5G SA/5G Core network
Ericsson and Vodafone enable Irish rugby team to use Private 5G SA network for 2023 Rugby World Cup
Ericsson and Vodafone Ireland have partnered to install a cutting-edge 5G Standalone Mobile Private Network (MPN) solution for the Irish rugby team to supply fast and reliable in-play data analysis ahead of the 2023 Rugby World Cup in September.
Previously the team relied on standard WiFi across stadiums and training facilities both at home and away. Now giving instant feedback on team plays and tactics, the 5G Standalone MPN solution and artificial intelligence technology ensures faster download and upload speeds and lower latency, which can be utilised for real-time performance analysis and decisions on the pitch.
Using this reliable connectivity, up to eight high-resolution video streams are captured by multiple cameras and a 5G connected drone and then analysed in real-time to collate data on team performance. The technology helps to improve the communication between management, coaches and players and maximises the time on pitch where the smallest tweak to a running line or defensive position, can have a significant impact on the weekend’s game.
Vodafone Ireland and Ericsson have worked closely with the IRFU and their Head of Analytics and Innovation, Vinny Hammond and his analysis team of John Buckley, Alan Walsh and Jack Hannon. This collaboration has led to a clear understanding of the specific performance outcomes sought by such an elite sports team and has supported the design and installation of the Ericsson Private 5G solution, which now enables the management team, coaches and players to feel the real benefit of instant feedback to enhance the ability to make decisions quikcly.
The new solution has been tested at the Irish team’s High Performance Centre and will be brought to France in a bespoke 5G connected van for the World Cup in September.
Vodafone Ireland Network Director, Sheila Kavanagh says: “At Vodafone, we are so proud of our support for the Irish Rugby team, so we’re delighted to bring further value through the delivery of this cutting-edge technology solution. Performance analysis has experienced massive changes in the past couple of decades. What started with pen and paper-based methods for collecting notational data has evolved to using cutting-edge computer-based technologies and artificial intelligence to collect ever increasing amounts of real-time information. Distilling and delivering this data back to the team at top speed requires a reliable, secure and scalable connectivity solution.”
“This 5G MPN, drone and additional technology will support Vinny Hammond and his analytics team to quickly breakdown and organise unstructured data and present it back in a clear manner to other coaching staff and management – helping them understand the performance of the plays and overall team, without delay. It’s fantastic to see it in use in the HPC, but we’re also really excited to support the team with 5G connectivity throughout their time at the World Cup in France with our fully kitted Connected Van. Our 5G MPN technology is a demonstration of how technology and connectivity innovation can enhance the business of sport and the performance of teams, bringing added layers of data and analysis to coaches, management, and their players.”
IRFU Head of Analytics and Innovation, Vinny Hammond says: “So much of our roles revolve around moving large quantities of data so we can analyse performance to understand what is working and what is not. Vodafone’s 5G MPN stretches the boundaries of what we can do in terms of how quickly we can analyse multiple high-resolution cameras and drone footage which ultimately informs our strategic decision making. The work John and Alan have done on this project in conjunction with Vodafone and Ericson has enabled us to push new boundaries at this years RWC. Being on our own 5G network also gives us that level of security and reliability that we really need, and we’ll have the added benefit of that connectivity with our 5G Connected Van, linking back to our High Performance centre, to reduce reliance on third party connectivity.”
John Griffin, Head of Ericsson Ireland, says: “5G is the ultimate platform of future innovation and our successful partnership with Vodafone continues to ensure new organisations like the IRFU can benefit from the low latency, high bandwidth, and secure connectivity of a 5G standalone private network. Our global leadership in 5G technology and accelerated software availability mean the IRFU will be one step ahead of their competitors on and off the field, giving them the best chance of success at an elite level of performance and revolutionizing the future of a key function within the sports industry.”
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/3/2023/ericsson-and-vodafone-help-irish-rugby-team-adopt-5g-technology-to-get-fast-in-play-data-analysis
BT and Ericsson wideband FDD trial over live 5G SA network in the UK
BT and Ericsson have successfully demonstrated 5G transmission using a wideband FDD (frequency division duplex) radio carrier (over 20 MHz) within a sub-3 GHz spectrum band. According to BT and Ericsson, this accomplishment is a major advancement in the progress of 5G networks, with implications that will greatly impact network capacity and performance.. The trial used existing Ericsson commercial hardware, including Baseband 6648 and Radio 4419. The software feature ‘Large Bandwidth Support Low-Band’ was activated to facilitate the testing, and Handsets powered by MediaTek Dimensity chips, specifically the MediaTek M80 Release-16 modem.

Source: BT Group
The trial was conducted on BT’s live network (EE brand name) in Bristol and Potters Bar, UK. It showcased the benefits of configuring a wide carrier bandwidth of 50 MHz (50 MHz downlink + 50 MHz uplink) within the 2.6 GHz band, along with downlink aggregation using two TDD (time division duplex) carriers in the 3.5 GHz band. This configuration led to a capacity uplift of over three times compared to a single FDD carrier. According to the joint statement, the trial also evaluated an intermediate carrier bandwidth of 30 MHz.
This result is particularly significant for the uplink in 5G Standalone (5G SA) networks. According to BT, currently, 5G SA relies on a single carrier for the uplink, but this trial demonstrates the potential to significantly boost uplink capacity using a wider carrier bandwidth. The technology partners stated that enabling 5G expansion in FDD bands is a crucial step in the rollout of EE’s 5G SA network. 5G SA is expected to offer superior experiences for consumers and businesses, meeting the increasing demand for data-driven applications like cloud gaming, virtual reality (VR), and emerging edge technologies. This achievement has the potential to enable higher capacity, improved network performance, and enhanced user experiences.
Greg McCall, Chief Networks Officer, BT Group, commented: “This breakthrough is the latest example of our commitment to maximizing the full potential of 5G for our customers. As network quality and accessibility improve, so too will innovation and the 5G services ecosystem. Demonstrating new network capabilities such as those announced today is critical to achieving this goal, and also paves the way to ensuring that 5G SA delivers new possibilities for our customers.”
Evangelia Tzifa, Chief Technology Officer, Networks & Managed Services, for Ericsson UK and Ireland said: “This is a great step forward for the deployment of 5G Standalone for EE in the UK. Ericsson innovative software capabilities such as large bandwidths for NR FDD as well as NR Carrier Aggregation enable a solid foundation for improved end user experience and network performance. This is a fundamental link for business success and the evolution to next-generation connectivity across the country.”
Dr. Ho-Chi Hwang, General Manager of Wireless Communication Systems and Partnerships at MediaTek, said: “This remarkable achievement of boosting uplink capacity is a fundamental step for the evolution from 5G Non-Standalone to 5G Standalone networks. By supporting an uplink connection in a single FDD carrier with a wider bandwidth, MediaTek Dimensity 5G chipsets already meet the surging demand for uplink data in a new era of mobile applications”.
References:
BT, Ericsson Wideband FDD Trial Showcase Breakthrough 5G SA Performance
Globe Telecom, HPE to deploy 5G SA network in the Philippines
Globe Telecom in the Philippines has partnered with Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) to roll out the first Private 5G Standalone (5G SA) network in the Philippines. According to Globe, this network introduces a new era of connectivity options for businesses, elevating cellular connectivity to unprecedented levels.
“The breakthrough private 5G standalone betwork brings us closer to a digitally transformed enterprise landscape,” said Yoke Kong Seow, chief technical advisor at Globe.
“5G offers a lot of surprising use cases. Exploring it and doing customer pilot deployment will bring meaningful results and opportunities. This successful demonstration of the first Private 5G SA Network heralds another innovation for our enterprise customers to experience,” he said.
The partnership with HPE offers flexibility in building the Private 5G network. Enterprises can choose to host the solution in the cloud, acquire a complete solution including HPE edge servers and Athonet software, or just license the software to integrate into existing infrastructure.
“With our Athonet technology, we are enabling a new era of connectivity for businesses,” said Loh Khai Peng, vice president for APAC sales at HPE. “HPE is proud to partner with Globe on this groundbreaking endeavor, providing solutions that are not only tailored for specific needs but are also scalable, secure, and highly reliable,” he said.
Built with technology from Athonet, a subsidiary of HPE, the network will deliver cellular connectivity to enterprises and organizations across the Philippines as an alternative or complementary solution to Wi-Fi and public mobile technologies.
Globe said, the Athonet 5G SA Starter Kit is a complete package with SIM cards, a radio, and a mobile core network, all housed within a convenient briefcase. This plug-and-play Private 5G SA Network offers features, including high-quality video and audio streaming, as well as lightning-fast download speeds of up to 780 Mbps and upload speeds of up to 150 Mbps.
Moreover, the kit operates as a stand-alone network, making it an ideal solution for businesses seeking reliable cellular connectivity. Additionally, this Private 5G SA Network works seamlessly with business applications via its N6 interface.
Private 5G SA networks offer improved security, customizable options, low latency, and high capacity. These networks excel at handling large-scale IoT deployments, especially for mission-critical operations.
According to Globe, the collaboration with HPE offers flexible Private 5G network solutions, including cloud-based options, edge servers with Athonet software, and customizable choices for scalability.
Globe’s Private 5G SA Network will redefine the future of businesses in the Philippines with increased productivity, cost-efficiency, and improved quality.
References:
Globe Telecom, HPE to roll out 5G SA network in the Philippines
Globe to Deploy Philippines’ First Private 5G Network With HPE
GSA 5G SA Core Network Update Report
GSA is tracking the emergence of the 5G SA core network, including the availability of chipsets and devices for customers, plus the testing and deployment of 5G SA networks by public mobile network operators as well as private network operators.
5G SA networks can be deployed in a variety of scenarios: as an overlay for a public 5G non-SA network, as a greenfield 5G deployment for a public network operator without a separate LTE network, or as a private network deployment for an enterprise, utility, education, government or other organization requiring its own private campus network.
GSA has identified 115 operators in 52 countries and territories worldwide that have been investing (?) in public 5G SA networks in the form of trials, planned or actual deployments (see Figure 1.). This equates to 21.4% of the 535 operators known to be investing in 5G licenses, trials or deployments of any type.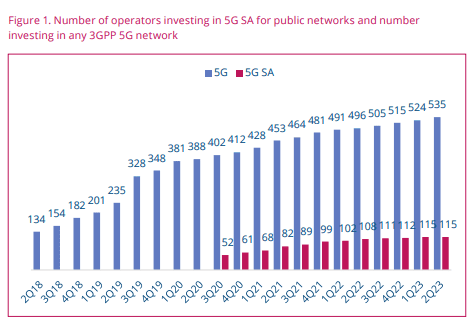
At least 36 operators in 25 countries and territories are now understood to have launched or deployed public 5G SA networks, two of which have only soft-launched their 5G SA networks.
NOTE: Incredibly, that’s a DECREASE from GSA’s June 5G SA report which stated “GSA has catalogued 41 operators as having deployed or launched 5G standalone (SA) in public networks.”
Also, 19 cellular network operators have been catalogued as deploying or piloting 5G SA for public networks, and 29 as planning to deploy or evaluating, testing or trialing the technology.
Several organizations are testing, piloting or deploying 5G SA technologies for private networks. As of May 2024, 66 (just over 13% of total cellular private networks) organizations are known to be working with 5G SA core networks. These organizations include manufacturers, academic institutions, commercial research institutes, construction, communications and IT services, rail and aviation industries.
The number of 5G SA devices as a percentage of all 5G devices announced has been steadily increasing. They accounted for 35.6% of 5G devices in December 2019, 49.7% in December 2020 and 54.6% in December 2021 and a large increase to 81.8% in December 2022. As of June 2023, they account for 85.8%.
Software upgrades are almost always needed to enable 5G SA capability for existing 5G devices. There is a range of form factors to cater for different users, including modules for equipment manufacturers and vendors; customer-premises equipment (CPE), routers and gateways for enterprise or industrial customers or their systems integrators; CPE for home and business broadband; phones; and battery-operated hot spots for portable services.
Smartphones make up over half (59.0%) of the announced 5G devices with stated 5G SA support (1,034 phones), followed by fixed wireless access CPE (246) and modules (220).
Spectrum Support in 5G SA Devices:
Selected sub-6 GHz frequencies are increasingly well supported in 5G SA devices. The pattern of most-supported bands in sub-6 GHz 5G SA devices largely matches the pattern for most-supported bands across all 5G devices, with C-band, 2.6 GHz, 2 GHz, 1.8 GHz and 700 MHz.
Sub-6 GHz support by band, announced 5G SA devices, most-supported bands by most devices. Support for millimeter wave is not yet common.
Chipsets are being developed to support this capability — GSA has currently only catalogued eight chipsets specifically supporting 5G SA in millimeter-wave spectrum (eight mobile processors and platforms). 320 393 397 421 449 519 739 741 743 817 846 979 1,025 1,115 1,183 1,257 1,309 1,444 1,465 n48 n25 n66 n71 n12 n2 n20 n40 n79 n38 n7 n8 n5 n3 n28 n77 n1 n41 n78 We can expect support for spectrum bands above 6 GHz to increase in the future, as these bands are being promoted as an option for deployment of private 5G networks by regulators in various countries, as well as being promoted as capacity bands for high-traffic locations in public networks.
Summary:
The market is seeing the emergence of a strong 5G SA ecosystem with chipsets, devices of many types and users of public as well as private networks. We can expect to see the market go from strength to strength.
–>This author opines the 5G SA market is going from nowhere to no place!
As it does, GSA will continue to track its evolution and will be looking out for important new trends as they emerge.
Topics likely to become more important in the coming year in this context include 5G carrier aggregation in SA networks, ultrareliable low-latency communications (can’t be accomplished till 3GPP Release 16 URLLC in the RAN spec has been completed and performance tested) capabilities to support machine-to-machine connections in 5G SA systems, increasing support for millimeter-wave connections, network slicing in 5G networks and the introduction of VoNR in 5G SA networks.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
GSM 5G-Market Snapshot Highlights – July 2023 (includes 5G SA status)
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
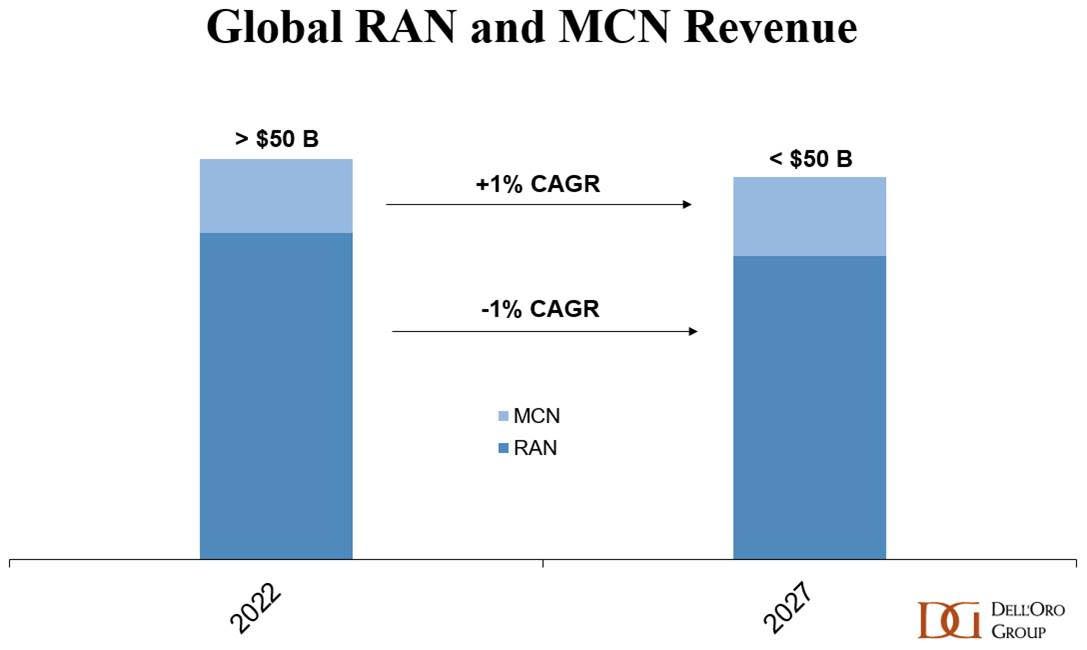
Dell’Oro: RAN Market to Decline 1% CAGR; Mobile Core Network growth reduced to 1% CAGR
According to a newly published forecast report by Dell’Oro Group,the Radio Access Network (RAN) market is done expanding for now. Following the 40% to 50% ascent between 2017 and 2021, RAN revenues flattened out in 2022 and these trends extended to 1Q 2023.
“Even if it is early days in the broader 5G journey, the challenge now is the comparisons are becoming more challenging in the more mature 5G markets and the upside with the slower-to-adopt 5G regions is not enough to extend the growth streak,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group.
“Meanwhile, growth from new revenue streams including Fixed Wireless Access and enterprise LTE/5G is not ramping fast enough to change the trajectory. With 5G-Advanced not expected to trigger a new capex cycle, the question now is no longer whether RAN will grow. The question now is, rather, how much will the RAN market decline before 6G comes along?” Pongratz added.
Additional highlights from the Mobile RAN 5-Year July 2023 Forecast Report:
- Global RAN is projected to decline at a 1 percent CAGR over the next five years.
- The less advanced 5G regions are expected to perform better while the more developed 5G regions, such as North America and China, are projected to record steeper declines.
- LTE is still handling the majority of the mobile data traffic, but the focus when it comes to new RAN investments is clearly on 5G. Even with the more challenging comparisons, 5G is projected to grow another 20 percent to 30 percent by 2027, which will not be enough to offset steep declines in LTE.
- With mmWave comprising a low single-digit share of the RAN market and skepticism growing about the MBB business case, it is worth noting that our position has not changed. We still envision that the mmWave spectrum will play a pivotal role in the long-term capacity roadmap.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Dell’Oro again lowered its forecasts for the Mobile Core Network market (which is now 5G SA core network), this time citing a slowdown in customer growth. It now predicts that the worldwide market for mobile core networks will expand at a CAGR of 1% over the next five years, having previously forecast a 2% CAGR as recently as January.
“We have reduced our forecast for the third consecutive time, primarily caused, this time, by an expected slowdown in subscriber growth,” said Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group.
Dave said that Dell’Oro has reduced its expectations for the Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) market (which requires 5G SA core network). It now anticipates MEC will have a CAGR of 31%, noting that commercially-viable enterprise applications are taking much longer to come to fruition than many had hoped.
“Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) are concerned about inflation, a possible recession, and political conflicts. They are therefore being restrained in their capital expenditures, another factor weighing in on a more conservative forecast,” said Bolan. “As we continue refining our count of MNOs that have launched 5G Standalone (5G SA) eMMB networks, we note that only 4 MNOs have commercially deployed new 5G SA networks compared to six in the first half of 2022,” he added.
Additional highlights from the Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Computing 5-Year July 2023 Forecast Report:
- Year-over-year MCN revenue growth rates are projected to be flat in 2026 and turn negative in 2027.
- The North America and China regions are expected to have negative CAGRs, while Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA), and Asia Pacific excluding China regions are expected to have the highest positive CAGRs.
Vodafone became one of those first-half 2023 launches, when it brought 5G Ultra to market in the UK in late June. In its latest Mobility Report, published around the same time, Ericsson noted that while around 240 telcos have launched commercial 5G services, only 35 of them have brought standalone 5G to market.
That should bode well for the mobile core market, and indeed it is faring better than the RAN space, in growth potential terms, at least.
Nonetheless, Dell’Oro predicts that year-on-year growth rates in mobile core network revenues will be flat by 2026 and turn negative the following year.
Dell’Oro Group’s Mobile RAN 5-Year Forecast Report offers a complete overview of the RAN market by region – North America, Europe, Middle East & Africa, Asia Pacific, China, and Caribbean & Latin America, with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue and unit shipments for 5GNR, 5G NR Sub 6 GHz, 5G NR mmW and LTE pico, micro, and macro base stations. The report also covers Open RAN, Virtualized RAN, small cells, and Massive MIMO. To purchase this report, please contact us by email at [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group’s Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Computing 5-Year July Forecast Report offers a complete overview of the market for Wireless Packet Core including MEC for the User Plane Function, Policy, Subscriber Data Management, and IMS Core with historical data, where applicable, to the present. The report provides a comprehensive overview of market trends by network function implementation (Non-NFV and NFV), covering revenue, licenses, average selling price, and regional forecasts for various network functions. To learn more about this report, please contact us at [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, security, enterprise networks, and data center infrastructure markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com.
References:
RAN Market to Decline at a 1 Percent CAGR Through 2027, According to Dell’Oro Group
Slower Subscriber Growth to Cut Mobile Core Network Market Growth, According to Dell’Oro Group
Heavy Reading Survey: 5G services require network automation
Heavy Reading’s 2023 5G Network Analytics and Automation Operator Survey aims to help the industry better understand the status of network analytics and automation and provide insights into operators’ strategies. (To download a copy, click here.) At the start of the survey, one question looks to understand which 5G services network operators believe to be the most valuable in supporting revenue growth.
Editor’s NOTE: It’s important to understand that ALL 5G SERVICES/FEATURES (such as network slicing) require a 5G SA core network rather than 5G NSA which uses 4G-LTE infrastructure for everything other than the 5G NR RAN.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
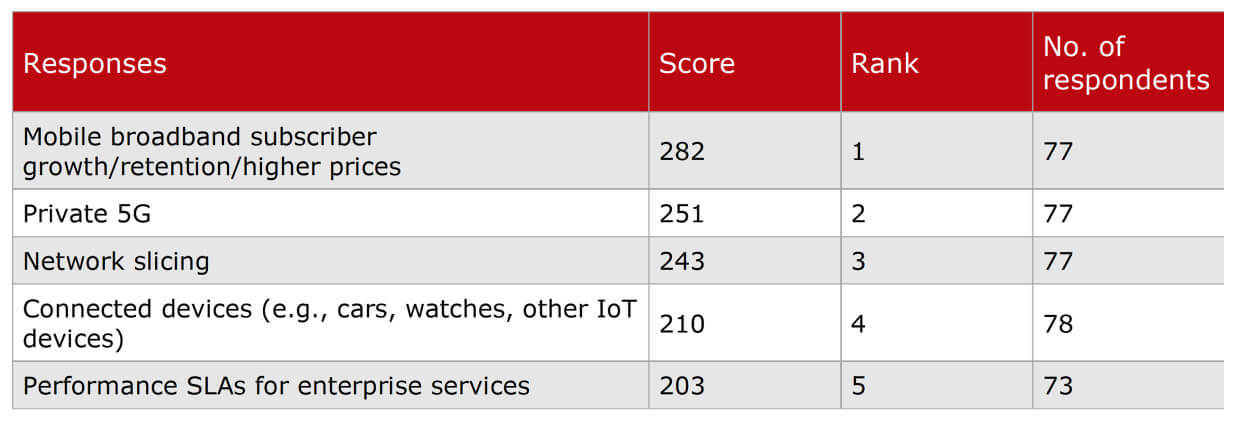
The table below shows the weighted average scores across several 5G services, with operators ranking “mobile broadband subscriber growth/retention/high prices” first and ahead of the other options.
Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) is the anchor service for 5G NSA and generates nearly all 5G revenue today. This scoring infers that operators are keen to grow their core businesses, which will involve greater efficiencies and new mobile packages that offer superior or premium features at an added cost.
“Private 5G” and “network slicing” rank second and third, respectively. Heavy Reading expects their importance and popularity to increase as additional operators deploy 5G SA and can support full autonomy. “Performance SLAs for enterprise services” is currently the lowest ranking (fifth) of all service choices but is likely to be a valuable market, especially for network slicing and private 5G.
“Connected devices (e.g., cars, watches, other IoT devices)” ranks just above performance SLAs in fourth. Internet of Things (IoT) is a sizeable market within 4G, but the massive machine-type communications (mMTC) use case has yet to be realized in 5G, as technologies such as RedCap remain underdeveloped.
Smaller network operators have a different opinion than larger operators on the revenue growth question.
For mobile operators with less than 9 million subscribers, private 5G ranks first. This result perhaps indicates that smaller operators feel they are already exploiting eMBB services and see little scope for further revenue growth with 5G SA.
Which services are the most attractive for 5G revenue growth in your organization? (Rank in order, where 1 = the most attractive)
Given the survey results above and the desire for operators to grow their revenue and retain customers, it is evident that automation will play a fundamental role in future 5G services underpinning cost efficiencies and quality of service. Service diversity and the 5G disaggregated cloud native infrastructure will mandate automation across the network (i.e., provisioning, testing, operation, fault resolution and maintenance), specifically for the following aspects:
Automated configuration: Automation tackles the scale and complexity of administration, management and lengthy configuration across large networks with multiple service solutions (e.g., private networks, network slicing, performance SLAs, etc.), offering significant time savings over manual effort.
- End-to-end 5G monitoring and visibility: 5G network visibility requires a dynamic and layered approach to monitor 5G cloud infrastructure, orchestration/containerized environments and the network domains and services. Service insights and SLA monitoring will be more granular. Examples include network slicing visibility per slice, user, session, location, etc., across KPIs like latency, jitter, packet drop and data rate.
- Network probes and testing: Active test agents provide near real-time visibility, making them better equipped to monitor dynamic cloud native environments and workload changes than more traditional reactive methods.
- Lifecycle and test management: Automated software deployment cycles (CI/CD) will be critical due to the increased cadence of software updates across virtual machines or cloud native deployments. In addition, automating network and service testing could enable the validation of services and configuration while assessing the perceived end-user quality of service.
- Artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML): These technologies will contribute heavily to automated processes, optimization and efficiencies, with AIOps processes assuring the network and its services. For example, AI/ML can help forecast network resources, user mobility patterns, RAN optimization, security anomaly prevention, fault prediction, etc.
Operators are highly motivated to deliver advanced services and drive business growth and revenue to recoup the costs of their significant 5G spectrum and network investments. However, supporting a diverse and evolving portfolio of 5G network services will require automation to provide service visibility, efficiencies and network performance excellence.
References:
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
Swisscom, Ericsson and AWS collaborate on 5G SA Core for hybrid clouds
Orange Business tests new 5G hybrid network service in France
Orange Business said that it has carried out tests of a new 5G service called “Mobile Private Network hybrid“at its office in Arcueil (Ile-de-France region). The telco claims the hybrid private network has several applications and is able to connect industrial equipment, tablets and autonomous vehicles, among other end points. It cited the example of ports as an area particularly suitable for hybrid network deployments.
Orange said it is “actively investing in the construction” of hybrid 5G networks in France. Its two units have been “constantly innovating to continue to develop services and use [cases],” the company added.
The new 5G service has been tested with a router from Ericsson owned Cradlepoint which is connected to both networks simultaneously and assigns data flows to the appropriate network based on predefined use cases and the application being used. The Cradlepoint router supports 5G SA and network slicing technology for business premises, with a hardened version available for industrial settings.
The test project hosted two use cases in two network slices, running on a laptop (“behind the router”): transmission of a video feed to the cloud on the public network to support a remote assistance use case, and an edge-based supervision application for an industrial process where all the data circulated on the private network. “The separation of data flows is complete from the application on the terminal to the core network.”

(Source: l_martinez / Alamy Stock Photo)
The network is operated by Orange in full and does not require the use of multiple SIM cards. Companies can use the solution for both critical and non-critical applications, with data flows isolated from the application on the terminal all the way to the core, and service quality adapted to each application. The company says it relies on local break-out technology, which allows for local routing of data flows, to offer stable low latencies. Orange also says the private network guarantees performance and offers higher data security than the public network.
Orange is one of few European operators that have started rolling out 5G SA networks, it has not yet officially launched one in France. In March, it announced it would start offering 5G SA in a handful of Spanish cities later this year. The telco will rely on Ericsson’s core technology, which will also be used in Belgium, Luxembourg and Poland.
References:
Orange intros managed hybrid-private 5G service for French enterprises
Samsung-Mediatek 5G uplink trial with 3 transmit antennas
Samsung Electronics and MediaTek have successfully conducted 5G standalone (SA) uplink tests, using three transmit (3Tx) antennas instead of the typical two, to demonstrate the potential for improved upload experiences with current smartphones and customer premise equipment (CPE).
Until recently, most talk about 5G SA industry firsts have focused on the downlink. However, the demands on uplink performance are increasing with the rise of live streaming, multi-player gaming and video conferences. Upload speeds determine how fast your device can send data to gaming servers or transmit high-resolution videos to the cloud. As more consumers seek to document and share their experiences with the world in real-time, enhanced uplink experiences provide an opportunity to use the network to improve how they map out their route home, check player stats online and upload videos and selfies to share with friends and followers.
While current smartphones and customer premise equipment (CPEs) can only support 2Tx antennas, this industry-first demonstration validated the enhanced mobile capability of 3Tx antenna support. This approach not only improves upload speeds but also enhances spectrum and data transmission efficiency, as well as overall network performance.
The test was conducted in Samsung’s lab, based in Suwon, Korea. Samsung provided its industry-leading 5G network solutions, including its C-Band Massive MIMO radios, virtualized Distributed Unit (vDU) and core. The MediaTek test device featuring its new M80-based CPE chipset began with one uplink channel apiece at 1,900MHz and 3.7GHz, but added an extra uplink flow using MIMO on 3.7GHz. Both companies achieved a peak throughput rate of 363Mbps, an uplink speed that is near theoretical peak using 3Tx antennas.

Source: ZTE
“We are excited to have successfully achieved this industry breakthrough with MediaTek, bringing greater efficiency and performance to consumer devices,” said Dongwoo Lee, Head of Technology Solution Group, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “Faster uplink speeds bring new possibilities and have the potential to transform user experiences. This milestone further demonstrates our commitment to improving our customers’ networks using the most advanced technology available.”
“Enhancing uplink performance using groundbreaking tri-antenna and 5G UL infrastructure technologies will ensure next-generation 5G experiences continue to impress users globally,” said HC Hwang, General Manager of Wireless Communication System and Partnership at MediaTek. “Our collaboration with Samsung has proved our combined technical capabilities to overcome previous limits, enhancing network performance and efficiency, opening up new possibilities for service providers and consumers to enjoy faster and more reliable 5G data connectivity.”
“With demands on mobile networks rising, enhancing upload performance is essential to improving consumer and enterprise connectivity, as well as application experiences,” said Will Townsend, VP & Principal Analyst at Moor Insights & Strategy. “Samsung and MediaTek have achieved an important 5G Standalone milestone in a demonstration which underscores a tangible network benefit and does so in a way that can help operators maximize efficiency.”
Samsung has pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions, including chipsets, radios and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio, from virtualized RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company currently provides network solutions to mobile operators that deliver connectivity to hundreds of millions of users worldwide.
References:
Ericsson and MediaTek set new 5G uplink speed record using Uplink Carrier Aggregation
Nokia achieves extended range mmWave 5G speed record in Finland
Huawei and China Telecom Jointly Release 5G Super Uplink Innovation Solution
https://www.telecomhall.net/t/5g-uplink-enhancement-technology-by-zte-white-paper/20183
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
According to a May 2023 report from the Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA), just 35 network operators in 24 countries and territories “are now understood to have launched or deployed public 5G SA networks.” That’s out of approximately 240 service providers which have now launched commercial 5G services, as per the recent Ericsson Mobility Report.
Dell’Oro’s Dave Bolan said, “Currently we count 43 live 5G SA networks for eMMB [enhanced mobile broadband]. For 2023, four [mobile network operators] have launched 5G SA networks,” he added. It should be noted that Dell’Oro doesn’t factor in fixed wireless access (FWA) or private 5G networks in its SA totals.
In Europe, Vodafone UK and Telefónica Spain join what remains a small set of network operators that have launched 5G SA, including Orange Spain and Vodafone Germany. Spain should provide an interesting study of what happens when two rival operators launch 5G SA service.
There are some glimmers of hope that 5G SA launches will accelerate soon. GSA (aka GSMA) has identified at least 1,063 announced devices with declared support for standalone 5G in sub-6GHz bands, 864 of which are commercially available. Furthermore, it said 116 operators in 53 countries and territories are now investing in 5G SA, including those that have actually deployed a public network. “This equates to 22.1% of the 524 operators known to be investing in 5G licenses, trials or deployments of any type,” the GSA said.
Separately, analysts say that 5G SA branding by network operators is quite confusing (we agree). Vodafone UK’s decision to use 5G Ultra for its 5G SA branding vs Telefonica using 5G+ are examples of that.
Gabriel Brown of Heavy Reading said, “customers don’t really know what it means, other than it denotes some form of technical advance.” He points out that 5G SA “requires a lot of investment and deep engineering expertise; this makes it a useful proxy for network quality. Operators need to take all the technical marketing opportunities they can get.”
“What happens when BT launches? Are they going to call it 5G+ or 5G Super Ultra or something like that? That’s going to make it even more confusing,” said Kester Mann, an analyst with CCS Insight. At the same time, he agrees that 5G standalone is a significant network upgrade and it makes sense that operators would want to gain a marketing edge over rivals that have yet to launch the service.
Notably, neither Vodafone nor Telefónica is charging extra for the more advanced 5G service, and both have focused on the improved speeds and reliability it will bring. They also emphasize eco-friendly aspects, such as lower energy consumption. However, Mann questioned Vodafone’s claim that customers with an eligible 5G Ultra device can expect up to 25% longer battery life. “Twenty-five percent faster than what?” he asked. “It’s a bit unclear.” However, such a claim would certainly be welcome news to consumers. “In a lot of our consumer research, battery life comes out as one of the common bugbears among people using mobile phones,” said Mann.
In the U.S., T-Mobile is the only network operator that’s deployed a 5G SA network. AT&T and Verizon have been talking about it for years, but the time frame for deployment has been pushed back several times.
Deloitte Global said it expects the number of mobile network operators investing in 5G SA networks via trials, planned deployments or rollouts to grow from more than 100 operators in 2022 to at least 200 by the end of this year.
One reason why there are relatively few 5G SA networks deployed is there are no implementation standards. 3GPP 5G Architecture specs, rubber stamped by ETSI, provide several options to realize a 5G cloud-native core network which leads to different implementations. 3GPP decided NOT to liaise their 5G non-radio aspects specs (including 5G Architecture and 5G Security) to ITU-T.
Here are the key 3GPP 5G system specs:
- TS 22.261, “Service requirements for the 5G system”
- TS 23.501, “System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 23.502 “Procedures for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 32.240 “Charging management; Charging architecture and principles”
- TS 24.501 “Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3”
The latest 3GPP 5G Architecture spec is System architecture for the 5G System (5GS) (3GPP TS 23.501 version 17.9.0 Release 17), published by ETSI on July 5, 2023.
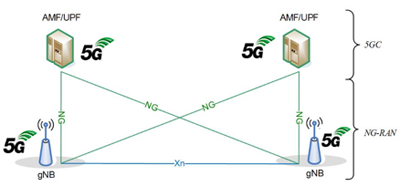
Source: 3GPP
Hence, the ITU JCA on IMT2020 and Beyond is dependent on other organizations for inputs to their roadmap. “The scope of JCA-IMT2020 is coordination of the ITU-T IMT-2020 standardization work with focus on non-radio aspects and beyond IMT2020 within ITU-T and coordination of the communication with standards development organizations, consortia and forums also working on IMT2020 and beyong IMT-2020 related standards.”
References:
https://www.silverliningsinfo.com/5g/5g-sa-springs-action
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
Orange-Spain deploys 5G SA network (“5G+”) in Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia and Seville
Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments
Tech Mahindra and Microsoft partner to bring cloud-native 5G SA core network to global telcos
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
https://urgentcomm.com/2023/01/19/standalone-5g-progress-remains-a-disappointment/
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/5g-system-overview
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/jca/imt2020/Pages/ToR.aspx
Telefónica launches 5G SA in >700 towns and cities in Spain
Telefónica has followed Orange with the official launch of a 5G standalone (SA) network in more than 700 towns and cities throughout Spain. The service is branded Movistar 5G+ even though it is just 3GPP defined real 5G (with its own core network , rather than 5G NSA which uses LTE core network). The new Telefónica 5G SA network uses Ericsson and Nokia network equipment. Huawei has been excluded from it because the European Commission wants to ban Huawei in the EU for its alleged espionage work for the Chinese government.
Telefonica said its 5G NSA service in the 700 MHz band is currently available to around 85 percent of the Spanish population across 2,200 municipalities. The Spanish operator also uses the 3.5 GHz band for 5G and invested EUR 20 million to secure the maximum possible 1 GHz of spectrum in the 2.6 GHz band.

“Movistar customers will be able to enjoy 5G+ automatically and at no additional cost both in large cities and in small municipalities thanks to a highly capillarity deployment that will allow ultra-fast speeds and very low latency to be obtained in practically all of Spain,” the company explained in a statement.
The launch of 5G+, which offers greater coverage and browsing speeds of up to 1,600 megabits per second (Mbps), will take place within the scope of Movistar’s deployment in the 3,500 MHz band. In practice, 5G+ translates into better mobile experience in content downloads at the speed of fiber optics, streaming High quality and uninterrupted gaming. It also offers greater coverage in crowded spaces such as a sporting event or a music concert, according to Telefónica.
Movistar currently covers a total of 11 cities with 5G SA: Madrid, Barcelona, Malaga, Seville, Palma de Mallorca, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Ávila, Segovia, Castellón, El Ferrol and Vigo. The goal for the end of the year is to have “extensive 5G SA coverage in most cities with more than 250,000 inhabitants,” as well as in smaller towns, so that the capillarity of the service continues to be consolidated. However, in order to enjoy this service it is necessary to have a mobile that supports 5G SA. For the moment, Movistar has the new Xiaomi terminals to which new brands will be added.
Gabriel Brown, principal analyst at Heavy Reading, notes that Movistar operates the biggest network in Spain and has the largest number of live 3.5GHz sites, according to the independent AntenasMoviles website.
Said deployment is completed with the coverage in the 700 MHz band that Movistar has been offering since last year and currently reaches more than 2,200 municipalities, with advantages such as improved indoor coverage. The so-called low band is complemented in 5G with that of 3,500 MHz, ideal for services that require a user experience at a very high transmission speed, both for rural areas and large urban centers. In this way, Movistar already offers 5G coverage to more than 85% of the population, reports the company.–
Orange leads 5G SA coverage as it already reaches more than twenty cities that cover 30% of the population in Spain. In the case of Vodafone and MásMóvil, 5G SA is expected to be available before March 2024.
Heavy Reading’s Brown said, “It will be interesting to see if this gives it an edge in SA. Orange Spain, meanwhile, says it will launch network slicing before the end of the year.”
References:
https://euro.eseuro.com/business/572316.html
Telefónica – Nokia alliance for private mobile networks to accelerate digital transformation for enterprises in Latin America
Orange-Spain deploys 5G SA network (“5G+”) in Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia and Seville