructure to enable new user and application trends. From these trends, it is expected that IMT-2030 provides a wide range of use cases while continuing to provide, inter alia, direct voice support as an essential communication. Furthermore, IMT-2030 technology is expected to drive the next wave of digital economic growth, as well as sustainable far-reaching societal changes, digital equality and universal connectivity. IMT-2030 is expected to further enhance security, privacy, and resilience.
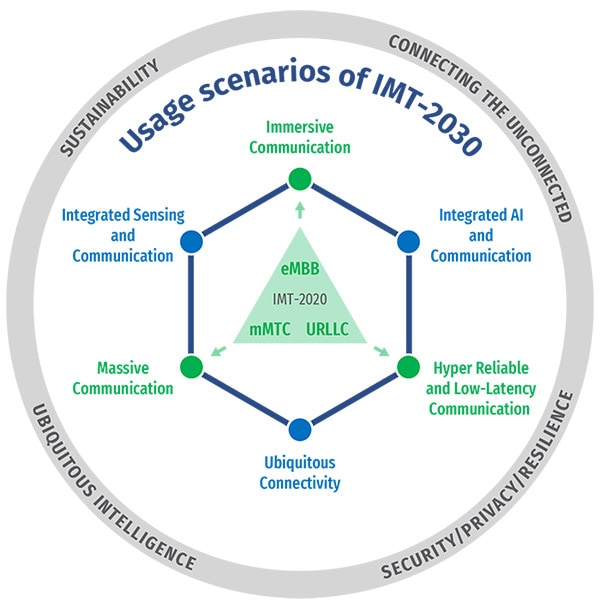
Source: Huawei
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Technology trends:
Report ITU-R M.2516 provides a broad view of future technical aspects of terrestrial IMT systems considering the timeframe up to 2030 and beyond, characterized with respect to key emerging services, applications trends, and relevant driving factors. It comprises a toolbox of technological enablers for terrestrial IMT systems, including the evolution of IMT through advances in technology and their deployment. In the following sub-sections, a brief overview of emerging technology trends and enablers, technologies to enhance the radio interface, and technologies to enhance the radio network are presented.
Emerging technology trends and enablers:
IMT-2030 is expected to consider an AI-native new air interface that uses AI to enhance the performance of radio interface functions such as symbol detection/decoding, channel estimation etc. An AI-native radio network would enable automated and intelligent networking services such as intelligent data perception, supply of on-demand capability etc. Radio networks that support AI services would be fundamental to the design of IMT technologies to serve various AI applications, and the proposed directions include on-demand uplink/sidelink-centric, deep edge, and distributed machine learning including federated learning.
The integration of sensing and communication functions in IMT-2030 systems would give new capabilities, enable innovative services and applications, and provide solutions with a higher degree of sensing accuracy. It would lead to benefits in enhancing performance and reducing overall cost, size, and power consumption of both systems, when it is combined with technologies such as AI, network cooperation, and multi-nodes cooperative sensing.
Computing services and data services are expected to become an integral component of the IMT 2030 system. It is expected to include processing data at the network edge close to the data source for real-time responses, low data transport costs, high energy efficiency and privacy protection, as well as scaling out device computing capability for advanced application computing workloads.
Device-to-device wireless communication with extremely high throughput, ultra-accuracy positioning and low latency would be an important communication paradigm for IMT-2030. Technologies such as THz technology, ultra-accuracy sidelink positioning, and enhanced terminal power reduction can be considered to support new applications.
Typical use cases for the 6 usage scenarios of IMT-2030:
| Immersive Communication |
|
| Massive Communication |
|
| Hyper Reliable & Low-Latency Communication |
|
| Ubiquitous Connectivity |
|
| Integrated AI and Communication |
|
| Integrated Sensing and Communication |
|
Source: Huawei
The Figure below summarizes the different dimensions of capabilities for IMT-2030, including 9 enhanced capabilities (peak data rate, user experienced data rate, spectrum efficiency, area traffic capacity, connection density, mobility, latency, reliability, and security/privacy/resilience) and 6 new capabilities (coverage, positioning, sensing-related capabilities, AI-related capabilities, sustainability, and interoperability). The range of values for the capabilities in the figure are estimated targets for research and investigation of IMT-2030. For each usage scenario, single or multiple values within the range would be developed in the future in other ITU-R Recommendations/Reports.
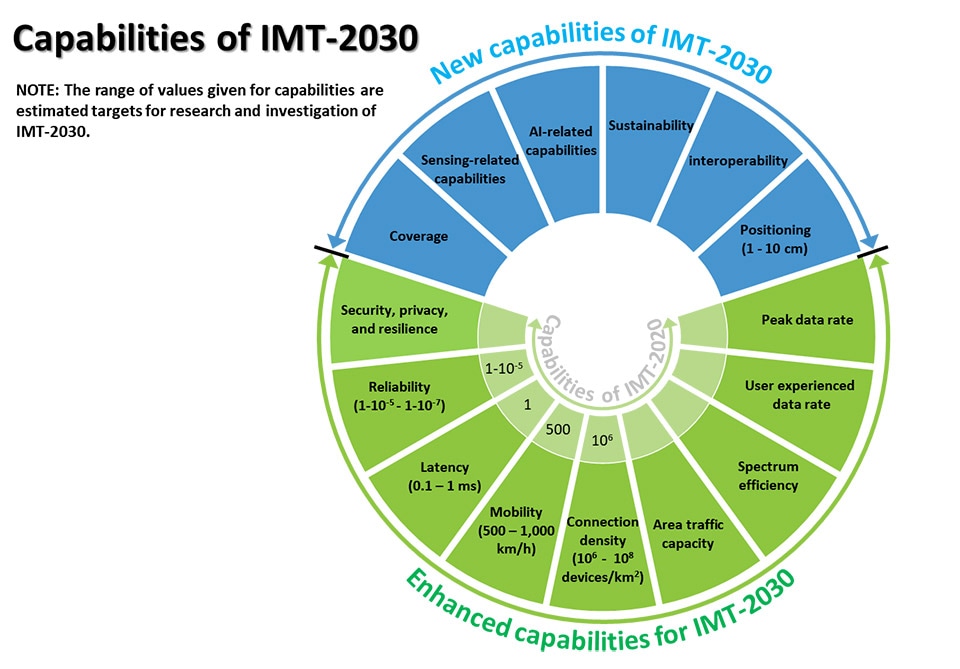
Source: Huawei
IMT-2030 envisages the use of a wide range of frequency bands ranging from sub-1 GHz up to sub-THz bands (low bands, mid bands (centimeterWave), mmWave bands and sub-THz bands). It expects that wider channel bandwidths may be needed to support future applications and services for IMT-2030 in a wide variety of deployments, including wide-area deployments. It is important to ensure that the current spectrum and newly assigned spectrum are harmonized.
References:
https://www.itu.int/md/R19-WP5D-230612-TD-0905/en (RESTRICTED TO TIES USERS)
https://research.samsung.com/blog/All-set-for-6G
IMT Vision – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
China’s MIIT to prioritize 6G project, accelerate 5G and gigabit optical network deployments in 2023
ABI Research and CCS Insight: Strong growth for satellite to mobile device connectivity (messaging and broadband internet access)

CCS Insight believes that these enhanced satellite networks have the capability to grow to deliver voice and data services as the constellations evolve. It adds that network operators will be able to offer these satellite services as add-ons to existing subscription packages, catering to the growing demand for ubiquitous connectivity.
As demand for enhanced global connectivity continues to rise, the analyst forecasts that 15% of global mobile subscribers are expected to own a smartphone that supports satellite messaging by 2027 and an additional 10% will benefit from satellite plans provided by their operator. By capitalizing on revenue streams generated through operators and supplementary services, CCCS believes that the direct-to-device satellite market is poised to amass $18bn in revenue by 2027. This market it said represented a “vast opportunity”, with an audience of more than 4.8 billion people who could access satellite services through a compatible smartphone. It calculated that as many as 493 million people worldwide lack any kind of mobile network coverage.
“Bringing satellite capabilities to mass-market smartphones marks a milestone in the telecom industry,” said Luke Pearce, senior analyst at CCS Insight. “This development creates exciting opportunities for consumers, manufacturers and operators and promises to help bridge the digital divide. The projected growth in revenue and subscribers highlights the potential this integration holds for expanding connectivity options – we’re witnessing the start of a new era where satellite services become an integral part of everyday smartphones.”
CCS Insight’s free report, Direct Satellite-to-Device Mobile Services, shares unique insight into the market for satellite-connected phones and unpacks its developing dynamics.
AST SpaceMobile achieves 4G LTE download speeds >10 Mbps during test in Hawaii
FCC Grants Experimental License to AST SpaceMobile for BlueWalker 3 Satellite using Spectrum from AT&T
New ITU report in progress: Technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 100 GHz (92 GHz and 400 GHz)
Introduction:
ITU-R Report R M.2376 contains studies of frequency ranges (6-100 GHz) for International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) technologies. It is envisioned that future IMT systems will need to support very high throughput data links to cope with the growth of the data traffic, new extremely bandwidth demanding use cases, as well as new capabilities of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). There has been academic and industry research and development ongoing related to suitability of mobile broadband systems in frequency bands above 92 GHz to enable services requiring tera-bit per second speeds. This has prompted researchers to consider the technical feasibility of higher frequency bands in IMT.
Overview:
This ITU-R preliminary draft new report in progress provides information on the technical feasibility of IMT in bands between 92 GHz and 400 GHz. This Report complements the studies carried in Report ITU-R M.2376. This technical feasibility Report includes information on propagation mechanisms and channel models, as well as newly developed technology enablers such as active and passive components, antenna techniques, deployment architectures, and the results of simulations and performance tests. Aspects of coexistence with incumbent radiocommunications services above 92 GHz are outside the scope of this document, and this report does not presuppose the inclusion of any item on a future World Radio Conference (WRC) agenda nor the decisions of a future WRC.
ITU-R WP5D emphasizes that the further development of the draft new Report ITU-R M.[IMT.ABOVE 100GHz] does not contain propagation prediction methods. It contains only results contributed by industry and academia of propagation measurements and simulation campaigns.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
From: Experiments bring hope for 6G above 100 GHz:
Channel models for 4G and 5G cannot simply be extended above 100 GHz; engineers must verify and fine-tune knowledge to correctly reflect the impact of the environment for various use cases. We must, for example, understand outdoor scenarios and indoor industrial scenarios where human bodies, vehicles, and environmental conditions such as rain propagation strongly influence signal propagation.
5G pioneered the use of millimeter wave frequencies with bandwidths up to 400 MHz per component carrier to enable transmission rates necessary for demanding real-time applications such as wireless factory automation. 6G technology is aiming at significantly higher transmission rates and lower latencies. Large contiguous frequency ranges for ultra-high data rates with bandwidths of several GHz are only available above 100 GHz.
With sonar, the transmitter and receiver are in the same place. As for channel sounding of electromagnetic waves, the transmitter and receiver are spatially separated. In time domain channel sounding, a modulated pulse signal with excellent autocorrelation properties, such as a Frank-Zadoff-Chu (FZC) sequence [1], serves as a “ping” whose channel impulse response (CIR) is recorded. This propagation-time measurement is very similar to the time-delay measurements performed in a GPS receiver in reference to the GPS satellites (and subsequently inferring the position information), where each satellite transmits its specific correlation sequence. The CIR includes both the direct propagation components (line of sight, LOS) and all reflection and scattering components (non-line-of-sight, NLOS) from objects in the environment (Figure 1). We can derive channel-model parameters and their values from the results.

Figure 1. Operating principle of time domain channel sounding: The channel impulse response (CIR) is measured by emitting an electromagnetic “ping” at the frequency of interest and capturing all returning signal components.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.itu.int/md/R19-WP5D-C-0679/en (RESTRICTED TO ITU TIES USERS)
https://www.itu.int/md/R1-WP5D-C-1654/en (RESTRICTED TO ITU TIES USERS)
ITU-R WP5D: Studies on technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 100 GHz
Samsung-Mediatek 5G uplink trial with 3 transmit antennas
Samsung Electronics and MediaTek have successfully conducted 5G standalone (SA) uplink tests, using three transmit (3Tx) antennas instead of the typical two, to demonstrate the potential for improved upload experiences with current smartphones and customer premise equipment (CPE).
Until recently, most talk about 5G SA industry firsts have focused on the downlink. However, the demands on uplink performance are increasing with the rise of live streaming, multi-player gaming and video conferences. Upload speeds determine how fast your device can send data to gaming servers or transmit high-resolution videos to the cloud. As more consumers seek to document and share their experiences with the world in real-time, enhanced uplink experiences provide an opportunity to use the network to improve how they map out their route home, check player stats online and upload videos and selfies to share with friends and followers.
While current smartphones and customer premise equipment (CPEs) can only support 2Tx antennas, this industry-first demonstration validated the enhanced mobile capability of 3Tx antenna support. This approach not only improves upload speeds but also enhances spectrum and data transmission efficiency, as well as overall network performance.
The test was conducted in Samsung’s lab, based in Suwon, Korea. Samsung provided its industry-leading 5G network solutions, including its C-Band Massive MIMO radios, virtualized Distributed Unit (vDU) and core. The MediaTek test device featuring its new M80-based CPE chipset began with one uplink channel apiece at 1,900MHz and 3.7GHz, but added an extra uplink flow using MIMO on 3.7GHz. Both companies achieved a peak throughput rate of 363Mbps, an uplink speed that is near theoretical peak using 3Tx antennas.

Source: ZTE
“We are excited to have successfully achieved this industry breakthrough with MediaTek, bringing greater efficiency and performance to consumer devices,” said Dongwoo Lee, Head of Technology Solution Group, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “Faster uplink speeds bring new possibilities and have the potential to transform user experiences. This milestone further demonstrates our commitment to improving our customers’ networks using the most advanced technology available.”
“Enhancing uplink performance using groundbreaking tri-antenna and 5G UL infrastructure technologies will ensure next-generation 5G experiences continue to impress users globally,” said HC Hwang, General Manager of Wireless Communication System and Partnership at MediaTek. “Our collaboration with Samsung has proved our combined technical capabilities to overcome previous limits, enhancing network performance and efficiency, opening up new possibilities for service providers and consumers to enjoy faster and more reliable 5G data connectivity.”
“With demands on mobile networks rising, enhancing upload performance is essential to improving consumer and enterprise connectivity, as well as application experiences,” said Will Townsend, VP & Principal Analyst at Moor Insights & Strategy. “Samsung and MediaTek have achieved an important 5G Standalone milestone in a demonstration which underscores a tangible network benefit and does so in a way that can help operators maximize efficiency.”
Samsung has pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions, including chipsets, radios and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio, from virtualized RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company currently provides network solutions to mobile operators that deliver connectivity to hundreds of millions of users worldwide.
References:
Ericsson and MediaTek set new 5G uplink speed record using Uplink Carrier Aggregation
Nokia achieves extended range mmWave 5G speed record in Finland
Huawei and China Telecom Jointly Release 5G Super Uplink Innovation Solution
https://www.telecomhall.net/t/5g-uplink-enhancement-technology-by-zte-white-paper/20183
Perú’s First Open Access Wholesale Fiber Optic Network
KKR, Telefónica Hispanoamérica, and Entel today announced agreements under which KKR will acquire a majority interest in PangeaCo and the existing fiber optic networks of Telefónica del Perú and Entel Perú to build Perú’s first nationwide open access wholesale fiber optics company with the mission to bring greater access to fiber optics connectivity across the country. The transaction will combine the existing fiber optic networks of PangeaCo, Telefónica del Perú, and Entel Perú into an independent company controlled by KKR. The newly formed network will be open access, allowing usage to all internet service providers for the first time. KKR plans to make approximately US$200 million of additional investment to more than double the ultra-fast fiber network from more than 2 million homes passed today to reach 5.2 million homes passed across 86 provinces by the end of 2026.
Telefonica did not disclose the value of the transaction but said the deal would cut its debt by 200 million euros ($217.8 million). According to a banking source close to the deal, the transaction valued 100% of the unit at about 550 million euros, including debt.
Under the terms of the agreement, KKR will acquire a controlling interest in PangeaCo, which will subsequently acquire the existing fiber optic networks of Telefónica del Perú and Entel Perú. Through the combination of these networks, KKR will establish ON*NET Fibra de Perú as the new name for the platform which will independently build and operate the nation’s largest fiber optic network with world-class quality standards. KKR will own a 54% interest in ON*NET Fibra de Perú alongside Telefónica Hispanoamérica, which will own 36%, and Entel Perú, which will own 10%.

The entire ON*NET Fibra de Perú fiber optic network will be open to use by all internet service providers, increasing competition in the wholesale market. Telefónica del Perú and Entel Perú will be anchor tenants on the expanded open access network, enabling both providers to reach a greater number of customers with ultra-high-speed offerings. The transaction does not impact the services provided by existing customers of PangeaCo, Telefónica del Perú or Entel Perú. Upon closing of the transaction, customers will benefit from the scale of the larger network.
In Perú, approximately 88% of households have mobile or fixed internet service, but less than 35% have access to high-speed fiber optic networks.1 KKR, as the controlling shareholder, intends for ON*NET Fibra de Perú to more than double the households reached by fiber optic network, including reaching municipal areas outside of Lima as well as middle- and low-income households. This transaction demonstrates continued investor confidence in Peruvian infrastructure and the commitment of the companies to contribute to the sustainable development of the digital connectivity in the country.
Today’s announcement builds on KKR’s success in expanding nationwide connectivity and increasing competition in Chile and Colombia. ON*NET Fibra de Chile has expanded access from 2.4 million homes passed to 3.7 million homes passed since KKR signed the acquisition in February 2021 and ON*NET Fibra de Colombia has increased homes passed from 1.2 million to 2.4 million since signing in July 2021.2 Both companies have attracted multiple internet service providers to utilize their open access networks.
KKR is making the investment through its KKR Global Infrastructure Investors III fund and plans to provide operational support to ON*NET Fibra de Perú through NEXO LatAm, a digital infrastructure business supporting KKR’s Infrastructure strategy across Latin America. KKR and NEXO LatAm have significant experience supporting the successful expansion of open access fiber optic investments. The transaction is subject to regulatory approvals, including the approval of the Peruvian antitrust agency (INDECOPI).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
From telecoms.com:
When Telefonica first sold a stake in its Chilean fibre business to KKR it had a footprint of 2.4 million homes passed. The deal valued the entire business at $1 billion. The Colombian fiber business that KKR bought into was valued at half that amount and just over half the footprint:1.2 million homes. Admittedly, the Colombia deal was inked two years ago and Chile even longer ago, and a fair bit has changed in the economic situation in that time. However, we can get a sense of the scale of spend we might be looking at.
KKR wants to share the progress made by those Chilean and Colombian ventures. ON*NET Fibra de Chile passed 3.7 million homes as of the end of 2022, while ON*NET Fibra de Colombia had doubled the number of homes passed to 2.4 million, it said, adding that both have attracted multiple ISP customers.
That surely bodes well for the new venture’s aims in Peru, where at present around 88% of households have mobile or fixed internet service, but less than 35% have access to high-speed fibre networks, KKR said, citing data from regulator OSIPTEL and market research firm Omdia (owned by Informa).
It should also help smooth the regulatory process. The deal needs a number of approvals, including that of Peruvian antitrust agency INDECOPI, but it’s hard to foresee any major difficulties, given that this is an established model across the region and one that seems to be working.
References:
https://telecoms.com/522583/telefonica-entel-and-kkr-ink-peru-fibre-deal/
Dell’Oro: Bright Future for Campus Network As A Service (NaaS) and Public Cloud Managed LAN
|
||
|