Telecom Challenges
Telecom network outages: causes, effects, and remedies for telecom providers & IT enterprise
Network outages, historically caused by misconfigurations, software defects, or hardware failures, are increasingly disruptive for several reasons, such as hyper-connectivity, single points of failure and over-reliance on concentrated hyperscaler cloud infrastructures. This leads to an expanded “blast radius” from single points of failure. The latest Cloudflare outage reveals that enterprises heavily reliant on a dangerously few major IT providers face critical single points of failure, leading to authentication issues, lost revenue, and broken customer experiences.
Cloudflare is a global cloud services and cybersecurity firm. It provides data centers, website and email security, protection from data loss and defences against cyber threats, among other things. It describes itself as providing an “immune system for the internet”, with technology that sits between its clients and the wider world that blocks billions of cyber threats daily. It also uses its global infrastructure to speed up internet traffic. It makes more than $500m – a quarter from nearly 300,000 customers operating in 125 countries, including China. Users of several heavy-traffic websites reported that they went offline at the same time as the Cloudflare outage.
Akamai’s Reuben Koh advocates for a distributed compute and edge architecture, which acts as autonomous cells to mitigate systemic risk and improve resilience via graceful degradation. He also suggests adopting strategies like graceful degradation and diversifying cloud providers which help telecom operators and other organizations limit the spread of outage disruption.

Computer outage, error or failure causing by software update mistake, operating system crash or cyber attack, server down or technical issue concept, people victims looking at computer laptop outage.

- Systemic Risk Assessment: Regulations, such as the EU’s Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) which is effective from January 17, 2025, are moving from assessing a single firm’s risk to evaluating the broader market impact of a critical third-party provider failure. DORA specifically designates critical ICT third-party providers subject to direct oversight.
- Operational Resilience Mandates: Jurisdictions are pushing firms to demonstrate the ability to maintain operations or safely exit a non-performing CSP relationship. This includes requirements for robust contingency and exit plans.
- Geographic Examples:
–Singapore is framing cloud infrastructure as essential national computing, issuing specific resilience guidelines.–Australia has issued warnings to financial institutions regarding over-dependence on a narrow set of US-based hyperscalers.–Japan is tightening scrutiny and expectations around managing third-party cloud risks.
- Continuous Discovery & Inventory: Telecom operators must maintain an up-to-date, comprehensive inventory of all APIs (managed, unmanaged, “shadow,” and “zombie”) across the enterprise.
- Shift-Left Security: Integrate security testing and design principles early into the software development lifecycle to identify and remediate vulnerabilities before APIs reach production environments.
- Implement Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): Adopt a “never trust, always verify” approach, assuming an attacker may already be internal. This means applying strict authentication and authorization controls at the API level, not just the network perimeter.
- Strong Authentication and Authorization: Use robust mechanisms like OAuth 2.0 and OpenID. Connect, employing the principle of least privilege to ensure entities only have the minimum necessary access.
- Runtime Protection and Monitoring: Implement API gateways for centralized traffic management, rate limiting to prevent Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks, and use behavioral analytics to detect anomalous activity indicative of abuse.
- Input Validation and Data Handling: Strictly validate and sanitize all data inputs to prevent injection attacks, and ensure APIs only expose necessary information to minimize data leakage.
- Human Oversight in AI: As AI and automation increase, maintain robust human oversight in change management and incident response, as AI systems can behave unpredictably. Telecom staff should be closely involved in change management and incident response, even as network automation increases.
Note 1. The UK’s Telecommunications Security Act – 2021 is a landmark law establishing mandatory, tough security standards for public telecom networks, making cybersecurity a legal duty for providers to protect critical infrastructure. It empowers regulator Ofcom, introduces penalties for non-compliance (up to 10% of turnover), and mandates adherence to specific security measures in the Code of Practice (CoP) through phased deadlines, requiring strong governance, supply chain security, and proactive threat management.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Conclusions:
Koh advocates for the implementation of resilient network architectures and improved operational maturity to enhance system fault tolerance. Key steps include distributed design, optimized operational protocols, comprehensive network visibility, and pragmatic capacity planning. These measures are becoming increasingly important as telecommunications infrastructure underpins essential societal functions.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
What telecom operators can learn from recent network outages
Cloudflare outage highlights enterprise infrastructure dependence
https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/feature/8-largest-IT-outages-in-history
España hit with major telecom blackout after power outage April 28th
Comcast frequent, intermittent internet outages + long outage in Santa Clara, CA with no auto-recovery!
AT&T wireless outage effected more than 74,000 U.S. customers with service disruptions lasting up to 11 hours for some
Rogers Telecommunications restores service after 19 hour outage disrupting life in Canada
GSMA, ETSI, IEEE, ITU & TM Forum: AI Telco Troubleshooting Challenge + TelecomGPT: a dedicated LLM for telecom applications
Rogers Telecommunications restores service after 19 hour outage disrupting life in Canada
IDC Report: Telecom Operators Turn to AI to Boost EBITDA Margins
Worldwide spending on telecommunication and pay TV services will reach $1,532 billion in 2025, representing an increase of +1.7% year-on-year, according to the International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Semiannual Telecom Services Tracker. The latest forecast is slightly more optimistic compared to the forecast published earlier this year, as it assumes a 0.1 percentage point higher growth of the total market value.
“The regional dynamics remain mixed, with inflationary effects, competition, and Average Revenue per User (ARPU) trends playing a central role in shaping market trajectories,” said Kresimir Alic, research director, Worldwide Telecom Services at IDC.
Global telecom operators are strategically adopting AI to drive significant business improvements across several key areas. The integration of AI technology is enhancing network operations, refining customer service interactions, and strengthening fraud prevention mechanisms which are reduce losses, reinforcing customer trust and regulatory compliance. With AI accelerating time-to-market for new services, telecoms can better monetize emerging technologies like 5G and edge computing.
“In the longer term, as AI continues to evolve, it will be increasingly recognized not as a mere technological enhancement, but as a strategic enabler poised to drive sustainable growth for telecommunications operators,” according to the report. This strategic adoption is accelerating time-to-market for new services, enabling better monetization of technologies like 5G and edge computing (which requires a 5G SA core network). It represents cautious optimism for a global connectivity services market that has been stagnant for many years.
- Network Planning and Operations: AI is heavily used to optimize network performance and manage the complexity of modern networks, including 5G and future 6G technologies. This involves:
- Predictive Maintenance: Anticipating hardware failures and network issues to ensure uninterrupted service and reduce downtime.
- Automation and Orchestration: Automating complex tasks and managing physical, virtual, and containerized network functions.
- Energy Efficiency: Making intelligent choices about radio access network (RAN) energy consumption and resource allocation to increase efficiency.
- Customer Experience (CX) and Service: Enhancing customer engagement and service is a top priority. This is achieved through:
- Personalized Services: Analyzing customer behavior and preferences to offer tailored products and marketing campaigns.
- Intelligent Virtual Assistants/Chatbots: Automating customer interactions and improving self-service capabilities.
- Churn Reduction: Using AI to predict customer churn and implement retention strategies.
- Business Efficiency and Productivity: Operators are focused on driving agility and productivity across the organization. This includes:
- Employee Productivity: Streamlining workflows and automating tasks using generative AI (GenAI) and agentic AI.
- Cost Reduction: Driving efficiency in operations to lower overall costs.
- Fraud Prevention: Deploying AI-enhanced systems to detect and mitigate fraud, protecting revenue streams and customer trust.
- New Revenue Opportunities: AI is seen as a cornerstone for developing new services, such as AI-as-a-Service, and monetizing existing network assets like 5G capabilities.
| Global Regional Services Revenue and Year-on-Year Growth (revenues in $B) | |||
| Global Region | 2024 Revenue | 2025 Revenue | 25/24
Growth |
| Americas | $568 | $574 | 1.0% |
| Asia/Pacific | $476 | $481 | 1.0% |
| EMEA | $462 | $477 | 3.2% |
| Grand Total | $1,507 | $1,532 | 1.7% |
| Source: IDC Worldwide Semiannual Services Tracker – 1H 2025 | |||
Mobile continues to dominate, driven by rising data consumption and the expansion of M2M applications, which are offsetting declines in traditional voice and messaging revenues.
Fixed data services are also expected to grow steadily, fueled by increasing demand for high-bandwidth connectivity.
In summary, IDC forecasts that the global connectivity services market is projected to grow at a compound annual rate of 1.5% over the next five years, maintaining a cautiously optimistic outlook. As highlighted by recent IMF forecasts, the overall market environment is expected to be less stimulating than in previous years, shaped by rising protectionism and persistent economic uncertainty in key regions. While declining inflation may ease cost pressures, it is also likely to reduce the inflation-driven boost to telecom service spending seen in recent cycles. Political instability in areas such as Eastern Europe and the Middle East adds further complexity to the growth landscape. Most notably, saturation in mature telecom markets continues to be the primary constraint on expansion, limiting upside potential in traditional service segments.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About IDC Trackers:
IDC Tracker products provide accurate and timely market size, vendor share, and forecasts for hundreds of technology markets from more than 100 countries around the globe. Using proprietary tools and research processes, IDC’s Trackers are updated on a semiannual, quarterly, and monthly basis. Tracker results are delivered to clients in user-friendly excel deliverables and on-line query tools.
For more information about IDC’s Worldwide Semiannual Telecom Services Tracker, please contact Kathy Nagamine at 650-350-6423 or [email protected].
About IDC:
International Data Corporation (IDC) is the premier global provider of market intelligence, advisory services, and events for the information technology, telecommunications, and consumer technology markets. With more than 1,000 analysts worldwide, IDC offers global, regional, and local expertise on technology and industry opportunities and trends in over 100 countries. IDC’s analysis and insight helps IT professionals, business executives, and the investment community to make fact-based technology decisions and to achieve their key business objectives. Founded in 1964, IDC is the world’s leading media, data and marketing services company that activates and engages the most influential technology buyers. To learn more about IDC, please visit www.idc.com. Follow IDC on Twitter at @IDC and LinkedIn.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://my.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS53913925&
https://my.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prEUR253369525
https://my.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=US53765725
Market research firms Omdia and Dell’Oro: impact of 6G and AI investments on telcos
Omdia: How telcos will evolve in the AI era
Dario Talmesio, research director, service provider, strategy and regulation at market research firm Omdia (owned by Informa) sees positive signs for network operators.
“After many years of plumbing, now telecom operators are starting to see some of the benefits of their network and beyond network strategies. Furthermore, the investor community is now appreciating telecom investments, after many years of poor valuation, he said during his analyst keynote presentation at Network X, a conference organized by Light Reading and Informa in Paris, France last week.
“What has changed in the telecoms industry over the past few years is the fact that we are no longer in a market that is in contraction,” he said. Although telcos are generally not seeing double-digit percentage increases in revenue or profit, “it’s a reliable business … a business that is able to provide cash to investors.”
Omdia forecasts that global telecoms revenue will have a CAGR of 2.8% in the 2025-2030 timeframe. In addition, the industry has delivered two consecutive years of record free cash flow, above 17% of sales.
However, Omdia found that telcos have reduced capex, which is trending towards 15% of revenues. Opex fell by -0.2% in 2024 and is broadly flatlining. There was a 2.2% decline in global labor opex following the challenging trend in 2023, when labor opex increased by 4% despite notable layoffs.
“Overall, the positive momentum is continuing, but of course there is more work to be done on the efficiency side,” Talmesio said. He added that it is also still too early to say what impact AI investments will have over the longer term. “All the work that has been done so far is still largely preparatory, with visible results expected to materialize in the near(ish) future,” he added. His Network X keynote presentation addressed the following questions:
- How will telcos evolve their operating structures and shift their business focuses in the next 5 years?
- AI, cloud and more to supercharge efficiencies and operating models?
- How will big tech co-opetition evolve and impact traditional telcos?
Customer care was seen as the area first impacted by AI, building on existing GenAI implementations. In contrast, network operations are expected to ultimately see the most significant impact of agentic AI.
Talmesio said many of the building blocks are in place for telecoms services and future revenue generation, with several markets reaching 60% to 70% fiber coverage, and some even approaching 100%.
Network operators are now moving beyond monetizing pure data access and are able to charge more for different gigabit speeds, home gaming, more intelligent home routers and additional WiFi access points, smart home services such as energy, security and multi-room video, and more.
While noting that connectivity remains the most important revenue driver, when contributions from various telecoms-adjacent services are added up “it becomes a significant number,” Talmesio said.
Mobile networks are another important building block. While acknowledging that 5G has been something of a disappointment in the first five years of the deployment cycle, “this is really changing” as more operators deploy 5G standalone (5G SA core) networks, Omdia observed.
Talmesio said: “At the end of June, there were only 66 telecom operators launching or commercially using 5G SA. But those 66 operators are those operators that carry the majority of the world’s 5G subscribers. And with 5G SA, we have improved latency and more devices among other factors. Monetization is still in its infancy, perhaps, but then you can see some really positive progress in 5G Advanced, where as of June, we had 13 commercial networks available with some good monetization examples, including uplink.”
“Telecom is moving beyond telecoms,” with a number of new AI strategies in place. For example, telcos are increasingly providing AI infrastructure in their data centers, offering GPU as-a-service, AI-related colocation, AI-RAN and edge AI functionality.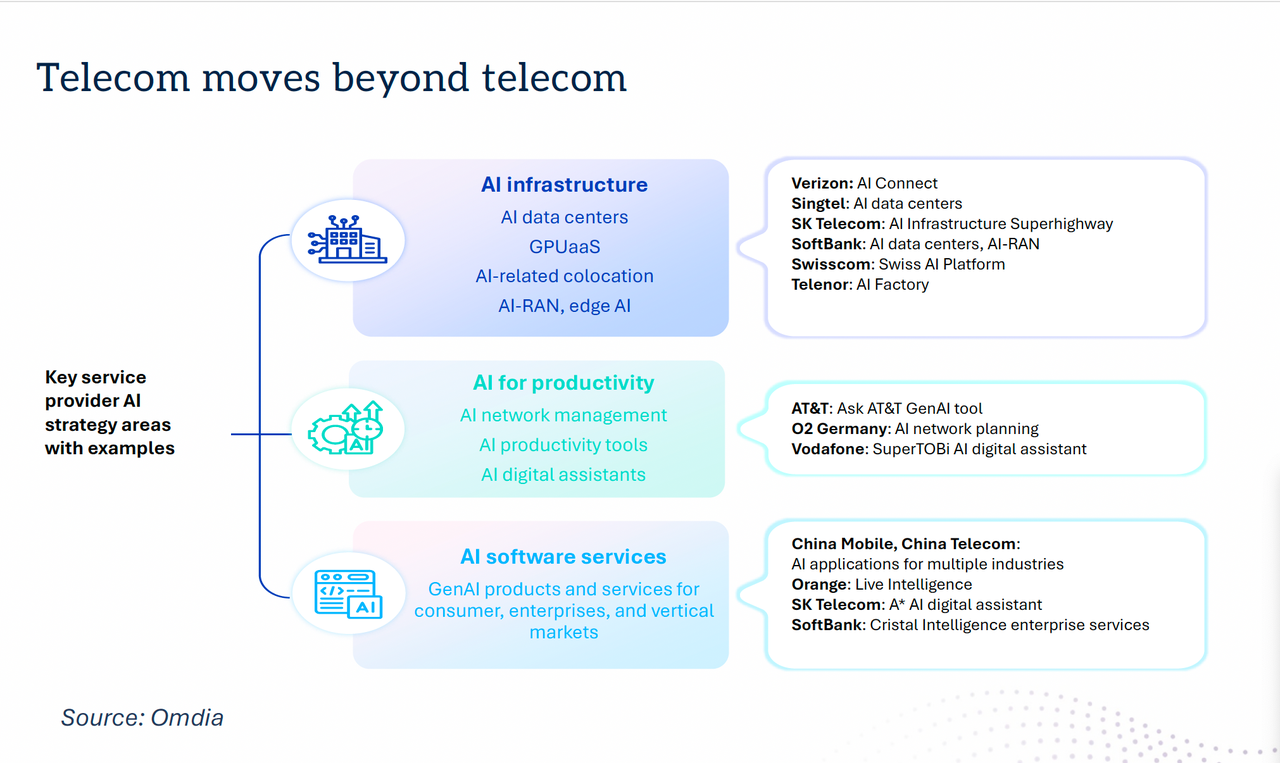

Dario Talmesio, Omdia
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
AI is also being used for network management, with AI productivity tools and AI digital assistants, as well as AI software services including GenAI products and services for consumer, enterprises and vertical markets.
“There is an additional boost for telecom operators to move beyond connectivity, which is the sovereignty agenda,” Talmesio noted. While sovereignty in the past was largely applied to data residency, “in reality, there are more and more aspects of sovereignty that are in many ways facilitating telecom operators in retaining or entering business areas that probably ten years ago were unthinkable for them.” These include cloud and data center infrastructure, sovereign AI, cyberdefense and quantum safety, satellite communication, data protection and critical communications.
“The telecom business is definitely improving,” Talmesio concluded, noting that the market is now also being viewed more favorably by investors. “In many ways, the glass is maybe still half full, but there’s more water being poured into the telecom industry.”
References:
https://networkxevent.com/speakers/dario-talmesio/
https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/technology-media-and-telecommunications/our-insights/pushing-telcos-ai-envelope-on-capital-decisions
Omdia on resurgence of Huawei: #1 RAN vendor in 3 out of 5 regions; RAN market has bottomed
Omdia: Huawei increases global RAN market share due to China hegemony
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Omdia: Cable network operators deploy PONs
Bloomberg: Higher borrowing costs hurting indebted wireless companies; industry is 2nd largest source of distressed debt
S&P Global estimates total outstanding debt in the speculative-grade U.S. telecom and cable sector is about $275.4 billion. Most of the telecom debt issuers took advantage of historically low interest rates in 2020 and 2021 to refinance their capital structures and push out maturities until 2026 and 2027. Wireless carriers spent heavily on acquiring spectrum licenses and building out their 5G networks, which led to significant debt loads and a very low ROI. For example, AT&T’s total debt increased significantly due to the C-band auction for 5G spectrum. It jumped from $182.98 billion at the end of 2020 to $209.08 billion in March 2021. Similarly, Verizon’s total debt climbed from $151.24 billion to $180.70 billion during the same period. Large debt loads can limit a company’s ability to invest in new technologies and infrastructure.
Billionaires who built their fortunes building out wireless networks when debt cost almost nothing are seeing their wealth evaporate. For example:
- Altice founder Patrick Drahi’s wealth has dropped almost 18% to $4.4 billion this year, according to the Bloomberg Billionaires Index. Altice has been the poster child for the industry’s travails recently. Last month, Altice spokesmen told creditors of its French operations that they would have to take a hit (impairment charge) in the restructuring of the €24.3 billion debt pile.
- Rakuten Group Inc.’s Hiroshi Mikitani’s fortune has shrunk 69% since 2021 after a push into mobile increased the firm’s losses. Rakuten announced earlier this month that it was looking at combining its financial units into a single group.
- Dish Network Corp. Chairman Charles Ergen has seen his riches shrink nearly 80% in less than three years as the company tries to transition from pay-TV to wireless services. Dish has been searching for ways to address upcoming debt maturities after scrapping a debt swap earlier this year when bondholders pushed back on the deal. Private credit firms have offered financing, Bloomberg News previously reported.
The stumbles in wireless highlight wider troubles across telecommunications, media and technology. Communications is the worst-performing junk sector in the US this year, Bloomberg Intelligence credit analyst Stephen Flynn wrote in a note this week, with several members of the index burdened with high leverage and facing large maturity walls. Annual returns from the industry’s junk bonds have turned negative this year as shown in this chart:
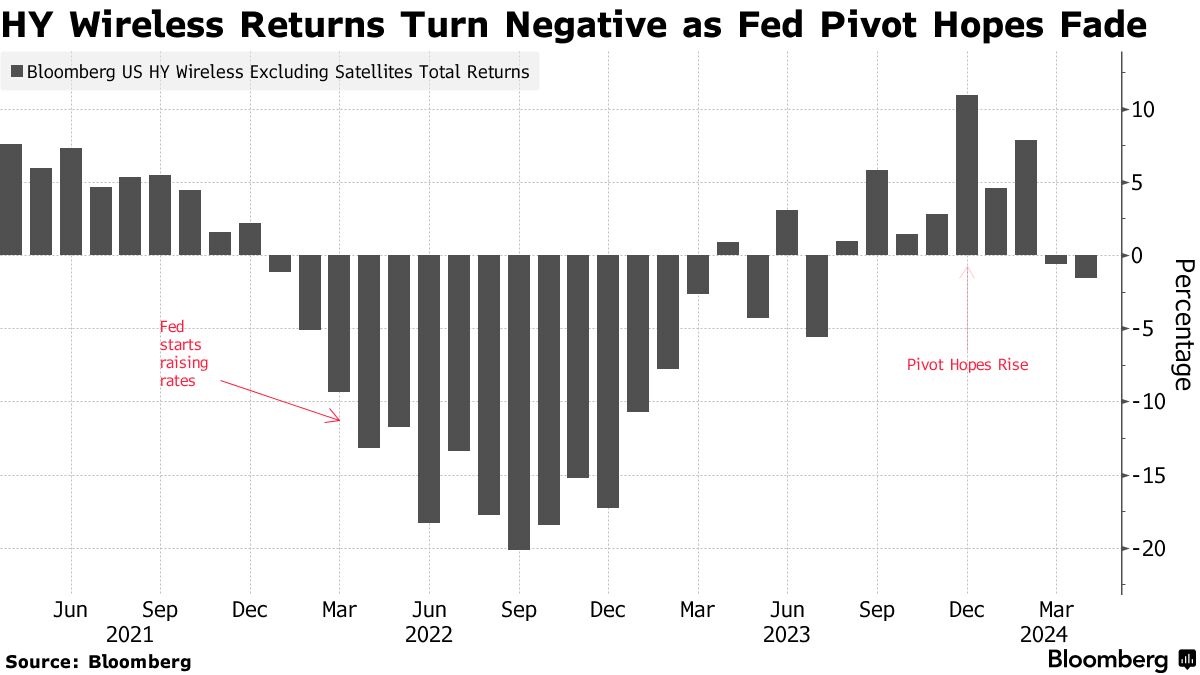
Wireless is the second biggest source of distressed debt globally (#1 is real estate) after the debt pile swelled to $35.3 billion, according to data compiled by Bloomberg News. That’s up more than 80% since early January! The fall in Altice bond prices sent the total level of distressed debt globally last week to the highest level since the middle of January.

Digicel, the Caribbean mobile operator founded by Irish businessman Denis O’Brien, imposed losses on bondholders and lenders earlier this year via what ratings company Moody’s described as a “distressed exchange.”
In summary, managing debt and addressing bad debt are crucial for the wireless industry to maintain financial stability and sustain growth. As interest rates fluctuate and operational challenges persist, wireless telecom companies must find effective strategies to mitigate these risks and optimize revenue assurance.
References:
https://www.bnnbloomberg.ca/telecom-tycoons-feel-pain-from-rising-mobile-woes-1.2065998
Where Have You Gone 5G? Midband spectrum, FWA, 2024 decline in CAPEX and RAN revenue
Telecom layoffs continue unabated as AT&T leads the pack – a growth engine with only 1% YoY growth?
MTN Consulting: Generative AI hype grips telecom industry; telco CAPEX decreases while vendor revenue plummets
Dell’Oro: Telecom Capex Growth to Slow in calendar years 2022-2024
FT: Telecom & Technology on the Ropes: Challenging Markets & Too Much Debt
Grandview Research: global telecom services market to compound at 6.2% from 2023 to 2030
According to Grandview Research, the global telecom services market size was valued at USD 1,805.61 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030.
Rising spending on the deployment of 5G infrastructures due to the shift in customer inclination toward next-generation technologies and smartphone devices is one of the key factors driving this industry. An increasing number of mobile subscribers, soaring demand for high-speed data connectivity, and the growing demand for value-added managed services are the other potential factors fueling the market growth. The global communication network has undoubtedly been one of the prominent areas for continued technological advancements over the past few decades.
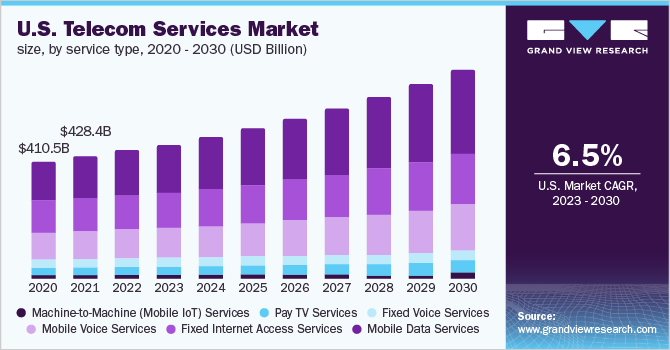
In 2022, the wireless networks accounted for a market share of more than 76.0% in the global market. The advent of cloud-computing technologies, artificial intelligence, and IoT is presumed to majorly contribute to the growth of wireless communication channels worldwide. Over the years, there has been a rapid deployment of systems for Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) that has enabled internet access to cellular devices in private homes, public spaces, airports, office buildings, cafeterias, and other areas. Such wireless densification to simplify work processes and automate routine test actions is presumed to prove beneficial, hence registering a robust CAGR in the forthcoming years.
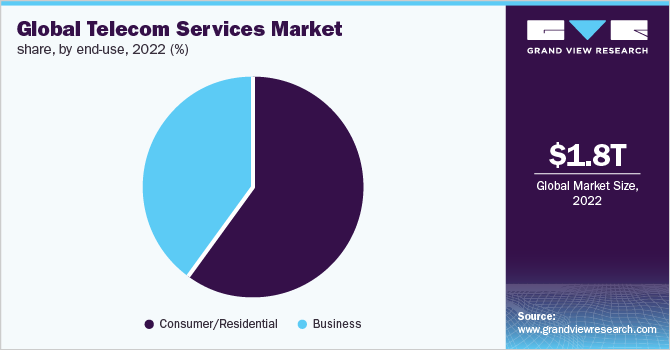
In 2022, the consumer/residential segment accounted for the largest revenue share of more than 59.0% and is projected to maintain its lead over the forecast period. The significant growth is ascribed to the proliferation of smartphones worldwide. There were more than 8 billion mobile subscribers recorded globally in 2020, wherein more than 60% of the population was using smartphones. The private telecom operators account for a larger subscriber base as compared to government-owned companies. In addition, the growing demand for OTT applications is contemplating the users to subscribe to wireless internet offerings, thereby significantly contributing to the deployment of communication networks at a broader level. Additionally, the growing trend of using ultra-high-definition videos and online gaming is expected to boost the segment growth over the forecast period.
In 2022, the Asia Pacific captured more than 33.0% of share and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.0% from 2023 to 2030. The region is likely to attract more than half of the new mobile subscribers by 2030. The regional market is primarily driven by e-commerce and retailer buy-in platforms, smartphone ubiquity, and investments in 5G networks. China, Japan, and India have emerged as significant contributors to regional market growth. According to industry expert analysis, in February 2022, China recorded 1.02 billion internet users, which is more than three times the number of the third-placed United States, which had just over 307 million. India recorded the second highest internet users in February 2022.
Some prominent players in the global telecom services market include:
- AT&T Inc.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT)
- China Mobile Ltd.
- Deutsche Telekom AG
- SoftBank Group Corp.
- China Telecom Corp Ltd.
- Telefonica SA
- Vodafone Group
- KT Corporation
- Bharati Airtel Limited
- Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited
- KDDI Corporation
- Orange SA
- BT Group plc
- Comcast Corporation
Telecom Services Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size value in 2023 | USD 1,885.41 billion |
| Revenue forecast in 2030 | USD 2,874.76 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030 |
| Base year for estimation | 2022 |
| Historical period | 2017 – 2021 |
| Forecast period | 2023 – 2030 |
| Quantitative units | Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2023 to 2030 |
| Report coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Segments covered | Service type, transmission, end-use, region |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Country scope | U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; France; Italy; China; Japan; India; South Korea; Brazil; Mexico |
| Key companies profiled | AT&T Inc.; Verizon Communications Inc.; NTT; China Mobile Ltd.; Deutsche Telekom AG; SoftBank Group Corp.; China Telecom Corp Ltd.; Telefonica SA; Vodafone Group; KT Corporation; Bharati Airtel Limited; Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited; KDDI Corporation; Orange SA; BT Group plc; Comcast Corporation |
| Customization scope | Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
| Pricing and purchase options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
References:
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/global-telecom-services-market
Technavio: APAC region leads global telecom services market with 33% growth
Canalys: Global cloud infrastructure services spending up 16% in Q3-2023
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom to Jointly Develop Telco-specific Large Language Models (LLMs)
IDC Telecom Services Tracker: Worldwide spending on Telecom and Pay TV services will increase by 2.0% in 2023
Worldwide spending on Telecom Services and Pay TV Services reached $1,478 billion in 2022, increasing by 2.2% year over year, according to the International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Semiannual Telecom Services Tracker. IDC expects Worldwide spending on Telecom and Pay TV services will increase by 2.0% next year and reach a total of $1,541 billion. The latest forecast is slightly more optimistic compared to the version published in November last year as it assumes a 0.3 percentage point higher growth in 2023. IDC believes this acceleration is a consequence of the increase in tariffs of telecommunication services fueled by inflation.
This is the second time in the last six months that we have increased our forecast for the telecom services market and positive adjustments have been made for all global regions. This confirms the thesis that inflation is equally happening in all parts of the world and that operators are all behaving in similar way when their profitability is threatened by the inflationary pressures. And what is more, the effects that we observe now are the outcome of the initial tariff adjustments that were generally happening in mid-2022. According to the latest IMF forecasts, inflation is here to stay for the next three years at least which means that operators will continue to increase tariffs, clients will be paying more for telco services, and the total nominal value of the market will be growing at faster pace. This is the explanation for why we increased our forecast not only for 2023, but for the entire first half of the forecast period.
| Global Regional Services Revenue and Year-on-Year Growth (revenues in $B) | |||
| Global Region | 2021 Revenue | 2022 Revenue | 22/21
Growth |
| Americas | $572 | $580 | 1.4% |
| Asia/Pacific | $467 | $481 | 3.0% |
| EMEA | $438 | $449 | 2.4% |
| Grand Total | $1,478 | $1,510 | 2.2% |
| Source: IDC Worldwide Semiannual Services Tracker – 2H 2022 | |||
Our forecast for Asia-Pacific was boosted by 0.7 percentage points, for Americas by 0.3 percentage points, and for EMEA by 0.1 percentage points. At the first sight, the magnitude of change in EMEA, region that is witnessing a higher-than-average inflation while struggling to find a replacement for the cheap Russian energy, might seem relatively low. It can be explained by 1) the war in Ukraine and the related economic sanctions imposed to Russia, the biggest market of the CEE subregion, and 2) significant slowdown of the major WE economies driven by the drastic growth of the central banks’ interest rates. The fact that during the previous update the EMEA region witnessed the highest upward revision should also be taken into consideration. Nonetheless, the fastest growth this year, as well as in the entire forecast period, is expected in the Asia/Pacific region, fueled by the relatively lower saturation of the markets in less-developed countries.
High inflation is not good news for any market, because the positive boost it produces is only nominal. A closer look at the forecasted growth rates reveals that they are much lower than the annual inflation rates published by monetary statisticians, which means that the market is witnessing a decline in value in real terms. For that reason, the telecom operators continue to heavily invest into advanced telco technologies. They hope that the migration to all-IP and new-generation access (NGA) broadband will help offset the fixed and mobile voice decline. They also believe that 5G will unlock new opportunities by allowing massive machine-type communications and ultra-reliable low-latency communications.
The companies are also increasing the pace of digitalization and software-ization of their business processes, create new go-to-market strategies based on data and intelligence, and deploy innovative business models based on telco-as-a-platform and co-creation within ecosystems. They also look for additional revenue streams in the non-telco areas such as IoT, data center, cloud, AR/VR, IT services, VoD, enterprise vertical solutions, financial solutions, cyber security, digital media, e-commerce, etc.
“Telecom operators are completely transforming – from providers of traditional commodity-style services they are becoming modern all-round full-stack technology suppliers,” says Kresimir Alic, Research Director, Worldwide Telecom Services. “In that way they become leaders of the digital transformation revolution and rightly hope they can acquire one of the central positions in the new digitalized world.”
About IDC Trackers:
IDC Tracker products provide accurate and timely market size, vendor share, and forecasts for hundreds of technology markets from more than 100 countries around the globe. Using proprietary tools and research processes, IDC’s Trackers are updated on a semiannual, quarterly, and monthly basis. Tracker results are delivered to clients in user-friendly excel deliverables and on-line query tools.
For more information about IDC’s Worldwide Semiannual Telecom Services Tracker, please contact Kathy Nagamine at 650-350-6423 or [email protected].
References:
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS50644723
Gartner: Robust growth for telecom equipment spending, tepid growth for telco services, PC sales flat
Dell’Oro: XGS, 25G, and Early 50G PON Rollouts to Fuel Broadband Spending
Synergy Research: Growth in Hyperscale and Enterprise IT Infrastructure Spending; Telcos Remain in the Doldrums
DZS Inc: 2023 Telecom Trends & Applications Changing the Broadband Industry
by Geoff Burke, DZS Inc. (a global provider of access networking infrastructure, service assurance and consumer experience software solutions). Edited by Alan J Weissberger
There are a handful of significant trends that will emerge over the next several months as service providers navigate their transformation and seek to find their Competitive EDGE. This post will focus on the increasing shift to multi-gigabit services, the growing importance of the network edge and how service providers are being transformed into “experience providers..
- Multi-Gigabit Broadband Services are Becoming the New Standard – The shift to gigabit services was both widespread and well suited for Gigabit Passive Optical Networking (GPON) However, new advanced applications will require symmetrical multi-gigabit speeds. The proliferation of multiple devices using these bandwidth-hungry apps is pushing service providers to begin to think 10 gig services and beyond for both business and residential services. The emergence of the metaverse, with Ultra High Definition (UHD) Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality/Extended Reality (AR/VR/XR) and gaming applications will continue push these boundaries.
- The Network Edge Continues to Rise as a Strategic Location – The rise of 10 Gigabit Symmetrical (XGS)-PON and multi-gigabit services that support the above mentioned applications and more is creating new challenges in the network – especially as these apps require symmetrical bandwidth. Service providers realize that they must push equipment as close to the subscriber as possible to optimize traffic management, but also to minimize latency, which is becoming increasingly important in the world of the metaverse and AR/VR/XR apps. Additionally, leveraging intelligence at the edge moves it closer to where data is actually created and consumed and where the subscriber experience is defined giving service providers increased agility in monitoring, managing and optimizing performance.
- Service Providers are Rapidly Transforming into Experience Providers – As the network becomes increasingly software defined and intelligent equipment is deployed closer to the edge, the ability for carriers to both gather meaningful information that can reflect and provide actionable insights into user experience grows dramatically. As a result, the concept of a true “experience provider” is emerging where subscriber problems can be anticipated and proactively addressed, and user needs can be addressed remotely and immediately in an extraordinarily personalized manner. This transformation is proving to have profound impacts on carrier performance, with dramatically reduced churn, faster responsiveness, better performance, and higher Average Revenue Per User (ARPU).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
DZS Inc says these Applications are Changing the Broadband Industry:
- Connected Home: WiFi everywhere
- Connected Business: Passive Optical LAN
- MDUs: delivering multi-gigabit services
- Multi-gigabit services: they are becoming a major source of differentiation for service providers
References:
https://dzsi.com/resources/blog/the-broadband-trends-that-will-define-2023-part-1/
Telecoms.com Survey Report assesses telecom industry in 2022 and outlook for 2023
Telecoms.com newly published survey report assesses the telecom industry’s performance over this year, as well as the views of the professionals participating in the survey on the outlook of 2023 and beyond. A general sense of optimism and achievement comes through as 63% of respondents believe that the business performance of telecoms in 2022 has been ‘excellent’ or ‘good’ while also reaching consensus on a positive outlook for next year.
Here are some of the key findings from the survey:
- More than two thirds view the industry’s business outlook for 2023 as positive, including about a third that believe the outlook to be very positive.
- Around two out of three respondents believe the industry’s performance in 2022 has been either excellent or good
- The majority of respondents believe 5G standalone (SA) core network will have a materially favorable effect on the adoption of 5G, but there remain many obstacles for deployment.
- Around one in three respondents report they have many service concepts to monetise as their capabilities evolve, but they find configuration and testing of services challenging.
- One in four respondents will upgrade existing BSS and charging stack to support new use cases for enterprise and B2B2X.
- Legacy infrastructure is considered the largest barrier to automated zero-touch services.
- Most respondents consider video delivery key for their telecom businesses, including more than a third who consider it a top priority.
- Healthcare and connected vehicles are the top two most interesting IoT use-cases.
- Nearly two thirds of respondents either plan to or have already deployed Open RAN commercially.

The survey report states that Security, Digital Transformation, IoT, and Broadband will be the top four areas for telecom businesses in 2023. 5G standalone core is identified as having a materially positive impact on the wider adoption of 5G. Nonetheless, high costs in network equipment and network deployment are still seen as the biggest key challenge for deploying standalone 5G.
Other challenges identified with broadband network and service automation include legacy infrastructure and siloed operations across technologies. Lack of skills and resources is also flagged as a key barrier to the deployment of IoT and also Open RAN technologies.
In terms of emerging services and technologies, Metaverse is identified with 60% as the most hyped emerging technology while more than half of respondents also view it as ‘not commercially interesting’. Meanwhile, the survey reports that more than four in five telecom professionals find video delivery as key for telecom businesses, including a third who consider it ‘top priority’.
References:
2022 has been a great year for telecoms, industry professionals say
Analysys Mason: Telecoms industry faces challenging conditions in 2023
Analysys Mason has warned of the challenges facing the telecoms industry in the year ahead. Like many other industries, the biggest issue facing the sector in 2023 is how it copes with the impact of inflation, particularly rising energy costs, and the reaction to any price rises that are passed on to customers. In addition, this is set against a backdrop of existing market challenges that are already testing the industry’s ability to deliver services, open up new revenue streams and return value to shareholders.
The industry is experiencing a mix of declining revenue and increasing investment costs. The sector has underperformed compared to the market index over the past decade, reporting a low return in 2021 (7 percentage points below the European market, and a similar performance against the markets in North America and Asia), and it has some of the highest capital expenditure thanks to network and infrastructure investments, particularly relating to deploying 5G, the further evolution of 5G architecture and the prospect of 6G.
“After a decade of low inflation and low interest rates, the telecoms sector faces the uncertainty of how it will be affected by these cost increases and the degree to which it can increase its own prices in response,” said Larry Goldman, Chief Analyst at Analysys Mason. “Combined with high investment costs and questions about potential returns, the market outlook is challenging as the telecoms industry tries to steer its path through price rises, rolling out network availability and launching new services.”
Here are Analysys Mason’s 10 most-compelling predictions for the telecoms, media and technology (TMT) sector in 2023. These predictions will be supported by more detailed predictions for specific areas; consumer and enterprise services, networks and software, and satellite.
The biggest issue for telecoms operators in 2023 will be coping with inflation and particularly rising energy costs. After a decade of low inflation and low interest rates, telecoms operators, like other businesses face the problem of managing rising costs and uncertainty about how much they can increase their own prices to cope.
Price rises for telecoms services will become a political issue
Elected officials have largely left pricing issues up to regulators for the past decade. Operators and regulators will be under pressure to moderate price increases, especially on consumer services. Operators will also be pushed to introduce, and publicise, ‘social’ tariffs for consumers in financial hardship, especially for fixed broadband services. We believe that operators will be able to raise retail prices, but it is possible that ARPU will not keep pace with inflation, meaning a cut in real terms. However, it is worth remembering that telecoms services are a relatively small part of any household budget and the annual price increases will be far lower than those for other products and services, such as food and energy.
Telecoms operators were relatively unscathed in the pandemic but must now cut costs
Some cost cutting will come from the automation that telcos have invested in in the past few years, but they must focus on reducing energy costs. One particular area will be decommissioning older networks more rapidly than previously planned.
Telecoms operators will maintain 5G investment plans despite few prospects of short-term returns
FTTP investment will continue to grow and infraco joint ventures will shoulder a greater share of the financial burden. Telcos will move to FTTP pushed by competition from other technologies and pulled by an increasing number of consumers demanding high-bandwidth services that are not adequately supported by current broadband connections or preferring FTTP for reasons such as its better reliability. Traditional telco capex budgets are constrained by the need to invest in 5G, but the long-term value of fibre (and utility-like models) will continue to attract outside investors.
The metaverse will not materialise in 2023, but many more telecoms operators will align their roadmap to fit the vision of an xR-centric future
Meta will continue to spend billions in R&D in 2023 with little return on investment in that timeframe: 2030 will be increasingly framed as ‘the year of the metaverse’. However, operators will take xR use-cases (like VR immersive calls, 3D video calling or digital twin technology) more seriously in 2023 and most will formulate a specific metaverse strategy (internally, if not externally) this year. Apple’s long-rumoured xR headsets may be launched in 2023 but are more likely in 2024.
Telecoms operators will not give up on digital services despite some mixed results
Some high-profile operators have recently left digital services areas (in particular, AT&T and Verizon sold their advertising divisions) and some are rumoured to be planning to divest assets (for example, Orange’s reported plans to sell Orange Bank), but these decisions should not be taken as signals that all operators in high-income countries are rethinking involvement in digital economy services. The US cable operators continue to invest in advertising initiatives, and European operators are likely to follow. TELUS is expected to generate more than 10% of its revenue from health services in 2023. Others are looking at digital education as a growth opportunity.
Private networks take-up will continue, but progress will not be smooth
Take-up of new private networks has been led by large organisations with networking teams and significant internal expertise. We expect this to continue in 2023, but if take-up is to be strong in the next tier of organisations, private networking solutions will need to be simpler and easier to buy. Suppliers will need to offer networks, devices, edge computing, spectrum and other capabilities as a package. Some form of opex/as-a-service pricing will need to be offered. If these developments do not happen, it is possible that adoption will stall.
Demand for multi-cloud connectivity will drive the launch of new solutions
Enterprise demand for SLA-based, on-demand multi-cloud connectivity and network-as-a-service (NaaS) platforms will accelerate because it will be imperative for many businesses to have cloud interconnection, app-to-app networking, zero-trust security and data-sovereignty-compliant traffic management across multiple public clouds and SaaS providers. Telecoms operators with large enterprise/B2B divisions will increasingly prioritise multi-cloud network investments using software-defined networking (SDN) and cloud-native IP networking technologies to gain ground against the alternative service providers that are dominating the market today.
Open RAN will expand in rural and enterprise environments but the crucial massive MIMO challenge will remain inadequately addressed
An ecosystem is developing around Open RAN in areas that are poorly addressed by traditional cellular architecture and operator models, namely rural extension and enterprise small cells. These deployments will gather momentum in 2023 as organisations such as the Telecom Infra Project address issues such as common testing models. However, significant challenges remain to achieve optimum performance in urban macro networks using Open RAN architecture, especially those incorporating massive MIMO. These challenges will take several more years to address to the satisfaction of large operators, and a separate and parallel ecosystem is likely to be established for macro Open RAN.
The use of SaaS deployment models will grow by 19% in the telecoms industry in 2023
This growth will come from both BSS and OSS application areas as operators use hosted applications to help them to transform their current IT stacks to support new 5G services or use them to transform legacy systems to cloud-native, cloud-delivered hosted applications. Application vendors that previously sold on-premises applications will launch increasing numbers of delivery options that will include SaaS.
Direct satellite-to-device connectivity will enter a second wave
Apple, Globalstar, SpaceX/Starlink and T-Mobile have made the first moves in this market, and we expect significant developments in 2023 from the likes of Inmarsat, Iridium, Samsung, other LEO/MEO satellite providers and major telecoms operators. The Apple/Globalstar and SpaceX/T-Mobile propositions are narrowband SoS/emergency-type services, but the competitive edge in this second wave of deals or partnerships will be announcements of two-way wideband or broadband propositions, as well as non-US coverage. Direct satellite-to-device connectivity will have more than 25 million subscribers by the end of 2023, whether it be through mobile satellite services or mobile operators’ terrestrial spectrum, making it a milestone year for this technology.
About Analysys Mason:
Analysys Mason is the world’s leading management consultancy focused on TMT, a critical enabler of economic, environmental and social transformation.
www.analysysmason.com
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.analysysmason.com/press/research-predictions-2023/
https://www.analysysmason.com/research/content/articles/research-predictions-2023/
https://www.analysysmason.com/research/content/short-reports/private-network-deployments-rma17/



