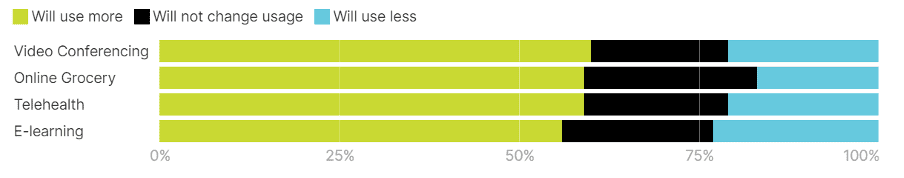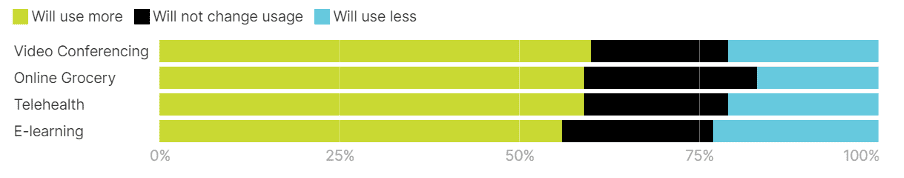Telecom and AI Status in the EU
By Afnan Khan with Ajay Lotan Thakur
Introduction
In the eerie silence of deserted streets and amidst the anxious hum of masked conversations, the world found itself gripped by the rapid proliferation of COVID-19. Soon labelled a global pandemic due to the havoc wreaked by soaring death tolls, it brought unprecedented disruption and accelerated the inevitable rise of the digital age. The era of digital transformation has swiftly transitioned, spawning a multitude of businesses catering to every human need. Today, our dependence on digital technology remains steadfast, with remote work becoming the norm and IT services spending increasing from $1.071 trillion in 2020 to $1.585 trillion. [1]
The chart below, sourced from Oliver Wyman Forum Analysis,[2] vividly illustrates our increasing dependence on technology. It presents findings from a survey conducted in the latter half of 2020 across eight countries – US, UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Singapore, and China. The survey reveals that 60% of respondents favoured increased use of video conferencing, while online grocery shopping and telehealth services each garnered 59% approval, and E-learning showed a strong preference at 56%. This data underscores how swiftly digital solutions integrated into our daily lives during the pandemic.
Source: Olive Wyman Forum Analysis [2]
Advancements in Telecom and AI Applications Across EU
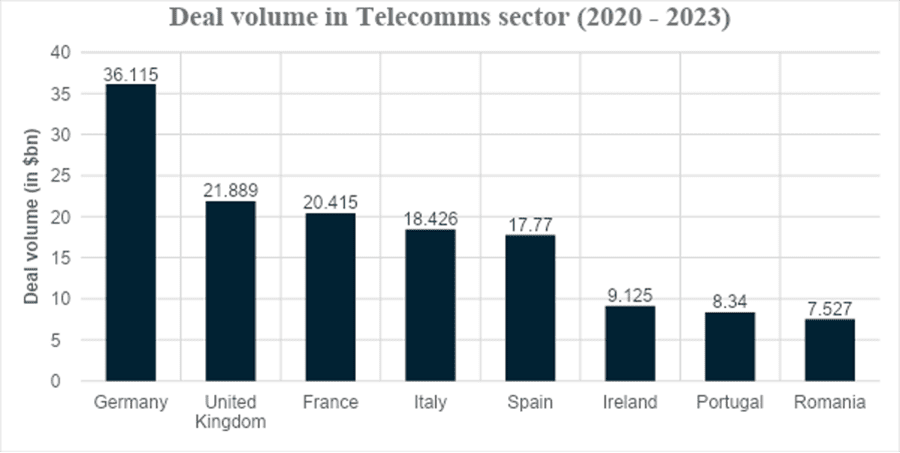
The graph below represents the project and infrastructure finance deal volume in the telecommunications sector from 2020 to 2023. The dominance of Germany is evident, with the deal volume reported to be $36.115 billion, followed by the UK at $21.889 billion. France follows closely in third place with a deal volume of $20.415 billion, representing significant market potential. The only other two countries with substantial figures are Italy and Spain, although there have been some promising deals closing in Ireland, Portugal, and Romania with large new financing deals in the project finance sector.
Source: Proximo Intelligence [5]
Deutsche Telekom, the national provider, has spearheaded advancements with AI-powered network optimisation tools. These tools leverage real-time analytics, resulting in a notable 20% enhancement in network performance and a 15% reduction in customer complaints. [14] While 2022 marked a pivotal year for the industry in Germany, the evolution of German fibre optics infrastructure has continued apace. Germany led Europe’s FTTH (Fibre to the Home) initiative, with significant financings closing throughout the year. According to Proximo Data, 16 European FTTH financings concluded in 2022, amassing nearly $26 billion in deal volume, with German deals accounting for almost $9 billion of that total.
Spain’s Telefónica has deployed an advanced AI-driven fraud detection system that effectively blocks over 95% of fraudulent activities. This initiative not only protects Telefónica from financial losses but also enhances security for its customers. [15] The adoption of AI for cybersecurity underscores a broader trend in the telecom industry towards leveraging advanced technologies to bolster trust and safeguard digital transactions.
Orange has introduced AI-driven chatbots that autonomously handle more than 90% of customer queries in France, resulting in a significant reduction in customer service costs by 40% and a notable increase in customer satisfaction rates by 25%. [16] This innovation represents a paradigm shift in customer service automation within the telecom sector, demonstrating the effectiveness of AI in improving operational efficiency and enhancing the overall customer experience.
Telecom Italia (TIM) has implemented AI-powered network security solutions to proactively detect and mitigate cyber threats in real-time, achieving a remarkable 60% reduction in cybersecurity. [17]
This strategic deployment of AI highlights TIM’s commitment to enhancing network resilience and safeguarding critical infrastructure from evolving cyber threats, setting a precedent for cybersecurity strategies in the telecommunications industry.
Predictive Analysis Enhancing Telecom Resilience
Interference mitigation strategies are essential for smooth digital operations in the post-pandemic world. Picture digital experts rapidly addressing problems from rogue networks and environmental noise, creating a digital shield against disruptions, and ensuring a seamless user experience. These strategies propel telecom companies towards better connectivity and user satisfaction.
These examples highlight the trend of using AI and predictive analytics to boost network performance in cities. As urban areas contend with population growth and increasing digital demands, telecom companies invest in advanced technologies. These reduce network congestion, enhance service reliability, and support sustainable urban development. This trend not only improves customer experience but also positions telecom providers as leaders in developing future smart cities.
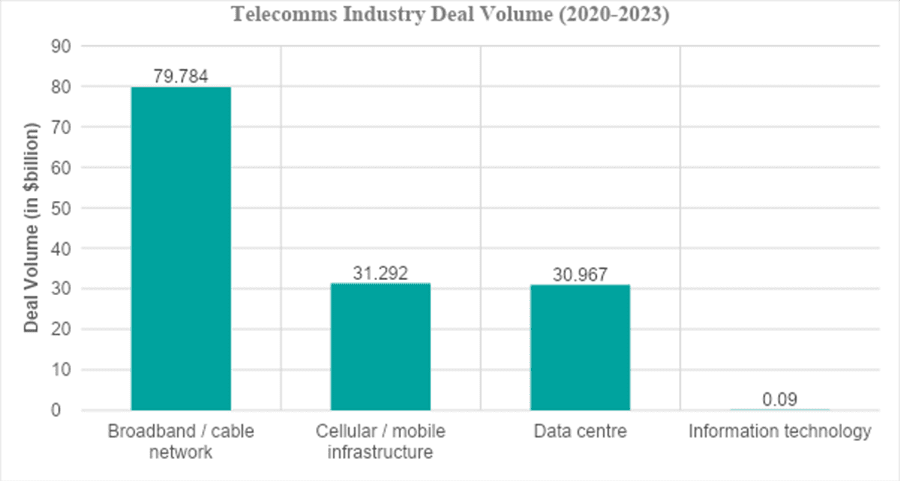
The chart below, from the Proximo Intelligence database, shows European deal volumes over the past three years, categorised by sub-sectors. The broadband and cable network sector leads with a deal volume of $79.784 billion from 86 deals out of a total 137 in project and infrastructure finance. Cellular and mobile infrastructure follows with $31.292 billion across 25 deals. Data centres, a growing trend, also report a deal volume of $30.967 billion across 25 deals.
Source: Proximo Intelligence [5]
In the post-COVID era, the adoption of predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring has accelerated, becoming a critical component of the new normal for businesses. These technologies enable companies to build more resilient infrastructures, proactively mitigate risks, and enhance operational efficiency. As businesses continue adapting to a rapidly changing environment, the integration of predictive maintenance solutions plays a pivotal role in sustaining long-term growth and stability.
Europe has seen profound impacts from these advancements, setting a precedent for global telecom strategies moving forward.
Future Trends and The Way Forward
European telecommunications face challenges shaped by regulatory frameworks, economic conditions, and technological advancements:
- Brexit introduces regulatory uncertainties for UK telecoms. [18]
- Germany’s GDPR compliance challenges demand heavy investment. [19]
- Spain faces economic instability affecting telecom investments. [20]
- France’s 5G deployment is delayed by regulatory barriers. [21]
- Italy’s 5G rollout is hindered by spectrum allocation challenges. [22]
- The Netherlands invests in cybersecurity for evolving threats. [23]
- Sweden focuses on bridging rural connectivity gaps. [24]
- Switzerland navigates complex regulatory landscapes for innovation. [25]
In the wake of COVID-19, with masks now a thing of the past and streets deserted only due to construction, digital technologies are transforming European telecommunications amidst regulatory shifts and economic uncertainties. Investments in infrastructure and AI innovations are pivotal, shaping the industry’s future and its adaptation to rapid change while driving economic recovery across Europe. How will the industry sustain innovation and meet growing digital demands ahead? Only time will tell.
References
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/203291/global-it-services-spending-forecast/
- https://www.oliverwyman.com/our-expertise/perspectives/health/2021/mar/why-4-technologies-that-boomed-during-covid-19-will-keep-people-.html
- https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- https://www.gov.uk/government/news/new-data-shows-small-businesses-received-213-billion-in-covid-19-local-authority-business-support-grants#:~:text=Press%20release-,New%20data%20shows%20small%20businesses%20received%20%C2%A321.3%20billion%20in,and%20arts%2C%20entertainment%20and%20recreation.
- Proximo Intelligence Data: www.proximoinfra.com
- Vodafone Press Release, 2022.
- “McKinsey & Company. “Predictive maintenance: The rise of self-maintaining assets.”
- Deloitte. “Predictive maintenance: Taking proactivity to the next level.”
- Forbes. “Why Virtual Assistants Are Becoming Essential for Businesses.”
- Statista. “Growth in Demand for Virtual Assistants in Europe.”
- TechRadar. “Vodafone’s AI traffic prediction cuts network congestion by 25% in London.”
- The Guardian. “BT/EE’s AI traffic prediction cuts network congestion by 30% in London.”
- FCC (2023). Spectrum Efficiency Report. Federal Communications Commission. Available at: https://www.fcc.gov/reports-research/reports/fcc-research/spectrum-efficiency.
- Deutsche Telekom’s AI-Powered Network Optimization,” TechInsights
- “Telefónica’s AI-Driven Fraud Detection,” TelecomsToday. Available at: TelecomsToday AI Fraud Detection
- “Orange’s AI-Enabled Customer Support,” AI Insider. Available at: AI Insider AI Customer Support
- “TIM’s AI-Powered Cybersecurity Measures,” CyberTechNews. Available at: CyberTechNews AI Cybersecurity
- TelecomsInsight. “Brexit’s Regulatory Impact on UK Telecoms.”
- DataPrivacyToday. “GDPR Compliance Challenges for German Telcos.”
- BusinessWire. “Spain’s Economic Recovery Challenges.”
- TelecomsObserver. “France’s Regulatory Roadblocks to 5G Deployment.”
- SpectrumInsight. “Italy’s Spectrum Allocation Challenges.”
- CyberDefenseMag. “Netherlands’ Cybersecurity Imperatives.”
- DigitalInclusionHub. “Sweden’s Rural Connectivity Initiatives.”
- RegTechInsights. “Switzerland’s Regulatory Adaptation Challenges.”
Afnan Khan is a Machine Learning Engineer specialising in Marketing Analytics, currently working as a Marketing Analyst at the Exile Group in London. He is involved in various projects, research, and roles related to Machine Learning, Data Science, and AI.
Ajay Lotan Thakur is a Senior IEEE Member, IEEE Techblog Editorial Board Member, BCS Fellow, TST Member of ONF’s Open-Source Aether (Private 5G) Project, Cloud Software Architect at Intel Canada.
Post COVID Telco AI Blueprint for the UK
By Afnan Khan with Ajay Lotan Thakur
Introduction
In the eerie silence of deserted streets and amidst the anxious hum of masked conversations, the world found itself gripped by the rapid proliferation of COVID-19. Soon labelled a global pandemic due to the havoc wreaked by soaring death tolls, it brought unprecedented disruption and accelerated the inevitable rise of the digital age. The era of digital transformation has swiftly transitioned, spawning a multitude of businesses catering to every human need. Today, our dependence on digital technology remains steadfast, with remote work becoming the norm and IT services spending increasing from $1.071 trillion in 2020 to $1.585 trillion. [1]
The chart below, sourced from Oliver Wyman Forum Analysis,[2] vividly illustrates our increasing dependence on technology. It presents findings from a survey conducted in the latter half of 2020 across eight countries – US, UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Singapore, and China. The survey reveals that 60% of respondents favoured increased use of video conferencing, while online grocery shopping and telehealth services each garnered 59% approval, and E-learning showed a strong preference at 56%. This data underscores how swiftly digital solutions integrated into our daily lives during the pandemic.
Accelerating Telecom Growth in Britain
Europe was among the hardest-hit regions by the pandemic, with death tolls exceeding 2.1 million. [3] This crisis accelerated the adoption of digital technologies, prompting businesses to invest in smarter, more sustainable operations to increase their longevity and stay relevant in the market.
In the United Kingdom, despite the government’s injection of £21.3 billion into the economy to support small businesses, the emphasis on digital transformation has been paramount. [4] The push towards digital solutions, including enhanced internet connectivity and robust data centres, underscores the long-term strategic shift towards a more resilient and technologically advanced business landscape.
Statistically, the UK telecom industry has experienced significant growth, driven by increased demand and advancements in network equipment. The shift towards digital dependency, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and the rise of remote work, is expected to be long-term. This trend has also led to a surge in 5G and data centre deals.
According to Proximo, a leading Project and Infrastructure Finance Journal, projects worth $30.967 billion have closed in Europe between 2020 and 2023, highlighting the critical role of data centres in boosting the telecommunications sector. Of this, the UK accounted for $14.133 billion across seven deals, comprising both refinancing and new financing deals, representing 45.6% of Europe’s total contribution. Notably, one of the recent financing deals to close was for Ark Data Centres, based in London, with the term loan reported to be in the region of £170 million for five years, aimed at supporting a significant data project in the UK – thus establishing the country as one of the market leaders in Europe. [5]
Telecom Landscape in the UK’s New Normal
Imagine having the ability to pinpoint precisely when hardware needs replacement, akin to pre-emptively replacing floorboards. Vodafone’s United Performance Management (UPM) facilitates real-time monitoring and proactive identification of anomalies. [6] Predictive maintenance can reduce unplanned downtime by 30-50%, lower maintenance costs by 10-40%, and extend asset lifespan by 20-40%. [7][8]
Virtual Assistants
The integration of virtual assistants has not only streamlined operations but has also emerged as one of the most sought-after roles, as reported by Forbes. [9] In the telecom industry, where customer service reigns supreme, consider the live example of broadband giant BT/EE. Their adoption of remote customer support in the post-COVID world has propelled them to the forefront as the leading data provider in the UK. Mirroring European trends, the demand for virtual assistant roles has surged by 20%, [10] spurred on by initiatives such as digital nomad visas in Spain and Portugal. This trend not only reflects the changing landscape of customer service but also signals significant injections into the economy.
Traffic congestion
In the hustle and bustle of post-pandemic London, navigating the city’s streets amidst fluctuating traffic patterns and network demands presents a unique challenge. Telecom companies are stepping up to the plate, leveraging cutting-edge AI and ML technologies to tackle these issues head-on. By predicting traffic patterns and dynamically managing network loads, they’re ensuring that Londoners experience optimal connectivity and responsiveness, even during peak hours when congestion is at its peak. Imagine this: congestion hotspots are pinpointed in real-time, and network resources are strategically directed to these areas, reducing disruptions. This means that residents and commuters alike enjoy a smoother, more reliable connection, whether they’re streaming, working remotely, or simply staying connected on the go.
One shining example is Vodafone, which has implemented AI-driven traffic prediction models specifically tailored to London’s intricate traffic patterns. The result? A remarkable 25% reduction in network congestion during peak hours, as reported by TechRadar. [11] This underscores the significance of bespoke solutions in addressing London’s unique challenges post-pandemic, solidifying network performance and reliability for the city’s diverse population and thriving businesses.
Another notable case is BT/EE, which has also deployed AI-driven traffic prediction models in London. This initiative led to a significant 30% reduction in network congestion during peak hours. [12] Such tailored AI solutions not only enhance operational efficiency but also demonstrate the telecom industry’s commitment to leveraging technology to improve urban infrastructure.
Dynamic Spectrum
In the dynamic realm of post-COVID technology, telecom pioneers are revolutionising spectrum management with dynamic spectrum allocation. Imagine a digital symphony where frequencies dance to the beat of demand, seamlessly adapting to surges in digital traffic. This innovative approach ensures uninterrupted connectivity, even in the busiest digital arenas. According to recent studies, dynamic spectrum allocation has shown to increase spectrum efficiency by up to 40%, supporting seamless connectivity for the data-hungry masses. [13] Telecom wizards are thus reshaping the digital landscape, delivering turbo-charged connectivity.
References
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/203291/global-it-services-spending-forecast/
- https://www.oliverwyman.com/our-expertise/perspectives/health/2021/mar/why-4-technologies-that-boomed-during-covid-19-will-keep-people-.html
- https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- https://www.gov.uk/government/news/new-data-shows-small-businesses-received-213-billion-in-covid-19-local-authority-business-support-grants#:~:text=Press%20release-,New%20data%20shows%20small%20businesses%20received%20%C2%A321.3%20billion%20in,and%20arts%2C%20entertainment%20and%20recreation.
- Proximo Intelligence Data: www.proximoinfra.com
- Vodafone Press Release, 2022.
- “McKinsey & Company. “Predictive maintenance: The rise of self-maintaining assets.”
- Deloitte. “Predictive maintenance: Taking proactivity to the next level.”
- Forbes. “Why Virtual Assistants Are Becoming Essential for Businesses.”
- Statista. “Growth in Demand for Virtual Assistants in Europe.”
- TechRadar. “Vodafone’s AI traffic prediction cuts network congestion by 25% in London.”
- The Guardian. “BT/EE’s AI traffic prediction cuts network congestion by 30% in London.”
Afnan Khan is a Machine Learning Engineer specialising in Marketing Analytics, currently working as a Marketing Analyst at the Exile Group in London. He is involved in various projects, research, and roles related to Machine Learning, Data Science, and AI.
Ajay Lotan Thakur is a Senior IEEE Member, IEEE Techblog Editorial Board Member, BCS Fellow, TST Member of ONF’s Open-Source Aether (Private 5G) Project, Cloud Software Architect at Intel Canada.
Vodafone: GenAI overhyped, will spend $151M to enhance its chatbot with AI
GenAI is probably the most “overhyped” technology for many years in the telecom industry, said Vodafone Group’s chief technology officer (CTO) Scott Petty at a press briefing this week. “Hopefully, we are reaching the peak of those inflated expectations, because we are about to drop into a trough of disillusionment,” he said.
“This industry is moving too quickly,” Petty explained. “The evolution of particularly GPUs and the infrastructure means that by the time you’d actually bought them and got them installed you’d be N minus one or N minus two in terms of the technology, and you’d be spending a lot of effort and resource just trying to run the infrastructure and the LLMs that sit around that.”
Partnerships with hyper-scalers remain Vodafone’s preference, he said. Earlier this year, Vodafone and Microsoft signed a 10-year strategic agreement to use Microsoft GenAI in Vodafone’s network.
Vodafone is planning to invest some €140 million ($151 million) in artificial intelligence (AI) systems this year to improve the handling of customer inquiries, the company said on July 4th. Vodafone said it is investing in advanced AI from Microsoft and OpenAI to improve its chatbot, dubbed TOBi, so that it can respond faster and resolve customer issues more effectively.
The chatbot was introduced into Vodafone’s customer service five years ago and is equipped with the real voice of a Vodafone employee.
The new system, which is called SuperTOBi in many countries, has already been introduced in Italy and Portugal and will be rolled out in Germany and Turkey later this month with other markets to follow later in the year, Vodafone said in a press release.
According to the company, SuperTOBi “can understand and respond faster to complex customer enquiries better than traditional chatbots.” The new bot will assist customers with various tasks, such as troubleshooting hardware issues and setting up fixed-line routers, the company said.

Vodafone is not about to expose Vodafone’s data to publicly available models like ChatGPT. Nor will the UK based telco create large language models (LLMs) on its own. Instead, a team of 50 data scientists are working on fine-tuning LLMs like Anthropic and Vertex. Vodafone can expose information to those LLMs by dipping into its 24-petabyte data “ocean,” created with Google. Secure containers within public clouds ensure private information is securely cordoned off and unavailable to others.
According to Petty’s estimates, the performance speed of LLMs has improved by a factor of 12 in the last nine months alone, while operational costs have decreased by a factor of six. A telco that invested nine months ago would already have outdated and expensive technology. Petty, moreover, is not the only telco CTO wary of plunging into Nvidia’s GPU chips.
“This is a very weird moment in time where power is very expensive, natural resources are scarce and GPUs are extremely expensive,” said Bruno Zerbib, the CTO of France’s Orange, at the 2024 Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Spain. “You have to be very careful with your investment because you might buy a GPU product from a famous company right now that has a monopolistic position.”
Petty thinks LLM processing may eventually need to be processed outside hyper-scalers’ facilities. “To really create the performance that we want, we are going to need to push those capabilities further toward the edge of the network,” he said. “It is not going to be the hype cycle of the back end of 2024. But in 2025 and 2026, you’ll start to see those applications and capabilities being deployed at speed.”
“The time it takes for that data to get up and back will dictate whether you’re happy as a consumer to use that interface as your primary interface, and the investment in latency is going to be critically important,” said Petty. “We’re fortunate that 5G standalone drives low latency capability, but it’s not deployed at scale. We don’t have ubiquitous coverage. We need to make sure that those things are available to enable those applications.”
Data from Ericsson supports that view, showing that 5G population coverage is just 70% across Europe, compared with 90% in North America and 95% in China. The figure for midband spectrum – considered a 5G sweet spot that combines decent coverage with high-speed service – is as low as 30% in Europe, against 85% in North America and 95% in China.
Non-standalone (NSA) 5G, which connects a 5G radio access network (RAN) to a 4G core (EPC), is “dominating the market,” said Ericsson.
Vodafone has pledged to spend £11 billion (US$14 billion) on the rollout of a nationwide standalone 5G network in the UK if authorities bless its proposed merger with Three. With more customers, additional spectrum and a bigger footprint, the combined company would be able to generate healthier returns and invest in network improvements, the company said. But a UK merger would not aid the operator in Europe’s four-player markets.
Petty believes a “pay for search” economic model may emerge using GenAI virtual assistants. “This will see an evolution of a two-sided economic model that probably didn’t get in the growth of the Internet in the last 20 years,” but it would not be unlike today’s market for content delivery networks (CDNs).
“Most CDNs are actually paid for by the content distribution companies – the Netflixes, the TV sports – because they want a great experience for their users for the paid content they’ve bought. When it’s free content, maybe the owner of that content is less willing to invest to build out the capabilities in the network.”
Like other industry executives, Petty must hope the debates about net neutrality and fair contribution do not plunge telcos into a long disillusionment trough.
References:
Vodafone CTO: AI will overhaul 5G networks and Internet economics (lightreading.com)
Vodafone UK report touts benefits of 5G SA for Small Biz; cover for proposed merger with Three UK?
ITU-R WP5D invites IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions
ITU-R has commenced the process of developing ITU-R Recommendations for the terrestrial components of the IMT-2030 (6G) radio interface(s). This work is guided by Resolutions ITU-R 56 and ITU-R 65. As you can see from the timeline below, the final IMT-2030 recommendation won’t be completed until 2030.
The ITU Radiocommunication Bureau has established a “Web page for the IMT-2030 submission and evaluation process” to facilitate the development of proposals and the work of the evaluation groups. The IMT-2030 web page will provide details of the process for the submission of proposals, and will include the RIT and SRIT submissions, evaluation group registration and contact information, evaluation reports and other relevant information on the development of IMT‑2030.
Candidate RITs (Radio Interface Technologies) or SRITs (Set of Radio Interface Technologies) will be evaluated by the ITU membership, standards organizations and other independent evaluation groups. Evaluation groups are requested to register with ITU-R1, preferably before [February/the end of 2027].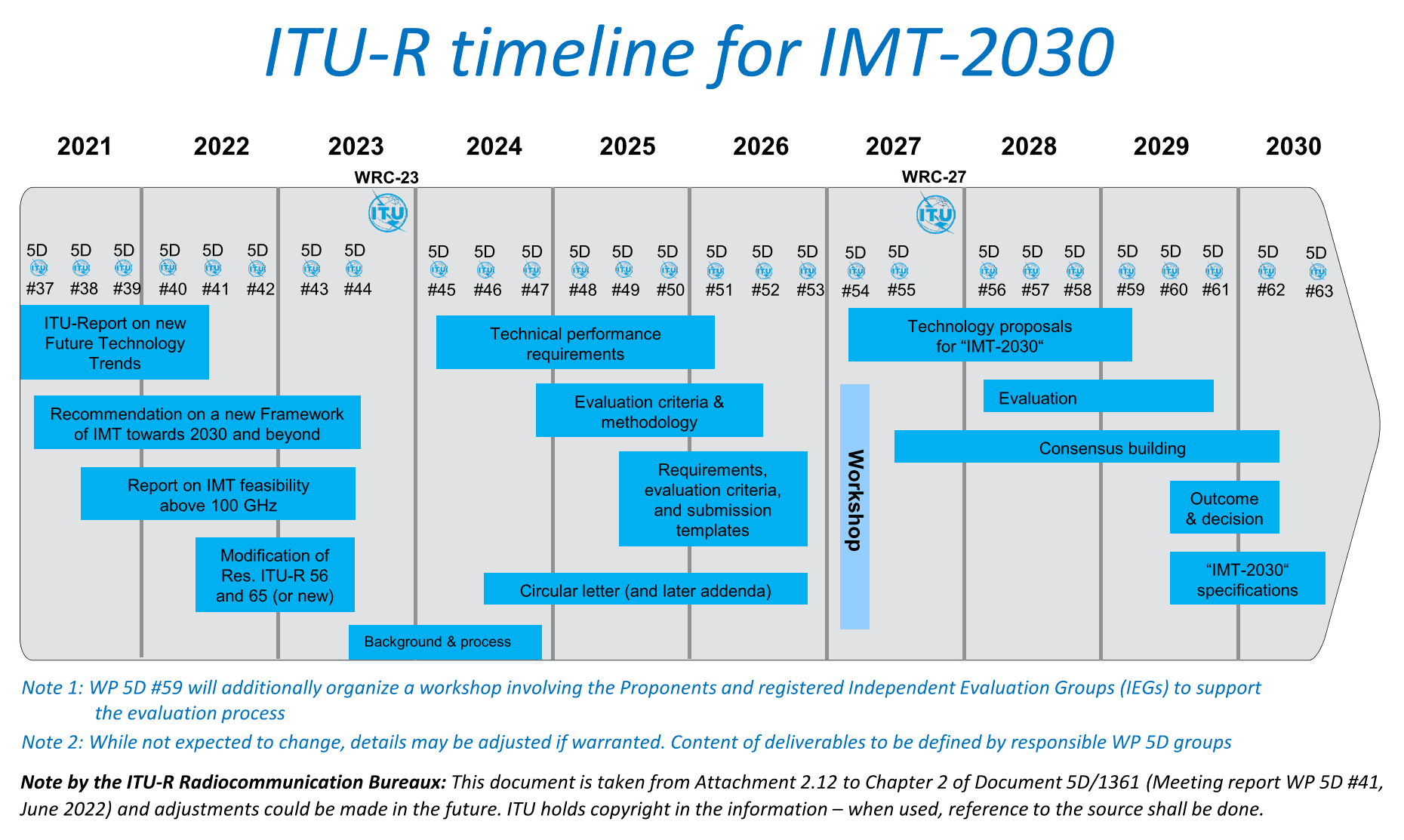
The evaluation groups are kindly requested to submit evaluation reports to the ITU-R in accordance with the evaluation process delineated on the IMT‑2030 web page. The evaluation reports will be considered in the development of the ITU-R Recommendation describing the radio interface specifications.
The evaluation guidelines, including the criteria and methodology, are to be finalized by WP 5D in June 2026. The availability of these guidelines on the IMT-2030 web page will be announced in a forthcoming Addendum to a Circular Letter calling for IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions.
3GPP’s contributions will most likely be presented to ITU-R WP5D by ATIS. It remains to be seen what other entities will submit IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT proposals.
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2030/Pages/default.aspx
https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/oth/0a/06/R0A060000C80001PDFE.pdf
Highlights of 3GPP Stage 1 Workshop on IMT 2030 (6G) Use Cases
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
IMT-2030 Technical Performance Requirements (TPR) from ITU-R WP5D
Draft new ITU-R recommendation (not yet approved): M.[IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND]
Mauritius Telecom Expands 5G Network Across the Island
Mauritius Telecom announced that its 5G network is now available island-wide. The company made this announcement during an event on June 18th, in the presence of the Minister of Information Technology, Communication, and Innovation. This nationwide deployment represents a major step forward in the digital transformation of the country, offering unprecedented technological prospects for individuals and businesses. It follows the initial deployment of its 5G network in 2021 [1.].
Up until now, the telco’s footprint was limited to six locations. With this expansion across populated areas, the mobile portfolio has been revamped to include 5G access under the my.t brand.
Note 1. Mauritius Telecom launched 5G in five specific areas in July 2021. Later, in April 2024, MT extended the 5G network to Rodrigues, expanding the operator’s 5G footprint to six locations.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

With this announcement, the company is now expanding the deployment of the 5G mobile network throughout the island, investing several billion Mauritian Rupees (1 Rp=$0.021). As part of this expansion into populated areas, the mobile portfolio has been revamped to include 5G access under the my.t brand.
Under my.t 5G, Mauritius Telecom promises download speeds of up to 1 Gbps, improved latency, and seamless connectivity, enabling multiple devices to connect simultaneously. The technology will also support innovations such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and the Internet of Things (IoT), the company said.
“The deployment of 5G island-wide is a significant step in enhancing the digital landscape of our country and transforming not only our personal digital experiences but our entire lives,” Mauritius Telecom said.
References:
https://www.telecom.mu/mediacentre/pdf/press-release-5g.pdf
https://mitci.govmu.org/News/SitePages/Mauritius-Telecom-launches-first-5G-network.aspx
Nokia to acquire Infinera for $2.3 billion, boosting optical network division size by 75%
Nokia has agreed to buy optical networking equipment vendor Infinera in a deal worth $2.3 billion. 70% of the sum will be paid in cash, the remaining 30% in Nokia shares. Nokia said it will accelerate its share buyback program to offset the dilution.
The acquisition will grow the size of its Optical Networks division by 75%, enabling the company to accelerate its product roadmap and increase its exposure to webscale customers, which account for around 30% of Infinera’s revenue.

Nokia and Infinera see a significant opportunity in merging to improve scale and profitability, enabling the combined business to accelerate the development of new products and solutions to benefit customers. The transaction aligns strongly with Nokia’s strategy, as it is expected to strengthen the company’s technology leadership in optical and increase exposure to webscale customers, the fastest growing segment of the market.
- Creates a highly scaled and truly global optical business with increased in-house technology capabilities and vertical integration.
- Strengthens Nokia’s optical position, specifically in North America.
- Accelerates Nokia’s customer diversification strategy, expanding webscale presence.
- Targeted net comparable operating profit synergies of EUR 200 million by 2027.
Nokia believes the transaction has compelling financial and strategic merit. The combination with Infinera is projected to accelerate Nokia’s journey to a double-digit operating margin in its Optical Networks business. Nokia targets to achieve EUR 200 million of net comparable operating profit synergies by 2027. This transaction along with the recently announced sale of Submarine Networks will create a reshaped Network Infrastructure built on three strong pillars of Fixed Networks, IP Networks and Optical Networks. Nokia targets mid-single digit organic growth for the overall Network Infrastructure business and to improve its operating margin to mid-to-high teens level.
The combined Nokia and Infinera will have a global market share of around 20%, broadly equal to Ciena (which acquired Nortel’s optical network division in November 2009 for $769 billion) but lagging behind Huawei’s 31%, according to J.P. Morgan analyst Samik Chatterjee.
“Ciena is less likely to make a competing bid given complexity in integrating competing optical portfolios as well as hurdles in regulatory approval given Ciena’s majority (51%) share of the North America market,” wrote Chatterjee in a research note.
Omdia (Informa) expects optical networking market sales to rise at a compound annual growth rate of 5% between now and 2029. A well-executed takeover may, then, give Nokia a growth story during a period of difficulty for its large mobile business group, responsible for about 44% of total sales last year.
The transaction is expected to be accretive to Nokia’s comparable EPS in the first year post close and to deliver over 10% comparable EPS accretion by 2027*, with a return on invested capital (RoIC) comfortably above Nokia’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
Pekka Lundmark, President and CEO of Nokia, said:
“In 2021 we increased our organic investment in Optical Networks with a view to improving our competitiveness. That decision has paid off and has delivered improved customer recognition, strong sales growth and increased profitability. We believe now is the right time to take a compelling inorganic step to further expand Nokia’s scale in optical networks. The combined businesses have a strong strategic fit given their highly complementary customer, geographic and technology profiles. With the opportunity to deliver over 10% comparable EPS accretion, we believe this will create significant value for shareholders.”
Federico Guillén, President of Network Infrastructure at Nokia, said: “Today, Network Infrastructure offers a unique portfolio across the fixed access, optical and IP networks domains built on leading technology innovation and a strong customer focus. This acquisition will further strengthen the optical pillar of our business, expand our growth opportunities across all our target customer segments and improve our operating margin. I am extremely pleased that we are bringing together these two talented and dedicated teams. Separately, we have long respected each other as competitors. Together, we find the logic of combination irresistible.”
David Heard, CEO of Infinera, said: “We are really excited about the value this combination will bring to our global customers. We believe Nokia is an excellent partner and together we will have greater scale and deeper resources to set the pace of innovation and address rapidly changing customer needs at a time when optics are more important than ever – across telecom networks, inter-data center applications, and now inside the data center. This combination will further leverage our vertically integrated optical semiconductor technologies. Furthermore, our stakeholders will have the opportunity to participate in the upside of a global leader in optical networking solutions.”
Compelling strategic benefits for Nokia, Infinera and customers:
- Improving global scale and product roadmap: The combination will increase the scale of Nokia’s Optical Networks business by 75%, enabling it to accelerate its product roadmap timeline and breadth; providing better products for customers and creating a business that can sustainably challenge the competition.
- The combined business will have significant in-house capabilities, including an expanded digital signal processor (DSP) development team, expertise across silicon photonics and indium phosphide-based semiconductor material sciences, and deeper competency in photonic integrated circuit (PIC) technology. The result will be a strong innovative player with a deep and diverse pool of optical networking talent and expertise.
- Gaining scale in North America optical market: The two companies have limited customer overlap, putting the combined business in a strong position in all regions (excluding China). Infinera has built a solid presence in the North America optical market, representing ~60% of its sales, which will improve Nokia’s optical scale in the region and complement Nokia’s strong positions in APAC, EMEA and Latin America.
- Building on Nokia’s commitment to investment in U.S. based manufacturing and advanced testing and packaging capabilities.
- Accelerating Nokia’s expansion into enterprise and particularly webscale: The combination of these two businesses is also expected to accelerate Nokia’s strategic goal of diversifying its customer base and growing in enterprise. Internet content providers (ICP or webscale as Nokia typically calls this segment) make up over 30% of Infinera’s sales. With recent wins in line systems and pluggables, Infinera is well established in this fast-growing market. Infinera has also recently been developing high-speed and low-power optical components for use in intra-data center (ICE-D) applications and which are particularly suited to AI workloads which can become a very attractive long-term growth opportunity. Overall, the acquisition offers an opportunity for a step change in Nokia’s penetration into webscale customers.
- Net comparable operating profit synergies of EUR 200 million: The combination is expected to deliver EUR 200 million of net comparable operating profit synergies by 2027*. Approximately one third of the synergies are expected to come from cost of sales due to supply chain efficiencies and the remainder from operating expenses due to portfolio optimization and integration along with reduced product engineering costs and standalone entity costs. Nokia expects one-time integration costs of approximately EUR 200 million related to the transaction.
- Creating value for shareholders: The transaction is expected to be accretive to Nokia’s comparable operating profit and EPS in year 1 and to deliver more than 10% comparable EPS accretion in 2027*. Nokia also expects the deal to deliver a return on invested capital (RoIC) comfortably above Nokia’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). In addition, Infinera’s investors will have the opportunity to participate in the exciting upside of investing in a global leader in optical networking solutions.
Transaction details:
Under the terms of the definitive agreement, Nokia is acquiring Infinera for $6.65 per share, which equates to an enterprise value of $2.3 billion. For each Infinera share, Infinera shareholders will be able to elect to receive either: 1) $6.65 cash, 2) 1.7896 Nokia shares, or 3) a combination of $4.66 in cash and 0.5355 Nokia shares for each Infinera share. All Nokia shares will be issued in the form of American Depositary Shares. The definitive agreement includes a proration mechanism so that the Nokia shares issued in the transaction do not exceed an amount equal to approximately 30% of the aggregate consideration that may be paid to Infinera shareholders.
References:
https://www.barrons.com/articles/infinera-stock-price-buy-sell-nokia-ciena-658c7898
https://www.infinera.com/press-release/nokia-to-acquire-infinera/
LightCounting: Q1 2024 Optical Network Equipment market split between telecoms (-) and hyperscalers (+)
Infinera, DZS, and Calnex Successfully Demonstrate 5G Mobile xHaul with Open XR
Orange Deploys Infinera’s GX Series to Power AMITIE Subsea Cable
Infinera trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project delivered 61.3 Tbps between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia
Dell’Oro: Campus Ethernet Switch Revenues dropped 23% YoY in 1Q-2024
Worldwide Campus Ethernet Switch [1.] revenues plummeted by 23% YoY in the 1st quarter of 2024 to a 2-year low, according to the Dell’Oro Group.
- The only two vendors that grew campus switch revenues year over year were Santa Clara, CA based Arista Networks and Ubiquiti [2.].
- Cisco’s campus switch revenues fell more than the worldwide average.
Note 1. With higher demand from new use cases for wired connectivity such as automation, analytics, and network visibility, and the need for new access switches to aggregate Wireless LAN access points, Dell’Oro Group is offering in-depth analysis specifically on Ethernet Switches built and optimized for deployment outside the data center, for the purpose of connecting users and things to the corporate Local Area Network (LAN).
“Basically, campus switches are really the networking gear to connect users and devices and laptops,” said Sameh Boujelbene, VP with Dell’Oro Group. “Access points are probably the number one application.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Note 2. Although headquartered in New York, NY, Ubiquiti wrote in a 2019 SEC filing:
“We use contract manufacturers, primarily located in China, Vietnam and Taiwan, to manufacture our products. Our relationships with contract manufacturers allow us to conserve working capital, reduce manufacturing costs and minimize delivery lead times while maintaining high product quality and the ability to scale quickly to handle increased order volume. Over the long term, our contract manufacturers are not required to manufacture our products for any specific period or in any specific quantity. If necessary, we expect that it would take approximately 3 to 6 months to transition manufacturing, quality assurance and shipping services to new providers.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Vendor backlogs of campus switch orders have now been completely run down, and the market is in a multi-quarter digestion cycle,” said Siân Morgan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “The shipments of most port speeds declined, and the Average Sales Price (ASP) also dropped on a YoY basis.
“However, in 1Q 2024, Arista had its third sequential quarter of (market) share gain, growing Campus Switch sales to large enterprises.
On the downside, Cisco’s Campus Switch shipments contracted sharply. This reduction contrasts with their shipments in 2023, when Cisco opened the “floodgate” for Catalyst and Meraki port shipments which had been on backorder,” added Morgan.

Additional highlights from the 1Q 2024 Ethernet Switch – Campus Report:
- The contraction in campus switch sales was broad-based across all regions, with the exception of Central America-Latin America (CALA).
- Some vendors bucked the price trend and were able to grow port ASPs thanks to richer product mixes.
- 5/5.0 Gbps switch ports are expected to return to growth as shipments of Wi-Fi 7 Access Points accelerate.
The Dell’Oro Group Ethernet Switch – Campus Quarterly Report offers a detailed view of Ethernet switches built and optimized for deployment outside the data center, to connect users and things to the Local Area Networks. The report contains in-depth market and vendor-level information on manufacturers’ revenue, ports shipped and average selling prices for both Modular and Fixed, and Fixed Managed and Unmanaged Ethernet Switches (100 Mbps, 1/2.5/5/10/25/40/50/100/400 Gbps), Power-over-Ethernet, plus regional breakouts as well as split by customer size (Enterprise vs. SMB) and vertical segments.
To purchase these reports, email [email protected]
References:
Campus Ethernet Switch Revenues Crash to a Two-Year Low in 1Q 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Dell’Oro: Broadband network equipment spending to drop again in 2024 to ~$16.5 B
Telefónica and Nokia partner to boost use of 5G SA network APIs
Telefónica and Nokia today announced an agreement to jointly explore new opportunities leveraging 5G Standalone (SA) capabilities for network APIs to support developers in creating new use cases for consumer, enterprise, and industrial customers.
Through this agreement, Telefónica will harness Nokia’s Network Exposure Function (NEF) for various purposes that enable developers to access the operator’s 5G network capabilities, like precise device location, enhanced notifications based on connectivity status, edge discovery, and more.

Having access to these capabilities will enhance developers’ capacity to build new applications and drive new service APIs for the industry.
Nokia’s NEF solution, based on 3GPP specifications, provides a process for interfacing with well-defined functions in the core network. It also enables API mashups so developers can combine multiple APIs from different core functions into a new customized API, which is easier for developers to use to create new applications. NEF is said to be “a robust platform for creating new services by consolidating APIs and presenting unified access to the API framework for in-house or 3rd party app developers.”
- Secure exposure of network services (voice, data connectivity, charging, subscriber data, etc.) towards 3rd party application over APIs
- Developer environment and SDK for operator and community
- Service mashup for creating end-to-end offering by combining any of the network assets into your application
- Integration layer that connects your application to operator’s network.
Last week, it was announced that Nokia Network as Code platform with developer portal will run on Google Cloud. The purpose is to promote specific use cases to the Google Cloud developer community, starting with healthcare. Google Cloud stresses it developers cover “all major industries and geographies”.
Nokia’s Network as Code platform brings together networks, systems integrators, and software developers, into a unified ecosystem that provides developers a simple way for integrating advanced 5G capabilities into their applications; without having to navigate the complexity of the underlying network technologies.
Nokia has signed collaboration agreements with 14 network operators and ecosystem partners, in Europe, North America, and South America, to use the platform since its launch in September 2023.
Quotes:
Cayetano Carbajo Martin, Core & Transport Director, Global CTIO at Telefónica said: “We are pleased to take this step with Nokia in recognition of the tremendous opportunity we have to further empower developers with the tools they require to deliver new use cases and experiences for their customers and beyond. This partnering agreement is about steering the industry in building new APIs and more use cases over 5G SA capabilities that have been launched across Telefonica’s main operations.”
Shkumbin Hamiti, Head of Network Monetization Platform, Cloud and Network Services at Nokia said: “There continues to be a rising recognition that sustaining closed networks is a thing of the past and that embracing ecosystems is the way forward for deepening collaboration and creating new use cases; delivering better customer experiences; and generating new revenue opportunities. Our agreement with Telefónica is added proof of the much greater telco ecosystem openness that we are now seeing today and we look forward to jointly working to support developers in harnessing a broader array of network capabilities.”
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core-networks/network-exposure-function/
https://www.nokia.com/networks/programmable-networks/network-as-code/
https://www.mobileeurope.co.uk/telefonica-nokia-aim-to-boost-use-of-5g-sa-network-apis/
Nokia, Google Cloud to help developers create 5G apps with telco APIs
Telefónica launches 5G SA in >700 towns and cities in Spain
Telefónica launches 5G SA in >700 towns and cities in Spain
TÉRAL Research: Sharp declines in Wireless Infrastructure Market 1Q-2024
The global wireless infrastructure market, including 2G/3G/4G/5G RAN and core networks, experienced significant declines both sequentially (-31%) and YoY (-26%) in 1Q-2024. However, these declines are not unprecedented.
“Such decline has happened before in 2002 and 2003 due to a sharp decrease in TDMA and PDC systems shipments, as well as in the post-LTE peak era from 2016 to 2019, when each year’s first quarter posted a 20%+ YoY decline. And that’s not all, looking at bellwether Ericsson’s networks sales historical data, 1Q was also down 20%+ sequentially during the 5G boom,” said Stéphane Téral, Founder and Chief Analyst at TÉRAL RESEARCH.
Huawei continues to be the largest wireless network infrastructure vendor, Nokia and ZTE Corporation’s lost market share, while Samsung Networks position was steady.
Téral states that 2024 marks the third consecutive year of a wireless disinvestment cycle yet the market is poised for a slight rebound in 2H2024 driven by open RAN and 5G upgrades.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Stéphane attended Oracle’s Applications & Industries Analyst Summit at the Oracle Conference Center in Redwood Shores, California. This two-day event showcased how Oracle is integrating Generative AI into its Fusion Data Intelligence Platform, enhancing ERP, EPM, SCM, HCM, and CX applications with AI-powered updates. Oracle’s industry verticals, particularly their 5G CSP monetization and digital experience strategies, promise to end the 5G monetization drought. With Oracle migrating databases to its cloud and leveraging AI, CSPs can expect increased efficiency and growth.
References:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/whats-new-t%C3%A9ral-research-t-ral-research-qsmec/
https://www.teralresearch.com/resources
Dell’Oro: RAN revenues declined sharply in 2023 and will remain challenging in 2024; top 8 RAN vendors own the market
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market has lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
Data infrastructure software: picks and shovels for AI; Hyperscaler CAPEX
For many years, data volumes have been accelerating. By 2025, global data volumes are expected to reach 180 zettabytes (1 zettabyte=1 sextillion bytes), up from 120 zettabytes in 2023.
In the age of AI, data is viewed as the currency for large language models (LLMs) and AI–enabled offerings. Therefore, demand for tools to integrate, store and process data is a growing priority amongst enterprises.
The median size of datasets required to train AI models increased from 5.9 million data points in 2010 to 750 billion in 2023, according to BofA Global Research. As demand rises for AI-enabled offerings, companies are prioritizing tools to integrate, store, and process data.
In BofA’s survey, data streaming/stream processing and data science/ML were selected as key use cases in regard to AI, with 44% and 37% of respondents citing usage, respectively. Further, AI enablement is accelerating data to the cloud. Gartner estimates that 74% of the data management market will be deployed in the cloud by 2027, up from 60% in 2023.
Data infrastructure software [1.] represents a top spending priority for the IT department. Survey respondents cite that data infrastructure represents 35% of total IT spending, with budgets expected to grow 9% for the next 12 months. No surprise that the public cloud hyper-scaler platforms were cited as top three vendors. Amazon AWS data warehouse/data lake offerings, Microsoft Azure database offerings, and Google BigQuery are chosen by 45%, 39% and 35% of respondents, respectively.
Note 1. Data infrastructure software refers to databases, data warehouses/lakes, data pipelines, data analytics and other software that facilitate data management, processing and analysis.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The top three factors for evaluating data infrastructure software vendors are security, enterprise capabilities (e.g., architecture scalability and reliability) and depth of technology.
BofA’s Software team estimates that the data infrastructure industry (e.g., data warehouses, data lakes, unstructured databases, etc.) is currently a $96bn market that could reach $153bn in 2028. The team’s proprietary survey revealed that data infrastructure is 35% of total IT spending with budgets expected to grow 9% over the next 12 months. Hyperscalers including Amazon and Google are among the top recipients of dollars and in-turn, those companies spend big on hardware.
Key takeaways:
- Data infrastructure is the largest and fastest growing segment of software ($96bn per our bottom-up analysis, 17% CAGR).
- AI/cloud represent enduring growth drivers. Data is the currency for LLMs, positioning data vendors well in this new cycle
- BofA survey (150 IT professionals) suggests best of breeds (MDB, SNOW and Databricks) seeing highest expected growth in spend
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
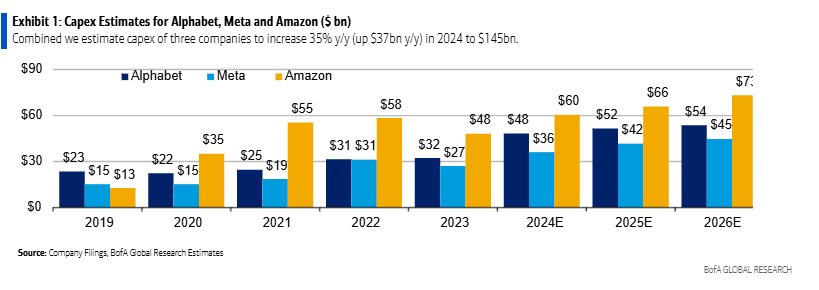
BofA analyst Justin Post expects server and equipment capex for mega-cap internet companies (Amazon, Alphabet/Google, Meta/Facebook) to rise 43% y/y in 2024 to $145bn, which represents $27bn of the $37bn y/y total capex growth. Despite the spending surge, Mr. Post thinks these companies will keep free cash flow margins stable at 22% y/y before increasing in 2025. The technical infrastructure related capex spend at these three companies is expected to see steep rise in 2024, with the majority of the increase for servers and equipment.
Notes:
- Alphabet categorizes its technical infrastructure assets under the line item ‘Information Technology Assets‘
- Amazon take a much a broader categorization and includes Servers, networking equipment, retail related heavy equipment & fulfillment equipment under ‘Equipment‘.
- Meta gives more details and separately reports Server & Networking, and Equipment assets.
In 2024, BofA estimates CAPEX for the three hyperscalers as follows:
- Alphabet‘s capex for IT assets will increase by $12bn y/y to $28bn.
- Meta, following a big ramp in 2023, server, network and equipment asset spend is expected to increase $7bn y/y to $22bn.
- Amazon, equipment spend is expected to increase $8bn y/y to $41bn (driven by AWS, retail flattish). Amazon will see less relative growth due to retail equipment capex leverage in this line.
On a relative scale, Meta capex spend (% of revenue) remains highest in the group and the company has materially stepped up its AI related capex investments since 2022 (in–house supercomputer, LLM, leading computing power, etc.). We think it‘s interesting that Meta is spending almost as much as the hyperscalers on capex, which should likely lead to some interesting internal AI capabilities, and potential to build a “marketing cloud“ for its advertisers.
From 2016-22, the sector headcount grew 26% on average. In 2023, headcount decreased by 9%. BofA expects just 3% average. annual job growth from 2022-2026. Moreover, AI tools will likely drive higher employee efficiency, helping offset higher depreciation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Source for all of the above information: BofA Global Research