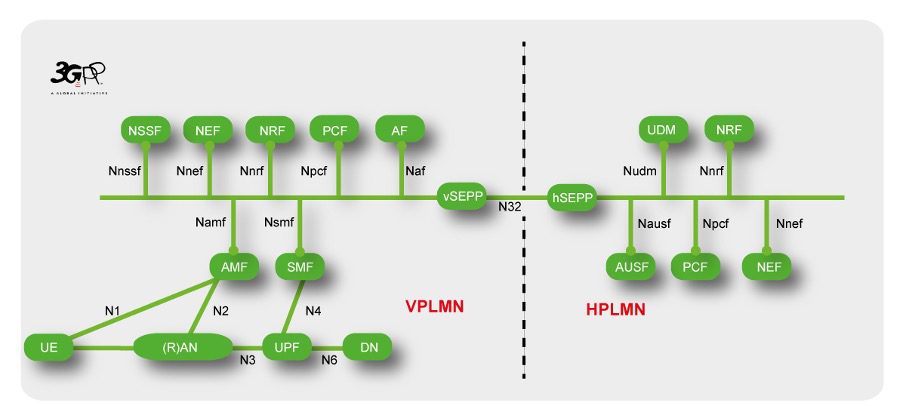
5G SA/5G Core network
GSA: More 5G SA devices, but commercial 5G SA deployments lag
Findings from the latest GSA report on the 5G standalone (SA) ecosystem include:
- 1,764 announced devices with claimed support for 5G SA, up 43.7% from 1,227 at the end of 2022.
- Devices with support for 5G SA account for 68.1% of all 5G devices, as of the end of March 2024, up from 43.3% in December 2019.
- 97 modems or mobile processors/platform chipsets state support for 5G SA, 93 of which are understood to be commercially available.
………………………………………………………………………..
Other Estimates of deployed 5G SA core networks:
According to a recent LinkedIn post by Kaneshwaran Govindasamy, at least 49 network 29 have launched or deployed public 5 , one of which has only soft-launched their 5G SA networks.
A February 2024 report from Counterpoint Research in February 2024 states that only 55 operators have commercially implemented 5G SA, with many more in testing and trial stages.
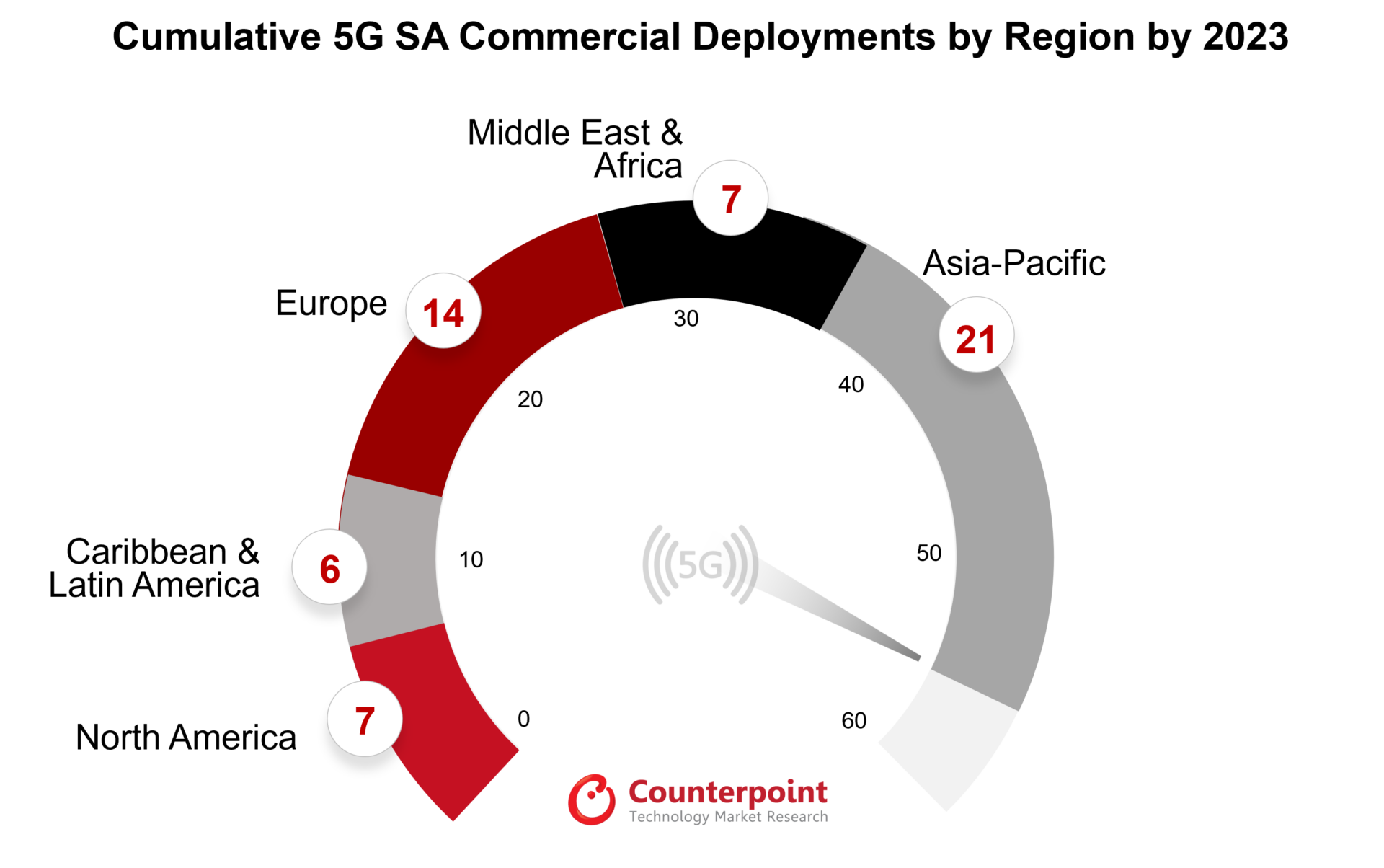
As of January 2024, Dell’Oro Group has identified 50 5G SA enhanced Mobile BroadBand (eMMB) networks that have been deployed worldwide. Dell’Oro Group’s Research Director, Dave Bolan, stated that the build-out of 5G SA networks is slower than expected, and that the number of new 5G SA networks deployed in 2023 (12) was lower than in 2022 (18). However, Bolan predicts that 2024 will see more 5G SA launches than 2022, and that 5G SA launches will occur in almost all global markets except Africa.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
It should be noted that there is only one 5G SA network deployed in the U.S. from T-Mobile. AT&T and Verizon have promised 5G SA for years but it’s not commercially deployed by either operator at this time.
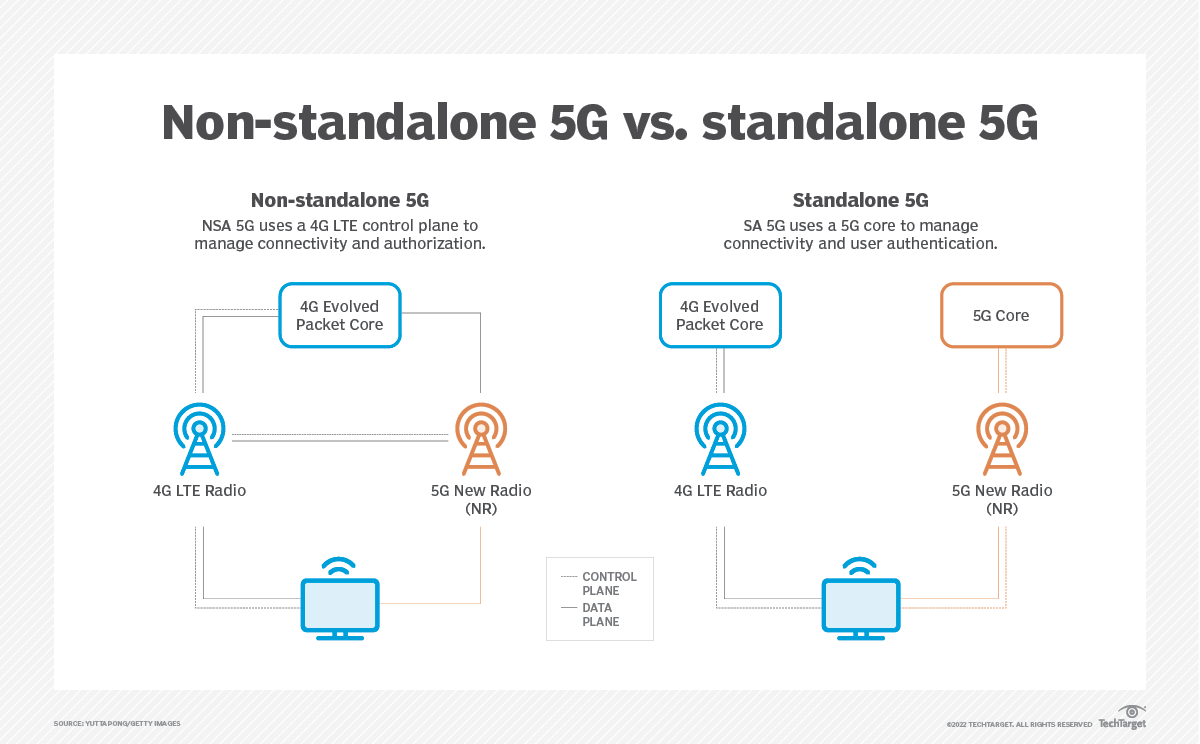
5G SA networks support higher-density device deployments and improved network performance. Without a 5G SA network, there are no 3GPP defined 5G features available, such as 5G Security, Network Slicing, MEC, etc.
References:
GSA 5G SA Core Network Update Report – Technology Blog
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
Mobile Core Market Stagnant Due to Lack of 5G Standalone Deployments, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.ericsson.com/en/5g/5g-sa
Ericsson on 5G use cases: remote surgery, augmented and virtual reality with AI agent all depend on 3GPP URLLC specs
5G for Remote Surgery:
This year, surgeons in Florida working with Ericsson, were able to operate on remote patients in Dubai and Shanghai, using 5G technology, according to Mischa Dohler, Ericsson vice president-emerging technologies.
A hospital in China used a 5G-enabled robot to perform spinal surgery on patients, and doctors used VR headsets to livestream the operation. The robot implanted over 62 pedicle screws in the patients’ spinal cord. Here’s a pic of that:
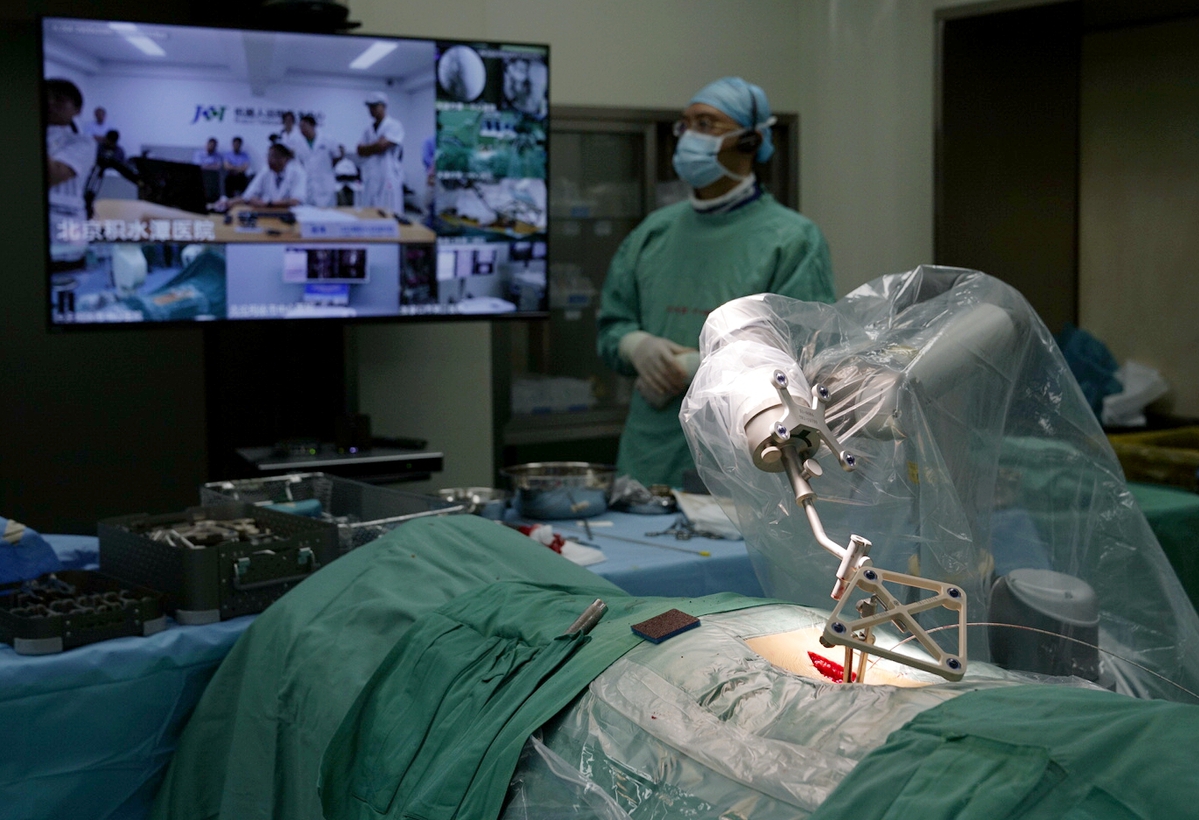
Photo by Wang Fei/For China Daily
Dohler said he’s working with the White House, FCC, NTIA, Food and Drug Administration and others to make remote surgery “a reality.” More widespread use of the technology won’t happen unless smaller carriers also get involved. We will have not only humans using your networks, but also machines more and more,” Dohler added.
Gartner’s market research underscores the importance of 5G SA, predicting that by 2025, it will be the foundation for the majority of applications demanding sub-10 millisecond latency. This transition is not merely a technical upgrade but a strategic enabler for industries poised to benefit from real-time data processing and decision-making. However, the ultra low latency depends on two 3GPP Release 16 specs – 1.] 5GNR enhancements for URLLC in the RAN and 2.]URLLC in the 5G SA core network– being completed, performance tested and implemented. That has not happened yet and without it there can’t be any 5G URLLC use cases like remote surgery!
Real-time remote surgeries, once a concept of futuristic medicine, are becoming a reality. The ability to perform surgical procedures from thousands of miles away, with real-time response and precision, could revolutionize healthcare accessibility and outcomes. For example, a pilot project involving 5G SA-enabled remote surgery successfully demonstrated how surgeons could operate with millisecond-level precision, mitigating geographical barriers to specialized medical care.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Ericsson’s Dohler predicted growing use of augmented and virtual reality and AI “agents,” computer programs capable of performing tasks autonomously, which people will use as part of their daily lives. New technology will require networks that can handle increased traffic, he said. New data traffic patterns “will hit you at some point this decade,” he said. “You will need to do some bold moves.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2024/3/cutting-the-cord-lifesaving-telesurgery-in-the-age-of-5g
https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201908/29/WS5d670e17a310cf3e355686fa.html
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/dawn-new-era-navigating-shift-from-5g-nsa-sa-tayroni-fkvre/
Swisscom (with Ericsson) to offer the world’s best and most sustainable mobile network
Swisscom, the leading network operator in Switzerland, is planning to transform its wireless 3G/4G/5G network into a “smart network” by extending its partnership with Ericsson for another three years. Under the partnership, Ericsson will continue to supply the hardware and software for Swisscom, enabling it to enhance its customer experience and further develop the mobile network with a focus on sustainability.
The strategic partnership between Swisscom and Ericsson dates back to 2015 and has been underscored by a series of wins in mobile network tests from key trade magazines.
Swisscom is extending its strategic partnership with Ericsson for another three years, aiming to transform its network into a smart network. Through automation, the use of artificial intelligence (AI), and increased innovation, the network will be modernized to continue providing the best customer experience now and in the future.
Another important development stream is marked by continuous spectrum refarming to New Radio (NR), with which the service provider prepares its network for 5G Standalone deployment with the possibility of launching new services.
Ericsson has long provided Swisscom with its cloud based Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) solution to support its telecom applications. With this new deal the service provider will now take on Ericsson’s Cloud Native Infrastructure solution (CNIS). For Swisscom, this means further enhancing the network’s well-established reliability and expanding the ability to host cloud-native telecom applications from Ericsson as well as from third-party providers. It will also help reduce overheads needed to manage the cloud platform and infrastructure, introduce further energy efficiencies, and optimize the total cost of ownership (TCO) overall. The deployment will bring together a close collection of telecom partner companies such as Extreme Networks and Dell Technologies, which contribute components, infrastructure and capabilities to the solution, all collaboratively engaged to ensure Swisscom and its subscribers enjoy the best possible network performance.

Image Credit: Ericsson
Gerd Niehage, CTIO Swisscom, explains, ” We’ve been working closely with Ericsson for over 10 years with a great amount of trust and success. We are now taking the next step in this long-standing strategic partnership as we endeavour to turn Switzerland’s best network into its smartest one. This will enable us to not only offer our customers the best customer experience, but also to place an even greater focus on sustainability and innovation.”
Daniel Leimbach, Head of Customer Unit Western Europe at Ericsson, adds, “In this innovative partnership, Swisscom’s characteristically Swiss pursuit of perfection meets the global technology leadership from Sweden’s Ericsson. Our common goal is to raise the bar even higher and continue to develop Switzerland’s best network into its smartest one. We have already set important benchmarks for the global development of the telecommunications market from within Switzerland in recent years.”
The far-reaching agreement, with a special focus on innovation, performance, and energy efficiency will see the introduction of Ericsson’s lightweight dual-band Radio 4490 as well as the company’s next-generation RAN processor from Ericsson’s RAN Compute portfolio, designed to serve all technologies from a single box and supporting real-time AI processing.
The agreement also includes deployment of Ericsson’s Massive MIMO portfolio across multiple sites as a part of the continued effort to expand coverage. It also will bring network improvements from the introduction of Ericsson’s Cloud Native Infrastructure Solution (CNIS) to support telecom applications across the business, and which enables software upgrades during operation and is also highly energy-efficient. Ericsson’s Intelligent Automation Platform (EIAP) and it’s open rApp (automation applications) ecosystem will also be introduced, offering the Swisscom network access to a wide range of new and innovative applications from Ericsson and other ecosystem members which will bring access to a host of new capabilities to create and maintain world-beating services. Here too, the focus is on performance and efficiency.
Swisscom aims to offer its customers the best and most sustainable network, so the new focus of the strategic partnership is to make the Swisscom network one of the most efficient mobile networks in the world.
Swisscom’s network is already fully powered by renewable energy, and the partners have taken a step further with the launch of an Energy Sustainability Programme (UK spelling) to intelligently reduce the energy consumption of mobile communications systems.
To maximize the partnership, Ericsson and Swisscom employees collaborate in mixed teams to drive innovations and projects forward for the continuous development of the mobile network. This close cooperation offers both companies opportunities to expand their competitive position and customer centricity. With the best network in Switzerland, Swisscom aims to strengthen the competitiveness of the Swiss economy and drive the country’s digital transformation.
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2024/4/swisscom-selects-ericsson-to-future-proof-mobile-network
Swisscom, Ericsson and AWS collaborate on 5G SA Core for hybrid clouds
Ericsson and ACES partner to revolutionize indoor 5G connectivity in Saudi Arabia
Telstra achieves 340 Mbps uplink over 5G SA; Deploys dynamic network slicing from Ericsson
BT Group, Ericsson and Qualcomm demo network slicing on 5G SA core network in UK
Finland’s Elisa, Ericsson and Qualcomm test uplink carrier aggregation on 5G SA network
Vodafone UK report touts benefits of 5G SA for Small Biz; cover for proposed merger with Three UK?
A new Vodafone report claims that small businesses in the UK could be missing out on up to £8.6 billion (US $10.8 billion) a year in productivity savings due to the very slow rollout of 5G standalone (5G SA) [1.]. The report states:
• Based on current progress rates, and without further action, by 2030 the UK would rank 5th on this index, scoring lower that Denmark, Finland, Sweden and the Netherlands. The UK would lose its position as one of the foremost places in Europe to start a new business.
• But an accelerated rollout of standalone 5G (5GSA) would allow the UK to jump three places from its current position by 2030, becoming the second-best place in Europe for business to secure the connectivity and digital competitiveness needed to grow.
Note 1. Vodafone defines 5G SA as follows:
Standalone 5G (5G SA) refers to the rollout of 5G connectivity on an entirely new network, as opposed to building upon the existing 4G network. Whilst this enables the network to enjoy some of the benefits of superfast connectivity, 5G SA is not subject to the limitations of the 4G networks, and is therefore able to support high-density deployments, such as smart sensors and real time data sharing.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….

The report cites agriculture as an example, where the use of 5G SA for activities such as real-time data monitoring and AI-based forecasting could help those laboring in the industry save on average at least 6% of their working hours.
In particular, the report’s sidebar on Agriculture states:
With agricultural activities tending to be much more spread out than other SME business operations, this means that having a reliable 5G-supported network is especially needed to reap the productivity rewards across new and exciting technological frontiers:
• Real-time data monitoring: Technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and real-time data sensors on a standalone 5G network can capture the status of virtually everything that farmers typically spend the most time on assessing: the weather, soil quality, and crop health.
By seeing data in real time, farmers can access the information they need and use technology to support decision-making for when to water crops or use pesticides – greatly reducing working hours and costs.
• AI decision-making and forecasting: With the wealth of uninterrupted data that can be collected on a standalone 5G network by smart technology, this enhances the information that AI can use to make more informed, faster recommendations to farmers than manually. AI programs can forecast things such as future crop health and optimised farming schedules to maximise crop yields.
• Precision machinery: New machine technology can also use data to determine more precise amounts of resources to use in the field for crop health, reducing wastage and saving time than if completed manually. Pioneering unmanned machinery, including for weeding and seeding, can save farmers more hours in the field to focus on other areas of the agricultural business.
Through a meta-analysis of surveys on how the 296,000 workers employed by agriculture SMEs typically spend their working times, we expect that they can save on average at least 6% of their working hours – or over 3.1 working weeks per worker – through a national standalone 5G network and the technologies it enables. This equates to all these workers collectively saving over 37.7 million working hours per year – delivering productivity savings of £112 million per year.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
A possible motivator of this report is Vodafone’s desire to complete its proposed merger with the UK’s Three, a deal that would allow Vodafone to rollout a nationwide 5G SA network. The report contends that a merger with Three would lift Vodafone from fifth to second place in a “European Index” that compares and ranks the competitiveness of each country’s 5G offerings for small businesses across 17 countries.
During a keynote at MWC Barcelona 2024, Vodafone Group CEO Margherita Della Valle commented that the proposed merger with Three will drive 5G “to all the areas that need it so badly.” She added “It will have a very positive impact on the U.K. economy. And we’ve also said it very clearly, we’re not going to change our pricing policies as a consequence.”
Vodafone said that it has committed to invest £11 billion ($13.9 billion) in 5G SA to cover 99% of the UK population by 2034 — should the merger with Three be approved by the regulators.
References:
https://www.fiercewireless.com/5g/vodafone-uk-sees-ps86bn-gain-smes-faster-5g-sa-rollout
https://www.fiercewireless.com/5g/three-ireland-launches-5g-standalone-ericsson
https://dgtlinfra.com/5g-standalone-sa/
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
Ericsson Mobility Report touts “5G SA opportunities”
Analysys Mason: 40 operational 5G SA networks worldwide; Sub-Sahara Africa dominates new launches
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
Where Have You Gone 5G? Midband spectrum, FWA, 2024 decline in CAPEX and RAN revenue
Nokia utilizes Intel technology to drive greater 5G SA core network energy savings
Nokia and Intel today announced that they are targeting greater energy efficiency improvements in 5G networks by using Xeon processors and power management software from Intel that will power Nokia’s cloud-native 5G Core solutions [1.] The two companies’ advances, building on years of innovation, will give communication service providers (CSPs) more leverage in reducing electricity usage and costs in their networks.
Note 1. The Nokia packet core provides key components needed for a webscale-class evolved packet core (EPC) and 5G core system (5GC). With its virtualized, cloud-native disaggregated and state-efficient design, it is well suited for multi-cloud environments. It is also infrastructure agnostic and independent of the underlying cloud infrastructure used for orchestration, lifecycle management (LCM) and infrastructure resource management.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In testing demonstrations, Nokia achieved approximately 40% runtime power savings using Nokia’s cloud-native 5G Core, integrated with Intel Infrastructure Power Manager (IPM) software and 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors*, while maintaining key network performance metrics.
Such energy savings are achieved through the careful integration of Nokia’s Core with Intel’s power modulation capabilities, which result in the energy consumption of the chips being proportional to the amount of traffic on the network – which varies considerably during any 24-hour period. Nokia intends to deliver these energy savings capabilities to the market as early as the second half of 2024, starting with Nokia’s Cloud Packet Core. Nokia and Intel will demonstrate these capabilities at MWC Barcelona at Intel’s booth 3E31.
The announcement underscores Nokia’s ongoing broader efforts to help CSPs and other network-dependent industries reduce their environmental footprint, become more resource efficient, and drive increased value from their networks. Nokia has set its key greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction target through the Science Based Targets (SBT) initiative, which is aligned with the goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C. Nokia was the first telecoms equipment vendor to have a science-based target accepted by the SBT initiative in 2017.
Marcelo Madruga, Head of Technology and Platforms, Products & Engineering, Cloud and Network Services at Nokia, said: “I am very pleased with the brilliant work that Nokia and Intel are doing to deliver very meaningful reductions in the energy footprint of 5G networks. Network data and computation usage only continues to grow, with the clear implication that has for continued energy demand growth. What we are doing today demonstrates not only superior software and technology but delivering on our broader commitments to cut carbon emissions across value chains.”
Alex Quach, Vice President & GM, Wireline and Core Network Division at Intel, said: “This is another solid proof point in the long-standing Intel-Nokia collaboration that highlights the strength of our teams in empowering CSPs with innovative solutions. Integrating the Intel Infrastructure Power Manager into Nokia’s widely deployed packet core software will help deliver the power savings CSPs require and strengthens network operations through intelligent resource allocation.”
Stéphane Demartis, VP Telco Cloud Infrastructure at Orange, said: “We are delighted to start a collaboration with Nokia and Intel to optimize our power consumption. This will provide a major step forward in delivering energy efficient solutions in the core network infrastructure. Orange is looking forward to working with Nokia and Intel to explore implementation of these innovations for a sustainable 5G Core network through the #Sylva project.”
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core-networks/cloud-packet-core/
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/newsroom/resources/2024-mwc-barcelona.html#gs.5dbwdb
https://www.nokia.com/events/mobile-world-congress/
Telstra achieves 340 Mbps uplink over 5G SA; Deploys dynamic network slicing from Ericsson
Australian telco Telstra announced this week that it has achieved a 5G uplink speed of 350 Mbps over 5G Standalone (SA) using sub-6 GHz frequencies in a live commercial network in partnership with Ericsson and Qualcomm. Telstra claims this as a new global record for 5G uplink speed, which is 100 times faster than the average 3G uplink speed.
Telstra’s new 5G SA uplink capability combines its mid-band spectrum holdings to create a 140MHz channel for sending data from the device to the network.
The tests were completed using a mobile test device powered by Qualcomm Technologies’ latest Snapdragon® 5G modem-RF System and an existing in-market NetGear Nighthawk M6 Pro Mobile Broadband device in the live commercial network on the Gold Coast.
The latest software from Ericsson brings together different combinations of frequency ranges and types to enable a single 5G uplink and downlink data channel.
By aggregating carrier bands, it considerably increases the uplink speeds, while the ability to use low band carriers in these combinations of frequencies delivers improved coverage and performance enhancements for the 5G SA Network.

Mr Amirthalingam says: “The uplink and downlink 5G data channels work together to provide a seamless and almost symmetrical like 5G service, meeting the increasing demand for data-intensive applications such as augmented and virtual reality, or sharing photos and memorable movie moments with friends.
“The technology also includes advanced features in the base station that can prioritise different types of data and applications and can support future differentiated services, like network slicing.”
“On top of this, Telstra also has the option to use the n5 (850MHz) carrier that is currently serving its 3G Network. “
“Our latest 5G Standalone uplink speed achievement is 100 times faster than the typical 3G uplink speed, which is great news for customers. Enterprise Applications such as these are increasingly becoming more uplink heavy with things like such as high-definition video surveillance cameras and the faster speeds and coverage will all provide a much better experience.”
“The ability to use low band frequencies and repurpose our 3G low band 850 MHz frequency to deliver 5G SA coverage when the 3G network closes on 30 June 2024, has the benefit of providing improved depth of coverage and enhancing the 5G experience for customers.”
“It’s a further example of how we are leading the way in 5G innovation and investment, and how we are committed to delivering the best and most advanced network for Australia.”
To test and validate this capability, Telstra worked with long-term partners Ericsson, the global leader in 5G network equipment, and Qualcomm, one of the world’s leading wireless chipset companies.
Emilio Romeo, Head of Ericsson Australia and New Zealand, says: “Ericsson’s latest software features enables Telstra to capitalize the full spectrum portfolio for a wider coverage whilst providing far superior data rates. Customers will be empowered to explore new experiences offered with 5G Standalone such as differentiated services and a range of applications, which will in turn drive network monetization.”
Durga Malladi, Senior Vice President and General Manager, Technology Planning & Edge Solutions Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., says: This live test proves that uplink carrier aggregation on 5G Standalone network has the potential to significantly increase upload speeds and capacity, thus unlocking new experiences for consumers.”
This latest achievement takes Telstra’s World-First count to 53 since the launch of 3G. It is only through its collaboration efforts with industry and its strategic partners, like Ericsson and Qualcomm, that it can deliver the technology innovation and leadership that its customers can benefit from.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Telstra has also implemented Ericsson’s Dynamic Network Slicing software for automated network orchestration. This software gives the operator a fully automated and monetizable network slicing orchestration capability to sell slicing services to enterprise customers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Telstra’s T25 to extend 5G coverage and offer enhanced customer experiences
Telstra wins most lots in Australia’s 5G mmWave auction
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
By Ajay Thakur with Alan J Weissberger
Abstract:
In this article, we endeavor to clarify some of the critical issues and questions related to implementing a cloud native 5G SA core network and how it differs from the traditional core network composed of hardware devices and software solutions. It’s important to note that NONE of the 3GPP defined 5G features can be realized without a 5G SA core. Those include: Network Automation, Network Function Virtualization, 5G Security, Network Slicing, Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC), Policy Control, Network Data Analytics, etc.
Communication Service Providers (CSPs) will need to do things differently (than 4G) in order to implement and use a 5G cloud native SA core. Various cloud native 5G SA core aspects include network planning, deployment, software upgrades, network monitoring, hardware and platform upgrades.
These will be examined and contrasted with traditional implementations, such as the 4G Evolved Packet Core (EPC).
Introduction:
3GPP introduced 5G SA core network architecture in release 15. Since then numerous new features (work items) have been introduced to specifications. 3GPP’s 5G SA’s specifications use virtualization and cloud native principles as the foundation. A few key 3GPP Technical Specifications (TSs) for 5G system are the following:
- TS 22.261, “Service requirements for the 5G system”.
- TS 23.501, “System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 23.502 “Procedures for the 5G System (5GS)
- TS 32.240 “Charging management; Charging architecture and principles”.
- TS 24.501 “Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3”
- TS 38.300 “NR; NR and NG-RAN Overall description; Stage-2”
- TS 23.527 “5G System; Restoration procedures Stage-2”
5G SA tries to resolve the challenges faced by network operators in the EPC deployments and how those challenges can be mitigated with new design.
Several important changes in the 5G SA core are support for a Service Based Architecture and Cloud Native implementation of 5G SA core. That will enable new 5G features and functions like Network Slicing, 5G Security, and MEC, among others.
To reap the benefits of Cloud Native SA, CSPs are required to adapt to new cloud native principles of network deployment, operation and monitoring. We shall examine various aspects of Life Cycle Management of 5G SA software and also ask some open ended questions on each aspect.
SBA architecture Diagram with multiple Interfaces:
- The Network diagram above shows the SBI interfaces in case of roaming. Each of the individual NF may be composed of one more micro-services. Each NF may come from different vendor. Since these NFs are available in containerized format, they may or may not share the same container orchestration platform.
Network Dimensioning:
- 5G SA solves the network expansion problem since the network can be scaled up/down by adding/removing commercial off the shelf hardware.
- Once we have all the NFs software releases available, operators can gather the compute, memory & network requirements for deployment.
- Operators would rely on auto scaling functionality provided by the 5G NF vendors to avoid over provisioning at the start. This is relatively much simpler compared to adding dedicated hardware for NF in case of EPC.
Deployment Options Selection/Planning
- Operators need to decide the type of deployment for the network like the 5G SA deployment on public cloud or on private cloud.
- Along with Public vs Private cloud decisions, the Operator also needs to decide on a Container orchestration engine. Container orchestration can be managed service or operator managed service. Popular container orchestration engine is Kubernetes (K8s).
- Next step would be to finalize or select one of the CI/CD tools which works for all the vendors and integrate that with the container orchestration platform.
- Also placement of the NFs needs to be decided, e.g. User Plane Function (UPF) could be on-prem close to RAN. It’s possible that the operator may place some of the RAN virtualized components in the cloud.
- These all are important decisions to be made before getting into the real deployment of the software.
- Some of the aspects here are due to Cloud Native 5G SA and were not applicable for EPC.
CI/CD:
- CI/CD landscape (https://landscape.cncf.io/) from CNCF shown in below Figure
- It can be seen from the CNCF project that there are many projects which are available for CI/CD
- Irrespective of Public or Private cloud, operators need to follow cloud native CI/CD principles for deploying the Core Network in the Cloud environment. CI/CD involves taking the software release from the vendor and running it against existing network functions and carrying out some minimum tests and once operator is satisfied with evaluation of the release then rollout the release in the network.
- Operators can decide to have a separate staging environments where new releases can soak for a certain period of time while few subscribers use the new release.
- CI/CD gives the option of rolling back the release if the operator is not happy with the performance of the new release.
- Now the challenge here would be, will the operator have single CI/CD tools used for deploying all the vendors’ solution OR would the operator use its own CI/CD tooling and integrate NFs from vendor it in its own environment. This is the decision the operator needs to take.
- Having Automated CI/CD infrastructure which takes the software releases from the vendors and passes it through multiple environments and all the way to the production environment is key.
- Without having an appropriate CI/CD environment it would be very difficult to manage all micro-services and their deployments.
- Public Cloud may come with inbuilt CI/CD solutions and would be easy for operators to start with.
- AWS offers multiple services around CI/CD and those are listed here – https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/cicd_for_5g_networks_on_aws/cicd-on-aws.html
- Azure offering can be found here https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/apps/cd/azure/cicd-data-overview?view=azure-devops
- Google Cloud CI/CD services can be found here – https://cloud.google.com/solutions/continuous-integration
Software Upgrade:
- Cloud Native 5G SA allows operator to upgrade some of the components easily instead of complete 5G Core update in one go. CI/CD framework would help in the software upgrades with minimal human intervention.
- Note that with Cloud Native principles the operator would get multiple patch/minor releases and may be some major releases throughout the life cycle of the software. So the traditional approach of pulling down complete hardware & upgrading it with new software is not required for microservice based solutions. But this really works as long as all microservices are truly built stateless and supports live upgrade.
- As an operator, it would be required to know the impact of each upgrade package and prepare for rollback in case something goes wrong during the upgrade cycle.
Network Monitoring:
- Traditionally, operators developed their own Network Monitoring solutions to monitor the health of EPC since there was no standard mechanism to get the metrics, statistics from the NFs,
- 5G SA follows Cloud Native principles; it is easy to get the logs, statistics, alerts, alarms from all microservices in a consistent manner. There are common tooling used by most of the cloud native applications and CNCF has multiple projects in these categories.
- CNCF supported Monitoring projects are shown below figure
-
- Tracing is important aspect to find out the bottleneck in the performance.
- Logging has been a traditional approach for debugging network issues. Below are the projects offered by CNCF in the logging area
- Public Cloud providers can extend the monitoring easily by generating Texts or email alerts as per CSPs needs.
- Operators can define their policies to retain the network performance monitoring output for a long time and can take backup of this easily through use of Public Cloud Providers data backup services.
- In the case of EPC these mechanisms were product dependent.
- Challenge in case of 5G SA would be each NF vendor may end up in using different tool and operators would have some challenges to converge all NF vendors to the common tooling.
Hardware & platform upgrade:
- In the traditional approach, providing hardware with updated operating systems and platforms was the responsibility of the equipment vendor. Now this responsibility has gone into either operator’s hand or sometimes in Public Cloud Provider’s hand. It depends on if the 5G SA is deployed on on-prem or on public cloud. Operators need to carefully plan for these upgrades without causing any downtime and of course follow the rolling upgrade patterns to avoid updating multiple entities at a time.
- If managed container orchestration is used, then these upgrades are seamlessly handled by Public Cloud Providers.
Vendor Lock In:
- In the case of EPC, vendor lock in was specific to NF & Radio Vendors. The 3GPP EPC specification allows the operators to swap NFs from one vendor with another and as long as NF supports the required Services. Point to note that this is less costly replacement compared to replacing one vendor with another vendor when NF had associated hardware.
- But with cloud native SA there is a chance that the operator may end up in building the tooling (CI/CD, monitoring etc.) over the period of time and this may lead to cloud provider lock in.
Conclusions:
The 5G SA core network provides a lot of flexibility and automation via cloud native deployments. However, the 3GPP 5G core specs contain a lot of implementation options, which network operators and their vendors must select to properly deploy a 5G core network. Making those decisions will likely require solid experience with operating applications on a cloud native platform. And that may be a reason that 5G SA core network rollouts have been so slow.
In the U.S. AT&T and Verizon have taken a very cautious approach to deploying their long ago promised 5G SA core networks. During the Brooklyn 6G Summit in November 2023, Chris Sambar, EVP for technology at AT&T said, ““I would say we are not moving as quickly as some of the other operators on the 5G standalone core, but we see the use cases that are coming, we understand when they’re coming, so we’re being very purposeful about getting there when we need to get there.” That’s despite AT&T outsourcing its 5G SA core network deployment to Microsoft Azure in June 2021. Yet Microsoft is the world’s second biggest cloud services provider with tons of experience running cloud native applications.
Summing up, Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group wrote, “The buildout of 5G SA networks is going slower than anticipated which is restraining growth in the marketplace. To date, we count fifty 5G SA eMBB (enhanced Mobile BroadBand) networks that have been commercially deployed worldwide by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). We counted 18 new 5G SA networks in 2022, but only 12 were launched in 2023. On a positive note, we believe a lot of work has been done in the background, preparing for 5G SA launches by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and we expect 2024 to have more launches than 2022.”
Ajay Lotan Thakur, Cloud Software Architect at Intel and IEEE Techblog Editorial Team member
References:
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
Ericsson Mobility Report touts “5G SA opportunities”
Analysys Mason: 40 operational 5G SA networks worldwide; Sub-Sahara Africa dominates new launches
Samsung and VMware Collaborate to Advance 5G SA Core & Telco Cloud
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
GSM 5G-Market Snapshot Highlights – July 2023 (includes 5G SA status)
Finland’s Elisa, Ericsson and Qualcomm test uplink carrier aggregation on 5G SA network
With Ericsson and Qualcomm doing the “heavy lifting,” Finland network operator Elisa conducted a live test of uplink carrier aggregation (CA) on its commercial 5G standalone (SA) network. Elisa operates commercial 5G SA networks, starting with its home market of Finland and following it up last year by deploying it in Estonia.
The three partners achieved an upload speed of 230 Mbps in a live 5G network using Uplink Carrier Aggregation. For this test, a 25MHz 2.6 GHz FDD (frequency division duplex) band was combined with a 100MHz 3.5 GHz TDD (time division duplex) band running on a mobile test device powered by Snapdragon® X75 5G Modem-RF System.
Ericsson’s Uplink Carrier Aggregation software combines mid-band FDD and mid-band TDD within the frequency range 1 (FR1), boosting speeds to enable uplink-heavy applications such as live streaming, broadcasts, cloud gaming, extended reality, and video-based use cases.
Uplink-heavy consumer applications on the rise:
According to Ericsson’s most recent Mobility Report, uplink accounted for a modest 8% of total traffic on a sample of four mobile networks analyzed. The applications that generated the largest volume of uplink traffic were personal cloud storage services, followed by comms services and video.
While 8% doesn’t seem like much, Ericsson emphasised that uplink volume is highly context dependent. For instance, there is likely to be more of it at a live event, like a concert or a sporting event, where users enthusiastically film and then share as much action as possible.
A growing amount of data traffic generated today is in the uplink, highlighting the need for new network capabilities to boost uplink speed and capacity and deliver seamless 5G user experience. For instance, concertgoers are recording and streaming videos live on their social media accounts. With fast uplink speeds, they can share their most exciting moments in real-time with friends and family without worrying about lags, congestion, or poor network quality.
In addition to Elisa, Vodafone has also been testing out uplink CA recently, as have Dish, BT and Telefónica.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Quotes:
Mårten Lerner, Head of Product Area Networks, Ericsson, says: “This latest technology milestone with our partners Elisa and Qualcomm Technologies unlocks high upload speeds in commercial 5G Standalone networks. With this game-changing software capability, we are enabling unparalleled user experience for applications such as live streaming, video conferencing, augmented reality/virtual reality and cloud gaming.”
Sami Rajamäki, Vice President, Network Services, Elisa, says: “We continue as a pioneer of 5G in Finland and develop our network services with our customers’ future needs in mind. The use of augmented reality and development towards metaverse will increase the demand for fast uplink connections. Therefore the top speeds achieved together with Ericsson and Qualcomm are an important step in the development of 5G Standalone network.”
Dino Flore, Vice President, Technology at Qualcomm Europe, Inc. says: “The uplink speed achieved with Elisa and Ericsson is a testament to the breakthrough performance of the Snapdragon X75 5G Modem-RF System. We are excited to see the innovative use cases Elisa can unlock for customers with their 5G Standalone network.”
Ericsson has a robust portfolio of software features that provide a boost in the uplink, and the feature deployed in this demo with Elisa and Qualcomm – FR1 Uplink Carrier Aggregation – became commercially available in the fourth quarter of 2023.
Visit the Ericsson booth in Hall 2 at MWC 2024 in Barcelona to see how a superior uplink performance is being enabled for use cases such as live streaming.
References:
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
Dish Wireless with Qualcomm Technologies and Samsung test simultaneous 5G 2x uplink and 4x downlink carrier aggregation
Ericsson and MediaTek set new 5G uplink speed record using Uplink Carrier Aggregation
BT tests 4CC Carrier Aggregation over a standalone 5G network using Nokia equipment
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
According to market research firm Omdia, there were 1.8 billion global 5G subscribers at the end of 2023 with 7.9 billion forecast by 2028. This growth trajectory, while substantial, is subject to various influencing factors such as infrastructure development, spectrum availability, device availability, and consumer demand. Kristin Paulin, Principal Analyst at Omdia, has a cautiously optimistic outlook for 5G. She emphasizes that innovation and cooperation are key to unlocking the full potential of 5G and its transformative impact.
Globally, the number of deployed 5G networks is now comparable to 4G LTE deployments. There are currently 296 commercial 5G networks worldwide, a number expected to grow to 438 by 2025.
In North America, 5G deployment was at 176 million connections as of the third quarter of 2023, a 14% increase from the previous quarter. This represents a 26% market share and a 46% penetration rate. However, there were only two U.S. 5G SA network providers – T-Mobile US and Dish Wireless– as of the end of 2023.
in contrast, Latin America and the Caribbean are still in the early stages of 5G adoption. However, the region shows promise with an expected quadrupling of 5G connections in 2023, reaching 46 million. By 2028, it is anticipated that the region will have 492 million 5G connections.
Jose Otero, Vice President of Caribbean and Latin America for 5G Americas, acknowledges the significance of 4G LTE and 5G as vital mobile communication technologies in Latin America. He anticipates more robust opportunities for 5G in the region, driven by upcoming spectrum auctions and wider access to 5G devices in 2024.
“The global 5G landscape shows positive momentum as innovation and collaboration continue to be the mainstays for long term progress.” said Chris Pearson, President of 5G Americas. “With the World Radio Conference wrapping up, it is important that international co-operation and efforts continue to ensure that spectrum and technology standards continue to propel this growth.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
According to a recent report by Dell’Oro Group, the Mobile Core Network (MCN) market growth rate has been reduced to less than a 1% CAGR (2023-2028).
“This is the fourth consecutive time we reduced the growth rate of the MCN market as the build-out of 5G Standalone (5G SA) networks continues to wane compared to 5G Non-standalone (5G NSA) networks,” said Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “The buildout of 5G SA networks is going slower than anticipated which is restraining growth in the marketplace. To date, we count fifty 5G SA eMBB (enhanced Mobile BroadBand) networks that have been commercially deployed worldwide by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). We counted 18 new 5G SA networks in 2022, but only 12 were launched in 2023. On a positive note, we believe a lot of work has been done in the background, preparing for 5G SA launches by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and we expect 2024 to have more launches than 2022.”
Note 1. Importantly, a 5G SA core network is required to realize 3GPP defined 5G features, like 5G Security, Network Slicing (3GPP’s technical specification (TS) 23.501 defines 5G system architecture with slicing included. TS 22.261 specifies the provisioning of network slices, association of devices to slices, and performance isolation during normal and elastic slice operation).
The 5G SA core network relies on a “Service-Based Architecture” (SBA) framework, where the architecture elements are defined in terms of “Network Functions” (NFs) rather than by “traditional” Network Entities.
5G SA core networks require “cloud-native” hardware and software that has a service-based architecture and decentralized functions. A “cloud-native” 5G core allows for flexible and efficient operation, as well as the effective adoption of new services.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
According to Verified Market Research, when the full 5G SA feature set is supported, enterprises can realize the following benefits:
- Further improvements to speed and reach, beyond what 5G NSA brings.
- Support for higher-density deployments of devices.
- Support for low-latency and real-time use cases.
- Support for enhanced enterprise site connectivity via network slicing.
- Better security than 5G NSA (which uses 4G LTE security methods and procedures).
- Simplification of the RAN and core compared to 5G NSA since 5G SA supports only 5G and leaves 4G and older standards behind — and even though the 5G SA core alone is more complex than a pure 4G core alone.
GSA claims that more than 121 network operators in 55 countries and territories have invested in public 5G standalone (SA) networks (but they don’t disclose how many of those have been commercially deployed (for example, AT&T and Verizon have been talking up 5G SA for years, but have yet to deploy it!). We trust Dell’Oro’s number of 5G SA eMBB networks deployed.
Findings from the latest GSA update on the 5G SA ecosystem/devices [2.] include:
- There are 2,130 announced devices with claimed support for 5G SA, up 35.7% from 1,569 at the end of 2022.
- Devices with support for 5G SA account for 90.3% of all 5G devices, as of the end of 2023, up from 35.6% in December 2019.
- 93 modems or mobile processors/platform chipsets state support for 5G SA, 90 of which are understood to be commercially available.
Note 2. It’s crucially important to realize that since all 5G SA core networks are different, a 5G SA device that works on one carrier’s network won’t work on any other without a new 5G SA download.
By the end of December 2023, GSA had identified:
• 28 announced form factors • 261 manufacturers with announced available or forthcoming 5G devices
• 2,358 announced devices, including regional variants, but excluding operator-branded devices that are essentially rebadged versions of other phones. Of these, at least 1,964 are understood to be commercially available:
• 1,255 phones, up 34 from November 2023. At least 1,168 of these are now commercially available, up 56 from November 2023
• 308 fixed wireless access customer-premises equipment (CPE) devices for indoor and outdoor uses, at least 209 of which are now commercially available
• 243 modules • 64 tablets • 33 laptops or notebooks • 77 battery-operated hot spots
• 179 industrial or enterprise routers, gateways or modems
• 13 in-vehicle routers, modems or hot spots
• 29 USB terminals, dongles or modems
• 168 other devices, including drones, head-mounted displays, robots, TVs, cameras, femtocells/small cells, repeaters, vehicle on-board units, keypads, a snap-on dongle/adapter, a switch, a vending machine and an encoder
• 1,098 announced devices with declared support for standalone 5G in sub-6 GHz bands, 904 of which are commercially available.
According to Verified Market Research, the market drivers for the 5G Technology Market can be influenced by various factors. These may include:
- Enhanced Data Speed and Capacity: In comparison to its predecessors (4G/LTE), 5G technology offers far faster data rates and more network capacity. Supporting the increasing need for high-bandwidth applications like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and Internet of Things (IoT) devices is imperative.
- Low Latency: The goal of 5G networks is to offer low-latency communication, which shortens the time it takes to send and receive data. This is critical for real-time interactive applications like industrial automation, remote surgery, and driverless cars.
- Growing Need for IoT Devices: One of the main factors driving 5G adoption is the spread of IoT devices across a number of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, smart cities, and agriculture. 5G is ideally suited for Internet of Things applications due to its low latency and capacity to connect a large number of devices concurrently.
- Rise of Edge Computing: The growth of edge computing is intimately related to 5G networks. Edge computing improves speed and lowers latency by bringing computing resources closer to end users and devices; this makes it a crucial enabler for applications like driverless cars and smart cities.
- Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing: By facilitating effective and dependable communication in smart factories, 5G is anticipated to play a significant role in the fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0. It makes it easier to incorporate technology like automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence into production processes.
- Telecommunications Infrastructure Upgrade: on order to roll out 5G networks, telecommunications service providers are actively spending on infrastructure upgrades. To improve capacity and coverage, new base stations and tiny cells must be installed.
- Government Initiatives and Support: Through legislative frameworks, financial aid, and other means, numerous governments across the globe are actively promoting the rollout of 5G technology. In the global digital landscape, these programmes seek to promote innovation, economic growth, and competitiveness.
- Competitive Environment and Industry Cooperation: Businesses are investing in 5G technology to obtain a competitive advantage due to the highly competitive nature of the telecommunications sector. Furthermore, partnerships between IT firms, telecom service providers, and other relevant parties are quickening the creation and implementation of 5G networks.
Several factors can act as restraints or challenges for the 5G Technology Market. These may include:
- Infrastructure Costs: Given that a large-scale deployment of base stations and small cells is necessary to support 5G, telecom operators may be discouraged by the substantial upfront expenditure necessary for creating and upgrading infrastructure.
- Spectrum Allocation and Availability: The effective operation of 5G networks depends on the allocation and availability of appropriate spectrum bands. Regulatory and geopolitical obstacles can make it difficult to get the necessary spectrum, which can hinder the deployment of 5G services.
- Security Concerns: There are worries about possible cybersecurity attacks due to the vast number of devices connected to 5G networks and the increased connection. Building confidence and promoting wider adoption require overcoming these issues and guaranteeing the security of network infrastructure.
- Interoperability Problems: There are interoperability problems since different generations of cellular technologies coexist. A seamless transition and the prevention of service interruptions depend on the seamless integration of various technologies.
- Regulatory Obstacles: The implementation of 5G networks faces a number of regulatory obstacles, such as spectrum auctions, licence requirements, and local law compliance. Uncertainties surrounding regulations may cause hold-ups and impede the rapid deployment of 5G services.
- Public Health and Safety Concerns: The general public’s reception of 5G networks may be impacted by worries about the possible health impacts of increasing exposure to radiofrequency radiation. Building public trust requires resolving these issues and maintaining clear lines of communication.
- Absence of Killer Applications: The deployment of 5G may be slowed back by the absence of compelling and widely applicable use cases. Creating cutting-edge, impactful apps that take advantage of 5G’s special features is essential to increasing demand.
- Global Economic uncertainty: Businesses’ and operators’ willingness to invest in the rollout of 5G technology can be impacted by economic downturns and uncertainty. Delays in infrastructure upgrades could result from financial considerations and budgetary restrictions.
Charts courtesy of Verified Market Research
References:
5G Continues Robust Momentum Growth and Drives Demand for More Wireless Spectrum
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/5g-system-overview
https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/5G-standalone-5G-SA
SK Telecom and Thales Trial Post-quantum Cryptography to Enhance Users’ Protection on 5G SA Network
Korean telco SK Telecom and digital security firm Thales have tested quantum-resistant cryptography based on a 5G standalone (5G SA) network. The trial is focused on encrypting and decrypting identity data on a 5G network to protect user privacy from future quantum threats. It was performed using Thales 5G Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC) SIM cards and a trial 5G standalone network environment from SKT. The test involved cryptographic algorithms designed to resist attacks from quantum computers, as well as ‘classical’ computers.
The end user identity on the 5G SA network is concealed and secured on the device side via the 5G SIM card. The security mechanisms involve cryptographic algorithms designed to resist attacks from future quantum computers, providing a level of security that is considered robust in the post-quantum era.

Photo Credit: rawpixel
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has been leading an initiative to standardize post-quantum cryptographic algorithms, and SKT and Thales have used the Crystals-Kyber one for this successful real condition trial. These post-quantum secure algorithms are being developed to withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers.
“This collaboration between SKT and Thales highlights our commitment to staying ahead of the curve in terms of cybersecurity and ensuring the safety of our customers’ data. PQC provides enhanced security through the use of cryptographic algorithms that are thought to be secure against quantum computer attacks. Going forward, we will combine PQC SIM with our additional Quantum expertise to achieve end-to-end quantum-safe communications,” said Yu Takki, Vice President and Head of Infra Technology Office of SKT.
“As quantum computers have the potential to break certain existing cryptographic algorithms, there is an emerging need to transition to cryptographic algorithms believed to be secure against quantum attacks. For 5G networks, Thales started to invest on cryptographic algorithms that are quantum-resistant to enhance continued communications security and privacy for users,” said Eva Rudin, SVP Mobile Connectivity & Solutions at Thales.
As quantum computing gets more reliable and presumably starts getting used more widely in the future, this type of security is going to become increasingly important. Nokia recently announced it had completed a proof of concept trial alongside Greek research consortium HellasQCI, demonstrating what it calls quantum-safe connectivity infrastructure.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, SK Broadband, an internet and paid TV service affiliate of SK Telecom, launched additional personalized internet protocol television (IPTV) services utilizing AI technology to enhance its competitiveness in the country’s paid TV market, the company said Wednesday.
About SK Telecom:
SK Telecom has been leading the growth of the mobile industry since 1984. Now, it is taking customer experience to new heights by extending beyond connectivity. By placing AI at the core of its business, SK Telecom is rapidly transforming into an AI company. It is focusing on driving innovations in areas of telecommunications, media, AI, metaverse, cloud and connected intelligence to deliver greater value for both individuals and enterprises.
For more information, please contact [email protected] or visit SKT’s LinkedIn page www.linkedin.com/company/sk-telecom.
About Thales:
Thales (Euronext Paris: HO) is a global leader in advanced technologies within three domains: Defence & Security, Aeronautics & Space, and Digital Identity & Security. It develops products and solutions that help make the world safer, greener and more inclusive.
References:
https://www.newswire.co.kr/newsRead.php?no=981374
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/sk-telecom-and-thales-trial-quantum-resistant-cryptography-for-5g-sa
https://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/tech/2023/12/133_365470.html