5G SA/5G Core network
Deutsche Telekom launches 5G private campus network with Ericsson; Sovereign Cloud for Germany with Google in Spring 2022
Overview:
Ericsson and Deutsche Telekom have partnered to deliver a new 5G Standalone (5G SA) private campus network offering, aimed at on-site business communications infrastructure. The new campus network offering is based on a local 5G infrastructure that is exclusively available for the customer’s digital applications. The 5G SA technology works without LTE anchors (as in 5G NSA) and offers all the technical advantages of 5G – even for particularly demanding and safety-critical use cases: fast data transmission rates, maximum network capacity and highly reliable connectivity with low latency.
With the advanced 5G SA technology, Deutsche Telekom and Ericsson support companies from a wide range of industries in developing innovative digital applications and making existing processes more efficient.
The newly offered 5G SA Campus network – powered by the Ericsson Private 5G portfolio – operates completely separated from the public mobile network: all components of the infrastructure from the antennas to the standalone core network to the network server are located on the customer’s premises. This ensures that sensitive data remains exclusively within the local campus network. The local connection of the customer infrastructure also enables particularly simple and fast processing of data via the private network. This standalone 5G architecture of “short distances” is most suitable for supporting business-critical applications that require ultra-short response times in the millisecond range. The 5G SA network operates on frequencies in the 3.7 to 3.8 GHz range that are specifically allocated to the enterprise. Thus, up to 100 MHz bandwidth is available for the exclusive use within the private campus network.
The new 5G private campus network is being launched in Germany under the name “Campus-Netz Private” – and will be offered to business customers in other European countries.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Analysis: It is quite interesting that Deutsche Telekom chose Ericsson as it’s 5G SA Core network vendor, rather than hyper-scalers like Amazon AWS or Microsoft Azure who are building 5G SA core networks for Dish Network and AT&T respectively. Amazon also offers its own private 5G network directly to enterprise customers. So does Microsoft which offers Azure private multi-access edge compute. Earlier this year, Fierce Wireless reported that Google did NOT have a private 5G network offering, but was partnering with other companies to offer one.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Sidebar:
Deutsche Telekom’s T-Systems has partnered with Google Cloud to build and deliver sovereign cloud services to German enterprises, healthcare firms and the public. The two companies say that the goal of this sovereign cloud is to allow customers to host their sensitive workloads while still being able to leverage all the benefits of the public cloud, such as scalability and reliability. The launch of the new Sovereign Cloud for Germany will take place ahead of schedule: Telekom’s business customer arm T-Systems and Google Cloud are launching their new sovereign cloud service in spring 2022. It will be available for all clients, initially out of the Frankfurt Google Cloud Region. Telekom and Google confirmed that they will jointly drive innovation for the cloud, closely aligned with the new German government’s digital plans which aims to build a public administration cloud based on a multi-cloud strategy and open interfaces, as well as meeting strict sovereignty and transparency requirements. To this end, the partners are setting up a Co-Innovation Center in Munich as announced in November 2021. In addition, executive briefing facilities in Munich and one in Berlin will be established for close collaboration with customers.
“Many companies in Germany state that sovereignty matters to them when choosing their Cloud provider. This is particularly important for key sectors such as public, healthcare and automotive,” Höttges said. “That’s why we’re delighted to offer a Sovereign Cloud that addresses additional European compliance requirements.”
In this new joint offering, T-Systems will manage a set of sovereignty controls and measures, including encryption and identity management. In addition, T-Systems will exercise a control function over relevant parts of the German Google Cloud infrastructure. Any physical or virtual access to facilities in Germany (such as routine maintenance and upgrades) will be under the supervision of T-Systems and Google Cloud.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
5G SA Campus Network: Full Control & Flexible Deployment:
Customers can adapt their private 5G SA network flexibly according to their own requirements as well as manage it independently: Whether for real-time communication of robots in factories or for connecting automated vehicles on company premises. Customers can prioritize data traffic within their campus network for specific applications as needed.
The mobile network is administered on site via a cloud-based network management portal by the customer’s IT staff – for example, the administration of users, 5G modules and SIM cards to access the 5G-SA campus network or to the machine control system. The closed system is characterized by its particularly high data security and reliability: Due to the redundant architecture of the local core network, the 5G SA campus network continues to function reliably even in the event of an interruption to the cloud-based management portal.
Managed service by Deutsche Telekom:
If business customers decide to deploy their own 5G SA network, Deutsche Telekom analyzes with them the critical business applications and the requirements for the private mobile network. Due to the simplified local infrastructure, the network can be built from planning to the handover to the customer within just three months. Network equipment supplier Ericsson provides the required modern 5G SA technology, while Telekom takes on the planning, deployment, operation as well as maintenance and optimization. Telekom also provides the set-up and updates so that companies can focus on their core business.
“When it comes to digitalization, industry and SMEs need a reliable partner,” says Hagen Rickmann, Managing Director Business Customers at Telekom Deutschland GmbH. “Together with Ericsson, we help business customers in every industry to increase their productivity and exploit their full potential using 5G standalone technology.”
Arun Bansal, Executive Vice President and Head of Market Area Europe & Latin America at Ericsson says: “Deutsche Telekom and Ericsson share a long-standing partnership in innovation, technology and services. Together, we offer secure, reliable and high-performance network solutions tailored to the specific business needs of our customers.”

Image Credit: Deutsche Telekom
5G Campus Network Private – Available for testing on site:
Deutsche Telekom has already been offering campus network solutions for enterprises since the beginning of 2019 and by now operates more than ten of such local networks based on 5G non-standalone technology or LTE across Germany. With the new fully private 5G SA Campus network solution, the company is expanding its business customer offering with the next development stage of 5G. The new product is being launched in Germany from now on under the name “Campus-Netz Private” – and is also offered to business customers in further European countries. For interested customers, mobile Campus 5G SA test systems are available to test their own use cases on site.
Use Cases and Industry Verticals:
There is currently a huge drive to get private 5G networks onto factory floors for manufacturing. There are some interesting examples of using IoT technology, feeding information back via high speed wireless connections, and analyzing data with machine learning/AI tools to optimize operations and do new things like predictive maintenance. Ericsson touts several industry verticals as candidates for its 5G private network offerings: Airports, Energy Utilities, Airports, Mining, Manufacturing, Ports, Offshore and Processing.
The drive towards business 5G adoptions is reflected In Ericsson’s Q4 2021 financials, in which private networks for enterprise were cited as one of the key drivers of its 41% YoY jump in profit. Evidently, Ericsson and Deutsche Telekom see a lot of potential in private 5G for industrial applications.
References:
https://www.telekom.com/en/media/media-information/archive/new-5g-standalone-campus-networks-645348
https://telecoms.com/513200/dt-and-ericsson-launch-new-5g-sa-campus-offering/
Why are 5G SA Core networks taking so long to be commercially deployed?
by Tim Sylvester, Founder and CEO of Integrated Roadways, a smart infrastructure technology provider, with Alan J Weissberger (editor)
5G SA deployments have significantly lagged market expectations for the same reason that 5G NSA has been so rapidly deployed. 5G NSA uses existing 4G LTE signaling , core network, macro-site infrastructure, requiring only updates to its software and hardware at existing tower sites .
On the other hand, 5G SA requires a completely new Distributed Antenna System (DAS) architecture for microcell / nano or small cell deployments that need significant infrastructure with nontraditional requirements.
Unlike macro-cell deployments for 4G LTE, the position of the 5G SA millimeter wave antenna is not very negotiable – with a 5-mile service radius, a 4G LTE antenna can move considerable distances without significant changes to the service area, while a 5G millimeter wave antenna needs to be in exactly the correct spot to deliver service in a significantly smaller radius. The small cell size of 5G SA means that covering the same territory as a macro-site is essentially impossible, restricting deployments of 5G SA to dense urban areas and along highly trafficked interstate and highway routes.
5G SA requires a new core network infrastructure. Prior cell service models were iterations on technologies used in POTS and internet services that were ported to IP networks and only the final link mode changed from wired to wireless, with an emphasis on coverage area and bandwidth. But 5G SA is more than a new, higher-bandwidth link, incorporating new focuses on reliability and ultra-low latency for ehealth, autonomy, M2M services, augmented reality and other real-time or near-real time applications. This requires more than the wireless link improvements as it makes the easy “cloud” data abstraction obsolete, as these applications and databases physical storage location is relevant to maintaining reliability and ultra-low latency.
5G SA also promises network slicing, network function virtualization, cloud-native service management, distributed microservices at the edge, and software defined networking. Delivery of 5G SA has many more moving parts and stakeholders than 5G NSA and requires collaboration of many industries including automotive, tech, and health. It does not permit a monolithic delivery from a handful of parties. At the same time, the business models for ehealth, autonomy, AR, and other key 5G enabled applications are still unproven and in development, meaning that the carriers are expected to take input from many new parties and make investments in markets that are still at-risk.
Aside from the industry risks and complications, the property owners that will permit 5G SA delivery are not aligned to traditional cell service incentives or priorities. Delivering widespread millimeter wave antennas required for 5G SA networks through a DAS requires a utility or municipal license to attach equipment to each required attachment point, or development of countless private owner site leases to install antennas on private property adjacent to the desired service area. The private-owner approach is functional primarily in urban areas. It can’t be relied upon for primary delivery in non-urban interstate and highway routes that lack the necessary power and fiber drops, or in areas that traditionally only have longitudinal transmission or distribution lines, without further increasing costs to implement frequent new utility drops that service a single user. The outcome is existing approaches are very expensive and time consuming.
Regardless of FCC 1TMR requirements, municipalities and utilities are reluctant to give up that number of pole attachments and accept the visual and safety implications of accommodating that amount of visible equipment mounted overhead. These complications have resulted in permitting fees as high as $10K per antenna, as reported by Sprint in San Diego during early 5G trials (before being absorbed by T-Mobile), which makes the costs and complications of deploying infrastructure daunting to the extent of being nearly impossible. Even when tolerated, there’s no guarantee that existing poles are in the correct locations, which is why AT&T has been deploying its own utility poles to ensure they have attachment points where they need them.
There’s also the significant obstacle of locating distributed micro datacenter space proximate to the antenna attachment points as required to deploy the edge services that are natively required by 5G SA.
The hard to swallow reality for 5G deployment is public agencies are the easiest means to deploy the system, as it conceptually allows a single construction and operations contract per municipal area or interstate/highway route, instead of thousands of independently negotiated agreements with individual property owners. However, municipalities have no obligation to issue these permits, and the mandate for public works is to provide roadways and utility easements, with an institutional preference towards preserving aesthetics and limiting safety issues from overhead mounted hardware. Public agencies are responsible for roads, not responsible for delivering cell services, regardless of the desires of the cell companies. Municipal obligations are not aligned to the preferences of the 5G SA delivery industry, and there is no clear or obvious resolution available using the traditional network MSP approaches.
That said, solutions are readily available, despite their non-obvious nature and departure from traditional network MSP approaches. What the cell industry needs to deploy 5G SA widely is:
● An approach that aligns municipal incentives with 5G SA DAS needs by ensuring 5G SA deployments result in improvements to core urban infrastructure that is the obligation and primary concern of public agencies who are required to permit such improvements
● Leveraging delivery of those necessary infrastructure improvement needs alongside 5G SA capabilities in a “dig once” approach to streamline deployment and lower costs
● Incorporating the edge networking and 5G antenna delivery infrastructure into an invisible infrastructure delivery that does not occupy poles or other overhead assets
As with so many technology obstacles, the solution isn’t found within the technology itself, but found with a change in perspective and better understanding the needs of the stakeholders.
If there were a smart infrastructure technology firm that had the capacity to deploy 5G SA infrastructure as a byproduct of improving core urban infrastructure, hiding all of the antennas and edge networking assets, enabling the delivery of a fully virtualized, sliceable, edge-enabled but cloud-native open access network, the obstacles to 5G SA delivery would be resolved in a manner that is agreeable to the network MSPs, municipal authorities, utilities, and citizens.
Now that the needs for a solution have been identified, the only remaining obstacle is to identify a company that is capable of delivering on these requirements and developing partnerships between the network MSPs and the municipalities to begin widespread deployments.
About Tim Sylvester:
Tim is a computer and electrical engineer. He is the Founder, CEO and Chief Technology Officer of Integrated Roadways, a smart infrastructure technology provider. Smart infrastructure is the integration of data, communications, power, and networking systems into core infrastructure like roads, highways, and bridges.
Smart Pavement system from Integrated Roadways
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Feb 8, 2022 Update from Dave Bolan of Dell’Oro Group:
As of December 31, 2021 there were 21 known 5G SA eMBB networks commercially deployed.
|
5G SA eMBB Network Commercial Deployments |
|
|
Rain (South Africa) |
Launched in 2020 |
|
China Mobile |
|
|
China Telecom |
|
|
China Unicom |
|
|
T-Mobile (USA) AIS (Thailand) True (Thailand) |
|
|
China Mobile Hong Kong |
|
|
Vodafone (Germany) |
Launched in 2021 |
|
STC (Kuwait) |
|
|
Telefónica O2 (Germany) |
|
|
SingTel (Singapore) |
|
|
KT (Korea) |
|
|
M1 (Singapore) |
|
|
Vodafone (UK) |
|
|
Smart (Philippines) |
|
|
SoftBank (Japan) |
|
|
Rogers (Canada) |
|
|
Taiwan Mobile |
|
|
Telia (Finland) |
|
|
TPG Telecom (Australia) |
|
Telenor expands cloud-based core network with AWS to deliver 5G and edge services for customers
Nordic network operator Telenor signed a strategic collaboration agreement with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to help expand its 5G core transformation, the telco said in a press release.
Telenor said that the new deal will allow it to deliver new 5G and edge services to enterprise customers worldwide. As part of the agreement, Telenor and AWS will invest in joint go-to-market activities in select industries—such as manufacturing, supply chain and logistics, and automotive—to enable more 5G and edge services for customers. Working with existing customers to demonstrate the possibilities of cloud-based resources, Telenor will scale its cloud footprint, while innovating to develop new services that use a combination of the most advanced and secure cloud technologies from AWS.
The agreement further expands the existing collaboration between both companies, with Telenor also becoming a member of the AWS Partner Network. Working with AWS, Telenor has already implemented an entire mobile core, running in the cloud, for Vimla, which is Telenor’s virtual mobile network operator (MVNO) brand in Sweden.
Running on AWS, Vimla’s mobile core is scalable, programmable, and employs self-service APIs, enabling Vimla to create new services for its customers. Vimla uses a wide range of AWS services, including Amazon ElastiCache, AWS Lambda and AWS Transit Gateway, among others.
The new cloud-based mobile core at Vimla is developed and managed as-a-service by Working Group Two, a company incubated by Telenor. The Nordic operator also said it plans to expand the work at Vimla to other areas in the company’s worldwide network.
As part of their collaboration, Telenor and AWS will continue to innovate in the areas of 5G edge for mobile private networks (MPNs) and edge computing. For example, Telenor 5G enabled a “network on wheels (NOW)” prototype powered by AWS. The NOW gives customers the ability to set up an autonomous private 5G network wherever it is needed. The NOW prototype is currently being used by the Norwegian defense material agency and the Norwegian Public Service broadcaster Norsk Rikskringkasting (NRK) for critical communication and remote production use cases, respectively. Internationally, Telenor’s Thailand brand dtac, launched a 5G private network proof-of-concept for Thai enterprises based on edge computing and the AWS Snow Family. This solution helps customers process real-time, artificial intelligence (AI)-based video analytics and other applications in remote locations.
Working with AWS, Telenor has already implemented an entire mobile core, running in the cloud, for Vimla—Telenor’s virtual mobile network operator brand in Sweden. Running on AWS, Vimla’s mobile core is scalable, programmable, and employs self-service APIs, enabling Vimla to create simple, innovative and valuable services for its customers. Vimla uses a wide range of AWS services, including Amazon ElastiCache, AWS Lambda, AWS Transit Gateway, and others to help scale elastically and provide a better service to more customers. The new cloud-based mobile core at Vimla is developed and managed as-a-service by Working Group Two, a company incubated by Telenor. As a result of driving network transformation on AWS, Telenor plans to expand the work at Vimla to other areas in the company’s worldwide network.
“Working with AWS, we are continuing to advance and modernize the telecoms industry—digitalizing and expanding our offerings beyond connectivity. Together, we are building on our individual strengths and scaling secure, robust, and advanced cloud services, alongside the latest networking technology, for our customers much faster than we could ever do before. Our shared ambition is to use scalable and flexible building blocks from AWS to continuously raise the bar for what’s possible,” said Sigve Brekke, president and CEO of Telenor Group.
“Telenor is pushing the boundaries of innovation by running their Vimla core on AWS. Cloud technology is allowing Telenor to scale their network in a way that was not possible before and is allowing them to experiment and develop new experiences for customers to keep them engaged, entertained, and online. We are pleased to collaborate with Telenor as they continue to expand this innovative work to other parts of their business,” said Adam Selipsky, CEO of AWS.
%20resized.jpg)
In addition to its home market in Norway and MVNO in Sweden, Telenor has operations in Denmark, Finland, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Thailand and Malaysia (and Myanmar, but it is trying to exit that market), but currently Telenor is not disclosing the details of which markets will be next or when the next deployment might happen.
Telenor and AWS have developed what they call a ‘Network On Wheels’ (NOW), which “gives customers the ability to set up an autonomous private 5G network wherever it is needed.” This model is already being used by the Norwegian Defence Material Agency for critical communications needs and by Norway’s public service broadcaster, Norsk Rikskringkasting (NRK), for remote production use cases.
In Thailand, Telenor group operator dtac has developed a 5G private network proof-of-concept for local enterprises using AWS Snow Family edge compute devices.
“This solution helps customers process real-time, artificial intelligence (AI)-based video analytics and other applications in remote locations, even in areas with intermittent connectivity,” Telenor said.
Ray Le Maistre of Telecom TV wrote: “Telenor has clearly identified AWS as the cloud partner that can help it with its specific need in both the consumer and enterprise markets, so this will be a relationship well worth tracking as the operational models are innovative.”
This author wonders what has become of Telenor’s deal with Nokia to launch a new cloud-native core solution in Denmark, Norway and Sweden. When it was announced in May 2020, Nokia said the deployment will “enhance performance and reliability and drive mobile broadband service agility as Telenor prepares for the introduction of 5G.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
The slow uptake of 5G Standalone (SA) networks is decreasing the growth for the overall Mobile Core Network (MCN), which also includes IMS Core and 4G Core (EPC). Dell’Oro Group [1.] forecasts worldwide MCN 5-year growth will be at a 3% compounded annual growth rate (CAGR).
- 5G MCN, IMS Core, and Multi-Access Network Computing (MEC) will have positive growth rates for the forecast period while 4G MCN will experience negative growth.
- By 2026, 99% of the revenue for network functions will be from cloud native Container-based CNFs.
Via email, Dave wrote: The journey for network virtualization started in 2015 with ETSI NFV. We went from Physical Network Functions (PNFs) to Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) to cloud-ready VNFs, to Cloud- Native VNFs (CNF), to Container-Based Cloud-Native VNFs. Container-Based (CNF) enable microservices.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, the Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) recently wrote that only 99 operators in 50 countries are investing in 5G standalone (SA) core network, which includes those planning/testing and launched 5G SA networks.
The GSA said at least 20 network operators (Dell’Oro says 13) in 16 countries or territories are believed to have launched public 5G SA networks. Another five have deployed the technology, but not yet launched commercial services or have only soft-launched them. So only 20.6% of the 481 5G network operators (investing in 5G licenses, trials or deployments of any type) have deployed 5G and that percentage is lower if you go by Dell’Oro’s 13 5G SA network operators.
From GSA’s The Power of Standalone 5G – published 19th January 2022:
Importantly, the 5G standalone core is cloud-native and is designed as a service-based architecture, virtualizing all software network functions using edge computing and providing the full range of 5G features. Some of these are needed in the enterprise space for advanced uses such as smart factory automation, smart city applications, remote control of critical infrastructure and autonomous vehicle operation. However, 5G standalone does mean additional investment and can bring complexity in running multiple cores in the network.
This will be a potential source of new revenue for service providers, as digital transformation — with 5G standalone as a cornerstone — will enable them to deliver reliable low-latency communications and massive Internet of things (IoT) connectivity to customers in different industry sectors. The low latency and much higher capacity needed by those emerging service areas will only be feasible with standalone 5G and packet core network architecture.
In addition, the service-based architecture opens up the ability to slice the 5G network into customized virtual pieces that can be tailored to the needs of individual enterprises, while maximizing the network’s operational efficiency. Advanced uses for 5G NR aren’t backward- compatible with LTE infrastructure, so all operators will eventually need to get to standalone 5G.
Standalone 5G metrics:
- Volume: Gbps per month
- Speed: Mbps (peak), Mbps (guaranteed)
- Location: Network Slice, service per location
- Latency per service or location (dependent on URLLC in the 5G RAN and 5G Core)
- Reliability or packet loss
- Number of devices per square km
- Dynamic service-level agreements per location
- Full end-to-end encryption and authentication
Source: CCS Insight
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Note 1. Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, networks, and data center IT markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Feb 8, 2022 Update from Dave Bolan of Dell’Oro Group:
As of December 31, 2021 there were 21 known 5G SA eMBB networks commercially deployed.
|
5G SA eMBB Network Commercial Deployments |
|
|
Rain (South Africa) |
Launched in 2020 |
|
China Mobile |
|
|
China Telecom |
|
|
China Unicom |
|
|
T-Mobile (USA) AIS (Thailand) True (Thailand) |
|
|
China Mobile Hong Kong |
|
|
Vodafone (Germany) |
Launched in 2021 |
|
STC (Kuwait) |
|
|
Telefónica O2 (Germany) |
|
|
SingTel (Singapore) |
|
|
KT (Korea) |
|
|
M1 (Singapore) |
|
|
Vodafone (UK) |
|
|
Smart (Philippines) |
|
|
SoftBank (Japan) |
|
|
Rogers (Canada) |
|
|
Taiwan Mobile |
|
|
Telia (Finland) |
|
|
TPG Telecom (Australia) |
|
References:
Slow Uptake for 5G Standalone Drags on Mobile Core Network Growth, According to Dell’Oro Group
Why It’s Important: Rakuten Mobile, Intel and NEC collaborate on containerized 5G SA core network
T-Mobile US: 5G SA Core network to be deployed 3Q-2020; cites 5G coverage advantage
Heavy Reading: “The Journey to Cloud Native” – Will it be a long one?
Heavy Reading: “The Journey to Cloud Native” – Will it be a long one?
To gauge how carriers are planning and implementing cloud-native technology, and in collaboration with Juniper, Nokia and Red Hat, Heavy Reading asked 92 global telco service providers about their plans for transition to cloud native. In their report, “The Journey to Cloud Native,” Heavy Reading analyzes the choices service providers are making along the road to cloud native and what challenges they are encountering along the way.
The migration to cloud native brings largescale shifts for the communications service providers (CSPs), including:
- The move to microservices
- Standardized access to these microservices via API exposure
- The integration of multiple operational layers and domains for application management
- Automation across the application lifecycle through the use of DevOps
These are profound changes to the application development and management environment of the CSPs, and will be tackled with dedicated internal resources and expanded partnerships with telecommunication equipment vendors (TEMs), integrators and hyper-scalers (Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Facebook, etc.).
Editor’s Note: There are no standards or implementation specs for “Cloud Native” 5G SA core network or anything else. Rakuten Symphony (Japan) and Reliance Jio (India) claim they are going to implement “Cloud Native” 5G SA core network themselves and sell the specifications and software to other service providers. Good luck! We think it will be a very long journey to cloud native for telecom network operators/5G SA core network service providers.
The prospect of cloud native:
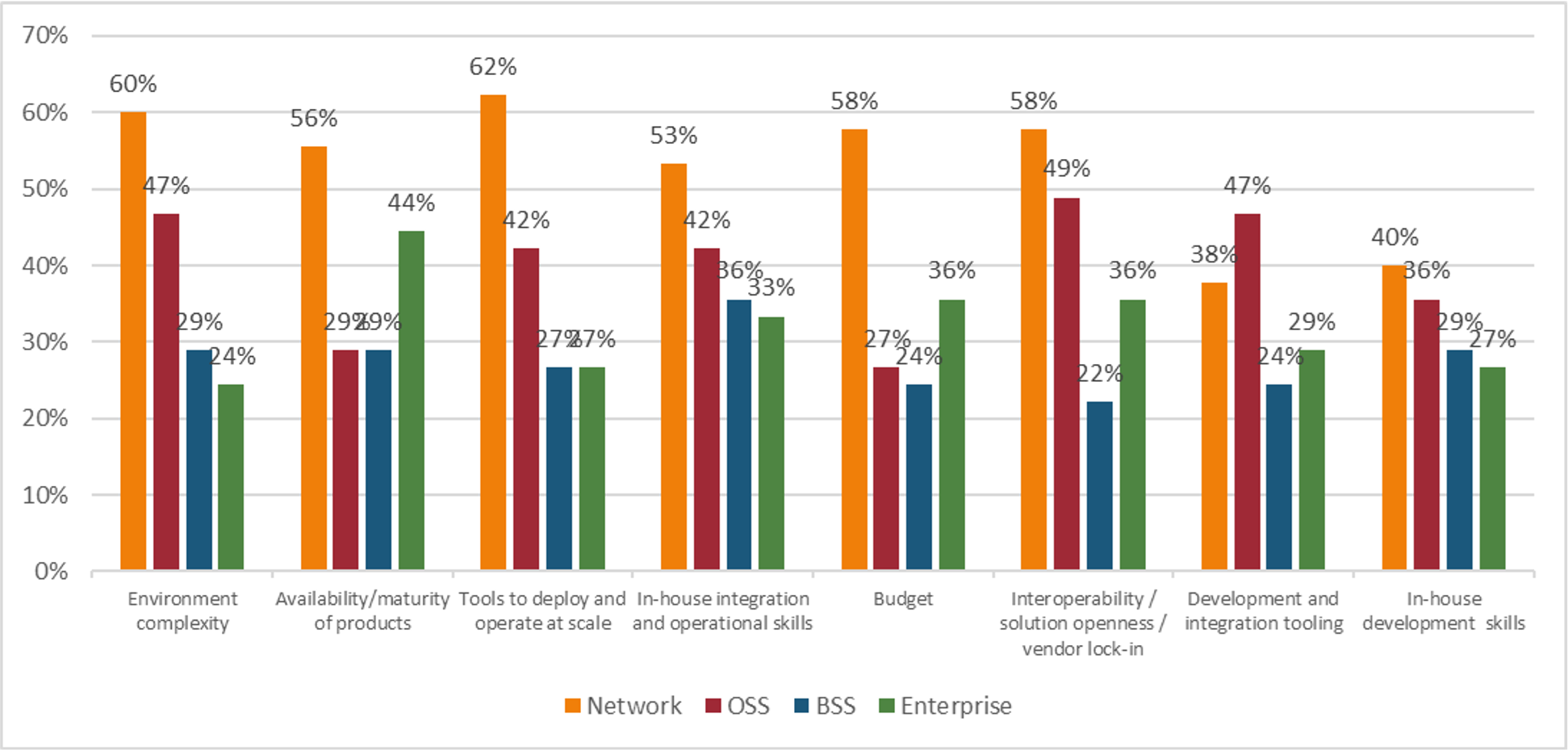
Heavy Reading queried the survey pool about where they were experiencing the greatest challenge in deploying cloud native: the network, operations support systems (OSS), business support systems (BSS), or the enterprise (see Figure 1). Heavy Reading established earlier in the survey that cloud native will be deployed first for network workloads. Respondents plan to transition workloads to the OSS business areas next, then BSS, and lastly, the enterprise.
In almost all cases, respondents ranked the challenges in that same order: first network, then OSS, BSS, and enterprise. The only challenges that were considered more severe in an area other than the network were “in-house development and integration skills” and “development and integration tooling,” where the OSS space was recognized as a greater challenge than the network. This is not surprising given that most Tier 1 carriers have dozens of OSS solutions in operation. They do much of any integration work between systems internally and some OSS systems are stand-alone – dedicated to siloed services.
Figure 1: The network space is seeing the most implementations and the most challenges N=92
Q: In which business areas are you experiencing significant challenges to going cloud native? Check all that apply. Source: Heavy Reading
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
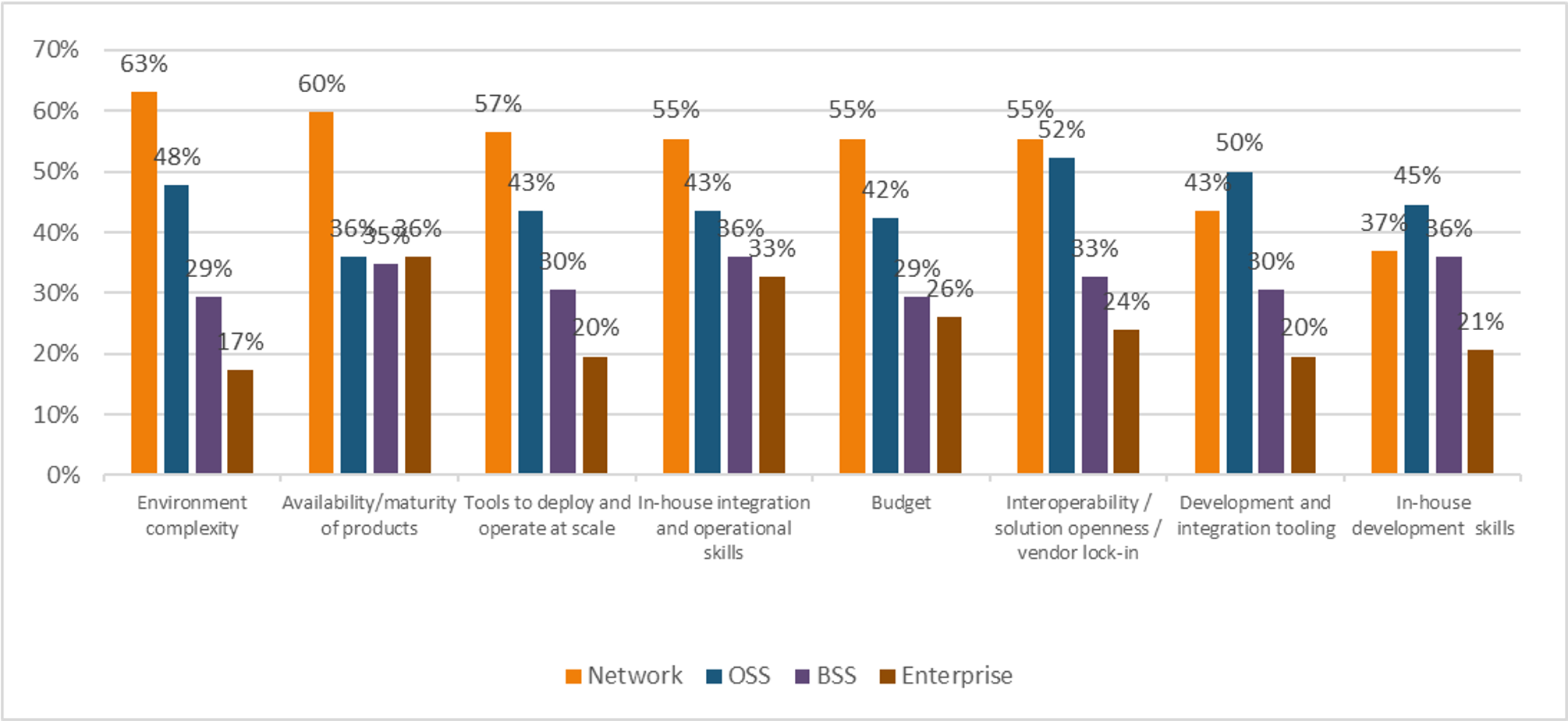
Looking only at the survey results from respondents who have already deployed cloud native, (see figure 2), which is half of the respondent pool, there are significant differences compared to the rest of the survey base. In the network area, “tools to deploy and operate at scale” is a greater challenge by 11 percentage points compared to respondents planning to deploy cloud native in one to two years.
“Budget” in the OSS area plummets between those who have not yet deployed cloud native, (57% of respondents considering it a challenge), and those who have already deployed cloud native, (27% of the respondents finding it to be a concern).
Those who have already deployed cloud native also consider all of the challenges in the enterprise area to be greater than the survey base as a whole and all of the challenges in the BSS area to be less of a challenge. Their firsthand experience with implementing cloud native in the network area has opened their eyes to the challenges that await them in the enterprise space. However, they are more confident that they have the support needed, near term, for BSS tasks which include billing, revenue, and customer management.
n=45: only respondents that have already implemented Cloud Native
Source: Heavy Reading
Heavy Reading’s findings might be a good indication that CSPs today are committed to their journey to cloud native, but face daunting challenges that will require expanded partnerships with the cloud-native ecosystem, including platform vendors, ISVs (Independent Software Vendors), TEMs (Telecom Equipment Manufacturers???) and hyper-scalers.
To gain more in-depth details of service providers’ perspective on cloud-native migration, download and read the full report now.
— Jennifer Clark, Principal Analyst, Cloud Infrastructure and Edge Computing, Heavy Reading
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/new-report-highlights-cloud-native-migration-challenges/a/d-id/774623?
https://www.lightreading.com/lg_redirect.asp?piddl_lgid_docid=773720
GSA: 200 global operators offer 5G services; only 20 (Dell’Oro says 13) have deployed 5G SA core network
200 global network operators in 78 countries are offering 5G mobile and/or fixed wireless services at the end of 2021, according to the GSA. 487 operators in 145 countries are investing in 5G, including trials and spectrum license acquisitions, up from 412 operators at the end of 2020.
Notably, only 187 of the operators offering 5G services provide 5G mobile services, in 72 countries. The others are delivering 5G fixed-wireless access (even though it’s not an IMT 2020 use case). In total, 83 operators in 45 countries/territories have launched 3GPP-compliant 5G fixed-wireless access services.
Only 99 operators in 50 countries are investing already in 5G standalone (SA) core network, which includes those planning/testing and launched 5G SA networks).
GSA has catalogued just 20 operators in 16 countries with 5G standalone deployed/launched in public networks.
13 January 2022 update from Dave Bolan of Dell’Oro Group:
We count 13 CSPs that commercially deployed 5G SA networks for enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) in 2021, and they were nowhere close to the aggressiveness in breadth and depth of the buildouts that we saw by the Chinese Service Providers in 2020, or for that matter in 2021. We thought all three CSPs in Korea would have launched by now, but so far only KT has launched.
And we expected AT&T and Verizon in the U.S., and the CSPs in Switzerland to have launched 5G SA in 2021. In spite of these disappointments, the projected growth rate for 2021 is 61% Y/Y for 2021 and lowering to 18% Y/Y for 2022 due to the expected decline in growth rate by the Chinese CSPs.

The 5G device market is growing much more quickly. The GSA counted 1,257 announced devices at year-end, up nearly 125 percent from 2020. Around half (614) are 5G phones, up more than 120 percent from 278 at the end of 2020.
In total, 857 of the devices are commercially available, up more than 155% from the 335 on the market at the end of 2020. GSA has identified 614 announced 5G phones, up more than 120% from 278 at the end of 2020.
References:
https://gsacom.com/technology/5g/
GSA: 5G Market Snapshot – 5G networks, 5G devices, 5G SA status
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
Progress report: Moving AT&T’s 5G core network to Microsoft Azure Hybrid Cloud platform
Introduction:
A little more than six months after AT&T announced it’s 5G SA Core Network would run on Microsoft Azure cloud platform, a Microsoft blog post by Shawn Hakl, VP of 5G strategy in Azure for Operators, provides a progress report on that crucial IT industry initiative. Microsoft received requests from many operators, partners, and customers to share more details of the evolution of Microsoft’s hybrid cloud technology to support AT&T’s 5G core network workloads.
Through Azure for Operators, Microsoft has forged close ties with AT&T personnel, product services groups, and partners. At the heart of the value Microsoft delivers in each of these relationships, is the way in which we leverage the power of the cloud to improve the next generation of telco networks. Microsoft aims to harness trends toward Software Defined Networking (SDN), Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs), and Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs) coupled with the service-based architecture of 5G, to begin digitally transforming the network.
That evolution involves introducing both hybrid cloud infrastructure and software, building scalable elastic carrier-grade networks, and using the power of AI and machine learning to build self-optimizing networks that can heal, defend, and provision themselves. These efforts will enable operators to hyper-automate the business itself, bringing down costs and improving the overall service experience. Azure for Operators represents the set of investments Microsoft is making to bring the power of the cloud to the network.
Microsoft’s efforts are aimed at getting workloads on the network to function on a carrier-grade hybrid cloud, which includes both public and dedicated on-premises cloud infrastructure. Telecommunication services are highly distributed and will likely become more so over time. As a result, the value of creating a carrier-grade hybrid cloud model lives in its ability to meet customers where they are—at the edge of the cloud, the edge of the network, or the edge of the enterprise.
AT&T Backgrounder on use of “SDN” and network virtualization:
In 2013, AT&T adopted an aggressive position on “Software Defined Networks (SDNs)” and network virtualization, with the ultimate goal of delivering 75 percent of their network using virtualized technology by 2020. With their own definition of SDN (not related to the ONF’s strict separation of control and data planes or using OpenFlow as the southbound interface between them). AT&T says they did meet those objectives, but this author is skeptical based on checks with AT&T employees that work in their central offices.
In the 2013-2020 time frame, there was no commercial cloud option available that included the necessary features and capabilities to enable carrier-grade cloud. AT&T created a mostly proprietary (not standards based as claimed) implementation of cloud technology that was deployed in their on-premises data centers. This initial integrated cloud evolved into a Network Cloud, and today, we’ve arrived at Network Cloud 2.7—representing seven years of experience developing on-premises cloud for network workloads.
With Microsoft’s recent acquisition of this technology, development teams from AT&T’s Network Cloud organization have moved into Azure for Operators, directly integrating the intellectual property into a Microsoft offering and assuring a seamless transition.
Unique AT&T – Microsoft Partnership:
Microsoft says their collaboration with AT&T is unique in three ways:
- It’s the first time that a tier-one operator has embraced commercial hybrid cloud technology to run mobility network workloads that support their existing consumer base.
- The effort is entirely focused on the mobility core network versus go-to-market collaborations at the edge.
- It’s a multi-vendor cloud-mobile core network system: Microsoft hybrid cloud technology supports the AT&T mobile core network that spans more than 60 cloud-native network functions (CNFs) and virtual network functions (VNFs) from 15 different vendors.

Network Cloud technology originally developed by AT&T can be utilized by multiple carriers, maintaining security, without losing differentiation, and with the added benefit of having many costs such as security patching, vendor updates, and regulatory changes delivered as part of a standard commercial product.
These capabilities will be combined with Microsoft’s edge platform, our hybrid management platform, Azure Arc, and our ecosystem of partners including equipment providers, hardware vendors, and software vendors. By joining the Network Cloud with our platform and growing ecosystem, we have achieved a carrier-grade hybrid cloud solution that will be delivered as the Azure for Operators platform. The roles of the partners are as follows:
- Microsoft develops the carrier-grade hybrid cloud technology that supports the AT&T mobility core network workloads.
- AT&T continues to select and manage the network applications (VNFs and CNFs) and their configurations to deliver mobility services to AT&T customers.
In other words, Microsoft is taking the AT&T Network Cloud technology, building it into Microsoft’s standard hybrid cloud product, and then delivering a carrier-grade hybrid cloud solution to the market and AT&T itself, where it can run at AT&T on-premises or on Azure public cloud. Microsoft hybrid cloud technology supports the AT&T mobility core network workloads used to deliver 5G connectivity that supports consumer, enterprise, and the FirstNet responder community. In terms of security, it’s important to note that Microsoft does not access AT&T customer data—AT&T continues to hold access to that data, and Microsoft cannot see it.
For AT&T, this collaboration puts them in a position to deliver new services faster and more flexibly across Azure public cloud and on-premises with common tooling and services, reducing time-to-market for a cloud-native approach.
Microsoft believes the result will be better resiliency across the network, cost advantages when it comes to scaling existing services, and a more effective introduction of new services resulting in continuous improvements to the customer experience.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Before joining Microsoft in 2020, Hakl was a longtime Verizon executive. He added that “Telecommunication services are highly distributed and will likely become more so over time. As a result, the value of creating a carrier-grade hybrid cloud model lives in its ability to meet customers where they are – at the edge of the cloud, the edge of the network, or the edge of the enterprise.”
James Crawshaw, a principal analyst of service provider operations and IT for research and consulting firm Omdia (owned by Informa in the UK), wrote on LinkedIn that Microsoft will have a lot of work to do to fully support AT&T’s complex core and cloud operations.
He also wrote that AT&T has a history of offloading networking systems. For example, the company in 2016 offloaded its ECOMP orchestration/automation system to the Linux Foundation open source community. However, “I don’t think that was a huge success,” Crawshaw wrote. He believes AT&T has replaced ECOMP (subsequently dubbed ONAP) elements with commercial orchestration systems in a number of areas. Here are are his exact words:
“When AT&T found that its ECOMP orchestration/automation system was getting too hard to manage they offloaded it to the Linux Foundation in the hope that the open source community would take care of it (ONAP). I don’t think that was a huge success (it was a failure, in this author’s opinion). I believe AT&T has actually replaced ECOMP/ONAP with commercial orchestration systems in a number of areas. Offloading its OpenStack-based cloud platform to Microsoft is a similar strategy. But if Microsoft struggles to turn a managed service into a repeatable product that they can sell to other operators around the world they may end up offloading it onto an IT services company whose business model is a better fit.”
Learn More:
Microsoft’s acquisition of AT&T’s Network Cloud, as well as Metaswitch Networks and Affirmed Networks, brings the anchor applications and telco know-how to build the features that are required for a carrier-grade hybrid cloud. These features, available to the entire partner ecosystem, contribute to an open, interoperable network that offers support to all operators. The message to operators from Microsoft is simple and straightforward: your partners and your customers—and the relationship is powered by our technology. For more information about the Azure for Operators strategy, refer to the e-book.
References:
AT&T 5G SA Core Network to run on Microsoft Azure cloud platform
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/jamescrawshaw_5g-telcocloud-activity-6884786261261881345-cqpb/
5G Security explained: 3GPP 5G core network SBA and Security Mechanisms
by Akash Tripathi with Alan J Weissberger
Introduction:
5G networks were deployed in increasing numbers this past year. As of December 2021, GSA had identified 481 operators in 144 countries or territories that were investing in 5G, up from 412 operators at the end of 2020. Of those, a total of 189 operators in 74 countries/territories had launched one or more 3GPP-compliant 5G services, up by 40% from 135 from one year ago.
Despite 5G’s much advertised potential, there are significant security risks, especially with a “cloud native” service based architecture, which we explain in this article.
New 5G services, functions and features have posed new challenges for 5G network operators. For example, bad actors could set up “secure” wireless channels with previously issued 5G security keys.
Therefore, it’s imperative for 5G operators to address end-to-end cyber security, using an array of novel techniques and mechanisms, which have been defined by 3GPP and (to a much lesser extent) by GSMA.
5G Security Requires 5G SA Core Network:
It’s important to distinguish between 5G NSA network security (which use 4G security mechanisms and 4G core network/EPC) vs. 5G SA network security (which uses 5G core network serviced base architecture and new 5G security mechanisms as defined by 3GPP).
Samsung states in a whitepaper:
▪ With the launch of 5G Stand Alone (SA) networks, 3GPP mitigates some long-standing 4G vulnerabilities to enable much stronger security.
▪ At the same time, the way the Service Based Architecture ‘explodes’ the new 5G Core opens up potentially major new vulnerabilities. This requires a fundamentally new approach to securing the 5G Core, including comprehensive API security.
▪ Operators can communicate 5G SA’s new security features to some business users. Communication to consumers is more challenging because the benefit of new security enhancements will only come into effect incrementally over many years.
▪ Mobile network security cannot depend on 3GPP alone. Operators must apply robust cyber security hygiene and operational best practice throughout their operations.
In addition, the 5G network infrastructure must meet certain critical security requirements, such as the key exchange protocol briefly described below.
There are many other risks and challenges, such as the rising shortage of well-trained cyber security and cyber defense specialists. We will address these in this article. But first, a backgrounder….
5G Core Network Service Based Architecture (SBA):
To understand 5G security specifications, one has to first the 3GPP defined 5G SA/core network architecture.
5G has brought about a paradigm shift in the architecture of mobile networks, from the classical model with point-to-point interfaces between network function to service-based interfaces (SBIs).
The 5G core network (defined by 3GPP) is a Service-Based Architecture (SBA), whereby the control plane functionality and common data repositories of a 5G network are delivered by way of a set of interconnected Network Functions (NFs), each with authorization to access each other’s services.
Network Functions are self-contained, independent and reusable. Each Network Function service exposes its functionality through a Service Based Interface (SBI), which employs a well-defined REST interface using HTTP/2. To mitigate issues around TCP head-of-line (HOL) blocking, the Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC) protocol may be used in the future.
Here’s an illustration of 5G core network SBA:
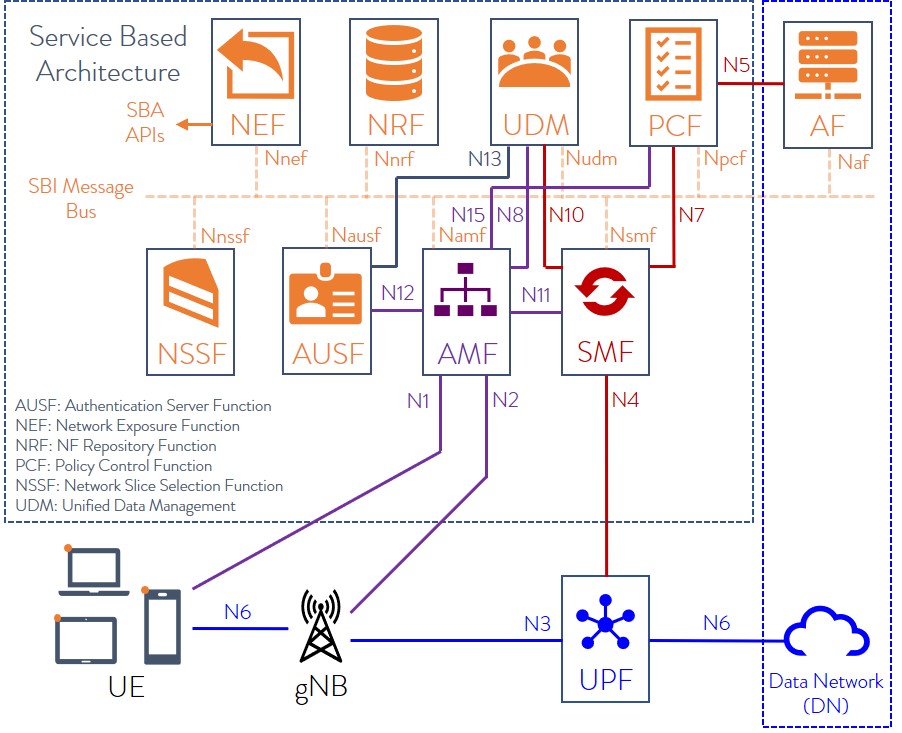
The 5G core network architecture (but not implementation details) is specified by 3GPP in the following Technical Specifications:
| TS 23.501 | System architecture for the 5G System (5GS) |
| TS 23.502 | Procedures for the 5G System (5GS) |
| TS 23.503 | Policy and charging control framework for the 5G System (5GS); Stage 2 |
The 5G network consists of nine network functions (NFs) responsible for registering subscribers, managing sessions and subscriber profiles, storing subscriber data, and connecting user equipment to the Internet using a base station. These technologies create a liability for attackers to carry out man-in-the-middle and DoS attacks against subscribers.
Overview of 3GPP 5G Security Technical Specifications:
The 5G security specification work are done by a 3GPP Working Group named SA3. For the 5G system security mechanisms are specified by SA3 in TS 33.501. You can see all versions of that spec here.
3GPP’s 5G security architecture is designed to integrate 4G equivalent security. In addition, the reassessment of other security threats such as attacks on radio interfaces, signaling plane, user plane, masquerading, privacy, replay, bidding down, man-in-the-middle and inter-operator security issues have also been taken in to account for 5G and will lead to further security enhancements.
Another important 3GPP Security spec is TS 33.51 Security Assurance Specification (SCAS) for the next generation Node B (gNodeB) network product class, which is part of Release 16.
It’s critically important to note that ALL 3GPP security spec features and functions are required to be supported by vendors, but the are ALL OPTIONAL for 5G service providers. That has led to inconsistent implementations of 5G security in deployed and planned 5G networks as per this chart, courtesy of Heavy Reading:
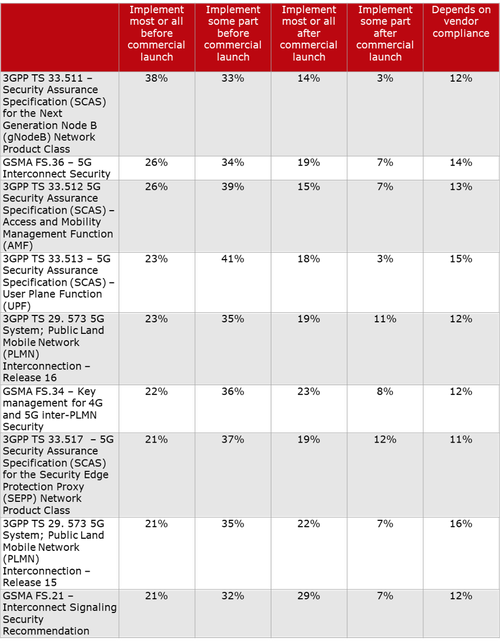
Scott Poretsky, Ericsson’s Head of Security, wrote in an email to Alan:
“The reason for the inconsistent implementation of the 5G security requirements is the language in the 3GPP specs that make it mandatory for vendor support of the security features and optional for the operator to decide to use the feature. The requirements are defined in this manner because some countries did not want these security features implemented by their national telecoms due to these security features also providing privacy. The U.S. was not one of those countries.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………..

Overview of Risks and Potential Threats to 5G Networks:
A few of the threats that 5G networks are likely to be susceptible to might include those passed over from previous generations of mobile networks, such as older and outdated protocols.
-
Interoperability with 2G-4G Networks
For inter-operability with previous versions of software or backward compatibility, 5G must still extend interoperability options with mobile gadgets adhering to the previous generation of cellular standards.
This inter-operability necessity ensures that vulnerabilities detected in the outmoded Diameter Signaling and the SS7 Interworking functions followed by 2G-4G networks can still be a cause of concern for the next-generation 5G network.
-
Issues related to data protection and privacy
There is a likely possibility of a cyber security attack such as Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack in a 5G network where a perpetrator can access personal data through the deployment of the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)-catchers or cellular rogue base stations masquerading as genuine mobile network operator equipment.
-
Possibility of rerouting of sensitive data
The 5G core network SBA itself could make the 5G network vulnerable to Internet Protocol (IP) attacks such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS). Similarly, network hijacking, which involves redirecting confidential data through an intruder’s network, could be another form of attack.
-
Collision of Politics and Technology
Government entities can impact 5G security when it comes to the production of hardware for cellular networks. For instance, various countries have new regulations that ban the use of 5G infrastructure equipment that are procured from Chinese companies (Huawei and ZTE) citing concerns over possible surveillance by the Chinese government.
-
Network Slicing and Cyberattacks
Network slicing is a 5G SA core network function (defined by 3GPP) that can logically separate network resources. The facility empowers a cellular network operator to create multiple independent and logical (virtual) networks on a single shared access. However, despite the benefits, concerns are being raised about security risks in the form of how a perpetrator could compromise a network slice to monopolize resources for compute-intensive activities.
3GPP Public Key based Encryption Schemes:
3GPP has introduced more robust encryption algorithms. It has defined the Subscription Permanent Identifier (SUPI) and the Subscription Concealed Identifier (SUCI).
- A SUPI is a 5G globally unique Subscription Permanent Identifier (SUPI) allocated to each subscriber and defined in 3GPP specification TS 23.501.
- SUCI is a privacy preserving identifier containing the concealed SUPI.

The User Equipment (UE) generates a SUCI using a Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme (ECIES)-based protection scheme with the public key of the Home Network that was securely provisioned to the Universal Subscriber Identity Module (USIM) during the USIM registration.
Through the implementation of SUCI, the chance of meta-data exploits that rely on the user’s identity are significantly reduced.
Zero Trust architecture:
As 5G will support a massive number of devices, Zero Trust can help private companies to authenticate and identify all connected devices and keep an eye on all the activities of those devices for any suspected transgression within the network. While it has been successfully tested for private enterprise networks, its capability for a public network like open-sourced 5G remains to be gauged.
Private 5G Networks:
A private 5G network will be a preferred mode for organizational entities that require the highest levels of security taking into account national interests, economic competitiveness, or public safety. A fully private 5G network extends an organization with absolute control over the network hardware as well as software set-up. All of those mechanisms can be proprietary as the 5G private network deployment is only within one company’s facilities (campus, building, factory floor, etc).
Future of 5G Security:
The next-generation 5G-based wireless cellular network has put the spotlight on new opportunities, challenges, and risks, which are mandatorily required as the 5G technology makes great strides.
The 5G security mechanisms will continue to evolve in 3GPP (with Release 17 and above). Many of them will be transposed to become (“rubber stamped”) ETSI standards.
Note that 3GPP has not submitted its 5G core network architecture or 5G security specifications to ITU-T which is responsible for all 5G (IMT 2020) non-radio standards.
Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), applicable as of May 25th, 2018 in all EU member states, harmonizes data privacy laws across Europe. It could serve as a model for network security and data protection initiatives outside the European Union.
Conclusions:
The 5G network has the possibility to enhance network and service security. While 5G comes with many built-in security controls by design, developed to enhance the protection of both individual subscribers and wireless cellular networks, there is a constant need to remain vigilant and a step ahead in terms of technological innovation to thwart possible new cyber-attacks.
An end-to-end security framework across all layers and all domains would be essential. Introducing best practices and policies around security and resilience will remain imperative to future-proof 5G networks.
References:
Strong Growth Forecast for 5G Security Market; Market Differentiator for Carriers
Report Linker: 5G Security Market to experience rapid growth through 2026
AT&T Exec: 5G Private Networks are coming soon + 5G Security Conundrum?
https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3169
5G Security Vulnerabilities detailed by Positive Technologies; ITU-T and 3GPP 5G Security specs
Author Bio:
Akash Tripathi is a Content Marketing strategist at Top Mobile Tech. He has 10+ years of experience in blogging and digital marketing. At Top Mobile Tech, he covers various how-to and tips & tricks related to iPhone and more related to technologies. For more about Akash, please refer to:
https://twitter.com/akashtripathi8
https://www.linkedin.com/in/akash-tripathi-42315959/
https://www.facebook.com/akash.tripathi.562
https://www.instagram.com/akashtripathi8/
Nokia to provide 5G SA core network for Volkswagen (private) and KDDI (public)
Nokia has deployed a 5G standalone (SA) core network at Volkswagen’s plant in Wolfsburg, Germany. The 5G private campus network covers the production development center and pilot hall at the plant. This network uses the Nokia Digital Automation Cloud (DAC) system to provide reliable and secure connectivity. Nokia’s DAC provides high-bandwidth and low-latency connectivity for sensors, machines, vehicles and other equipment.
Volkswagen will use the network to improve efficiency in production. The company is initially testing the wireless upload of data to manufactured vehicles and intelligent networking of robots and wireless assembly tools.
“By deploying private wireless to explore and develop its potential in manufacturing, Volkswagen underscores its leading position in leveraging digitalization to enhance efficiency and productivity,” commented Chris Johnson, head of Global Enterprise business for Nokia. “We are delighted to support this effort with the Nokia Digital Automation Cloud and our extensive experience in private wireless networks.”
The pilot network will allow Volkswagen to test whether 5G technology helps the company meet the demanding requirements of vehicle production, as well as increases efficiency and flexibility in series production of the future.
“Predictable wireless performance and the real-time capabilities of 5G have great potential for smart factories in the not-so-distant future. With this pilot deployment, we are exploring the possibilities 5G has to offer and are building our expertise in operating and using 5G technology in an industrial context,” said Dr.-Ing. Klaus-Dieter Tuchs, network planning at Volkswagen.
Nokia’s work with Volkswagen at its main German plant aligns with the vendor’s private 5G ambitions, as reported by German newspaper Handelsblatt in 2019. The company said at the time that it expects to provide 5G networks for German companies following the opening of the application procedure for local firms intending to use 5G frequencies on industrial campuses, highlighting not only its intention to offer its service for network planning, but also aims to operate the networks.
Nokia’s private network reach extends beyond Germany of course. The vendor has worked with industrial-type partners on LTE, 5G-ready and IP/MPLS networks around the world including at the Zeebrugge port in Belgium, the Irish Aviation Authority and the Société du Grand Paris (SGP), the state owned industrial company responsible for the Grand Paris Express metro project.

Resources:
Nokia Industrial Private Wireless
https://www.nokia.com/networks/industry-solutions/private-wireless/industry/
Nokia Digital Automation Cloud | Nokia
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
On December 2nd, Nokia announced that Japanese network operator KDDI selected Nokia’s 5G Core and Converged Charging software to support its transition to a fully automated, cloud-native 5G SA Core network architecture.
Nokia’s cloud-native 5G Core’s near zero-touch automation capabilities help operators drive greater scale and reliability. Following the evolution of KDDI’s networks to 5G standalone core, subscribers will experience lower latency, increased bandwidth and higher capacity.
Nokia’s open 5G Core architecture gives KDDI the flexibility to be responsive to market demands while controlling costs by streamlining operations and unlocking crucial capabilities, such as network slicing. Developed around DevOps principles, Nokia’s 5G Core will automate the lifecycle management of KDDI’s networks, as well as enable continuous software delivery and integration.
Nokia will also deploy 5G monetization and data management software solutions including cloud-native Converged Charging, Signaling, Policy Controller, Mediation and Registers to capture new 5G revenue opportunities, enhance business velocity and agility, and streamline the operator’s network operations.
References:
Nokia deploys 5G private network at Volkswagen plant in Germany
Dell’Oro: 5G SA Core network launches accelerate; 14 deployed
According to a recently published report from Dell’Oro Group, revenues for the Mobile Core Network (MCN) market are poised for growth in 2022. The outlook has turned positive, starting in 4Q 2021, as 5G Standalone (SA) commercial launches begin to accelerate.
“The expected growth rate for 2022 is more optimistic than reported last quarter with the commercial deployments of more 5G SA enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) networks,” stated Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “We count 14 commercial 5G SA networks deployed by Communication Service Providers for eMBB services. Five of the 14 5G SA networks went commercial after the close of 3Q 2021 quarter. Europe had a surprising uptick in 3Q 2021 with 5G SA network commercial launches primarily in Germany,” Bolan added.
Additional highlights from the 3Q 2021 Mobile Core Network Report:
- MCN market revenues declined into negative growth year-over-year and quarter-over-quarter.
- The slowdown is attributed to a slowing of the 5G SA network buildouts in China.
- 5G Packet Core revenues for the quarter were spread across only six vendors: Ericsson, Huawei, Mavenir, NEC, Nokia, and ZTE.
13 January 2022 Update (SA=Stand Alone; eMBB=Enhanced Mobile Broadband 5G use case):

The Dell’Oro Group Mobile Core Network Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, shipments, and average selling prices for Evolved Packet Core, 5G Packet Core, Policy, Subscriber Data Management, and IMS Core including licenses by Non-NFV and NFV, and by geographic regions. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
Opinion:
It’s this author’s belief that the 5G SA core network market will be dominated by the hyperscale cloud service providers. In particular, Amazon AWS, Microsoft AZURE, Google Cloud, Oracle Cloud. 5G SA core network enables many hyped capabilities, such as network slicing, MEC, VoNR, automation, virtualization and others.
Addendum:
Please refer to Dave Bolan’s COMMENT in the box below this article. You can download a free whitepaper from the link there.
References:
5G Standalone Commercial Launches Accelerate Mobile Core Market, According to Dell’Oro Group
The Sorry State of 5G SA Core Networks- Smart Communications in Phillipines
Telcos Loss: Private 5G & MEC/5G SA Core Network – Cloud Giants Take Market Share