Ericsson to build 5G network in Greenland; demos 5G microwave backhaul with O2 Telefónica
Swedish telecom equipment maker Ericsson has been contracted to build a 5G network in Greenland, initially covering three towns, local telecom service provider Tusass said on Friday.
Deploying Ericsson equipment and Netgear routers, Tusass will bring high-speed wireless internet to the sparsely populated island without resorting to expensive and hard-to-deploy cables, the company said. A further 10 towns, including Greenland’s capital Nuuk, are set to follow next.
Tusass said it plans to invest around 1 billion Danish crowns ($131.3 million) to secure and expand Greenland’s infrastructure and improve communication.
Greenland, an island of just 56,000 people, is part of the Kingdom of Denmark but has broad autonomy.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Ericsson and O2 Telefónica successfully demo 5G wireless backhaul for non-urban areas. In the latest of their joint projects in mobile transport, Ericsson and O2 Telefónica have successfully demoed 5G wireless backhaul for rural and suburban coverage. This technology milestone has shown that the companies can deliver speeds of up to 10 Gbps over a distance of more than 10 km and demonstrate fiber-like microwave connectivity.

The result of this important demo showed that microwave backhaul over traditional bands can support the continued build-out of high-performing 5G networks and enhanced mobile broadband services from urban to suburban and rural areas – one of the key challenges facing communications service providers in scaling up their 5G deployment.
“We deliver fast mobile 5G connections to millions of customers across Germany. Bringing digitalization to suburban and rural areas through mobile connectivity and fast 5G network rollout has therefore priority for us,” says Aysenur Senyer, Director of Transport Networks at O2 Telefónica.
“Together with our partner Ericsson, we are pioneering new powerful microwave solutions using Carrier Aggregation and MIMO technology to backhaul 5G traffic over long distances in rural areas, when fiber is not an option. This type of technology enables us to deliver fiber-like connectivity via microwave and further accelerate our 5G deployment.”
Ricardo Queirós, Head of Microwave Systems, Business Area Networks, Ericsson, says: “Access to high-speed mobile services is key to bridging the digital divide. This joint demo with O2 Telefónica in Germany demonstrates how microwave backhaul can efficiently spread high-performing 5G to regions outside the traditional dense urban areas.”
“Wireless backhaul has been instrumental to the success of mobile networks and their nationwide coverage. Now it is time to push the boundaries and evolve microwave transmission technology to enable high-performance 5G coverage on a much broader scale,” Queirós adds.
The shift to working from home during the Covid-19 pandemic illustrated the need for fast and reliable connectivity in non-urban environments, and the challenge has been to maintain telecom-grade availability beyond distances of two to three kilometers.
The ability to deliver such high data speeds over distances of more than 10 km – the cruising altitude of a commercial jet – opens up a new world of possibilities for the delivery of low-latency, reliable broadband in harder-to-reach areas.
Traditionally, such areas have been difficult to service, as high capacities require broad bandwidths that usually only have been available in millimeter wave frequency bands (E-band). The E-band is more impacted by rain compared to the lower frequency bands, which makes it more difficult to deliver consistent service over long distances during adverse weather conditions.
Technical details
In the joint demo with O2 Telefónica in Germany, the key innovation is the ability to use MIMO with high modulation in the 112MHz channels (commercial MIMO solutions support up to 56 MHz channels), which were combined with Carrier Aggregation to enable similar capacities to E-band in the lower frequency bands. The demo solution has extended the hop-length with extremely high capacity even in less favorable weather conditions.
The backhaul link utilized the 18GHz frequency band, dual antennas in a MIMO configuration, and commercial MINI-LINK radios together with a pre-commercial baseband algorithm that allowed the use of MIMO in 2x 112 MHz channels. MIMO ensures the efficient use of limited spectrum resources. The same capacity without MIMO would demand a 448 MHz bandwidth in a cross-polar setup.
Microwave backhaul is commonly seen as a more cost- and time-efficient option compared to fiber deployment. The O2 Telefónica demo has shown that high availability and high capacity can also be achieved with wireless transport.
The demo is the latest in a series of collaborations with O2 Telefónica in Germany stretching back over several years. Ericsson is one of the service provider’s main suppliers in all areas of microwave technology and the two companies have carried out several successful joint projects around microwave technology, with more planned for the future.
References:
https://www.reuters.com/business/media-telecom/ericsson-wins-greenland-5g-deal-2022-09-30/
Deutsche Telekom Achieves End-to-end Data Call on Converged Access using WWC standards
Wireline and wireless services are delivered today from two distinct technology implementations with separate network cores. 5G WWC standards offer a path to a fully converged broadband access network that integrates wireless and wireline operations on a common 5G Core.
Using these 5G Wireless Wireline Convergence (WWC) standards [1.] in an industry first proof-of-concept, Deutsche Telekom has validated in a lab trial the feasibility of converging the fixed network control plane into a 5G Core to steer traffic from a 5G residential gateway in its Bonn laboratory. The traffic was then routed along the entire wireline access chain to the core network.
Note 1. The GSMA’s 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), the Broadband Forum (BBF) and CableLabs have united to create technical reports and specifications defining the services and systems required to support 5G wireless and wireline convergence (5G WWC) architectures. Their resulting work is detailed within BBF’s TR-456 (Fixed Mobile Convergence / FMC) and CableLabs WR-TR-5WWC-ARCH and rolled-up within 3GPP Release 16 Technical Specification TS 23.316. The IETF have also been engaged in providing guidance around user plane protocol revisions while the IEEE, ITU-T SG15 and Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) have been engaged with timing/synchronization requirements and other service specifications.
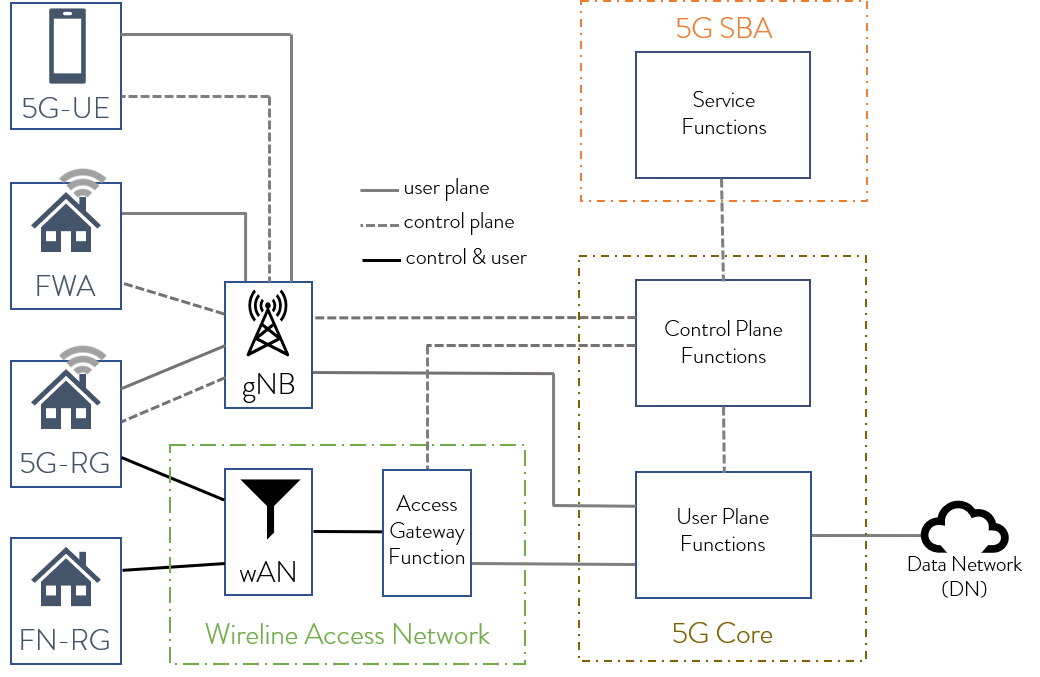
The Access Gateway Function (AGF) supporting wireless wireline convergence in a 5G Core
“Convergence will allow us to optimize our network assets and deliver new, differentiated service experiences to our customers regardless of the access used,” says Ahmed Hafez, VP Network Convergence, Deutsche Telekom. „Our tests prove the feasibility of the convergence architecture by controlling residential gateways in our fixed network from a common 5G Core.
It is critical now that the vendor ecosystem implements the standards into their product roadmaps, speeding up the time to market for end-to-end convergent solutions.”
The proof of concept was conducted on a trial system in Deutsche Telekom’s lab environment. For the 5G residential gateway, which provides the connection between the networked equipment within a home or small office to the 5G Core, a Deutsche Telekom developed prototype was used.
5G Core as common core:
CCA Conference: U.S. Regional Carriers Deploying 5G, actively looking at Fixed Wireless+ CTIA on 5G
Competitive Carriers Association (CCA) conference :
Small and regional carriers are taking different approaches to 5G and fixed wireless, said Eric Boudriau, Ericsson North America head-customer unit regional carriers, at the Competitive Carriers Association (CCA) [1.] conference on September 28th in Portland, OR. “Everybody starts from a different position,” he said. Fixed wireless is “really, really accelerating” in the U.S. and internationally, he said. Other executives stressed the importance of addressing federal infrastructure rules to better fund wireless. The discussion was streamed live from Portland, Oregon.
Note 1. CCA was founded in 1992 by nine rural and regional wireless carriers as a carrier centric organization. Since its founding, CCA has grown to become the nation’s leading association for competitive wireless providers serving all areas of the United States.
Alaska’s GCI deployed 5G in its first market in the spring of 2020, in the middle of the COVID-19 pandemic, said John Myhre, vice president-wireless technology. “We’ve done very well,” he said. “We are continuing to roll out 5G as we roll through different markets.” GCI hasn’t decided what spectrum bands it will use for a fixed-wireless offering, Myhre said. “As a fixed and mobile provider, we have options,” he said. “It’s making sure that we fit the market and the requirement against the technology, not try to force it. In Alaska, everything is just really big. Any project that we do is a big project.” GCI is laying fiber to reach the Aleutian Islands, he noted, in a $58 million project requiring more than 800 miles of undersea cable to reach rural markets.
“We are actively looking at fixed (wireless),” with trials to start in the next 18 months, he said. Wisconsin-based Cellcom launched 5G in February, said CEO Brighid Riordan. The carrier is deploying some fixed wireless using 4G and citizens broadband radio service spectrum and has found the roll out challenging, she said. “We love our trees in Wisconsin, we love the lakes,” she said. “When there’s a valley, when there are trees, it provides a challenge,” she said. Small carriers need government funding to reach some markets, Riordan said. “If it were easy to provide broadband to every rural person in America, it would already be done,” she said: “There’s not necessarily a business case for these very rural customers.”
UScellular is still deploying 5G, market-by-market, said Rebecca Thompson, vice president-government affairs. The carrier started with high-band, she said. “As we get access to some more of our mid-band spectrum we’ll have a much more robust 5G product in the future,” she said. When the provider will get some of its licenses remains to be determined. “There’s some clearing and coordination … and we will still have to actually get the licenses for some of that spectrum,” she said. Mid-band “has proven to really help with geographic reach in a cost effective way” and “is really critical to deploy in rural areas,” The “good news” is fixed wireless is “mature — it’s ready, it’s reliable, it’s offering speeds that people want at home,” Thompson said. It shouldn’t be a foregone conclusion” that the NTIA’s broadband, equity, access and deployment program won’t fund fixed wireless, she added.
UScellular wants to see “less of the thumb on the scale” favoring fiber, she said. Federal funds so far are biased toward fiber and the wireless industry has to fight for more neutral rules for making awards, Boudriau said. Fixed wireless may see the most deployment “where the government isn’t involved,” Myhre said: “We have areas where we may not get funding, but we still have a need.”
References:
https://www.cca-convention.org/
https://www.ccamobile.org/about-cca#AboutUs
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
CTIA at MWC-Las Vegas:
CTIA President Meredith Baker said Wednesday at the start of the Mobile World Congress in Las Vegas. “We’re here to talk about what 5G is,” she said: “5G is innovation. 5G is competition, and most importantly, 5G is here.”
Baker said the wireless industry needs “the right policies” from the government. “Take C band as proof,” she said. “Turning on a portion of that spectrum saw speeds increase up to 50%, and that was 100 MHz. Imagine what 150 or 200 more could do. Well, we shouldn’t have to imagine. … We need more mid-band — licensed mid-band in large contiguous blocks.” The wireless industry also needs Congress to extend the FCC’s auction authority, set to expire Friday, and designate more bands for auction, she said.
Baker also discussed the importance of fixed wireless. “For many Americans, the first 5G killer app is home broadband,” she said. “The fastest growing broadband provider is now a wireless company,” she said. U.S. wireless carriers already offer fixed service to 70 million homes, she noted.
More than 300 million AT&T customers are covered by 5G, all of the company’s major handsets support the new generation of wireless “and we’ve got business models being created,” said David Christopher, executive vice president-business development and strategic alliances. “But it is early days,” he said. Christopher spoke with Recon Analytics’ Roger Entner.
“We’re two years in,” Entner responded: “At this point in the 4G period we still thought that sending pictures was the killer app for 4G. We were wrong.” Deploying a new G “is not a 100-meter dash,” he said. “This will take years.”
“There’s a very good chance that we don’t know what the killer app for 5G is,” Christopher said. Augmented reality and the massive IoT will be important. The median speeds of 5G are already four times that of 4G two years ago, he said: “Latency is a stickier wicket. … It’s something that will certainly get better.” In some cases, better speed is “masking” the need for improved latency, he said.
Reference:
https://communicationsdaily.com/article/view?search_id=595619&id=1374622
Highlights of GSA Private-Mobile-Networks August 2022 report
A new report by the Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA), the Private-Mobile-Networks August 2022 report, has identified 66 MNO’s and 70 countries/territories where organisations are involved with private mobile network projects. This equates to 889 organisations deploying LTE or 5G Private Mobile Networks (PMN) in one or more locations – up from 794 reported in June 2022.
Manufacturing is the major adopter of Private Mobile Networks with 165 identified companies, growth of almost 50% from the end of 2021, with other strong interest from education, mining, and power utilities sectors.
LTE is the dominant technology, used in 672 of the private mobile networks for which GSA has data, whilst 5G is being deployed by 354 organisations. 5G Standalone currently accounts for just thirty-seven deployments.
The USA leads the way with the most organisations deploying private networks based on LTE or 5G, followed by Germany, China, the UK, and Japan.
Joe Barrett, President of the Global mobile Suppliers Association called private mobile networks a microcosm of the wider 4G and 5G ecosystem and reported “a strong positive correlation between liberalised spectrum and the adoption of private mobile networks.”
An executive summary of the report is available from the GSA website based on dataset of over 50 equipment vendors, 66 operators and 70 countries and territories.
References:
https://totaltele.com/private-mobile-network-deployments-now-in-70-countries/
C&W Networks Upgrades Pan Caribbean Submarine Cable Networks with Ciena
C&W Networks, a wholesale telecommunications service provider, announced an agreement with Ciena to upgrade its CFX-1 (Colombia-Florida Express) and EWC (East West Cable) submarine cable networks to deliver advanced broadband and IP services of up to 400Gb/s. These network upgrades will help address the soaring bandwidth needs of C&W Networks’ telco and internet service provider (ISP) customers.
C&W Networks operates the largest submarine multi-ring fiber-optic network in the greater Caribbean, Central American and Andean regions, providing reliable connectivity to approximately 40 countries. The 2400km CFX-1 express cable connects the United States, Jamaica and Colombia with less than 25ms latency, while the 1,700km EWC cable links the British Virgin Islands, Jamaica and the Dominican Republic.

“Online content, especially streaming video, continues to drive robust demand for data and high-speed connectivity in the regions we serve. The additional capacity we’re turning up on CFX-1 and EWC with Ciena allows us to meet this demand head-on, enriching our service offerings for customers while sustainably and cost-effectively extending the lifespan of these cable systems,” stated Chris Coles, Vice President and General Manager, C&W Networks.
Ciena’s GeoMesh Extreme, which utilizes the 6500 Packet-Optical Platform powered by WaveLogic 5 Extreme coherent optics, delivers C&W Networks’ new increased capacity with scalable service speeds on existing undersea systems. With Ciena’s latest technology, the CFX-1 cable connecting the U.S. with Colombia and Jamaica is transformed to provide a 10-fold capacity increase of over 32Tb/s with 100Gb/s–400Gb/s services.
Visibility and end-to-end management of the cable network is possible with Ciena’s Manage, Control and Plan (MCP) domain controller and Ciena Services provides deployment and reconfiguration services to accelerate time to revenue and ensure project success.
“C&W Networks’ submarine cables cross the ocean to bring the pan-Caribbean region new opportunities and economic growth through connectivity,” said Ian Clarke, Vice President of Global Submarine Solutions, Ciena. “With our GeoMesh Extreme, they’re able to do that while maximizing spectral efficiency and minimizing the cost-, space- and power-per-bit transported, resulting in lower total cost of ownership and greater competitive advantage.”
About C&W Networks
C&W Networks, part of Cable & Wireless Communications, Limited and wholly owned subsidiary of Liberty Latin America, Ltd, is a wholesale telecommunications service provider that offers broadband, IP capacity to global, regional and local telecom carriers, TV cable companies, Internet Service Providers and Network Integrators. C&W Networks operates the largest subsea multi-ring fiber-optic network throughout the greater Caribbean, Central American and Andean region along with the most comprehensive fully meshed MPLS network in the region. Connecting approximately 40 markets, the company’s fully protected ringed submarine fiber optic network spans more than 50,000 km. Cable routes include the Caribbean Optical-ring System (ARCOS-1), Colombia-Florida Express (CFX-1), EC-Link cable system, Fibralink, Maya 1, Eastern Caribbean Fiber System (ECFS), Taino-Carib, East-West Cable (EWC), Cayman-Jamaica Fiber System (CJFS), Caribbean-Bermuda U.S (CBUS), Americas II, Gemini Bermuda, Antillas 1, Pacific Caribbean Cable System (PCCS), and Amerigo Vespucci, Alonso De Ojeda, Saba Statia Cable System (SSCS). C&W Networks also operates terrestrial networks in the US and various Caribbean and LATAM markets. For more information, please visit www.cwnetworks.com.
About Ciena
Ciena is a networking systems, services and software company. We provide solutions that help our customers create the Adaptive Network™ in response to the constantly changing demands of their end-users. By delivering best-in-class networking technology through high-touch consultative relationships, we build the world’s most agile networks with automation, openness, and scale. For updates on Ciena, follow us on Twitter @Ciena, LinkedIn, the Ciena Insights blog, or visit www.ciena.com.
References:
AT&T wins another U.S. government contract: $119M to modernize CBP voice and data networks
AT&T said Monday it secured a contract valued at $119 million over 11 years, if all options are exercised, to modernize the U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s (CBP) voice and data networks. The contract is an expansion of AT&T’s work for the agency and the services will include virtual private networking services, cloud connectivity as well as national security and emergency preparedness services, among others.
CBP has tasked AT&T to modernize the agency’s voice and data networks supporting around 60,000 government employees including agents and other personnel. The agency awarded the order through the governmentwide Enterprise Infrastructure Solutions vehicle, AT&T said Monday.
“This new task order allows us to deliver our advanced communications capabilities to support the important work CBP’s agents do, day in and day out, to protect our nation at all points of entry: from our borders to airports and seaports,” Stacy Schwartz, a vice president for AT&T’s public sector and FirstNet business unit, said in a press release.
Examples of areas covered under the order include virtual private networking services, cloud connectivity, national security and emergency preparedness services, and unified communications. CBP can also use the order to acquire managed trusted Internet Protocol services, as well as IP-based voice capabilities.
U.S. Customs and Border Protection is one of the world’s largest law enforcement organizations with more than 60,000 employees. It is charged with keeping terrorists and their weapons out of the U.S. while facilitating lawful international travel and trade. On a typical day, CBP apprehends more than 1,000 individuals for suspected crimes; screens more than 1 million international travelers; prevents 404 dangerous pests from entering the U.S.; processes more than 74,000 truck, rail and sea containers; and seizes nearly 4 tons of illicit drugs.
CBP aims to enhance the nation’s security through innovation, intelligence, collaboration and trust. It requires reliable, highly secure voice and data communications among its agents to support its comprehensive approach to managing U.S. borders, customs operations, immigration, and agricultural protection. AT&T was selected to modernize CBP’s voice and data networks to support CBP’s mission objectives.

Image Credit: CBP
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In addition to the CBP contract, AT&T in April scored a $15 million contract to upgrade the Army National Guard’s command and control network. Prior to that, it secured $161 million to update and consolidate the U.S. Coast Guard’s data networks.
AT&T’s slew of government contracts also includes task orders from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the Department of Homeland Security, the Treasury Department and the Department of Transportation.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Regarding AT&T (T) as an attractive value investment, Petar Mirkovic wrote:
“We believe that a combination of the recently refocused strategy centered on its core competencies as a “stable and boring” telecom, a high dividend yield surpassing the U.S. average, and a substantial margin of safety thanks to a decade low investor sentiment creates great value for potential investors.”
References:
AT&T to Upgrade U.S. Customs and Border Protection Networks (att.com)
AT&T books $119M CBP network task order – Washington Technology
AT&T scoops up $119M contract to upgrade CBP network (fiercetelecom.com)
AT&T Stock: A Buy At All-Time Low Investor Sentiment (NYSE:T) | Seeking Alpha
Point Topic: Global Broadband Tariff Benchmark Report- 2Q-2022
In the twelve months to the close of Q2 2022, global residential fixed line broadband subscribers saw their average monthly charges decrease by 4% on copper, cable and fiber-based tariffs. Across the three technologies the average bandwidth increased by 22% year-on-year (y-o-y), due to the increased innovation and proliferation of fiber-based networks globally. Business subscribers continued to struggle with rising monthly charges, with the average monthly charge increasing by 12% and the average downstream speed standing at 426 Mbps compared to residential tariff averages of 464 Mbps.
The Asia-Pacific region retained its dominant bandwidth position with average speeds of 1,146 Mbps, up from 1,355 Mbps in Q4 2021 and 1,135 Mbps y-o-y, followed by North America, Western Europe, and Southeast Asia with the three regions reaching a combined average of around 465 Mbps.
Qatar, Switzerland and Southeast Asian countries still remain at the top of the league by average bandwidth along Italy, France and Bulgaria; these countries all rank in the top ten cheapest for residential broadband in terms of average cost per Mbps being less than $0.10 PPP.


In Q2 2022, the combined average download bandwidth grew by 20% compared to Q2 2021 and stood at 426 Mbps. This was caused by the boost in the average speed over cable and especially fibre, 14% and 22% respectively. Copper maintained largely the same average download speed compared to the previous quarter. However, the overall global average monthly cost across the three technologies has increased by just over 12% from $217 PPP to $244 PPP at the close of Q2 2022
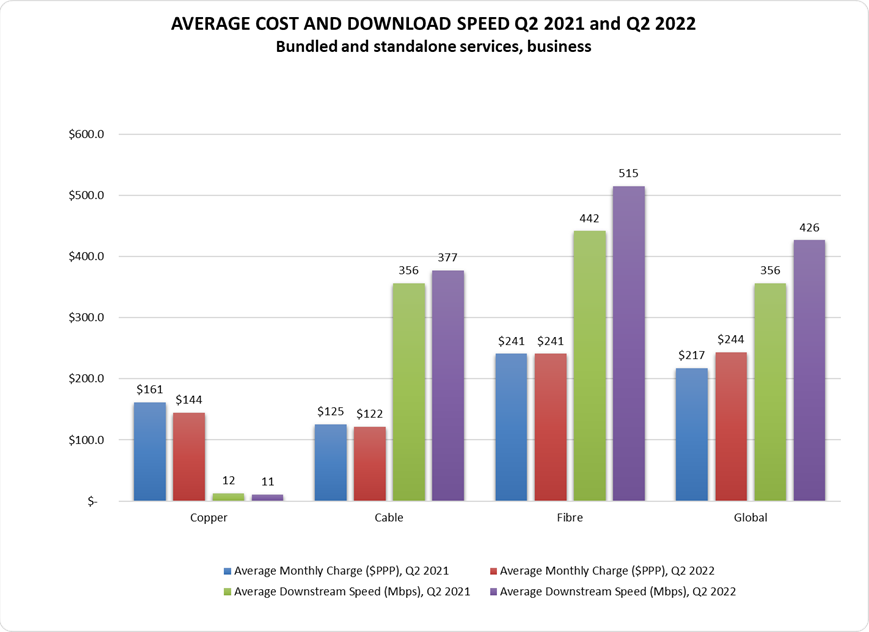

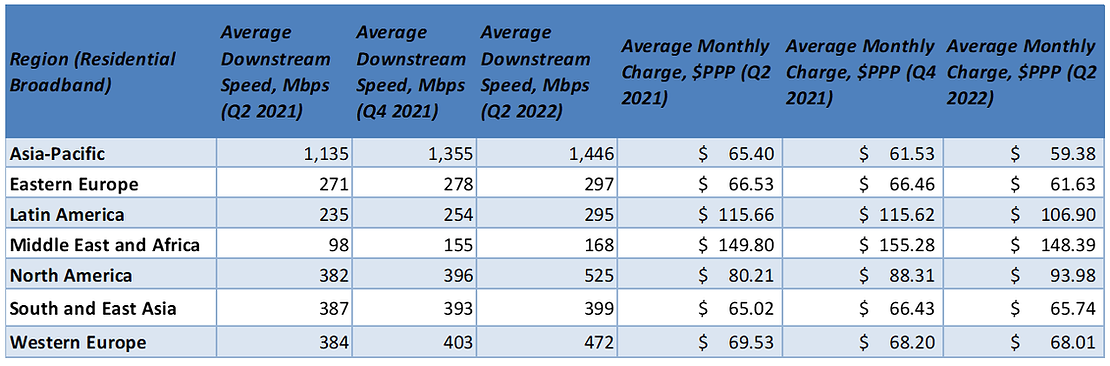


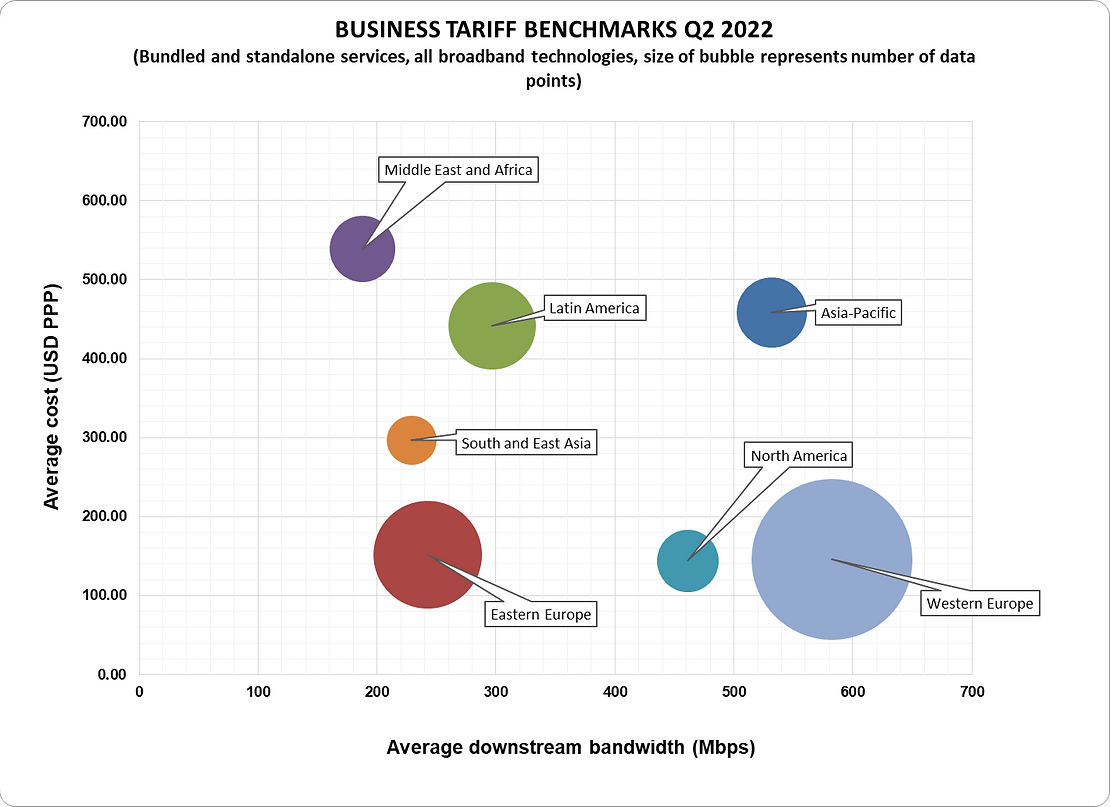
References:
Global Broadband Tariff Benchmark Report, Q2 2022 (point-topic.com)
Synergy & IDC: Hosted and Cloud Services are driving the Unified Communications & Collaboration Markets
In a new report, Synergy Research Group states that spending on premises and cloud collaboration grew 8% from 2021 and is now approaching $15 billion per quarter. The on-premise portion of the market continues to decline steadily and now accounts for only 20% of the total, down from 30% two years ago.
The transition from enterprise use of on-premise products to cloud and hosted services has also been a boon for the collaboration market, which has benefitted in a big way from increased demand due to the rise of hybrid working during the pandemic. It includes as-a-service (aaS) software such as UCaaS (unified communications), CCaaS (contact center) and CPaaS (communications platform). These three services together grew 17% from last year and now account for more than $7 billion in quarterly spending.

Based on worldwide Q2 revenues Microsoft is the overall leader in total collaboration and continues to hold a steady market share, thanks to a broad portfolio of collaboration products and services. Cisco is the overall number two ranked vendor but is seeing its market share under pressure from Microsoft and companies propelled by the Covid pandemic. The biggest challenger is Zoom, which is now the number three ranked vendor driven by extraordinary growth rates over the last four years. Twilio is the fourth biggest vendor and now has a growth rate far in excess of the other three, as it dominates the rapidly emerging CPaaS market. Twilio’s CPaaS revenue run rate has now reached $2.5 billion per year. Other major vendors with particularly high growth rates include RingCentral, NICE, Five9 and Sinch.
“The impacts of the pandemic opened a tremendous new market opportunity within collaboration, especially in video conferencing services and devices, rapidly driving change that would otherwise have taken a decade to achieve,” said Jeremy Duke, Synergy Research Group’s founder and Chief Analyst “The collaboration market continues to evolve rapidly, as new technologies and services emerge that increase both management capabilities and productivity of in-office, remote and hybrid workers.”
IDC released a similar analysis of the global Unified Communications & Collaboration (UC&C) market, stating that it grew 11.4% YoY for Q2, reaching $14.8 billion. The market was up about 3% compared to Q1. IDC researchers noted that UC&C growth will continue as a result of increased interest in video conferencing, collaboration and UCaaS technologies.
“We’re seeing more strategic buying decisions by organizations versus fewer short-term reactive decisions in the recent past,” said Rich Costello, senior research analyst for Unified Communications and Collaboration at IDC, in a statement. “While the overall market remains a growth story, providers are starting to see some sales cycles return to the pre-covid pace.”
Some UC&C market specifics include the following:
- Hosted Voice/UC Public Cloud (UCaaS) revenue grew 17.0% year over year and 4.3% sequentially to almost $5.2 billion in 2Q22.
- UC Collaboration (including video conferencing software and cloud services) increased 10.2% annually and 1.3% sequentially to $7.2 billion in revenue in the quarter.
- IP Phone revenue increased 7.9% year over year and 13.9% quarter over quarter to $525 million in 2Q22.
- IP Phone shipments increased 2.8% year over year and 11.6% compared to 1Q22 to 4.5 million units shipped in the quarter.
- Enterprise Videoconferencing Room Endpoints (i.e., large video room endpoints) revenue increased 15.6% annually and 27.4% sequentially to more than $525.6 million in the quarter.
- Videoconferencing Huddle Room Endpoints revenue increased 24.7% year over year and 22.4% quarter over quarter to $263 million in 2Q22.
“We’re seeing more strategic buying decisions by organizations versus fewer short-term reactive decisions in the recent past,” said Rich Costello, senior research analyst, Unified Communications and Collaboration at IDC. “While the overall market remains a growth story, providers are starting to see some sales cycles return to the pre-covid pace.”
The UC&C market saw the following overall positive results in 2Q22 from a regional perspective:
- In North America (U.S. and Canada), UC&C revenue was up 10.1% year over year and 3.6% sequentially to just over $7.0 billion in 2Q 2022.
- Asia/Pacific (including Japan) revenue was up 16.8% year over year and 4.1% compared to 1Q22 to almost $3.0 billion in the quarter.
- EMEA revenue growth was up 8.9% year over year but just 1.0% sequentially to $4.2 billion in the quarter.
- Latin America revenue increased 20.9% year over year and 3.8% sequentially to $551.5 million in 2Q22.
UC&C Vendor Highlights
- Microsoft’s total worldwide UC&C revenue was $5.7 billion in 2Q22, up 22.7% year over year and 4.9% sequentially, representing a 38.3% share of the worldwide UC&C market for the quarter.
- Cisco’s total worldwide UC&C revenue was almost $1.2 billion, up 1.0% year over year and 8.6% sequentially, representing an 8.0% share of the worldwide UC&C market in 2Q22.
- Zoom’s total worldwide UC&C revenue increased 7.2% annually and 2.1% sequentially to more than $1.0 billion in the quarter, representing a 7.0% share of the worldwide UC&C market for 2Q22.
- RingCentral’s total worldwide UC&C revenue grew 29.8% year over year and 5.1% quarter over quarter to $424 million, representing a 2.9% share of the worldwide UC&C market for 2Q 2022.
References:
CEA-Leti RF Chip Enables Ultralow-Power IoT Connectivity For Remote Devices Via Astrocast’s Nanosatellite Network
CEA, a technology-research organization, and Astrocast, a leading global satellite Internet of Things network operator, have announced their successful collaboration on a low-cost, bidirectional communication module that enables corporations to communicate with their remote assets in areas not covered by terrestrial networks.
The module’s L-band chip, based on a new architecture developed by CEA-Leti, is a key hardware component that enables Astrocast customers to cost-efficiently communicate with their assets in the field via its network. It was completed earlier this year in an expedited project between the research institute and Astrocast, and is embedded in Astrocast’s RF module, called Astronode S.
The chip’s architecture is split over the RF core and digital processing and control units. It is fully optimized to support Astrocast’s dedicated bidirectional ground-to-satellite protocol and provides an optimal trade-off between link budget and low-power and low-cost constraints. The chip also embeds all low-earth orbit (LEO), satellite-specific features such as satellite detection and robustness to Doppler shift.
The miniaturized, surface-mount module communicates with terrestrial devices via Astrocast’s constellation of LEO satellites. Using the L-band spectrum, the network primarily targets maritime, oil & gas, agriculture, land transport and environmental applications in which ubiquitous coverage is required.

“Terrestrial IoT networks cover only about 15 percent of the planet, which leaves vast remote and rural areas where our global satellite network provides coverage that is crucial for our target markets,” said Laurent Vieira de Mello, Astrocast’s COO. “Leveraging its expertise embedded in a preliminary version of the RF chip, CEA-Leti developed its chip and delivered the final prototype to meet our requirements and time-to-market goals. They managed the chip technology transfer to our industrialization, qualification and production partner.”
The project’s critical time-to-market window was managed through a flexible collaboration model covering both prototype and industrialization phases.
“An accelerated time-to-market goal drove this project from the outset,” said Michel Durr, business development manager at CEA-Leti. “We pioneered this RF technology in 2019, and our team customized it for Astrocast up to production in only three years.”
CEA-Leti’s industrial tester used for characterization was key to accelerating from prototype to production, which enabled prototype characterization in parallel on the tester and in the lab, Durr explained.
“This process provided a short-loop debug capability with all skills available at CEA-Leti, and enabled us to deliver fully validated inputs to Astrocast’s industrialization partner for an easier industrial test-program development,” he said.
The low-energy, compact, surface-mount Astronode S module for highly integrated, battery-powered IoT systems offers a total cost of ownership up to three times lower than traditional satellite IoT alternatives.
References:
Juniper Research: 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) to Generate $2.5 Billion in Global Network Operator Revenue by 2023
According to Juniper Research, the revenue generated by telecom operators from 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) services is expected to increase by 480 percent between 2022 and 2023, from $515 million to $2.5 billion. Broadband and Internet of Things (IoT) networks are just two examples of the usage of FWA services, which offer high-speed Internet connectivity using cellular-enabled CP (Customer Premises Equipment).
According to the research company, 5G FWA revenue for telecom operators will total $24 billion globally by 2027. This increase is attributed to 5G’s advanced capabilities, such as ultra-low latency and increased data processing, which enables it to offer connectivity services that were previously impossible with 4G technology. The company predicted that, with 96% of total sales coming from the consumer market, operators would earn the most money.
A compelling user proposition for FWA solutions must be provided by telcos through the bundling of extra services like video streaming, gaming, and smart home security, according to Juniper Research. This will enhance user experience and give telcos a competitive edge over technologies like FTTP (fiber to the property).
The advantages of FWA are now on par with those of services provided by fiber-based networks. By offering last-mile solutions supported by their current 5G infrastructure, operators have an immediate chance to make income from internet subscriptions directly to end customers, according to research author Elisha Sudlow-Poole.
The Juniper Research survey also recognized private 5G networks as a significant monetization prospect, giving superior network capabilities to 4G. According to the research company, smart manufacturing, shipping ports, and airports are the most likely sectors where telcos would implement 5G FWA. In order to maximize return on investment, it also advises operators to collaborate with fiber optic networks in conjunction with 5G FWA to facilitate the last mile solution.
Juniper Research asserted operators should bundle services including video streaming, gaming and smart home security into their FWA offerings to better compete with FTTP. The company cited private networks as a key revenue opportunity for operators due to the superior network capabilities compared with 4G. Smart manufacturing, shipping and airports are also key use cases.
Juniper Research also indicated operators should use 5G FWA to provide last mile connectivity, by treating it as a collaborative effort with fibre networks to maximize performance and return on investment. Recent GSMA Intelligence research showed 83 operators across 29 countries have launched FWA.
Juniper Research author Elisha Sudlow-Poole concluded by saying:
“The benefits of FWA are now comparable with services using fiber-based networks. Operators have an immediate opportunity to generate revenue from broadband subscriptions directly to end users by providing last-mile solutions underpinned by their existing 5G infrastructure.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
5G Fixed Wireless Access Forecasts Report 2022-27: Share, Size (juniperresearch.com)
https://www.juniperresearch.com/whitepapers/how-operators-will-capitalise-on-5g-fixed-wireless
Juniper Research backs 5G FWA for growth spurt – Mobile World Live




