FTTP build out boom continues: AT&T and Google Fiber now offer Gig speeds to residential/business customers
AT&T has extended its symmetrical 2-Gig and 5-Gig to parts of its full fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) footprint. The expansion (the full list can be viewed here) follows AT&T’s initial launch of multi-gig services to more than 70 US markets.
AT&T said this expansion includes parts of its fiber footprint spanning more than 100 U.S. metro areas.
AT&T Fiber and their Hyper-Gig speeds will be introduced to 7 all-new fiber metro areas in Texas, Oklahoma and Ohio by year-end 2022. Customers in these areas can sign up to be alerted when AT&T Fiber is available to their address through the company’s Notify Me service by visiting att.com/notifyme.
AT&T said it will continue to expand multi-gig capabilities inside its FTTP footprint in 2022, and reiterated plans to expand fiber to more than 30 million customer locations by the end of 2025. Markets on tap for fiber builds include Abilene, Tyler, Victoria, Wichita Falls, and Longview, Texas; Lawton, Oklahoma; and Youngstown, Ohio.
Pricing on AT&T’s new multi-gig remain at the levels announced last month:
- Residential 2-Gig for $110 per month, or business 2-Gig for $225 per month
- Residential 5-Gig for $180 per month, or business 5-Gig for $395 per month
“We’re thrilled to bring our fastest speeds and our best internet experience to more homes and businesses across the country,” said Rick Welday, Executive Vice President & GM of Broadband, AT&T. “The energy and momentum we have in the marketplace is unmistakable and we are proud to be bringing connectivity to more people every single day.”
“The importance of high-speed broadband internet service has never been clearer,” said Bob O’Donnell, President of TECHnalysis Research. “Whether it’s ongoing hybrid work efforts with bandwidth-hungry video meetings, increasing reliance on high-resolution streaming video content, growing interest in online gaming and more, US consumers recognize the need and value of high-quality internet. Multi-gig fiber ups the ante and answers those demands with faster, reliable, symmetrical download and upload speeds.”
AT&T Fiber is internet that upgrades everything! There’s a big difference in the architectural nature of fiber compared to cable. Cable was designed to provide TV content to households, while fiber was designed specifically to provide high-speed internet. Fiber allows high-capacity tasks, such as uploading large documents during video calls and gaming, to flow seamlessly, even during high-usage times.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
AT&T’s gig FTTP offering comes as Frontier Communications, Verizon Communications and Ziply Fiber, get more aggressive with their own multi-gig offerings. Cablecos like CableOne,Suddenlink Communications (asubsidiary of Altice USA), and Comcast/Xfinity are also offering gig download speeds to residential subscribers.

FTTX (Node, Curb, Building, Home) architectures vary with regard to the distance between the optical fiber and the end user. The building on the left is the central office; the building on the right is one of the buildings served by the central office. Dotted rectangles represent separate living or office spaces within the same building.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Meanwhile, long dormant (and presumed dead) Google Fiber has moved ahead with the debut of a top-tier broadband service for business users that delivers 2 Gbit/s downstream and 1 Gbit/s upstream. Google Fiber’s Webpass fixed wireless services currently deliver up to 1 Gbit/s. Business 2 Gig is available to any business address in any Google Fiber service area. You can Sign up today to see where truly fast, affordable internet can take your business!
Google Fiber’s new business tier costs $250 per month. It’s being bundled with a static IP address (for components such as web and email servers), a Wi-Fi 6 router and a tri-band mesh extender. The new 2-Gig business tier sells for the same price previously affixed to Google Fiber’s 1-Gig service for business, which has been reduced to $100 per month.
Google Fiber introduced its $100 per month, 2-Gig residential service in the fall of 2020, and initially tested it in Nashville, Tennessee, and Huntsville, Alabama. The company has since launched 2-Gig in other FTTP markets, including Atlanta; Austin; Charlotte, North Carolina; San Antonio; Kansas City (Missouri and Kansas); Orange County; Provo and Salt Lake City, Utah; The Triangle, North Carolina. Google Fiber is in the process of launching services in West Des Moines, Iowa, where it tangles with Mediacom Communications.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2022/expands-hyper-gig-fiber-offering.html
https://about.att.com/ecms/dam/pages/internet-fiber/ATT-Fiber-market-cities.pdf
For more information or to check availability for all speed tiers of AT&T Fiber, visit att.com/hypergig
https://fiber.google.com/blog/2022/your-business-now-even-faster/
Ziply Fiber deploys 2 Gig & 5 Gig fiber internet tiers in 60 cities – AT&T can now top that!
Analysts: Increased Fiber internet services may force cablecos to alter pricing & deploy FTTP
China’s GalaxySpace launches 6 satellites to test LEO internet constellation
China start-up GalaxySpace has launched China’s first low-Earth orbit (LEO) broadband satellite constellation, reported state-owned news outlet CGTN, which it hopes will one day offer an alternative choice to SpaceX’s Starlink service. These satellites will be part of a testing network of satellite internet, nicknamed “Mini-spider Constellation,” the company said.
Six 5G-capable satellites were deployed, joining a seventh test satellite that was launched back in January 2020. Each one boasts 40 Gbps of capacity and can provide 30 minutes of coverage before handing off to the next satellite. It’s worth noting also – given the Chinese government’s penchant for keeping tabs on the populace – that each one is also capable of taking pictures and video. According to GalaxySpace’s website, design and production of these six satellites took just 11 months to deploy.
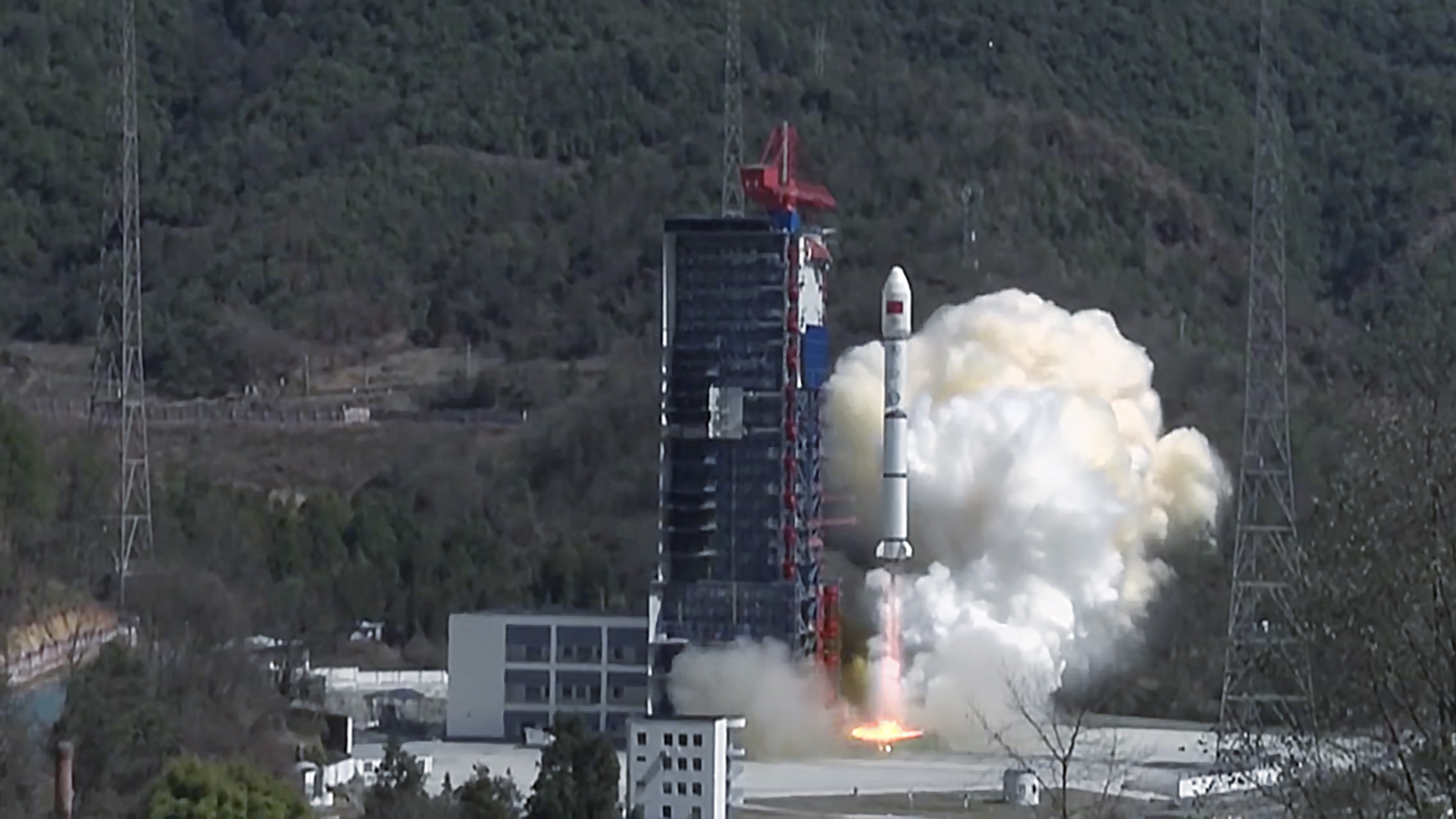

“Today’s launch proved that China has the capability to build satellite internet constellation at large scale, which includes the ability to mass-produce satellites at low cost as well as to operate in network,” the company’s co-founder Chang Ming told CGTN. “This will promote the development of the technology for integrating remote sensing and low-orbit communication satellites for commercial use,” he added.
GalaxySpace plans to launch 1,000 satellites, an impressive figure, but relatively small considering Starlink already has 2,000 in orbit and plans to launch many tens of thousands more. It is due to put another 48 into orbit on Wednesday; it also made the news last week when CEO Elon Musk claimed Starlink was the only non-Russian comms system still up and running in some parts of Ukraine.

GalaxySpace’s low-Earth-orbit broadband communication satellites. /GalaxySpace
Low-Earth orbit is set to become even more crowded once Amazon gets round to launching its Project Kuiper operation. Last November the company sought the Federal Communications Commission (FCC)’s permission to deploy and operate no fewer than 7,774 LEO satellites. Meanwhile, separately from GalaxySpace, the Chinese government has set a target of creating a 13,000-strong fleet of LEO broadband satellites that will offer nationwide coverage. Lets not forget smaller players like OneWeb as well, which in February successfully launched a further 34 LEO satellites, increasing the size of its fleet to 428, well on the way to its target of 648 in total.
With many other LEO constellations also in the works, it is little wonder that recent forecasts from Northern Sky Research (NSR) predict that satellite communications will become the biggest single sector of the global space economy in terms of revenue by 2030. The research firm reckons the overall space market will generate cumulative revenue of $1.25 trillion by 2030.
There is also renewed interest in high-altitude platform systems (HAPS), which are designed to offer connectivity from the stratosphere. Recent highlights include UK-based Stratospheric Platforms, which last week carried out a successful test of its HAPS technology over Saudi Arabia. In addition, Japan’s NTT recently brought together various partners, including Airbus and Sky Perfect JSAT Corporation, to study the feasibility of HAPS-based internet services.
References:
Stratospheric Platforms demos HAPS based 5G; will it succeed where Google & Facebook failed?
New partnership targets future global wireless-connectivity services combining satellites and HAPS
Cisco’s 5G pitch: Private 5G, 5G SA Core network, optical backhaul and metro infrastructure
At MWC 2022 in Barcelona, Cisco revealed its Private 5G market strategy together with partners. It was claimed to usher in “a new wave of productivity for enterprises with mass-scale IoT adoption.” Cisco’s 5G highlights:
- Cisco Private 5G as-a-Service delivered with global partners offers enterprise customers reduced technical, financial, and operations risks with managing enterprise private 5G networks.
- Cisco has worked in close collaboration with two leading Open RAN vendors to include O-RAN technology as part of Cisco Private 5G and is currently in customer trials with Airspan and JMA.
- Multiple private 5G pilots and projects are currently underway spanning education, entertainment, government, manufacturing, and real estate sectors.
- 5G backhaul and metro infrastructure via routed optical networking (rather than optical transceivers like those sold by Ciena)
Cisco Private 5G:
The foundation of the solution is built on Cisco’s industry-leading mobile core technology and IoT portfolio – spanning IoT sensors and gateways, device management software, as well as monitoring tools and dashboards. Open Radio Access Network (ORAN) technology is a key component of the solution. Cisco is working in close collaboration with ORAN vendors, JMA and Airspan, and is currently in customer trials utilizing their technology.
Key differentiators of Cisco Private 5G for Enterprises:
- Delivered as-a-Service: Delivered together with global service providers and system integration partners, the offer reduces technical, financial, and operational risks for enterprise private 5G networks.
- Complementary to Wi-Fi: Cisco Private 5G integrates with existing enterprise systems, including existing and future Wi-Fi versions – Wi-Fi 5/6/6E, making operations simple.
- Visibility across the network and devices: Using a simple management portal, enterprise IT teams can maintain policy and identity across both Wi-Fi and 5G for simplified operations.
- Pay-as-you-use subscription model: Cisco Private 5G is financially simple to understand. With pay-as-you-use consumption models, customers can save money with no up-front infrastructure costs, and ramp up services as they need.
- Speed time to productivity: Businesses can spare IT staff from having to learn, design, and operate a complex, carrier class private network.
Key Benefits of Cisco Private 5G for Partners:
- Path to Profitability for Cisco Partners: For its channel partners, Cisco reduces the required time, energy, and capital to enable a faster path to profitability.
- Private Labeling: Partners can private label/use their own brand and avoid initial capital expenses and lengthy solution development cycles by consuming Cisco Private 5G on a subscription basis. Partners may also enhance Cisco Private 5G with their own value-added solutions.

“Cisco has an unbiased wireless strategy for the future of hybrid work. 5G must work with Wi-Fi and existing IT environments to make digital transformation easy,” said Jonathan Davidson, Executive Vice President and General Manager, Mass-Scale Infrastructure Group, Cisco. “Businesses continuing their digitization strategies using IoT, analytics, and automation will create significant competitive advantages in value, sustainability, efficiency, and agility. Working together with our global partners to enable those outcomes with Cisco Private 5G is our unique value proposition to the enterprise.”
The concept of private networks running on cellular spectrum isn’t new — about 400 private 4G LTE networks exist today — but Cisco expects “significantly more than that in the 5G world,” Davidson said. “We think that in conjunction with the additional capacity or also the need for high-value asset tracking is really important.”
During a MWC interview with Raymond James, Davidson said, “Mobile networks aren’t mobile for very long. They have to get to a wired infrastructure,” and therein lies multiple roles for Cisco to play in the telco market.
Cisco’s opportunity in the telco space includes the buildout of new backhaul and metro infrastructure to handle increased capacity and bandwidth, its IoT Control Center, private networks, and the core of mobile network infrastructure.
“We continue to be a market leader in that space,” Davidson said, referring to Cisco’s 4G LTE and 5G network core products. More than a billion wireless subscribers are connected to Cisco’s 4G LTE core, and it plays a central role on T-Mobile’s 5G standalone core, which serves more than 100 million subscribers on a converged 4G LTE and 5G core, he added.
Davidson also expects Cisco’s flattened infrastructure, or routed optical networking, to gain momentum in wireless networks. But first, a definition. For Cisco, optical refers to the technology that moves bits from point A to point B, not optical transceivers.
“Our belief is there is going to be a transition in the market towards what we call routed optical networking. And this means that takes traditional transponders and moves them from being a shelf, or a separate box, or a device, and turns them into a pluggable optic, which you then plug into a router,” he said.
That’s where Cisco’s $4.5 billion acquisition of Acacia Communications comes into play. In October 2021, we reported that Cisco’s Acacia unit is working together with Microschip to validate the interoperability of their 400G pluggable optics components – Microchip’s DIGI-G5 OTN processor and META-DX1 terabit secured-Ethernet PHY and Acacia’s 400G pluggable coherent optics.
The second phase of this type of network transformation involves the replacement of modems that exist in optical infrastructure with routers that carry pluggable transponders, Davidson added. The third phase places private line emulation onto that same infrastructure.
Supporting Comments:
“DISH Wireless is proud to partner with Cisco to bring smart connectivity to enterprise customers through dedicated private 5G networks. Together, we have the opportunity to drive real business outcomes across industries. We’re actively collaborating with Cisco on transformational projects that will benefit a variety of sectors, including government and education, and we’re working to revolutionize the way enterprises can manage their own networks. As DISH builds America’s first smart 5G network™, we’re offering solutions that are open, secure and customizable. Teaming with Cisco is a great next step, and we look forward to offering more innovative solutions for the enterprises of today and beyond.”
— Stephen Bye, Chief Commercial Officer, DISH Wireless
“Cisco is busting the myth that enterprises can’t cross Wi-Fi, private 5G and IoT streams. Enterprises are now tantalizingly closer to full visibility over their digital and physical environments. This opens up powerful new ways to innovate without compromising the robust control that enterprises require.”
— Camille Mendler, Chief Analyst Enterprise Services, Omdia
“Developing innovative, customized 5G private network solutions for the enterprise market is a major opportunity to monetize the many advantages of 5G technology. Airspan is proud to be one of the first leading Open RAN partners to participate in the Cisco Private 5G solution and offer our cutting edge 5G RAN solutions including systems and software that are optimized for numerous enterprise use cases.”
— Eric Stonestrom, Chairman and CEO, Airspan
“This partnership opens a world of new possibilities for enterprises. With simple downloaded upgrades, our all-software RAN can operate on the same physical infrastructure for 10+ years—no more hardware replacements every 36 months. And as the only system in the world that can accommodate multiple operators on the same private network, it eliminates the need to build separate networks for new licensed band operators.”
— Joe Constantine, Chief Technology & Strategy Officer, JMA
“5G marks a milestone in wireless networking. For organizations, it opens many new opportunities to evolve their business models and create a completely new type of digital infrastructure. We see strong demand in all types of sectors including manufacturing and mining facilities, the logistics and automotive industries, as well as higher education and the healthcare sector. As a leading Cisco Global Gold Partner, we are excited to help drive this evolution. Thanks to our deep expertise, international capability, and close partnership with Cisco, we can support companies in integrating Private 5G into their enterprise networks,”
— Bob Bailkoskiis, Logicalis Group CEO.
“NEC Corporation is working on multiple 5G initiatives with Cisco. We have a Global System Integrator Agreement (GSIA) partnership for accelerating the deployment of innovative 5G IP transport network solutions worldwide. Work is in progress to connect Cisco’s Mobile Core and NEC’s radio over Cisco’s 5G Showcase in Tokyo, a world leading 5G services incubation hub. Leveraging NEC’s applications, Cisco and NEC will investigate expanding the technical trials including Private 5G in manufacturing, construction, transportation, and others.”
—Yun Suhun, General Manager, NEC Corporation
Industry Projects Underway
Cisco is working together with its partners on Private 5G projects for customers across a wide range of industries including Chaplin, Clair Global, Colt Technology Services, ITOCHU Techno-Solutions Corporation, Madeira Island, Network Rail, Nutrien, Schaeffler Group, Texas A&M University, Toshiba, Virgin Media O2, Zebra Technologies and more. See news release addendum for project details and supporting comments.
Final Thoughts:
“Radio access networks themselves are between $30 billion and $40 billion a year. Depending on who you talk to, optical (networking) can be between $10 billion and $15 billion a year. And then routing is below $10 billion a year,” Davidson said. “Our belief is that the optical total addressable market will start to shift over time as routed optical networks become more prevalent, because it will move from the optical domain into the optic transceiver market,” he added.
Finally, although Cisco repeatedly insists it has no interest in becoming a RAN supplier, it remains strongly supportive of Open RAN. The RAN market “is still closed, it’s locked in, even though there are standards,” he said.
“People do not do any interoperability testing between vendors, which is fundamentally changing with open RAN” because operators are forcing vendors to make their equipment interoperate with open RAN implementations, Davidson concluded.
References:
Microchip and Cisco-Acacia Collaborate to Progress 400G Pluggable Coherent Optics
Additional Resources:
- Cisco Private 5G
- Blog: Private 5G Delivered on Your Terms, Masum Mir, Vice President and General Manager, Mobile, Cable and IoT
Data Bridge: 5G Chipset Market Expected to Reach $2,519.78 Billion by 2029 with CAGR of 49.02%
Data Bridge Market Research has released a new report, “5G Chipset Market Report-Development Trends, Threats, Opportunities and Competitive Landscape” focusing on primary and secondary drivers, market share, market size, sales volume, leading segments and geographical analysis of 5G silicon.
The 5G chipset market will exhibit a CAGR of 49.02% for the forecast period of 2022-2029 and is likely to reach the $2,519.78 billion by 2029. The rise in the cellular IoT (internet of things) connections will influence the growth rate of the 5G chipset market. The upsurge in the demand for high speed internet and broad network coverage is a key element driving market expansion. The 5G chipset market is also being driven by factors such as rising mobile data traffic and increasing need for smart technologies.
Furthermore, technological advancements and increase in the popularity of 5G-enabled smartphones will enhance the growth rate of 5G chipset market. Also, the upsurge in the demand for ultra-reliable and low-latency data networks capable of providing seamless connectivity will act as a major factor influencing the growth of 5G chipset market.
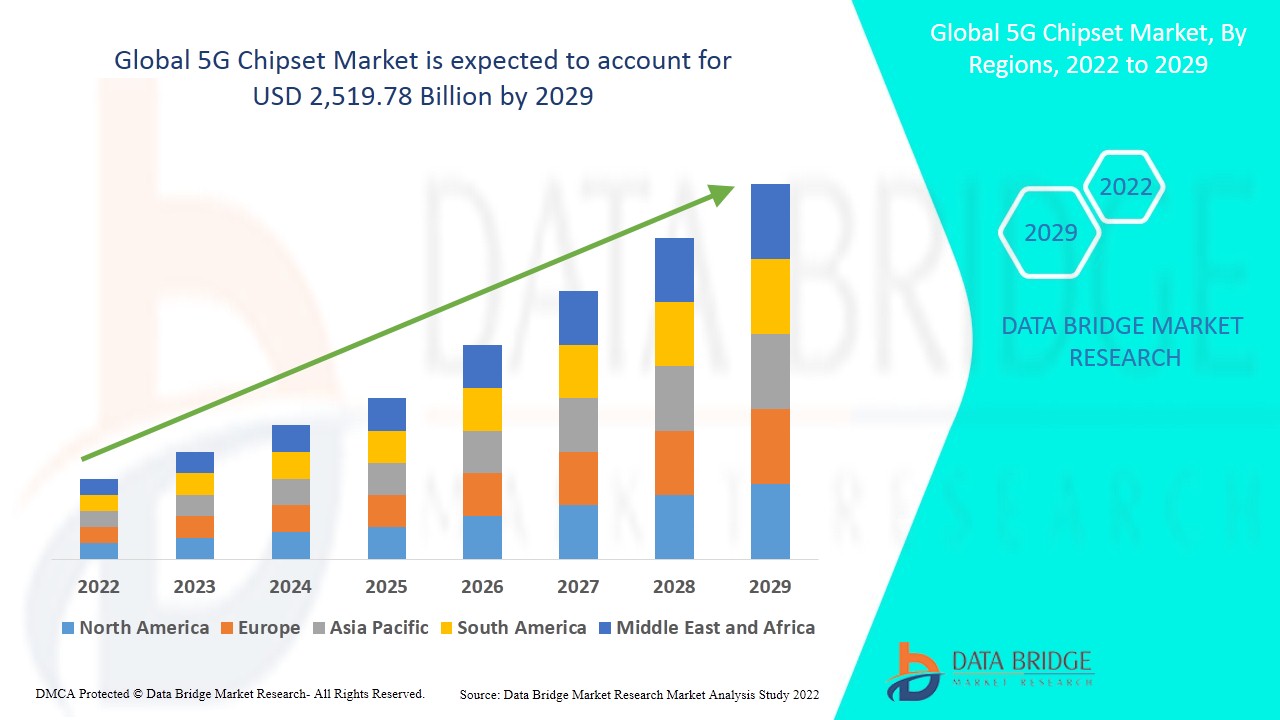
Asia-Pacific dominates the 5G chipset market and will continue to flourish its trend of dominance due to the growing level of investment in research and development, increase in developments in emerging 5G enabled smartphones and base stations supporting 5G frequencies in this region. North America is expected to grow during the forecast period of 2022-2029 due to the rapidly rising automotive and consumer electronics sectors in this region.
Top Players Analyzed in the Report:
- Analog Devices
- Texas Instruments
- NXP Semiconductors
- Broadcom
- Huawei Technologies
- Qualcomm Technologies
- SAMSUNG
- Xilinx
- Nokia
- Intel Corporation
- Infineon Technologies
- IBM
- Renesas Electronics Corporation
- Qorvo, Marvell
- Unisoc (Shanghai) Technologies
- Skyworks Solutions
- Anokiwave
Key Market Segmentation:
- On the basis of frequency type, the 5G Chipset Market has been segmented as sub-6Hz, between 26 and 39 GHz and above 39 GHz.
- Based on processing node type, the 5G chipset market has been segmented into 7 nm, 10 nm and others.
- Global 5G chipset market on the basis of chipset type has been segmented as application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC), millimeter wave integrated circuit (mmWave IC) and cellular integrated circuit (cellular IC).
- Based on deployment type, the 5G chipset market has been segmented into telecom base station equipment, smartphones/tablets, connected vehicles, connected devices, broadband access gateway and others. Apart from telecom base station equipment, all other categories can be further sub-segmented into single-mode and multi-mode. Single-mode can be divided into standalone and non-standalone.
- Based on end user, the 5G chipset market has been segmented as energy and utilities, manufacturing, IT and telecom, media and entertainment, transportation and logistics, healthcare and others.
Recent Developments:
In January 2021, MediaTek had launched chipset to power 5G smartphones. They launched new Dimensity 1200 and Dimensity 1100 5G smartphone chipset along with the developed AI, camera and multimedia properties for superior 5G experience. Both chipsets support every generation of connectivity, from 2G to 5G, as well as the most up-to-date connectivity capabilities.
In June 2021, start-up EdgeQ had launched industry’s first 5G Chipset-as-a-Services for 5G wireless infrastructure market. Customers can configure 5G and AI services with EdgeQ’s innovative software defined 5G base station-on-a-chip technology, which changes the industry to a service-oriented, pay-as-you-go structure.
In May 2021, Qualcomm had launched 5G modem elevated for industrial IoT. The Qualcomm 315 5G IoT modem enables global 5G NR sub-6GHz bands and functions in stand-alone (SA) alone mode, with the flexibility to transition to LTE as required. It can be operated over private or public 5G networks, using network slicing or in isolation.
References:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-5g-chipset-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/checkout/buy/singleuser/global-5g-chipset-market
Dell’Oro Group: Open RAN Momentum Is Solid; RAN equipment prices to increase
by Stefan Pongratz, VP at Dell’Oro Group
Introduction:
Open RAN ended 2021 on a solid footing. Preliminary estimates suggest that total Open RAN revenues—including O-RAN and OpenRAN radios and baseband—more than doubled for the full year 2021, ending at a much higher level than had been expected going into the year. Adoption has been mixed, however. In this blog, we review three Open RAN-related topics: (1) a recap of 2021, (2) Mobile World Congress (MWC) takeaways, and (3) expectations for 2022.
2021 Recap:
Looking back to the outlook we outlined a year ago, full-year Open RAN revenues accelerated at a faster pace than we originally expected. This gap in the output ramp is primarily the result of higher prices. LTE and 5G macro volumes were fairly consistent with expectations, but the revenue per Open RAN base stations was higher than we modeled going into 2021, especially with regard to brownfield networks. Asymmetric investment patterns between the radio and the baseband also contributed to the divergence, though this is expected to normalize as deployments increase. In addition, we underestimated the 5G price points with some of the configurations in both the Japanese and US markets.
Not surprisingly, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region dominated the Open RAN market in 2021, supported by large-scale greenfield OpenRAN and brownfield O-RAN deployments in Japan.
From a technology perspective, LTE dominated the revenue mix initially but 5G NR is now powering the majority of investments, reflecting progress both in APAC and North America.

Mobile World Congress (MWC) Barcelona 2022:
Open RAN revenues are coming in ahead of schedule, bolstering the narrative that operators want open interfaces. Meanwhile, the progress of the technology, especially with some of the non-traditional or non-top 5 RAN suppliers has perhaps not advanced at the same pace. This, taken together with the fact that the bulk of the share movements in the RAN market is confined to traditional suppliers, is resulting in some concerns about the technology gap between the traditional RAN and emerging suppliers. A preliminary assessment of Open RAN-related radio and baseband system, component, and partnership announcements at the MWC 2022 suggests this was a mixed bag, with some suppliers announcing major portfolio enhancements.
Among the announcements that most stood out is the one relating to Mavenir’s OpenBeam radio platform. After focusing initially on software and vRAN, Mavenir decided the best way to accelerate the O-RAN ecosystem is to expand its own scope to include a broad radio portfolio. The recently announced OpenBeam family includes multiple O-RAN 7.2 macro and micro radio products supporting mmWave, sub 6 GHz Massive MIMO, and sub 6 GHz Non-Massive MIMO.

NEC announced a major expansion of its O-RAN portfolio, adding 18 new O-RUs, covering both Massive MIMO and non-Massive MIMO (4T4R, 8T8R, 32T32R, 64T64R). NEC also recently announced its intention to acquire Blue Danube.
Another major announcement was Rakuten Symphony’s entry into the Massive MIMO radio market. Rakuten Symphony is working with Qualcomm, with the objective of having a commercial Massive MIMO product ready by the end of 2023.
Recent Massive MIMO announcements should help to dispel the premise that the O-RAN architecture is not ideal for wide-band sub-6 GHz Massive MIMO deployments. We are still catching up on briefings, so it is possible that we missed some updates. But for now, we believe there are six non-top 5 RAN suppliers with commercial or upcoming O-RAN Sub-6 GHz Massive MIMO GA: Airspan, Fujitsu, Mavenir, NEC, Rakuten Symphony, and Saankhya Labs.
Putting things into the appropriate perspective, we estimate that there are more than 20 suppliers with commercial or pending O-RAN radio products, most prominently: Acceleran*, Airspan, Askey*, Baicells*, Benetel*, BLiNQ*, Blue Danube, Comba, CommScope*, Corning*, Ericsson, Fairwaves, Fujitsu, JMA*, KMW, Mavenir, MTI, NEC, Nokia, Parallel Wireless, Rakuten Symphony, Saankhya Labs, Samsung, STL, and Verana Networks* (with the asterisk at the end of a name indicating small cell only).
The asymmetric progress between basic and advanced radios can be partially attributed to the power, energy, and capex tradeoffs between typical GPP architectures and highly optimized baseband using dedicated silicon. As we discussed in a recent vRAN blog, both traditional and new macro baseband component suppliers—including Marvell, Intel, Qualcomm, and Xilinx—announced new solutions and partnerships at the MWC Barcelona 2022 event, promising to close the gap. Dell and Marvell’s new open RAN accelerator card offers performance parity with traditional RAN systems, while Qualcomm and HPE have announced a new accelerator card that will allegedly reduce operator TCO by 60%.
2022 Outlook:
Encouraged by the current state of the market, we have revised our Open RAN outlook upward for 2022, to reflect the higher baseline. After more than doubling in 2021, the relative growth rates are expected to slow somewhat, as more challenging comparisons with some of the larger deployments weigh on the market. Even with the upward short-term adjustments, we are not making any changes at this time to the long-term forecast. Open RAN is still projected to approach 15% of total RAN by 2026.
In summary, although operators want greater openness in the RAN, there is still much work ahead to realize the broader Open RAN vision, including not just open interfaces but also improved supplier diversity. Recent Open RAN activities—taken together with the MWC announcements—will help to ameliorate some of these concerns about the technology readiness, though clearly not all. Nonetheless, MWC was a step in the right direction. The continued transition from PowerPoint to trials and live networks over the next year should yield a fuller picture.
Addendum:
“Following twenty years of average macro base station price declines in the 5% to 10% range, we are now modeling RAN [radio access network] prices to increase, reflecting a wide range of factors,” Stefan Pongratz, an analyst at research and consulting firm Dell’Oro Group, wrote in response to questions from Light Reading. “In addition to the changing vendor landscape and regional aspects coming into play with China’s overall share expected to decline going forward, we have also assumed there will be some COGS [cost of goods sold] inflation due to supply-demand mismatches, though the ability for everyone to pass this on [to their customers] remains limited.”
About the Author:
Stefan Pongratz joined Dell’Oro Group in 2010 and is responsible for the firm’s Mobile RAN market and Telecom Capex research programs. While at the firm, Mr. Pongratz has expanded the RAN research and authored multiple Advanced Research Reports to ensure the program is evolving to address new RAN technologies and opportunities including small cells, 5G, Open RAN, Massive MIMO, mmWave, IoT, private wireless, and CBRS. He built the Telecom Capex coverage detailing revenues and investments of over 50 carriers worldwide.
Cloud Native Computing Foundation -Kubernetes and container technologies; ABI Research 5G Telco Cloud-Native Platforms
I. Cloud Native Computing Foundation:
Are the ITU, ETSI, IETF SDO’s obsolete with the move to “cloud native” telecom? Maybe so. The Cloud Native Computing Foundation® (CNCF®), which builds sustainable ecosystems for cloud native software, recently announced the addition of 68 new Silver and end user members and end user supporters. These new members will work side by side with over 775 other members to build and use the cloud native technology that is enabling organizations across the world to respond to the challenges of 5G, edge, massive scale, and more.
For sure, “cloud native,” which is recommended by 3GPP for 5G SA core networks, has replaced and knocked out the previously highly touted NFV and SDN which never realized critical market mass, despite outrageous claims that they would usher in a new era/ new epoch and replace all conventional hardware based telecom equipment.
According to the CNCF Annual Survey, 2021 was the year that Kubernetes crossed the chasm, with 96% of organizations who participated in the survey either using or evaluating Kubernetes. Adoption has also increased measurably across CNCF projects, notably by 500% for containerd, 53% for Fluentd, and 43% for Prometheus.
“We have seen an acceleration in new member growth which we can attribute to the maturation and ubiquity of Kubernetes and container technology,” said Priyanka Sharma, executive director of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. “CNCF’s projects have been integral in helping end users like Allianz Direct, Fidelity Investments, and Vodafone respond to pressing and evolving infrastructure challenges. We are thrilled to have so many new members on board to continue our mission to make cloud native computing ubiquitous.”

About the newest Silver Members:
- Airlock covers all functions of modern application security, combining web application and API protection (WAAP) with customer identity management (cIAM) deployable on-premises, in the cloud, or as lightweight security micro gateway, designed specifically for use in container environments.
- Akuity was founded by Argo co-creators Hong Wang and Jesse Suen and is on a mission to help companies modernize their Kubernetes tooling by leveraging Argo, the leading open-source suite of Kubernetes-native application delivery tools.
- Amido is the cloud-native consultancy for better business outcomes.
- Argonaut is the first cloud platform that enables engineers to manage infrastructure and application deployments in one place, focusing on developer experience.
- Automat-IT delivers exceptional CI, CT, CD, DevOps, Cloud services, and 24×7 support, to large enterprises, startups and everything in between, to untangle IT complexities and deploy ‘time to market’ technologies.
- Avisi is a Software Development and Cloud Services Company that offers Managed Services using the Change-mindset, allowing their customers to continuously innovate their mission-critical software.
- Axcelinno is an IT Technology Consultancy and Professional Services company that helps organizations define and implement their DevSecOps adoption and cloud migration.
- Baolande is a listed high-tech corporation founded in 2008, it focuses on providing infrastructure software, intelligent operation and maintenance products and solutions for innovational digitalized business.
- Clastix is a tech company providing a unique blend of products and services to accelerate the Cloud Native revolution, delivered from 100% upstream open-source components.
- CloudCasa by Catalogic is a powerful, cyber-resilient, backup service for protecting Kubernetes workloads, cloud databases, and cloud native applications, that is free to start using.
- Cloud Kinetics (CK) is a leading cloud MSP (managed services provider) with operations in Singapore, Indonesia, Vietnam, India, Malaysia, Thailand, USA and Germany.
- CloudMatos, pioneering the world of self-governed cloud infrastructure, our solution provides self-healing, awareness, resilience, security, and intelligent remediation to your cloud infrastructure by deploying policy driven governance, security controls, networking controls, and more using IAC or PAC.
- CodeZero allows developers to work on software in a Kubernetes cluster creating parity between their local machine and production.
- Cortex gives organizations visibility into the status and quality of their microservices and helps teams drive adoption of best practices so they can deliver higher quality software.
- CrafterCMS is an open-source, Git-based headless CMS for enterprises that seek faster and easier development of large-scale, content–rich digital experiences such as global personalized websites, customer portals, employee intranets, OTT video, e-commerce, consumer mobile apps, AR/VR, and more.
- Cribl is an observability pipeline company built to reduce, normalize, enrich, and route observability data to where it has the most value.
- DataCore Software delivers the industry’s most flexible, intelligent, and powerful software-defined storage solutions for block, file, object, and container storage, helping more than 10,000 customers worldwide modernize how they store, protect, and access data.
- Daugherty Business Solutions is an advisory services and technology consulting firm delivering results through innovation and technology.
- Era Software observability data management offers modern IT and security organizations the ability to route, ingest, store, and analyze massive amounts of data to get actionable insights in seconds.
- Expert Thinking is a team of industry-certified cloud experts who will partner with your organisation, supporting every stage of your cloud journey – rapidly optimising your use of the ever-changing cloud technology landscape at scale to maximise value and benefit for your organisation.
- Finout‘s cost management platform combines your AWS, K8s, Datadog & Snowflake invoices into one mega bill, enabling an unparalleled view of your cloud spend in minutes with no heavy lifting.
- Fournine is a leading multi-cloud solution provider empowering enterprises’ digital transformation with key cloud native development solutions such as Kubernetes, DevOps, and building and delivering container based applications.
- GienTech is a leading financial digital consulting and software provider based on full stack information technology in the world, moreover, an expert in digital transformation services in key industries.
- Helios is a production-readiness platform that leverages OpenTelemetry to give developers the power to understand, troubleshoot, and test distributed applications, so they can deliver production-ready code faster – and with more confidence.
- Innogrid is Korea’s leading cloud computing solution and service company that supports successful digital transformation based on cloud native environments.
- itopia makes hybrid work easy for software teams by delivering containerized developer environments in a browser, enabling companies to onboard developers fast and prevent exfiltration with precise security controls, and devs to launch spaces with all their tools pre-installed and start coding in seconds.
- KPMG is a global network of professional firms providing Audit, Tax and Advisory services with 227,000 outstanding professionals working together to deliver value in 146 countries and territories.
- KSOC is an event-driven SaaS platform built to automatically remediate Kubernetes security risks and enforce least privilege access control across distributed cluster infrastructures.
- Lightlytics empowers teams of all sizes to code and deploy configurations with speed and confidence.
- Lightrun is the world’s first IDE-native developer observability platform, that enables engineering teams to continuously identify and tackle critical issues in live applications without hotfixes, redeployments, or restarts by securely adding read-only logs, metrics, and traces in real-time and on-demand
- mogenius is a code to cloud platform that deploys and runs any application on a fully automated cloud infrastructure by simply connecting to a code repository.
- Mondoo is an easy to use security platform for DevOps and Security practitioners who want to automate manual security processes, find misconfigurations, and improve their security posture.
- Mycelial is the Edge Native platform for distributed, local-first applications.
- NHN Cloud is a leading cloud service provider based in South Korea, offering public, private, and hybrid cloud in various industries with reliable, flexible, and secure services.
- Okteto enables organizations to instantly spin up pre-configured environments in the cloud and start developing within seconds.
- OnGres (“ON postGRES”) is a highly specialized Postgres startup, creators of the Open Source project StackGres, the most advanced platform for running Enterprise Postgres on Kubernetes.
- Orca Security provides instant-on security and compliance for public cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and GCP - without the gaps in coverage, alert fatigue, and operational costs of agents or sidecars.
- Oxeye.io delivers an application security testing platform designed for cloud-native apps and modern architectures, offering a contextual, effortless, and comprehensive solution to ensure no vulnerable code ever reaches production.
- Polar Signals is an observability company focusing on continuous profiling, empowering every developer to understand performance measurements down to the source code line number across their entire infrastructure to safe cost on cloud bills, improve performance, and improve the reliability of software.
- Posedio, based in Austria, specialises in the cloud-native journey of enterprise customers in the DACH region, providing deep technical knowledge and hands-on experience in running applications at scale.
- ProfiSea is an Israeli DevOps and Cloud boutique company that implements best practices of GitOps, DevSecOps, Kubernetes-based Cloud environments deployment automation and provides FinOps premium services using a unique AI-based Cloud management platform.
- RNG Technology is a leading cloud native digital acceleration technology partner that provides fully managed & engineered multi-cloud IaaS, BaaS, DRaaS, BCaaS, Kubernetes and DevOps solutions enabling enterprises to rapidly accelerate the delivery of innovative solutions.
- ScaleFlash is a software-defined, cloud native storage for Kubernetes, providing persistent storage for stateful Kubernete under Bare Metal DPU Servers connected with low latency RDMA network to achieve multi-milllion of IOPS performance.
- Scribe makes software trustworthy, by allowing software producers to attest to it and consumers to validate.
- Seekret is an API-first platform that empowers developers with revolutionary eBPF-powered APIOps through automation, governance, and observability.
- Spyderbat provides Linux runtime security, protecting dynamic environments by proactively tracking all user activities by their causal connections to detect and resolve external attacks, misconfigurations, and insider threats.
- Successive Technologies is an Enterprise Cloud Consulting Company that helps you leverage most popular container orchestration with their enterprise-class managed Kubernetes services to make cluster management and integration workflows easy and effective.
- True is an Amsterdam-based Managed Service Provider with 20+ years of experience in hosting scalable SaaS applications.
- Uffizzi is an open-source full-stack preview engine that provides on-demand cloud environments powered by Kubernetes and configured with Docker Compose.
- VNET Group, a leading carrier- and cloud-neutral Internet data center services provider in China, provides hosting and related services, including IDC services, cloud services, and business VPN services.
- Webera has the vision to help innovators build their own platforms by providing DevOps services breaking down silos, improving workflows, and using cloud-native technologies. See what happens when technology gets out of the way.
- Whitestack is delivering unprecedented value to the IT and Telecom industries, changing the existing paradigms by deploying open-source solutions that help Data Centers, Telcos and Corporations to implement hyper-scalable clouds, for mission-critical workloads.
- Wowjoy Technology is dedicated to providing healthcare digital platform construction and data services to governments and medical institutions. All products and applications are developed and served upon cloud native architecture.
- Zoi is a cloud-native IT consulting company that bridges the gap between hidden champions and the latest cloud technology – born in “THE LÄND”, made in the Cloud.
About the newest End User Members:
- Bancolombia: Colombian financial group with 147 years of history that provides financial and non-financial services to more than 20 million clients in Colombia, Panama, El Salvador and Guatemala.
- BMO Financial Group is a highly diversified financial services provider – North America’s 8th largest bank by assets, providing a broad range of personal and commercial banking, wealth management and investment banking products and services to more than 12 million customers globally.
- Fannie Mae advances equitable and sustainable access to homeownership and quality, affordable rental housing for millions of people across America.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation, headquartered in Bethesda, Maryland, is a global security and aerospace company that employs approximately 114,000 people worldwide and is principally engaged in the research, design, development, manufacture, integration and sustainment of advanced technology systems, products, and services.
- LSEG: Your trusted global financial markets infrastructure and data provider.
- ZenHub helps scaling teams get ship done, with enhanced visibility for software projects, automated agile experiences, and real-team productivity insights.
About the newest End User Supporters:
- BitMEX, founded in 2014, is one of the world’s leading cryptocurrency derivatives exchanges with a fully verified user base and the creator of the Perpetual Swap.
- FATMAP is the leading app for the mountains, featuring thousands of routes and guidebooks, professional terrain tools, national TOPO maps (including a 3D IGN map), and downloadable maps for offline use – it’s everything you need for your next adventure.
- MasterClass‘s mission is to unlock human potential by inspiring a learning lifestyle in everyone.
- TomTom is a geolocation company that provides maps, navigation software, real-time traffic information, and APIs.
- Vermiculus delivers innovative, modern, and high-quality solutions for clearing houses and exchanges all around the world. Leading the way with cloud-based and AI powered microservices.
About the newest Non-Profit Members:
- Cispi‘s goal is to promote cloud computing and open source in Israel.
- The Open Compute Project Foundation (OCP) was initiated in 2011 with a mission to apply the benefits of open source collaboration to hardware and rapidly increase the pace of innovation in, near and around the data center’s networking equipment, general purpose and GPU servers, storage devices and appliances, and scalable rack designs, and now being applied to advance the telecom industry & EDGE infrastructure.
Additional Resources
- CNCF Newsletter
- CNCF Twitter
- CNCF Blog
- Learn About CNCF Membership
- Learn About CNCF End User Supporters
- Join the CNCF conversation on Slack
About Cloud Native Computing Foundation
Cloud native computing empowers organizations to build and run scalable applications with an open source software stack in public, private, and hybrid clouds. The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) hosts critical components of the global technology infrastructure, including Kubernetes, Prometheus, and Envoy. CNCF brings together the industry’s top developers, end users, and vendors, and runs the largest open source developer conferences in the world. Supported by more than 500 members, including the world’s largest cloud computing and software companies, as well as over 200 innovative startups, CNCF is part of the nonprofit Linux Foundation. For more information, please visit www.cncf.io.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
II. ABI Research did an in-depth and objective evaluation of the telco cloud platforms offered by eleven 5G Telco Cloud-Native Platform players. The companies are evaluated in the following order of ranking:
- Market Leaders: VMware, Red Hat
- Mainstream: Nokia, ZTE, Canonical, Huawei, Google, Ericsson, Wind River
- Followers: AWS, Microsoft Azure
“CSPs are looking to enable cloud-native 5G capabilities through the deployment of a horizontal platform that can span their entire network from the core to RAN to edge. Some of the key criteria that CSPs are looking for include the ability to build a multi-vendor network and avoid vendor lock-in. As the 5G SBA value proposition revolves around providing services on-demand through microservices and cloud-native principles, flexibility, agility, and scalability become major factors CSPs look out for when choosing a platform,” says Kangrui Ling, Industry Analyst at ABI Research.
VMware and Red Hat are assessed as leaders in the market, with VMware coming out on top due to their strong multi-vendor Network Function (NF) partnership program supporting more than 220 NFs. Red Hat follows closely behind with their Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform and hybrid cloud and multi-cloud capabilities. Both providers are also top innovators, with VMware offering a variety of telco-specific features, including RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC), SD-WAN, and orchestrators, while Red Hat offers auto-scaling of clusters and zero-touch provisioning through solutions such as Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes, Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform, and Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM).
“Cloud native is critical for telco applications in 5G, and is crucial in bringing automation, scale, performance, efficient operations, faster time to market, an improved CI/CD pipeline, and the easy introduction of new software and features. Newer trends are also emerging which include multi-vendor capabilities and hybrid cloud/multi cloud support as networks become more open and disaggregated,” concludes Ling.
These findings are from ABI Research’s 5G Telco Cloud-Native Platforms competitive ranking report. This report is part of the company’s 5G Core & Edge Networks research service, which includes research, data, and ABI Insights. Competitive Ranking reports offer comprehensive analysis of implementation strategies and innovation, coupled with market share analysis, to offer unparalleled insight into a company’s performance and standing in comparison to its competitors.
About ABI Research:
ABI Research is a global technology intelligence firm delivering actionable research and strategic guidance to technology leaders, innovators, and decision makers around the world. Our research focuses on the transformative technologies that are dramatically reshaping industries, economies, and workforces today.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
MTN and Rakuten MoU: Open RAN trials using RCP in South Africa, Nigeria and Liberia
Africa’s largest mobile network operator MTN Group and Rakuten Symphony signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to run live 4G and 5G OpenRAN Proof of Concept (PoC) trials in South Africa, Nigeria and Liberia using the Rakuten Communications Platform (RCP). The trials will start in 2022 and combine RCP OpenRAN equipment with advanced automation and autonomous network capabilities. The products are currently deployed by Rakuten Mobile in Japan and include cloud orchestration, zero-touch provisioning and automation of radio site commissioning and network integration.
The trials will enable the launch of new services more quickly, cost-effectively and seamlessly, MTN said. The mobile operator and Rakuten Symphony will be collaborating with systems integrators Accenture and Tech Mahindra to conduct the trials in the three countries.
“We are pleased to announce our partnership with Rakuten Symphony to deploy live 4G and 5G Open RAN trials across South Africa, Nigeria and Liberia. In line with our belief that everyone deserves the benefits of a modern connected life, we are committed to actively driving the rapid expansion of affordable 4G and 5G coverage across markets in Africa,” said Mazen Mroue, MTN Group Chief Technology & Information Systems Officer. “We have announced our support towards the deployment of Open RAN technology in 2021 to modernize our radio access network footprint. Through this partnership we hope to target innovation and cost efficiencies that will enable us to continue delivering an exceptional customer experience.”
The solutions, currently deployed by Rakuten Mobile in Japan, include cloud orchestration, Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) and automation of radio site commissioning and network integration.
Image – left to right: Amith Maharaj, MTN Group Executive, Network Planning and Design; Tareq Amin, CEO Rakuten Symphony; Rabih Dabboussi, Chief Revenue Officer, Rakuten Symphony.
“We’re excited to take this next step in our partnership with MTN,” said Rabih Dabboussi, Chief Revenue Officer of Rakuten Symphony. “This PoC will demonstrate how one of the world’s top-tier brownfield mobile operators can utilize Rakuten Symphony’s network automation and orchestration solutions for cost-effective network transformation and timely deployment of next-generation network services to their customers across Africa.”
Rakuten Mobile made a full-scale launch of commercial services on the world’s first fully virtualized cloud-native mobile network in 2020 in Japan, and launched Rakuten Symphony in 2021 to bring its innovations to other operators. Rakuten Symphony brings together Rakuten’s telco products, services and systems under a single banner to offer 4G and 5G infrastructure and platforms to customers worldwide.
MTN has already been testing open RAN equipment in several markets and is an active member of the Telecom Infra Project. The network operator announced several other Open RAN suppliers last year which were: Altiostar, Mavenir, Parallel Wireless, Tech Mahindra and Voyage.
About the MTN Group:
Launched in 1994, the MTN Group is a leading emerging market operator with a clear vision to lead the delivery of a bold new digital world to our customers. We are inspired by our belief that everyone deserves the benefits of a modern connected life. The MTN Group is listed on the JSE Securities Exchange in South Africa under the share code ‘MTN’. Our strategy is Ambition 2025: Leading digital solutions for Africa’s progress.
About Rakuten Symphony:
Rakuten Symphony is reimagining telecom, changing supply chain norms and disrupting outmoded thinking that threatens the industry’s pursuit of rapid innovation and growth. Based on proven modern infrastructure practices, its open interface platforms make it possible to launch and operate advanced mobile services in a fraction of the time and cost of conventional approaches, with no compromise to network quality or security. Rakuten Symphony has headquarters in Japan and local presence in the United States, Singapore, India, Europe and the Middle East Africa region.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://symphony.rakuten.com/newsroom/mtn-group-and-rakuten-symphony-mou
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/mtn-picks-suppliers-for-openran-roll-out-in-africa–1386900
Bloomberg: 5G in the U.S. Has Been a $100 Billion Box Office Bomb
From the very start of 5G deployments three years ago, there have been challenges with the technology, like when AT&T confusingly branded 4G as “5G E.” Conspiracy theorists have tagged 5G as a source of harmful radiation and a spreader of the coronavirus.
More recently, airlines and the FAA have complained that C-Band frequencies could interfere with radar and jeopardize air safety. To date, the biggest knock against 5G is that it’s been a nonevent. And, by the time it’s in full force, big tech companies including Amazon, Microsoft, and Google may have beaten the wireless carriers to the kinds of data-hungry applications that superfast 5G networks have been expected to spawn. At FCC auctions, U.S. carriers spent $118B on 5G spectrum- about twice as much as they spent on 4G.
Source: FCC
The higher speeds and greater capacity of 5G are needed to meet growing demand for services such as high-definition video streaming. However, the big improvement with 5G technology was supposed to be Ultra High Reliability and Ultra Low Latency (URLLC), which was to spawn a wide variety of new mission critical and real time control applications. That hasn’t happened because the ITU-R M.2150 RAN standard (based on 3GPP release 15 and 16) doesn’t meet the URLLC performance requirements in ITU M.2410 while the 3GPP Release 16 URLLC in the RAN spec (which was to meet those requirements) has not been completed or performance tested.
Also, all the new 5G features, such as network slicing, can only be realized with a 5G SA core network, but very few have actually been deployed. Adjunct capabilities, like virtualization, automation, and multi-access edge computing also require a “cloud native” 5G SA core network. Finally, the highly touted 5G mmWave services (like Verizon’s Ultra-Wideband) consume a tremendous amount of power, require line of sight communications, and have limited range/coverage.
Lacking a compelling reason to persuade customers to upgrade, carriers have been offering $1,000 5G phones for free to help jump-start the conversion process. Such promotions are needed because 5G isn’t even among the top four reasons people switch carriers, according to surveys by Roger Entner of Recon Analytics Inc. Those reasons typically include price or overall network reliability.
Ironically, one area where 5G has had early success is in providing wireless home broadband service (aka Fixed Wireless Access or FAA). That’s because 5G was designed for mobile- not fixed- communications and FAA was not even a targeted use case by either ITU-R or 3GPP. Nonetheless, as faster 5G mid-band frequencies are built out, customers are finding a wireless alternative to landline providers. This threat to cablecos is likely to spark price battles as the cable operators respond by offering cheaper mobile phone service of their own.
This was not the way 5G was envisioned or promoted. Carriers were rolling out 5G to deliver an “oh, wow” experience that customers would willingly pay extra for. Instead the technology has become a standard feature in an arena where mobile phone companies and cable operators are battling it out with similar packages. As that reality started to take hold, the carriers pointed to bigger, more immediate opportunities such as selling 5G to large companies and governments. “It became apparent a while ago that the most compelling use cases for 5G would revolve around businesses rather than consumers,” GlobalData’s Parker said.
To help make that happen, the major carriers formed partnerships with the so-called webscalers, the big cloud service providers including Amazon’s AWS, Microsoft’s Azure, Google, and Meta Platforms that handle data storage, online ordering, and video streaming for big companies. Each cloud giant sees 5G as a valuable entry into new classes of services, such as secure private networks to replace Wi-Fi, factory automation, and edge computing, which brings network hardware closer to end users to increase speeds.
To help make that happen, the major carriers formed partnerships with the so-called webscalers, the big cloud service providers including Amazon’s AWS, Microsoft’s Azure, Google, and Meta Platforms that handle data storage, online ordering, and video streaming for big companies. Each cloud giant sees 5G as a valuable entry into new classes of services, such as secure private networks to replace Wi-Fi, factory automation, and edge computing, which brings network hardware closer to end users to increase speeds.
The wireless carriers are staking their futures on these workplace roles. But because no 5G hyperconnected, cloud-powered commercial ecosystem has been built before, tech giants and telecommunications companies are collaborating to tackle the challenge.
While new partnerships are still being announced and big 5G projects are moving through the planning stages, executives at the wireless companies say they’re confident they can play a role in the information technology infrastructure of the future. “I’m proud to be the only carrier in the world that has partnership agreements with all three of the big webscalers,” says Verizon Communications Inc.’s business services chief Tami Erwin. “We’re creating the platform for the metaverse to really accelerate.”
As 4G showed, the carriers could create a higher-functioning network, but it was other companies such as Uber, Netflix, and Facebook that cashed in on the connectivity. 5G is set to expand the overall pie again, but the size of the carriers’ slice isn’t certain—bad news because they spent $118.4 billion on 5G airwave auctions, almost double the $61.8 billion they paid for 4G spectrum.
T-Mobile US Inc., which has taken the lead in U.S. 5G deployment, plans to focus on its core network strength as the tech giants sort things out, says Neville Ray, T-Mobile’s president of technology. “Facebook, Apple, Microsoft, Google—all of these massive companies are lining up huge investments in this space, and they need mobile networks in a way that they never did before,” he says. “They will need network capabilities that they simply don’t have any desire to build.”
That’s led a bunch of would-be competitors to work arm-in-arm to create a collective business model. “We have a great partnership with Microsoft,” says AT&T’s Sambar. “We’re a customer of Amazon, and they’re a customer of ours. We’re all friends today, we keep a close eye on each other. You have to cooperate to make this happen.”
The carriers provide businesses with a roster of services including voice, data, network management, and security, and they’ll want to keep control of those relationships as services emerge in 5G, says longtime Wall Street industry analyst Peter Supino. But as the cloud providers gain a bigger role in a business’s network infrastructure, running everything from robotics on the production floor to in-office wireless data systems, the carriers’ role may shift to more of a wholesale supplier of network capacity and mobile cellular service to the cloud companies, according to Supino.
“Over time, I’m confident that the cloud operators will provide too much convenience to be ignored,” he says. “The benefits of 5G will be significant, and they will mostly accrue to people who aren’t the telco carriers.”
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/power-verizon-5g-ultra-wideband-coming
Stratospheric Platforms demos HAPS based 5G; will it succeed where Google & Facebook failed?
UK-based Stratospheric Platforms (SPL) claims it’s demonstrated the world’s first successful High Altitude Platform Satellite (HAPS) based 5G base station. The 5G coverage from the stratosphere demonstration took place in Saudi Arabia.
–> That’s quite a claim since there are no ITU-R standards or 3GPP implementation specs for HAPS or satellite 5G. Current 5G standards and 3GPP specs are for terrestrial wireless coverage.
A SPL stratospheric mast – which for the purposes of the demonstration had been installed on a civilian aircraft – delivered high-speed coverage to a 5G mobile device from an altitude of 14 kilometres to a geographical area of 450 square kilometres.
SPL says their The High Altitude Platform (HAP) will be certified from the outset for safe operations in civil airspace. Some attributes are the following:
- The HAP will have endurance of over a week on station due its lightweight structure and huge power source.
- Designed to be strong enough to fly through the turbulent lower altitudes to reach the more benign environment of the stratosphere, where it will hold-station.
- A wingspan of 60 metres and a large, reliable power source enables a 140kg communications payload.
- Design life of over 10 years with minimal maintenance, repair and overhaul costs
- Extensive use of automation in manufacturing processes will result in a low cost platform.
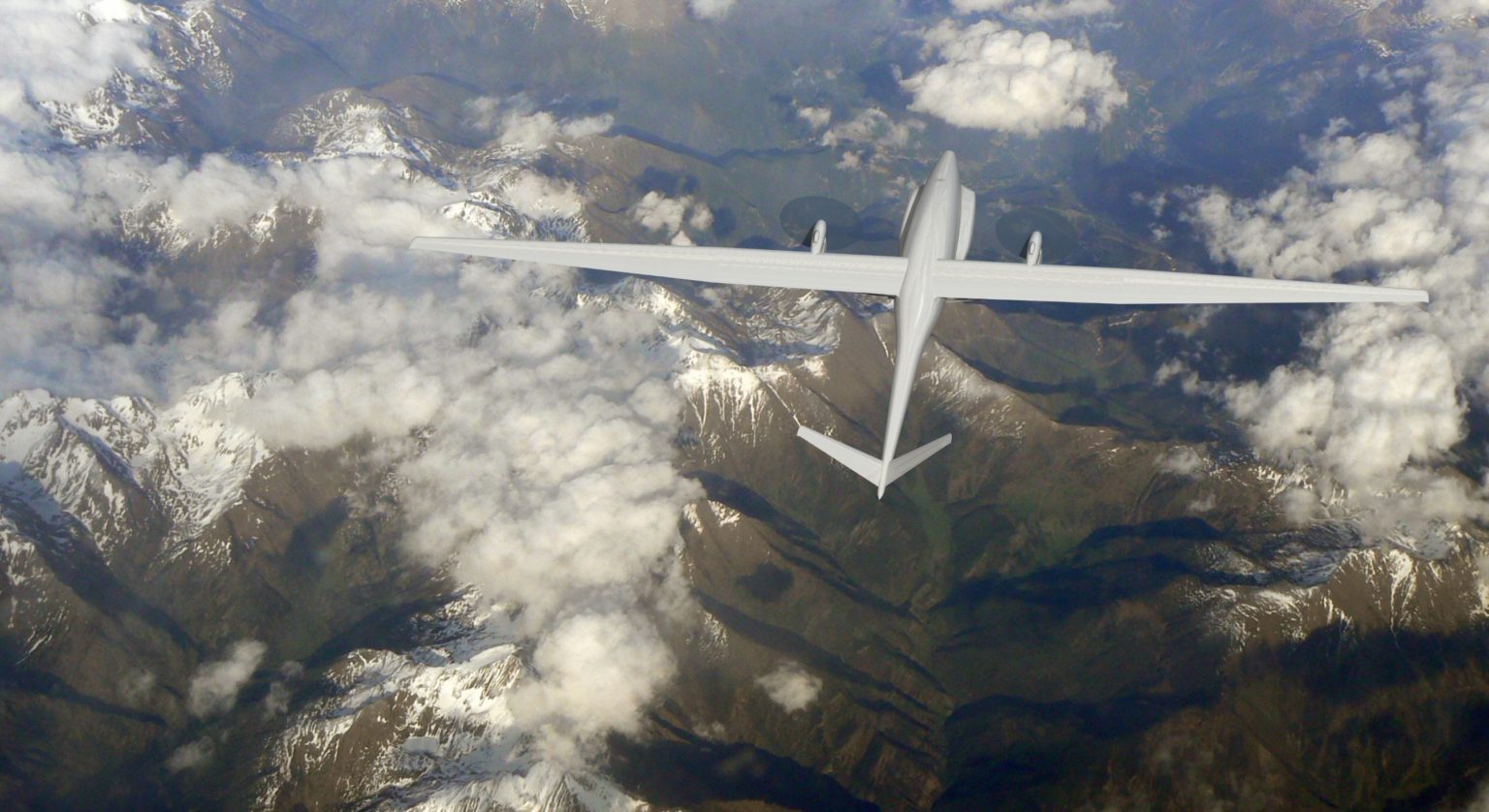

Source: Stratospheric Platforms
The joint team established three-way video calls between the land-based test site, a mobile device operated from a boat and a control site located 950 km away. Further land and heliborne tests demonstrated a user could stream 4K video to a mobile phone with an average latency of 1 millisecond above network speed. Signal strength trials, using a 5G enabled device moving at 100 km/h, proved full interoperability with ground-based masts and a consistent ‘five bars’ in known white spots.
Richard Deakin, CEO Stratospheric Platforms said, “Stratospheric Platforms has achieved a world-first. This is a momentous event for the global telecoms industry proving that a 5G telecoms mast flying near the top of the earth’s atmosphere can deliver stable broadband 5G internet to serve mobile users with ubiquitous, high-speed internet, over vast areas.”
Deakin added, “The trial has proved that 5G can be reliably beamed down from an airborne antenna and is indistinguishable from ground-based mobile networks. Our hydrogen-powered ‘Stratomast’ High Altitude Platform currently under development, will be able to fly for a week without refuelling and cover an area of 15,000 km2 using one antenna.”
The successful demonstration that a High Altitude Platform can deliver 5G Internet from the stratosphere means that mobile users can look forward to the capability of 5G mobile internet, even in the remotest areas of the world.
CITC Governor, H.E. Dr Mohammed Altamimi commented “the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is at the cutting edge of technological innovation and our partnership with Stratospheric Platforms’ with the support of the Red Sea Project and General Authority of Civil Aviation (GACA) has demonstrated how we can deliver ‘always on’, ultra-fast broadband to areas without ground based 5G masts.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Background and Analysis:
SPL was founded in Cambridge in 2014. In 2016, Deutsche Telekom became its biggest single shareholder and launch customer. It came out of hiding in 2020 with a demonstration in Germany of an aerial LTE base station.
Should SPL turn its HAPS vision into a sustainable, commercial reality, it will have succeeded where some much bigger names have failed. Google had a grand vision to offer long range WiFi connectivity from a fleet of balloons. Project Loon launched its first – and what turned out to be only – commercial service in Kenya in 2018. After nine years, Google gave up on Project Loon in 2021. In 2015 Google also dabbled with a drone-based HAPS service called Project Titan, but that came to an end in 2016.
Similarly Facebook attempted to roll out drone-based connectivity under the Aquila brand in 2016, but threw in the towel two years later. Facebook then posted what they believe will be “the next chapter in high altitude connectivity.”
These inauspicious examples don’t seem to have deterred SPL from pursuing HAPS connectivity, and it isn’t the only one trying. This past January, Japan’s NTT announced it is working with its mobile arm DoCoMo, aircraft maker Airbus, and Japanese satcoms provider Sky Perfect JSAT to look into the feasibility of HAPS-based connectivity.
So the momentum is building for HAPS based wireless connectivity but it won’t go mass market till standards emerge.
References:
https://www.stratosphericplatforms.com/
https://www.stratosphericplatforms.com/news/world-first-5g-transmission/
https://www.stratosphericplatforms.com/category/news/
https://telecoms.com/513882/5g-haps-inches-forward-with-saudi-trial/
New partnership targets future global wireless-connectivity services combining satellites and HAPS
Facebook & AT&T to Test Drones for Wireless Communications Capabilities
After 9 years Alphabet pulls the plug on Loon; Another Google X “moonshot” bites the dust!
MoffettNathanson: Robust broadband and FWA growth, but are we witnessing a fiber bubble?
According to a new comprehensive, market research report from MoffettNathanson (written by our colleague Craig Moffett), Q4 2021 broadband growth, at +3.3%, “remains relatively robust,” and above pre-pandemic levels of about +2.8%.
Meanwhile, the U.S. fixed wireless access (FWA market) captured ~ 38% share of broadband industry net adds in the fourth quarter of 2021. Approximately half of Verizon’s FWA customers are coming from commercial accounts, T-Mobile has indicated that about half its FWA customers are coming from former cable Internet subscribers. FWA’s strong Q4 showing left cable’s flow share at just 66%, about the same as cable’s share of installed US broadband households. “In other words, Cable likely neither gained nor lost share during the quarter, and instead merely treaded water,” Moffett noted. FWA “has gone from low-level background noise to suddenly a major force, with Verizon and T-Mobile alone capturing more than 300K FWA subscribers in the fourth quarter,” Craig noted. However, he isn’t sure that wireless network operators will allocate enough total bandwidth capacity for FWA to fully scale.
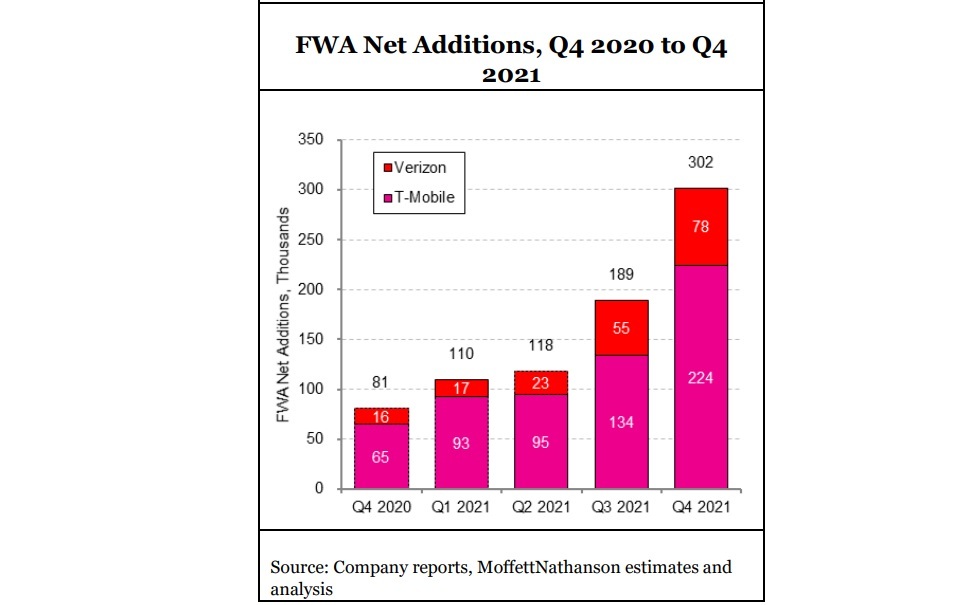
In 2020, a year that witnessed a surge in broadband subs as millions worked and schooled from home, the growth rate spiked to 5%. Here’s a snapshot of the broadband subscriber metrics per sector for Q4 2021:
Table 1:
| Sector | Q4 2021 Gain/Loss | Q4 2020 Gain/Loss | Year-on-Year Growth % | Total |
| Cable | +464,000 | +899,000 | +3.8% | 79.43 million |
| Telco | -26,000 | +21,000 | -0.4% | 33.51 million |
| FWA* | +302,000 | +81,000 | +463.9% | 869,000 |
| Satellite | -35,000 | -35,000 | -6.6% | 1.66 million |
| Total Wireline | +437,000 | +920,000 | +2.8% | 112.95 million |
| Total Broadband | +704,000 | +966,000 | +3.3% | 115.48 million |
| * Verizon and T-Mobile only (Source: MoffettNathanson) |
||||
U.S. broadband ended 2021 with a penetration of 84% among all occupied households. According to US Census Bureau data, new household formation, a vital growth driver for broadband, added just 104,000 to the occupied housing stock in Q4 2021, versus +427,000 in the year-ago period. Moffett said the “inescapable conclusion” is that growth rates will continue to slow, and that over time virtually all growth will have to stem from new household formation.
Factoring in competition and other elements impacting the broadband market, MoffettNathanson also adjusted its subscriber forecasts for several cable operators and telcos out to 2026. Here’s how those adjustments, which do not include any potential incremental growth from participation in government subsidy programs, look like for 2022:
- Comcast: Adding 948,000 subs, versus prior forecast of +1.25 million
- Charter: Adding 958,000 subs, versus prior forecast of +1.22 million
- Cable One: Adding 39,000, versus prior forecast of +48,000
- Verizon: Adding 241,000, versus prior forecast of +302,000
- AT&T: Adding 136,000, versus prior forecast of +60,000
Are we witnessing a fiber bubble?
“The market’s embrace of long-dated fiber projects rests on four critical assumptions. First, that the cost-per-home to deploy fiber will remain low. Second, that fiber’s eventual penetration rates will be high. Third, that these penetration gains can be achieved even at relatively high ARPUs. And fourth, that the capital to fund these projects remains cheap and plentiful.
None of these assumptions are clear cut. For example, there is an obvious risk that all the jostling for fiber deployment labor and equipment will push labor and construction costs higher. More pointedly, we think there is a sorely underappreciated risk that the pool of attractive deployment geographies – sufficiently dense communities, preferably with aerial infrastructure – will be exhausted long before promised buildouts have been completed.
Revenue assumptions, too, demand scrutiny. Cable operators are increasingly relying on bundled discounts of broadband-plus-wireless to protect their market share. What if the strategy works, even a little bit? And curiously, the market’s infatuation with fiber overbuilds comes at a time when cable investors are growing increasingly cautious about the impact of fixed wireless. Won’t fixed wireless dent the prospects of new overbuilds just as much (or more) as those of the incumbents.”
Moffet estimates that about 30% of the U.S. population has been overbuilt by fiber over the past 20 years, and that the number is poised to rise as high as 60% over the next five years. But the big question is whether there’s enough labor and equipment to support this magnitude of expansion. “Our skepticism about the prospects for all of the fiber plans currently on the drawing board is not born of doubt that there is enough labor to build it all so much as it is that the cost of building will be driven higher by excess demand,” Moffett explained. “There are already widespread reports of labor shortages and attendant higher labor costs,” he added.
“The outlook for broadband growth for all the companies in our coverage, particularly the cable operators, is more uncertain than at any time in memory. IMarket share trends are also more uncertain that they have been in the past. Cable continues to take share from the telcos, but fixed wireless, as a new entrant, is now taking share from all players. Share shifts between the TelCos and cable operators are suppressed by low move rates, likely due in part to supply chain disruptions in the housing market. This is likely dampening cable growth rates. In at least some markets, returns will likely be well below the cost of capital,” Moffett forecasts.
References:
U.S. Broadband: Are We Witnessing a Fiber Bubble? MoffetNathanson research note (clients and accredited journalists)


_1646295038.JPG)
