5G Market Status
GSM 5G-Market Snapshot Highlights – July 2023 (includes 5G SA status)
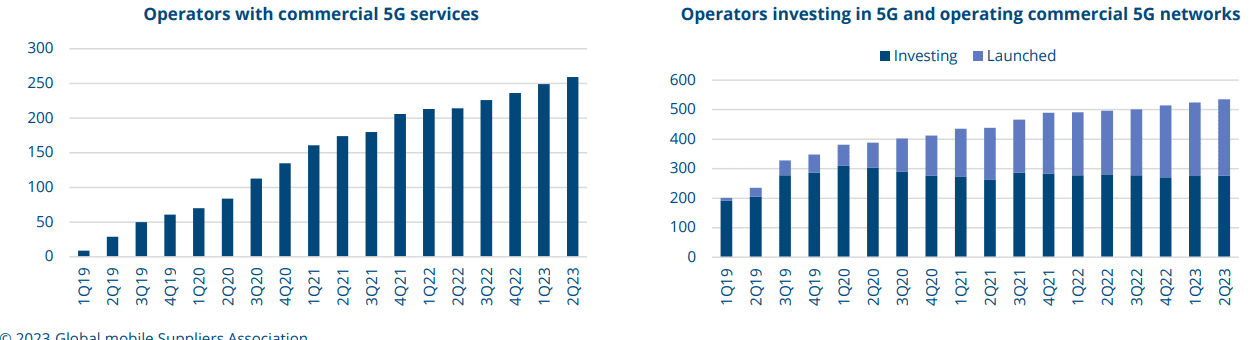
By the end of June 2023, GSA had identified 535 network operators in 162 countries and territories were investing in 5G, including trials, acquisition of licences, planning, network deployment and launches.
This number excludes nearly 200 additional companies awarded priority access licences in the U.S. auction of CBRS spectrum, which could potentially be used for 5G
Of those, a total of 259 operators in 102 countries and territories had launched one or more 3GPP-compliant 5G services 252 operators in 100 countries and territories had launched 5G mobile services 113 operators in 62 countries and territories had launched 3GPP-compliant 5G fixed wireless access services (just over 43% of those with launched 5G services)
13 operators had announced soft launches of their 5G networks that are not counted in the above launch figures 115 operators are identified as investing in 5G standalone (including those evaluating/testing, piloting, planning and deploying, as well as those that have launched 5G standalone networks).
GSA has catalogued 41 operators as having deployed or launched 5G standalone (SA) in public networks.
115 network operators are identified as investing in standalone 5G (including those evaluating, testing, piloting, planning and deploying as well as those that have launched standalone 5G networks).
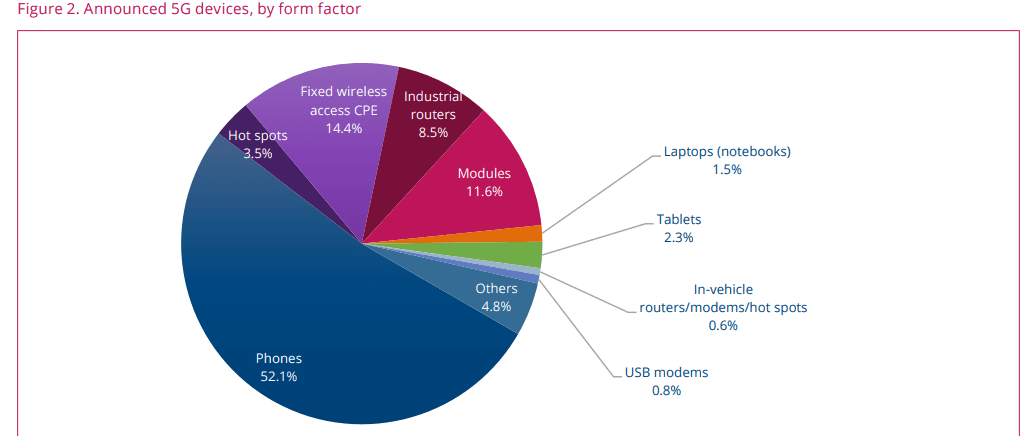
GSA has catalogued 2,039 announced 5G devices, up by more than 62% from 1,257 at the start of 2022 GSA has identified 1,083 announced 5G phones, up more than 76% from 613 at the start of 2022
There are at least 1,650 commercially available 5G devices, up more than 66% annually from 990
References:
GSA: 5G Device Ecosystem June 2023 Summary
GSA FWA Report: 38 commercially launched 5G FWA networks in the EU; Speeds revealed
Malaysia’s Maxis agreement with DNB to provide nationwide 5G services
Malaysian telco Maxis executed a 5G access agreement with state-run network operator Digital Nasional (DNB), according to local press reports.
Maxis said it will seek its shareholders’ approval for the execution of the agreement, at an extraordinary general meeting to be carried out in the third quarter. If the agreement is approved, Maxis will become the last of the country’s mobile operators to agree to execute the 5G access agreement with DNB.
Telekom Malaysia, CelcomDigi, YTL Communications and U Mobile have all agreed to the wholesale access agreement with the state-run network operator.
“DNB remains the single neutral wholesale network provider to undertake the deployment of 5G infrastructure and network nationwide as at the latest practicable date. Therefore, the entry into the access agreement with DNB will enable Maxis to provide the 5G services to its customers,” the company said in a filing to the local stock exchange.
The filing also indicated the price to be paid by Maxis to execute the agreement is yet to be determined and may be subject to periodic reviews conducted by the Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission as well as a by DNB.

DNB was set up by the Malaysian government in 2021 as a special purpose vehicle to develop the country’s 5G network infrastructure, which private telecommunications firms would use to offer 5G services to their customers.
However, Malaysia’s 5G roll-out by DNB had raised concerns over pricing and transparency, as well as worries that a single state-run 5G network would result in a nationalized monopoly.
Due to these concerns, the new prime minister, Anwar Ibrahim, had previously announced an overall review of the rollout of the national 5G network due to the lack of transparency. In May, the government announced it will enable the deployment of a second 5G network in 2024, adding that a new entity will be created to manage Malaysia’s second 5G network.
Malaysia’s Communications and Digital Minister Fahmi Fadzil recently said that DNB will continue to roll out 5G network infrastructure in the country until 80% coverage is achieved by the end of this year. The Malaysian government also confirmed that DNB will be taken over by a private entity once it achieves its 5G population coverage target.

Grand View Research: 5G New Radio Market to be Worth $251.37B by 2030
The global 5G New Radio (5G NR) market size is expected to reach $251.37 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 29.1% from 2023 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc.
The market research firm says the 5G New Radio (NR) market is being driven by a number of factors, including the increasing demand for high-speed and low-latency connectivity, the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications, and the increasing adoption of cloud-based technologies.
Additionally, the need for faster and more reliable communication networks to support emerging applications such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality and virtual reality, and remote healthcare is also driving the growth of the 5G New Radio market.
Key Industry Insights & Findings from the report:
- The hardware segment dominated the market in 2022 owing to the growing need for sophisticated radio units like as massive MIMO and beamforming, which provide higher coverage and capacity while also assisting in resource optimization, is a crucial element driving the segment growth.
- The Sub-6 GHz segment dominated the market in 2022 owing to Sub-6 GHz spectrum bands ability to provide a strong combination of coverage and capacity, making them suited for offering high-speed connection to large numbers of users, is a primary driver driving sector expansion.
- The Standalone (SA) segment is projected to expand at the highest CAGR owing to the advantages over Non-Standalone (NSA), including faster network performance and lower latency.
- The Ultra-reliable Low-latency Communications (URLLC) segment is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period. The growing need for mission-critical applications requiring high reliability and low latency is propelling the URLLC segment in the 5G New Radio (NR) market.
- However, neither the current 3GPP specs or ITU-R M.2150 standards meet the URLLC performance requirements in ITU-R M.2410. That is because 3GPP Release 16 URLLC in the RAN has yet to be completed and performance tested.
- The manufacturing segment is projected to expand at the highest CAGR over the forecast period. The potential of 5G NR technology to provide real-time monitoring and management of industrial processes, which leads to higher efficiency and productivity, is a key element influencing the segment growth.
- Asia Pacific dominated the regional market in 2022. The region has a sizable population and a rising number of mobile customers, which is fueling demand for innovative apps and high-speed internet services.
Industry Insights:
The telecom and IT segment dominated the market in 2022 and accounted for more than 30.0% share of the global revenue. The growing adoption of cloud-native technologies, which allow operators to virtualize network functions and deploy them on cloud infrastructure, is a significant factor contributing to segment growth. With the increased speed, bandwidth, and capacity of 5G, telecommunication companies can offer faster and more reliable mobile connectivity to their customers, enabling new applications and services that were not possible with previous generations of wireless technology. This includes things like virtual and augmented reality, high-definition video streaming, and real-time gaming. Additionally, 5G networks are highly customizable, allowing telecommunication and IT companies to tailor their services to meet the specific needs of different industries and use cases.
 To learn more about this report, request a free sample copy
To learn more about this report, request a free sample copy
The manufacturing segment is projected to expand at the highest CAGR over the forecast period. The ability of 5G NR technology to enable real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes, leading to greater efficiency and productivity is a significant factor contributing to the segment growth. For instance, 5G NR can facilitate the use of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) sensors and devices, which can provide real-time data on machine performance, production line throughput, and other critical metrics. This data can be used to optimize processes, reduce downtime, and improve quality control. Additionally, 5G NR can enable remote access and control of manufacturing equipment, allowing for greater flexibility and responsiveness in managing production processes. These benefits can lead to increased profitability and competitiveness for manufacturers, driving the adoption of 5G NR solutions in the manufacturing industry.
Regional Insights:
The Asia Pacific region dominated the market in 2022 and accounted for more than 38.0% share of the global revenue. The increasing adoption of 5G technology in countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India is a major factor contributing to the regional growth. The region has a large population and a growing number of mobile subscribers, which is driving the demand for high-speed internet services and advanced applications. The governments in these countries are also investing heavily in the development of 5G infrastructure, which is expected to provide significant opportunities for telecom companies and network equipment providers in the region. Additionally, the region is witnessing a significant increase in the use of smartphones and other mobile devices, which is driving the demand for 5G-enabled devices and services.
 To learn more about this report, request a free sample copy
To learn more about this report, request a free sample copy
The North America region is projected to expand at the highest CAGR over the forecast period. Significant investment is being made in the development and implementation of 5G infrastructure in the area, owing to the growing demand for high-speed internet access, IoT applications, and cloud services. Furthermore, the use of technologies such as artificial intelligence, edge computing, and big data analytics is increasing, which is pushing the demand for high-performance 5G networks. Collaborations between telecom firms and technological behemoths to build and implement 5G networks and services are also developing in the area. In addition, the area has been an early user of 5G-enabled smartphones and other gadgets, which is projected to boost market development in the future years. Furthermore, the region has been an early adopter of 5G-enabled smartphones and other devices, which is expected to further drive the growth of the market in the coming years.
Key Companies & Market Share Insights:
Leading industry players are investing heavily in R&D to expand their product lines, which will help the 5G New Radio (NR) market thrive. Participants in the market are also expanding their global presence through a variety of strategic initiatives such as new product launches, collaborations, mergers and acquisitions, and cooperation. For instance, in February 2023, Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, a telecommunication technology company, introduced new 5G indoor radio equipment and software to offer corporate use cases and monetization potential. Additionally, the telecom equipment manufacturer unveiled ten new radio devices spanning RAN and Transport to expand its range, with the goal of reaching net zero emissions in networks.Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson has also introduced the IRU 8850 radio for single or multi-operator deployment in medium to large venues such as airports, workplaces, and stadiums. The system can service up to eight venues from a single centralized site, with a 10km fiber reach.
Competitors in the 5G New Radio (NR) industry must provide cost-effective solutions in order to thrive and grow in a more competitive and evolving market environment. In the market, many companies are forming partnerships and working together with other market participants. They may take use of one other’s skills and resources in this way, giving their clients more comprehensive and integrated solutions. In order to expand into new areas and attract more customers, businesses are also expanding their geographical presence. Collaborations with regional players, investments in network infrastructure, and targeted marketing initiatives are all options. Some of the prominent players in the global 5G New Radio market include:
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Samsung
- Intel Corporation
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Fujitsu
- NEC Corporation
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- Keysight Technologies
5G New Radio Market Report Scope:
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size value in 2023 | USD 42.16 billion |
| Revenue forecast in 2030 | USD 251.37 billion |
| Growth rate | CAGR of 29.1% from 2023 to 2030 |
| Base year of estimation | 2022 |
| Historical data | 2019 – 2021 |
| Forecast period | 2023 – 2030 |
| Quantitative units | Revenue in USD billion, and CAGR from 2023 to 2030 |
| Report coverage | Revenue forecast, company market share, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Segments covered | Offering, operating frequency, architecture, application, industry, region |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Country scope | U.S.; Canada; UK; Germany; Spain; China; India; Japan; South Korea; Australia; Brazil; Mexico; Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA); UAE; South Africa . |
| Key companies profiled | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.; Qualcomm Technologies, Inc; Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson; Samsung; Intel Corporation; Cisco Systems Inc.; Fujitsu; NEC Corporation; Verizon Communications Inc.; Keysight Technologies. |
| Customization scope | Free report customization (equivalent to up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope |
| Pricing and purchase options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
References:
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/5g-new-radio-nr-market-report
Omdia forecasts weaker 5G market growth in near term, 4G to remain dominant
GSA: 5G Device Ecosystem June 2023 Summary
Highlights:
- The number of announced 5G devices rose by 1.2% between April and May 2023, reaching a total of 1,965 devices. Of these, 1,579 are understood to be commercially available, representing 80.4% of all announced 5G devices. This is an increase of 48.7% in the number of commercial 5G devices since the end of May 2022. Highlights this edition include:
- 233 manufacturers with announced available or forthcoming 5G devices
1,965 announced devices, of which at least 1,579 are understood to be commercially available
Not all devices are available immediately and specification details remain limited for some. We expect devices to continue to become more widely available and for more information about announced devices to emerge as they reach the market. - The number of commercially available devices has been growing steadily since the start of the year and should continue in this manner. GSA will continue to track and report on 5G device launches during the coming year. Its GAMBoD database contains important details about device form factors, features and support for spectrum bands. Summary statistics are released in this regular monthly publication.
By the end of May 2023, GSA had identified:
• 26 announced form factors
• 233 manufacturers with announced available or forthcoming 5G devices
• 1,965 announced devices, including regional variants, but excluding operator-branded devices that are essentially rebadged
versions of other phones. Of these, at least 1,579 are understood to be commercially available:
• 1,024 phones (up 15 from April 2023), at least 942 of which are now commercially available (up 14 from April 2023)
• 283 fixed wireless access customer-premises equipment (CPE) devices for indoor and outdoor uses, at least 183 of which are
now commercially available
• 227 modules
• 167 industrial or enterprise routers, gateways or modems
• 68 battery-operated hot spots
• 46 tablets
• 29 laptops or notebooks
• 12 in-vehicle routers, modems or hot spots
• 15 USB terminals, dongles or modems
• 94 other devices, including drones, head-mounted displays, robots, TVs, cameras, femtocells/small cells, repeaters, vehicle
on-board units, keypads, a snap-on dongle/adapter, a switch, a vending machine and an encoder
• 1,063 announced devices with declared support for 5G standalone in sub-6 GHz bands, 864 of which are commercially available.
- Not all devices are available immediately and specification details remain limited for some. We expect devices to continue to become more widely available and for more information about announced devices to emerge as they reach the market.
- The number of commercially available devices has been growing steadily since the start of the year and should continue in this manner.
- GSA will continue to track and report on 5G device launches during the coming year. Its GAMBoD database contains important details about device form factors, features and support for spectrum bands. Summary statistics are released in this regular monthly publication.
References:
GSA FWA Report: 38 commercially launched 5G FWA networks in the EU; Speeds revealed
GSA: 200 global operators offer 5G services; only 20 (Dell’Oro says 13) have deployed 5G SA core network
GSA: 5G Market Snapshot – 5G networks, 5G devices, 5G SA status
Kearney’s “5G Readiness Index 2022” and How to Monetize 5G
A new report from management consultancy Kearney analyzes a year of 5G progress across 33 countries around the world. The Kearney “5G Readiness Index 2022” assesses 5G and how close countries are to realizing all the potential and benefits of widespread 5G in the context of the overall maturity of a country’s telecoms market and its socio-economic position. The report covers 33 countries, all of which had launched 5G by the third quarter of 2022. To be included, countries must have launched 5G by the fourth quarter of 2021.
“Europe is falling behind on 5G!” is a cry we heard at the latest Mobile World Congress. The Kearney 5G Readiness Index 2021 reflected it, and our 2022 Index confirms it, at least for now (see Figure 1).

11 out of 28 countries tracked have at least one operator with a standalone 5G core network launched. Asia leads with seven countries, while Europe trails with just Finland and Germany reaching this point. Only in two countries have all operators launched standalone cores—Singapore and China—opening up their markets for a 5G transformation.
This year’s Index reveals that only 10 countries have made high band spectrum available, and operators in just five of them (the United States, Australia, South Korea, Thailand, and Japan) have launched full commercial services within it. So far, no European countries have gotten this far, although select services have been launched on limited mmWave licenses, including in Germany. The lack of availability of mmWave spectrum is disappointing because its advantages are the cornerstone of new, high speed 5G-enabled services.
The Index identified more key developments during the past year:
- The United States continues to push ahead of other countries. Its regulator has provided spectrum in all three band classes, and national operators have made the most of it by launching services. One operator has launched a standalone 5G core. Canada also has an operator offering 5G services via its new standalone core.
- South Korea, which ranked second in the 2021 Index, has dropped to fifth because it has not made low band spectrum available, despite high subscriber penetration.
- Most Nordic countries are pulling ahead, thanks to wider spectrum availability and broader deployment across bands, but Sweden is held back by the lack of mmWave spectrum as full availability of 26 GHz isn’t planned before 2025. This slows Sweden down and risks muting consumer excitement.
- Germany moved from laggard to leader of the EU4 (France, Germany, Italy, and Spain) plus the United Kingdom, thanks to operators launching 5G in multiple bands. Only one operator has launched a 5G standalone core.
- France now trails other larger European countries because of its late launch of 5G (November 2020) and customers’ apparent limited interest in it.
- A strong showing in the Middle East (Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Qatar) is a testament to their networks’ quality and strong rollouts. Penetration is 9 to 11 percent. A Saudi operator has launched a standalone 5G core.
- Australia was one of the first countries to launch 5G, has continuously expanded spectrum access across all bands, and enjoys successful commercialization. It has 18 percent 5G penetration, the second highest in the Index.
Kearney also uncovered the following findings:
- Take-up (as a percentage of total subscribers in the first quarter, 2022) is paltry across Europe. Switzerland is the best with 13 percent but launched in April 2019. Belgium is the worst offender at 1.7 percent of connections. Take-up is 31 percent in South Korea.
- In South Korea, the government has announced a push for creating an ecosystem of companies that innovate and leverage 5G (aiming for 1,800 5G service firms by 2026). They understand operators won’t be solo drivers but enablers.
- Rollout of new capacity in the United States allows operators to launch impactful services, such as 5G fixed wireless access (FWA). One operator is using
- 5G to equip ambulances with high-quality video feeds that medical professionals can view while patients are en route.
Europe is behind, but not irreparably so. Vigilance and focus are required, together with operators’ preparation to win with 5G when their countries have reached ready status.
Monetize 5G step-by-step, building up to an ecosystem of products, services, and partners:

Currently, 5G lacks killer uses cases to drive customer uptake. Without seductive 5G products or services, people won’t see its benefits. Yet, operators wonder whether advancing investment in 5G is wise. It’s classic chicken-and-egg, but it will start somewhere, spearheaded by first-mover operators along with third-party providers that will figure out what will make everyone want 5G. Plan monetization first with small steps, and then plan the ecosystem to realize its potential.
It still may seem like early days in the 5G journey, but time grows shorter for European telcos to catch up with the United States and other markets. Getting your strategy rolling now is the only way to take advantage of the European market when it becomes fully 5G ready.
References:
Ericsson Mobility Report: 5G monetization depends on network performance
Moody’s skeptical on 5G monetization; Heavy Reading: hyperscalers role in MEC and telecom infrastructure
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
PwC report on Monetizing 5G should be a wake up call to network operators!
How 5G network operators can stay competitive and grow their business
UScellular Launches 5G Mid-Band Network in parts of 10 states
UScellular today announced the launch of its 5G mid-band network, with customers in parts of 10 states who now have access to the benefits of the company’s faster and stronger network. UScellular’s 5G mid-band technology combined with a mid-band enabled device can provide up to 10x faster speeds than its 4G LTE network and low-band 5G. This technology has more capacity, enhances the mobile experience, and has business and fixed wireless applications.
By the end of June, UScellular’s 5G mid-band network will be available mainly in parts of Illinois, Iowa and Wisconsin, including sections of Rockford, Ill., Des Moines, Iowa and Milwaukee. Communities in Maine, Missouri, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Oregon, Virginia and Washington are also included in the initial rollout. By the end of the year, the company plans to cover more than 1 million households in its operating footprint with its 5G mid-band network. The company is using 5G network equipment from Nokia and Ericsson.
“We view mid-band as the sweet spot of 5G because it provides broad coverage, low latency and fast speeds – enabling more people to connect to what matters most at home or on-the-go,” said Mike Irizarry, executive vice president and chief technology officer for UScellular. “As we approach serving 100,000 High-Speed Internet customers later this summer, mid-band will play an important role in furthering the reach and enhancement of that product. We’ve made it a priority to expand the technology to more communities in the coming years.”
Broader 5G coverage (see map) with mid-band technology provides customers and businesses with even faster data connection speeds for a better experience. UScellular will continue to expand its device portfolio, including adding more options for its High-Speed Internet product and additional IoT devices, to further enhance its mobile and fixed connectivity offerings.
UScellular now offers customers low-band, mid-band and high-band mmWave 5G speeds and services. The company expects nearly 3 million households in its operating footprint will have access to 5G mid-band connectivity by the end of 2024.
UScellular’s 5G mid-band network is using 3.45 GHz spectrum that was purchased through Auction 110 granted in 2022. The company is partnering with Nokia and Ericsson for its mid-band buildout. The company was among the top five bidders in the FCC’s 3.45 GHz Auction 110, where it spent over $579 million. It also acquired C-band spectrum for about $1.46 billion in 2021; that spectrum starts to become available later this year.

UScellular did not need to coordinate with the Department of Defense (DoD) for the 3.45 GHz sites that are part of this launch, but DoD coordination is needed for some sites that are to be deployed in the future, according to a company spokesperson.
Speaking at the Wireless Infrastructure Association’s Connect(X) conference in New Orleans last month, Irizarry said the company expects a “rapid acceleration” of its mid-band spectrum 5G deployment to occur in 2024.
About UScellular:
UScellular is the fourth-largest full-service wireless carrier in the United States, providing national network coverage and industry-leading innovations designed to help customers stay connected to the things that matter most. The Chicago-based carrier provides a strong, reliable network supported by the latest technology and offers a wide range of communication services that enhance consumers’ lives, increase the competitiveness of local businesses and improve the efficiency of government operations.
Through its After School Access Project, the company has pledged to provide hotspots and service to help up to 50,000 youth connect to reliable internet. Additionally, UScellular has price protected all of its plans, promising not to increase prices through at least the end of 2024.
To learn more about UScellular, visit one of its retail stores or www.uscellular.com.
References:
https://www.uscellular.com/coverage-map
https://www.fiercewireless.com/5g/uscellular-lights-345-ghz-parts-10-states
US Cellular touts 5G millimeter wave and cell tower agreement with Dish Network
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
The number of 5G subscriptions will surge from 934 million in 2022 to 3.1 billion in 2027 -a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 27% – according to a study from ABI Research. Further, 5G traffic is forecast to increase from 293 Exabytes (EB) in 2022 to 2,515 EB in 2027, at a CAGR of 54%.
ABI’s forecast is largely based on an increase in 5G Core (5GC) networks. To date, more than 35 5GC networks are operating in 5G standalone (SA) mode. 5GC is expected to lead to a growth in devices connected to the network and the traffic routed through it.
“5GC holds potential for operators to monetize further existing cellular connectivity for traditional mobile broadband (MBB) use cases but also offers scope for operators to expand cellular capabilities in new domains. Additionally, 5GC also offers innovation potential for committed telcos to establish new operating models for growth outside of the consumer domain,” explains Don Alusha, Senior Analyst, 5G Core and Edge Networks, at ABI Research.
5GC presents Communications Service Providers (CSPs) with a fluid and dynamic landscape. In this landscape, there is no static offering (requirements constantly change), no uniform offering (one shoe does not fit all), and no singular endpoint (one terminal with multiple applications). 5GC guides the industry into edge deployments and topologies. CSPs step out of the four walls of either their virtual Data Center (DC) or physical DC to place network functionality and compute as close to their customers as possible. This constitutes decentralization, a horizontal spread of network assets and technology estate that calls for a ‘spread’ in the operating model.
The shift from a centralized business (e.g. with 4G EPC) to a decentralized business (5G SA core network) stands to be a significant trend in the coming years for the telecoms industry. Against that backdrop, the market will demand that CSPs learn to drive value bottom-up. “What customers need” is the starting point for companies like AT&T, BT, Deutsche Telekom, Orange, and Vodafone. In other words, in this emerging landscape, there will be enterprise-specific, value-based, and niche engagements where the business strategy sets the technology agenda. So, it is rational to conclude that a “bottom-up” approach may be required to deliver unique value and expand business scope. That said, CSPs may be better equipped to drive sustained value creation if they learn to build their value proposition, starting from enterprise and industrial edge and extending to core networks.
“A 5G cloud packet core can potentially unlock new transactions that supplement existing volume-centered modus operandi with a local, bottom-up value play for discrete engagements. But the power of a bottom-up model is not enough. To monetize a 5G cloud packet core at scale, some of the existing top-down intelligence is needed too. Learning how to operate in this hybrid top-down and the emerging bottom-up, horizontally stratified ecosystem is a journey for NTT Docomo, Rakuten Mobile, Singtel, Softbank, and Telstra, among other CSPs. In the impending cellular market, an effective and efficient operating model must contain both control and lack of control, both centralization and decentralization and a hybrid of bottom-up plus some of the ‘standard’ top-down intelligence. The idea is that CSPs’ operating model should flexibly fit and change in line with new growing market requirements, or new growth forays may hit a roadblock,” Alusha concludes.
Editor’s Note:
It’s critically important to understand that the 3GPP defined 5G core network protocols and network interfaces enable the entire mobile system. Those include call and session control, mobility management, service provisioning, etc. Moreover, the 3GPP defined 5G features can ONLY be realized with a 5G SA core network. Those include: Network Automation, Network Function Virtualization, 5G Security, Network Slicing, Edge Computing (MEC), Policy Control, Network Data Analytics, etc
Figure 1: Overview of the 5G system
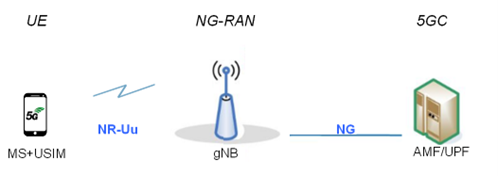
The 5GC architecture relies on a “Service-Based Architecture” (SBA) framework, where the architecture elements are defined in terms of “Network Functions” (NFs) rather than by “traditional” Network Entities. Via interfaces of a common framework, any given NF offers its services to all the other authorized NFs and/or to any “consumers” that are permitted to make use of these provided services. Such an SBA approach offers modularity and reusability.
Figure 2: 5G SA Core Network Architecture
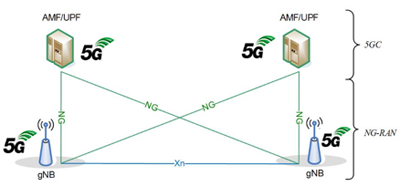
The 5G SA architecture can be seen as the “full 5G deployment,” not needing any part of a 4G network to operate.
Finally, 3GPP has not liased their 5G system architecture specifications to ITU-T so there are no ITU-T standards for 5G SA Core Network or any other 5G non-radio specification. Instead, 3GPP sends their specs to ETSI which rubber stamps them as “ETSI standards.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
These findings are from ABI Research’s 5G Core Market Status and Migration Analysis report. This report is part of the company’s 5G Core & Edge Networks research service, which includes research, data, and analyst insights. Based on extensive primary interviews, Application Analysis reports present an in-depth analysis of key market trends and factors for a specific technology.
About ABI Research
ABI Research is a global technology intelligence firm delivering actionable research and strategic guidance to technology leaders, innovators, and decision makers around the world. Our research focuses on the transformative technologies that are dramatically reshaping industries, economies, and workforces today.
References:
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/5g-system-overview#
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core/5g-core/
A few key 3GPP Technical Specifications (TSs) are listed here:
- TS 22.261, “Service requirements for the 5G system”.
- TS 23.501, “System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 23.502 “Procedures for the 5G System (5GS)
- TS 32.240 “Charging management; Charging architecture and principles”.
- TS 24.501 “Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3”
- TS 38.300 “NR; NR and NG-RAN Overall description; Stage-2”
Vodafone Idea (Vi) to launch 5G services “soon;” Awards optical network equipment contract to ZTE
Hindustan Times: Although India telco competitors Reliance Jio and Airtel have launched and made fully operational their 5G services in several regions, the Aditya Birla Group and Vodafone Group collaboration telco is yet to announce the launch of next generation service. However, Kumar Mangalam Birla, chairman of the Aditya Birla Group, indicated that the Vi will soon launch 5G services. Speaking on the side-lines of the AIMA Awards to CNBC -TV18, Birla said, “5G rollout will begin soon.” He did not, however, provide a specific launch date.
Kumar Mangalam Birla is chairman of Aditya Birla Group.(YouTube/@IIT Bombay Official Channel)
Vi is now lagging far behind in the race to 5G with being the only private telecom operator to not have this next-gen services. In October of last year, Bharti Airtel launched its Airtel 5G Plus service in select areas. Reliance Jio, its competitor, is also offering Jio True 5G in multiple locations. The state-owned telecom operator BSNL is also planning to launch 5G by this August.
Vodafone Idea has been losing subscribers. The debt-ridden telco lost 2.47 million subscribers in December 2022. During the same period, Mukesh Ambani-led Reliance Jio gained 1.7 million subscribers, followed by Airtel, which gained 1.52 million subscribers, reported Business Insider.
Airtel, like its rival Reliance Jio, is offering 5G services at the same tariff levels as 4G, luring users away from competitors, primarily Vodafone Idea. According to data from the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India, the number of porting requests increased over the last year to more than 12 million in November.
References:
Communications Minister: India to be major telecom technology exporter in 3 years with its 4G/5G technology stack
Adani Group to launch private 5G network services in India this year
Hindu businessline: Indian telcos deployed 33,000 5G base stations in 2022
Nokia Executive: India to Have Fastest 5G Rollout in the World; 5Gi/LMLC Missing!
At long last: India enters 5G era as carriers spend $ billions but don’t support 5Gi
Bharti Airtel to launch 5G services in India this August; Reliance Jio to follow
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Vodafone Idea earlier this month awarded a fresh optical transmission equipment network order worth around Rs 230 crore to Chinese company ZTE for Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh-Chhattisgarh. The telco is upgrading its network, and for a fresh network deployment or upgrade and maintenance, telcos have to take approval from the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) and provide information regarding vendors and their technology. Notably, ZTE hasn’t been given the trusted sources approval by the NSCS (India’s National Security Council), said an ET report. Vodafone Idea’s optical transmission network has deployments from both Huawei and ZTE across all telecom circles.
Airtel, another Indian telecom operator, had last year awarded a telecom infrastructure expansion contract worth Rs 150 crore to Huawei. Under the deal, Huawei upgraded and expanded Airtel’s National Long Distance (NLD) network. Airtel awarded a similar contract to Huawei worth Rs 300 crore in 2021. Both these contracts were given to Huawei despite the latter not having the trusted sources approval.
PwC report on Monetizing 5G should be a wake up call to network operators!
A PwC report titled, “The challenge of monetizing 5G,” states that capital expenditures and operating expenses will likely be very high with the deployment of 5G standalone networks and their fully virtualized, cloud-native architectures. Yet returns have been anemic across all generations, ranging from 1.5% to 4.5% of return on assets.
PwC’s 26th Annual Global CEO Survey found that 46% of telco CEOs believe that if their companies continue on their current paths, their businesses would not be economically viable in 10 years.
Source: PwC
As 5G becomes an everyday reality for both investors and consumers, carriers are going to face increasing pressure on two fronts:
1. Improve return on assets
As capital markets and stakeholders begin to focus on investment returns in a high-inflation environment, there will be growing scrutiny on telcos and wireless carriers, especially in comparison to other capital-intensive investment opportunities. An exemplar cloud services provider (CSP) has demonstrated ROA of 17% to 20%+ over the past five years, which compares to the 2% to 3% ROA range of MNOs. The ROA of MNOs approximates that of regulated entities like utilities, which explains investor angst.
2. Deliver on demanding service-level agreements to support 5G “killer apps,” such as metaverse applications (really?)
Improving ROA is intrinsically tied to successfully managing the costs and revenues of 5G applications. Many operators face a growing clamor from application providers and up-stack players to create “metaverse-capable networks,” without much clarity on how application revenue will be shared with them. Network operators risk becoming trapped in a “give more, get less” scenario of providing pure-play connectivity, while up-stack companies monetize the 5G applications.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
For those who believe 5G FWA is the way to monetize 5G, PwC warned that’s not likely. The market research firm’s analysis showed FWA services could cost more than 22-times as much as mobile connectivity services. That’s due to costs associated with delivering data tied to specific latency or QoS service-level agreements (SLAs). Immersive and augmented experiences — such as virtual-reality apps, mobile metaverse and gaming — could cost three to four times as much. Network costs related to the Internet of Things (IoT) are even more challenging to estimate and track, primarily because of the extremely wide range of connected devices and applications available.
The report also found that FWA services could have up to 40-times less revenue potential. This is due to FWA services being price limited by competing fiber or cable internet options.
“Most FWA subscribers are willing to pay only as much as wireline plans cost, yet they expect a similar quality of service for internet connectivity,” the report notes.
PwC Partner Dan Hays explained during an interview with SDx Central at the MWC Barcelona 2023 event that operators should approach FWA and other alternative 5G connection services like IoT with reasonable financial and operational expectations. “Fixed-wireless access is a great way to fill out excess capacity, if you have it,” Hays said. “You see some of the carriers making that play.”
“It’s not a cure all by any means,” Hays said, explaining, “we look at it as not a business model but really a technology. It’s a technology choice that you can use.”
Hays said that operators are indeed being “really thoughtful” in managing capacity to serve FWA customers, but that can potentially run into a problem down the road where a particular site can no longer support a high-bandwidth FWA connection. “Do they fire you as a customer at some point,” he said.
In conclusion, PwC states:
Carriers will be increasingly challenged to demonstrate better returns on invested capital for massive 5G capital outlays, while simultaneously meeting the demanding service-level agreements of future 5G applications. Network costs are likely higher — and revenue potential is likely lower — than carriers understand for these applications. Critical strategies for improving ROA and monetizing 5G successfully involve accurately valuing network features, quantifying network costs and communicating them to all stakeholders, as well as improving 5G offer management, pricing and service evolution.
References:
https://www.pwc.com/us/en/tech-effect/emerging-tech/5g-monetization.html
GSMA Intelligence: 5G connections to double over the next two years; 30 countries to launch 5G in 2023
GSMA Intelligence forecasts 5G connections are expected to double over the next two years, expedited by technological innovations and new 5G network deployments in more than 30 countries in 2023. Of the new networks to be deployed in 2023, it is expected that 15 will be 5G Standalone (SA) networks. As of January 2023, there were 229 commercial 5G networks globally and over 700 5G smartphone models available to users.
GSMA Intelligence, announced its latest 5G forecast during MWC Barcelona 2023, point to a significant period of growth in terms of mobile subscribers and enterprise adoption. Consumer connections surpassed one billion at the end of 2022 and will increase to around 1.5 billion this year – before reaching two billion by the end 2025.
India will lead the 5G expansion globally in 2023, with the expansion of services from Airtel and Jio in 2023 expected to be pivotal to the region’s ongoing adoption. GSMA Intelligence predicts there will be four 5G networks in India by the end of 2025, accounting for 145 million additional users. With operators such as Jio announcing ambitions to connect as many as 100 million homes across India to its 5G FWA network, the number of FWA users looks likely to grow substantially over the next few years, the report added.

Growth will also come from key markets within APAC and LATAM, such as Brazil and India, which have recently launched 5G networks. India will be especially significant, with the expansion of services from Airtel and Jio in 2023 expected to be pivotal to the region’s ongoing adoption. GSMA Intelligence predicts there will be four 5G networks in India by the end of 2025, accounting for 145 million additional users.
Many of the new 5G markets scheduled to launch networks in 2023 are in developing regions across Africa – including Ethiopia and Ghana – and Asia. Today, 5G adoption in the sub-Saharan region sits below 1% but will reach over 4% by 2025 and 16% in 2030, largely thanks to a concerted effort from industry and government organizations to provide connectivity to citizens.
“Until now, 5G adoption has been driven by relatively mature markets and consumer use cases like enhanced mobile broadband, but that’s changing. We’re now entering a second wave for 5G that will see the technology engage a diverse set of new markets and audiences,” said Peter Jarich, Head of GSMA Intelligence. “The extension to new use cases and markets will challenge the mobile ecosystem to prove that 5G truly is flexible enough to meet these diverse demands in a way that’s both inclusive and innovative.”
The Rise of 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA):
As of January 2023, more than 90 FWA broadband service providers (the vast majority of which are mobile operators) had launched commercial 5G-based fixed wireless services across over 48 countries. This means around 40% of 5G commercial mobile launches worldwide currently include an FWA offering.
In the U.S., T-Mobile added over half a million 5G FWA customers in Q4 2021 and Q1 2022 combined. By 2025, it expects to have eight million FWA subscribers, while Verizon is targeting five million FWA subscribers for the same period. The conventional wisdom holds that FWA is primarily useful as a rural service, targeted mostly at the previously unserved or underserved. Verizon says their FWA service is primarily urban and suburban service with target customers that are dissatisfied with terrestrial broadband services. Verizon has increasingly come to view FWA as an integral part of their broadband access offering everywhere that FiOS isn’t available.
Reliance Jio (India) announced ambitions to connect as many as 100 million homes across India to its 5G FWA network, the number of FWA users looks likely to grow substantially over the next few years.
While the majority of current 5G FWA deployments focus on the 3.5–3.8 GHz bands, several operators around the world are already using 5G mmWave spectrum as a capacity and performance booster to complement coverage provided by lower bands.
Only 7% of 5G launches have been in 5G mmWave spectrum so far but this looks set to change given 27% of spectrum allocations and 35% of trials are already using 5G mmWave bands. Furthermore, in 2023 alone, the industry will see ten more countries assigned 5G mmWave spectrum for use – a significant increase from the 22 countries who have been assigned it to date. Spain received the first European 5G mmWave spectrum allocation this year, resulting in Telefónica, Ericsson and Qualcomm launching its first commercial 5G mmWave network at MWC Barcelona 2023.
Enterprise IoT Driving Growth:
The figures from GSMA Intelligence also suggest that, for operators, the enterprise market will be the main driver of 5G revenue growth over the next decade. Revenues from business customers already represent around 30% of total revenues on average for major operators, with further potential as enterprise digitization scales. Edge computing and IoT technology presents further opportunities for 5G, with 12% of operators having already launched private wireless solutions – a figure that will grow with a wider range of expected IoT deployments in 2023.
Another major development for the enterprise will be the commercial availability of 5G Advanced (3GPP Release 18) in 2025. Focusing on uplink technology, 5G Advanced will improve speed, coverage, mobility and power efficiency – and support a new wave of business opportunities. GSMA’s Network Transformation survey showed half of operators expect to support 5G Advanced commercial networks within two years of its launch. While this is likely optimistic, it presents the ecosystem with a clear opportunity to execute on.
Editor’s Note:
GSMA’s 5G forecast is a direct contradiction to Omdia’s which expects weaker 5G growth in the near term. Which forecast do you believe?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References: