VC4 Advances OSS Transformation with an Efficient and Reliable AI enabled Network Inventory System
By Juhi Rani assisted by IEEE Techblog editors Ajay Lotan Thakur and Sridhar Talari Rajagopal
Introduction:
This year, 2025, VC4 [a Netherlands Head Office (H/O) based Operational Support System (OSS) software provider] has brought sharp industry focus to a challenge that many experience in telecom. Many operators/carriers still struggle with broken, unreliable, and disconnected inventory systems. While many companies are demoing AI, intent-based orchestration, and autonomous networks, VC4’s newly branded offering, Service2Create (or S2C as it’s known to some), is refreshingly grounded. Also as we have learnt very quickly, bad data into AI is a “no-no”. None of the orchestration and autonomous networks, will work accurately if your OSS is built on flawed data. The age-old saying “Garbage in, Garbage out” comes to mind.
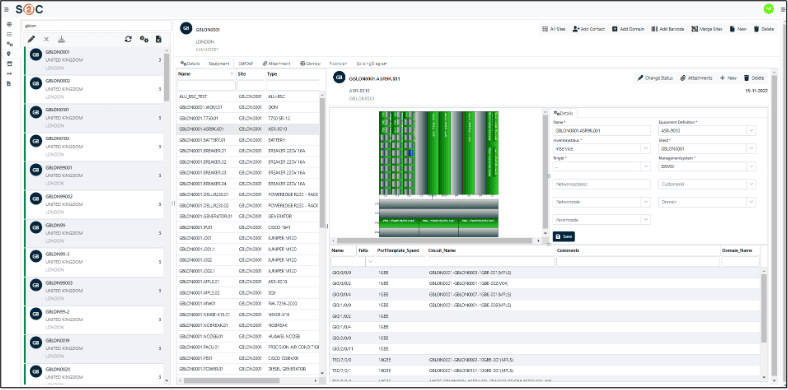
VC4’s platform, Service2Create (S2C), is a next-generation OSS inventory system that supports the evolving needs of telecom operators looking to embrace AI, automate workflows, and run leaner, smarter operations. Service2Create is built from over two decades of experience of inventory management solutions – IMS. By focusing on inventory accuracy and network transparency, S2C gives operators a foundation they can trust.
Inventory: The Most Underestimated Barrier to Transformation
In a post from TM Forum, we observed that operators across the world are making huge investments in digital transformation but many are slowed by a problem closer to the ground: the inability to know what exactly is deployed in the network, where it is, and how it’s interconnected.
VC4 calls this the “silent blocker” to OSS evolution.
Poor mis-aligned inventory undermines everything. It breaks service activations, triggers unnecessary truck rolls, causes billing mismatches, and frustrates assurance teams. Field engineers often discover real-world conditions that don’t match what’s in the system, while planners and support teams struggle to keep up. The problem doesn’t just stop with network data.
In many cases, customer records were also out of date or incomplete… and unknown inventory can also be a factor. Details like line types, distance from the central office, or whether loading coils were present often didn’t match reality. For years, this was one of the biggest issues for operators. Customer databases and network systems rarely aligned, and updates often took weeks or months. Engineers had to double-check every record before activating a service, which slowed delivery and increased errors. It was a widespread problem across the industry and one that many operators have been trying to fix ever since.
Over time, some operators tried to close this gap with data audits and manual reconciliation projects, but those fixes never lasted long. Networks change every day, and by the time a cleanup was finished, the data was already out of sync again.
Modern inventory systems take a different approach by keeping network and customer data connected in real time. They:
- Continuously sync with live network data so records stay accurate.
- Automatically validate what’s in the field against what’s stored in the system.
- Update both customer and network records when new services are provisioned.
In short, we’re talking about network auto-discovery and reconciliation, something that Service2Create does exceptionally well. This also applies for unknown records, duplicate records and records with naming inconsistencies/variances.
It is achieved through continuous network discovery that maps physical and logical assets, correlates them against live service models, and runs automated reconciliation to detect discrepancies such as unknown elements, duplicates, or naming mismatches. Operators can review and validate these findings, ensuring that the inventory always reflects the true, real-time network state. A more detailed explanation can be found in the VC4 Auto Discovery & Reconciliation guide which can be downloaded for free.
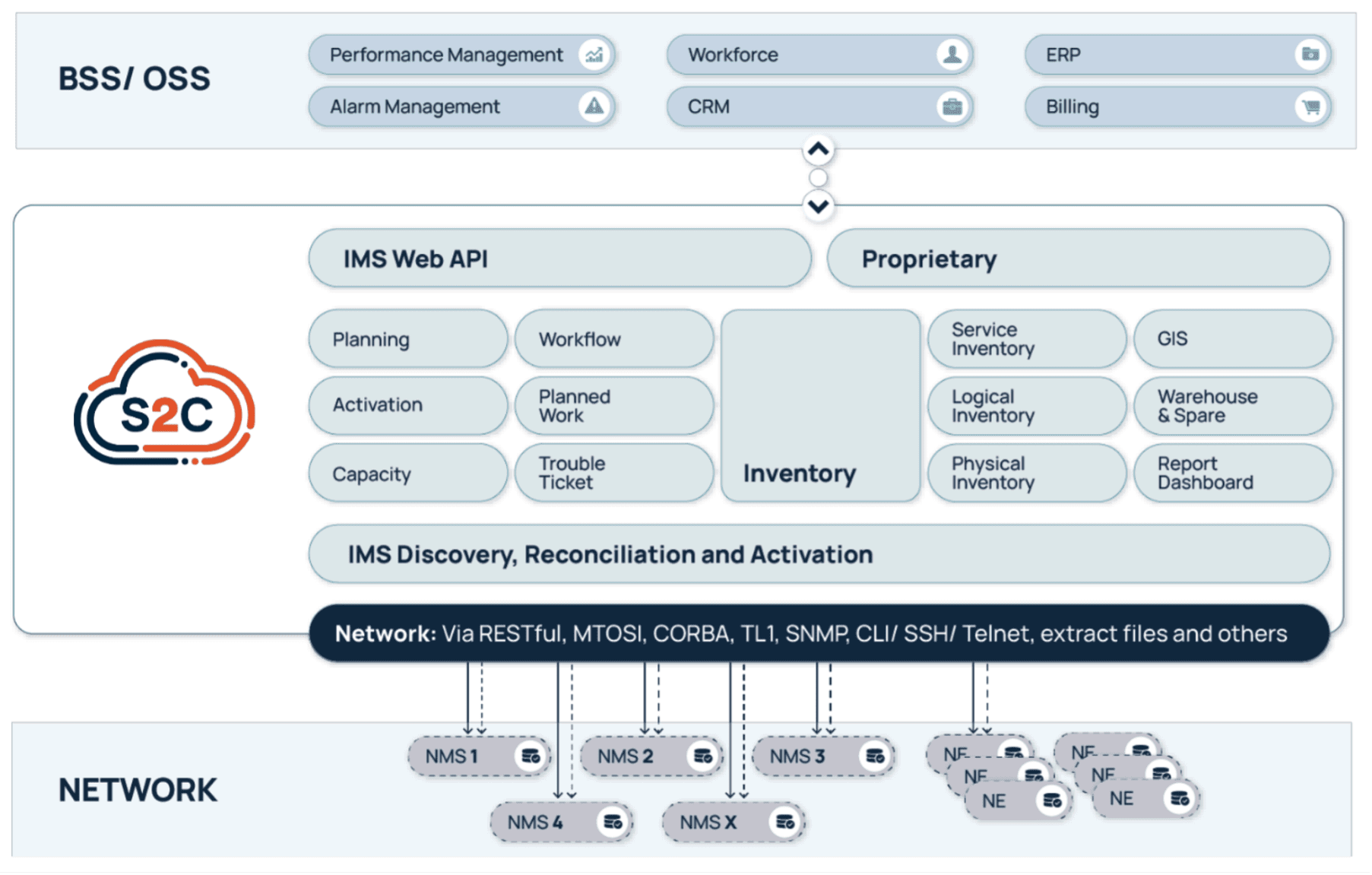
Service2Create: Unified, Reconciled, and AI-Ready
Service2Create is designed to reflect the actual, current state of the network across physical, logical, service and virtual layers. Whether operators are managing fiber rollout, mobile backhaul, IP/MPLS cores, or smart grids, S2C creates a common source of truth. It models infrastructure end-to-end, automates data reconciliation using discovery, and integrates with orchestration platforms and ticketing tools.
To make the difference clearer here is the table below shows how Service2Create compares with the older inventory systems still used by many operators. Traditional tools depend on manual updates and disconnected data sources, while Service2Create keeps everything synchronized and validated in real time.
Comparison between legacy inventory tools and Service2Create (S2C)
| Feature | Legacy OSS Tools | VC4 Service2Create (S2C) |
|---|---|---|
| Data reconciliation | Manual or periodic | Automated and continuous |
| Inventory accuracy | Often incomplete or outdated | Real-time and verified |
| Integration effort | Heavy customization needed | Standard API-based integration |
| Update cycle | It takes days or weeks | Completed in hours |
| AI readiness | Low, needs data cleanup | High, with consistent and normalized data |
What makes it AI-ready isn’t just compatibility with new tools, it’s data integrity. VC4 understands that AI and automation only perform well when they’re fed accurate, reliable, and real-time data. Without that, AI is flying blind.
Built-in Geographic Information System (GIS) capabilities help visualize the network in geographic context, while no/low-code workflows and APIs support rapid onboarding and customization. More than software, S2C behaves like a data discipline framework for telecom operations.
Service2Create gives operators a current, trusted view of their network, improving accuracy and reducing the time it takes to keep systems aligned.
AI is Reshaping OSS… But only if the Data is Right
AI is driving the next wave of OSS transformation from automated fault resolution and dynamic provisioning to predictive maintenance and AI-guided assurance. But it’s increasingly clear: AI doesn’t replace the need for accuracy; it demands it.
In 2025, one common thread across operators and developers was this: telcos want AI to reduce costs, shorten response times, and simplify networks. According to a GSMA analysis, many operators continue to struggle as their AI systems depend on fragmented and incomplete datasets, which reduces overall model accuracy.
VC4’s message is cutting through: AI is only as useful as the data that feeds it. Service2Create ensures the inventory is trustworthy, reconciled daily with the live network, and structured in a way AI tools can consume. It’s the difference between automating chaos and enabling meaningful, autonomous decisions.
Service2Create has been adopted with operators across Europe and Asia. In national fiber networks, it’s used to coordinate thousands of kilometers of rollout and maintenance. In mixed fixed-mobile environments, it synchronizes legacy copper, modern fiber, and 5G transport into one unified model.
Designed for Operational Reality
VC4 didn’t build Service2Create for greenfield labs or ideal conditions. The platform is designed for real-world operations: brownfield networks, legacy system integrations, and hybrid IT environments. Its microservices-based architecture and API-first design make it modular and scalable, while its no/low-code capabilities allow operators to adapt it without long customization cycles. See the diagram below.
S2C is deployable in the cloud or on-premises and integrates smoothly with Operational Support System / Business Support System (OSS/BSS) ecosystems including assurance, CRM, and orchestration. The result? Operators don’t have to rip and replace their stack – they can evolve it, anchored on a more reliable inventory core.
What Industry Analysts are Saying
In 2025, telco and IT industry experts are also emphasizing that AI’s failure to deliver consistent ROI in telecom is often due to unreliable base systems. One IDC analyst summed it up: “AI isn’t failing because the models are bad, it’s failing because operators still don’t know what’s in their own networks.”
A senior architect from a Tier 1 European CSP added, “We paused a closed-loop automation rollout because our service model was based on inventory we couldn’t trust. VC4 was the first vendor we saw this year that has addressed this directly and built a product around solving it.”
This year the takeaway is clear: clean inventory isn’t a nice-to-have. It’s step one.
Looking Ahead: AI-Driven Operations Powered by Trusted Inventory
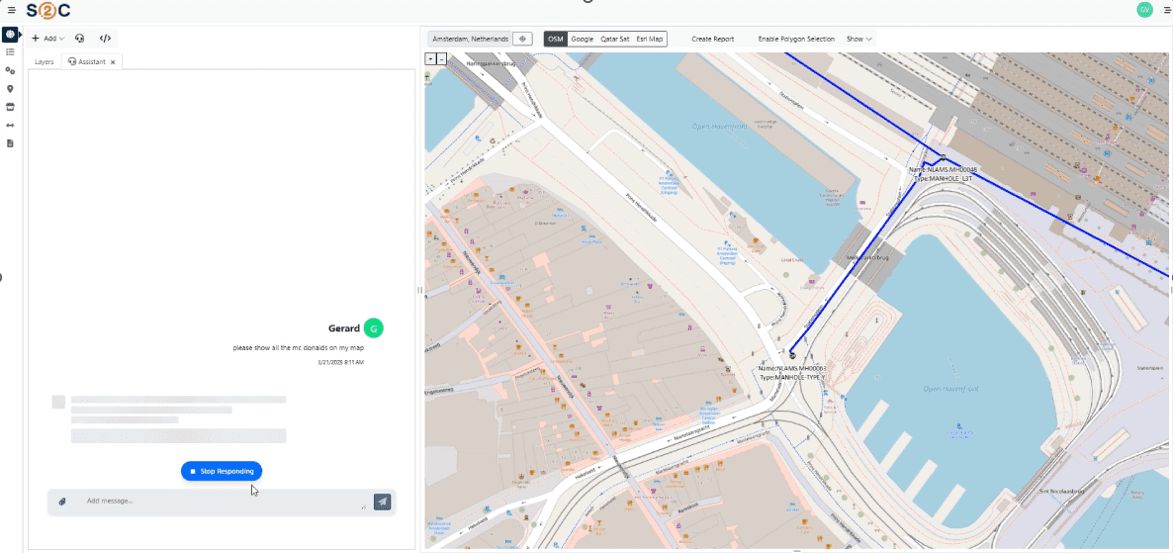
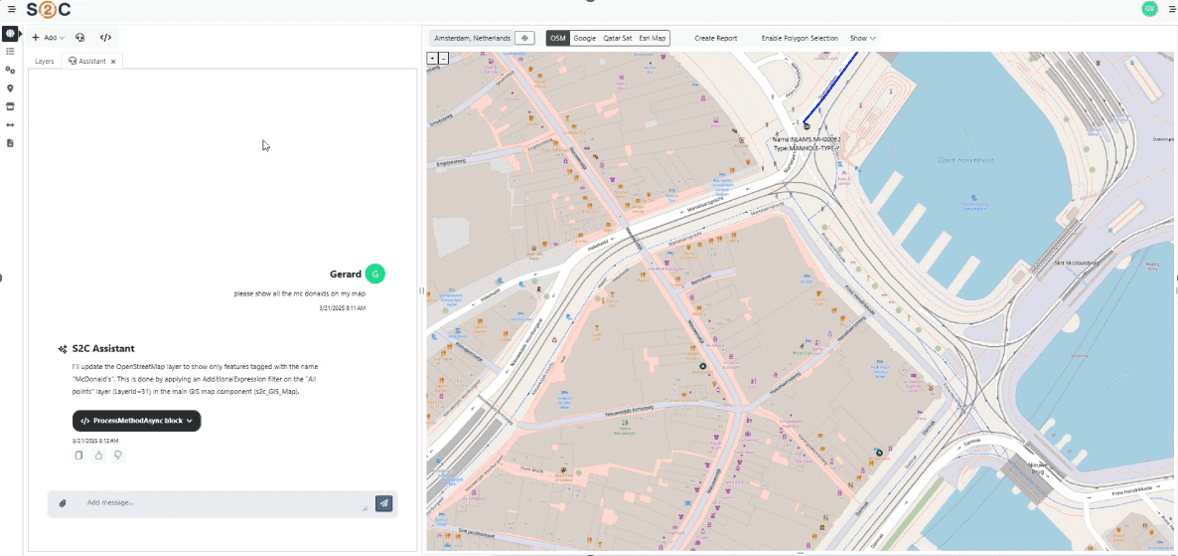
VC4 is continuing to enhance Service2Create with capabilities that support AI-led operations. Currently, S2C is enhanced with AI-powered natural language interfaces through Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers. This creates a revolutionary way for users to access their data and makes it also easier for them to do so. Simply ask for what you need, in plain language, and receive instant, accurate results from your systems of record.
The S2C platform now offers multiple synchronized access methods:
- Natural Language Interface
- Ask questions in plain language: “Show me network capacity issues in Amsterdam”
- AI translates requests into precise system queries
- No training required – productive from day one
- Direct API Access via MCP
- Programmatic access using Language Integrated Query (LINQ) expressions
- Perfect for integrations and automated workflows
- Industry-standard authentication (IDP)
- S2C Visual Platform
- Full-featured GUI for power users
- Parameterized deeplinks for instant component access
- Low/no-code configuration capabilities
- Hybrid Workflows
-
- Start with AI chat, graduate to power tools
- AI generates deeplinks to relevant S2C dashboards
Export to Excel/CSV for offline analysis
-
What It All Comes Down To
Digital transformation sounds exciting on a conference stage, but in the trenches of telecom operations, it starts with simpler questions. Do you know what’s on your network? Can you trust the data? Can your systems work together?
That’s what Service2Create is built for. It helps operators take control of their infrastructure, giving them the confidence to automate when ready and the clarity to troubleshoot when needed.
VC4’s approach isn’t flashy. It’s focused. And that’s what makes it so effective – a direction supported by coverage from Subseacables.net, which reported on VC4’s partnership with AFR-IX, to automate and modernize network operations across the Mediterranean.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About the Author:
Juhi Rani is an SEO specialist at VC4 B.V. in the Netherlands. She has successfully directed and supervised teams, evaluated employee skills and knowledge, identified areas of improvement, and provided constructive feedback to increase productivity and maintain quality standards.
Juhi earned a B. Tech degree in Electronics and Communications Engineering from RTU in Jaipur, India in 2015.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ajay Lotan Thakur and Sridhar Talari Rajagopal are esteemed members of the IEEE Techblog Editorial Team. Read more about them here.
ITU’s Facts and Figures 2025 report: steady progress in Internet connectivity, but gaps in quality and affordability
Overview:
The world’s online population grew by more than 240 million people in 2025, according to a new ITU Facts and Figures 2025 report. The new estimates confirm continuing progress in expanding digital connectivity, while pointing to differences in quality that impact how users benefit from Internet use. Globally, an estimated 6 billion people – about three-quarters of the world’s population – are using the Internet in 2025, up from a revised estimate of 5.8 billion in 2024. However, 2.2 billion people remain offline, down from a revised estimate of 2.3 billion in 2024. Overall, the report’s findings underline the importance of digital infrastructure, affordable services and skills training to ensure that everyone can truly benefit from advancing technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI).
“In a world where digital technologies are essential to so much of daily life, everyone should have the opportunity to benefit from being online,” said ITU Secretary-General Doreen Bogdan-Martin. “This report highlights how today’s digital divides are being defined by speed, reliability, affordability, and skills, all of which we must prioritize as we work toward our mission of universal connectivity.”
Connectivity’s quality challenge:
For the first time, Facts and Figures estimates the total number of 5G subscriptions, which now account for about one-third – or around 3 billion – of all mobile broadband subscriptions worldwide.
In 2025, 5G networks are estimated to cover 55 per cent of the world’s population, reflecting strong momentum in advanced mobile technologies. Coverage, however, remains uneven, with 84 per cent of people in high-income countries having access to 5G, compared with only 4 per cent in low-income countries.
While Facts and Figures shows that 4G and 3G services are available to most of the global population, these services are not best suited for keeping pace with advancing technologies.
Estimates in the report reveal deep contrasts in intensity of use as an indicator of the quality gap. A typical user in a high-income country now generates nearly eight times more mobile data than one in a low-income country.
Making connectivity meaningful:
Facts and Figures 2025 highlights that affordability and digital skills remain essential to achieving universal and meaningful connectivity – reached when everyone can access the Internet with high-quality service, at an affordable cost, whenever and wherever needed.
Globally, the median price of a data-only mobile broadband basket decreased, but access remains unaffordable in around 60 per cent of low- and middle-income countries.
Data also suggest that most Internet users possess basic skills, while more advanced capabilities – such as online safety, problem-solving and digital content creation – are being developed more slowly.
“Reliable data are the foundation of effective digital policies and of our shared vision to connect the world,” said ITU’s Telecommunication Development Bureau Director Cosmas Luckyson Zavazava. “
Achieving that vision will require sustained and well-targeted efforts – in infrastructure, in digital skills, and in data systems. By working together and directing resources where the needs are greatest, we can ensure that no one is left behind and that everyone benefits fully and safely from the opportunities of the digital age.”
The report underscores the persistence of several digital divides:
- 94 per cent of people in high-income countries use the Internet, in contrast to only 23 per cent in low-income countries;
- 96 per cent of those offline live in low- and middle-income countries;
- 77 per cent of men are online compared to 71 per cent of women;
- 85 per cent in urban areas are online versus 58 per cent in rural areas;
- 82 per cent of 15–24-year-olds use the Internet, compared with 72 per cent of the rest of the population.
Facts and Figures 2025 provides global, regional and income group estimates for indicators related to Internet use, mobile network coverage, Internet subscriptions, Internet traffic, affordability, digital skills and mobile phone ownership.

Getty Images – credit: fotograzia
About the ITU:
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations agency for digital technologies, driving innovation for people and the planet with 194 Member States and a membership of over 1,000 companies, universities, civil society, and international and regional organizations. Established in 1865, ITU coordinates the global use of the radio spectrum and satellite orbits, establishes international technology standards, drives universal connectivity and digital services, and is helping to make sure everyone benefits from sustainable digital transformation, including the most remote communities. From artificial intelligence (AI) to quantum, from satellites and submarine cables to advanced mobile and wireless broadband networks, ITU is committed to connecting the world and beyond. Learn more: www.itu.int
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/Pages/PR-2025-11-17-Facts-and-Figures.aspx
An Uncertain Future for the Global Internet
NTT DOCOMO successful outdoor trial of AI-driven wireless interface with 3 partners
NTT DOCOMO has successfully executed the world’s premier outdoor field trial of real-time transceiver systems leveraging artificial intelligence (AI)-driven wireless technology, a critical advancement for sixth-generation (6G) mobile communications (AKA IMT 2030).
Conducted in collaboration with parent company NTT, Inc. (NTT), Nokia Bell Labs, and SK Telecom Co., Ltd, the field trials were held across three sites in Yokosuka City, Kanagawa Prefecture. The results validated that the application of AI optimized system throughput (transmission speed), achieving up to a 100% improvement over conventional, non-AI methods under identical environmental conditions, effectively doubling communication speeds.
Wireless communication quality can be compromised by fluctuations in radio propagation environments, leading to unstable connections. To mitigate this challenge, the partners developed “AI-AI technology,” which applies AI to both the transmitting and receiving ends of the wireless interface. This system dynamically optimizes modulation and demodulation schemes based on prevailing radio conditions, facilitating stable communication across diverse use cases. The efficacy of this technology had previously been confirmed in indoor environments.
The recent field trials aimed to verify the technology’s stable performance in complex outdoor settings, where radio conditions are subject to greater variability from factors such as temperature, weather, and physical obstructions.
This innovative AI wireless technology was evaluated across three distinct outdoor courses with varying propagation conditions, including the presence of obstacles and terminal mobility:
- Course 1: A public road featuring gentle curves, with a test vehicle traveling up to 40 km/h.
- Course 2: An environment with partial signal obstructions.
- Course 3: A road with minimal obstructions, with a test vehicle traveling up to 60 km/h.
In all test scenarios, the technology demonstrated its ability to compensate for signal degradation, confirming enhanced communication speeds. Specifically, in the highly complex propagation conditions of Course 1, the AI-AI technology yielded an average throughput improvement of 18% and a maximum increase of 100% compared to traditional methods.
These findings enable higher-speed data transmission for users and allow network operators to enhance spectrum efficiency and deliver superior quality of service (QoS). The successful outdoor validation marks a significant milestone toward the practical implementation of 6G systems, which promise a combination of high wireless transmission efficiency and reduced power consumption. NTT DOCOMO remains committed to refining this technology under a wide range of conditions and accelerating R&D efforts toward 6G realization, while simultaneously collaborating with global partners on 6G standardization (in 3GPP and ITU-R WP5D) and deployment.
This new technology will be featured at the NTT R&D FORUM 2025 hosted by NTT, scheduled from November 19–21 and November 25–26, 2025.
These three AI-wireless field trials represent the latest joint effort stemming from the collaborative AI research partnership of DOCOMO, parent NTT, Nokia Bell Labs, and SK Telecom Co, which was established at Mobile World Congress (MWC) in February 2024.
NTT Docomo has forged additional 6G alliances with a range of partners, including Ericsson, domestic Japanese suppliers Fujitsu and NEC, and testing specialists Keysight Technologies and Rohde & Schwarz.
This year has seen an increase in partnerships among Korean and Japanese operators. Earlier this month, KDDI‘s research partnership with Nokia Bell Labs was announced, focusing on achieving 6G energy efficiency and enhanced network resilience. Samsung and SoftBank entered into a memorandum of understanding (MoU) last month to co-develop prospective next-generation technologies, encompassing 6G, AI-driven Radio Access Networks (AI RAN), and Large Telecom Models (LTMs).
In a separate MoU signed in March, KT‘s and Samsung’s collaboration was formalized to jointly advance 6G antenna technology. Additionally, KT has maintained a separate research engagement with Nokia centered on semantic communications research.
About NTT DOCOMO:
NTT DOCOMO, Japan’s leading mobile operator with over 91 million subscribers, is one of the global leaders in 3G, 4G and 5G mobile network technologies.
Under the slogan “Bridging Worlds for Wonder & Happiness,” DOCOMO is actively collaborating with global partners to expand its business scope from mobile services to comprehensive solutions, aiming to deliver unsurpassed value and drive innovation in technology and communications, ultimately to support positive change and advancement in global society.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.docomo.ne.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2025/1117_00.html
https://www.docomo.ne.jp/english/
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/ntt-docomo-doubles-6g-throughput-in-ai-trials
NTT DOCOMO OREX brand offers a pre-integrated solution for Open RAN
NTT’s IOWN provides ultra low latency and energy efficiency in Japan and Hong Kong
NTT & Yomiuri: ‘Social Order Could Collapse’ in AI Era
NTT Docomo will use its wireless technology to enter the metaverse
Expose: AI is more than a bubble; it’s a data center debt bomb
We’ve previously described the tremendous debt that AI companies have assumed, expressing serious doubts that it will ever be repaid. This article expands on that by pointing out the huge losses incurred by the AI startup darlings and that AI poster child Open AI won’t have the cash to cover its costs 9which are greater than most analysts assume). Also, we quote from the Wall Street Journal, Financial Times, Barron’s, along with a dire forecast from the Center for Public Enterprise.
In Saturday’s print edition, The Wall Street Journal notes:
OpenAI and Anthropic are the two largest suppliers of generative AI with their chatbots ChatGPT and Claude, respectively, and founders Sam Altman and Dario Amodei have become tech celebrities.
What’s only starting to become clear is that those companies are also sinkholes for AI losses that are the flip side of chunks of the public-company profits.
OpenAI hopes to turn profitable only in 2030, while Anthropic is targeting 2028. Meanwhile, the amounts of money being lost are extraordinary.
It’s impossible to quantify how much cash flowed from OpenAI to big tech companies. But OpenAI’s loss in the quarter equates to 65% of the rise in underlying earnings of Microsoft, Nvidia, Alphabet, Amazon and Meta together. That ignores Anthropic, from which Amazon recorded a profit of $9.5B from its holding in the loss-making company in the quarter.
OpenAI committed to spend $250 billion more on Microsoft’s cloud and has signed a $300 billion deal with Oracle, $22 billion with CoreWeave and $38 billion with Amazon, which is a big investor in rival Anthropic.
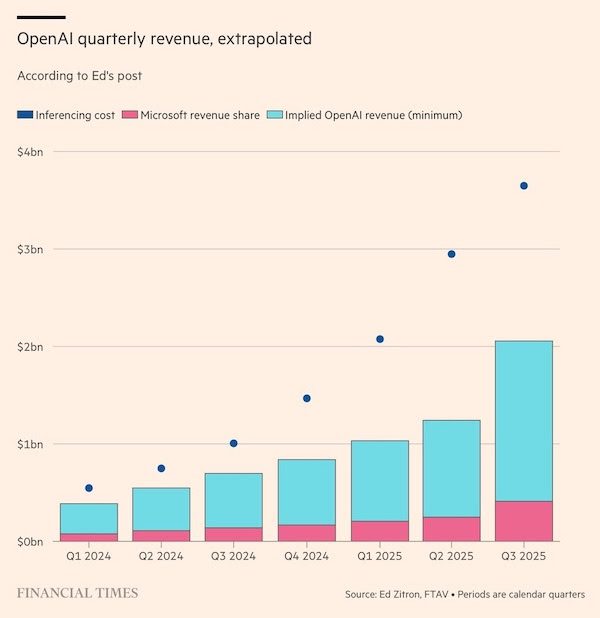
OpenAI doesn’t have the income to cover its costs. It expects revenue of $13 billion this year to more than double to $30 billion next year, then to double again in 2027, according to figures provided to shareholders. Costs are expected to rise even faster, and losses are predicted to roughly triple to more than $40 billion by 2027. Things don’t come back into balance even in OpenAI’s own forecasts until total computing costs finally level off in 2029, allowing it to scrape into profit in 2030.
The losses at OpenAI that has helped boost the profits of Big Tech may, in fact, understate the true nature of the problem. According to the Financial Times:
OpenAI’s running costs may be a lot more than previously thought, and that its main backer Microsoft is doing very nicely out of their revenue share agreement.
OpenAI appears to have spent more than $12.4bn at Azure on inference compute alone in the last seven calendar quarters. Its implied revenue for the period was a minimum of $6.8bn. Even allowing for some fudging between annualised run rates and period-end totals, the apparent gap between revenues and running costs is a lot more than has been reported previously.
The apparent gap between revenues and running costs is a lot more than has been reported previously. If the data is accurate, then it would call into question the business model of OpenAI and nearly every other general-purpose LLM vendor.
Also, the financing needed to build out the data centers at the heart of the AI boom is increasingly becoming an exercise in creative accounting. The Wall Street Journal reports:
The Hyperion deal is a Frankenstein financing that combines elements of private-equity, project finance and investment-grade bonds. Meta needed such financial wizardry because it already issued a $30B bond in October that roughly doubled its debt load overnight.
Enter Morgan Stanley, with a plan to have someone else borrow the money for Hyperion. Blue Owl invested about $3 billion for an 80% private-equity stake in the data center, while Meta retained 20% for the $1.3 billion it had already spent. The joint venture, named Beignet Investor after the New Orleans pastry, got another $27 billion by issuing bonds that pay off in 2049, $18 billion of which Pimco purchased. That debt is on Beignet’s balance sheet, not Meta’s.
Dan Fuss, vice chairman of Loomis Sayles told Barrons: “We are good at taking credit risk,” Dan said, cheerfully admitting to having the scars to show for it. That is, he added, if they know the credit. But that’s become less clear with the recent spate of mind-bendingly complex megadeals, with myriad entities funding multibillion-dollar data centers. Fuss thinks current data-center deals are too speculative. The risk is too great and future revenue too uncertain. And yields aren’t enough to compensate, he concluded.
Increased wariness about monster hyper-scaler borrowings has sent the cost of insuring their debt against default soaring. Credit default swaps (CDS) more than doubled for Oracle since September, after it issued $18 billion in public bonds and took out a $38 billion private loan. CoreWeave’s CDS gapped higher this past week, mirroring the slide of the data-center company’s stock.
According to the Bank Credit Analyst (BCA), capex busts weigh on the economy, which further hits asset prices, the firm says. Following the dot-com bust, a housing bubble grew, which burst in the 2008-09 financial crisis. “It is far from certain that a new bubble will emerge (after the AI bubble bursts) this time around, in which case the resulting recession could be more severe than the one in 2001,” BCA notes.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The widening gap between the expenditures needed to build out AI data centers and the cash flows generated by the products they enable creates a colossal risk which could crash asset values of AI companies. The Center for Public Enterprise reports that it’s “Bubble or Nothing.”

Should economic conditions in the tech sector sour, the burgeoning artificial intelligence (AI) boom may evaporate—and, with it, the economic activity associated with the boom in data center development.
Circular financing, or “roundabouting,” among so-called hyperscaler tenants—the leading tech companies and AI service providers—create an interlocking liability structure across the sector. These tenants comprise an incredibly large share of the market and are financing each others’ expansion, creating concentration risks for lenders and shareholders.
Debt is playing an increasingly large role in the financing of data centers. While debt is a quotidian aspect of project finance, and while it seems like hyperscaler tech companies can self-finance their growth through equity and cash, the lack of transparency in some recent debt-financed transactions and the interlocked liability structure of the sector are cause for concern.
If there is a sudden stop in new lending to data centers, Ponzi finance units ‘with cash flow shortfalls will be forced to try to make position by selling out position’—in other words to force a fire sale—which is ‘likely to lead to a collapse of asset values.’
The fact that the data center boom is threatened by, at its core, a lack of consumer demand and the resulting unstable investment pathways, is itself an ironic miniature of the U.S. economy as a whole. Just as stable investment demand is the linchpin of sectoral planning, stable aggregate demand is the keystone in national economic planning. Without it, capital investment crumbles.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Postscript (November 23, 2025):
In addition to cloud/hyperscaler AI spending, AI start-ups (especially OpenAI) and newer IT infrastructure companies (like Oracle) play a prominent role. It’s often a “scratch my back and I’ll scratch yours” type of deal. Let’s look at the “circular financing” arrangement between Nvidia and OpenAI where capital flows from Nvidia to OpenAI and then back to Nvidia. That ensures Nvidia a massive, long-term customer and providing OpenAI with the necessary capital and guaranteed access to critical, high-demand hardware. Here’s the scoop:
- Nvidia has agreed to invest up to $100 billion in OpenAI over time. This investment will be in cash, likely for non-voting equity shares, and will be made in stages as specific data center deployment milestones are met.
- OpenAIhas committed to building and deploying at least 10 gigawatts of AI data center capacity using Nvidia’s silicon and equipment, which will involve purchasing millions of Nvidia expensive GPU chips.
Here’s the Circular Flow of this deal:
- Nvidia provides a cash investment to OpenAI.
- OpenAI uses that capital (and potentially raises additional debt using the commitment as collateral) to build new data centers.
- OpenAI then uses the funds to purchase Nvidia GPUs and other data center infrastructure.
- The revenue from these massive sales flows back to Nvidia, helping to justify its soaring stock price and funding further investments.
What’s wrong with such an arrangement you ask? Anyone remember the dot-com/fiber optic boom and bust? Critics have drawn parallels to the “vendor financing” practices of the dot-com era, arguing these interconnected deals could create a “mirage of growth” and potentially an AI bubble, as the actual organic demand for the products is difficult to assess when companies are essentially funding their own sales.
However, supporters note that, unlike the dot-com bubble, these deals involve the creation of tangible physical assets (data centers and chips) and reflect genuine, booming demand for AI compute capacity although it’s not at all certain how they’ll be paid for.
There’s a similar cozy relationship with the $1B Nvidia invested in Nokia with the Finnish company now planning to ditch Marvell’s silicon and replace it by buying the more expensive, power hungry Nvidia GPUs for its wireless network equipment. Nokia, has only now become a strong supporter of Nvidia’s AI RAN (Radio Access Network), which has many telco skeptics.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/big-techs-soaring-profits-have-an-ugly-underside-openais-losses-fe7e3184
https://www.ft.com/content/fce77ba4-6231-4920-9e99-693a6c38e7d5
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/three-ai-megadeals-are-breaking-new-ground-on-wall-street-896e0023
Can the debt fueling the new wave of AI infrastructure buildouts ever be repaid?
AI Data Center Boom Carries Huge Default and Demand Risks
Big tech spending on AI data centers and infrastructure vs the fiber optic buildout during the dot-com boom (& bust)
AI spending boom accelerates: Big tech to invest an aggregate of $400 billion in 2025; much more in 2026!
Gartner: AI spending >$2 trillion in 2026 driven by hyperscalers data center investments
Amazon’s Jeff Bezos at Italian Tech Week: “AI is a kind of industrial bubble”
FT: Scale of AI private company valuations dwarfs dot-com boom
NTT’s IOWN provides ultra low latency and energy efficiency in Japan and Hong Kong
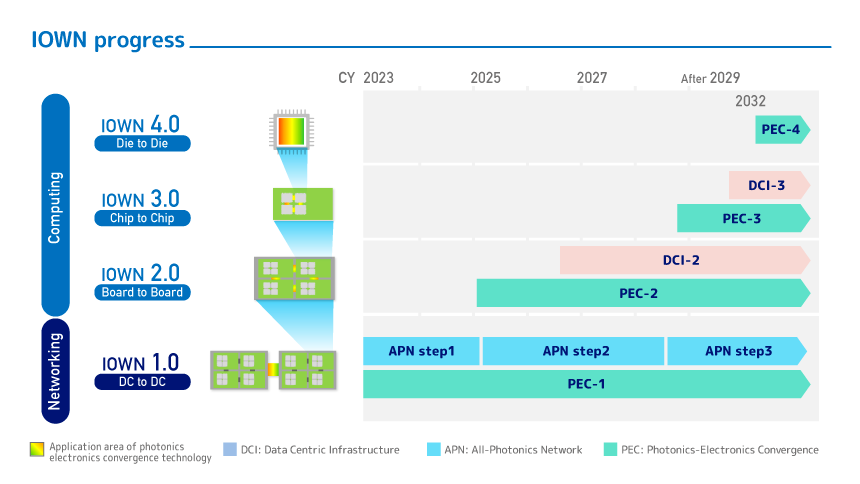
The rapid uptake of generative AI in data centers and semiconductor factories is causing a surge in power consumption, which is predicted to reach 11 times the current level by 2033. To address this issue, the NTT Group has proposed the “IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network)” concept, which aims to improve energy efficiency and achieve ultra-low latency and high-capacity communications through innovative optical communications technology.
By utilizing optical communications technology, IOWN aims to achieve dramatically low-power, high-quality, high-capacity, and low-latency communications by migrating from conventional electronics-based networks to photonics (optical)-based networks.
“Our research and development efforts are focused on achieving 1/200th the current level of latency, 125x the current level of capacity, and 100x the current level of power efficiency by 2032,” said NTT’s Tetsushi Shoji.
NTT Group is working toward “IOWN 1.0,” a goal that will see the network become all-optical. Even with current networks using optical fiber, data is repeatedly converted into electrical signals through routers and switches. However, if communication from terminal to terminal were to be entirely optical, the power consumption required for conversion would be significantly reduced.
Furthermore, communication latency is expected to be reduced. “Traditional communications involve delays because data passes through multiple nodes. However, with the IOWN APN (All Photonics Network), data reaches its destination directly, dramatically improving communication latency,” says Shoji.
On August 29, 2024, a 2,893-km IOWN APN demonstration experiment connecting Tokyo and Taiwan. The optical transport connection linked the Chunghwa Telecom Headquarter in Taipei City with the Musashino R&D Center in Musashino, Japan, achieving an ultra-low latency of approximately 17 milliseconds over an approximately 3,000 km network. Latency fluctuations were also extremely small, The innovative application was showcased publicly at the NTT R&D Forum 2024 in November 2024.

NTT Group is also considering optical fiber inside computers as part of its IOWN 2.0 and beyond concept.
Currently, the wiring inside computers uses electrical signals, and as processing speeds increase, problems with power consumption and heat generation become more serious. To solve this, the goal is to opticalize communication between boards and chips, dramatically improving data transfer efficiency.
“Ultimately, by utilizing optical fiber even inside computers, we believe it will be possible to improve power efficiency by 100 times and communication speeds by 125 times,” says Shoji.
Source: NTT Group
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Nearly two weeks ago, NTT Docomo Business and NTT Com Asia launched the APN InterLink service, which is targeted at Hong Kong’s financial services sector. This all optical/photonic network, promised in the late 1990s, eliminates Optical to Electrical to Optical (OEO) repeaters, thereby greatly improving transmission performance.
“As an all-photonic solution, data is transmitted entirely at the speed of light with minimal conversion, resulting in significantly reduced latency and jitter. This capability enables mission-critical applications such as real-time trading and advanced AI workloads,” said Steven So, chief technology officer at NTT Com Asia.
So noted that recent performance tests have shown that an all-photonic network substantially improves upon a traditional setup.
In Japan, NTT Data and NTT West collaborated with MUFG Bank to conduct a successful test of APN during a live IT migration involving multiple data centers situated 50km to 100km apart. The demonstration included long-distance, synchronous database management system replication between locations up to 2,500km apart. The results showed less than one second of downtime.
“This highlights how APN addresses next-generation infrastructure requirements of the financial services sector,” So said. ” IOWN APN can deliver ultra-low latency, high-capacity, and energy-efficient network photonics-based connectivity to address their needs – where every millisecond counts in the digital world.”
References:
https://www.ntt.com/business/services/xmanaged/lp/itsmf/202511-nttcom.html
https://group.ntt/en/group/iown/function/
NTT pins growth on IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network)
Sony and NTT (with IOWN) collaborate on remote broadcast production platform
RAN silicon rethink – from purpose built products & ASICs to general purpose processors or GPUs for vRAN & AI RAN
The global RAN market has been declining for several years, putting pressure on network equipment vendors to cut costs and rethink their commitment to purpose built/custom RAN silicon products or ASICs. In 2022, the market for RAN equipment and software generated about $45 billion in revenues, according to research by Omdia, an Informa company. By 2024, annual revenue had tumbled to $35 billion – a 22.22% drop (and even worse in real dollars when you include inflation). As a result. it has become harder to justify the cost of expensive purpose-built silicon for the shriveling RAN market sector.

The Radio Access Network (RAN) is the segment of the mobile network interfacing the end-users and the mobile core network. In it’s IMT 2020 and IMT 2030 recommendations, ITU-R refers to the interface between a wireless endpoint and RAN equipment (base station or small cell) as the Radio Interface Technology or RIT). The core network specifications all come from 3GPP which has ETSI rubber stamp them.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ericsson and Samsung appear increasingly reliant on Intel for RAN silicon, while Nokia has been dependent on Marvell, but is planning to use NVIDIA GPUs in the near future (much more below). Let’s look at RAN silicon offerings from Intel, Marvell and NVIDIA:
-
Key RAN silicon offerings from Intel include:
- Intel Xeon with Intel vRAN Boost: The primary processors for network and edge applications include specific Intel Xeon 6 SoCs (System-on-Chips) that integrate Intel’s vRAN Boost accelerators directly on the die. This integration helps offload demanding Layer 1 (physical layer) processing, such as forward error correction, from the general-purpose CPU cores.
- Integrated Accelerators: These built-in accelerators are designed to improve performance-per-watt and increase capacity for RAN workloads. Intel’s approach is to provide high performance using common, off-the-shelf hardware with specialized acceleration, contrasting with other approaches that might rely entirely on general-purpose CPUs.
- FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Arrays): Through its acquisition of Altera, Intel offers FPGAs which can also be used in some RAN applications, allowing for flexible, programmable hardware solutions.
- Intel has a significant market share in 5G base station silicon and its upcoming Granite Rapids processors (part of the Xeon 6 family) are being developed to maintain its strong position in this market, including for Massive MIMO applications. The company faces strong competition, but its next-generation processors aim to improve performance and efficiency for both core and edge computing in 5G networks. massive MIMO into future chips, such as the upcoming Granite Rapids generation.
- OCTEON Fusion Processors: These are baseband processors optimized for cost, power, and programmability, widely used in both traditional and Open RAN (O-RAN) architectures. The latest iteration, the OCTEON 10 Fusion processor, provides comprehensive in-line 5G Layer 1 acceleration, enabling RAN virtualization in cloud data centers.
- OCTEON Data Processing Units (DPUs): The OCTEON TX2 and OCTEON 10 families are multi-core ARM-based processors that handle 5G transport processing, security, and edge inferencing for the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC). They incorporate hardware accelerators for AI/ML functions, enabling optimized edge processing.
- AtlasOne Chipset: This is a 50Gbps PAM4 DSP (Digital Signal Processor) and TIA (Transimpedance Amplifier) chipset solution for 5G fronthaul, optimized for high performance and power efficiency in integrated, O-RAN, and vRAN architectures.
- Ethernet Switches and PHYs: Marvell’s Prestera switches and Alaska Ethernet physical layer (PHY) devices are used in carrier infrastructure to provide the necessary networking connectivity for 5G base stations and data centers.
- Marvell also works with partners to integrate its technology into accelerator cards, such as the Dell Open RAN Accelerator Card powered by the OCTEON Fusion platform, to provide carrier-grade vRAN solutions. Furthermore, Marvell offers custom ASIC design services for hyper-scalers and telecom customers who need highly optimized, specific silicon solutions for their unique 5G and AI infrastructure requirements.
3. NVIDIA’s new silicon platform for AI Radio Access Networks (AI-RAN) is the NVIDIA Aerial RAN Computer, which is built on the next-generation Blackwell architecture. The primary system for AI-RAN deployment is the NVIDIA Aerial RAN Computer-1, which utilizes the NVIDIA GB200 NVL2 platform.
Key NVIDIA RAN components and features include:
- NVIDIA Blackwell GPU: The core graphics processor that features 208 billion transistors and provides significant performance improvements for AI and data processing workloads compared to previous generations.
- NVIDIA Grace CPU: The GB200 NVL2 platform combines two Blackwell GPUs with two NVIDIA Grace CPUs, connected by a high-speed NVLink-C2C (Chip-to-Chip) interconnect to form a powerful, unified superchip.
- NVIDIA Aerial Software: The hardware runs a full software stack that includes NVIDIA Aerial CUDA-Accelerated RAN libraries and NVIDIA AI Enterprise software for 5G and future 6G networks.
- Specialized Networking: The platform uses NVIDIA BlueField-3 Data Processing Units (DPUs) for real-time data transmission and precision timing, and NVIDIA Spectrum-X Ethernet for high-speed networking, which are critical for RAN performance.
- The goal of this platform is to enable wireless telcos to run both traditional RAN and AI workloads concurrently on a common, energy-efficient, software-defined infrastructure, thereby creating new revenue opportunities and preparing for 6G.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
To many stakeholders, piggybacking on the general purpose processors used in PCs and data centers might be more sensible, but that would require Virtual RAN (vRAN), which replaces custom silicon with such general-purpose processors. However, it is a very small share of the RAN compute or baseband subsector. Omdia says it was just 10% in 2023, but the market research firm expects that share to more than double by 2028. It that forecast pans out, vRAN could conceivably replace some of the custom RAN silicon business with general purpose processors.
Lat year, Ericsson allocated approximately $5.7 billion of its R & D budget to design and development of ASICs for Layer 1 (PHY), the most demanding part of the baseband. It relies on Intel for other RAN silicon functionality. If virtual RAN claims a bigger share of a low- or no-growth market, Ericsson’s returns on the same level of investment in ASICs would decline because they wouldn’t be needed for vRAN. Also, Intel’s Granite Rapids could markedly narrow the performance and cost gap with purpose-built RAN chips.
“We are doing trials on many platforms,” said Per Narvinger, the head of Ericsson’s mobile networks business group, in reference to that taste testing of different chips. “But the more important thing is that we have actually created this disaggregation of and separation of hardware and software.”
The aim is to have a set of RAN software deployable on multiple hardware platforms. However, that is not achievable with ASICs, which create a tight union between hardware and software (they are inextricably tied together). The general-purpose options identified by Narvinger were AMD, Intel and Nvidia. Currently, Intel remains Ericsson’s sole silicon commercial vendor. Despite Ericsson’s professed enthusiasm for )single vendor) open RAN, its business today is nearly all about purpose-built 5G.
In sharp contrast, Samsung’s retreat from custom RAN silicon has appeared rapid. It is without doubt the biggest mainstream vendor of virtual RAN products, and there is barely interest in the purpose-built 5G technology it has developed with Marvell. The RAN that Samsung has built for Verizon in the US is entirely virtual. It is about to do the same in parts of Europe for Vodafone. Canada’s Telus purchases both virtual and purpose-built 5G products from Samsung. But Bernard Bureau, the operator’s vice president of wireless strategy, says the virtual now outperforms the traditional and is also significantly less expensive. The processors, as in the case of Ericsson, come exclusively from Intel.
- Ericsson’s primary concern likely centers on the hardware architecture utilized for Forward Error Correction (FEC), a resource-intensive Layer 1 function. While Intel’s Granite Rapids and preceding platforms integrate the FEC accelerator directly within the main processor, AMD provides this functionality via an external accelerator card. Ericsson has historically favored integrated solutions, citing the use of separate cards as an added expense.
- Samsung is evaluating virtualized RAN software that potentially obviates the need for a dedicated hardware accelerator when deployed on AMD’s high-core-count processors. Samsung is confident that the increased core density of AMD’s offerings can manage the computational load of a software-only FEC implementation, and a commercial offering may be imminent. Samsung’s transition to AMD processors from Intel would require minimal changes to existing software written for Intel’s x86 instruction set architecture.
Nokia’s situation is more complicated due to NVIDIA’s recent $1 billion investment in the company. An apparent condition is that Nokia will designing 5G and 6G network equipment that uses Nvidia’s GPUs. As we noted in yesterday’s IEEE Techblog post, many telcos regard those GPUs as an expensive and energy-hungry component, which makes using them a risky move by Nokia. Presumably, Nokia cannot use the money it has received from NVIDIA to develop 5G Advanced and 6G software specifically for Marvell’s special purpose RAN silicon. If Nokia develops RAN software that runs on NVIDIA GPUs it conceivably could be repurposed for another GPU platform rather than specialized RAN silicon or an ASIC. And the only viable GPU alternative to NVIDIA at this time (outside of China) is AMD.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/slow-death-of-custom-ran-silicon-opens-doors-for-amd
Omdia on resurgence of Huawei: #1 RAN vendor in 3 out of 5 regions; RAN market has bottomed
China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
Intel FlexRAN™ gets boost from AT&T; faces competition from Marvel, Qualcomm, and EdgeQ for Open RAN silicon
Analysis: Nokia and Marvell partnership to develop 5G RAN silicon technology + other Nokia moves
Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison, Nokia and Nvidia AI-RAN research center in Indonesia amongst telco skepticism
Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison (Indosat) Nokia, and Nvidia have officially launched the AI-RAN Research Centre in Surabaya, a strategic collaboration designed to advance AI-native wireless networks and edge AI applications across Indonesia. This collaboration, aims to support Indonesia’s digital transformation goals and its “Golden Indonesia Vision 2045.” The facility will allow researchers and engineers to experiment with combining Nokia’s RAN technologies with Nvidia’s accelerated computing platforms and Indosat’s 5G network.

According to the partners, the research facility will serve as a collaborative environment for engineers, researchers, and future digital leaders to experiment, learn, and co-create AI-powered solutions. Its work will centre on integrating Nokia’s advanced RAN technologies with Nvidia’s accelerated computing platforms and Indosat’s commercial 5G network. The three companies view the project as a foundation for AI-driven growth, with applications spanning education, agriculture, and healthcare.
The AI-RAN infrastructure enables high-performance software-defined RAN and AI workloads on a single platform, leveraging Nvidia’s Aerial RAN Computer 1 (ARC-1). The facility will also act as a distributed computing extension of Indosat’s sovereign AI Factory, a national AI platform powered by Nvidia, creating an “AI Grid” that connects datacentres and distributed 5G nodes to deliver intelligence closer to users.
Nezar Patria, vice minister of communication and digital affairs of the Republic of Indonesia said: “The inauguration of the AI-RAN Research Centre marks a concrete step in strengthening Indonesia’s digital sovereignty. The collaboration between the government, industry, and global partners such as Indosat, Nokia, and Nvidia demonstrates that Indonesia is not merely a user but also a creator of AI technology. This initiative supports the acceleration of the Indonesia Emas 2045 vision by building an inclusive, secure, and globally competitive AI ecosystem.”
Vikram Sinha, president director and CEO of Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison said: “As Indonesia accelerates its digital transformation, the AI-RAN Research Centre reflects Indosat’s larger purpose of empowering Indonesia. When connectivity meets compute, it creates intelligence, delivered at the edge, in a sovereign manner. This is how AI unlocks real impact, from personalised tutors for children in rural areas to precision farming powered by drones. Together with Nokia and Nvidia, we’re building the foundation for AI-driven growth that strengthens Indonesia’s digital future.”
From a network perspective, the project demonstrates how AI-RAN architectures can optimize wireless network performance, energy efficiency, and scalability through machine learning–based radio signal processing.
Ronnie Vasishta, senior vice president of telecom at Nvidia added: “The AI Grid is the biggest opportunity for telecom providers to make AI as ubiquitous as connectivity and distribute intelligence at scale by tapping into their nationwide wireless networks.”
Pallavi Mahajan, chief technology and AI officer at Nokia said: “This initiative represents a major milestone in our journey toward the future of AI-native networks by bringing AI-powered intelligence into the hands of every Indonesian.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Wireless Telcos are Skeptical about AI-RAN:
According to Light Reading, the AI RAN uptake is facing resistance from telcos. The problem is Nvidia’s AI GPUs are very costly and not GPUs power-efficient enough to reside in wireless base stations, central offices or even small telco data centers.
Nvidia references 300 watts for the power consumption of ARC-Pro, which is much higher than the peak of 40 watts that Qualcomm claimed more than two years ago for its own RAN silicon when supporting throughput of 24 Gbit/s. How ARC-Pro would measure up on a like-for-like basis in a commercial network is obviously unclear.
Nvidia also claims a Gbit/s-per-watt performance “on par with” today’s traditional custom silicon. Yet the huge energy consumption of GPU-filled telco data centers does not bear that out.
“Is there a case for a wide-area indiscriminate rollout? I am not sure,” said Verizon CTO Yago Tenorio, during the Brooklyn 6G Summit, another telecom event, last week. “It depends on the unit cost of the GPU, on the power efficiency of the GPU, and the main factor will always be just doing what’s best for the basestation. Don’t try to just overcomplicate the whole thing monetizing that platform, as there are easier ways to do it.”
“We have no way to justify a business case like that,” said Bernard Bureau, the vice president of wireless strategy for Canada’s Telus, at FYUZ. “Our COs [central offices] are not necessarily the best places to run a data center. It would mean huge investments in space and power upgrades for those locations, and we’ve got sunk investment that can be leveraged in our cell sites.”
Light Reading’s Iain Morris wrote, “Besides turning COs into data centers, operators would need to invest in fiber connections between those facilities and their masts.”
How much spectral efficiency can be gained by using Nvidia GPUs as RAN silicon?
“It’s debatable if it’s going to improve the spectral efficiency by 50% or even 100%. It depends on the case,” said Tenorio. Whatever the exact improvement, it would be “really good” and is something the industry needs, he told the audience.
In April, Nokia’s rival Ericsson said it had tested “AI-native” link adaptation, a RAN algorithm, in the network of Bell Canada without needing any GPU. “That’s an algorithm we have optimized for decades,” said Per Narvinger, the head of Ericsson’s mobile networks business group. “Despite that, through a large language model, but a really small one, we gained 10% of spectral efficiency.”
Before Nvidia invested in Nokia, the latter claimed to have sufficient AI and machine-learning capabilities in the custom silicon provided by Marvell Technology, its historical supplier of 5G base station chips.
Executives at Cohere Technology praises Nvidia’s investment in Nokia, seeing it as an important AI spur for telecom. Yet their own software does not run on Nvidia GPUs. It promises to boost spectral efficiency on today’s 5G networks, massively reducing what telcos would have to spend on new radios. It has won plaudits from Vodafone’s Pignatelli as well as Bell Canada and Telstra, both of which have invested in Cohere. The challenge is getting the kit vendors to accommodate a technology that could hurt their own sales. Regardless, Bell Canada’s recent field trials of Cohere have used a standard Dell server without GPUs.
Finally, if GPUs are so critical in AI for RAN, why has neither Ericsson or Samsung using Nvidia GPU’s in their RAN equipment?
Morris sums up:
“Currently, the AI-RAN strategy adopted by Nokia looks like a massive gamble on the future. “The world is developing on Nvidia,” Vasishta told Light Reading in the summer, before the company’s share price had gained another 35%. That vast and expanding ecosystem holds attractions for RAN developers bothered by the diminishing returns on investment in custom silicon.”
“Intel’s general-purpose chips and virtual RAN approach drew interest several years ago for all the same reasons. But Intel’s recent decline has made Nvidia shine even more brightly. Telcos might not have to worry. Nvidia is already paying a big 5G vendor (Nokia) to use its technology. For a company that is so outrageously wealthy, paying a big operator to deploy it would be the next logical step.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://capacityglobal.com/news/indosat-nokia-and-nvidia-launch-ai-ran-research-centre-in-indonesia/
https://www.telecoms.com/ai/indosat-nokia-and-nvidia-open-ai-ran-research-centre-in-indonesia
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/nokia-and-nvidia-s-ai-ran-plan-hits-telco-resistance
https://resources.nvidia.com/en-us-aerial-ran-computer-pro
Nvidia pays $1 billion for a stake in Nokia to collaborate on AI networking solutions
Dell’Oro: AI RAN to account for 1/3 of RAN market by 2029; AI RAN Alliance membership increases but few telcos have joined
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
Dell’Oro: RAN revenue growth in 1Q2025; AI RAN is a conundrum
The case for and against AI-RAN technology using Nvidia or AMD GPUs
AI RAN Alliance selects Alex Choi as Chairman
AST SpaceMobile to deliver U.S. nationwide LEO satellite services in 2026
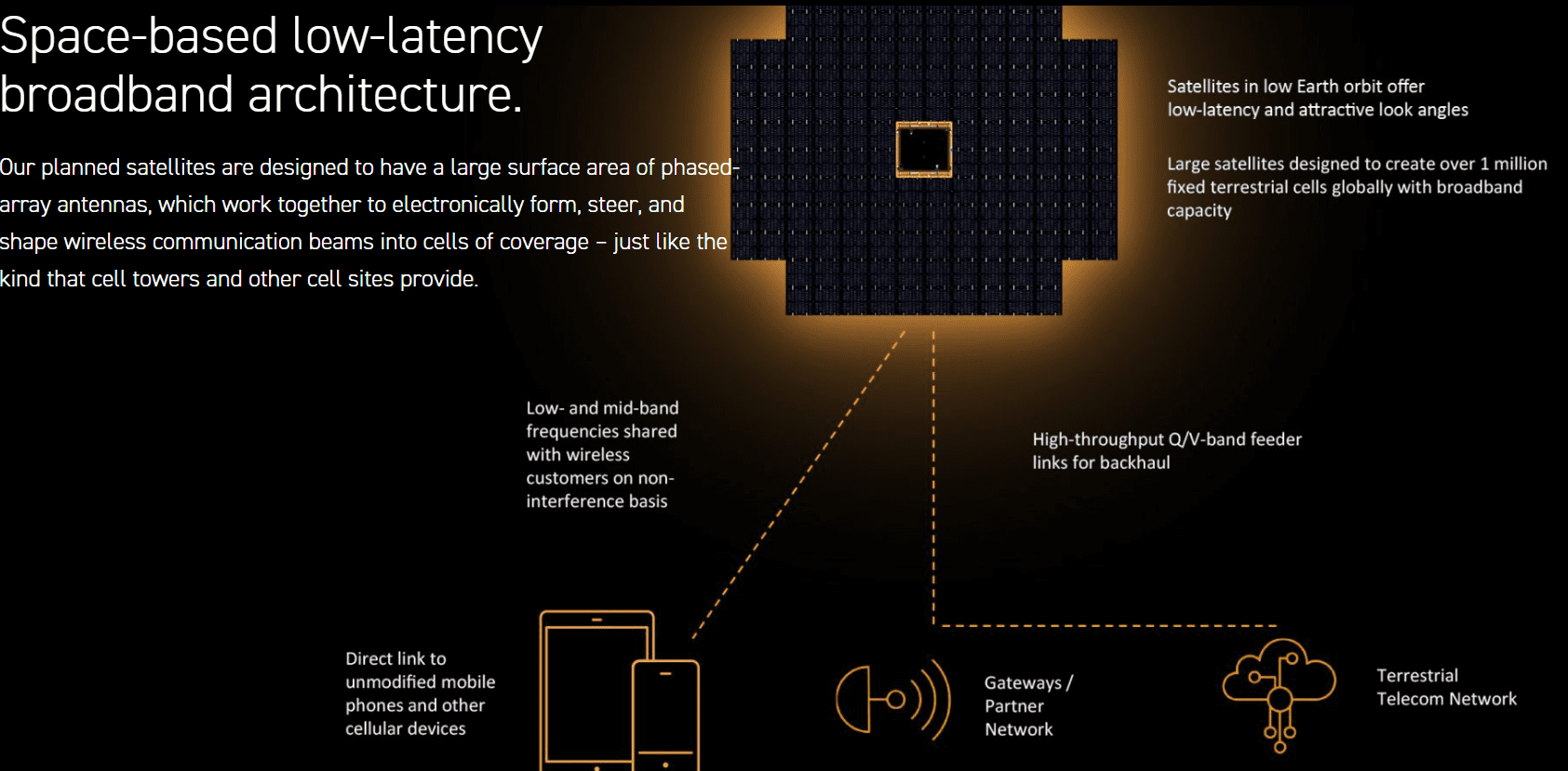
LEO satellite broadband startup AST SpaceMobil Inc. has secured over $1 billion in total contracted revenue commitments from commercial partners, demonstrating strong commercial traction. The company has signed definitive commercial agreements with major telecom operators such as Verizon, AT&T and Saudi Telecom Group (stc) for direct-to-device (D2D) services, thereby expanding its commercial ecosystem. All told, AST has commercial agreements with over 50 mobile network operators with nearly 3 billion subscribers globally.
The company has strengthened its financial position with over $3.2 billion in cash and liquidity, ensuring funding for its satellite constellation and global service expansion. While it has yet to generate revenue from its LEO satellite broadband service, it reported $14.7 million revenue in the third quarter, up from $1.1 million in the previous year, driven by gateway sales to operators and US government contracts.
Importantly, AST said it expects to deliver “intermittent nationwide” LEO satellite service in selected markets in early 2026 with “continuous” service planned for later in 2026 as more satellites are added, according to CEO Abel Avellan, speaking on the company’s third quarter earnings call. In particular:
“We expect to continue scale deployment efforts early next year as we progress activation of an intermittent nationwide service by early 2026 and prepare for continued service later in 2026.”
AST remains committed to its target to have 45 to 60 BlueBird satellites in orbit by the end of 2026, which would enable continuous service across the US, Europe, Japan and “other strategic markets.” Longer-term, the aim is to expand the service to “all targeted” markets with 90 satellites.
Five launches for AST’s next generation BlueBird satellites are planned to take place by the end of the first quarter in 2026, after which launches will be once every one or two months to meet the goal of 45 to 60 satellites in orbit. Of the initial five launches, the first is scheduled for mid-December from India and the remaining four will be from Cape Canaveral with partners SpaceX and Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin. The latter’s New Glenn rocket can take up to eight BlueBird satellites while SpaceX’s Falcon 9 can carry up to three satellites.
Source: AST SpaceMobile website
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Avellan also said on the call:
“We showcased Canada’s first successful space-based direct-to-cell voice-over LTE call, video call, and other broadband data and video streaming activations. We believe Canada will represent another attractive market for our direct-to-device cellular broadband service. Space-based cellular broadband connectivity is an industry that we invented, and a recent technology milestone with Verizon and Bell follows several breakthroughs using our direct-to-device technology, including the first-ever 4G and 5G voice calls, voice-over LTE calls, live video calls, streaming, full internet access, and tactical non-terrestrial network connectivity for military and defense purposes, from space to modified smartphones.”
“Our direct-to-device cellular broadband network will help our partners deliver on one of their highest priorities, which is extending connectivity for their customers as part of our effort to deliver on those priorities. We are advancing partners and ecosystem network integration as we progress towards service activation in key partner markets.”
AST has ramped up manufacturing capacity so that it will produce six satellites per month from December, adding that these are “the largest satellites ever launched” into low Earth orbit (LEO). “We’re breaking a world record every time that we take a satellite out of the factory,” Avellan said.
The AST CEO is “very confident in the launch campaign.” The company has built 19 satellites so far and will have built 40 by around the end of March next year. “That matches very well with the launches that we had already financially committed and are in the manifest of our launch partners to take them,” Avellan added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
It should be noted that T-Mobile US started offering Starlink-based D2D services (called T-Satellite) in July this year. Therefore, AT&T and Verizon D2D services with AST will be many months behind their arch rival.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Andy Johnson, AST’s chief financial officer, described the company’s performance in 2025 as a time of “rapid growth” as it gets closer to its ambition to build its broadband satellite constellation. “The transition from an emerging R&D-focused startup to an operating company on the path to optimizing our manufacturing and launch cadence has been hard yet invigorating and gratifying work for our now nearly 1,800-person worldwide workforce,” he added.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://investors.ast-science.com/quarterly-results
https://ast-science.com/spacemobile-network/our-technology/
AT&T deal with AST SpaceMobile to provide wireless service from space
AST SpaceMobile: “5G” Connectivity from Space to Everyday Smartphones
AST SpaceMobile achieves 4G LTE download speeds >10 Mbps during test in Hawaii
AST SpaceMobile completes 1st ever LEO satellite voice call using AT&T spectrum and unmodified Samsung and Apple smartphones
AST SpaceMobile Deploys Largest-Ever LEO Satellite Communications Array
FCC Grants Experimental License to AST SpaceMobile for BlueWalker 3 Satellite using Spectrum from AT&T
Highlights and Summary of the 2025 Brooklyn 6G Summit
Last week’s Brooklyn 6G Summit, hosted by Nokia and the NYU Wireless research center, explored two critical pillars of 6G development: artificial intelligence (AI) and value creation. Speakers and panelists from technology, business, academia and regulation organizations came together to shape the future of wireless in a three-day event on the campus of the NYU Tandon School of Engineering.
More than 300 participants, including more than 60 speakers and panelists, attended this year’s gathering at the New York University (NYU) Brooklyn campus, and many more tuned in for the livestream, to provide an eclectic gathering of academia, industry analysts, service providers, equipment vendors and startups from various corners of the telecom industry. These included a wide swath of customers, partners, engineers and innovators, as well as representatives from Verizon Wireless, KDDI Research, Intel, NTT DOCOMO, Qualcomm, Axiom Space and more.
A series of keynote addresses, lively panels and physical demonstrations showcased a wide range of 6G topics surrounding AI and value creation, such as energy efficiency, security, network digital twins, the integration of Non-Terrestrial Networks and more.
Nokia President and CEO Justin Hotard (x-Intel) led off in a recorded fireside chat with Nokia’s new chief technology and AI officer Pallavi Mahajan, in which he described how Nokia will be at the heart of a new hyper-digital 6G world and the AI Super-cycle and AI-Native networks that will accompany it. “What’s going to change as we look ahead is the opportunity for AI to be a bridge between the physical and the digital world. We realize that for networks to be valuable in this world they need to actually be different. They need to be designed from the start for AI.”
The evolution from 5G (IMT 2020) to 6G (IMT 2030) is expected to generate faster speeds, lower latency and better performance. But 6G looks to offer much more value in creating a fusion of the digital, physical and human worlds, according to Summit participants.
NVIDIA Senior Vice President Ronnie Vasishta highlighted the centrality of AI to the 6G future: “6G really distributes AI to the entire population and enterprises. It’s the connectivity fabric for AI, and it cannot be underestimated how important that is,” he said. “When you look at a dynamic world and you also start to use the network as a sensor, AI becomes essential. It’s very different from the 5G world.”
Arpit Mehta, the Head of Americas Carrier Product Management at Meta, discussed the future of immersive experience with AI glasses, while wearing a pair of futuristic spectacles on his face as he described what they could do.
“6G, so far, in my view needs to solve two priorities: the uplink problem and the device problem,” said Yago Tenorio, SVP Strategy at Verizon Wireless, explaining what needed to be done to unlock the vast 6G potential. “What matters to the customer is: give him a native, cellular, connected sensor network that he can deploy around him in any way he wants.”
Lively panel discussions included those on AI data, the role of verticals in 6G value creation and the impact of large telco models and network digital twins.
There was also a special segment devoted to the Nokia Bell Labs centennial celebration, in which Nokia Bell Labs President for Core Research Peter Vetter outlined how the 6G advancements of today stand on the shoulders of giants from the past 100 years of Bell Labs technology. “The big innovations that happened at Bell Labs in our 100-year history shaped our wireless industry,” Vetter said. “But we are not only reflecting on what happened in the past, we reflect and highlight what we are doing to shape the next 100 years. And that starts for the 6G era in the next decade.”
The summit included nearly 40 demonstrations from Nokia and participating companies, showcasing the vast potential of future 6G networks. It also featured an Open House, where NYU Wireless students showcased a wide range of cutting-edge technologies on campus, such as nanotech labs, various robotic arms, robots and even robotic dogs. Later, some of these same students took on their professors in the first 6G Brooklyn Summit Game Show. The Jeopardy-style game included categories such as history, fundamentals, spectrum, 6G, AI/ML and Non-Terrestrial Networks. In a crowd-pleasing upset, which bode well for the future of technology, the students emerged victorious by a decisive margin. In was an outcome that did not trouble in the least one of the professors who participated.
“We always want our students to do better than we did, so I’m delighted they beat us,” said NYU Wireless founder Ted Rappaport. One of the main characteristics of the Brooklyn 6G Summit is the focus on strong collaboration between industry and academia to shape the future 6G-era together. Appropriately, the opening panel was devoted to the U.S. academic view of 6G. “When you bring people together when there is a new technology, you can make great strides,” Rappaport added. “It’s how you build a comfort level and a consensus on what’s most important. We are doing that for 6G.”
The summit honored several trailblazers in telecommunication technology. The annual Pioneer Award was presented to Dave Forney, namesake of the influential Forney algorithm in coding theory and the inventor of the modern modem. The Lifetime Academic Achievement Award was bestowed upon Prof. Andrea Goldsmith, the president of Stony Brook University (SBU) and the former Dean of Engineering and Applied Science at Princeton, who shared her captivating life story and trailblazing path as a female technologist in a celebratory dinner in her honor.
It all added up to what Head of Nokia Standards Peter Merz said was a hopeful message for the future. “We had candid discussions with excellent people that are moving the ecosystem forward. There is still a lot of work to be done but I am confident that we as a community will make it happen,” he concluded.
References:
https://www.nokia.com/blog/the-12th-brooklyn-summit-marks-a-tipping-point-toward-the-6g-era/
Nokia Bell Labs and KDDI Research partner for 6G energy efficiency and network resiliency
Nokia and Rohde & Schwarz collaborate on AI-powered 6G receiver years before IMT 2030 RIT submissions to ITU-R WP5D
Nvidia pays $1 billion for a stake in Nokia to collaborate on AI networking solutions
Nokia Bell Labs and KDDI Research partner for 6G energy efficiency and network resiliency
Nokia Bell Labs and KDDI Research have partnered to advance 6G technology, focusing on improving network energy efficiency and resilience. The collaboration combines KDDI’s real-world network data and operational insights with Nokia Bell Labs’ expertise in energy consumption models and programmable network architectures. This joint research agreement, signed on November 5, 2025, builds on a long history of cooperation and aims to accelerate the development and deployment of sustainable, intelligent 6G networks.
Under this new agreement, the two companies are conducting research in two key areas of 6G:
- mMIMO energy efficiency: New techniques for reducing base-station energy consumption while enhancing communication, specifically targeted at proposed 6G spectrum.
- Distributed programmable core network services for 6G: New mobile core technologies that will ensure continuous communication during infrastructure failures and natural disasters.
KDDI Research and Nokia Bell Labs will demonstrate their initial work in mMIMO energy efficiency at the Brooklyn 6G Summit Nov 5 – 7.
Peter Vetter, President, Core Research, Nokia Bell Labs:
“Tackling the inherent challenges in a new generation of networking requires close collaboration in the industry. Working side by side, KDDI Research and Nokia Bell Labs can advance the state of the art in networking thanks to different perspectives on the problems and possible solutions. Ultimately, the joint outcomes will make 6G a more resilient, efficient and intelligent technology.”
Satoshi Konishi, President and CEO, KDDI Research:
“Through our strategic and close collaboration with Nokia Bell Labs, we aim to accelerate R&D initiatives and further strengthen the ‘Power to Connect’ toward 6G. We strive to continuously deliver new value to our customers and make meaningful contributions to societal progress.”
References:
KDDI unveils AU Starlink direct-to-cell satellite service
KDDI Partners With SpaceX to Bring Satellite-to-Cellular Service to Japan
KDDI Deploys DriveNets Network Cloud: The 1st Disaggregated, Cloud-Native IP Infrastructure Deployed in Japan
AWS Integrated Private Wireless with Deutsche Telekom, KDDI, Orange, T-Mobile US, and Telefónica partners
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
Nokia’s Bell Labs to use adapted 4G and 5G access technologies for Indian space missions
Nokia and Rohde & Schwarz collaborate on AI-powered 6G receiver years before IMT 2030 RIT submissions to ITU-R WP5D
Highlights of Nokia’s Smart Factory in Oulu, Finland for 5G and 6G innovation
Will the wave of AI generated user-to/from-network traffic increase spectacularly as Cisco and Nokia predict?
Nokia Bell Labs claims new world record of 800 Gbps for transoceanic optical transmission
Nokia Bell Labs sets world record in fiber optic bit rates