Geopolitical tensions arise in Asia over subsea fiber optic cable projects; U.S. intervened to flip SeaMeWe-6 contractor
Multimillion-dollar undersea/subsea fiber optic cable projects have become the latest focal point of geopolitical tensions in Asia as China intensifies its highly contested claims over the South China Sea, writes Nikkei Asia’s Singapore correspondent Tsubasa Suruga. These cables are crucial for keeping information flowing throughout the region and across the Pacific. Most countries require builders to get approval if they plan to lay cables in their territorial waters, but not in their exclusive economic zones, which extend 200 nautical miles out from a country’s coast.
China, however, insists that projects within its self-proclaimed “nine-dash line” — an area encompassing virtually the entire South China Sea — need Beijing’s approval. A nonobjection letter must be obtained from China’s People’s Liberation Army before the formal application process can even begin. Beijing imposes the policy even though an international tribunal found in 2016 that the nine-dash line lacked a legal basis.
“It is no secret the whole industry is more confronted by politics,” said Takahisa Ohta, senior director of the submarine network division at NEC, one of the world’s top three suppliers of subsea cables. Some of the companies involved, like Singtel, are looking for ways to diversify their routes.
Tay Yang Hwee, a 30-year industry veteran who heads subsea cable development at the Singaporean telecom provider, said it is “exploring alternate paths” for connecting data hubs, but he admits it is “very difficult” to avoid the South China Sea as a whole.
The Singapore-to-France cable would have been HMN Tech’s biggest such project to date, cementing it as the world’s fastest-rising subsea cable builder, and extending the global reach of the three Chinese telecom firms that had intended to invest in it.
But the U.S. government, concerned about the potential for Chinese spying on these sensitive communications cables, ran a successful campaign to flip the contract to SubCom through incentives and pressure on consortium members. It’s one of at least six private undersea cable deals in the Asia-Pacific region over the past four years where the U.S. government either intervened to keep HMN Tech from winning that business, or forced the rerouting or abandonment of cables that would have directly linked U.S. and Chinese territories.
SubCom had no comment on the SeaMeWe-6 battle, and HMN Tech did not respond to requests for comment. In a statement last year about infrastructure projects, the White House briefly noted that the U.S. government helped SubCom to win the Singapore-to-France cable contract, without giving details. China’s foreign ministry did not respond to requests for comment. China Telecom, China Mobile, China Unicom and Orange did not respond to requests for comment. Microsoft declined to comment.
Undersea cables are central to U.S.-China technology competition. Across the globe, there are more than 400 cables running along the seafloor, carrying over 95% of all international internet traffic, according to TeleGeography, a Washington-based telecommunications research firm. These data conduits, which transmit everything from emails and banking transactions to military secrets, are vulnerable to sabotage attacks and espionage, a U.S. government official and two security analysts told Reuters.
The potential for undersea cables to be drawn into a conflict between China and self-ruled Taiwan was thrown into sharp relief last month. Two communications cables were cut that connected Taiwan with its Matsu islands, which sit close to the Chinese coast. The islands’ 14,000 residents were disconnected from the internet.
Taiwanese authorities said they suspected a Chinese fishing vessel and a Chinese freighter caused the disruption. However, they stopped short of calling it a deliberate act and said there was no direct evidence showing the Chinese ships were to blame. China, which considers Taiwan a breakaway province, has ratcheted up military and political efforts to force the island to accept its dominion.
Deutsche Telekom exec: AI poses massive challenges for telecom industry
Deutsche Telekom’s VP of technology strategy, Ahmed Hafez, co-hosted the DSP Leaders World Forum 2023 session entitled “Creating a framework for the AI-native telco” this week in the UK. He said that AI will deliver the telecom sector its biggest ever challenges and opportunities, but to take advantage of the benefits that AI will bring the industry needs to figure out a way to evolve from being opportunistic to becoming AI-native.
To date, the telecom sector has been exploring the potential of AI without looking at the bigger picture, and that holistic view needs to be taken in order to figure out the best way to go, Hafez believes.
Like so many other pundits and cheerleaders, Hafez regards the impact of AI as “the biggest transformation we will ever encounter.” And this is not only about the magnitude of what AI will do, but also the pace – it will outpace our understanding of things so fast, so we need to be ready…
“Previous transformations have [happened at an] accommodating pace – they were not changing so fast that we couldn’t comprehend or adapt to them. In order for us to adapt to AI, we need to transform as individuals, not [just as] companies. On an individual level you need to be able to comprehend what’s going on and pick the right information.”
To illustrate the magnitude of the challenges that AI will deliver to the telecom sector, Hafez presented a few supporting statistics:
- The AI market was worth $136bn in 2022 and is set to be worth $1.8tn by 2030
- The telecom AI market alone was worth $2.2bn in 2022
- Global private investment in AI reached $91.9bn in 2022
- AI delivers a 40% increase in business productivity, according to a study by Accenture (Hafez thinks that number is too low, that productivity gains will be much higher)
- There are already thousands of AI-focused companies – by 2018 there were already nearly 3,500
- AI will drive the need for 500x compute power between now and 2030 (“What does that mean for telcos? How can we deal with that?” asked Hafez)
- In terms of human resources, 63% of executives believe their biggest skills shortage is in AI expertise
- Three in every four CEOs believe they don’t have enough transparency when it comes to AI and are concerned about skewed bias in the AI sector
So a lot of eye-opening trends that should give the telecom industry food for thought, especially when it comes to attracting employees with AI skills. “How will we get the people we need if there are thousands of AI companies” attracting the experts, he asked.
Hafez also related how he encountered what he described as some “depressing” information about how unattractive telecom operators are to potential employees, especially those of a younger generation. Of the top-50 most attractive companies in advanced economies for employees, none of them are telcos: “This is a worrying trend… we need to become more attractive to the younger generations,” he noted.
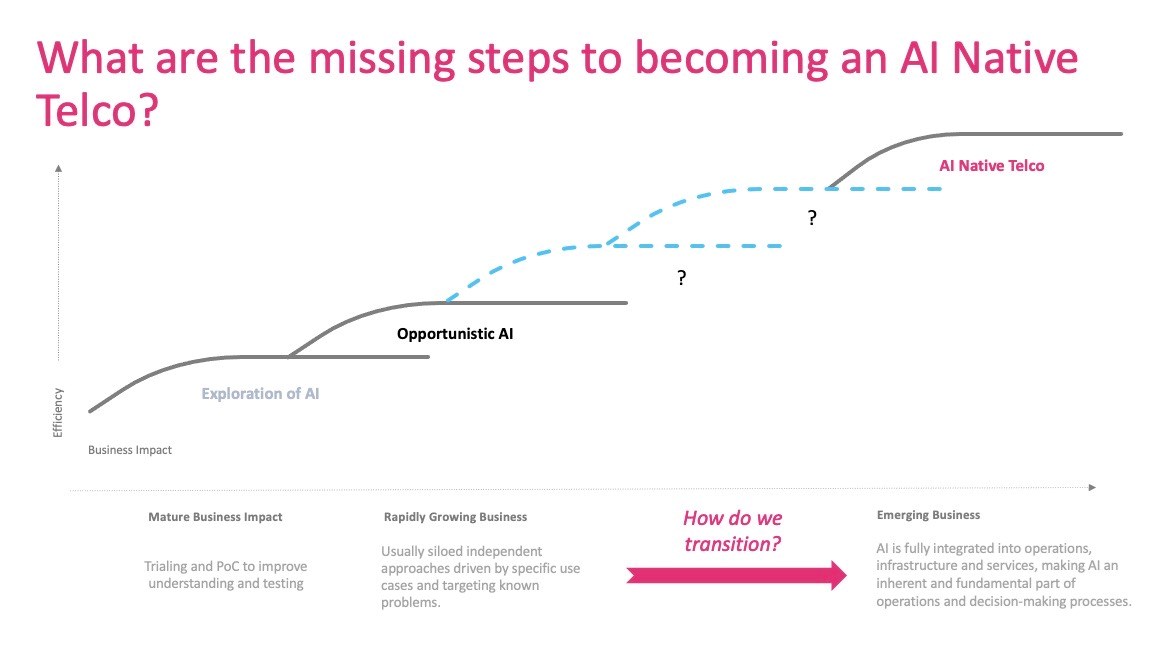
The telecom industry began exploring the use of AI in earnest less than 10 years ago, noted the DT executive, when it started looking into its potential with proofs of concept and trials. “Then we took the opportunistic approach to AI – use case-based, where you find a good use case, you implement it and it’s concrete. There’s nothing bad about that, as it’s the right thing to do… and we’ve been doing that for a while and it’s delivering value. That’s fine as long as you are doing a few tens of use cases.”
But using AI at scale, which is what the industry needs to do to become AI-native, where AI is fully integrated into everything and becomes part of all operations and decision-making processes, throws up a lot of new questions about how the sector progresses from being opportunistic to becoming AI-native – what are the missing steps, Hafez asked?
Source: Deutsche Telekom
“Once we start to ask, what would the future be with AI in everything we do, in every appliance, in every application, in every network component, it would be over the top. You would have data that is being worked on by five or six AI engines, creating different things…. You would have not just tens of use cases, but hundreds, or thousands. Are we prepared for that? Are we ready to embrace such scale? Are we building AI for scale? I don’t think so.
“We are building AI trying to get things done – which is okay. But in order for us to get through this journey, through this transformation, what stages do we need to pass through? What are the steps that we need to take to… make sure that the problem is clear. If we have a huge amount of AI, do we run the risk of conflicting AI? So if I have AI for energy efficiency and I have another one that actually improves network quality, could they create conflicts? Can they be a problem? If I have AI that is on the optical layer and AI on the IP layer, can they make different decisions because they consume data differently?
“If we look at things from this perspective, do we need, within our organisations, another stream of hiring people and the need to upskill leadership? Do we need to upskill ourselves to help our teams? What do we need to do? If you look at technologies, do we need to change the perspective of how, for example, the 3GPP is building the standards in order to make sure the standards are AI friendly? Do we need separate standard bodies to look at AI? What would be their functions? What would be their scope?” asked Hafez.
And does the industry need a framework that can provide guidance so that the telecom sector can develop in the same direction with its use of AI?
“This is the discussion we want to have, and I hope the message is clear – we have a great opportunity, but opportunities do not come without challenges,” he cautioned.
Hafez set the scene for a great discussion with his fellow speakers, Juniper’s chief network strategist Neil McRae, Rakuten Symphony CMO Geoff Hollingworth, Nokia’s CTO for Europe Azfar Aslam, and Digital Catapult’s CTO Joe Butler – and it’s fair to say there were differences of opinion! You can view the full session on demand here.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Here are some specific examples of how AI is being used in the telecom industry in 2023:
Network optimization:
AI is being used to analyze data from network sensors to identify potential problems before they occur. This allows telecom providers to take proactive steps to fix problems and prevent outages. For example, companies are using AI to predict network congestion and proactively reroute traffic to avoid outages. 5G networks began to roll out in 2019 and are predicted to have more than 1.7 billion subscribers worldwide – 20% of global connections — by 2025. AI is essential for helping CSPs build self-optimizing networks (SONs) to support this growth. These allow operators to automatically optimize network quality based on traffic information by region and time zone. AI in the telecom industry uses advanced algorithms to look for patterns within the data, enabling telecoms to both detect and predict network anomalies. As a result of using AI in telecom, CSPs can proactively fix problems before customers are negatively impacted.
Customer service automation and Virtual Assistants:
AI-powered chatbots can answer customer questions and resolve issues without the need for human intervention. This can free up customer service representatives to focus on more complex issues. For example, Verizon is using AI to power its Virtual Assistant, which can answer customer questions about billing, service plans, and technical support.
Predictive Maintenance:
AI-driven predictive analytics are helping telecoms provide better services by utilizing data, sophisticated algorithms, and machine learning techniques to predict future results based on historical data. This means operators can use data-driven insights to monitor the state of equipment and anticipate failure based on patterns. Implementing AI in telecoms also allows CSPs to proactively fix problems with communications hardware, such as cell towers, power lines, data center servers, and even set-top boxes in customers’ homes. In the short term, network automation and intelligence will enable better root cause analysis and prediction of issues. Long term, these technologies will underpin more strategic goals, such as creating new customer experiences and dealing efficiently with emerging business needs.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for Telecoms:
CSPs have vast numbers of customers engaged in millions of daily transactions, each susceptible to human error. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a form of business process automation technology based on AI. RPA can bring greater efficiency to telecom functions by allowing telcos to more easily manage their back-office operations and large volumes of repetitive and rules-based actions. RPA frees up CSP staff for higher value-add work by streamlining the execution of complex, labor-intensive, and time-consuming processes, such as billing, data entry, workforce management, and order fulfillment. According to Statista, the RPA market is forecast to grow to 13 billion USD by 2030, with RPA achieving almost universal adoption within the next five years. Telecom, media, and tech companies expect cognitive computing to “substantially transform” their companies within the next few years.
Fraud Prevention:
Telecoms are harnessing AI’s powerful analytical capabilities to combat instances of fraud. AI and machine learning algorithms can detect anomalies in real-time, effectively reducing telecom-related fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized network access and fake profiles. The system can automatically block access to the fraudster as soon as suspicious activity is detected, minimizing the damage. With industry estimates indicating that 90% of operators are targeted by scammers on a daily basis – amounting to billions in losses every year – this AI application is especially timely for CSPs.
Revenue Growth:
AI in telecommunications has a powerful ability to unify and make sense out of a wide range of data, such as devices, networks, mobile applications, geolocation data, detailed customer profiles, service usage, and billing data. Using AI-driven data analysis, telecoms can increase their rate of subscriber growth and average revenue per user (ARPU) through smart upselling and cross-selling of their services. By anticipating customer needs using real-time context, telecoms can make the right offer at the right time over the right channel.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.telecomtv.com/content/network-automation/towards-the-ai-native-telco-47596/
https://www.telecomtv.com/content/dsp-leaders-forum/
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases
Allied Market Research: Global AI in telecom market forecast to reach $38.8 by 2031 with CAGR of 41.4% (from 2022 to 2031)
SK Telecom inspects cell towers for safety using drones and AI
The case for and against AI in telecommunications; record quarter for AI venture funding and M&A deals
Global AI in Telecommunication Market at CAGR ~ 40% through 2026 – 2027
Cybersecurity threats in telecoms require protection of network infrastructure and availability
China to launch world’s first 5G cruise ship via China Telecom Corp Ltd Shanghai Branch
Samsung bets on software centric network architectures supporting virtualized services
Kim Woojune, President and General Manager of Samsung Networks [1.] asserted that software capabilities will change the telecommunications landscape, as the South Korean tech giant bets on virtualized services. Kim said that future networks will be transformed more into software-centric architecture, versus the hardware-based networks the world has built and relied upon for about 150 years.
Note 1. Kim was appointed president and general manager of Samsung’s Networks business in December 2022
“Software has become a key driver of innovation, and this transition to software is also a natural shift in the networks industry,” Kim said in a speech at Nikkei’s Future of Asia forum. “Software brings more flexibility, more creativity and more intelligence,” he added.
Kim said the next transition in the network business has already started, as global telecom operators such as Verizon in the U.S., and KDDI and Rakuten in Japan are building their virtualized networks.
In February, Samsung announced that it was selected by KDDI to provide its cloud-native 5G Standalone (SA) Core network for the operator’s commercial network across Japan. The company said that this will usher in a new generation of services and applications available to KDDI’s consumers and enterprise customers — including smart factories, automated vehicles, cloud-based online gaming and multi-camera live streaming of sports events. Samsung and KDDI also successfully tested network slicing over their 5G SA Core network.
The Samsung executive asked global governments to embrace the shift, saying their role “should be to maximize the benefit of this extra use.”
Samsung is also winning contracts with cable providers, like Comcast, where it’s working to deploy 5G RAN solutions to support its efforts to deliver 5G access to consumers and business customers in the U.S. using CBRS and 600 MHz spectrum, Kim noted. Comcast is the first operator to use Samsung’s new 5G CBRS Strand Small Cell, a compact and lightweight solution designed to be installed on outdoor cables. It consists of a radio, baseband, cable modem and antennas, all in one form factor. The solution is also equipped with Samsung’s in-house designed chipset, a second-generation 5G modem SoC, which delivers increased capacity and performance.
References:
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
KDDI claims world’s first 5G Standalone (SA) Open RAN site using Samsung vRAN and Fujitsu radio units
Samsung announces 5G NTN modem technology for Exynos chip set; Omnispace and Ligado Networks MoU
Samsung in OpenRAN deal with NTT DOCOMO; unveils 28GHz Radio Unit (RU)
Samsung achieves record speeds over 10km 5G mmWave FWA trial in Australia
https://www.fiercewireless.com/tech/samsungs-woojune-kim-reflects-vran-leadership-us-inroads
LightCounting: Wireless infrastructure market dropped both YoY and sequentially in 1Q23
In the 1stQ2023, the global wireless infrastructure market declined 3% YoY and 17% sequentially, according to LightCounting. Starting a new year with a sequential decline is typical but a YoY drop is abnormal and suggests a declining pattern is in the making. This trend confirms that we have entered the post-peak era.
While the U.S. market posted its steepest drop, the strong 5G rollouts in India and a 5G rebound in Japan, along with stable and sustained activity in EMEA and China, respectively, were not enough to keep the wireless infrastructure market out of the decline. On the open vRAN front, DISH in the U.S., Rakuten Mobile in Japan, and a few Rakuten Symphony customers kept the market flat YoY and produced double digit sequential growth.
Despite a weak quarter, Huawei retook its lead at the expense of Ericsson, which reported weak 1Q23 results that led to a market share loss. In the meantime, Nokia benefited from the 2 leaders’ market share loss and gained 1% point. ZTE also gained share at the expense of Huawei and Ericsson while Samsung’s share remained stable.
“We have passed the 5G peak and have entered the second year of a disinvestment cycle. The 5G investment cycle that started in 2019 and ended in 2021 was driven by hundreds of communications service providers (CSPs), including the world’s largest cellular footprints (i.e., China). At the moment, India’s massive 5G rollout is preventing the situation from getting worse but this will end soon,” said Stéphane Téral, Chief Analyst at LightCounting Market Research.
As a result, this year, LightCounting expects the wireless infrastructure market to slightly decline in 2023 (compared to 2022) with India in the lead. In the long run, our service provider 20-year wireless infrastructure footprint pattern analysis points to a 2022-2028 CAGR of -3% characterized by low single-digit declines through 2027, which appears to be the bottom leading to flatness or slight growth in 2028. In fact, we expect 5G to slightly pick up in 2027, driven by upgrades needed to prepare networks for 6G. Given the ongoing 6G activity, we believe something labeled 6G will be deployed in 2028.
Highlights from Dell’Oro’s 1Q 2023 RAN report:
- Top 5 RAN 1Q 2023 RAN suppliers include Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, and Samsung.
- Top 4 RAN 1Q 2023 RAN suppliers outside of China include Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei, and Samsung.
- Nokia recorded the highest growth rate among the top 5 suppliers, while Ericsson and Samsung both lost some ground in the first quarter.
- The report also shows that Nokia’s RAN revenue share outside of China has been trending upward over the past five quarters.
- The Asia Pacific RAN market has been revised upward to reflect the higher baseline in India.
Open RAN and vRAN highlights from Dell’Oro’s 1Q 2023 RAN report:
- After more than doubling in 2022, Open RAN revenue growth was in the 10 to 20 percent range in the first quarter while the vRAN market advanced 20 to 30 percent.
- Positive developments in the Asia Pacific region were dragged down by more challenging comparisons in the North America region.
- Short-term projections remain unchanged – Open RAN is still projected to account for 6 to 10 percent of the 2023 RAN market.
- Top 5 Open RAN suppliers by revenue for the 2Q 2022 to 1Q 2023 period include Samsung, NEC, Fujitsu, Rakuten Symphony, and Mavenir.
| Historical data accounts for sales of the following vendors: | ||
| Vendor | Segments | Source of Information |
| Affirmed Networks (acquired by Microsoft, April 2020) | vEPC, 5GC | Estimates |
| Altran | vRAN | Estimates |
| Altiostar | vRAN (CU, DU) | Estimates |
| Amdocs | 5GC | Estimates |
| ASOCS | vRAN (DU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Baicell | RAN (RU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Benetel | Open RAN (RU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Cisco | EPC, vEPC, 5GC | Survey data and estimates |
| China Information and Communication Technologies Group (CICT) | RAN | Estimates |
| Comba Telecom | RAN/vRAN (RU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| CommScope (acquired Phluido vRAN patents, October 2020) | vRAN (RU, DU) | Estimates |
| Corning | vRAN | Estimates |
| Dell | vRAN (DU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Enea | 5GC | Estimates |
| Ericsson | RAN, vRAN, 2/3G Core, EPC, vEPC, 5GC | Estimates |
| Fairwaves | RAN/vRAN (RU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Fujitsu | RAN | Survey data and estimates |
| HPE | 2G/3G core, 5GC | Estimates |
| Huawei | RAN, vRAN, 2/3G Core, EPC, vEPC, 5GC | Survey data and estimates |
| JMA Wireless | vRAN | Estimates |
| KMW | RAN/vRAN (RU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Kontron | vRAN (DU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Mavenir (acquired ip.access, September 2020) | vEPC, vRAN, 5GC | Survey data and estimates |
| Metaswitch (acquired by Microsoft, May 2020) | 5GC, vEPC and 2G/3G core | Estimates |
| Movandi | RAN/vRAN (RU/repeater) | Estimates |
| MTI Mobile | vRAN (RU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Node-H | vRAN (small cells) | Estimates |
| Nokia | RAN, vRAN, 2/3G Core, EPC, vEPC, 5GC | Survey data and estimates |
| NEC (including Blue Danube) | RAN, vRAN (RU), EPC, 5GC | Survey data and estimates |
| Oracle | 5GC | Estimates |
| Parallel Wireless | vRAN (CU, DU) | Estimates |
| Pivotal | RAN/vRAN (RU/mmWave repeater) | Estimates |
| Quanta Cloud Technology (QCT) | vRAN (DU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Qucell | RAN, vRAN | Estimates |
| Ribbon Communications | 2G/3G core | Survey data and estimates |
| Samsung | RAN, vRAN, vEPC, 5GC | Estimates |
| Silicom | Open RAN (DU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| SuperMicro Computer | vRAN (DU) | None, supplies other RAN/vRAN vendors |
| Verana Networks | RAN/vRAN (RU/mmWave) | Estimates |
| ZTE | RAN, vRAN, 2/3G Core, EPC, vEPC, 5GC | Survey data and estimates |
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
The number of 5G subscriptions will surge from 934 million in 2022 to 3.1 billion in 2027 -a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 27% – according to a study from ABI Research. Further, 5G traffic is forecast to increase from 293 Exabytes (EB) in 2022 to 2,515 EB in 2027, at a CAGR of 54%.
ABI’s forecast is largely based on an increase in 5G Core (5GC) networks. To date, more than 35 5GC networks are operating in 5G standalone (SA) mode. 5GC is expected to lead to a growth in devices connected to the network and the traffic routed through it.
“5GC holds potential for operators to monetize further existing cellular connectivity for traditional mobile broadband (MBB) use cases but also offers scope for operators to expand cellular capabilities in new domains. Additionally, 5GC also offers innovation potential for committed telcos to establish new operating models for growth outside of the consumer domain,” explains Don Alusha, Senior Analyst, 5G Core and Edge Networks, at ABI Research.
5GC presents Communications Service Providers (CSPs) with a fluid and dynamic landscape. In this landscape, there is no static offering (requirements constantly change), no uniform offering (one shoe does not fit all), and no singular endpoint (one terminal with multiple applications). 5GC guides the industry into edge deployments and topologies. CSPs step out of the four walls of either their virtual Data Center (DC) or physical DC to place network functionality and compute as close to their customers as possible. This constitutes decentralization, a horizontal spread of network assets and technology estate that calls for a ‘spread’ in the operating model.
The shift from a centralized business (e.g. with 4G EPC) to a decentralized business (5G SA core network) stands to be a significant trend in the coming years for the telecoms industry. Against that backdrop, the market will demand that CSPs learn to drive value bottom-up. “What customers need” is the starting point for companies like AT&T, BT, Deutsche Telekom, Orange, and Vodafone. In other words, in this emerging landscape, there will be enterprise-specific, value-based, and niche engagements where the business strategy sets the technology agenda. So, it is rational to conclude that a “bottom-up” approach may be required to deliver unique value and expand business scope. That said, CSPs may be better equipped to drive sustained value creation if they learn to build their value proposition, starting from enterprise and industrial edge and extending to core networks.
“A 5G cloud packet core can potentially unlock new transactions that supplement existing volume-centered modus operandi with a local, bottom-up value play for discrete engagements. But the power of a bottom-up model is not enough. To monetize a 5G cloud packet core at scale, some of the existing top-down intelligence is needed too. Learning how to operate in this hybrid top-down and the emerging bottom-up, horizontally stratified ecosystem is a journey for NTT Docomo, Rakuten Mobile, Singtel, Softbank, and Telstra, among other CSPs. In the impending cellular market, an effective and efficient operating model must contain both control and lack of control, both centralization and decentralization and a hybrid of bottom-up plus some of the ‘standard’ top-down intelligence. The idea is that CSPs’ operating model should flexibly fit and change in line with new growing market requirements, or new growth forays may hit a roadblock,” Alusha concludes.
Editor’s Note:
It’s critically important to understand that the 3GPP defined 5G core network protocols and network interfaces enable the entire mobile system. Those include call and session control, mobility management, service provisioning, etc. Moreover, the 3GPP defined 5G features can ONLY be realized with a 5G SA core network. Those include: Network Automation, Network Function Virtualization, 5G Security, Network Slicing, Edge Computing (MEC), Policy Control, Network Data Analytics, etc
Figure 1: Overview of the 5G system
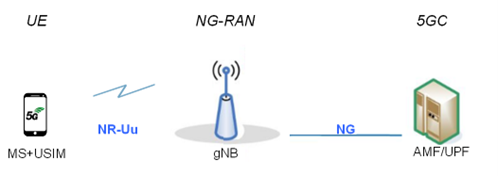
The 5GC architecture relies on a “Service-Based Architecture” (SBA) framework, where the architecture elements are defined in terms of “Network Functions” (NFs) rather than by “traditional” Network Entities. Via interfaces of a common framework, any given NF offers its services to all the other authorized NFs and/or to any “consumers” that are permitted to make use of these provided services. Such an SBA approach offers modularity and reusability.
Figure 2: 5G SA Core Network Architecture
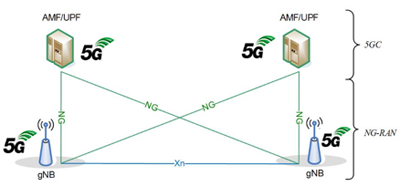
The 5G SA architecture can be seen as the “full 5G deployment,” not needing any part of a 4G network to operate.
Finally, 3GPP has not liased their 5G system architecture specifications to ITU-T so there are no ITU-T standards for 5G SA Core Network or any other 5G non-radio specification. Instead, 3GPP sends their specs to ETSI which rubber stamps them as “ETSI standards.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
These findings are from ABI Research’s 5G Core Market Status and Migration Analysis report. This report is part of the company’s 5G Core & Edge Networks research service, which includes research, data, and analyst insights. Based on extensive primary interviews, Application Analysis reports present an in-depth analysis of key market trends and factors for a specific technology.
About ABI Research
ABI Research is a global technology intelligence firm delivering actionable research and strategic guidance to technology leaders, innovators, and decision makers around the world. Our research focuses on the transformative technologies that are dramatically reshaping industries, economies, and workforces today.
References:
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/5g-system-overview#
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core/5g-core/
A few key 3GPP Technical Specifications (TSs) are listed here:
- TS 22.261, “Service requirements for the 5G system”.
- TS 23.501, “System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 23.502 “Procedures for the 5G System (5GS)
- TS 32.240 “Charging management; Charging architecture and principles”.
- TS 24.501 “Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3”
- TS 38.300 “NR; NR and NG-RAN Overall description; Stage-2”
Big 5 Event: wireless connectivity use cases for healthcare, network slicing, security and private networks
Emerging use cases for wireless telecommunications technology was discussed at the Big 5G event in Austin, TX last week in a panel session titled, “Future connectivity use cases and the Holy Grail: Private networks, metaverse, 6G and beyond.” The questions addressed included:
- Who is monetizing private networks and what are we learning from their experiences?
- Should telcos move past targeting only large enterprise customers for 5G services?
- When will the metaverse take off?
- How are telcos gearing up for 6G and what are the expectations?
Jodi Baxter, vice president for 5G and IoT connectivity at Telus, described the numerous emerging applications of 5G in healthcare. One example is a connected ambulance project carried out with Alberta Health Services, where, thanks to 5G, doctors can remotely issue authorizations necessary for stroke medication, which needs to be administered within a narrow time window.
Some of the applications developed for the healthcare sector can also be included in telcos’ offerings to corporate customers. Baxter said Telus has included remote doctor and nurse consultations in 5G bundles for small businesses, which can help their staff retention rates. Healthcare companies are also looking at more specific applications, with Baxter citing the example of a healthcare company that would wish to track hip and knee replacements with 5G.
While sustainability is often seen as an unprofitable endeavor, Baxter argued technology can help customers see a return on investment. One of Telus’s projects in this area uses drones and 5G for reforestation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Omdia’s research has shown that about a fifth of midsized to large enterprises “want to invest in 5G network slicing in the next two years, but most people cannot find a commercial offer,” said Camille Mendler, chief analyst of enterprise services at Omdia. “[It’s] not there yet, which is a problem, right?” she added. Note that 5G network slicing requires a 5G SA core network, which most 5G service providers have yet to deploy.
Baxter noted that network slicing will be a game changer for security and transportation of critical data. The panel pointed to autonomous vehicles as another potential application that will require its own slice. She also said slicing will be important for ensuring applications from private 5G networks also have a macro capability.
Lori Thomas, senior vice president for strategic engagement and transformation at MetTel, pointed out that a lot of government agencies are currently looking to bring specific functionalities from the private network onto the public network, and make them accessible in edge devices such as laptops and tablets.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
William Britton, vice president for information technology and CIO at California Polytechnic State University, said it is not always easy to figure out how products offered by telecom companies apply to specific use cases. The university has been told to “go elsewhere” by providers when it has approached them about possible 5G applications, as the solutions on offer did not meet requirements, he said.
Speaking about the particular needs of his university, he highlighted the significant demand for bandwidth during limited events, such as course registration, as well as ad hoc scenarios like high data throughput during online gaming events.
A big concern for universities in general is cybersecurity. Britton points out that the education sector has become a massive target for cyberattacks, such as malware and ransomware. Indeed, research suggests that attacks on educational organizations grew by 44% in 2022, while data from endpoint protection firm Emsisoft suggests that the number of individual schools impacted by ransomware attacks also grew.
Security is a major priority for organizations everywhere, not just in the education sector. Thomas points to IoT, where vast amounts of data travel at high speeds, which is particularly attractive for bad actors. Once 5G can be coupled with blockchain, she noted, data security will improve.
One way to look at specific use cases is through innovation labs, with Thomas saying in the short term these can accelerate the time to revenue. She pointed to MetTel’s partnership with SpaceX and VMware, which saw the latter company’s software-defined wide area network deployed over Starlink to bring high-bandwidth communications to remote areas.
Thomas also said demand for more bandwidth was one of the key trends in the public sector. Customers are, according to her, looking at technologies including 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) and satellites to secure it.
A lot of innovation has focused on private networks, but the “real money” lies outside of them, said Mendler. No further details were provided.

Omdia’s Camille Mendler says companies cannot find commercial network slicing.
Source: JLeitner Photography
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
NTT and Cisco launch IoT as a Managed Service for Enterprise Customers
NTT and Cisco have teamed up to launch a suite of repeatable IoT solutions that can be sold as a managed service. The partnership brings together NTT’s edge infrastructure, managed services, and IT systems integration expertise and Cisco’s IoT capabilities. Together, they promise to offer IoT services that encompass real-time data insights, enhanced security, improved decision-making, and reduced operational costs through predictive maintenance, asset tracking, and supply chain management.
NTT and Cisco are targeting opportunities in the manufacturing, transportation, healthcare and utility sectors, where they claim there is growing demand for edge computing and IoT solutions. The team has already begun working with Belgian public water distribution utility, Compagnie Intercommunale Liégeoise des Eaux (CISE). CISE has deployed thousands of LoRaWAN sensors on its infrastructure, giving it the visibility it needs to improve efficiency in the areas of water quality, consumption, distribution, and maintenance. It’s being delivered as a managed service by NTT and Cisco.

“We are accelerating our IoT business initiatives to deliver a powerful portfolio of repeatable services that can be tailored to meet customer demand for these kinds of solutions,” said Devin Yaung, SVP of group enterprise IoT products and services at NTT, in a statement. “We’re doubling down on NTT’s IoT capabilities to meet customer demand,” said Yaung. “What we’re doing is pulling together our collective knowledge and skillsets, and putting the full power of NTT behind it, to better service our customers and the increasing need to outfit or retrofit their organisations with the connectivity and visibility they need to improve day-to-day business operations.”
“We are excited to work together to help transition our customers to this IoT-as-a-service model so they can quickly realise the business benefits across industries and around the globe,” added Samuel Pasquier, VP of product management, industrial IoT networking, at Cisco.
According to IoT Analytics, global enterprise IoT spending is expected to grow 19% to $238 billion in 2023, up from $201 billion in 2022. By 2027, it could reach as high as $483 billion.
References:
https://iot-analytics.com/iot-market-size/?utm_source=IoT+Analytics+Master+People+List
STELLAR Broadband offers 10 Gigabit Symmetrical Fiber Internet Access in Hudsonville, Michigan
STELLAR Broadband, a fiber internet and technology service provider, will provide leading edge technologies and Internet connectivity up to 10Gbps to Elmwood Lake Apartments in Hudsonville, Michigan.
Elmwood Lake Apartments is a suburban haven of elevated comfort, where sweet serenity meets desirable convenience. From cozy interiors and relaxing leisure spaces to an idyllic setting next to private Elmwood Lake, the welcoming apartments in Hudsonville, MI, are ready to deliver a heightened living experience.
“With STELLAR Broadband, residents of Elmwood Lake Apartments will enjoy the fastest and most reliable internet service available. STELLAR Broadband’s fiber optic network provides symmetrical speeds of up to 10Gbps so residents can stream, game, and work from home without any lag or buffering,” said Richard Laing, president of STELLAR Broadband.
“Bosgraaf Homes has been building homes in West Michigan for four generations. Over the years, we’ve seen the industry change dramatically thanks to advances in technology. Construction methods have evolved, and the amenities that homeowners expect have grown more sophisticated. We’re grateful for our partnership with STELLAR Broadband, a company that has been at the forefront of the industry for 22 years. Their experience and leadership have helped us make the transition into multi-family housing,” said Mike Bosgraaf, president of Bosgraaf Homes.
The first in the U.S. to bring 10Gbps Internet to the apartment in student housing, STELLAR today serves over 149 communities totaling over 10,000 residents with a wide range of technology solutions, from managed Wi-Fi, TV, and access control to security.
“DTN is excited to partner with Bosgraaf Homes and STELLAR Broadband to provide Elmwood Lake residents with a unique and enjoyable experience. Bosgraaf is building beautiful homes that will be easy to lease, and STELLAR will provide residents and our office with the best possible internet service,” said Dayle Braden, DTN property manager.
“We’ve seen and have been on the forefront of technology evolving from a desired amenity to a necessity. We are proud to partner with Bosgraaf to provide the high-quality technology that their residents expect and deserve,” Laing stated.
About Spartan Net Co, dba STELLAR Broadband:
STELLAR Broadband is the largest residential fiber internet service provider in Michigan, servicing over 149 communities with multi-Gigabit fiber internet. STELLAR provides technology design and installation services for the full portfolio of technologies for multi-tenant developments, including network design, structured wiring, consulting, door entry and access control, engineered Wi-Fi, security, voice, television services, and various Internet of Things solutions. To learn more, visit: www.stellarbb.com
References:
Opensignal’s new Coverage Experience metric finds Singapore #1 in 5G
Opensignal is now measuring coverage experience to track 5G network quality. Their analysts believe coverage more accurately reflects users’ expectations and experience. Opensignal’s new Coverage Experience metric measures the geographic coverage of populated areas on a 10-point scale to represent the experience users receive as they travel around areas where they would reasonably expect to find coverage. The new Coverage Experience metric completes the picture of how expansive a market’s coverage is, along with the coverage experienced by our users on each national operator within the market.
Singapore, which rolled out 5G two years after the USA, is now on par in offering the world’s best experience – both countries rate a 10. In Singapore, Singtel rates 7.9, StarHub 7.1, and M1 7.0 out of 10.
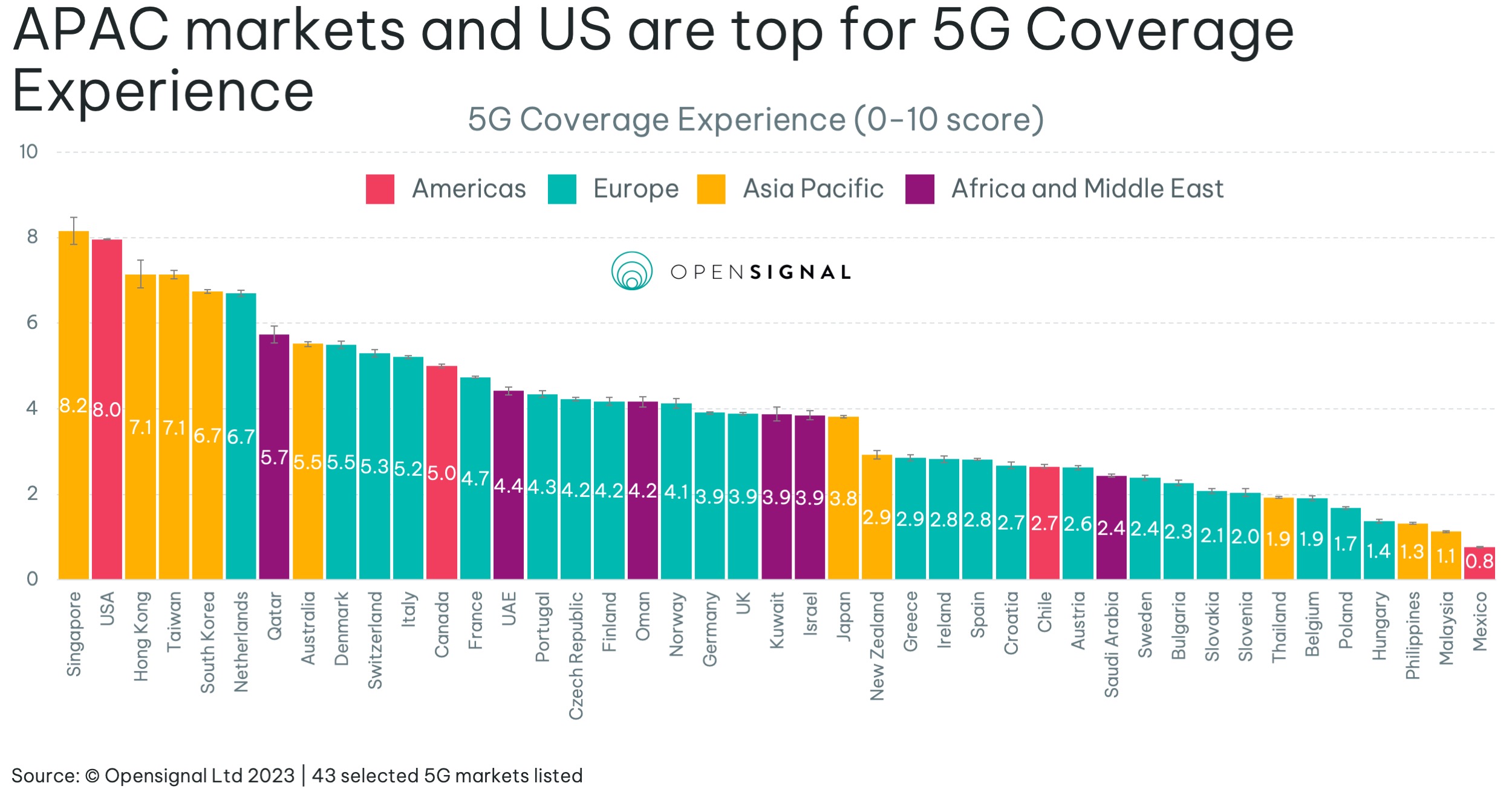
South Korea and the USA score relatively high for 5G Coverage Experience — with the USA statistically tying for the top spot with Singapore. This is due to, in part, more widespread deployments of 5G in the USA on low frequency bands, enabling greater geographic reach compared to many other markets with large land areas.
Hong Kong, Taiwan, South Korea and the Netherlands round out the leaderboard.
Some telcos have opened up a massive lead over their competitors. Australia’s Telstra rates 5.2 points out of 10, almost double both of its rivals. In Japan, NTT Docomo scores 3.3, while newcomer Rakuten (which has just signed a 5G roaming agreement with KDDI) is just 0.4. In Europe, Belgium scores just 1.9, while Sweden, Austria, Spain, Greece and Ireland all tally below 3 points.
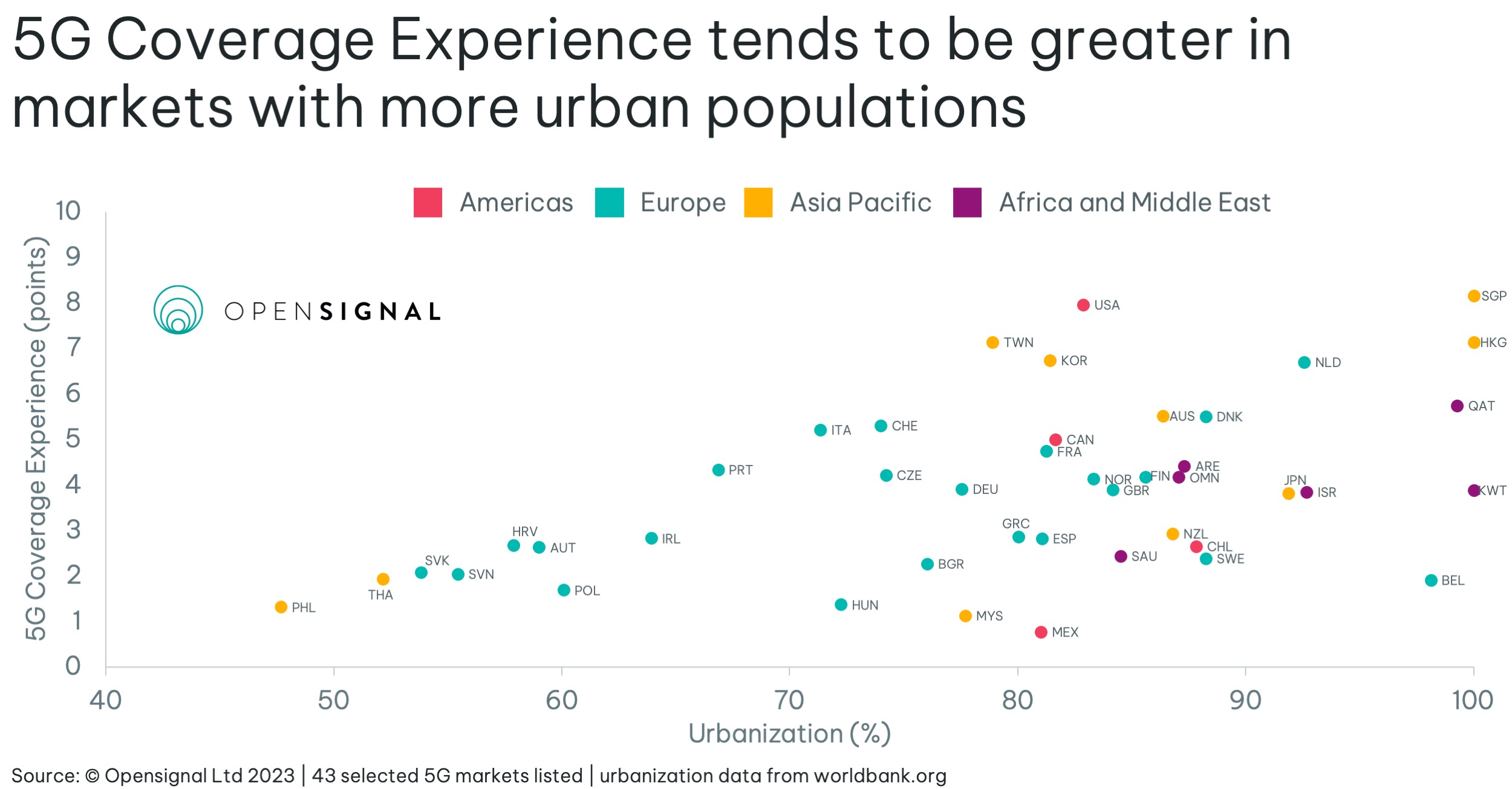
A higher percentage of urbanization in a market means that — all else being equal — operators are able to serve proportionally more users with the same number of base stations, which reflects in higher 5G Coverage Experience across such markets. The graph above shows that the score increases along with urbanization percentage, with markets below 65% struggling to score above three points.
Some markets such as Singapore and Hong Kong have nearly 100% of their population living in urban areas. This greatly benefits them when it comes to rolling out infrastructure for 5G. Singapore launched 5G two years after the USA and South Korea, yet it ranks joint first for 5G Coverage Experience.
Coverage is an important metric as it quantifies the extent to which users will be able to use their network in their home market. Opensignal’s new Coverage Experience metric represents the real-world experience users receive as they travel around areas where they would reasonably expect to find coverage.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Robert Clark of Light Reading wrote:
he one shortcoming of the 5G survey is the lack of data from India and China, the Asian giants who by their size are among the biggest drivers of global 5G. India’s absence is understandable as it’s still a nascent 5G market. In the case of China, where not even domestic organizations are allowed to track network performance, it’s hardly a surprise that foreign research efforts are blocked as well.
Chinese telcos and the Ministry for Industry and IT are barely any more informative. Their favored metric is base station population, which reveals nothing about user or geographic reach.
Right now China’s base station total, which is faithfully tallied up monthly, is 2.38 million – supposedly representing more than 60% of the global number. China Mobile and the China Telecom-Unicom partnership account for roughly half each.
The fact that some 600 million customers have signed up for China 5G may suggest they are happy enough with their user experience. On the other hand, that another 600 million have become ‘5G customers’ while remaining on the 4G network may indicate that they think 5G is simply better value.
References:
https://www.opensignal.com/2023/05/17/understanding-5g-and-overall-coverage-worldwide
https://cdn.opensignal.com/public/202305_coverage_operators_charts_5g_0.pdf
UAE’s Du demonstrates 5G VoNR with Huawei and Nokia
Du, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Integrated Telecommunications Company, has achieved a significant milestone by successfully demonstrating Voice over 5G (3GPP) New Radio (VoNR) capabilities in collaboration with Huawei and Nokia. The demonstration showcases the cutting-edge 5G core network developed in partnership with Huawei and the utilisation of Nokia’s IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Platform.
Du said the successful demonstration of VoNR represents a crucial step towards future immersive calling applications for 5G and the realization of complete 5G Standalone (SA) capabilities. With VoNR, du is able to provide seamless 5G connections, offering enhanced call setup times and uninterrupted high-speed data transmission.
According to the statement, customers connected to VoNR will experience slightly faster call setup times and continued file downloads in the background during a phone call without switching to 4G network technology. 5G Voice calls to conserve battery by eliminating the need to switch to 4G.
Du said, “It is thrilled to announce the upgrade to the most cutting-edge 5G-enabled Network as a Service (NaaS) architecture. This enhanced Network will strengthen Du’s relationship with their partners.”
VoNR leverages the advanced capabilities of 5G SA, such as network slicing, which requires a constant connection to a 5G core. This integration of technologies opens up a world of possibilities for du and its customers, enabling the delivery of innovative services like 3D audio and holographic calls, providing an immersive communication experience.
Saleem AlBlooshi, Chief Technology Officer at Du, said: “The successful demonstration of 5G network VoNR capabilities represents a significant milestone at a time when the digital sector is entering a new era. It enables unprecedented simultaneous voice and data transmissions and provides incredibly rapid connectivity transmission rates. We are thrilled to announce, in collaboration with our key partners, the upgrade to the most cutting-edge 5G-enabled Network as a Service (NaaS) architecture. This enhanced network will strengthen our relationship with our partners while also fostering service innovation to improve the customer experience and push the boundaries of what is possible.”
The successful demonstration of VoNR highlights Du’s commitment to staying at the forefront of technological advancements and delivering superior connectivity solutions to its customers.
As the demand for seamless and immersive 5G experiences grows, du’s continued efforts to enhance its network capabilities will contribute to shaping the future of communication and content consumption.

References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core-networks/voice-over-5g-vo5g-core/




