5G SA/5G Core network
Cloud RAN with Google Distributed Cloud Edge; Strategy: host network functions of other vendors on Google Cloud
At MWC 2023 Barcelona, Google Cloud announced that they can now run the radio access network (RAN) functions as software on Google Distributed Cloud Edge, providing communications service providers (CSPs- AKA telcos) with a common and agile operating model that extends from the core of the network to the edge, for a high degree of programmability, flexibility, and low operating expenses. CSPs have already embraced open architecture, open-source software, disaggregation, automation, cloud, AI and machine learning, and new operational models, to name a few. The journey started in the last decade with Network Functions Virtualization, primarily with value added services and then deeper with core network applications, and in the past few years, that evolved into a push towards cloud-native. With significant progress in the core, the time for Cloud RAN is now, according to Google. However, whether for industry or region-specific compliance reasons, data sovereignty needs, or latency or local data-processing requirements, most of the network functions deployed in a mobile or wireline network may have to follow a hybrid deployment model where network functions are placed flexibly in a combination of both on-premises and cloud regions. RAN, which is traditionally implemented with proprietary hardware, falls into that camp as well.
In 2021,the company launched Google Distributed Cloud Edge (GDC Edge), an on-premises offering that extends a consistent operating model from our public Google Cloud regions to the customer’s premises. For CSPs, this hybrid approach makes it possible to modernize the network, while enabling easy development, fast innovation, efficient scale and operational efficiency; all while simultaneously helping to reduce technology risk and operational costs. GDC Edge became generally available in 2022.

Google Cloud does not plan to develop its own private wireless networking services to sell to enterprise customers, nor does the company plan to develop its own networking software functions, according to Gabriele Di Piazza, an executive with Google Cloud who spoke at MWC 2023 in Barcelona. Instead, Google Cloud would like to host the networking software functions of other vendors like Ericsson and Mavenir in its cloud. It would also like to resell private networking services from operators and others.
Rather than develop its own cloud native 5G SA core network or other cloud networking software (like Microsoft and AWS are doing), Google Cloud wants to “avoid partner conflict,” Di Piazza said. Google has been building its telecom cloud story around its Anthos platform. That platform is directly competing against the likes of AWS and Microsoft for telecom customers. According to a number of analysts, AWS appears to enjoy an early lead in the telecom industry – but its rivals, like Google, are looking for ways to gain a competitive advantage. One of Google’s competitive arguments is that it doesn’t have aspirations to sell network functions. Therefore, according to Di Piazza, the company can remain a trusted, unbiased partner.

Image Credit: Google Cloud
Last year, the executive said that moving to a cloud-native architecture is mandatory, not optional for telcos, adding that telecom operators are facing lots of challenges right now due to declining revenue growth, exploding data consumption and increasing capital requirements for 5G. Cloud-native networks have significant challenges. For example, there is a lack of standardization among the various open-source groups and there’s fragmentation among parts of the cloud-native ecosystem, particularly among OSS vendors, cloud providers and startups.
In recent years, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Oracle and other cloud computing service providers have been working to develop products and services that are specifically designed to allow telecom network operator’s to run their network functions inside a third-party cloud environment. For example, AT&T and Dish Network are running their 5G SA core networks on Microsoft Azure and AWS, respectively.
Matt Beal, a senior VP of software development for Oracle Communications, said his company offers both a substantial cloud computing service as well as a lengthy list of network functions. He maintains that Oracle is a better partner for telecom network operators because of it. Beal said Oracle has long offered a wide range of networking functions, from policy control to network slice management, that can be run inside its cloud or inside the cloud of other companies. He said that, because Oracle developed those functions itself, the company has more experience in running them in a cloud environment compared with a company that hasn’t done that kind of work. Beal’s inference is that network operators ought to partner with the best and most experienced companies in the market. That position runs directly counter to Google’s competitive stance on the topic. “When you know how these things work in real life … you can optimize your cloud to run these workloads,” he said.
While a number of other telecom network operators have put things like customer support or IT into the cloud, they have been reluctant to release critical network functions like policy control to a cloud service provider.
References:
https://cloud.google.com/solutions/telecommunications
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/telecommunications
Comcast selects Nokia’s 5G SA Core software to support its mobile connectivity efforts
Today, Comcast announced it will roll out Nokia’s 5G Stand Alone Core networking software to support its deployment of CBRS and 600MHz spectrum to Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile customers in its service areas across the United States.
Comcast will deploy that spectrum in select, high-traffic areas in support of both residential and business customers that take mobile services from the operator. Deploying fresh spectrum in those areas will give Comcast a greater degree of ownership economics with wireless and help to offset a portion of the MVNO costs associated with its pact with Verizon. Those deployments will also build on Comcast’s current Wi-Fi offload strategy that involves millions of access points deployed in customer homes and in certain metro areas.
Nokia will supply Comcast with its 5G Stand Alone Core networking software, including Packet Core, delivering near zero touch automation and ultra low latency capabilities, as well as operations software and consulting services. These offerings will support Comcast’s efforts to deliver enhanced 5G access to consumer and business customers in the U.S. using Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) and 600 MHz spectrum.
By combining Nokia’s software with Comcast’s targeted, capital-light network design, Comcast can cost-effectively deliver enhanced 5G and WiFi mobile connectivity to its more than five million Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile customers. Comcast and Nokia are currently conducting field trials, which includes Comcast employee testing.
As the demand for reliable Internet access inside and outside of the home and office rapidly increases, Comcast’s mid-band (CBRS) and low-band (600MHz) spectrum enable the company to supplement its existing Xfinity WiFi network and cellular network partnership with additional targeted 5G coverage in certain high-traffic areas within its service territory.
Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile services are built for the way people use mobile today, with the Internet at the core of the experience. Calls and texts are free, and customers can experience the freedom of paying by the gig or unlimited, and switch between payment options at any time for any line on their account. For complete pricing and availability details, please visit Xfinity Mobile or Comcast Business Mobile.
Nokia claims to be leading the 5G Standalone Core market, with over 80 communication service provider (CSP) customers around the world. In addition, 25 of the top 40 CSPs by revenue rely on Nokia Core network products.

Comcast and Nokia are currently conducting field trials, including tests with Comcast employees. Comcast didn’t reveal the location of its test markets, but the announcement indicates the operator is finally starting to gear up this important piece of its wireless strategy.
This deal comes more than two years after the company bid for and won licensed CBRS spectrum. Comcast also spent $1.7 billion on 600MHz spectrum licenses in 2017.
Though Comcast has no plans to deploy a national wireless network, it estimates that its current spectrum holdings cover roughly 80% of its homes passed and about 50% of the US population.
Tom Nagel, SVP, Wireless Strategy at Comcast, said: ”We are pleased to be working with Nokia to enable Comcast’s advanced 5G mobile products and services for our customers. Combining Nokia’s industry-leading solutions with Comcast’s targeted network design and new dual SIM technology allows us to create exciting next-generation wireless offerings.”
Fran Heeran, SVP & General Manager of Core Networks, Cloud and Network Services, at Nokia, said: “We are delighted to partner with Comcast and provide Nokia’s advanced 5G Core portfolio to deliver innovative 5G customer offerings securely, at scale, and with advanced operational efficiencies.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Last fall, Comcast announced it would use Samsung radios, including strand-mounted small cells, for its targeted 5G network. Comcast will deploy separate Samsung radios for the CBRS and 600MHz bands and use its wireline network to help backhaul traffic.
At the time, Comcast confirmed to Light Reading that its wireless network deployment is “using a multi-vendor solution but not within an open RAN framework.”
Comcast’s wireless network evolution is underway as the operator continues to grow a mobile business that launched almost six years ago. Comcast added a record 365,000 mobile lines in Q4 2022, raising its total to 5.31 million.
Meanwhile, Comcast recently introduced a limited-time service convergence bundle for new customers that offers one unlimited mobile line and a 200Mbit/s home broadband service (with the Wi-Fi gateway included) for $50 per month – for a period of 24 months.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g-and-beyond/comcast-shares-wireless-wealth-with-nokia/d/d-id/783415
Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core/5g-core/
Highlights of Qualcomm 5G Fixed Wireless Access Platform Gen 3; FWA and Cisco converged mobile core network
With 5G deployed in more than 90 countries globally, network operators are increasingly considering 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) to enable more homes and businesses can connect and enjoy the power of connected broadband experiences.
This week, Qualcomm unveiled its 5G Fixed Wireless Access Platform Gen 3, the world’s first fully-integrated 5G advanced-ready FWA platform. Besides benefitting from Snapdragon X75 capabilities, Qualcomm FWA Gen 3 key features include:
- Extended-range mmWave and Sub-6 GHz
- Qualcomm Tri-Band Wi-Fi 7 with expert Multi-Link operation for blazing-fast lower latency, reliable connections, and mesh capability for seamless coverage
- Quad-core central processing unit (CPU) and hardware acceleration boosts
- Self-install capabilities facilitated by Qualcomm Dynamic Antenna Steering technology
- Qualcomm RF Sensing Suite to enable indoor mmWave Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) deployments
- Support for 5G Dual-SIM Dual Active (DSDA) and Dual-SIM Dual Standby (DSDS) configurations
Qualcomm FWA Gen 3 is claimed to be the world’s first fully-integrated 5G advanced (???)-ready FWA platform, which includes support for Sub-6 GHz, mmWave, and Wi-Fi 7 connectivity, and boosted with quad-core CPU and hardware acceleration to drive a wide range of applications and value-added services.
The new platform features:
- The recently announced Snapdragon X75 5G Modem-RF, enabling breakthrough 5G performance to achieve unmatched speeds, coverage, and link robustness
- Qualcomm QTM567 mmWave Antenna Module, providing reliable and extended mmWave coverage
- Wi-Fi 7 with 10Gb ethernet, delivering multi-gigabit speeds and wire-like latency to virtually every device in the home
- Converged mmWave-sub 6 hardware architecture, reducing footprint, cost, board complexity, and power consumption
These capabilities will help OEMs accelerate time to launch, improve performance, and lower development effort for building cutting-edge FWA CPEs at scale. The Qualcomm FWA Gen 3 provides a fully-integrated solution that enables product development for multiple mobile broadband product categories and enables OEMs to offer a diverse product portfolio to their customers.
Qualcomm FWA Gen 3 includes the following features:
- Increased coverage through extended range mmWave and extended-range sub-6GHz with eight receiver antennas and support for power class 1.5 (PC 1.5)
- Enhanced self-install capabilities with Qualcomm Dynamic Antenna Steering Gen2
- Qualcomm RF Sensing Suite to help accelerate indoor mmWave CPEs deployments
- Flexible software architecture with support for multiple frameworks, including OpenWRT and RDK-B
- The Qualcomm FWA Gen 3 encapsulates the next-gen modem-RF system technologies intended to springboard 5G forward with superior 5G speeds and flexibility. This breakthrough connectivity is enabled by several capabilities including:
- Unrivalled spectrum aggregation
- Multi-Gigabit speed
- Improved uplink coverage with FDD uplink MIMO and uplink carrier aggregation (CA)
- Significant performance increase with Wi-Fi 7 advanced features:
- Tri-Band support in the 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz spectrum bands with 320MHz and 4K QAM modulation
- Multi-Link technology enabling lower latency in heavily congested home environments
With WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) and 5G connectivity, the platform offers consumers a faster and more reliable internet connection in the home. They can tap into the increased capacity and bandwidth offered by Wi-Fi and 5G to deliver multi-gigabit speeds, enabling consumers to connect all their devices and enjoy improved user experiences.
Qualcomm Resources:
Learn more about Fixed Wireless Access and its benefits here and here. Additionally, check out more on our latest Snapdragon X75 5G Modem-RF System enabling this technology here. Solutions such as this, powered by our one technology roadmap, including foundational 5G technologies, further position Qualcomm as the edge partner of choice for the cloud economy. Qualcomm makes an intelligently connected world possible.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
FWA and a Converged Mobile Core Network:
In a blog post today, Matt Price of Cisco states that FWA is a great tool for reducing the digital divide when it comes to accessibility and affordability. The economics for providing Internet services were in need of a change and FWA offers some good ones – reducing trenching requirements, increasing serviceable area, offering self-install customer equipment (CPE), and even providing a common wireless network architecture that can serve both Fixed Wireless Access and Mobile Access services. To achieve these goals, Cisco strongly recommends 5G service providers deploy 5G SA core networks, which the vendor has implemented as a converged 4G/5G core for T-Mobile US.
Other carriers, like Verizon [1.] have deployed a 5G NSA FWA network.
Note 1. Verizon has increasingly come to view FWA as an integral part of their broadband access offering everywhere that FiOS isn’t available. At the same time, the telco has argued (with increasing confidence) that the often-assumed capacity constraints on FWA are not only addressable, but that they are not an issue. Verizon views 5G FWA as a major growth opportunity- much more so than 5G mobile services, according to Sowmyanarayan Sampath, Executive Vice President and CEO of Verizon Business. It’s also interesting that Telkom in South Africa and Safaricom in Kenya have deployed 5G NSA networks for FWA but NOT yet for 5G mobile service.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
5G SA’s network architecture can flexibly deploy User Plane Function (UPF) nodes to anchor a FWA subscriber’s user plane traffic for peering at the nearest edge aggregation point. Unlike a typical mobile device such as a cell phone, fixed wireless devices are meant to be always-on and connected for serving end user devices. Meaning that the latency and reliability we commonly expect from traditional wireline services is expected from fixed wireless services too.
In 2022, T-Mobile US became the fastest growing U.S. Internet Service Provider—doubling their number of FWA customers in the past six months. With over 2 million FWA subscribers and counting, the scalability and flexibility of having a Converged Core has proven invaluable to T-Mobile. Being able to deploy UPF nodes for Fixed Wireless Access in remote locations while managing the Session Management Function (SMF) nodes at a central site(s) is effective for scaling the network, optimizing the usage of the transport infrastructure to deliver better end-user latency.

Scaling and extending Fixed Wireless Access with the flexible deployment of UPF nodes, optimizing the routing for user plane traffic. Source: Cisco
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
It’s estimated that around 70% of communication service providers today offer a form of Fixed Wireless Access services, most of them still using 4G LTE, which delivers a fraction of the performance of fiber. Upgrading network architectures to meet the needs of new 5G services needs a smooth plan for the transition. Cisco believes that can begin in the mobile core network. With a Converged 4G/5G Core, communication service providers can migrate from 4G to 5G without disruption while scaling to serve the needs of millions of new subscribers.
For More Information:
Learn more about the Cisco Converged Core, and how we are helping rural communities bridge the digital divide. Find out how T-Mobile and Cisco Launched the World’s Largest Cloud Native Converged Core Gateway, read the December 2022 press release.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Next-level connectivity: Unveiling our new 5G FWA Platform | Qualcomm
https://blogs.cisco.com/sp/getting-to-the-core-of-the-digital-divide-with-5g-fixed-wireless-access
https://www.verizon.com/about/blog/fixed-wireless-access
Ericsson: Over 300 million Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) connections by 2028
Research & Markets: 5G FWA Global Market to hit $38.17B by 2026 for a CAGR of 87.1%
Dell’Oro: FWA revenues on track to advance 35% in 2022 led by North America
JC Market Research: 5G FWA market to reach $21.7 billion in 2029 for a CAGR of 65.6%
5G FWA launched by South Africa’s Telkom, rather than 5G Mobile
Orange-Spain deploys 5G SA network (“5G+”) in Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia and Seville
Orange-Spain has deployed a commercial 5G SA network in several cities, with more to follow this year. The network will be available in Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia and Seville. The network operator claims it is the first network operator to deploy a commercial 5G SA network in Spain which is called 5G+. 90% coverage is promised in these cities, and more locations are going to be plugged in over the course of 2023.
There will be no extra charge for Orange users to use 5G+, but initially at least they’ll need either a Samsung S22, Xiaomi 12, Xiaomi 12T, S22+, S22 Ultra or Xioami 12 Pro series handset to connect to it.
Orange says it has spent €531 million buying up 5G frequencies in all bands throughout the various auctions from 2016 to the most recent one in December 2022, and we’re told it is the operator with the most spectrum in the 3.5 GHz band.
Orange already deployed 5G services in 1,529 towns and cities in 52 provinces across Spain, surpassing its initial target for the full year. The telco has chosen the following 5G SA vendors:
- Ericsson’s 5G SA core network for Belgium, Spain, Luxembourg and Poland
- Nokia’s 5G SA core network for France and Slovakia, and Nokia’s Subscriber Data Management for all countries
- Oracle Communications for 5G core signaling and routing in all countries
Opinion:
Orange-Spain refers to its 5G SA network as 5G+, implying an enhanced form of 5G which it is not! It is true 5G because you don’t get any 5G features/functions with 5G NSA. The Orange press release describes 5G SA as a ‘standard that completes the deployment of 5G technology’ – which is only partially true, because there is no standard for 5G SA.

5G+ is also good news for business customers, as per the press release:
“In addition, for enterprises, 5G+ meets the need for flexible, scalable, reliable and secure connectivity for real-time applications. Through its network slicing capability, Orange’s network will be able to offer virtual networks that will be responsible for allocating the necessary network resources to guarantee the provision of critical services or meet specific customer needs, offering different levels of quality, availability, privacy and security.”
Orange Spain is currently offering 5G services through frequencies in the 3.5 GHz and 700 MHz bands. Last year, when Orange announced its deployment of 5G in the 700 MHz band, it said it would offer this technology progressively over the course of 2022 in more than 1,100 towns and cities, 820 of them having between 1,000 and 50,000 citizens.
In the last spectrum auction, Orange secured 2×10 megahertz in the 700 MHz band, which adds to the 110 megahertz in the 3.5 GHz band already owned by Orange. The company invested a total of 523 million euros (currently $559 million) in the acquisition of these frequencies.
Why have 5G SA rollouts been so slow?
The move from NSA to SA 5G architecture is incredibly complex – seemingly more so than initially anticipated by operators around the world. In the UK, for example, BT’s CTO Howard Watson described the shift as a “sea change in the underlying architecture” late last year, telling journalists the company would take their time to ensure a smooth transition.
Meanwhile, the global economic situation is making network rollouts more expensive and reducing customer spending, leaving operators unsure if they will be able to get a quick return on investment.
As a result, we are left with a mobile industry in no major hurry to upgrade to 5G SA, but is instead happy to bide its time and wait to learn lessons from early adopters – including Orange. For these reasons, the marketing around 5G SA and also mmWave is going to be tricky for wireless network operators who are not familiar with the inner workings of the industry and the particulars of how this roll out was executed, and who may simply assume they already bought 5G years ago.
References:
https://telecoms.com/519893/orange-spain-switches-on-5g-sa-network-dubbed-5g/
https://totaltele.com/5g-orange-launches-5g-standalone-in-spain/
Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments
There was steady growth in 5G network coverage in 2022, with the number of subscribers reaching almost 1 billion worldwide. Although most of the 5G deployments in 2022 were in the developed economies of the world, Counterpoint Research expects that the bulk of 5G network roll outs in 2023 will be in emerging markets. This will drive the continuing transition from 5G NSA to 5G SA. To date, 42 network operators have deployed 5G SA commercially.
Counterpoint Research ‘s recently published 5G SA Tracker is a culmination of an extensive study of the 5G SA market. It provides details of all operators with 5G SA cores in commercial operation at the end of 2022, with market share by region, vendor and by frequency band. As shown in Exhibit 1, the Asia-Pacific region led the world at the end of 2022, followed by North America and Europe, with the other regions – Middle East and Africa and Latin America – lagging behind.
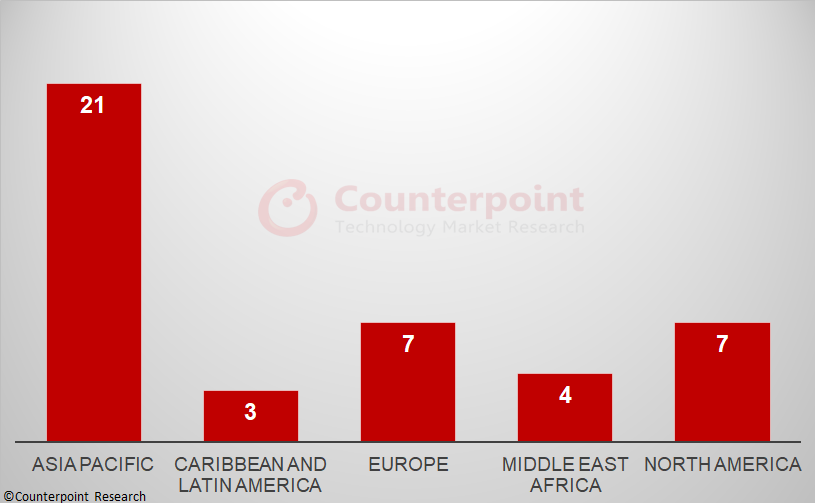
Key Points:
Key points discussed in the report include:
- Operators – 42 operators have deployed 5G SA commercially [1.] with many more testing and in trials. Most of the deployments are in the developed economies of the world with those in emerging economies lagging. In some markets, operators have adopted a “wait-and-see” approach and are looking for evidence of successful use cases before switching from 5G NSA to SA. The ongoing economic headwinds might also delay commercial deployment of SA particularly during the first half of 2023.
Note 1. By the end of 2022, Dell’Oro Group had identified 39 MNOs that had deployed 5G SA eMMB networks.
- Vendors – Ericsson and Nokia lead the 5G SA Core market globally and are benefiting from the geopolitical sanctions on Chinese vendors Huawei and ZTE in some markets. Asian vendors Samsung and NEC are mainly focused on their respective domestic markets, but and are expanding their reach to Tier-2 operators and emerging markets, while US vendor Mavenir is active across all regions, with multiple deployments due to become live in 2023, including several with Tier-1 operators.
- Spectrum – most operators are deploying 5G in mid-band frequencies, for example, n78, as it provides faster speeds and good coverage. A small number of operators have also launched commercial services in the sub-1GHz and millimetre wave bands. FWA seems to be the most popular use case at present but there is a lot of interest in edge services and network slicing as well.
Report Overview:
Counterpoint Research’s 5G SA Core Tracker, January 2023 tracker provides an overview of the 5G Standalone (SA) market, highlighting the key trends and drivers shaping the market, plus details of commercial launches by vendor, by region and by frequency band. In addition, the tracker provides details about the 5G SA vendor ecosystem split into two categories: public operator and private network markets.
Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Market Update
- 5G SA Market Deployments
- Commercial Deployment by Operators
- Network Engagements by Region
- Network Engagements by Deployments Status
- Leading 5G Core Vendors
- Mobile Core Vendor Ecosystem
- 5G Core Vendors Market Landscape
- Outlook
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
During its recent Q4 2022 earnings call, Nokia CEO Pekka Lundmark was asked about 5G SA core networks. Lundmark said, “Obviously 5G standalone is now the name of the game because you need 5G standalone in terms of getting the full benefits of 5G. There is going to be a lot of investment in 5G core, and operators will be implementing some critical important services like slicing, which require investment in the 5G core.”
That’s an understatement because 5G SA is needed to realize 3GPP defined 5G features and functions, like security and network slicing. 5G NSA, which is mostly deployed today, is actually 4G with 3GPP 5G-NR for the RAN.
References:
Update on 5G Stand-Alone (SA) Core Networks
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network & MEC revenues to be > $50 billion by 2027
Global Data: Wireless telcos don’t know how to market 5G SA
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
Why are 5G SA Core networks taking so long to be commercially deployed?
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market driven by 5G SA networks in China
Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Market—A Look into 2023
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
Ericsson, Intel and Microsoft demo 5G network slicing on a Windows laptop in Sweden
Ericsson, Intel and Microsoft successfully demonstrating end-to-end 5G standalone (SA) network slicing capabilities on a Windows laptop at Ericsson’s Lab in Sweden. This pioneering trial demonstrates the applicability of the technology on devices beyond smartphones, paving the way for new business/enterprise opportunities and for consumer use cases such as mobile gaming and collaboration applications for 5G cellular-connected laptops.
The trial used User Equipment Route Selection Policy (URSP), which enables devices to automatically select between different slices according to which application they are using. It also used Ericsson’s Dynamic Network Slicing Selection, Ericsson’s dual-mode 5G Core, and Ericsson’s RAN Slicing capabilities to ‘secure end-user service differentiation.’
Network slicing has long been seen as vital to capturing the value that a 5G network can provide for communications service providers (CSPs) and enterprises. The market for network slicing alone in the enterprise segment is projected at USD 300 billion by 2025, according to the GSMA. By demonstrating a single Windows 11 device can make use of multiple slices, which are used according to the on-device usage profiles and network policies defined at the CSP level, the partners show the flexibility and range of potential use cases available using this technology.
This trial illustrates the opportunities for 5G monetization beyond smartphone devices and opens the door to a wider 5G device ecosystem, allowing CSPs and other members of the telecoms and IT world to expand their horizons when considering opportunities to generate profitable use cases for 5G. Laptop type devices, in particular, are vital to enterprise productivity. The inclusion of Windows 11 laptops in the ranks of devices that can be used for commercializing 5G network slicing is a sign of the ecosystem maturing. Network slicing capabilities will benefit consumer and enterprise segments by defining specific Service Level Agreement per slice for existing and emerging Windows applications and use cases, such as real-time enterprise applications like Microsoft Teams and Office365, game/media streaming, and emerging AI and augmented reality/extended reality (AR/XR) applications.
Sibel Tombaz, Head of Product Line 5G RAN at Ericsson, said: “Expanding the range of devices for network slicing to include laptops will allow new business segments to create a variety of use cases for consumer and enterprises. We have shown, together with Intel and Microsoft, how ecosystem collaboration can open new possibilities. We will continue to strengthen Ericsson’s network slicing capabilities and work with industry partners to enable more applications on several devices, spreading the benefits of 5G in the consumer and enterprise segments.”
Ian LeGrow, Microsoft Corporate Vice-President of Core OS Innovation said: “We are thrilled to showcase our cutting-edge technology and its ability to deliver fast, dependable and secure 5G connectivity on Windows 11. Partnering with Intel and Ericsson only further solidifies our commitment to innovation and openness in our platform.”
This ground-breaking network slicing demo will be showcased jointly with Intel and Microsoft in the Ericsson Hall during MWC Barcelona 2023 from February 27 to March 2.
Andrew Wooden of telecoms.com wrote:
“There are so many tests and trials going on, and while technically seem to signal a bit of incremental progress each time, it can be easy to lose the context of what is supposed to be offered while digging around in the weeds of experimental telecoms architecture. That said if trials like this can keep the emphasis on how they provide some extra money-making opportunities for those in the business of flogging 5G, and some genuine benefits for the rest of us, perhaps it will gain some traction when they show it off in Barcelona.”
Source: Viavi Solutions
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2023/2/ericsson-intel-and-microsoft-show-network-slicing-capabilities-on-a-laptop-for-consumer-and-enterprise-applications
https://www.ericsson.com/en/network-slicing#dynamicnetworksliceselection
https://www.ericsson.com/en/core-network/5g-core
https://telecoms.com/519733/ericsson-intel-and-microsoft-slice-up-a-network-and-feed-it-to-a-laptop/
Ericsson and Nokia demonstrate 5G Network Slicing on Google Pixel 6 Pro phones running Android 13 mobile OS
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
https://www.viavisolutions.com/en-us/5g-network-slicing
Network Slicing and 5G: Why it’s important, ITU-T SG 13 work, related IEEE ComSoc paper abstracts/overviews
Update on 5G Stand-Alone (SA) Core Networks
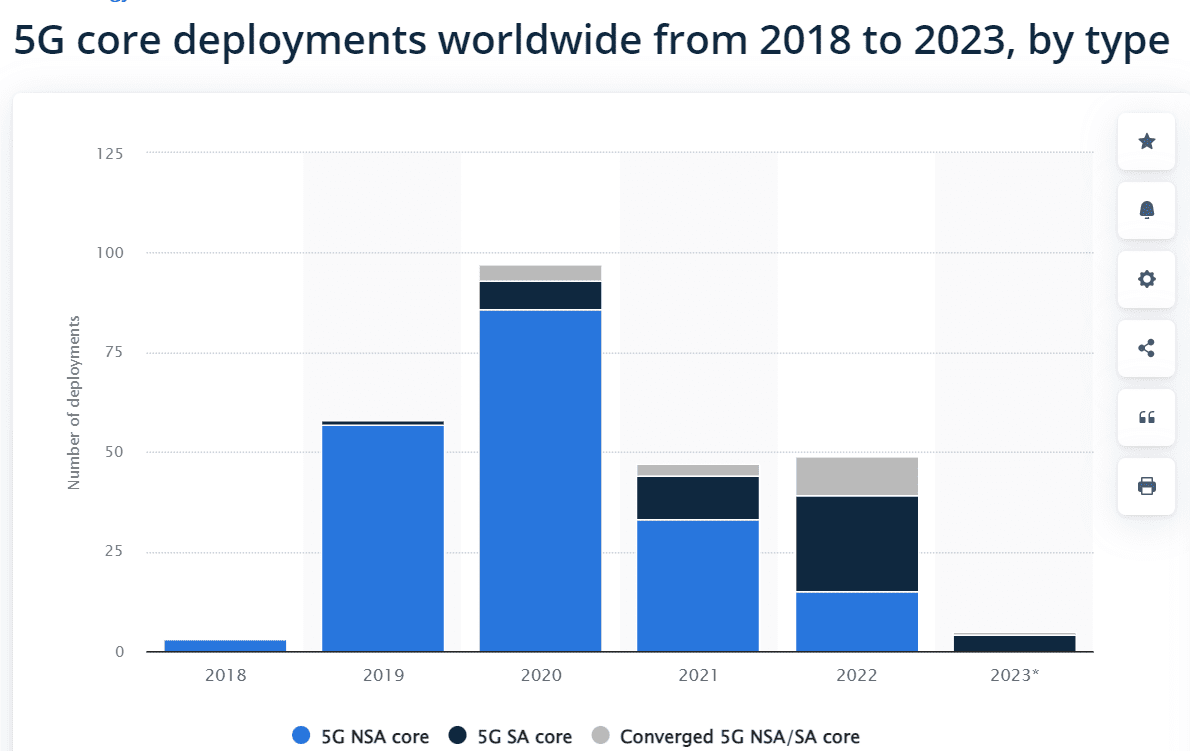
Statista:
The type of 5G cores currently deployed remains dominated with about 75% of non-standalone (NSA) cores, or cores using the preexisting 4G network infrastructure. However, 5G standalone (SA) cores, which require more up-front costs and development yet may provide faster and more scalable connection, are forecast to outstrip NSAs and consist of 24 of the 49 5G core launches in 2022. All but one of the 5G launches announced for 2023 are standalone.
GSA:
Network Operators are increasingly experimenting with and deploying 5G standalone (SA) networks. With a totally new, cloud-based, virtualized, microservices-based core infrastructure, some of the anticipated benefits of introducing 5G SA technologies include faster connection times (lower latency), support for massive numbers of devices, programmable systems enabling faster and more-agile creation of services and network slices, with improved support for management of service-level agreements within those slices, and the advent of voice over New Radio (VoNR) technology. The introduction of 5G SA is expected to facilitate simplification of architectures, improve security and reduce costs.
The 5G SA technology is expected to enable customisation and open up new service and revenue opportunities tailored to enterprise, industrial and government customers.
GSA is tracking the emergence of the 5G SA system, including the availability of chipsets and devices for customers, plus the testing and deployment of 5G SA networks by public mobile network operators as well as private network operators. This report is the latest in an ongoing series summarizing market trends, drawing on data collected in GSA’s various databases covering chipsets, devices, spectrum and networks.
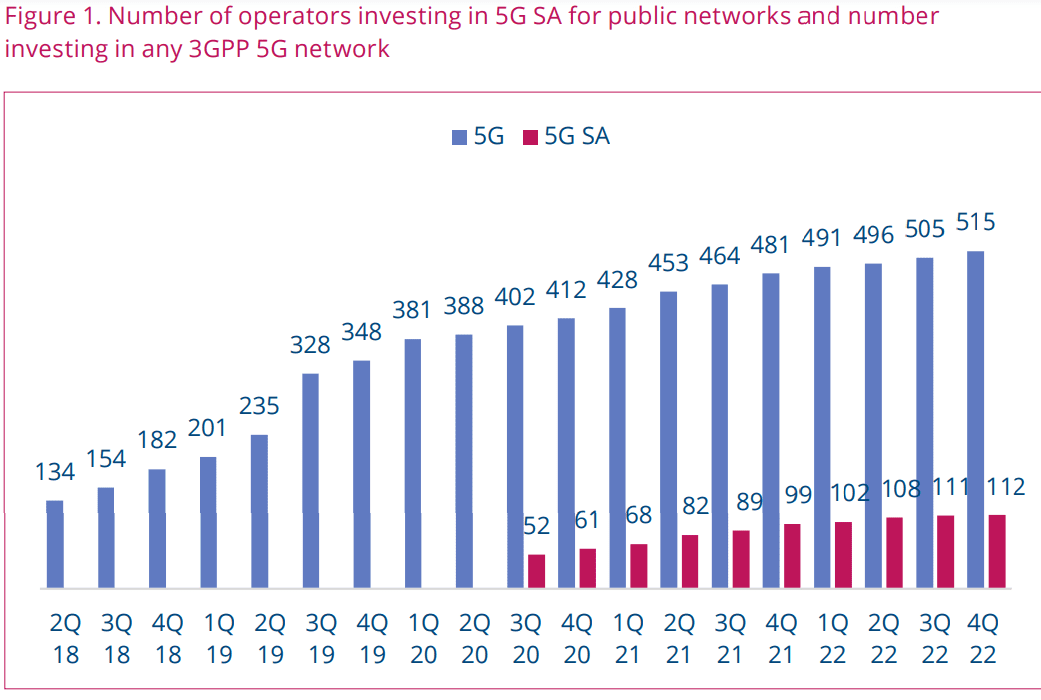
GSA has identified 112 operators in 52 countries and territories worldwide that have been investing in public 5G SA networks in the form of trials, planned or actual deployments . This equates to almost 21.7% of the 515 operators known to be investing in 5G licences, trials or deployments of any type.
At least 32 operators in 21 countries and territories are now understood to have launched public 5G SA networks, two of which have only soft-launched their 5G SA networks. In addition to these, 21 operators have been catalogued as deploying or piloting 5G SA for public networks, and 31 as planning to deploy the technology, showing that launches of 5G SA look set to continue apace. GSA has also recorded 19 operators as being involved in evaluations, tests or trials of 5G SA.
As of the last update in December 2022, GSA had collated information about 955 organisations known to be deploying LTE or 5G private mobile networks.
Countries and territories with operators identified as investing in public 5G SA networks have been granted a licence suitable for the deployment of a private LTE or 5G network so far. Of those, 391 are known to be using 5G networks (excluding those labelled as 5G-ready) for private mobile network pilots or deployments. Of those, 41 (slightly more than 10% of them) are known to be working with 5G SA already. They include manufacturers, academic organizations, commercial research institutes, construction, communications and IT services, rail and aviation organizations.
Dell’Oro Group:
At the close of 2022, we identified 39 mobile network operators that have commercially launched 5G SA eMMB networks.
References:
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1330511/5g-core-deployments-worldwide-by-type/
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/5g-system-overview
https://www.ericsson.com/en/core-network/5g-core
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
Samsung Electronics and KDDI announced the successful demonstration of Service Level Agreements (SLA) assurance network slicing in a field trial conducted in Tokyo, Japan. For the first time in the industry, the companies proved their capabilities to generate multiple network slices using a RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) on a live commercial 5G Standalone (SA) network. The RIC, provided by Samsung in this field trial, is a software-based component of the Open RAN architecture that optimizes the radio resources of the RAN to improve the overall network quality.
Network slicing (which requires a 5G SA core network) enables multiple virtual networks to be created within a single physical network infrastructure, where each slice is dedicated for a specific application or service — serving different purposes. For instance, 5G SA network operators can create a low latency slice for automated vehicles, an IoT slice for smart factories and a high bandwidth slice for live video streaming — all within the same network. This means that a single 5G SA network can support a broad mix of use cases simultaneously, accelerating the delivery of new services and meeting the tailored demands of various enterprises and consumers.
“Network slicing will help us activate a wide range of services that require high performance and low latency, benefitting both consumers and businesses,” said Toshikazu Yokai, Managing Executive Officer, General Manager of Mobile Network Technical Development Division at KDDI. “Working with Samsung, we continue to deliver the most innovative technologies to enhance customer experiences.”
Through this field trial conducted in Q4 of 2022, KDDI and Samsung proved their capabilities of SLA assurance to generate multiple network slices that meet SLA requirements, guaranteeing specific performance parameters — such as low latency and high throughput — for each application. Samsung also proved the technical feasibility of multiple user equipment (UE)-based network slices with quality assurance using the RIC, which performs advanced control of RAN as defined by the O-RAN Alliance.
“Network slicing will open up countless opportunities, by allowing KDDI to offer tailor-made, high-performance connectivity, along with new capabilities and services, to its customers,” Junehee Lee, Executive Vice President, Head of Global Sales & Marketing, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “This demonstration is another meaningful step forward in our efforts to advance technological innovation and enrich network services. We’re excited to have accomplished this together with KDDI and look forward to continued collaboration.”
For more than a decade, the two companies have been working together, hitting major 5G networks milestones that include: KDDI’s selection of Samsung as a 5G network solutions provider, end-to-end 5G network slicing demonstration in the lab, 5G network rollout on 700MHz and the deployment of 5G vRAN on KDDI’s commercial network.
Samsung has pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions including chipsets, radios and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio from virtualized RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company is currently providing network solutions to mobile operators that deliver connectivity to hundreds of millions of users around the world.
References:
Ericsson and Nokia demonstrate 5G Network Slicing on Google Pixel 6 Pro phones running Android 13 mobile OS
Nokia and Safaricom complete Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial
Deutsche Telekom demos end to end network slicing; plans ‘multivendor’ open RAN launch in 2023
Is 5G network slicing dead before arrival? Replaced by private 5G?
Telefonica in 800 Gbps trial and network slicing pilot test
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
Network Slicing and 5G: Why it’s important, ITU-T SG 13 work, related IEEE ComSoc paper abstracts/overviews
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network & MEC revenues to be > $50 billion by 2027
According to a recently published report from Dell’Oro Group, the Mobile Core Networks (MCN) [1.] and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) market revenues are expected to reach over $50 billion by 2027.
Note 1. The Mobile Core Network is in a transitional stage from 4G to 5G and a new type of core network called the 5G Core Service Based Architecture (SBA). The 5G Core SBA is designed to be a universal core that can be the core for mobile and fixed wireless networks, wireline networks, and Wi-Fi networks. This includes the ability to be the core for 2G/3G/4G, so only one core is necessary for the long term. In addition, the IMS Core will migrate into the 5G Core SBA.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“The MNC and MEC market revenues are expected to grow at a 2 percent CAGR (2022-2027). We expect the MCN market for the China region to reach maturity first—due to its early start on 5G SA deployments—and is projected to have -4 percent CAGR throughout the forecast period,” stated Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group.
“The worldwide market, excluding China, is projected to have a 3 percent CAGR. The Asia Pacific (APAC) and the Europe, Middle, East, and Africa (EMEA) region are expected to have the highest CAGRs throughout the forecast period as MNOs accelerate the deployments of 5G SA networks and expand their respective coverage footprints.
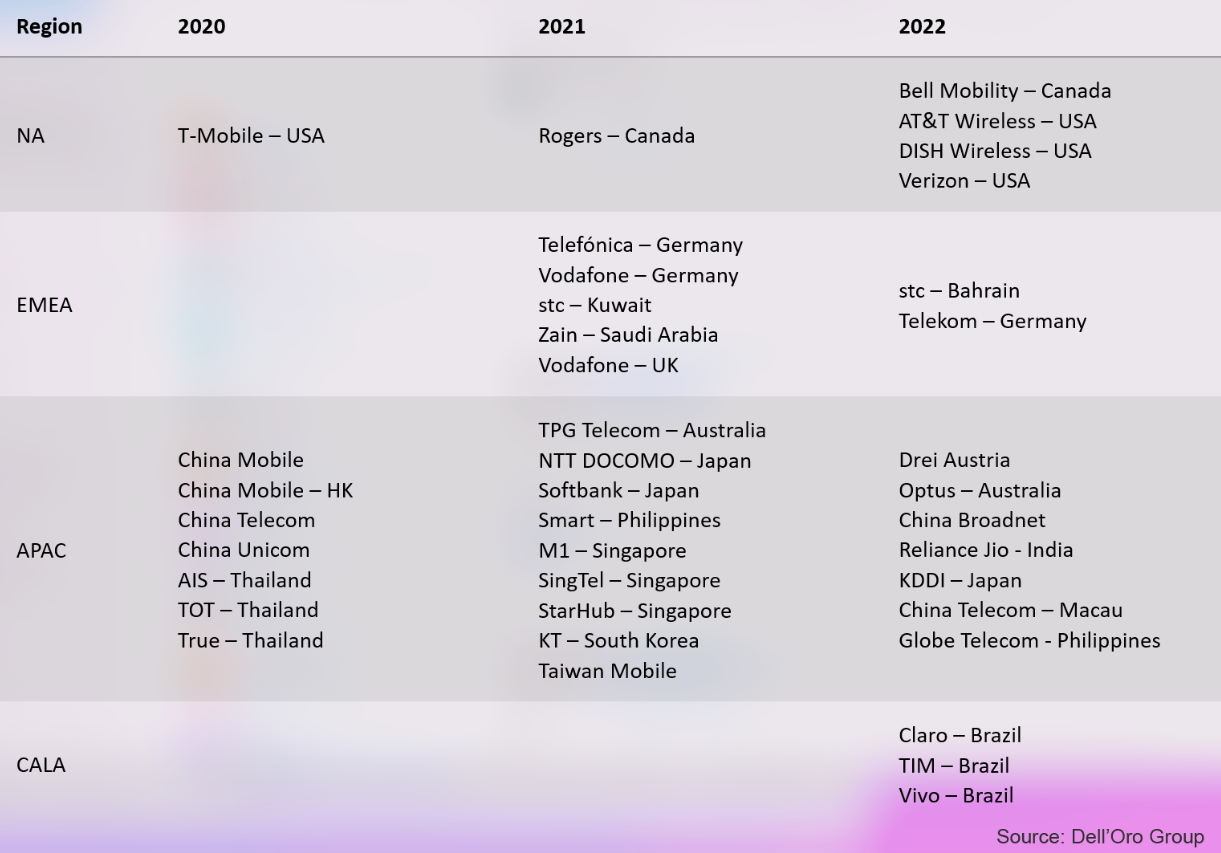
“There were hopes early in the year that many more [SA networks] would be launched in 2022, but the hopes were lowered as the year progressed,” Bolan explained. At the close of 2022, Dell’Oro identified 39 MNOs (Mobile Network Operators) that have commercially launched 5G SA eMMB networks.
“Reliance Jio, China Telecom-Macau, and Globe Telecom were new MNOs added to the list of 39 MNOs launching 5G SA eMMB networks in the fourth quarter of 2022. Reliance Jio has announced a very aggressive deployment schedule to cover most of India by the end of 2023. In addition, AT&T and Verizon plan large expansions to their 5G SA coverage in 2023, raising the projected Y/Y growth rate for the total MCN and MEC market for 2023 higher than 2022,” added Bolan.
Additional highlights from the January 2023 MCN and MEC 5-Year forecast report:
- The MEC segment of the MCN market will have the highest CAGR, followed by the 5G MCN market and the IMS Core market.
- As networks migrate to 5G SA, the 4G MCN market is expected to decline at a double-digit percentage CAGR.
The Dell’Oro Group Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Computing Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, shipments, and average selling prices for Evolved Packet Core, 5G Packet Core, Policy, Subscriber Data Management, and IMS Core including licenses by Non-NFV and NFV, and by geographic regions. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
From Deloitte:
“The coming migration to 5G standalone core networks is expected to allow for increased device density, reliability, and latency, opening the door to advanced enterprise applications,” according to several analysts from Deloitte’s Technology, Media & Telecommunications industry group.
“5G SA’s big attraction for MNOs are the new service and revenue opportunities it creates, Along with near-zero latency and massive device density, 5G SA enables MNOs to provide customers – specifically enterprise customers – access at scale to fiber-like speeds, mission-critical reliability, precise location services, and tailored network slices with guaranteed service levels.”
Deloitte expects the number of mobile network operators investing in 5G SA networks – with trials, planned deployments, or rollouts – to double from more than 100 operators in 2022 to at least 200 by the end of 2023.

References:
Mobile Core Network Market to Reach over $50 billion by 2027, According to Dell’Oro Group
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market driven by 5G SA networks in China
Tech Mahindra and Microsoft partner to bring cloud-native 5G SA core network to global telcos
India’s Tech Mahindra and Microsoft have announced a collaboration to enable cloud-powered 5G SA core network for telecom operators worldwide. As a part of the collaboration, Tech Mahindra will provide its expertise, comprehensive solutions, and managed services offerings to telecom operators for their 5G SA Core networks. Tech Mahindra will provide its expertise like “Network Cloudification as a Service” and AIOps to global telecom operators for their 5G Core networks. AIOps will help operators combine big data and machine learning to automate network operations processes, including anomaly detection, predicting fault and performance issues.
CP Gurnani, Managing Director and Chief Executive Officer, Tech Mahindra said, “Today, it is critical to leverage next-gen technologies to build relevant and resilient services and solutions for customers across the globe. At Tech Mahindra, we are well-positioned to help telecom operators realize the full potential of their networks and provide innovative and agile services to their customers while also helping them meet their ESG commitments. Our collaboration with Microsoft will further strengthen our service portfolio by combining our deep expertise across the telecom industry with Microsoft Cloud. Further to this collaboration, Tech Mahindra and Microsoft will work together to help telecom operators simplify and transform their operations in order to build green and secure networks by leveraging the power of cloud technologies. At Tech Mahindra, we are well-positioned to help telecom operators realize the full potential of their networks and provide innovative and agile services to their customers while also helping them meet their ESG commitments.”
Tech Mahindra believes the 5G core network will enable use cases such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), IoT (Internet of Things, and edge computing. Of course, 5G URLLC performance requirements, especially ultra low latency, in the RAN and core network must be met first, which they are not at this time. The company will leverage the Microsoft Azure cloud for its sustainability solution iSustain to measure and monitor KPIs across all three aspects of E, S & G. iSustain will help operators address the challenge of measuring and reducing carbon emissions from the networks while meeting demands of the countless energy intense digital technologies, from AR/ VR to IoT.
Anant Maheshwari, President, Microsoft India said, “Harnessing the power of Microsoft Azure, telecom operators can provide more flexibility and scalability, save infrastructure cost, use AI to automate operations, and differentiate their customer offerings. The collaboration between Tech Mahindra and Microsoft will help our customers build green and secured networks with seamless experiences across the Microsoft cloud and the operator’s network. Azure provides operators with cloud solutions that enable them to create new revenue generating services and move existing services to the cloud. Through our collaboration with Tech Mahindra, Microsoft will further help telcos overcome challenges, drive innovation and build green and secured networks that provide seamless experiences by leveraging the power of Microsoft Cloud for Operators.”
The partnership is in line with Tech Mahindra’s NXT.NOWTM framework, which aims to enhance the ‘Human Centric Experience’, Tech Mahindra focuses on investing in emerging technologies and solutions that enable digital transformation and meet the evolving needs of the customer.
About Tech Mahindra:
Tech Mahindra offers innovative and customer-centric digital experiences, enabling enterprises, associates and the society to Rise. We are a USD 6 billion organization with 163,000+ professionals across 90 countries helping 1279 global customers, including Fortune 500 companies. We are focused on leveraging next-generation technologies including 5G, Blockchain, Metaverse, Quantum Computing, Cybersecurity, Artificial Intelligence, and more, to enable end-to-end digital transformation for global customers. Tech Mahindra is the only Indian company in the world to receive the HRH The Prince of Wales’ Terra Carta Seal for its commitment to creating a sustainable future. We are the fastest growing brand in ‘brand strength’ and amongst the top 7 IT brands globally. With the NXT.NOWTM framework, Tech Mahindra aims to enhance ‘Human Centric Experience’ for our ecosystem and drive collaborative disruption with synergies arising from a robust portfolio of companies. Tech Mahindra aims at delivering tomorrow’s experiences today and believes that the ‘Future is Now.’

References: