Author: Alan Weissberger
WRC-23 concludes with decisions on low-band/mid-band spectrum and 6G (?)
The World Radiocommunication Conference 2023 (WRC-23) [1.] in Dubai, UAE ended on Friday. Regulators agreed on new mobile low-band spectrum (below 1 GHz) and mid-band spectrum in the 3.5 GHz and 6 GHz ranges. They also discussed 6G (which is an oxymoron to this author since the many problems we’ve identified with 5G have not been resolved).
Note 1. WRC’s are held every four years under the auspices of the International Telecommunication Union Radio communications sector (ITU-R). They are intended to harmonize spectrum usage across the world so that network operators, equipment vendors and others can avoid international fragmentation and leverage global economies of scale.

“WRC-23 has provided a clear roadmap for mobile services to continue to evolve and expand for the benefit of billions across the globe,” said John Giusti, Chief Regulatory Officer at the GSMA. “The GSMA believes that no-one should be left behind in the digital age and the decisions of WRC-23 will allow us to deliver a brighter future where mobile brings communities together, delivers industrial agility and provides economic growth. Implementation of the WRC-23 decisions will support global digital ambitions, deliver greater digital equality and unlock the full power of connectivity.”
The detailed WRC-23 provisional final acts may be read here.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Final harmonization of the 3.5 GHz band (3.3-3.8 GHz) – the pioneer 5G band – was achieved across Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA) as well as throughout the Americas.
A new band – the 6 GHz band (6.425-7.125 GHz) – was identified for mobile in every ITU Region – EMEA, the Americas and the Asia Pacific. Countries representing more than 60% of the world’s population asked to be included in the identification of this band for licensed mobile at WRC-23. The 6 GHz spectrum is now the harmonized home for the expansion of mobile capacity for 5G-Advanced and beyond.
“The 6GHz band is the only remaining mid-band spectrum currently available to respond to the data traffic growth in the 5G-Advanced era,” GSMA said in a statement. As the primary international organization representing the 5G industry, it has been pushing for 5G operations in the 6GHz band. “The WRC-23 decision to harmonize the 6GHz band … is a pivotal milestone, bringing a population of billions of people into a harmonized 6GHz mobile footprint. It also serves as a critical developmental trigger for manufacturers of the 6GHz equipment ecosystem,” GSMA said.
ITU-APT Foundation of India said the agreement also opens the path for opening the lower 6 GHz band from 5925-6425 MHz for unlicensed usage to promote innovation in the country.
However, the 6 GHz band approval at WRC-23 may not affect the U.S. market. U.S. regulators at the FCC in 2020 reserved the entire 6GHz band for Wi-Fi and other unlicensed operations, over the objections of the 5G industry.
“If the United States doesn’t present alternative frequency ranges for 5G services that can be internationally harmonized, 5G operations in the 6GHz band could be adopted in more regions. This would allow Chinese equipment to proliferate in regions where the plan is adopted, setting back efforts to make Wi-Fi 6 in the band an international standard,” warned Jeffrey Westling, director of technology and innovation policy at the American Action Forum US nonprofit, in a post published prior to the start of WRC-23.
Jessica Rosenworcel, chairwoman of the FCC, approved the WRC-23’s work. “The WRC was not just weeks of work in Dubai, but also years of preparation by the FCC, experts across the government, and our telecommunications industry,” she said in a statement. “The delegation’s accomplishments will promote innovation in unlicensed spectrum including Wi-Fi, support 5G connectivity, pave the way for 6G, and bolster U.S. leadership in the growing space economy. We now look forward to getting to work on preparations for WRC-27.”
“Thank you to Deputy Assistant Secretary Steve Lang for his able leadership and to the FCC staff along with the entire U.S. delegation for their exceptional and tireless efforts at WRC-23,” said FCC Commissioner Anna M. Gomez in a statement. “WRC-23 was the culmination of years of collaboration and hard work between our strong interagency team, the telecommunications industry, and our regional and international partners. The delegation’s accomplishments on terrestrial licensed and unlicensed spectrum as well as space allocations will advance science and economic prosperity worldwide.”
The U.S. Department of State also issued a media note on the delegation’s work at WRC-23 here.
The Wi-Fi Alliance, a U.S. trade group designed to promote the technology in unlicensed bands, also cheered the new 6GHz decision at the WRC-23. The association supported the FCC’s decision to allocate the entire 6GHz band for unlicensed operations.
“The conference adopted an international treaty provision to explicitly recognize that this spectrum is used by wireless access systems such as Wi-Fi,” the Wi-Fi Alliance said in a statement about the WRC-23 decision on 6GHz. The Wi-Fi Alliance noted that WRC-23 identified the 6GHz band for licensed operations in Europe, Africa and a few other countries, but not globally.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
WRC-23 also set out a path towards greater digital equality by defining mobile use of more low-band spectrum in the 470-694 MHz band in EMEA. Low bands can help expand capacity for the internet connectivity of rural communities as their signals reach over wide areas. WRC-23’s new low-band mobile allocations will be an important tool to break down the barriers towards digital equality in the EMEA region and lower the urban/rural connectivity divide.
“Over half the world is connected to the mobile internet today,” said Luciana Camargos, Head of Spectrum at the GSMA. “But, as mobile connectivity develops, we need to ensure that we can deliver services for everyone. The great legacy of WRC-23 will be in allowing us to do so sustainably, affordably and in a way that delivers for the whole planet. We cannot stop here – WRC-23 is only the starting gun and now governments will need to act on its decisions, enabling new mobile technologies that embrace sustainability and unleashing the full potential of mobile to deliver a better tomorrow for our planet.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
WRC-23 attendees also moved forward on the topic of 6G. Prior to the start of the three week conference in Dubai, the ITU adopted a resolution intended to guide the development of a 6G standard. During the conference, regulators agreed to study the 7-8.5GHz band for 6G in time for the next ITU conference in 2027. That spectrum band aligns with proposals from Ericsson and others for early 6G operations to sit between 7 GHz and 20 GHz.
“This global agreement [on the 7-8.5GHz band] ensures the ongoing growth of 5G around the world and paves the way for 6G from 2030 onwards,” wrote the Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) in a statement. “Technical work now starts to determine the sharing and compatibility of 6G with incumbent uses of the identified spectrum.”
Joe Barrett, President of GSA, commented: “The global agreement reached by ITU represents a significant milestone not just in the continued growth of 5G and 5G-Advanced connectivity, but also in the path to 6G. The entire global mobile ecosystem can now innovate with confidence and a clear sense of the spectrum requirements for 6G, both in terms of its future availability and compatibility with other users of the spectrum. At GSA we appreciate the hard work and diligence of ITU and its members that has gone into reaching this welcome global agreement at WRC-23. GSA’s Spectrum Group will continue to contribute studies and technical analysis to international, regional and individual country policymakers and regulators to facilitate the timely availability of spectrum for use by mobile network operators. As an industry, we now look forward to continued 5G growth, 6G innovation and the socio-economic benefits mobile connectivity brings globally.”
Like this author, the Financial Times is not enthusiastic about 6G:
“CB Insights shows that mentions of 5G during earnings calls peaked in 2021 and have since fallen. Network operator capital spending growth is expected to dip next year. Operators want to see better returns on their investment in 5G before they contemplate further network upgrades.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/opb/act/R-ACT-WRC.15-2023-PDF-E.pdf
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/6ghz-satellites-and-6g-addressed-at-wrc-23#close-modal
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-399175A1.pdf
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-399195A1.pdf
GSA welcomes agreement on future of 5G and 6G spectrum at WRC-23
https://www.ft.com/content/e59a4818-c630-4dac-9c36-477a0c99a9cd
Highlights of LightCounting’s December 2023 Quarterly Market Update on Optical Networking
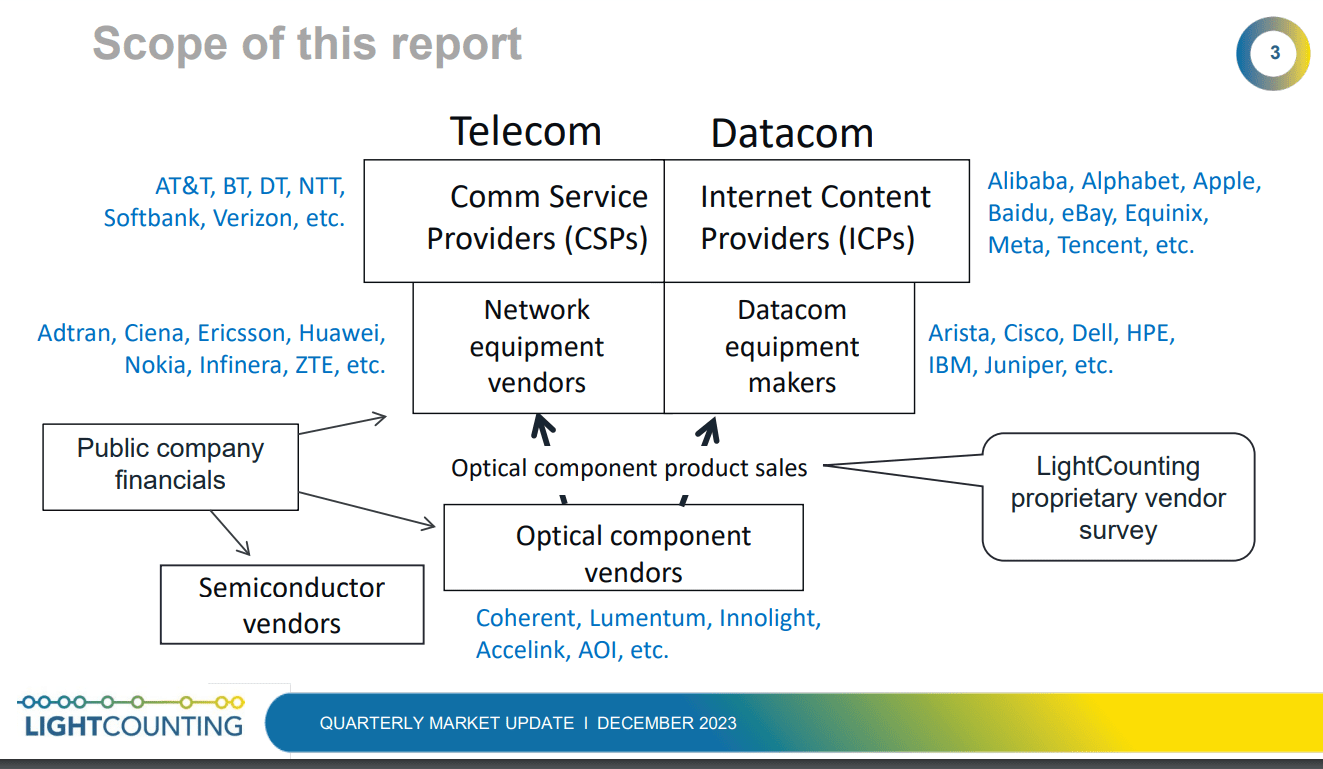
LightCounting’s Quarterly Market Update report [1.] for Q3 2023 revealed that the optical communications industry financial results were disappointing.
Every financial market indicator that the market research firm tracks – ICP (Integrated Communications Provider) and CSP (Communications Service Provider) capex, datacom and networking equipment, and semiconductor (x-Nvidia) and optical components sales – all had negative growth compared to Q3 2022.
Note 1. LightCounting’s Quarter Market Update reports are designed to provide an easy-to-digest snapshot of optical transceiver growth trends, backed up by detailed quarter-by-quarter sales data collected via LightCounting’s proprietary vendor survey. Performance metrics and commentary for top-tier telecom and internet service providers, network and datacom equipment makers, and optical component and semiconductor vendors are also included to provide an understanding of what drives sales trends at the transceiver level.
- Alphabet and Microsoft had record capital expenditures.
- Arista, Broadcom, Calix, Innolight, and Nvidia all reported record revenues.
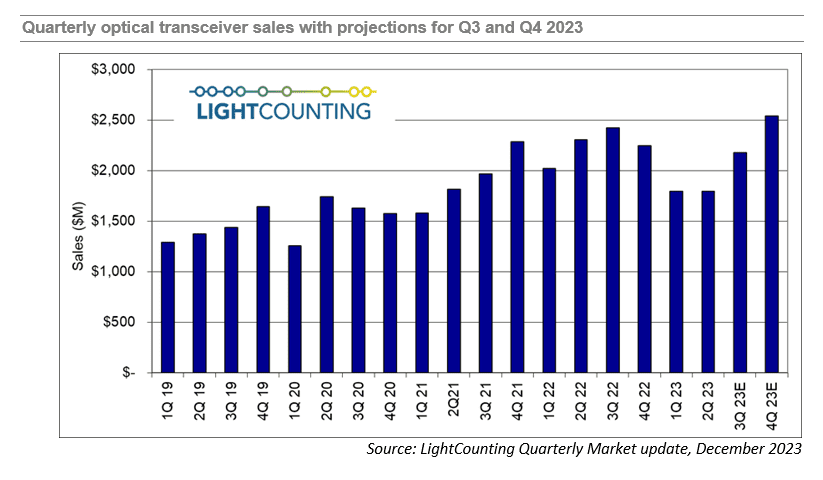
LightCounting is projecting, based on its current analysis, that sales increased in Q3 and will increase further in Q4, to a new record high, as shown in the figure below. This data includes estimates for 400G and 800G transceivers manufactured by Nvidia internally.
The expectation of growth in Q4 carries over to 2024 as well and is consistent with the guidance given by several companies ranging from Alphabet and Amazon to Coherent and Lumentum. The big caveat is that growth in 2024 will be tightly focused on AI-related infrastructure, and growth in demand for those products is expected to far outstrip demand in other segments like traditional telco and enterprise networks. Most of the growth in the optical components and modules market will come from sales of 800G transceivers.
References:
https://www.lightcounting.com/report/december-2023-quarterly-market-update-199
LightCounting: Will Network Transformation resolve telecom’s paradox?
Industry Analysts: Important Optical Networking Trends for 2023
MTN Group and NEC XON deploy Africa’s first 400G optical transponder using TIP’s Phoenix
Deutsche Telekom Network Day: Fiber, Mobile Network, Open RAN and 5G SA Launch in 2024
2023 Deutsche Telekom (DT) Highlights:
- Fiber offensive: more than 2.5 million new fiber connections made possible in 2023, reaching a total of more than ten million fiber households in 2024
- 5G front-runner: 5G population coverage of 96%, 5G Standalone also for private customers in 2024
- State-of-the-art technologies: Artificial intelligence supports fiber and mobile rollout
- EURO 2024: Deutsche Telekom connects all stadiums, fan zones & team quarters, data gift for all mobile customers
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Deutsche Telekom announced that it has successfully enabled more than 2.5 million new fiber connections this year, thereby realizing its fiber plant expansion target. The company invested EUR 2.5 billion in fiber expansion, expanding coverage in almost 3,500 towns and municipalities. According to the announcement, the company projects a total investment of EUR 30 billion in the fiber optic rollout by 2030.
Its Fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network is set to reach eight million households by the end of the year, with plans to extend this to ten million fiber optic connections by 2024.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In mobile, Deutsche Telekom currently provides 5G coverage to 96 percent of the population, serving 80 million people through a network of over 80,000 5G antennas, including 10,000 in the 3.5 GHz band spread across more than 800 cities and municipalities. The network delivers download speeds of up to 1 Gbps.
The company aims to achieve 99 percent 5G coverage for the German population by 2025 and plans to launch 5G Standalone (SA) core network for private customers in 2024. DT indicates that 10,000 antennas are compatible with 5G SA in the 3.6 GHz band, covering more than 800 cities and municipalities. This is up from 9,700 antennas in August 2023.
Deutsche Telekom’s business customers are already using 5G SA technology with functions such as network slicing. For example, for live TV transmission of media or in 5G campus networks for industry and research. “In the coming year, 5G SA should then offer all customers real added value,” DT said.
Meanwhile, rival operators Telefónica Deutschland (O2 Germany) and Vodafone Germany already offer standalone 5G services.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
DT began the deployment of its open radio access network (O-RAN) in Germany in December, in collaboration with Nokia and Fujitsu. The first O-RAN commercial deployment will be in Neubrandenburg. Nokia and Fujitsu are supplying the necessary technology components.
“Open RAN increases the choice of manufacturers and therefore our flexibility. The open access network enables more automation. And makes our networks even more resilient. This benefits the people that our mobile network connects,” says Claudia Nemat.
The German telco expects to have 3,000 O-RAN compatible antennas by the end of 2026.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Deutsche Telekom also says it’s using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in network expansion and mobile communications. AI aids in analyzing and evaluating cell usage and capacity utilization, with the ongoing development of a large language model for telco-specific applications in collaboration with SK Telekom. Additionally, AI contributes to enhanced network security through automated pattern recognition, according to the company.
References:
https://www.telekom.com/en/media/media-information/archive/telekom-network-day-2023-1055364
https://www.fiercewireless.com/wireless/deutsche-telekom-plans-5g-standalone-launch-2024
NTT advert in WSJ: Why O-RAN Will Change Everything; AT&T selects Ericsson for its O-RAN
We cover both NTT’s Open RAN ad in the WSJ and AT&T’s selection of Ericsson as their primary Open RAN vendor:
This NTT-WSJ ad was a huge shock to me as I did not expect NTT to be so optimistic about Open RAN deployments as it would cannibalize their existing 3G/4G/5G RAN. Here’s the copy/paste of the WSJ advertisement:
Introduction:
With data consumption accelerating, and demand for high-speed data soaring, the growth of the global O-RAN alliance is taking the future of connectivity to the next level.
Allowing mobile network operators to share network integration costs and enabling interoperation between different vendors’ cellular network equipment are just two of the revolutionary benefits driving O-RAN’s adoption worldwide. As a pioneer in this ecosystem, Japanese operator NTT Docomo has established the OREX brand to deliver its O-RAN solution to mobile users anticipating the instantaneous communication that 6G will bring.
Innovating the Future of Connectivity:
The expanding O-RAN universe consists of more than 300 mobile operators, vendors and academic and research institutions worldwide. With consumer 5G connections alone predicted to reach 2 billion by 2025—doubling from 1 billion in 2022—and 6G technology in sight, further adoption of O-RAN plays a vital role in the future of global connectivity. As a co-founder of the global O-RAN alliance, Japanese operator NTT DOCOMO is one of the innovators transforming mobile connectivity through open, intelligent and interoperable mobile networks.
What is O-RAN?
An open-ended, non-proprietary version of the Radio Access Network (RAN) system used for mobile networks, O-RAN stands for open radio access network (Open RAN) and is an ecosystem and architecture for flexible networks capable of leveraging 5G—and beyond—wireless communications. Using radio waves to connect users (consumer or business) to the mobile network, it allows interoperation between different vendors’ cellular network equipment. It is also a connector for accessing key web applications. Whereas RAN technology currently comes as a single-vendor hardware- and software-integrated architecture, O-RAN is a multi-supplier solution that can disaggregate hardware and software with open interfaces and virtualization.
What Are the Business Benefits?
Put simply, O-RAN reduces the total cost and increases the flexibility of network ownership for the benefit of consumers and enterprises that use sensors, smartphones and similar remote wireless devices. A clear alternative to vendor lock-in, the sharing of network integration costs among a number of mobile network operators—instead of that cost being shouldered by a single operator—makes it more competitive. As well as increased connectivity for vendors and network operators, O-RAN offers greater accessibility, technological flexibility, supply-chain diversity, and scalable mobile networks. New features are introduced quickly via software, reducing maintenance time while also making further innovation and greater competition possible. NTT Docomo’s OREX has been established to deliver its O-RAN solution, providing robust support for international operators and a customized user experience.
Opening up Mobile Networks:
The global O-RAN alliance is expanding as the technology matures. Adoption is growing fastest in North America and Asia Pacific, where there is high data consumption, rising demand for high-speed data and the integration of AI and cloud computing. These two regions are predicted to dominate the global market over the next five years. In Europe, both Germany and the U.K. have established initiatives to develop and support their solutions. Leading telecom companies in the Netherlands, Spain, and Italy are developing O-RAN technology, as are two of India’s three major operators. More prospective markets exist in Asia, Africa and South America.
The Journey to 6G:
Designed to make cloud computing and the mobile internet ubiquitous, 6G-enabled technologies will greatly impact business when commercially available around 2030. Potentially 100 times faster than 5G, 6G is the next-generation technology that will enable lightning-speed device connections and O-RAN technology has the flexibility to adopt it. 6G will transform how companies communicate, process information, train employees and much more. NTT Docomo is leveraging the knowledge gained from its unique experience in building mobile networks with multiple equipment vendors since the 4G era, and its OREX offering integrates the strengths of 13 partners including Dell, Intel, Fujitsu, and others to offer a strong value proposition for the global shift to O-RAN.

……………………………………………………………………………………………….
AT&T selected Ericsson as its Open RAN equipment supplier, yet the Swedish network equipment vendor does not have any open RAN certifications with the O-RAN Alliance. AT&T said Open RAN will cover 70% of its wireless traffic in the United States by late 2026. Beginning in 2025, the company will scale this Open RAN environment throughout its wireless network in coordination with multiple suppliers such as Corning Incorporated, Dell Technologies, Ericsson, Fujitsu, and Intel.
“AT&T is taking the lead in open platform sourcing in our wireless network,” said Chris Sambar, Executive Vice President, AT&T Network. “With this collaboration, we will open up radio access networks, drive innovation, spur competition and connect more Americans with 5G and fiber. We are pleased that Ericsson shares our supp
“High-performance and differentiated networks will be the foundation for the next step in digitalization. I am excited about this future and happy to see our long-term partner, AT&T, choosing Ericsson for this strategic industry shift – moving to open, cloud-based and programmable networks. Through this shift, and with open interfaces and open APIs, the industry will see new performance-based business models, creating new ways for operators to monetize the network. We are truly proud to be partnering with AT&T in the industrialization of Open RAN and help accelerate digital transformation in the U.S.,” said Börje Ekholm, President and CEO, Ericsson.
AT&T will use this new collaboration with Ericsson to enhance its wireless network in North America and expand the most reliable 5G network.1 The expected spend under the Ericsson contract is below what the company expects to spend for wireless capital expenditure over the next 5 years. Given the interdependence between fiber and wireless, and the increasing desire for customers to have one connectivity provider across fixed broadband and wireless, the company sees economically attractive opportunities to expand its fiber footprint in the coming years as well.
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
References:
https://partners.wsj.com/ntt/innovating-the-future/innovating-the-future-of-connectivity/
https://about.att.com/story/2023/commercial-scale-open-radio-access-network.html
https://www.o-ran.org/testing-integration#certification-badging
NTT DOCOMO OREX brand offers a pre-integrated solution for Open RAN
Samsung in OpenRAN deal with NTT DOCOMO; unveils 28GHz Radio Unit (RU)
Another Open RAN Consortium: 5G Open RAN Ecosystem led by NTT
CoreSite Enables 50G Multi-cloud Networking with Enhanced Virtual Connections to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect
Note 1. CoreSite is a subsidiary of American Tower Corporation and a member of Oracle PartnerNetwork (OPN).
Note 2. Oracle FastConnect enables customers to bypass the public internet and connect directly to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and other Oracle Cloud services. With connectivity available at CoreSite’s data centers, FastConnect provides a flexible, economical private connection to higher bandwidth options for your hybrid cloud architecture. Oracle FastConnect is accessible at CoreSite’s data center facilities in Northern Virginia and Los Angeles through direct fiber connectivity. FastConnect is also available via the CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange® in seven CoreSite markets, including Los Angeles, Silicon Valley, Denver, Chicago, New York, Boston and Northern Virginia.
The integration of Oracle FastConnect and the CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange offers on-demand, virtual connectivity and access to best in class, end-to-end, fully redundant connection architecture.

Image Credit: CoreSite
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The connectivity of FastConnect and the OCX can offer customers deploying artificial intelligence (AI) and data-intensive applications the ability to transfer large datasets securely and rapidly from their network edge to machine learning (ML) models and big data platforms running on OCI. With the launch of the new OCX capabilities to FastConnect, businesses can gain greater flexibility to provision on-demand, secure bandwidth to OCI with virtual connections of up to 50 Gbps.
With OCI, customers benefit from best-in-class security, consistent high performance, simple predictable pricing, and the tools and expertise needed to bring enterprise workloads to cloud quickly and efficiently. In addition, OCI’s distributed cloud offers multicloud, hybrid cloud, public cloud, and dedicated cloud options to help customers harness the benefits of cloud with greater control over data residency, locality, and authority, even across multiple clouds. As a result, customers can bring enterprise workloads to the cloud quickly and efficiently while meeting the strictest regulatory compliance requirements.
“The digital world requires faster connections to deploy complex, data-intense workloads. The simplified process offered through the Open Cloud Exchange enables businesses to rapidly scale network capacity between the enterprise edge and cloud providers,” said Juan Font, President and CEO of CoreSite, and SVP of U.S. Tower. “These enhanced, faster connections with FastConnect can provide businesses with a competitive advantage by ensuring near-seamless and reliable data transfers at massive scale for real-time analysis and rapid data processing.”
OCI’s extensive network of more than 90 FastConnect global and regional partners offer customers dedicated connectivity to Oracle Cloud Regions and OCI services – providing customers with the best options anywhere in the world. OCI is a deep and broad platform of cloud infrastructure services that enables customers to build and run a wide range of applications in a scalable, secure, highly available, and high-performance environment. From application development and business analytics to data management, integration, security, AI, and infrastructure services including Kubernetes and VMware, OCI delivers unmatched security, performance, and cost savings.
The new Open Cloud Exchange capabilities on FastConnect will be available in Q4 2023.
Related Resources:
- Watch What is The Open Cloud Exchange® and How Can It Simplify and Automate Your Cloud Connectivity?
- Open Cloud Exchange® Solution Brochure
- Trust CoreSite Data Centers to Enable Your AI Strategy
- Why businesses partner with CoreSite
About CoreSite:
CoreSite, an American Tower company (NYSE: AMT), provides hybrid IT solutions that empower enterprises, cloud, network, and IT service providers to monetize and future-proof their digital business. Our highly interconnected data center campuses offer a native digital supply chain featuring direct cloud onramps to enable our customers to build customized hybrid IT infrastructure and accelerate digital transformation. For more than 20 years, CoreSite’s team of technical experts has partnered with customers to optimize operations, elevate customer experience, dynamically scale, and leverage data to gain competitive edge. For more information, visit CoreSite.com and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter.
References:
IEEE Santa Clara Valley (SCV) Lecture and Tour of CoreSite Multi-Tenant Data Center
https://www.coresite.com/cloud-networking/oracle-fastconnect
Nokia and du (UAE) complete 5G-Advanced RedCap trial; future of RedCap?
Nokia and United Arab Emirates (UAE) telco du announced the conclusion of what it claimed to be UAE’s first 5G-Advanced 5G Reduced Capability (RedCap) trial over a commercial network. Nokia said that this recent trial showcased the readiness of du’s 5G network for innovative use cases in areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), wearables and Industry 4.0 to address 5G monetization challenges.
RedCap, sometimes referred to as (3GPP) 5G NR Light, is a reduced set of 5G capabilities intended for devices like wearables and low-cost hotspots that have low battery consumption, lower costs and lower bandwidth requirements. Introduced with 3GPP Release 17, 5G RedCap is designed for devices currently served by LTE CAT-4 but provides equivalent or better in performance with up to 150 Mbps theoretical maximum downlink throughput. This technology helps reduce the complexity, cost and size of 5G devices. The RedCap specification will be included in ITU-R M.2150-1.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The trial participants used MediaTek’s T300 series RedCap test equipment in du’s 5G Standalone (SA) Radio Access Network (RAN) built with Nokia’s AirScale radio products, leveraging the existing mid-band Spectrum. This will follow extending RedCap over low band frequencies, ensuring extreme coverage and connectivity. Notably, the low band in 600MHz, is a vital connectivity band currently under discussion at the World Radio Conference WRC-23 taking place in Dubai.
With RedCap devices expected to be commercially available from 2024, it will significantly augment du’s diversified use case portfolio to include cost-efficient 5G home wireless, wearables, video surveillance, and wireless industrial sensors.
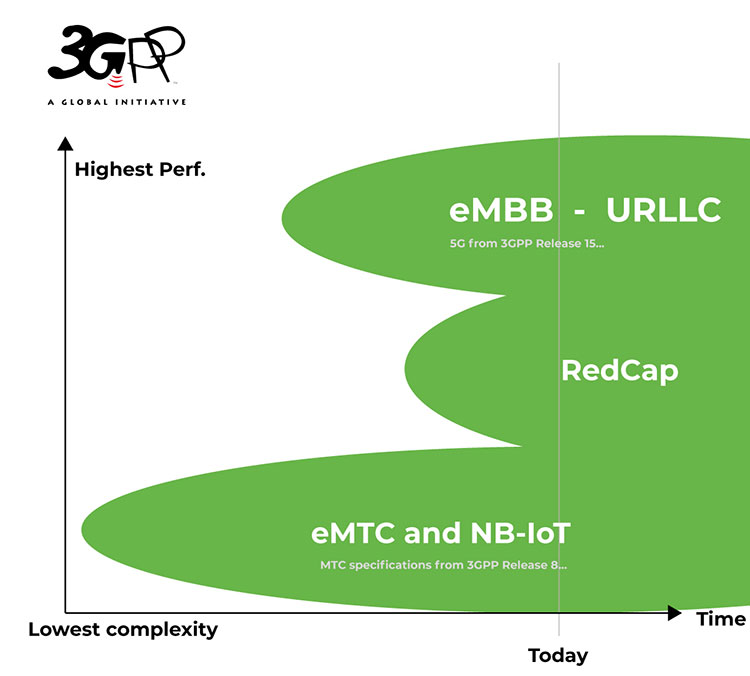
5G devices commonly feature intricate hardware and energy-intensive capabilities, resulting in higher cost, size, and power consumption. RedCap technology is dedicated to streamlining 5G devices, specifically targeting compact IoT devices like wearables and health trackers, as well as ruggedized routers and sensors for environmental or condition-based monitoring. These devices exhibit lower demands for battery life and reduced bandwidth requirements. RedCap ensures they sustain performance while optimizing their power efficiency. Nokia has been instrumental in driving the evolution of RedCap IoT functionality in collaboration with the telecommunications industry.
Saleem Alblooshi, Chief Technology Officer at du, said: “This collaboration introduces the revolutionary 5G-Advanced RedCap functionalities, enabling seamless connectivity of RedCap devices to cutting-edge 5G networks. Nokia’s unparalleled innovation simplifies and pioneers the development of 5G devices, particularly wearables and small IoT devices, significantly enhancing LTE-CAT4 performance and optimizing energy efficiency. These remarkable technological advancements are pivotal in propelling Industry 4.0 revolution.”
Mikko Lavanti, Senior Vice President at Nokia MEA, said: “This new collaboration between du and Nokia represents not only a significant step forward in the monetization of 5G technology but also solidifies the UAE’s position as a pioneer in the evolution of 5G use cases for society and enterprises. As the collaboration progresses, both companies are poised to revolutionize the way we experience and interact with 5G technology, unlocking unprecedented possibilities for innovation and connectivity.”
Dr. Ho-Chi Hwang, General Manager of Wireless Communication System and Partnerships at MediaTek, said: “It’s essential to bring new capabilities of 5G to the UAE, and this trial is an important step in that direction. We are proud to have provided our RedCap devices to further develop the ecosystem for 5G monetization. We hope, by pioneering the technology in the Middle East and Africa region, MediaTek will be able to assure our customers of more innovative 5G products and services coming their way.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Future of RedCap:

Counterpoint Research expects that 5G RedCap modules will make up 18% of total cellular IoT module shipments by 2030—what it describes as “significant market potential, particularly in developing nations where the cost is key to wide technology adoption for digital transformation.”
“If we want to tackle some of these interesting business cases and really get the price point so the business can take off, then we need to provide the right types of options,” said Paul Harris, principal architect in the Office of the CTO at Viavi Solutions. “People don’t want to be paying for chipsets that are too performant in the wrong types of devices.” Harris also noted that standards work on RedCap continues, with a series of recommendations on reducing RedCap’s performance even further with support of just five megahertz of bandwidth, even lower data rates and reduced peak data rates as well as additional power savings in the form of Extended Discontinuous Reception (allowing longer periods during which a device can power off). While that work on “eRedCap” is still taking shape in Release 18 and additional features may be available to scale down RedCap further in Release 19. “It’s still kind of a moving target and probably will continue to be, but there will probably be different categories that get introduced of RedCap as it goes on,” he said. Harris goes on to offer up a potential vision of a RedCap market where there is a gradual progression into some parts of the market addressed with the initial Rel. 17 RedCap options, and that by Rel. 19, a scaled-back RedCap market could open up for even lower-complexity, lower data-rate devices that then leads to an explosion of 5G sensor devices.
“5G is absolutely the directional technology,” said Bill Stone, VP of technology development and planning at Verizon. “I do think it’s inevitable that we’ll be seeing all of IoT evolve over time, and it’s going to be starting as soon as next year. We’re going to see all of the IoT device community moving over to 5G, because that’s where—with 5G NR SA—we’re going to see the potential for much longer lifecycles [and] the ability to support that, to make commitments for longer-term support of IoT devices.”
References:
Standards leadership in action: How Nokia convinced the 5G world that less is more
Ericsson, Vodafone and Qualcomm: 1st Reduced Capability 5G data call in Europe
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/redcap
ITU-R M.2150-1 (5G RAN standard) will include 3GPP Release 17 enhancements; future revisions by 2025
Google announces Gemini: it’s most powerful AI model, powered by TPU chips
Google claims it has developed a new Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) system and Large Language Model (LLM) more powerful than any currently on the market, including technology developed by ChatGPT creator OpenAI. Gemini can summarize text, create images and answer questions. Gemini was trained on Google’s Tensor Processing Units v4 and v5e.
Google’s Bard is a generative AI based on the PaLM large language mode. Starting today, Gemini will be used to give Bard “more advanced reasoning, planning, understanding and more,” according to a Google blog post.
While global users of Google Bard and the Pixel 8 Pro will be able to run Gemini now, an enterprise product, Gemini Pro, is coming on Dec. 13th. Developers can sign up now for an early preview in Android AICore.
Gemini comes in three model sizes: Ultra, Pro and Nano. Ultra is the most capable, Nano is the smallest and most efficient, and Pro sits in the middle for general tasks. The Nano version is what Google is using on the Pixel, while Bard gets Pro. Google says it plans to run “extensive trust and safety checks” before releasing Gemini Ultra to select groups.
Gemini can code in Python, Java, C++, Go and other popular programming languages. Google used Gemini to upgrade Google’s AI-powered code generation system, AlphaCode. Next, Google plans to bring Gemini to Ads, Chrome and Duet AI. In the future, Gemini will be used in Google Search as well.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Market Impact:
Gemini’s release and use will present a litmus test for Google’s technology following a push to move faster in developing and releasing AI products. It coincides with a period of turmoil at OpenAI that has sent tremors through the tight knit AI community, suggesting the industry’s leaders is far from settled.
The announcement of the new GenAI software is the latest attempt by Google to display its AI portfolio after the launch of ChatGPT about a year ago shook up the tech industry. Google wanted outside customers to perform testing on the most advanced version of Gemini before releasing it more widely, said Demis Hassabis, chief executive officer of Google DeepMind.
“We’ve been pushing forward with a lot of focus and intensity,” Hassabis said, adding that Gemini likely represented the company’s most ambitious combined science and engineering project to date.
Google said Wednesday it would offer a range of AI programs to customers under the Gemini umbrella. It touted the software’s ability to process various media, from audio to video, an important development as users turn to chatbots for a wider range of needs.
The most powerful Gemini Ultra version outperformed OpenAI’s technology, GPT-4, on a range of industry benchmarks, according to Google. That version is expected to become widely available for software developers early next year following testing with a select group of customers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Role of TPUs:
While most GenAI software and LLM’s are processed using NVIDIA’s neural network processors, Google’s tensor processing units (TPUs) will power Gemini. TPUs are custom-designed AI accelerators, which are optimized for training and inference of large AI models. Cloud TPUs are optimized for training large and complex deep learning models that feature many matrix calculations, for instance building large language models (LLMs). Cloud TPUs also have SparseCores, which are dataflow processors that accelerate models relying on embeddings found in recommendation models. Other use cases include healthcare, like protein folding modeling and drug discovery.
Google’s custom AI chips, known as tensor processing units, are embedded in compute servers at the company’s data center. Photo Credit: GOOGLE
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Competitors:
Gemini and the products built with it, such as chatbots, will compete with OpenAI’s GPT-4, Microsoft’s Copilot (which is based on OpenAI’s GPT-4), Anthropic’s Claude AI, Meta’s Llama 2 and more. Google claims Gemini Ultra outperforms GPT-4 in several benchmarks, including the massive multitask language understanding general knowledge test and in Python code generation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Everything to know about Gemini, Google’s new AI model (blog.google)
Google Reveals Gemini, Its Much-Anticipated Large Language Model (techrepublic.com)
T-Mobile combines Millimeter Wave spectrum with its 5G Standalone (SA) core network
T-Mobile, with the help of with Ericsson and Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., has tested millimeter wave (mmWave) on its production 5G SA network (note that mmWave identifies higher frequencies used on a 5G RAN, while 5G SA refers to a true 5G core network). The Un-carrier aggregated eight channels of mmWave spectrum to reach download speeds topping 4.3 Gbps without relying on low-band or mid-band spectrum to anchor the connection. T-Mobile also aggregated four channels of mmWave spectrum on the uplink, reaching speeds above 420 Mbps.
In the latest revision of ITU-R M.1036- Frequency Arrangements for IMT-the following mmWave bands were approved:
-Frequency arrangements in the band 24.25-27.5 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 45.5-47 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 47.2-48.2 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 66-71 GHz
In the U.S., Verizon has historically been the carrier promoting 5G mmWave, which they dubbed “5G Ultra Wideband.” The telco claims they’ve achieved 1.26 Gbps upload speed using 5G Ultra Wideband. With uploading data becoming increasingly important for video chats, uploading large files or live streaming video. “We have achieved remarkable speed in downloading using various combinations of spectrum in our world-class spectrum portfolio,” said Adam Koeppe, Senior Vice President of Technology Planning at Verizon. “This new achievement indicates how much additional performance we can unleash for our customers on the uplink as we aggregate different combinations of spectrum.”
T-Mobile took the opposite path, focusing on mid and low-band spectrum for its 5G network…until now. 5G mmWave can deliver very fast speeds because it offers massive capacity. But the signal doesn’t travel very well through obstacles, making it less ideal for mobile phone users who aren’t sitting still. That’s why T-Mobile has implemented a multi-band spectrum strategy using low-band to blanket the country and mid-band and high-band (Ultra Capacity) to deliver insanely fast speeds to nearly everyone. Now the Un-carrier is testing 5G mmWave on 5G SA for crowded areas like stadiums and, potentially, for fixed wireless service.
“We’ve been industry leaders – rolling out the first, largest and fastest 5G standalone network across the country – and now we’re continuing to push the boundaries of wireless technology,” said Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology at T-Mobile. “We’ve always said we’ll use millimeter wave where it makes sense, and this test allows us to see how the spectrum can be put to use in different situations like crowded venues or to power things like fixed-wireless access when combined with 5G standalone.”
T-Mobile is the U.S. leader in 5G [1.] delivering the largest, fastest and most awarded 5G network in the country. The Un-carrier’s 5G network covers more than 330 million people across two million square miles — more than AT&T and Verizon combined. 300 million people nationwide are covered by T-Mobile’s super-fast Ultra Capacity 5G with over 2x more square miles of coverage than similar mid-band 5G offerings from the Un-carrier’s closest competitors. According to Ookla’s quarterly speed test reports, T-Mobile’s 5G network has consistently outperformed AT&T’s and Verizon’s when it comes to median download speed.
Note 1. AT&T is the leading provider of mobile services in the U.S. with 229.1 subscribers as of Q2 2023, followed by: Verizon: 143.3 million (Q2 2023),,T-Mobile US: 117.9 million (Q3 2023), Dish Wireless: 7.5 million (Q3 2023), and uscellular: 4.6 million (Q3 2023).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
T-Mobile also offers wireless solutions to connect homes and businesses. 5G Home Internet (FWA) is available to over 50 million homes today, plus Small Business Internet and Business Internet is available across the country. This means millions of homes and businesses can finally ditch traditional ISPs for fast, reliable and hassle-free internet service with T-Mobile. The telco’s FWA customer base increased by 557,000 during Q3, giving it a total of 4.2 million. It has allowed T-Mobile to offer a compelling alternative to fixed broadband, but its service comes with the caveat that speeds will fluctuate depending on demand.
The extra capacity offered by mmWave could help to offer a faster, more consistent connection, making it even more appealing. However, the propagation challenges of mmWave spectrum means customers will have to ensure their FWA hub is sitting on the right shelf or window sill to establish a fast, reliable connection. Addressing complaints as customers struggle to put their hub in the right spot may be a problem for the Un-carrier.
Editor’s Note:
The NTIA will study the following bands in the next two years, noting that the spectrum could support a range of uses, including mobile broadband (IMT), drones and satellite operations:
- 3.1 GHz-3.45 GHz
- 5.03 GHz-5.091 GHz
- 7.125 GHz-8.4 GHz
- 18.1 GHz-18.6 GHz
- 37.0 GHz-37.6 GHz
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/network/t-mobile-revs-up-millimeter-wave-with-5g-standalone
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-achieves-upload-speeds-surpassing-1-gbps
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/t-mobile-finally-puts-mmwave-to-work-in-5g-sa-network
https://www.telecoms.com/wireless-networking/t-mobile-network-speeds-still-way-ahead-of-verizon-at-t
U.S. Launches National Spectrum Strategy and Industry Reacts
Ericsson Mobility Report touts “5G SA opportunities”
State of 5G SA:
“It’s been exciting to see the industry evolve in the last decade or so, and see first-hand the massive growth of 4G and the arrival of 5G,” said Fredrik Jejdling Executive Vice President and Head of Business Area Networks and Publisher of Ericsson Mobility Report.
The latest edition of Ericsson’s Mobility Report opens with the assertion that “5G standalone brings new opportunities,” which sounds promising, but there’s nothing in the report which shows what those opportunities are.
Ericsson says that 40 service providers have deployed or launched 5G SA in public networks, which agrees with Analysys Mason’s findings. To put that in context, around 280 service providers globally have launched commercial 5G with the overwhelming being 5G NSA.

Dell’Oro counted just seven 5G SA launches to date in 2023, while the GSA – which worked with Ericsson on the stats for its Mobility Report – shared data that also showed little growth in 5G SA this year.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- 1. 6 bn Global 5G mobile subscriptions are projected to reach 1.6 billion by the end of 2023.
- 30% 5G mid-band population coverage outside mainland China has increased from 10 percent in 2022 to around 30 percent at the end of 2023.
- 56 GB Global mobile data traffic consumption per smartphone is expected to reach 56 GB per month at the end of 2029.
Ericsson predicts that there will be 1.6 billion 5G subs in the world by the end of this year, or 18% of all mobile subscriptions, driven by North America, where 5G penetration will reach 61%. As recently as June, the network equipment vendor forecast that the year-end 5G total would hit 1.5 billion, so clearly the market is increasing faster than expected. In the third quarter there were 163 million 5G subscriber additions taking the total to 1.4 billion by the end of September. As such, the year-end target look eminently achievable.
Ericsson puts total global 5G subscriptions at 5.3 billion by the end of 2029, by which date 5G network coverage should reach 85% of the population, up from 45% at the end of this year.
“With more than 600 million 5G subscriptions added globally this year, and rising in every region, it is evident that the demand for high performance connectivity is strong,” said Fredrik Jejdling, Executive Vice President and Head of Networks, at Ericsson. “The roll-out out of 5G continues and we see an increasing number of 5G standalone networks being deployed, bringing opportunities to support new and more demanding applications for both consumers and enterprises,” he added.
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/5g-subs-exceed-expectations-but-they-re-not-standing-alone
Analysys Mason: 40 operational 5G SA networks worldwide; Sub-Sahara Africa dominates new launches
GSA 5G SA Core Network Update Report
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market has lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017
MTN Group and NEC XON deploy Africa’s first 400G optical transponder using TIP’s Phoenix
NEC Corporation and MTN Group have successfully deployed Africa’s first 400G optical transponder solution using “Phoenix.” This initiative marks a significant milestone for the telecommunications industry in Africa, with the potential to revolutionize the way optical networks are built and operated, thereby transforming internet delivery across the continent.
Phoenix is part of the Telecom Infra Project’s (TIP) Open Optical and Packet Transport (OOPT) project group, a collaborative effort involving multiple telecom operators and technology providers. Phoenix is a network device, known as a white box L0/L1 transponder, that can transmit data at speeds of up to 400 gigabits per second. The solution has met TIP’s rigorous test requirements, earning it a Controlled Environment Silver Badge, indicative of its readiness for deployment. Its disaggregated nature allows it to be programmed to run any vendor’s software, offering operators unprecedented flexibility in hardware and software selection. This disaggregation leads to cost reductions, accelerates innovation, and enables quicker and easier deployment of new network services.
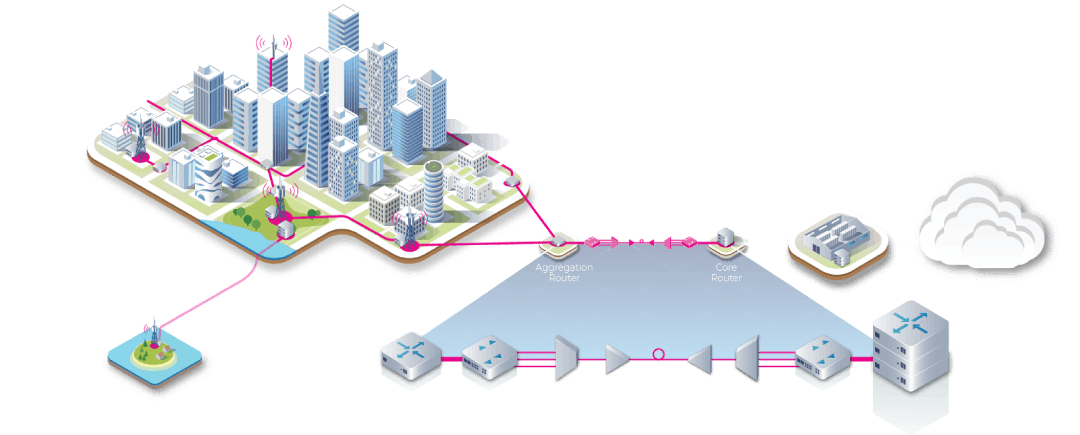
Image Credit: Telecom Infra Project
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“We are thrilled to receive the Silver Badge recognition from TIP, acknowledging our commitment to promoting open and disaggregated solutions with the Phoenix optical transponder,” said Sou Satou, Senior Director of the Network Solutions Business Division at NEC Corporation. “Our dedication to TIP and the development of open products in the optical transport market remains a top priority for NEC,” she added.
The deployment of Phoenix is designed to accelerate internet connectivity and optimise network operations, thereby democratising access to information. It aims to make affordable internet more widely available across Africa, fulfilling a critical societal need.
Demonstrating its commitment to innovation, MTN has embraced this state-of-the-art technology, integrating it into its production network, specifically across its optical network between Johannesburg and Centurion in South Africa, further demonstrating the technology’s interoperability and backwards compatibility.
“The deployment of Phoenix with NEC Corporation is a significant step toward fulfilling a crucial promise to our customers, to deliver accessible, reliable, and fast internet,” said Amith Maharaj, Executive – Network Design and Planning. “This initiative is part of our ongoing efforts to embrace the latest technologies available that ultimately empower communities across Africa,” he added.
“Disaggregation is the future of networking, and we are proud to be at the forefront of this evolution,” said Anthony Laing, General Manager of Networking at NEC XON. “Through our partnership with MTN, we’ve established NEC XON as a trusted leader in disaggregated networking.”
By leading in the adoption of Phoenix, NEC Corporation and MTN Group are setting a precedent for telecom operators worldwide, offering a scalable and cost-efficient solution that meets the burgeoning demands of a digitally connected society.
This initiative marks a significant milestone for the telecommunications industry in Africa, the companies say, with the potential to revolutionize the way optical networks are built and operated. By leading this initiative, MTN believes it is ultimately helping customers with improved, cost-effective connectivity.
About MTN:
MTN is Africa’s largest mobile network operator, providing voice, data, fintech, digital, enterprise, wholesale and API services to more than 292 million customers in 19 markets.
About NEC XON:
NEC XON is a leading pan-African ICT-systems integrator, specializing in cutting-edge Communications, Enterprise and Retail, Infrastructure and Energy, and Safety and Security solutions. Operating in 54 African countries and with a strong presence in 16 of them, NEC XON has established regional headquarters in South, East, and West Africa.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://telecominfraproject.com/oopt/
Bell and FirstLight: 3 new wavelength routes with triple redundancy and speeds up to 400G b/sec
China Mobile to deploy 400G QPSK by the end of 2023
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport market to hit $17B by 2027; Lumen Technologies 400G wavelength market
Heavy Reading: Coherent Optics for 400G transport and 100G metro edge
Cignal AI: NA Optical Network Spending to Accelerate; IEEE 802.3ct; NeoPhotonics 400G Multi-Rate Transceiver