Month: December 2024
U.S. Weighs Ban on Chinese made TP-Link router and China Telecom
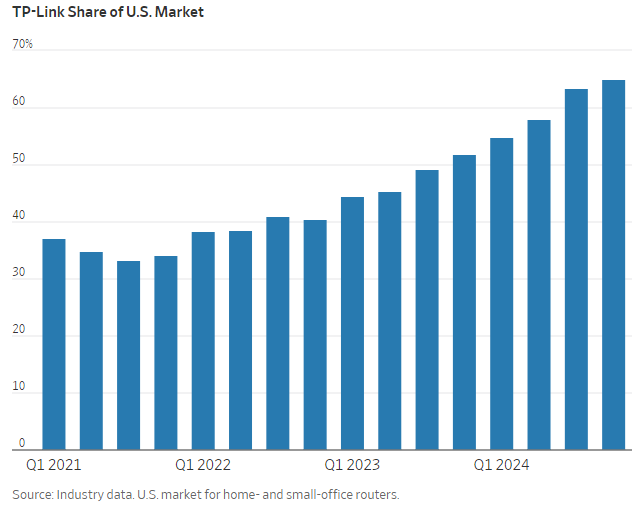
Today, the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) reported that the U.S. is considering banning the sale of China made TP-Link internet routers over concerns the home networking devices pose a security risk. Government authorities may ban the popular routers which have been linked to Chinese cyberattacks. TP-Link has roughly 65% of the U.S. market for routers for homes and small businesses. It is also the top choice on Amazon.com, and powers internet communications for the Defense Department and other federal government agencies.
Investigators at the U.S. Commerce, Defense and Justice departments have opened their own probes into the company, and authorities could ban the sale of TP-Link routers in the U.S. next year, according to people familiar with the matter. An office of the Commerce Department has subpoenaed TP-Link, some of the people said. If its routers are banned from the U.S., it would mark the biggest extraction of Chinese telecom equipment from the country since the Trump administration in 2019 ordered Huawei Technologies ripped out of American infrastructure.
TP-Link routers are routinely shipped to customers with security flaws, which the company often fails to address, according to people familiar with the matter. While routers often have bugs, regardless of their manufacturer, TP-Link doesn’t engage with security researchers concerned about them, the WSJ said. However, TP-Link told CBS MoneyWatch that the company’s “security practices are fully in line with industry security standards in the U.S.”
TP-Link router. Photo: Meghan Petersen/WSJ
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
TP-Link has also joined with more than 300 internet providers in the U.S. to be the router that is mailed to new homes that sign up for their services. Federal contracting documents show TP-Link routers supply everything from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration to the Defense Department and Drug Enforcement Administration, and the routers are sold at online military exchanges. The company’s market dominance has been achieved in part through lower prices. Its routers are cheaper than competitors, often by more than half, according to market data.
TP-Link sells in the U.S. through a business unit based in California. According to business records, TP-Link co-founder Zhao Jianjun is the chief executive of the California operation and he and his brother still ultimately control all global TP-Link entities. A spokeswoman for that unit said TP-Link assesses potential security risks and takes action to address known vulnerabilities.
“We welcome any opportunities to engage with the U.S. government to demonstrate that our security practices are fully in line with industry security standards, and to demonstrate our ongoing commitment to the U.S. market, U.S. consumers, and addressing U.S. national security risks,” the spokeswoman said.
Asked to comment about potential actions against TP-Link, Liu Pengyu, a spokesman for the Chinese Embassy in Washington, said the U.S. was using the guise of national security to “suppress Chinese companies.” He added that Beijing would “resolutely defend” the lawful rights and interests of Chinese firms.
TP-Link’s U.S. growth took off during the pandemic, when people were sent home to work and needed reliable internet. The company climbed from around 20% of the U.S. market for home and small-business routers in 2019 to around 65% this year. It took an additional 5% of the market in just the third quarter of this year, according to industry data. The TP-Link spokeswoman disputed the industry data but said the company’s market share has grown in the U.S.
An analysis from Microsoft published in October found that a Chinese hacking entity maintains a large network of compromised network devices mostly comprising thousands of TP-Link routers. The network has been used by numerous Chinese actors to launch cyberattacks. These actors have gone after Western targets including think tanks, government organizations, nongovernment organizations and Defense Department suppliers.
The Defense Department earlier this year opened an investigation into national-security vulnerabilities in Chinese routers, according to people familiar with the matter. The House Select Committee on the Chinese Communist Party in August urged the Commerce Secretary to investigate TP-Link because it presents an “unusual degree of vulnerabilities.” The House of Representatives in September passed legislation that called for a study of the national-security risks posed by routers with ties to foreign adversaries, on which the Senate has yet to act.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, the U.S. Commerce Department is moving to further crack down on China Telecom’s U.S. unit over concerns it could exploit access to American data through their U.S. cloud and internet businesses by providing it to Beijing, a source told Reuters. The source confirmed a New York Times report that the department last week sent China Telecom Americas a preliminary determination that its presence in U.S. networks and cloud services poses U.S. national security risks and gave the company 30 days to respond.
Previously, the FCC moved to shrink China Telecom’s presence in the U.S. In October 2021, nine months into Mr. Biden’s term, the Commission revoked all licenses for China Telecom Americas to provide ordinary phone services in the United States, saying it was “subject to exploitation, influence and control by the Chinese government.” That left in place China Telecom’s network nodes on U.S. telecom networks and carrier neutral data centers with the power to “peer in” to internet and phone traffic. That ability would be stripped under the Commerce Department order, assuming that the Trump administration went along. China Telecom Americas did not respond to messages left at its office in Herndon, Va.
“We’ve been taking a hard look at where Chinese technologies are in the United States and asking ourselves the question of, is this an acceptable level of risk?” Anne Neuberger, the deputy national security adviser for cyber and emerging technologies, said in an interview on Monday. “For a number of years, these companies have operated networks and cloud service businesses in the U.S., which involved network equipment that’s co-located with our internet infrastructure. And while in the past we may have viewed this as an acceptable level of risk, that is no longer the case.”
The F.C.C. action to block China Telecom from most of its business in the United States did not prevent Volt Typhoon — China’s placement of malicious code in the electric grid and water and gas pipeline networks — or Salt Typhoon, the surveillance effort that was uncovered over the summer. Taken together, officials say, they amount to the most significant assault on American critical infrastructure in the digital age.
Speaking last week at the Paley Center for Media in Manhattan, Gen. Timothy D. Haugh, the director of the National Security Agency and commander of U.S. Cyber Command, said, “If I look at today, the PRC is not deterred,” using the initials for the People’s Republic of China. He declined to say whether his forces were conducting offensive operations against China in retaliation for any of its recent incursions into American networks.
On Sunday, President-elect Donald J. Trump’s incoming national security adviser, Representative Mike Waltz, a Florida Republican, suggested on CBS’s “Face the Nation” that the new administration would be much more tempted to use offensive cyber-actions against China. “We need to start going on offense and start imposing, I think, higher costs and consequences to private actors and nation-state actors that continue to steal our data, that continue to spy on us and that, even worse, with the Volt Typhoon penetration, that are literally putting cyber time bombs on our infrastructure, our water systems, our grids, even our ports,” he said.
Officials have said they do not believe that the Chinese hackers have been ousted from the networks of at least eight telecommunications firms, including the nation’s two largest, Verizon and AT&T. That suggests that China’s hackers retain the capability to escalate.
Since Microsoft first alerted the telecommunications firms over the summer that they had found evidence of hackers deep in their systems, the Biden administration has struggled to come up with a response. It created a task force inside the White House, and the issue is considered so serious that the group meets almost daily. Chief executives of the affected firms have been summoned to the Situation Room to come up with a joint plan of action.
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/tp-link-router-china-us-ban/
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/12/16/us/politics/biden-administration-retaliation-china-hack.html
Aftermath of Salt Typhoon cyberattack: How to secure U.S. telecom networks?
WSJ: T-Mobile hacked by cyber-espionage group linked to Chinese Intelligence agency
China backed Volt Typhoon has “pre-positioned” malware to disrupt U.S. critical infrastructure networks “on a scale greater than ever before”
FBI and MI5 Chiefs Issue Joint Warning: Chinese Cyber Espionage on Tech & Telecom Firms
Quantum Technologies Update: U.S. vs China now and in the future
5G network slicing progress report with a look ahead to 2025
The “true” version of 5G is 5G standalone (SA), which eliminates the need for a 4G anchor network and supports all 3GPP defined 5G functions, like 5G Security, Voice over 5G New Radio (VoNR) and network slicing. As we’ve noted for years, 5G SA has proven difficult to deploy, partially because there are no standards for implementation – only 3GPP 5G Architecture specs (rubber stamped as ETSI standards, but never submitted to the ITU for consideration as one or more ITU-T recommendations).
Network slicing is only possible with a 5G SA core network. Operators which have deployd 5G SA are using and planning to use 5G network slices for a variety of use cases, including: a priority slice for first responders, support financial or mission-critical applications, or offer broadcasters a dedicated fast 5G layer to transfer video from cameras to production teams at sporting or other live events.

Image Credit: SDx Central
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In the U.S., T-Mobile is the only major carrier offering 5G SA and has been moving forward with network slicing deployments. Verizon said recently that its 5G network slicing public safety field demonstration in Phoenix, Arizona, is operational but still in trials. AT&T has tested prioritized access to its network, but so far has not yet provided a 5G SA network to support network slicing . That’s despite outsourcing development to Microsoft Azure cloud platform in June 2021.
T-Mobile recently launched “T-Priority,” a network slice for first responders supported by the network operator’s 5G SA core network. The wireless telco told regulators at the end of 2023:
“Network slicing involves creating customized, software-defined, virtual networks – or ‘slices’ – that are each logically separated and individually optimized to meet the specific needs of each application. Within a slice, network functions are defined in software and customized to the use case supported by that slice. For example, network slicing allows providers to use a single 5G network to deliver high-intensity network resources to support a small number of robots on a factory floor, while at the same time delivering low-intensity network resources to a very large number of meter-reading sensors on a utility network.”
Overseas, BT, Orange Belgium, Singtel, China Telecom, Reliance Jio, and Telia Finland have deployed network slicing, among other 5G carriers. Singtel’s app-based network slicing is designed to improve the performance of consumer and enterprise applications.
Nokia recently said it tested a network slicing application with network operator Liberty Global and Belgian shipping company Seafar. Nokia said the shipping company could use its API platform to purchase an ultra-low latency slice of Liberty Global’s Telenet 5G standalone network to maneuver Seafar’s ships through ports without having to slow down.
“Slicing will be critical to enabling enterprise cases and providing network solutions for many use cases for which a stand-alone purpose-built network is not feasible,” Nokia stated in a February meeting between CEO Pekka Lundmark and a variety of top FCC officials, including FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel.
The GSMA, which is NOT a standards development organization, launched its “Open Gateway” campaign last year. Earlier this year the group said that 47 mobile operators representing 239 mobile networks and 65% of wireless connections around the world have signed up. Currently, GSMA and its partners are developing a wide range of APIs for text messaging, location information, billing, quality of service – and network slicing among other applications.
Several analysts believe that network slicing will see more growth next year:
“There will be definitely more rollouts of network slicing capabilities as 5G SA networks mature, and as 5G NSA networks move to SA in the next few years,” AvidThink principal analyst Roy Chua said in an email. “Using a network slice for privacy/security/isolation or for ensuring QoS (live broadcasts, sporting events, emergency and disaster support) will likely continue.”
Lead analyst at Techsponential Avi Greengart agreed that more network slicing deployments will happen in the coming year as more operators upgrade to 5G SA. “Network slicing has been a long-touted feature of 5G, and we’re starting to see it used for large venues (ex: sports stadiums) and public safety,” he told Fierce Network. Greengart warned that slicing is not a panacea for private networks or Wi-Fi.
“I do think that network slicing will be operator specific,” noted neXt Curve executive analyst Leonard Lee. “There is still the open question of what the generally monetizable services will be and the scenarios that make them viable. This, each operator will be answering for themselves on their own timeline. For outside observers, it will be like watching a kettle boil,” he said, adding a note of caution.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/network-automation/2025-preview-network-slicing-gets-real
https://www.fierce-network.com/wireless/network-slicing-slides-more-vigorously-2025
https://www.sdxcentral.com/5g/definitions/key-elements-5g-network/5g-network-slicing/
FCC Draft Net Neutrality Order reclassifies broadband access; leaves 5G network slicing unresolved
ABI Research: 5G Network Slicing Market Slows; T-Mobile says “it’s time to unleash Network Slicing”
Telstra achieves 340 Mbps uplink over 5G SA; Deploys dynamic network slicing from Ericsson
Ericsson, Intel and Microsoft demo 5G network slicing on a Windows laptop in Sweden
Is 5G network slicing dead before arrival? Replaced by private 5G?
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
Lumen Technologies to connect Prometheus Hyperscale’s energy efficient AI data centers
The need for more cloud computing capacity and AI applications has been driving huge investments in data centers. Those investments have led to a steady demand for fiber capacity between data centers and more optical networking innovation inside data centers. Here’s the latest example of that:
Prometheus Hyperscale has chosen Lumen Technologies to connect its energy-efficient data centers to meet growing AI data demands. Lumen network services will help Prometheus with the rapid growth in AI, big data, and cloud computing as they address the critical environmental challenges faced by the AI industry.
Rendering of Prometheus Hyperscale flagship Data Center in Evanston, Wyoming:

……………………………………………………………………………….
Prometheus Hyperscale, known for pioneering sustainability in the hyperscale data center industry, is deploying a Lumen Private Connectivity Fabric℠ solution, including new network routes built with Lumen next generation wavelength services and Dedicated Internet Access (DIA) [1.] services with Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection layered on top.
Note 1. Dedicated Internet Access (DIA) is a premium internet service that provides a business with a private, high-speed connection to the internet.
This expanded network will enable high-density compute in Prometheus facilities to deliver scalable and efficient data center solutions while maintaining their commitment to renewable energy and carbon neutrality. Lumen networking technology will provide the low-latency, high-performance infrastructure critical to meet the demands of AI workloads, from training to inference, across Prometheus’ flagship facility in Wyoming and four future data centers in the western U.S.
“What Prometheus Hyperscale is doing in the data center industry is unique and innovative, and we want to innovate alongside of them,” said Ashley Haynes-Gaspar, Lumen EVP and chief revenue officer. “We’re proud to partner with Prometheus Hyperscale in supporting the next generation of sustainable AI infrastructure. Our Private Connectivity Fabric solution was designed with scalability and security to drive AI innovation while aligning with Prometheus’ ambitious sustainability goals.”
Prometheus, founded as Wyoming Hyperscale in 2020, turned to Lumen networking solutions prior to the launch of its first development site in Aspen, WY. This facility integrates renewable energy sources, sustainable cooling systems, and AI-driven energy optimization, allowing for minimal environmental impact while delivering the computational power AI-driven enterprises demand. The partnership with Lumen reinforces Prometheus’ dedication to both technological innovation and environmental responsibility.
“AI is reshaping industries, but it must be done responsibly,” said Trevor Neilson, president of Prometheus Hyperscale. “By joining forces with Lumen, we’re able to offer our customers best-in-class connectivity to AI workloads while staying true to our mission of building the most sustainable data centers on the planet. Lumen’s network expertise is the perfect complement to our vision.”
Prometheus’ data center campus in Evanston, Wyoming will be one of the biggest data centers in the world with facilities expected to come online in late 2026. Future data centers in Pueblo, Colorado; Fort Morgan, Colorado; Phoenix, Arizona; and Tucson, Arizona, will follow and be strategically designed to leverage clean energy resources and innovative technology.
About Prometheus Hyperscale:
Prometheus Hyperscale, founded by Trenton Thornock, is revolutionizing data center infrastructure by developing sustainable, energy-efficient hyperscale data centers. Leveraging unique, cutting-edge technology and working alongside strategic partners, Prometheus is building next-generation, liquid-cooled hyperscale data centers powered by cleaner energy. With a focus on innovation, scalability, and environmental stewardship, Prometheus Hyperscale is redefining the data center industry for a sustainable future. This announcement follows recent news of Bernard Looney, former CEO of bp, being appointed Chairman of the Board.
To learn more visit: www.prometheushyperscale.com
About Lumen Technologies:
Lumen uses the scale of their network to help companies realize AI’s full potential. From metro connectivity to long-haul data transport to edge cloud, security, managed service, and digital platform capabilities, Lumenn meets its customers’ needs today and is ready for tomorrow’s requirements.
In October, Lumen CTO Dave Ward told Light Reading that a “fundamentally different order of magnitude” of compute power, graphics processing units (GPUs) and bandwidth is required to support AI workloads. “It is the largest expansion of the Internet in our lifetime,” Ward said.
Lumen is constructing 130,000 fiber route miles to support Meta and other customers seeking to interconnect AI-enabled data centers. According to a story by Kelsey Ziser, the fiber conduits in this buildout would contain anywhere from 144 to more than 500 fibers to connect multi-gigawatt data centers.
REFERENCES:
https://www.lightreading.com/data-centers/2024-in-review-data-center-shifts
Will billions of dollars big tech is spending on Gen AI data centers produce a decent ROI?
Superclusters of Nvidia GPU/AI chips combined with end-to-end network platforms to create next generation data centers
Initiatives and Analysis: Nokia focuses on data centers as its top growth market
Proposed solutions to high energy consumption of Generative AI LLMs: optimized hardware, new algorithms, green data centers
Deutsche Telekom with AWS and VMware demonstrate a global enterprise network for seamless connectivity across geographically distributed data centers
Nokia sees new types of 6G connected devices facilitated by a “3 layer technology stack”
Nokia says they are seeing a growing demand for new types of wireless connected devices beyond just smartphones—things like smartwatches, health monitors, and even cars that communicate with each other. 3GPP has been working to keep up with these demands, expanding their standards to include these new types of devices and even satellite connectivity for when you’re out of range.
Some of these envisioned expansions have not had commercial market market success, sparking an industry rethink of cellular devices. The 6G era, however, offers an opportunity for the industry to support device proliferation and innovation that includes disruptive and yet to be invented devices.

Nokia sees several key developments are set to transform the cellular technology landscape:
- Advanced and more reliable connectivity: 6G promises not just faster internet but also improved support in challenging environments like remote areas or during emergencies. This might include satellite connections for when you’re out of the usual network range.
- IoT and sustainability: The Internet of Things (IoT) is set to become a major part of 6G. Devices with low-power wide-area (LPWA) connectivity will play a crucial role in making industries more efficient and sustainable. 6G must support LPWA features to anticipate 4G sunset and operators’ commitment to support LPWA services for 10+ years.
- Universal Connectivity: 6G will aim to unify different types of connections—like terrestrial networks and non-terrestrial networks—so that all devices can connect through a common air interface to achieve economy of scale and competitiveness.
- Fixed Wireless Access (FWA): This technology, which provides high-speed internet to homes and businesses, is expected to grow rapidly. 6G will need to support this expansion while also catering to emerging needs such as high-performance gaming, immersive virtual reality experiences and possible spectrum constraints.
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption will be crucial. 6G will focus on making devices more efficient, especially for tasks like notifications and messaging, which will help address energy consumption goals.
A single Technology Stack will open the door for a bevy of new 6G devices that address the above requirements. To ensure a successful commercialization of 6G, the industry must take the 4G/5G learnings into consideration and specify a scalable Technology Stack that maximizes commonalities between the needs of different devices so that each device segment has the volume potential to become commercially successful. Such a stack would be composed of three layers:
- Basic Layer: This foundational layer will be common to all devices, supporting essential functions like low-power operation, small data transmission, notifications and emergency services that are compatible with both traditional and satellite networks.
- Broadband Layer: For devices that need high-speed data, such as wearables, traffic cameras and connected cars, this layer will ensure fast, reliable connectivity and minimal latency.
- Extreme Broadband Layer: This top layer will cater to advanced devices like smartphones and virtual reality systems, offering ultra-fast data rates, sophisticated physical world sensing and integration with artificial intelligence.
In this approach a chipset implementing a given layer must also implement all the layers below:

The aim of this scalable, modular technology approach is to streamline device compatibility and development. Initially, the focus will likely be on mobile broadband devices. However, a single Technology Stack introduces a scalable air interface, meaning that essential technology components for LPWA devices will already be developed, as they share features with mobile broadband devices.
This approach will likely lead to the emergence of three main chipset types: LPWA chipsets (covering the basic layer), broadband chipsets (covering both basic and broadband layers), and extreme broadband chipsets (covering all layers).
The greatest potential of a single Technology Stack lies in its ability to support a wide range of devices without requiring major network overhauls. This gradual and adaptable deployment ensures that as new devices come online, the existing network can handle them without significant upgrades.
Nokia concludes by stating that 6G specifications should have a scalable solution resulting in fewer chipset options. This objective can be achieved through a single and modular Technology Stack that cuts across three major chipset types. This approach will not only streamline device development but also encourage a healthier ecosystem of both current and future devices, including those that are still on the drawing board.
Editor’s Notes:
-
Radio Access Network (RAN):
- Massive MIMO:To serve multiple users simultaneously with high capacity.
- Terahertz band spectrum:High-frequency bands offering extremely high data rates but with limited range.
- Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS): To manipulate radio waves for better signal propagation and coverage.
- Advanced modulation and coding techniques: To optimize data transmission efficiency.
- Massive MIMO:To serve multiple users simultaneously with high capacity.
2. ITU-R WP5D sets the RAN (RIT/SRIT) functional requirements for 6G while 3GPP generates the specifications to realize them as well as the core network. 3GPP specs are then rubber stamped by ETSI with the RAN related specs contributed to WP 5D to eventually become ITU-R recommendations (RIT/SRIT standards). That was the case for 5G with ITU-R M.2150 including 3GPP as well as other RIT/SRITs (from TSDSI 5Gi and ETSI/DECT for IoT).
References:
6G – Follow the journey to the next generation networks (Ericsson)
Ericsson and e& (UAE) sign MoU for 6G collaboration vs ITU-R IMT-2030 framework
Rakuten Symphony exec: “5G is a failure; breaking the bank; to the extent 6G may not be affordable”
India’s TRAI releases Recommendations on use of Tera Hertz Spectrum for 6G
KT and LG Electronics to cooperate on 6G technologies and standards, especially full-duplex communications
Chinese engineers field test a “6G” network with semantic communications on 4G infrastructure
Nokia and Eolo deploy 5G SA mmWave “Cloud RAN” network
Nokia and Finnish telco and digital service provider Eolo have deployed what they claim is Europe’s first 5G standalone mmWave network, which they call a “5G Cloud RAN.”
- Nokia’s Cloud RAN solution ready for commercial deployment following a successful deployment with Elisa in Espoo, Finland powered by Red Hat OpenShift
- Cloud RAN supports Elisa’s efforts to provide more agile network services to its customers, by transforming network usage closer to the network edge
- Nokia’s anyRAN approach offers customers more flexibility, openness, security, and choice in their selection of cloud infrastructure
- Piloting cloud-native models offers Elisa valuable insight moving toward the 6G era
Nokia is providing its AirScale Massive MIMO radios, baseband software, and AI-powered MantaRay network management solution. It is also supplying its Shikra mmWave radios which, are suitable for dense urban environments and also able to deliver FWA connectivity of up to 1 Gbit/s to rural or underserved communities where wired infrastructure fears to tread.
The commercial deployment completed end-to-end 5G voice and data calls with Nokia’s 5G Cloud RAN solution including its AirScale Massive MIMO radios, baseband software, and AI-powered MantaRay network management solution. Nokia’s high-performance, energy-efficient Cloud RAN architecture seamlessly integrates with all leading cloud or server infrastructures. Elisa utilized Dell XR8620 servers as well as Red Hat OpenShift, the industry’s leading hybrid cloud application platform powered by Kubernetes, to support cloud-native RAN functions across the network. By integrating with Red Hat OpenShift, service providers have the option to scale their 5G network footprint and quickly introduce new services. The deployment verified areas such as capacity, performance, features, life cycle management, automation, and energy management.
As a pioneer of 5G services in Finland, Elisa is pursuing network cloudification and extending this transformation from the network core towards the access network. Cloudification plays a key role in the scalability of network services and allows the operator to meet customers’ changing needs. With Cloud RAN Elisa is able to shift the network computing power closer to the customers, whose network usage is transforming closer to the network edge. AI-powered applications are likely to accelerate the demand for edge computing in the future.
A benefit of the early adoption of Cloud RAN is trialing the new cloud-native production model, which differs significantly from earlier models, involves a whole new ecosystem. Deploying the first commercial 5G cloud network in Europe puts Elisa in a strong position while moving towards the 6G era – which is predicted to be increasingly cloud-native. Additionally, cloudification plays a key role in Elisa’s journey towards self-driving and self-healing autonomous networks.
Nokia is helping its global customers get their Cloud RAN networks up and running much faster, removing complexity, and ensuring openness and flexibility. Nokia has already completed numerous end-to-end 5G data calls in multi-supplier setups with hardware and software from its best-in-class ecosystem of leading industry partners. It is further evidence of Nokia’s flexible anyRAN approach that provides the best choice of strategic options for communications service providers and enterprises for their RAN evolution with purpose-built, hybrid, or Cloud RAN solutions, enabling customers to monetize their networks.
Kalle Lehtinen, Chief Technology Officer, Elisa said: “This successful Cloud RAN deployment with Nokia is another important step on our cloudification which started with cloudifying the network core and edge, and now includes the radio access network. We continue to pioneer new technologies in our journey towards autonomous operations helping us to continue innovating and delivering best customer experience.”
Honoré LaBourdette, vice president, Telco, Media, Entertainment & Edge Ecosystem, Red Hat, commented: “Red Hat is excited to continue our partnership with Nokia by helping service providers implement RAN for full end-to-end cloudification and automation of next-generation networks. Cloud RAN’s significance lies not only in providing an efficient and flexible way to deploy applications and derive value at the edge but also in boosting collaboration and innovation across the ecosystem. With Red Hat OpenShift, we’re making this vision a reality by offering a consistent hybrid cloud foundation that empowers businesses to build and scale the applications of the future.”
Aji Ed, Head of Cloud RAN at Nokia, said: “This successful collaboration with Elisa confirms that our Cloud RAN solution is ready for commercial deployment. Under our anyRAN approach, we work very closely with strategic partners like Red Hat and bring together best-in-class partner solutions to offer true flexibility and scalability to operators and enterprises. For our customers, cloudification will enable new revenue models and monetization options.”
Resources:
Webpage: Nokia Cloud RAN
Webpage: Nokia anyRAN
Webpage: Nokia AirScale Baseband
Event: Triangulates – Collaboration for Cloud RAN success
Whitepaper: Cloud RAN: Unlocking the power of 5G for a smarter, connected future
Ericsson and O2 Telefónica demo Europe’s 1st Cloud RAN 5G mmWave FWA use case
Ericsson and Google Cloud expand partnership with Cloud RAN solution
Will billions of dollars big tech is spending on Gen AI data centers produce a decent ROI?
One of the big tech themes in 2024 was the buildout of data center infrastructure to support generative (Gen) artificial intelligence (AI) compute servers. Gen AI requires massive computational power, which only huge, powerful data centers can provide. Big tech companies like Amazon (AWS), Microsoft (Azure), Google (Google Cloud), Meta (Facebook) and others are building or upgrading their data centers to provide the infrastructure necessary for training and deploying AI models. These investments include high-performance GPUs, specialized hardware, and cutting-edge network infrastructure.
- Barron’s reports that big tech companies are spending billions on that initiative. In the first nine months of 2024, Amazon, Microsoft, and Alphabet spent a combined $133 billion building AI capacity, up 57% from the previous year, according to Barron’s. Much of the spending accrued to Nvidia, whose data center revenue reached $80 billion over the past three quarters, up 174%. The infrastructure buildout will surely continue in 2025, but tough questions from investors about return on investment (ROI) and productivity gains will take center stage from here.
- Amazon, Google, Meta and Microsoft expanded such investments by 81% year over year during the third quarter of 2024, according to an analysis by the Dell’Oro Group, and are on track to have spent $180 billion on data centers and related costs by the end of the year. The three largest public cloud providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure and Google Cloud, each had a spike in their investment in AI during the third quarter of this year. Baron Fung, a senior director at Dell’Oro Group, told Newsweek: “We think spending on AI infrastructure will remain elevated compared to other areas over the long-term. These cloud providers are spending many billions to build larger and more numerous AI clusters. The larger the AI cluster, the more complex and sophisticated AI models that can be trained. Applications such as Copilot, chatbots, search, will be more targeted to each user and application, ultimately delivering more value to users and how much end-users will pay for such a service,” Fung added.
- Efficient and scalable data centers can lower operational costs over time. Big tech companies could offer AI cloud services at scale, which might result in recurring revenue streams. For example, AI infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) could be a substantial revenue driver in the future, but no one really knows when that might be.
Microsoft has a long history of pushing new software and services products to its large customer base. In fact, that greatly contributed to the success of its Azure cloud computing and storage services. The centerpiece of Microsoft’s AI strategy is getting many of those customers to pay for Microsoft 365 Copilot, an AI assistant for its popular apps like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. Copilot costs $360 a year per user, and that’s on top of all the other software, which costs anywhere from $72 to $657 a year. Microsoft’s AI doesn’t come cheap. Alistair Speirs, senior director of Microsoft Azure Global Infrastructure told Newsweek: “Microsoft’s datacenter construction has been accelerating for the past few years, and that growth is guided by the growing demand signals that we are seeing from customers for our cloud and AI offerings. “As we grow our infrastructure to meet the increasing demand for our cloud and AI services, we do so with a holistic approach, grounded in the principle of being a good neighbor in the communities in which we operate.”
Venture capitalist David Cahn of Sequoia Capital estimates that for AI to be profitable, every dollar invested on infrastructure needs four dollars in revenue. Those profits aren’t likely to come in 2025, but the companies involved (and there investors) will no doubt want to see signs of progress. One issue they will have to deal with is the popularity of free AI, which doesn’t generate any revenue by itself.
An August 2024 survey of over 4,600 adult Americans from researchers at the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, Vanderbilt University, and Harvard University showed that 32% of respondents had used AI in the previous week, a faster adoption rate than either the PC or the internet. When asked what services they used, free options like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, Meta Platform’s Meta AI, and Microsoft’s Windows Copilot were cited most often. Unlike 365, versions of Copilot built into Windows and Bing are free.
The unsurprising popularity of free AI services creates a dilemma for tech firms. It’s expensive to run AI in the cloud at scale, and as of now there’s no revenue behind it. The history of the internet suggests that these free services will be monetized through advertising, an arena where Google, Meta, and Microsoft have a great deal of experience. Investors should expect at least one of these services to begin serving ads in 2025, with the others following suit. The better AI gets—and the more utility it provides—the more likely consumers will go along with those ads.


Productivity Check:
We’re at the point in AI’s rollout where novelty needs to be replaced by usefulness—and investors will soon be looking for signs that AI is delivering productivity gains to business. Here we can turn to macroeconomic data for answers. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, since the release of ChatGPT in November 2022, labor productivity has risen at an annualized rate of 2.3% versus the historical median of 2.0%. It’s too soon to credit AI for those gains, but if above-median productivity growth continues into 2025, the conversation gets more interesting.
There’s also the continued question of AI and jobs, a fraught conversation that isn’t going to get any easier. There may already be AI-related job loss happening in the information sector, home to media, software, and IT. Since the release of ChatGPT, employment is down 3.9% in the sector, even as U.S. payrolls overall have grown by 3.3%. The other jobs most at risk are in professional and business services and in the financial sector. To be sure, the history of technological change is always complicated. AI might take away jobs, but it’s sure to add some, too.
“Some jobs will likely be automated. But at the same time, we could see new opportunities in areas requiring creativity, judgment, or decision-making,” economists Alexander Bick of the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis and Adam Blandin of Vanderbilt University tell Barron’s. “Historically, every big tech shift has created new types of work we couldn’t have imagined before.”
Closing Quote:
“Generative AI (GenAI) is being felt across all technology segments and subsegments, but not to everyone’s benefit,” said John-David Lovelock, Distinguished VP Analyst at Gartner. “Some software spending increases are attributable to GenAI, but to a software company, GenAI most closely resembles a tax. Revenue gains from the sale of GenAI add-ons or tokens flow back to their AI model provider partner.”
References:
AI Stocks Face a New Test. Here Are the 3 Big Questions Hanging Over Tech in 2025
Big Tech Increases Spending on Infrastructure Amid AI Boom – Newsweek
Superclusters of Nvidia GPU/AI chips combined with end-to-end network platforms to create next generation data centers
Ciena CEO sees huge increase in AI generated network traffic growth while others expect a slowdown
Proposed solutions to high energy consumption of Generative AI LLMs: optimized hardware, new algorithms, green data centers
SK Telecom unveils plans for AI Infrastructure at SK AI Summit 2024
Huawei’s “FOUR NEW strategy” for carriers to be successful in AI era
Initiatives and Analysis: Nokia focuses on data centers as its top growth market
India Mobile Congress 2024 dominated by AI with over 750 use cases
Reuters & Bloomberg: OpenAI to design “inference AI” chip with Broadcom and TSMC
Ciena CEO sees huge increase in AI generated network traffic growth while others expect a slowdown
Today, Ciena reported better than expected revenue of $1.12 billion in its 4th quarter, which was above analyst expectations of around $1.103 billion. Orders were once again ahead of revenue, even though the company had expected orders to be below revenue just a few months ago. A closer look at key metrics reveals mixed results, with some segments like Software and Services showing strong growth (+20.6% year-over-year) and others like Routing and Switching experiencing significant declines (-38.4% year-over-year).
Increased demand for the company’s Reconfigurable Line Systems (RLS), primarily from large cloud providers. And he said the company was also doing well selling its WaveLogic coherent optical pluggables, which optimize performance in data centers as they support traffic from AI and machine learning.
Ciena’s Managed Optical Fiber Networks (MOFN) technology is designed for global service providers that are building dedicated private optical networks for cloud providers. MOFN came about a few years ago when cloud providers wanted to enter countries where they weren’t allowed to build their own fiber networks. “They had to go with the incumbent carrier, but they wanted to have control of their network within country. It was sort of a niche-type play. But we’ve seen more recently, over the last 6-9 months, that model being more widely adopted,” Smith said. MOFN is becoming more widely utilized, and the good news for Ciena is that cloud providers often request that Ciena equipment be used so that it matches with the rest of their network, according to Smith.

Image Credit: Midjourney for Fierce Network
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The company also said it now expects average annual revenue growth of approximately 8% to 11% over the next three years. “Our business is linked heavily into the growth of bandwidth around the world,” CEO Gary Smith said after Ciena’s earnings call. “Traffic growth has been between 20% and 40% per year very consistently for the last two decades,” Smith told Light Reading.
Ciena believes huge investments in data centers with AI compute servers will ultimately result in more traffic traveling over U.S. and international broadband networks. “It has to come out of the data center and onto the network,” Smith said of AI data. “Now, quite where it ends up being, who can know. As an exact percentage, a lot of people are working through that, including the cloud guys,” he said about the data traffic growth rate over the next few years. “But one would expect [AI data] to layer on top of that 30% growth, is the point I’m making,” he added.
AI comes at a fortuitous time for Ciena. “You’re having to connect these GPU clusters over greater distances. We’re beginning to see general, broader traffic growth in things like inference and training. And that’s going to obviously drive our business, which is why we’re forecasting greater than normal growth,” Smith said.
Smith’s positive comments on AI traffic are noteworthy in light of some data points showing a slowdown in the rate of growth in data traffic on global networks. For example:
- OpenVault recently reported that monthly average broadband data consumption in the third quarter inched up 7.2%, the lowest rate of growth seen since the company began reporting these trends in 2012.
- In Ericsson’s newest report, Fredrik Jejdling, EVP and head of business area networks, said: “We see continued mobile network traffic growth but at a slower rate.”
- Some of the nation’s biggest Content Data Network (CDN) providers – including Akamai, Fastly and Edgio – are struggling to come to terms with a historic slowdown in Internet traffic growth. Such companies operate the content delivery networks that convey video and other digital content online.
- “In terms of traffic growth, it is growing very slowly – at rates that we haven’t seen in the 25-plus years we’ve been in this business. So it’s growing very, very slow,” Akamai CFO Ed McGowan said recently. “It’s just been a weak traffic environment.”
“The cloud providers themselves are building bigger infrastructure and networks, and laying track for even greater growth in the future as more and more of that AI traffic comes out of the data center,” Smithsaid. “So that’s why we’re predicting greater growth than normal over the next three years. It’s early days for that traffic coming out of the data center, but I think we’re seeing clear evidence around it. So you’re looking at an enormous step function in traffic flows over the next few years,” he concluded.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/data-centers/ciena-ceo-prepare-for-the-ai-traffic-wave
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/cienas-ceo-says-companys-growth-linked-ai
Summit Broadband deploys 400G using Ciena’s WaveLogic 5 Extreme
DriveNets and Ciena Complete Joint Testing of 400G ZR/ZR+ optics for Network Cloud Platform
Telco spending on RAN infrastructure continues to decline as does mobile traffic growth
Analysys Mason & Light Reading: cellular data traffic growth rates are decreasing
TechCrunch: Meta to build $10 billion Subsea Cable to manage its global data traffic
Initiatives and Analysis: Nokia focuses on data centers as its top growth market
RWA, CWA and EchoStar file FCC petitions against T-Mobile’s acquisition of UScellular
The Rural Wireless Association (RWA), Communications Workers of America (CWA), and EchoStar (owns Dish Network) all filed FCC petitions requesting the agency reject T-Mobile’s proposed acquisition of “substantially all” of UScellular’s wireless operations, including some spectrum.
The proposed transaction would remove UScellular from the U.S. telecom market, thereby eliminating one of the last few remaining regional wireless network operators and strengthening T-Mobile’s position across the 21 states where UScellular maintains operations.
Public interest and consumer groups (include Public Knowledge, New America’s Open Technology Institute and Community Broadband Networks Initiative) also opposed approval. They argued that the proposed merger between T-Mobile and UScellular would “result in the loss of the fifth largest marketplace competitor with a network covering approximately 10 percent of the country’s population, reallocate spectrum resources predominantly to the three top wireless carriers only to make it nearly impossible for a fourth competitor to emerge in the market, and waste valuable funding secured for building out 5G networks.”
The deal is relatively small as telecom mergers go — valued at about $4.4 billion, including $2 billion in assumed debt — but has ignited substantial opposition. UScellular is the nation’s fifth-largest wireless carrier.

“T-Mobile is asking for the commission’s blessing to further entrench its dominance over the wireless voice and broadband markets, making it harder for others (like EchoStar) to compete. The commission should deny this transaction, which threatens to substantially harm competition while offering only illusory public interest benefits,” EchoStar wrote in a new filing to the FCC.
“The merger would substantially lessen competition in local markets where UScellular operates, hurting workers, consumers and other rural carriers. The commission should reject the proposed transaction as currently structured and require specific enforceable measures … to ensure that the merger remains in the public interest,” wrote the Communications Workers of America (CWA), a union that counts thousands of members inside AT&T and Verizon but has struggled to unionize workers in T-Mobile. The Rural Wireless Association also voiced its opposition.
This past May, T-Mobile said it would purchase around 30% of UScellular’s spectrum holdings, all of its 4.5 million customers and its retail stores in a deal worth $4.4 billion. T-Mobile has also said it will make job offers to “a significant number” of UScellular’s employees as part of the transaction. Following T-Mobile’s announcement, both AT&T and Verizon inked deals to acquire roughly $1 billion each worth of UScellular’s spectrum. T-Mobile officials still expect to close the UScellular transaction next year.
“I don’t know how many mergers you’ve heard of in the past that are like, yeah, I can promise you better networks and lower prices right from the get-go, and the company, of course, will benefit from the synergies, and it’s highly accretive. So this is going to be a win all the way around, and I’m confident the government will see it that way as well,” T-Mobile CEO Mike Sievert said this week at an investor event.
However, the U.S. Department of Justice (DoJ) advised a deeper review of T-Mobile’s UScellular proposed acquisition due to T-Mobile’s foreign owner Deutsche Telekom, which indirectly holds 50.42% of T-Mobile’s stock and also holds a proxy agreement that authorizes it to vote additional shares.
Many pundits expect T-Mobile to ultimately close on its purchase of UScellular thanks to the incoming Trump administration, which is expected to be more friendly to acquisitions than the Biden administration has been. As a precedent, Donald Trump’s first administration immediately approved T-Mobile’s $26 billion purchase of Sprint in 2020.
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/ecfs/document/1209299836114/1
https://www.fcc.gov/ecfs/document/120973502037/1
T-Mobile to acquire UScellular’s wireless operations in $4.4 billion deal
Google’s new quantum computer chip Willow infinitely outpaces the world’s fastest supercomputers
Overview:
In a blog post on Monday, Google unveiled a new quantum computer chip called Willow, which demonstrates error correction and performance that paves the way to a useful, large-scale quantum computer. Willow has state-of-the-art performance across a number of metrics, enabling two major achievements.
- The first is that Willow can reduce errors exponentially as we scale up using more qubits. This cracks a key challenge in quantum error correction that the field has pursued for almost 30 years.
- Second, Willow performed a standard benchmark computation in under five minutes that would take one of today’s fastest supercomputers 10 septillion (that is, 1025) years — a number that vastly exceeds the age of the Universe.

Google’s quantum computer chip, Willow. Photo Credit…Google Quantum AI
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Quantum computing — the result of decades of research into a type of physics called quantum mechanics — is still an experimental technology. But Google’s achievement shows that scientists are steadily improving techniques that could allow quantum computing to live up to the enormous expectations that have surrounded this big idea for decades.
“When quantum computing was originally envisioned, many people — including many leaders in the field — felt that it would never be a practical thing,” said Mikhail Lukin, a professor of physics at Harvard and a co-founder of the quantum computing start-up QuEra. “What has happened over the last year shows that it is no longer science fiction.”
As a measure of Willow’s performance, Google used the random circuit sampling (RCS) benchmark. Pioneered by its team and now widely used as a standard in the field, RCS is the classically hardest benchmark that can be done on a quantum computer today. You can think of this as an entry point for quantum computing — it checks whether a quantum computer is doing something that couldn’t be done on a classical computer.

Random circuit sampling (RCS), while extremely challenging for classical computers, has yet to demonstrate practical commercial applications. Image Credit: Google AI.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Willow’s performance on this benchmark is astonishing: It performed a computation in under five minutes that would take one of today’s fastest supercomputers 1025 or 10 septillion years. If you want to write it out, it’s 10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 years. This mind-boggling number exceeds known timescales in physics and vastly exceeds the age of the universe. It lends credence to the notion that quantum computation occurs in many parallel universes, in line with the idea that we live in a multiverse, a prediction first made by David Deutsch.
Google’s assessment of how Willow outpaces one of the world’s most powerful classical supercomputers, Frontier, was based on conservative assumptions. For example, we assumed full access to secondary storage, i.e., hard drives, without any bandwidth overhead — a generous and unrealistic allowance for Frontier. Of course, as happened after we announced the first beyond-classical computation in 2019, we expect classical computers to keep improving on this benchmark, but the rapidly growing gap shows that quantum processors are peeling away at a double exponential rate and will continue to vastly outperform classical computers as we scale up.

In a research paper published on Monday in the science journal Nature, Google said its machine had surpassed the “error correction threshold,” a milestone that scientists have been working toward for decades. That means quantum computers are on a path to a moment, still well into the future, when they can overcome their mistakes and perform calculations that could accelerate the progress of drug discovery. They could also break the encryption that protects computers vital to national security.
“What we really want these machines to do is run applications that people really care about,” said John Preskill, a theoretical physicist at the California Institute of Technology who specializes in quantum computing. “Though it still might be decades away, we will eventually see the impact of quantum computing on our everyday lives.”
Sidebar –Quantum Computing Explained:
A traditional computer like a laptop or a smartphone stores numbers in semiconductor memories or registers and then manipulates those numbers, adding them, multiplying them and so on. It performs these calculations by processing “bits” of information. Each bit holds either a 1 or a 0. But a quantum computer defies common sense. It relies on the mind-bending ways that some objects behave at the subatomic level or when exposed to extreme cold, like the exotic metal that Google chills to nearly 460 degrees below zero inside its quantum computer.
Quantum bits, or “qubits,” behave very differently from normal bits. A single object can behave like two separate objects at the same time when it is either extremely small or extremely cold. By harnessing that behavior, scientists can build a qubit that holds a combination of 1 and 0. This means that two qubits can hold four values at once. And as the number of qubits grows, a quantum computer becomes exponentially more powerful. Google builds “superconducting qubits,” where certain metals are cooled to extremely low temperatures.
Many other tech giants, including Microsoft, Intel and IBM, are building similar quantum technology as the United States jockeys with China for supremacy in this increasingly important field. As the United States has pushed forward, primarily through corporate giants and start-up companies, the Chinese government has said it is pumping more than $15.2 billion into quantum research.
With its latest superconducting computer, Google has claimed “quantum supremacy,” meaning it has built a machine capable of tasks that are beyond what any traditional computer can do. But these tasks are esoteric. They involve generating random numbers that can’t necessarily be applied to practical applications, like drug discovery.
Google and its rivals are still working toward what scientists call “quantum advantage,” when a quantum computer can accelerate the progress of other fields like chemistry and artificial intelligence or perform tasks that businesses or consumers find useful. The problem is that quantum computers still make too many errors.
Scientists have spent nearly three decades developing techniques — which are mind-bending in their own right — for getting around this problem. Now, Google has shown that as it increases the number of qubits, it can exponentially reduce the number of errors through complex analysis.
Experts believe it is only a matter of time before a quantum computer reaches its vast potential. “People no longer doubt it will be done,” Dr. Lukin said. “The question now is: When?”
References:
https://blog.google/technology/research/google-willow-quantum-chip/
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/12/09/technology/google-quantum-computing.html
Quantum Computers and Qubits: IDTechEx report; Alice & Bob whitepaper & roadmap
Bloomberg on Quantum Computing: appeal, who’s building them, how does it work?
China Mobile verifies optimized 5G algorithm based on universal quantum computer
SK Telecom and Thales Trial Post-quantum Cryptography to Enhance Users’ Protection on 5G SA Network
Quantum Technologies Update: U.S. vs China now and in the future
Can Quantum Technologies Crack RSA Encryption as China Researchers Claim?
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
At the 2024 Digital Technology Ecosystem Conference last week, China Telecom executives identified AI, 5G new calling and satellite-to-phone services as its handset priorities for 2025. The state-owned network operator, like other China telcos, is working with local manufacturers to build the devices it wants to sell through its channels.
China Telecom’s smartphone priorities align with its major corporate objectives. As China Telecom vice president Li Jun explained, devices are critical right across the business. “Terminals are an extension of the cloud network, a carrier of services, and a user interface,” he said.
China Telecom Vice President Li Jun
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
China Telecom Deputy General Manager Tang Ke, introduced the progress of China Telecom and its partners in AI and emerging terminal ecosystem cooperation. He stated that in 2024, China Telecom will achieve large-scale development of basic 5G services, with over 120 million new self-registered users annually and more than 140 models of phones supporting 5G messaging.
In terms of emerging businesses, leading domestic smartphone brands fully support direct satellite connection, with 20 models available and over 4 million units activated. Leading PC brands fully integrate Tianyi Cloud Computer, further enriching applications in work, education, life, and entertainment scenarios. Domestic phones fully support quantum secure calls, with over 50 million new self-registered users. Terminals fully support the upgrade to 800M, reaching over 100 million users. Besides phones to support direct-to-cell calling, it also hoped to develop low-cost positioning tech using Beidou and 5G location capabilities.
China Telecom continues to promote comprehensive AI upgrades of terminals, collaborating with partners to expand AI terminal categories and provide users with more diverse choices and higher-quality experiences. Tang Ke revealed that, at the main forum of the “2024 Digital Technology Ecosystem Conference,” China Telecom will release its first operator-customized AI phone.
Tang Ke emphasized that in the AI era, jointly building a collaborative and mutually promoting AI terminal ecosystem has become the inevitable path of industry development. Ecosystem participants must closely coordinate in technology, industry, and business to offer users the best AI experience. China Telecom will comprehensively advance technical collaboration, accelerating coordination from levels such as chips, large models, and intelligent agents, and promoting the construction of AI technology frameworks from both the device and cloud sides. The company will comprehensively push terminal AI upgrades, accelerating the AI development of wearables, healthcare, education, innovation, and industry terminals, based on key categories such as smartphones, cameras, cloud computers, and smart speakers.
Deputy Marketing Director Shao Yantao laid out the company’s device strategy for the year ahead. He said China Telecom’s business was based on networks, cloud-network integration and quantum security, with a focus on three technology directions – AI, 5G and satellites. With AI, it aims to carry out joint product development with OEM partners to build device-cloud capabilities and establish AI models. The state owned telco will pursue “domestic and foreign” projects in cloud-based AI mobile phones.
Besides smartphones, other AI-powered products next year would likely include door locks, speakers, glasses and watches, Shao said. The other big focus area is 5G new calling, based on new IMS DC (data channel) capabilities, with the aim of opening up new use cases like screen sharing and interactive games during a voice call.
China Telecom would develop its own open-source IMS DC SDK to support AI, payments, XR and other new functionality, Shao said. But he acknowledged the need to build cooperation across the industry ecosystem. The network operator and its partners would also collaborate on Voice over WiFI and 3CC carrier aggregation for 5G-Advanced devices, he added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) claims that China has built and activated over 4.1 million 5G base stations, with the 5G network continuously extending into rural areas, achieving “5G coverage in every township.” 5G has been integrated into 80 major categories of the national economy, with over 100,000 application cases accumulated. The breadth and depth of applications continue to expand, profoundly transforming lifestyles, production methods, and governance models.
The meeting emphasized the need to leverage the implementation of the “Sailing” Action Upgrade Plan for Large-scale 5G Applications as a means to vigorously promote the large-scale development of 5G applications, supporting new types of industrialization and the modernization of the information and communications industry, thereby laying a solid foundation for building a strong network nation and advancing Chinese-style modernization.
References:
https://www.c114.com.cn/news/22/c23811.html
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1279613.html
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1279469.html