5G SA/5G Core network
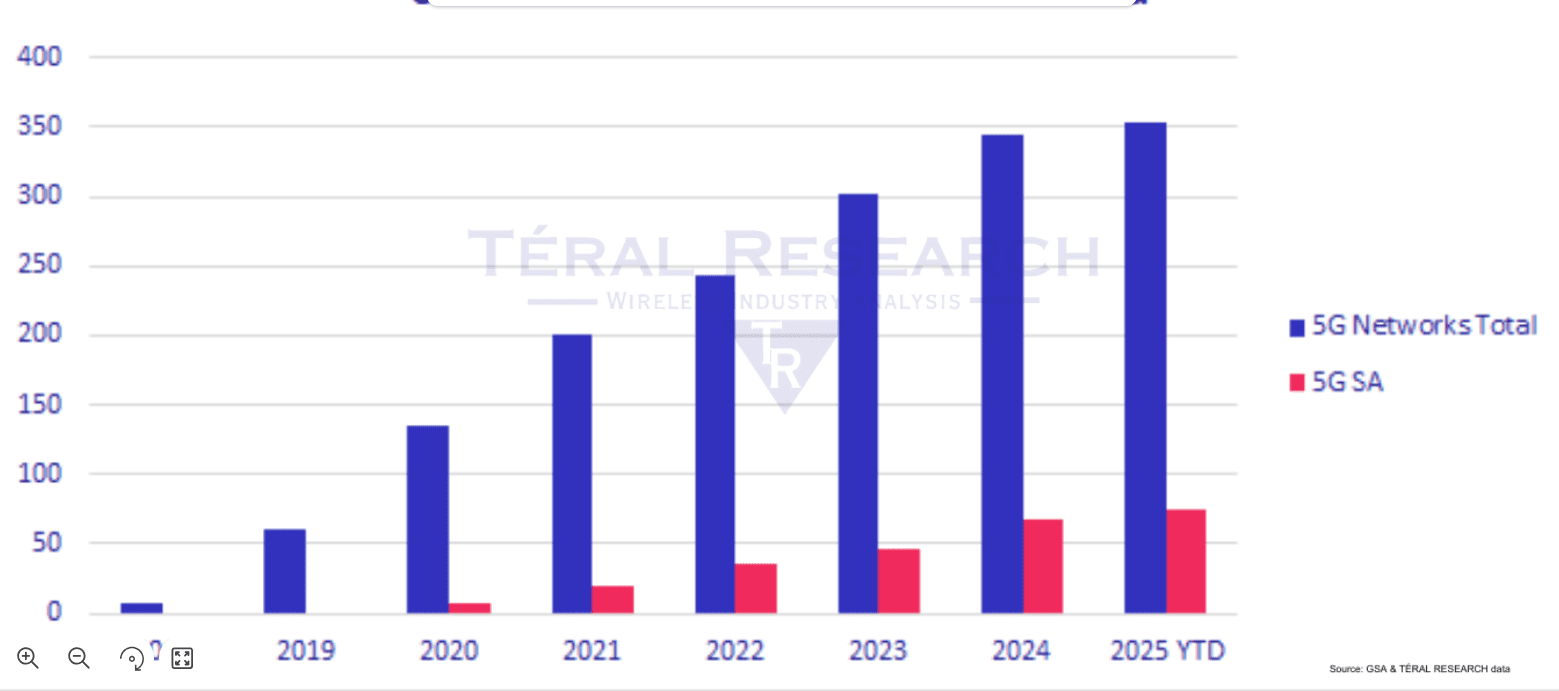
Téral Research: 5G SA core network deployments accelerate after a very slow start
5G deployments started with the non-standalone (NSA) mode (using a 4G core network) and are now gradually migrating to Stand Alone (SA) core network to unleash a plethora of use cases. 5G SA offers improved latency and bandwidth, enabling advanced services and applications. 5G SA features a new sophisticated service-based architecture (5G SBA) developed by the 3GPP. Although many of the network functions (NFs) featured in the 5G SBA come from existing ones currently active in 2G/3G and 4G networks, novel functions such as the network slice selection function (NSSF) are being introduced.
After a very slow start during the past five years, Téral Research [1.] says the migration to 5G SA has increased. Of the total 354 commercially available 5G public networks reported at the end of 1Q25, 74 are 5G SA – up from 49 one year ago. This growth is being driven by the success of fixed wireless access (FWA), a wider range of 5G SA-compatible devices, and the rise of voice over new radio (VoNR). Téral is also seeing increased adoption of private cloud for SA core deployments, with data sovereignty concerns shaping CSP strategies. Network slicing, which requires 5G SA, is moving from theory to practice—now extending to critical use cases like military applications.
Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, and ZTE Corporation continue to lead the vendor landscape, but with more than 550 networks yet to migrate, the 5G SA Core market is only beginning to scale. With 20% growth expected this year, the next phase of 5G is officially underway.
Note 1. Based on a communications service provider (CSP) survey and discussions with many vendors, Téral Research’s 5G SA report analyzes several of the 5G Core SBA functions and provides global and regional market sizes and forecasts by focusing on the NFs implemented by CSPs (e.g., UDM, UDR, AUSF, NRF, NEF and NSSF, PCF, BSF, CHF) to enable use cases beyond enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), fixed wireless access (FWA), and private 5G.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2024 had the highest number of 5G SA commercial launches: 21 networks went live to offer commercial 5G SA services last year. The success of FWA services, the introduction of smartphone plans enabled by the increasing number of available 5G SA devices, and the rise of VoNR drove this SA migration.
Key findings include:
-
Network slicing is taking off for various services, including for military use cases.
-
The single vendor approach remains predominant for each domain.
-
67% of 5G SA core deployment are cloud-based but due to data sovereignty concerns,
CSPs favor private cloud infrastructures.
-
The global 2024 market for 5G SA Core + SDM + Policy & Charging grew 12% YoY and hit $3.8B, slightly below our forecast.
-
Sustained by its domestic market, Huawei leads global 2024 sales for 5G SA Core + SDM + Policy & Charging, followed by Ericsson and Nokia, respectively. However, Nokia leads the global commercial 5G SA footprint. ZTE comes in fourth place for global total sales and second for 5G SA core sales behind Huawei.
In the meantime, technical challenges related to 5G network architecture complexity, 3GPP methods for exchanging information across 4G vs. 5G, policy orchestration and enforcement, real-time analytics and insights and data analytics are still lingering but being solved.
Built on a solid CSP pipeline of 559 cellular networks in the world that have yet to be migrated to 5G SA, Téral’s model produced a forecast that shows the global 5G SA Core/5G Data Management/5G Policy market to cross the $4B bar by year-end, which is 20% YoY growth. Last year’s downward revision put our forecast on track and therefore we have not made any significant change in this forecast update.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Editor’s Note: In 2025, about a dozen more mobile network operators (MNOs) are expected to deploy 5G Standalone (SA) networks, according to Fierce Network and Moniem-Tech. This will include some major CSPs like AT&T and Verizon, who have previously deployed 5G SA on a limited basis. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In the long run, Teral foresees a significant ramp up in CSPs’ migration to 5G SA that adds to the ongoing activity continuously fueled by the emergence of new use cases going beyond eMBB, FWA, and private 5G. Therefore, Téral expects the market to grow at a 2025-2030 CAGR of 11%. Asia Pacific will remain the largest market throughout the forecast period and 5G SA core the most important domain to start with, followed by 5G Data Management.
Finally, the disaggregated multi-domain nature of 5G core SBA brings a broad range of contenders that include the traditional telecom network equipment vendors, a few mobile core specialists, a handful of subscriber data management (SDM) specialists, a truck load of policy and charging rules function (PCRF) players, the OSS/BSS providers and the system integrators and providers of IT services.
References:
Téral Research :: June 2025 5G SA Core, SDM and Policy
Ookla: Europe severely lagging in 5G SA deployments and performance
Vision of 5G SA core on public cloud fails; replaced by private or hybrid cloud?
GSA: More 5G SA devices, but commercial 5G SA deployments lag
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks and FWA
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market has lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
Google Cloud targets telco network functions, while AWS and Azure are in holding patterns
Overview:
Network operators have used public clouds for analytics and IT, including their business and operational support systems, but the vast majority have been reluctant to rely on hyper-scaler public clouds to host their network functions. However, there have been a few exceptions:
1. AWS counts Boost Mobile, Dish Network, Swisscom and Telefónica Germany as network operators running part of their 5G network in its public cloud. In a cloud-native 5G stand alone (SA) core network, the network functions are virtualized and run as software, rather than relying on dedicated hardware.
a] Dish Network is using Nokia’s cloud-native, 5G standalone core software which is deployed on the AWS public cloud. This includes software for subscriber data management, device management, packet core, voice and data core, and integration services. Dish invokes several AWS services, including Regions, Local Zones and Outposts, to host its 5G core network and related components.
b] Swisscom is migrating its core applications, including OSS/BSS and portions of its 5G core, to AWS according to Business Wire. This is part of a broader digital transformation strategy to modernize its infrastructure and services.
c] Telefónica Germany (O2 Telefónica) has moved its 5G core network to Amazon Web Services (AWS). This move, in collaboration with Nokia, makes them the first telecom company to switch an existing 5G core to a public cloud provider, specifically AWS. They launched their 5G cloud core, built entirely in the cloud, in July 2024, initially serving around one million subscribers.
2. Microsoft’s Azure cloud is running AT&T and the Middle East’s Etisalat 5G core network. AT&T is using Microsoft’s Azure Operator Nexus platform to run its 5G core network, including both standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) deployments, according to AT&T and Microsoft. This move is part of a strategic partnership between the two companies where AT&T is shifting its 5G mobile network to the Microsoft cloud. However, AT&T’s 5G core network is not yet commercially available nationwide.
3. Ericsson has partnered with Google Cloud to offer 5G core as a service (5GCaaS) leveraging Google Cloud’s infrastructure. This allows operators to deploy and manage their 5G core network functions on Google’s cloud, rather than relying solely on traditional on-premises infrastructure. This Ericsson on-demand service recently launched with Google seems aimed mainly at smaller telcos, keen to avoid big upfront costs, or specific scenarios. To address much bigger needs, Google has an Outposts competitor it markets under the brand of Google Distributed Cloud (or GDC).
A serious concern with this Ericsson -Google offering is cloud provider lock-in, i.e. that a telco would not be able to move its 5GCaaS provided by Ericsson to an alternative cloud platform. Going “native,” in this case, meant building on top of Google-specific technologies, which rules out any prospect of a “lift and shift” to AWS, Microsoft or someone else, said Eric Parsons, Ericsson’s vice president of emerging segments in core networks, on a recent call with Light Reading.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Google Cloud for Network Functions:
Angelo Libertucci, Google’s global head of telecom told Light Reading, the “timing is right” for a Google campaign that targets telco networks after years of sluggish industry progress. “The pressures that telcos are dealing with – the higher capex, lower ARPU [average revenue per user], competitiveness – it’s been a tough two years and there have been a number of layoffs, at least in North America,” he told Light Reading at last week’s Digital Transformation World event in Copenhagen.
“We run the largest private network on the planet,” said Libertucci. “We have over 2 million miles of fiber.” Services for more than a billion users are supported “with a fraction of the people that even the smallest regional telcos have, and that’s because everything we do is automated,” he claimed.
“There haven’t been that many network functions that run in the cloud – you can probably name them on less than four fingers,” he said. “So we don’t think we’ve really missed the boat yet on that one.” Indeed, most network functions are still deployed on telco premises (aka central offices).
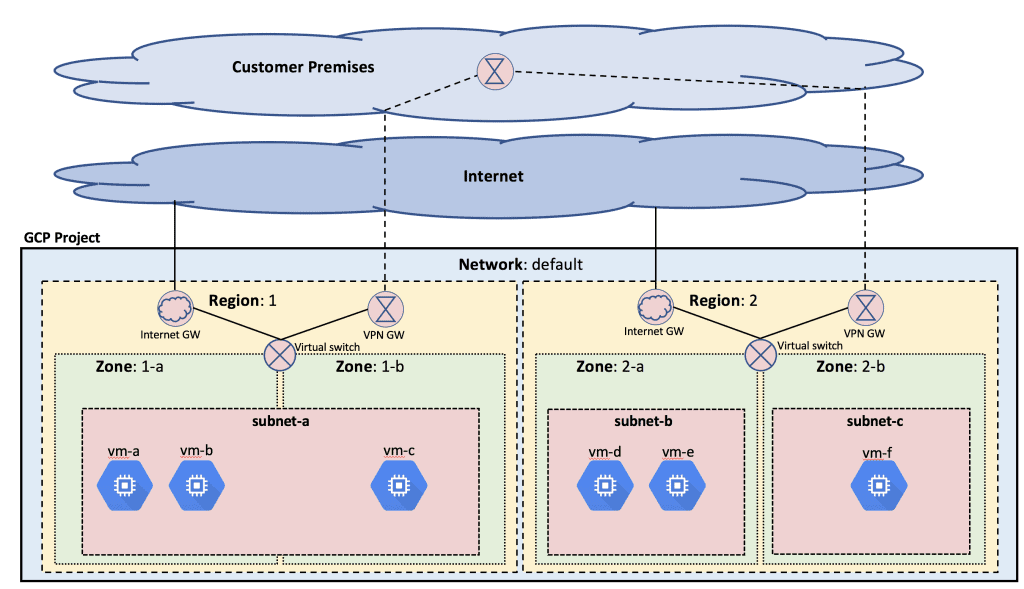
Image Credit: Google Cloud Platform
Deutsche Telekom has partnered with Google earlier this year to build an agentic AI called RAN Guardian, which can assess network data, detect performance issues and even take corrective action without manual intervention. Built using Gemini 2.0 in Vertex AI from Google Cloud, the agent can analyze network behavior, detect performance issues, and implement corrective actions to improve network reliability, reduce operational costs, and enhance customer experiences. Deutsche Telekom keeps the network data at its own facilities but relies on interconnection to Google Cloud for the above listed functions.
“Do I then decide to keep it (network functions and data) on-prem and maintain that pre-processing pipeline that I have? Or is there a cost benefit to just run it in cloud, because then you have all the native integration? You don’t have any interconnect, you have all the data for any use case that you ever wanted or could think of. It’s much easier and much more seamless.” Such autonomous networking, in his view, is now the killer use case for the public cloud.
Yet many telco executives believe that public cloud facilities are incapable of handling certain network functions. European telcos including BT, Deutsche Telekom, Orange and Vodafone, have made investments in their own private cloud platforms for their telco workloads. Also, regulators in some countries may block operators from using public clouds. BT this year said local legislation now prevents it from using the public cloud for network functions. European authorities increasingly talk of the need for a “sovereign cloud” under the full control of local players.
Google does claim to have a set of “sovereign cloud” products that ensure data is stored in the country where the telco operates. “We have fully air-gapped sovereign cloud offerings with Google Cloud binaries that we’ve done in partnership with telcos for years now,” said Libertucci. The uncertainty is whether these will always meet the definition. “If sovereign means you can’t use an American-owned organization, then that’s another part of the definition that somehow we will have to find a way to address,” he added. “If you are cloud-native, it’s supposed to be easier to move to any cloud, but with telco it’s not that simple because it’s a very performance-oriented workload,” said Libertucci.
What’s likely, then, is that operators will assign whole regions to specific combinations of public cloud providers and telco vendors, he thinks, as they have done on the network side. “You see telcos awarding a region to Huawei and another to Ericsson with complete separation between them. They might choose to go down that route with network vendors as well and so you may have an Ericsson and Google part of the network.”
“We’re a platform company, we’re a data company and we’re an AI company,” said Libertucci. “I think we’re happy now with being a platform others develop on.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Cloud RAN Disappoints:
Outside a trial with Ericsson almost two years ago, there is not much sign of Google activity in cloud RAN, the use of general-purpose chips and cloud platforms to support RAN workloads. “So far, no one’s really pushed us down into that area,” said Libertucci. AWS, by contrast, has this year begun to show off an Outposts server built around one of its own Graviton central processing units for cloud RAN. Currently, however, it does not appear to be supporting a cloud RAN deployment for any telco.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/cloud/google-preps-public-cloud-charge-at-telecom-as-microsoft-wobbles
Deutsche Telekom and Google Cloud partner on “RAN Guardian” AI agent
Ookla: Europe severely lagging in 5G SA deployments and performance
According to a new joint study from Omdia and Ookla, Europe has had the poorest 5G SA availability and performance among major regions. In Q4 2024, China (80%), India (52%), and the United States (24%) led the world in 5G SA availability based on Speedtest® sample share, markedly ahead of Europe (2%).
The European region also lagged behind its peers in performance, with the median European consumer experiencing 5G SA download speeds of 221.17 Mbps—lower than those in the Americas (384.42 Mbps) and both Developed (237.04 Mbps) and Emerging (259.73 Mbps) Asia Pacific. The interplay of earlier deployments, a more diversified multi-band spectrum strategy, and greater operator willingness to invest in the 5G core to monetize new use cases have driven rollouts at a faster pace in regions outside Europe.
The European Commission has championed measures to accelerate private investment in 5G SA, highlighting network slicing—a flagship capability of cloud-native core networks—as a key potential driver of its broader industrial strategy in sectors such as precision manufacturing, defense and clean energy. Up until this point, high-quality public data examining Europe’s progress in 5G SA—and benchmarking its competitive position relative to other global regions—has been scarce. In its latest annual report, Connect Europe, the trade body representing Europe’s telecoms operators, noted that “there is limited information available about the extent of operators’ rollout of 5G SA.”
Advanced network capabilities enabled by the technology remain stubbornly limited to just a few operators in leading markets such as the U.S., according to the study, while Europe lags behind its peers on several 5G SA performance indicators, “raising concerns about the bloc’s competitiveness in the technology.”
Network operator investment per capita also lags in Europe as per the below chart:
When faced with choices among investments in fiber, 5G RAN, and 5G SA core, the latter frequently loses out, since operators can still launch a “5G” network by leveraging alternative technologies. There is also a lack of 5G SA-compatible devices, especially devices with User Equipment Routing Selection Policy (URSP) technology, which allows a device to dynamically select a slice (or multiple slices) provisioned by an operator. However, only Android 12/iOS 17 mobile devices support that largely unknown technology.
While capital spending on the 5G core transition is now increasing rapidly, European network operators will remain committed to strict cost discipline Based on Omdia’s Q3 2024 quarterly core software market share and forecast, the research firm believes that the global core market revenue from both 4G and 5G network functions will grow with a five-year CAGR of 3.2% between 2023 and 2028. When considering the spending in 5G core software, the forecasted growth with a five-year CAGR during the same period is of 17.0%.
Omdia now forecasts that 5G SA core spending in EMEA will grow with a five-year CAGR of 26.2% between 2023 and 2028. Nonetheless, as a prerequisite, deploying the 5G core also requires a good 5G radio coverage, to avoid a degraded experience where the 5G coverage is limited or nonexistent, and where the user falls back on 4G-LTE or 2G/3G. This means operators must invest in 5G RAN, which is usually considered the highest capex draining activity for an operator. While 5G is known for very high throughput speeds using mid-band (and particularly C-band) spectrum, these bands need to be complemented by sub-GHz spectrum deployment, in order to offer improved in-building and wide area coverage. This rollout has been slow in many European markets, with 5G availability in all countries outside the Nordics remaining significantly lower than that in the United States and China, according to Ookla’s Q4 2024 Speedtest Intelligence® data.
One bright spot is that Europe has made progress on achieving low latency on its 5G networks. In Q4 2024, the average country-wide median latency in Europe was 32 milliseconds (ms) compared to 35 ms in the Americas and 36 ms in Emerging Asia Pacific region.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/eurobites-europe-behind-on-5g-sa-study
https://www.ookla.com/s/media/2025/02/ookla_omdia-5GSA_0225.pdf
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks and FWA
GSA 5G SA Core Network Update Report
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
Vision of 5G SA core on public cloud fails; replaced by private or hybrid cloud?
Nokia and Eolo deploy 5G SA mmWave “Cloud RAN” network
Nokia, BT Group & Qualcomm achieve enhanced 5G SA downlink speeds using 5G Carrier Aggregation with 5 Component Carriers
Ericsson’s sales rose for the first time in 8 quarters; mobile networks need an AI boost
Ericsson today said sales in its key networks unit grew 4% in the 4th quarter as contract wins and network investments by some large customers contributed to a 70% jump in North America (NA) sales, but its cloud software and enterprise units both saw sales and earnings decline. Revenue in the NA region rebounded sharply in the third quarter and continued to do so in the fourth quarter, helped by deliveries under a major AT&T “Open RAN” contract that began last year and will continue into 2025. AT&T’s Open RAN plan is for 70% of its wireless network traffic to flow across open-capable platforms by late 2026.
India has largely completed a rapid phase of network upgrades that saw deployments peak in 2023, and operator investments in the country have now normalized, Ericsson said. Total sales rose 1.4% to 72.91 billion kronor, after declining at double-digit rates in both 2023 and 2024.
“The near-term market recovery is in the hands of our customers, but our confidence in the stabilizing market is growing,” Chief Executive Borje Ekholm said on an analyst call Friday. “We are starting to see a change in sentiment.” He later said, “5G has not been built out. If you take the North American market, 5G standalone is not rolled out [1.]. London in Europe has very limited buildout. Most of the time when you get the 5G icon on your phone, you are basically on dynamic spectrum sharing using 4G spectrum.”
Note 1. Not true. Both T-Mobile and Dish Network have deployed 5G SA networks.
“I think the whole world is moving from a cost-optimized supply chain to resilience. You need to factor in resilience in the supply chain and that is why we built a US factory, and we are investing to increase capacity in the U.S. as well,” said Ekholm.
On that analysts call, Chief Financial Officer Lars Sandstrom said the company has production in North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia and India, so it has the opportunity to move production between different sites depending on President Trump’s plans. “Of course tariffs could have an impact going into 2025, but I think we’re all waiting a little bit to what is going to happen there,” he said, adding that there might also be tariff exemptions for critical products.
Ericsson said restructuring charges rose to 1.6 billion kronor in the quarter, mainly related to redundancies, efficiency measures and right-sizing operations to align with lower demand in some markets. The company said that restructuring charges for 2025 are expected to remain at elevated levels. Indeed, Ericsson has heavily cut costs, eliminating 9,400 “internal and external” jobs in 2024. The net reduction leaves the company with 94,236 employees, down from 99,952 a year earlier and more than 111,000 back in 2017, when Ekholm first took charge. Over this period, it has retreated from various activities in TV and cloud hardware to concentrate on 5G, although its $6.2 billion takeover of Vonage in 2022 brought additional staff into the business.
Ekholm acknowledged what IEEE Techblog readers already know – that mobile network data traffic growth has slowed down, which reduces demand for Ericsson’s products. Ericsson’s response has included putting heavy emphasis on the concept of programmability, whereby 5G networks could be dynamically adapted to support different services and scenarios, including artificial intelligence (AI) applications.
“The network needs to be prepared for the AI traffic,” said Ekholm. “It’s going to require more uplink. It’s going to require a different performance of the network. That, I think, may be more important in the next few years as a traffic definition. So yes, overall traffic is probably going to continue to taper down. But I think the demand coming from the new applications on top will materially impact the way you need to invest in the network.” However, that AI RAN initiative is in its infancy and yet to be commercially deployed.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ericsson-boosted-by-us-but-axed-9-400-jobs-last-year
https://about.att.com/story/2023/commercial-scale-open-radio-access-network.html
vRAN market disappoints – just like OpenRAN and mobile 5G
The case for and against AI-RAN technology using Nvidia or AMD GPUs
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks (?) and FWA (!)
Beyon partners with Ericsson to build energy-efficient wireless networks in Bahrain
Ericsson and e& (UAE) sign MoU for 6G collaboration vs ITU-R IMT-2030 framework
Dell’Oro: RAN market still declining with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung top vendors
Ericsson on 5G use cases: remote surgery, augmented and virtual reality with AI agent all depend on 3GPP URLLC specs
Nokia (like Ericsson) announces fresh wave of job cuts; Ericsson lays off 240 more in China
Swisscom (with Ericsson) to offer the world’s best and most sustainable mobile network
Vision of 5G SA core on public cloud fails; replaced by private or hybrid cloud?
For several years, many telecom analysts said it was inevitable that network operators would move telco workloads, especially their 5G SA core network software, into the giant data centers operated by Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure. For example:
- In June 2021, AT&T made an agreement with Microsoft to run its 5G SA core network in the Azure public cloud platform. However, that 5G SA network is still not commercially available!
- In July 2023, India’s Tech Mahindra and Microsoft announced they’d collaborate to enable cloud-powered 5G SA core network for telecom operators worldwide. So far we don’t know of any takers?
- Dish Network outsourced its entire 5G infrastructure (including 5G SA core network) to run on the AWS public cloud platform which went live in February 2022. See Figure 1. below
- In May 2024, O2 Telefónica in Germany and Nokia announced the deployment of 5G standalone core software on Amazon Web Services (AWS).

Figure 1. DISH 5G Cloud Architecture
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
However, the expected big move to telco public cloud did not happen in 2024! “No operators have core applications in the public cloud,” David Hennessy, the chief technology officer of the UK’s Three, told Light Reading earlier this year. 5G networks are spread across the geographies they serve. Hosting all functions in a single place just isn’t possible. Even the core, the domain allowing for the most centralization, is increasingly distributed across multiple facilities at the network “edge.” As a result, network operators are not using public cloud platforms for their 5G SA core or mission critical applications.
T-Mobile-US (the “un carrier”) has deployed its own 5G SA network. Cisco and Nokia are the primary vendors that built T-Mobile’s 5G SA core network. Some European network operators are resistant to use of the public cloud for telco-specific workloads. Those include the UK’s BT, which previously invested time and effort in building its own telco cloud with Canonical, a UK software company. Germany’s Deutsche Telekom has something similar called T-CaaS. Orange also has built a homegrown cloud based 5G SA network. Spain’s Telefónica is still not fully convinced by the other benefits of the public cloud providers. Automation is currently more advanced when both the core network software and infrastructure come from Ericsson than it is when Telefónica takes the core from Nokia and the infrastructure from AWS, according to Cayetano Carbajo, the operator’s director for core networks.
Carbajo is clearly disturbed by the lack of infrastructure standardization in a world of multiple different cloud offerings. Various telcos are working on this through an initiative called Sylva, overseen by the Linux Foundation. The fruit of it should be the ability for Telefónica to move network applications from one cloud to another without having to make big changes. Yet public cloud service providers are not even listed as sponsors on the Sylva website.
The alternative is to keep the 5G core on premises or in a private cloud. The latter might be used by other workloads, but – as the designation implies – it would not be shared with other companies. In general, 5G network operators have distributed their previously centralized workloads around a nationwide network, bringing resources into closer proximity with end-user devices. That results in lower latency as well as other service improvements.
For example, BT hosts its control plane functions at eight UK sites and its user plane software at 16 sites. Replicating this in the traditional public cloud, which relies on a smaller number of giant facilities, would be difficult if not impossible to do. As a result, IBM-owned Red Hat and Broadcom-owned VMware, the best-known cloud-computing players in this area, now propose to bring their software into a telco’s facilities. Microsoft calls it the “hybrid” cloud.
There was a bad omen for public cloud advocates in June when Microsoft revealed it was cutting telecom jobs and abandoning Affirmed Networks and Metaswitch, core network software developers it bought in high-profile deals several years ago. Clearly, Microsoft is retreating from the development of network applications.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/cloud/2024-in-review-a-bad-year-for-public-cloud-in-telecom
Public cloud economics aren’t adding up for some telcos
The public cloud has failed to crack telecom
Telefónica still not fully sold on public cloud after AWS move
Telenor has a go at public cloud but needs AWS to help
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks (?) and FWA (!)
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
AT&T 5G SA Core Network to run on Microsoft Azure cloud platform
Tech Mahindra and Microsoft partner to bring cloud-native 5G SA core network to global telcos
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/industries/telco-meets-aws-cloud-deploying-dishs-5g-network-in-aws-cloud/
Analysis of Dish Network – AWS partnership to build 5G Open RAN cloud native network
https://www.lightreading.com/cloud/the-public-cloud-has-failed-to-crack-telecom
5G network slicing progress report with a look ahead to 2025
The “true” version of 5G is 5G standalone (SA), which eliminates the need for a 4G anchor network and supports all 3GPP defined 5G functions, like 5G Security, Voice over 5G New Radio (VoNR) and network slicing. As we’ve noted for years, 5G SA has proven difficult to deploy, partially because there are no standards for implementation – only 3GPP 5G Architecture specs (rubber stamped as ETSI standards, but never submitted to the ITU for consideration as one or more ITU-T recommendations).
Network slicing is only possible with a 5G SA core network. Operators which have deployd 5G SA are using and planning to use 5G network slices for a variety of use cases, including: a priority slice for first responders, support financial or mission-critical applications, or offer broadcasters a dedicated fast 5G layer to transfer video from cameras to production teams at sporting or other live events.

Image Credit: SDx Central
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In the U.S., T-Mobile is the only major carrier offering 5G SA and has been moving forward with network slicing deployments. Verizon said recently that its 5G network slicing public safety field demonstration in Phoenix, Arizona, is operational but still in trials. AT&T has tested prioritized access to its network, but so far has not yet provided a 5G SA network to support network slicing . That’s despite outsourcing development to Microsoft Azure cloud platform in June 2021.
T-Mobile recently launched “T-Priority,” a network slice for first responders supported by the network operator’s 5G SA core network. The wireless telco told regulators at the end of 2023:
“Network slicing involves creating customized, software-defined, virtual networks – or ‘slices’ – that are each logically separated and individually optimized to meet the specific needs of each application. Within a slice, network functions are defined in software and customized to the use case supported by that slice. For example, network slicing allows providers to use a single 5G network to deliver high-intensity network resources to support a small number of robots on a factory floor, while at the same time delivering low-intensity network resources to a very large number of meter-reading sensors on a utility network.”
Overseas, BT, Orange Belgium, Singtel, China Telecom, Reliance Jio, and Telia Finland have deployed network slicing, among other 5G carriers. Singtel’s app-based network slicing is designed to improve the performance of consumer and enterprise applications.
Nokia recently said it tested a network slicing application with network operator Liberty Global and Belgian shipping company Seafar. Nokia said the shipping company could use its API platform to purchase an ultra-low latency slice of Liberty Global’s Telenet 5G standalone network to maneuver Seafar’s ships through ports without having to slow down.
“Slicing will be critical to enabling enterprise cases and providing network solutions for many use cases for which a stand-alone purpose-built network is not feasible,” Nokia stated in a February meeting between CEO Pekka Lundmark and a variety of top FCC officials, including FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel.
The GSMA, which is NOT a standards development organization, launched its “Open Gateway” campaign last year. Earlier this year the group said that 47 mobile operators representing 239 mobile networks and 65% of wireless connections around the world have signed up. Currently, GSMA and its partners are developing a wide range of APIs for text messaging, location information, billing, quality of service – and network slicing among other applications.
Several analysts believe that network slicing will see more growth next year:
“There will be definitely more rollouts of network slicing capabilities as 5G SA networks mature, and as 5G NSA networks move to SA in the next few years,” AvidThink principal analyst Roy Chua said in an email. “Using a network slice for privacy/security/isolation or for ensuring QoS (live broadcasts, sporting events, emergency and disaster support) will likely continue.”
Lead analyst at Techsponential Avi Greengart agreed that more network slicing deployments will happen in the coming year as more operators upgrade to 5G SA. “Network slicing has been a long-touted feature of 5G, and we’re starting to see it used for large venues (ex: sports stadiums) and public safety,” he told Fierce Network. Greengart warned that slicing is not a panacea for private networks or Wi-Fi.
“I do think that network slicing will be operator specific,” noted neXt Curve executive analyst Leonard Lee. “There is still the open question of what the generally monetizable services will be and the scenarios that make them viable. This, each operator will be answering for themselves on their own timeline. For outside observers, it will be like watching a kettle boil,” he said, adding a note of caution.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/network-automation/2025-preview-network-slicing-gets-real
https://www.fierce-network.com/wireless/network-slicing-slides-more-vigorously-2025
https://www.sdxcentral.com/5g/definitions/key-elements-5g-network/5g-network-slicing/
FCC Draft Net Neutrality Order reclassifies broadband access; leaves 5G network slicing unresolved
ABI Research: 5G Network Slicing Market Slows; T-Mobile says “it’s time to unleash Network Slicing”
Telstra achieves 340 Mbps uplink over 5G SA; Deploys dynamic network slicing from Ericsson
Ericsson, Intel and Microsoft demo 5G network slicing on a Windows laptop in Sweden
Is 5G network slicing dead before arrival? Replaced by private 5G?
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks and FWA
Ericsson’s November 2024 Mobility Report predicts that global 5G standalone (SA) connections will top 3.6 billion by 2030. That compares to 890 million at the end of 2023. Over that same period of time, 5G SA as a proportion of global mobile subscriptions is expected to increase from 10.5% to 38.4%, while average monthly smartphone data consumption will grow to 40 GB from 17.2 GB. By the end of the decade, 80% of total mobile data traffic will be carried by 5G networks.
That rosy forecast is in sharp contrast to the extremely slow and disappointing pace of 5G SA deployments to date. In January, Dell’Oro counted only 12 new 5G SA deployments in 2023, compared to the 18 in 2022. “The biggest surprise for 2023 was the lack of 5G SA deployments by AT&T, Verizon, British Telecom EE, Deutsche Telekom, and other Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) around the globe. As we’ve stated for years, 5G SA is required to realize 5G features like security, network slicing, and MEC to name a few.”
Fifty 5G Standalone enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) networks commercially deployed (2020 – 2023):
The report states, “Although 5G population coverage is growing worldwide, 5G mid-band is only deployed in around 30% of all sites globally outside of mainland China. Further densification is required to harness the full potential of 5G.” Among the report highlights:
- Global 5G subscriptions will reach around 6.3 billion in 2030, equaling 67% of total mobile subscriptions.
- 5G subscriptions will overtake 4G subs in 2027.
- 5G is expected to carry 80% of total mobile data traffic by the end of 2030.
- 5G SA subscriptions are projected to reach around 3.6 billion in 2030.
Source: Ericsson Mobility Report -Nov 2024
“Service differentiation and performance-based opportunities are crucial as our industry evolves,” said Fredrik Jejdling, EVP and head of Ericsson’s networks division. “The shift towards high-performing programmable networks, enabled by openness and cloud, will empower service providers to offer and charge for services based on the value delivered, not merely data volume,” he added.
The Mobility Report provides two case studies in T-Mobile US and Finland’s Elisa – both of which have rolled out network slicing on their 5G SA networks and co-authored that section of the report:
- T-Mobile has been testing a high priority network slice to carry mission-critical data during special events.
- Elisa has configured a slice to support stable, high-capacity throughput for users of its premium fixed-wireless access (FWA) service, called Omakaista.
The Mobility Report doesn’t say if those two telcos are deriving any monetary benefit from network slicing, or more broadly from their 5G SA networks.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) market has momentum:
- Ericsson predicts FWA connections will reach 159 million this year, up from 131 million in 2023.
- By 2030, connections are expected to hit 350 million, with 80% carried by 5G networks.
- In four out of six regions, 83% or more wireless telcos now offer FWA.
- The number of FWA service providers offering speed-based tariff plans – with downlink and uplink data parameters similar to cable or fiber offerings – has increased from 30% to 43% in the last year alone.
- An updated Ericsson study of retail packages offered by mobile service providers reveals that 79% have a FWA offering.
- There are 131 service providers offering FWA services over 5G, representing 54 percent of all FWA service providers.
- In the past 12 months, Europe has accounted for 73%of all new 5G FWA launches globally.
- Currently, 94% of service providers in the Gulf Cooperation Council region offer 5G FWA services.
- In the U.S. two service providers (T-Mobile US and Verizon) originally set a goal to achieve a combined 11–13 million 5G FWA connections by 2025. After reaching this target ahead of schedule, they have now revised their goal to 20–21 million connections by 2028.
- The market in India is rapidly accelerating, with 5G FWA connections reaching nearly 3 million in just over a year since launch. • An increasing number of service providers are launching FWA based on 5G standalone (SA).
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report/reports/november-2024
https://www.ericsson.com/4ad0df/assets/local/reports-papers/mobility-report/documents/2024/ericsson-mobility-report-november-2024.pdf
5G Advanced offers opportunities for new revenue streams; 3GPP specs for 5G FWA?
FWA a bright spot in otherwise gloomy Internet access market
Where Have You Gone 5G? Midband spectrum, FWA, 2024 decline in CAPEX and RAN revenue
GSA: More 5G SA devices, but commercial 5G SA deployments lag
Vodafone UK report touts benefits of 5G SA for Small Biz; cover for proposed merger with Three UK?
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
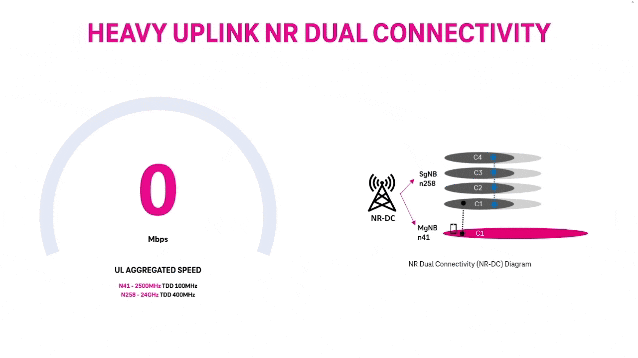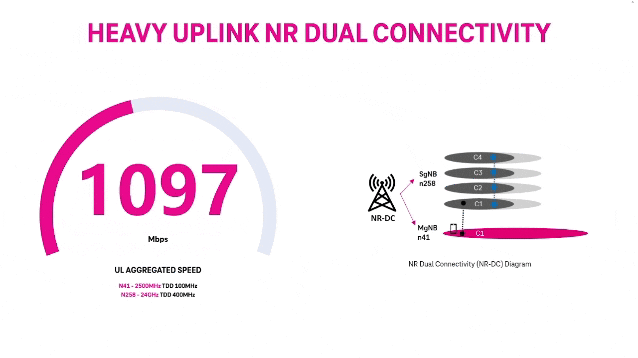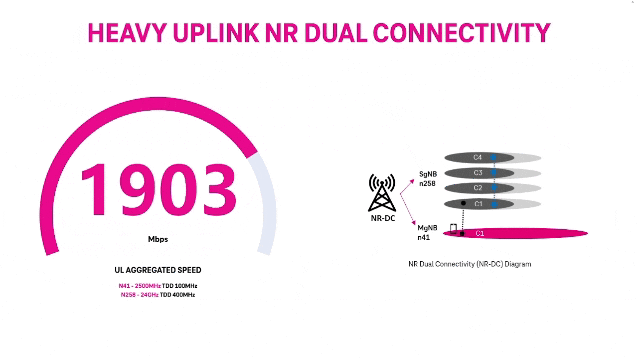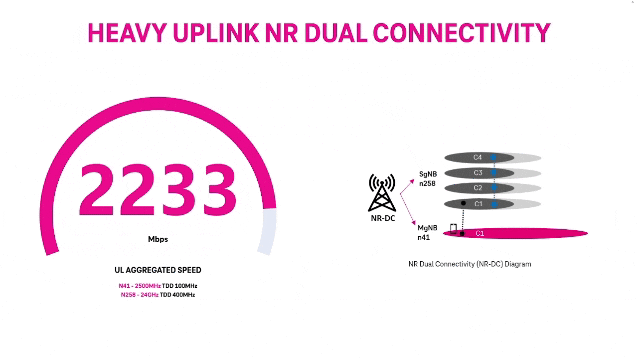
T‑Mobile achieves record 5G Uplink speed with 5G NR Dual Connectivity
T-Mobile US claims it broke a world record with its 5G standalone (SA) network via a new feature called New Radio Dual Connectivity (5G DC) [1.]. With 5G DC. The so called “Un-carrier” was able to massively increase uplink throughput and capacity, reaching peak speeds of 2.2 Gbps — that’s the fastest recorded anywhere in the world — and demonstrates the technology’s potential to create serious efficiencies in how data is transmitted from devices to the network.
Note 1. New Radio Dual Connectivity (NR-DC) is a dual connectivity configuration that uses the 5G standalone core (specified by 3GPP but not standardized by ITU-R or ITU-T). In this configuration, both the primary and secondary RAN nodes are 5G gNBs. NR-DC was was specified in 3GPP Release 15 along with simultaneous receive (Rx) / transmit (Tx) band combinations for NR CA/DC.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
To put T-Mo’s 2.2 Gbps uplink speed into context, the latest report from connectivity data specialist Ookla puts the median mobile upload speed in the U.S. at 8.41 Mbps, although that’s across networks. T-Mobile is ahead of major rivals AT&T and Verizon with a median upload speed of 12.19 Mbps.
In June Ookla stated that while U.S. network operators have invested heavily in improving 5G download speeds, “5G upload and latency performance need more attention.” Its data at the time showed Verizon and T-Mobile had comparable 5G upload at just above 15 Mbps, while AT&T lagged somewhat at closer to the 10 Mbps mark.
5G DC enables the Un-carrier to aggregate 2.5 GHz and mmWave spectrum, allowing for an insane boost to uplink throughput and capacity. In this test, T-Mobile was able to allocate 60% of the mmWave radio resources for uplink where previous use cases typically allowed up to 20%. Completed on T-Mobile’s 5G SA production network in SoFi Stadium in Southern California with equipment and 5G DC solution from Ericsson and a mobile test smartphone powered by a flagship Snapdragon® X80 5G Modem-RF System from Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., this test changes the game for providers looking to offer customers and businesses the best experience possible at crowded events.
“With 5G DC, T-Mobile is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible to create better experiences in the places that matter most to our customers,” said Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology at T-Mobile. “This accomplishment is a testament to the network we’ve built over the last five years and our ability to deliver unparalleled capabilities that extend beyond the devices in our pockets.”
For those in the know, download speeds typically reign as the top network performance metric, but with recent strides in uplink capabilities and increasingly demanding tasks, upload speed is becoming more important than ever, especially for live events, mobile gaming and extended reality applications.
Because of this, SoFi Stadium served as the perfect test site for 5G DC. Every year, millions of people flock to the stadium for the latest football game or to catch their favorite artists in concert. Naturally, all these people want to post, livestream and share their experiences in real-time, which can sometimes be a challenge at crowded events with limited capacity. Not to mention broadcast crews who need to upload high-definition content to production teams in real-time for those watching at home. With 5G DC and T-Mobile, all of this gets done faster than ever, alleviating posting FOMO and production crew headaches.
Mårten Lerner, Head of Product Area Networks at Ericsson, said: “High uplink speeds are essential for delivering immersive experiences and reliable 5G connectivity. This mirrors one of our key objectives with the recent launch of Ericsson 5G Advanced, which is to elevate user experience by enhancing network performance for more interactive applications. This 5G uplink speed milestone, achieved with T-Mobile and Qualcomm, underscores our commitment to taking user experience to unprecedented levels.”
“We are incredibly proud to achieve yet another world record with T-Mobile. This groundbreaking achievement shows what could be possible with 5G DC and how it can bring new, unparalleled experiences to consumers, especially at large events like football games and concerts,” said Sunil Patil, Vice President, Product Management, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. “We will continue our close collaboration with global innovators like T-Mobile and Ericsson to push the boundaries and unlock the full potential of 5G.”
5G network covers more than 330 million people across two million square miles. More than 300 million people nationwide are covered by T-Mobile’s super-fast Ultra Capacity 5G with over 2x more square miles of coverage than similar mid-band 5G offerings from the Un-carrier’s closest competitors.
For more information on T-Mobile’s network, visit T-Mobile.com/coverage.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/network/t-mobile-shatters-for-5g-uplink-speed
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/t-mobile-us-uses-5g-dc-to-claim-uplink-speed-record
Telstra achieves 340 Mbps uplink over 5G SA; Deploys dynamic network slicing from Ericsson
Finland’s Elisa, Ericsson and Qualcomm test uplink carrier aggregation on 5G SA network
Ericsson and MediaTek set new 5G uplink speed record using Uplink Carrier Aggregation
Samsung-Mediatek 5G uplink trial with 3 transmit antennas
Dish Wireless with Qualcomm Technologies and Samsung test simultaneous 5G 2x uplink and 4x downlink carrier aggregation
BT, Nokia and Qualcomm demonstrate 2CC CA on uplink of a 5G SA network
Telefónica and Nokia partner to boost use of 5G SA network APIs
Telefónica and Nokia today announced an agreement to jointly explore new opportunities leveraging 5G Standalone (SA) capabilities for network APIs to support developers in creating new use cases for consumer, enterprise, and industrial customers.
Through this agreement, Telefónica will harness Nokia’s Network Exposure Function (NEF) for various purposes that enable developers to access the operator’s 5G network capabilities, like precise device location, enhanced notifications based on connectivity status, edge discovery, and more.

Having access to these capabilities will enhance developers’ capacity to build new applications and drive new service APIs for the industry.
Nokia’s NEF solution, based on 3GPP specifications, provides a process for interfacing with well-defined functions in the core network. It also enables API mashups so developers can combine multiple APIs from different core functions into a new customized API, which is easier for developers to use to create new applications. NEF is said to be “a robust platform for creating new services by consolidating APIs and presenting unified access to the API framework for in-house or 3rd party app developers.”
- Secure exposure of network services (voice, data connectivity, charging, subscriber data, etc.) towards 3rd party application over APIs
- Developer environment and SDK for operator and community
- Service mashup for creating end-to-end offering by combining any of the network assets into your application
- Integration layer that connects your application to operator’s network.
Last week, it was announced that Nokia Network as Code platform with developer portal will run on Google Cloud. The purpose is to promote specific use cases to the Google Cloud developer community, starting with healthcare. Google Cloud stresses it developers cover “all major industries and geographies”.
Nokia’s Network as Code platform brings together networks, systems integrators, and software developers, into a unified ecosystem that provides developers a simple way for integrating advanced 5G capabilities into their applications; without having to navigate the complexity of the underlying network technologies.
Nokia has signed collaboration agreements with 14 network operators and ecosystem partners, in Europe, North America, and South America, to use the platform since its launch in September 2023.
Quotes:
Cayetano Carbajo Martin, Core & Transport Director, Global CTIO at Telefónica said: “We are pleased to take this step with Nokia in recognition of the tremendous opportunity we have to further empower developers with the tools they require to deliver new use cases and experiences for their customers and beyond. This partnering agreement is about steering the industry in building new APIs and more use cases over 5G SA capabilities that have been launched across Telefonica’s main operations.”
Shkumbin Hamiti, Head of Network Monetization Platform, Cloud and Network Services at Nokia said: “There continues to be a rising recognition that sustaining closed networks is a thing of the past and that embracing ecosystems is the way forward for deepening collaboration and creating new use cases; delivering better customer experiences; and generating new revenue opportunities. Our agreement with Telefónica is added proof of the much greater telco ecosystem openness that we are now seeing today and we look forward to jointly working to support developers in harnessing a broader array of network capabilities.”
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core-networks/network-exposure-function/
https://www.nokia.com/networks/programmable-networks/network-as-code/
https://www.mobileeurope.co.uk/telefonica-nokia-aim-to-boost-use-of-5g-sa-network-apis/
Nokia, Google Cloud to help developers create 5G apps with telco APIs
Telefónica launches 5G SA in >700 towns and cities in Spain
Telefónica launches 5G SA in >700 towns and cities in Spain
How Network Repository Function Plays a Critical Role in Cloud Native 5G SA Network
NRF (Network Repository Function) facilitates cloud-native 5G networks by enabling dynamic and efficient discovery of peer Network Functions, enhancing scalability.
Ajay Lotan Thakur
Introduction:
DNS (Domain Name Service) has been widely used by networks to discover 3G and 4G Network Functions (NFs). Every time there is a change in the network, this entails adding or updating records in the DNS server. This solution was not cohesive. The 5G Network Repository Function (NRF), which was introduced in the 5G specification, addresses this issue. Every Network Function needs to register its profile with NRF when it’s ready to service the APIs. Every NF type contains unique information in the NF profile. For example, Session Management Function (SMF) might provide the set of Data Network Names (DNN) it serves.
It’s important to note is that SMF may still choose User Plane Function (UPF) using proprietary logic because the UPF interface to NRF is still optional. In this article we shall see various advantages provided by 3GPP’s NRF network function over traditional 3G/4G networks.
Advantages of 5G NRFs:
Using 5G Network Resource Function (NRF) for discovering peer Network Functions (NFs) compared to relying on DNS servers in 4G networks brings several advantages:
- Efficiency in Resource Discovery: NRF offers a more efficient and dynamic way of discovering peer NFs within the network. Unlike DNS servers, which rely on static records and hierarchical lookup mechanisms, NRF enables direct discovery of available NFs, reducing latency and enhancing resource utilization. NRF can search the NFs based on many parameters like load, slice Ids, DNN name etc.
- Enhanced Security: NRF can incorporate security features such as authentication and authorization mechanisms, ensuring that only authorized NFs can be discovered and accessed. This helps in mitigating security threats such as DNS spoofing or cache poisoning, which are concerns in traditional DNS-based architectures.
- Support for Network Slicing: NRF is well-suited for 5G network slicing, where multiple virtualized networks coexist on the same physical infrastructure. It allows for efficient discovery and allocation of NFs specific to each network slice, enabling tailored services and resource optimization.
- Service Orchestration: NRF facilitates service orchestration by providing real-time information about the available NFs and their capabilities. This enables dynamic service composition and adaptation based on changing network conditions and application requirements. NRF can be used to put some of the NFs under maintenance mode as well.
- Low Latency: With NRF, the latency in discovering and connecting to peer NFs is significantly reduced compared to DNS-based approaches. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time communication or low-latency services, such as edge computing or autonomous vehicles. In case NRF is overloaded then it can scale-out to bring down the latency.
- Scalability: NRF architecture is designed to handle the scalability demands of 5G networks, where the number of NF instances and their dynamic nature can be high. It allows for efficient scaling of network resources without relying on centralized DNS servers, which may face scalability challenges under heavy loads. This allows Network Functions to implement dynamic scale in & scale out without touching any DNS servers.
- Dynamic Network Updates: NRF supports dynamic updates of network information, allowing for real-time changes in the availability and status of NF instances. These are NRF notifications supported as per 3gpp specification. In contrast, DNS records may require time to propagate changes across the network, leading to potential inconsistencies or delays in service discovery. Each NF can update its profile as and when it sees changes.
Conclusions:
Overall, leveraging NRF for NF discovery in 5G networks offers improved efficiency, scalability, low latency, security, and support for advanced network functionalities compared to relying solely on DNS servers in 4G networks.
References:
3GPP TS 23.501 – System Architecture for the 5G System
3GPP TS 29.510 – Network Function Repository Services
GSA: More 5G SA devices, but commercial 5G SA deployments lag
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
Ericsson Mobility Report touts “5G SA opportunities”
Analysys Mason: 40 operational 5G SA networks worldwide; Sub-Sahara Africa dominates new launches
Samsung and VMware Collaborate to Advance 5G SA Core & Telco Cloud
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
GSM 5G-Market Snapshot Highlights – July 2023 (includes 5G SA status)
About the Author:
Ajay Lotan Thakur, Senior IEEE Member, IEEE Techblog Editorial Board Member, BCS Fellow, TST Member of ONF’s open source Aether (Private 5G) Project, Cloud Software Architect at Intel Canada.

Blog post edited by Alan J Weissberger