CoreSite Enables 50G Multi-cloud Networking with Enhanced Virtual Connections to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect
Note 1. CoreSite is a subsidiary of American Tower Corporation and a member of Oracle PartnerNetwork (OPN).
Note 2. Oracle FastConnect enables customers to bypass the public internet and connect directly to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and other Oracle Cloud services. With connectivity available at CoreSite’s data centers, FastConnect provides a flexible, economical private connection to higher bandwidth options for your hybrid cloud architecture. Oracle FastConnect is accessible at CoreSite’s data center facilities in Northern Virginia and Los Angeles through direct fiber connectivity. FastConnect is also available via the CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange® in seven CoreSite markets, including Los Angeles, Silicon Valley, Denver, Chicago, New York, Boston and Northern Virginia.
The integration of Oracle FastConnect and the CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange offers on-demand, virtual connectivity and access to best in class, end-to-end, fully redundant connection architecture.

Image Credit: CoreSite
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The connectivity of FastConnect and the OCX can offer customers deploying artificial intelligence (AI) and data-intensive applications the ability to transfer large datasets securely and rapidly from their network edge to machine learning (ML) models and big data platforms running on OCI. With the launch of the new OCX capabilities to FastConnect, businesses can gain greater flexibility to provision on-demand, secure bandwidth to OCI with virtual connections of up to 50 Gbps.
With OCI, customers benefit from best-in-class security, consistent high performance, simple predictable pricing, and the tools and expertise needed to bring enterprise workloads to cloud quickly and efficiently. In addition, OCI’s distributed cloud offers multicloud, hybrid cloud, public cloud, and dedicated cloud options to help customers harness the benefits of cloud with greater control over data residency, locality, and authority, even across multiple clouds. As a result, customers can bring enterprise workloads to the cloud quickly and efficiently while meeting the strictest regulatory compliance requirements.
“The digital world requires faster connections to deploy complex, data-intense workloads. The simplified process offered through the Open Cloud Exchange enables businesses to rapidly scale network capacity between the enterprise edge and cloud providers,” said Juan Font, President and CEO of CoreSite, and SVP of U.S. Tower. “These enhanced, faster connections with FastConnect can provide businesses with a competitive advantage by ensuring near-seamless and reliable data transfers at massive scale for real-time analysis and rapid data processing.”
OCI’s extensive network of more than 90 FastConnect global and regional partners offer customers dedicated connectivity to Oracle Cloud Regions and OCI services – providing customers with the best options anywhere in the world. OCI is a deep and broad platform of cloud infrastructure services that enables customers to build and run a wide range of applications in a scalable, secure, highly available, and high-performance environment. From application development and business analytics to data management, integration, security, AI, and infrastructure services including Kubernetes and VMware, OCI delivers unmatched security, performance, and cost savings.
The new Open Cloud Exchange capabilities on FastConnect will be available in Q4 2023.
Related Resources:
- Watch What is The Open Cloud Exchange® and How Can It Simplify and Automate Your Cloud Connectivity?
- Open Cloud Exchange® Solution Brochure
- Trust CoreSite Data Centers to Enable Your AI Strategy
- Why businesses partner with CoreSite
About CoreSite:
CoreSite, an American Tower company (NYSE: AMT), provides hybrid IT solutions that empower enterprises, cloud, network, and IT service providers to monetize and future-proof their digital business. Our highly interconnected data center campuses offer a native digital supply chain featuring direct cloud onramps to enable our customers to build customized hybrid IT infrastructure and accelerate digital transformation. For more than 20 years, CoreSite’s team of technical experts has partnered with customers to optimize operations, elevate customer experience, dynamically scale, and leverage data to gain competitive edge. For more information, visit CoreSite.com and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter.
References:
IEEE Santa Clara Valley (SCV) Lecture and Tour of CoreSite Multi-Tenant Data Center
https://www.coresite.com/cloud-networking/oracle-fastconnect
Nokia and du (UAE) complete 5G-Advanced RedCap trial; future of RedCap?
Nokia and United Arab Emirates (UAE) telco du announced the conclusion of what it claimed to be UAE’s first 5G-Advanced 5G Reduced Capability (RedCap) trial over a commercial network. Nokia said that this recent trial showcased the readiness of du’s 5G network for innovative use cases in areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), wearables and Industry 4.0 to address 5G monetization challenges.
RedCap, sometimes referred to as (3GPP) 5G NR Light, is a reduced set of 5G capabilities intended for devices like wearables and low-cost hotspots that have low battery consumption, lower costs and lower bandwidth requirements. Introduced with 3GPP Release 17, 5G RedCap is designed for devices currently served by LTE CAT-4 but provides equivalent or better in performance with up to 150 Mbps theoretical maximum downlink throughput. This technology helps reduce the complexity, cost and size of 5G devices. The RedCap specification will be included in ITU-R M.2150-1.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The trial participants used MediaTek’s T300 series RedCap test equipment in du’s 5G Standalone (SA) Radio Access Network (RAN) built with Nokia’s AirScale radio products, leveraging the existing mid-band Spectrum. This will follow extending RedCap over low band frequencies, ensuring extreme coverage and connectivity. Notably, the low band in 600MHz, is a vital connectivity band currently under discussion at the World Radio Conference WRC-23 taking place in Dubai.
With RedCap devices expected to be commercially available from 2024, it will significantly augment du’s diversified use case portfolio to include cost-efficient 5G home wireless, wearables, video surveillance, and wireless industrial sensors.
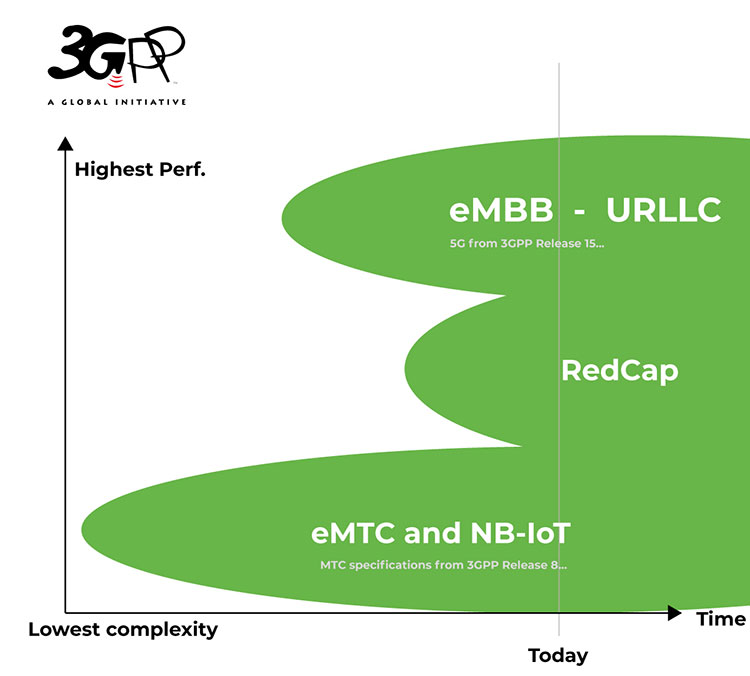
5G devices commonly feature intricate hardware and energy-intensive capabilities, resulting in higher cost, size, and power consumption. RedCap technology is dedicated to streamlining 5G devices, specifically targeting compact IoT devices like wearables and health trackers, as well as ruggedized routers and sensors for environmental or condition-based monitoring. These devices exhibit lower demands for battery life and reduced bandwidth requirements. RedCap ensures they sustain performance while optimizing their power efficiency. Nokia has been instrumental in driving the evolution of RedCap IoT functionality in collaboration with the telecommunications industry.
Saleem Alblooshi, Chief Technology Officer at du, said: “This collaboration introduces the revolutionary 5G-Advanced RedCap functionalities, enabling seamless connectivity of RedCap devices to cutting-edge 5G networks. Nokia’s unparalleled innovation simplifies and pioneers the development of 5G devices, particularly wearables and small IoT devices, significantly enhancing LTE-CAT4 performance and optimizing energy efficiency. These remarkable technological advancements are pivotal in propelling Industry 4.0 revolution.”
Mikko Lavanti, Senior Vice President at Nokia MEA, said: “This new collaboration between du and Nokia represents not only a significant step forward in the monetization of 5G technology but also solidifies the UAE’s position as a pioneer in the evolution of 5G use cases for society and enterprises. As the collaboration progresses, both companies are poised to revolutionize the way we experience and interact with 5G technology, unlocking unprecedented possibilities for innovation and connectivity.”
Dr. Ho-Chi Hwang, General Manager of Wireless Communication System and Partnerships at MediaTek, said: “It’s essential to bring new capabilities of 5G to the UAE, and this trial is an important step in that direction. We are proud to have provided our RedCap devices to further develop the ecosystem for 5G monetization. We hope, by pioneering the technology in the Middle East and Africa region, MediaTek will be able to assure our customers of more innovative 5G products and services coming their way.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Future of RedCap:

Counterpoint Research expects that 5G RedCap modules will make up 18% of total cellular IoT module shipments by 2030—what it describes as “significant market potential, particularly in developing nations where the cost is key to wide technology adoption for digital transformation.”
“If we want to tackle some of these interesting business cases and really get the price point so the business can take off, then we need to provide the right types of options,” said Paul Harris, principal architect in the Office of the CTO at Viavi Solutions. “People don’t want to be paying for chipsets that are too performant in the wrong types of devices.” Harris also noted that standards work on RedCap continues, with a series of recommendations on reducing RedCap’s performance even further with support of just five megahertz of bandwidth, even lower data rates and reduced peak data rates as well as additional power savings in the form of Extended Discontinuous Reception (allowing longer periods during which a device can power off). While that work on “eRedCap” is still taking shape in Release 18 and additional features may be available to scale down RedCap further in Release 19. “It’s still kind of a moving target and probably will continue to be, but there will probably be different categories that get introduced of RedCap as it goes on,” he said. Harris goes on to offer up a potential vision of a RedCap market where there is a gradual progression into some parts of the market addressed with the initial Rel. 17 RedCap options, and that by Rel. 19, a scaled-back RedCap market could open up for even lower-complexity, lower data-rate devices that then leads to an explosion of 5G sensor devices.
“5G is absolutely the directional technology,” said Bill Stone, VP of technology development and planning at Verizon. “I do think it’s inevitable that we’ll be seeing all of IoT evolve over time, and it’s going to be starting as soon as next year. We’re going to see all of the IoT device community moving over to 5G, because that’s where—with 5G NR SA—we’re going to see the potential for much longer lifecycles [and] the ability to support that, to make commitments for longer-term support of IoT devices.”
References:
Standards leadership in action: How Nokia convinced the 5G world that less is more
Ericsson, Vodafone and Qualcomm: 1st Reduced Capability 5G data call in Europe
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/redcap
ITU-R M.2150-1 (5G RAN standard) will include 3GPP Release 17 enhancements; future revisions by 2025
Google announces Gemini: it’s most powerful AI model, powered by TPU chips
Google claims it has developed a new Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) system and Large Language Model (LLM) more powerful than any currently on the market, including technology developed by ChatGPT creator OpenAI. Gemini can summarize text, create images and answer questions. Gemini was trained on Google’s Tensor Processing Units v4 and v5e.
Google’s Bard is a generative AI based on the PaLM large language mode. Starting today, Gemini will be used to give Bard “more advanced reasoning, planning, understanding and more,” according to a Google blog post.
While global users of Google Bard and the Pixel 8 Pro will be able to run Gemini now, an enterprise product, Gemini Pro, is coming on Dec. 13th. Developers can sign up now for an early preview in Android AICore.
Gemini comes in three model sizes: Ultra, Pro and Nano. Ultra is the most capable, Nano is the smallest and most efficient, and Pro sits in the middle for general tasks. The Nano version is what Google is using on the Pixel, while Bard gets Pro. Google says it plans to run “extensive trust and safety checks” before releasing Gemini Ultra to select groups.
Gemini can code in Python, Java, C++, Go and other popular programming languages. Google used Gemini to upgrade Google’s AI-powered code generation system, AlphaCode. Next, Google plans to bring Gemini to Ads, Chrome and Duet AI. In the future, Gemini will be used in Google Search as well.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Market Impact:
Gemini’s release and use will present a litmus test for Google’s technology following a push to move faster in developing and releasing AI products. It coincides with a period of turmoil at OpenAI that has sent tremors through the tight knit AI community, suggesting the industry’s leaders is far from settled.
The announcement of the new GenAI software is the latest attempt by Google to display its AI portfolio after the launch of ChatGPT about a year ago shook up the tech industry. Google wanted outside customers to perform testing on the most advanced version of Gemini before releasing it more widely, said Demis Hassabis, chief executive officer of Google DeepMind.
“We’ve been pushing forward with a lot of focus and intensity,” Hassabis said, adding that Gemini likely represented the company’s most ambitious combined science and engineering project to date.
Google said Wednesday it would offer a range of AI programs to customers under the Gemini umbrella. It touted the software’s ability to process various media, from audio to video, an important development as users turn to chatbots for a wider range of needs.
The most powerful Gemini Ultra version outperformed OpenAI’s technology, GPT-4, on a range of industry benchmarks, according to Google. That version is expected to become widely available for software developers early next year following testing with a select group of customers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Role of TPUs:
While most GenAI software and LLM’s are processed using NVIDIA’s neural network processors, Google’s tensor processing units (TPUs) will power Gemini. TPUs are custom-designed AI accelerators, which are optimized for training and inference of large AI models. Cloud TPUs are optimized for training large and complex deep learning models that feature many matrix calculations, for instance building large language models (LLMs). Cloud TPUs also have SparseCores, which are dataflow processors that accelerate models relying on embeddings found in recommendation models. Other use cases include healthcare, like protein folding modeling and drug discovery.
Google’s custom AI chips, known as tensor processing units, are embedded in compute servers at the company’s data center. Photo Credit: GOOGLE
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Competitors:
Gemini and the products built with it, such as chatbots, will compete with OpenAI’s GPT-4, Microsoft’s Copilot (which is based on OpenAI’s GPT-4), Anthropic’s Claude AI, Meta’s Llama 2 and more. Google claims Gemini Ultra outperforms GPT-4 in several benchmarks, including the massive multitask language understanding general knowledge test and in Python code generation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Everything to know about Gemini, Google’s new AI model (blog.google)
Google Reveals Gemini, Its Much-Anticipated Large Language Model (techrepublic.com)
T-Mobile combines Millimeter Wave spectrum with its 5G Standalone (SA) core network
T-Mobile, with the help of with Ericsson and Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., has tested millimeter wave (mmWave) on its production 5G SA network (note that mmWave identifies higher frequencies used on a 5G RAN, while 5G SA refers to a true 5G core network). The Un-carrier aggregated eight channels of mmWave spectrum to reach download speeds topping 4.3 Gbps without relying on low-band or mid-band spectrum to anchor the connection. T-Mobile also aggregated four channels of mmWave spectrum on the uplink, reaching speeds above 420 Mbps.
In the latest revision of ITU-R M.1036- Frequency Arrangements for IMT-the following mmWave bands were approved:
-Frequency arrangements in the band 24.25-27.5 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 45.5-47 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 47.2-48.2 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 66-71 GHz
In the U.S., Verizon has historically been the carrier promoting 5G mmWave, which they dubbed “5G Ultra Wideband.” The telco claims they’ve achieved 1.26 Gbps upload speed using 5G Ultra Wideband. With uploading data becoming increasingly important for video chats, uploading large files or live streaming video. “We have achieved remarkable speed in downloading using various combinations of spectrum in our world-class spectrum portfolio,” said Adam Koeppe, Senior Vice President of Technology Planning at Verizon. “This new achievement indicates how much additional performance we can unleash for our customers on the uplink as we aggregate different combinations of spectrum.”
T-Mobile took the opposite path, focusing on mid and low-band spectrum for its 5G network…until now. 5G mmWave can deliver very fast speeds because it offers massive capacity. But the signal doesn’t travel very well through obstacles, making it less ideal for mobile phone users who aren’t sitting still. That’s why T-Mobile has implemented a multi-band spectrum strategy using low-band to blanket the country and mid-band and high-band (Ultra Capacity) to deliver insanely fast speeds to nearly everyone. Now the Un-carrier is testing 5G mmWave on 5G SA for crowded areas like stadiums and, potentially, for fixed wireless service.
“We’ve been industry leaders – rolling out the first, largest and fastest 5G standalone network across the country – and now we’re continuing to push the boundaries of wireless technology,” said Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology at T-Mobile. “We’ve always said we’ll use millimeter wave where it makes sense, and this test allows us to see how the spectrum can be put to use in different situations like crowded venues or to power things like fixed-wireless access when combined with 5G standalone.”
T-Mobile is the U.S. leader in 5G [1.] delivering the largest, fastest and most awarded 5G network in the country. The Un-carrier’s 5G network covers more than 330 million people across two million square miles — more than AT&T and Verizon combined. 300 million people nationwide are covered by T-Mobile’s super-fast Ultra Capacity 5G with over 2x more square miles of coverage than similar mid-band 5G offerings from the Un-carrier’s closest competitors. According to Ookla’s quarterly speed test reports, T-Mobile’s 5G network has consistently outperformed AT&T’s and Verizon’s when it comes to median download speed.
Note 1. AT&T is the leading provider of mobile services in the U.S. with 229.1 subscribers as of Q2 2023, followed by: Verizon: 143.3 million (Q2 2023),,T-Mobile US: 117.9 million (Q3 2023), Dish Wireless: 7.5 million (Q3 2023), and uscellular: 4.6 million (Q3 2023).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
T-Mobile also offers wireless solutions to connect homes and businesses. 5G Home Internet (FWA) is available to over 50 million homes today, plus Small Business Internet and Business Internet is available across the country. This means millions of homes and businesses can finally ditch traditional ISPs for fast, reliable and hassle-free internet service with T-Mobile. The telco’s FWA customer base increased by 557,000 during Q3, giving it a total of 4.2 million. It has allowed T-Mobile to offer a compelling alternative to fixed broadband, but its service comes with the caveat that speeds will fluctuate depending on demand.
The extra capacity offered by mmWave could help to offer a faster, more consistent connection, making it even more appealing. However, the propagation challenges of mmWave spectrum means customers will have to ensure their FWA hub is sitting on the right shelf or window sill to establish a fast, reliable connection. Addressing complaints as customers struggle to put their hub in the right spot may be a problem for the Un-carrier.
Editor’s Note:
The NTIA will study the following bands in the next two years, noting that the spectrum could support a range of uses, including mobile broadband (IMT), drones and satellite operations:
- 3.1 GHz-3.45 GHz
- 5.03 GHz-5.091 GHz
- 7.125 GHz-8.4 GHz
- 18.1 GHz-18.6 GHz
- 37.0 GHz-37.6 GHz
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/network/t-mobile-revs-up-millimeter-wave-with-5g-standalone
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-achieves-upload-speeds-surpassing-1-gbps
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/t-mobile-finally-puts-mmwave-to-work-in-5g-sa-network
https://www.telecoms.com/wireless-networking/t-mobile-network-speeds-still-way-ahead-of-verizon-at-t
U.S. Launches National Spectrum Strategy and Industry Reacts
Ericsson Mobility Report touts “5G SA opportunities”
State of 5G SA:
“It’s been exciting to see the industry evolve in the last decade or so, and see first-hand the massive growth of 4G and the arrival of 5G,” said Fredrik Jejdling Executive Vice President and Head of Business Area Networks and Publisher of Ericsson Mobility Report.
The latest edition of Ericsson’s Mobility Report opens with the assertion that “5G standalone brings new opportunities,” which sounds promising, but there’s nothing in the report which shows what those opportunities are.
Ericsson says that 40 service providers have deployed or launched 5G SA in public networks, which agrees with Analysys Mason’s findings. To put that in context, around 280 service providers globally have launched commercial 5G with the overwhelming being 5G NSA.

Dell’Oro counted just seven 5G SA launches to date in 2023, while the GSA – which worked with Ericsson on the stats for its Mobility Report – shared data that also showed little growth in 5G SA this year.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- 1. 6 bn Global 5G mobile subscriptions are projected to reach 1.6 billion by the end of 2023.
- 30% 5G mid-band population coverage outside mainland China has increased from 10 percent in 2022 to around 30 percent at the end of 2023.
- 56 GB Global mobile data traffic consumption per smartphone is expected to reach 56 GB per month at the end of 2029.
Ericsson predicts that there will be 1.6 billion 5G subs in the world by the end of this year, or 18% of all mobile subscriptions, driven by North America, where 5G penetration will reach 61%. As recently as June, the network equipment vendor forecast that the year-end 5G total would hit 1.5 billion, so clearly the market is increasing faster than expected. In the third quarter there were 163 million 5G subscriber additions taking the total to 1.4 billion by the end of September. As such, the year-end target look eminently achievable.
Ericsson puts total global 5G subscriptions at 5.3 billion by the end of 2029, by which date 5G network coverage should reach 85% of the population, up from 45% at the end of this year.
“With more than 600 million 5G subscriptions added globally this year, and rising in every region, it is evident that the demand for high performance connectivity is strong,” said Fredrik Jejdling, Executive Vice President and Head of Networks, at Ericsson. “The roll-out out of 5G continues and we see an increasing number of 5G standalone networks being deployed, bringing opportunities to support new and more demanding applications for both consumers and enterprises,” he added.
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/5g-subs-exceed-expectations-but-they-re-not-standing-alone
Analysys Mason: 40 operational 5G SA networks worldwide; Sub-Sahara Africa dominates new launches
GSA 5G SA Core Network Update Report
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market has lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017
MTN Group and NEC XON deploy Africa’s first 400G optical transponder using TIP’s Phoenix
NEC Corporation and MTN Group have successfully deployed Africa’s first 400G optical transponder solution using “Phoenix.” This initiative marks a significant milestone for the telecommunications industry in Africa, with the potential to revolutionize the way optical networks are built and operated, thereby transforming internet delivery across the continent.
Phoenix is part of the Telecom Infra Project’s (TIP) Open Optical and Packet Transport (OOPT) project group, a collaborative effort involving multiple telecom operators and technology providers. Phoenix is a network device, known as a white box L0/L1 transponder, that can transmit data at speeds of up to 400 gigabits per second. The solution has met TIP’s rigorous test requirements, earning it a Controlled Environment Silver Badge, indicative of its readiness for deployment. Its disaggregated nature allows it to be programmed to run any vendor’s software, offering operators unprecedented flexibility in hardware and software selection. This disaggregation leads to cost reductions, accelerates innovation, and enables quicker and easier deployment of new network services.
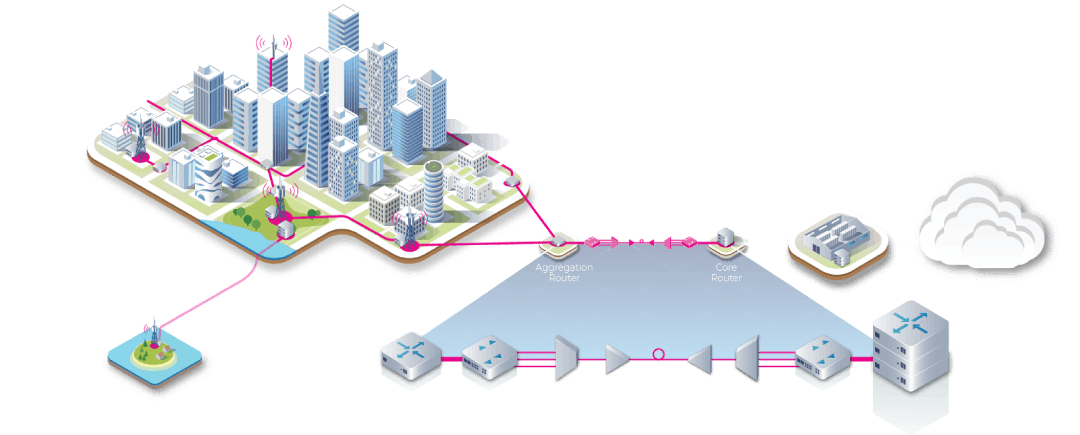
Image Credit: Telecom Infra Project
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“We are thrilled to receive the Silver Badge recognition from TIP, acknowledging our commitment to promoting open and disaggregated solutions with the Phoenix optical transponder,” said Sou Satou, Senior Director of the Network Solutions Business Division at NEC Corporation. “Our dedication to TIP and the development of open products in the optical transport market remains a top priority for NEC,” she added.
The deployment of Phoenix is designed to accelerate internet connectivity and optimise network operations, thereby democratising access to information. It aims to make affordable internet more widely available across Africa, fulfilling a critical societal need.
Demonstrating its commitment to innovation, MTN has embraced this state-of-the-art technology, integrating it into its production network, specifically across its optical network between Johannesburg and Centurion in South Africa, further demonstrating the technology’s interoperability and backwards compatibility.
“The deployment of Phoenix with NEC Corporation is a significant step toward fulfilling a crucial promise to our customers, to deliver accessible, reliable, and fast internet,” said Amith Maharaj, Executive – Network Design and Planning. “This initiative is part of our ongoing efforts to embrace the latest technologies available that ultimately empower communities across Africa,” he added.
“Disaggregation is the future of networking, and we are proud to be at the forefront of this evolution,” said Anthony Laing, General Manager of Networking at NEC XON. “Through our partnership with MTN, we’ve established NEC XON as a trusted leader in disaggregated networking.”
By leading in the adoption of Phoenix, NEC Corporation and MTN Group are setting a precedent for telecom operators worldwide, offering a scalable and cost-efficient solution that meets the burgeoning demands of a digitally connected society.
This initiative marks a significant milestone for the telecommunications industry in Africa, the companies say, with the potential to revolutionize the way optical networks are built and operated. By leading this initiative, MTN believes it is ultimately helping customers with improved, cost-effective connectivity.
About MTN:
MTN is Africa’s largest mobile network operator, providing voice, data, fintech, digital, enterprise, wholesale and API services to more than 292 million customers in 19 markets.
About NEC XON:
NEC XON is a leading pan-African ICT-systems integrator, specializing in cutting-edge Communications, Enterprise and Retail, Infrastructure and Energy, and Safety and Security solutions. Operating in 54 African countries and with a strong presence in 16 of them, NEC XON has established regional headquarters in South, East, and West Africa.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://telecominfraproject.com/oopt/
Bell and FirstLight: 3 new wavelength routes with triple redundancy and speeds up to 400G b/sec
China Mobile to deploy 400G QPSK by the end of 2023
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport market to hit $17B by 2027; Lumen Technologies 400G wavelength market
Heavy Reading: Coherent Optics for 400G transport and 100G metro edge
Cignal AI: NA Optical Network Spending to Accelerate; IEEE 802.3ct; NeoPhotonics 400G Multi-Rate Transceiver
MTN Consulting: Generative AI hype grips telecom industry; telco CAPEX decreases while vendor revenue plummets
Ever since Generative (Gen) AI burst into the mainstream through public-facing platforms (e.g. ChatGPT) late last year, its promising capabilities have caught the attention of many. Not surprisingly, telecom industry execs are among the curious observers wanting to try Gen AI even as it continues to evolve at a rapid pace.
MTN Consulting says the telecom industry’s bond with AI is not new though. Many telcos have deployed conventional AI tools and applications in the past several years, but Gen AI presents opportunities for telcos to deliver significant incremental value over existing AI. A few large telcos have kickstarted their quest for Gen AI by focusing on “localization.” Through localization of processes using Gen AI, telcos vow to eliminate language barriers and improve customer engagement in their respective operating markets, especially where English as a spoken language is not dominant.
Telcos can harness the power of Gen AI across a wide range of different functions, but the two vital telco domains likely to witness transformative potential of Gen AI are networks and customer service. Both these domains are crucial: network demands are rising at an unprecedented pace with increased complexity, and delivering differentiated customer experiences remains an unrealized ambition for telcos.
Several Gen AI use cases are emerging within these two telco domains to address these challenges. In the network domain, these include topology optimization, network capacity planning, and predictive maintenance, for example. In the customer support domain, they include localized virtual assistants, personalized support, and contact center documentation.
Most of the use cases leveraging Gen AI applications involve dealing with sensitive data, be it network-related or customer-related. This will have major implications from the regulatory point of view, and regulatory concerns will constrain telcos’ Gen AI adoption and deployment strategies. The big challenge is the mosaic of complex and strict regulations prevalent in different markets that telcos will have to understand and adhere to when implementing Gen AI use cases in such markets. This is an area where third-party vendors will try to cash in by offering Gen AI solutions that are compliant with regulations in the respective markets.
Vendors will also play a key role for small- and medium-sized telcos in Gen AI implementation, by eliminating constraints due to the lack of technical expertise and HW/SW resources, skilled manpower, along with opex costs burden. Key vendors to watch out for in the Gen AI space are webscale providers who possess the ideal combination of providing cloud computing resources required to train large language models (LLM) coupled with their Gen AI expertise offered through pre-trained models.
Other key points from MTN Consulting on Gen AI in the telecom industry:
- Network operations and customer support will be key transformative areas.
- Telco workforce will become leaner but smarter in the Gen AI era.
- Strict regulations will be a major barrier for telcos.
- Vendors key to Gen AI integration; webscale providers set for more telco gains.
- Lock-in risks and rising software costs are key considerations in choosing vendors.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
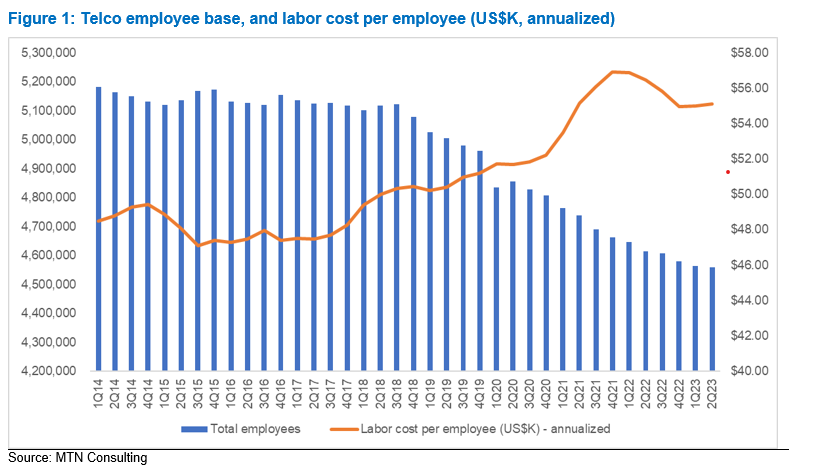
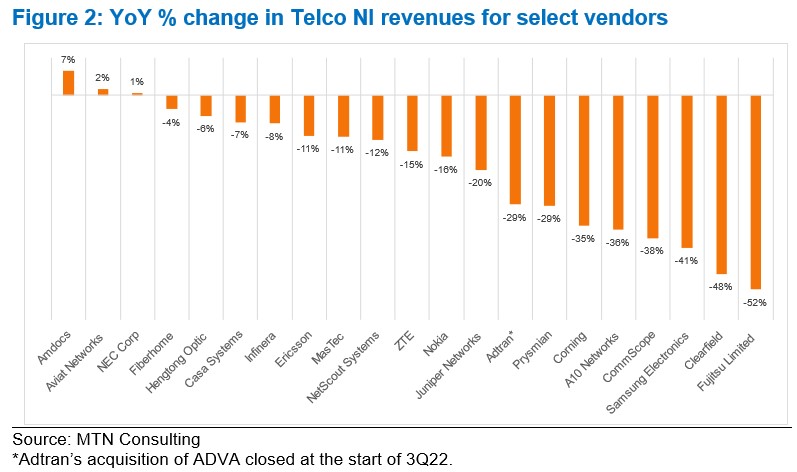
Separately, MTN Consulting’s latest forecast called for $320B of telco capex in 2023, down only slightly from the $328B recorded in 2022. Early 3Q23 revenue reports from vendors selling into the telco market call this forecast into question. The dip in the Americas is worse than expected, and Asia’s expected 2023 growth has not materialized.
Key vendors are reporting significant YoY drops in revenue, pointing to inventory corrections, macroeconomic uncertainty (interest rates, in particular), and weaker telco spending. Network infrastructure sales to telcos (Telco NI) for key vendors Ericsson and Nokia dropped 11% and 16% YoY in 3Q23, respectively, measured in US dollars. By the same metric, NEC, Fujitsu and Samsung saw +1%, -52%, and -41% YoY growth; Adtran, Casa, and Juniper declined 29%, 7%, and 20%; fiber-centric vendors Clearfield, Corning, CommScope, and Prysmian all saw double digit declines.
MTN Consulting will update its operator forecast formally next month. In advance, this comment flags a weaker spending outlook than expected. Telco capex for 2023 is likely to come in around $300-$310B.
MTN Consulting’s Network Operator Forecast Through 2027: “Telecom is essentially a zero-growth industry”
MTN Consulting: Top Telco Network Infrastructure (equipment) vendors + revenue growth changes favor cloud service providers
Proposed solutions to high energy consumption of Generative AI LLMs: optimized hardware, new algorithms, green data centers
Cloud Service Providers struggle with Generative AI; Users face vendor lock-in; “The hype is here, the revenue is not”
Global Telco AI Alliance to progress generative AI for telcos
Amdocs and NVIDIA to Accelerate Adoption of Generative AI for $1.7 Trillion Telecom Industry
Bain & Co, McKinsey & Co, AWS suggest how telcos can use and adapt Generative AI
Generative AI Unicorns Rule the Startup Roost; OpenAI in the Spotlight
Generative AI in telecom; ChatGPT as a manager? ChatGPT vs Google Search
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases
MTN Consulting: Satellite network operators to focus on Direct-to-device (D2D), Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud-based services
MTN Consulting on Telco Network Infrastructure: Cisco, Samsung, and ZTE benefit (but only slightly)
MTN Consulting: : 4Q2021 review of Telco & Webscale Network Operators Capex
Vodafone Germany deploys Ericsson 5G radio to cut energy use up to 40%
Vodafone Germany has partnered with Ericsson to deploy new power-saving radio technology on its 5G network. The radio unit 6646 bundles three different frequencies (900, 800 and 700 MHz) and radio cells in one system in the control center located at the bottom of a mobile base station. By bundling the active technology, 5G base stations function with 32-40% less power.

The advantage of mobile radio stations with area frequencies is that they provide particularly large areas with stable and reliable mobile radio coverage. By bundling the active technology of different frequency ranges and several radio cells in one unit, they now require between 32 and 40 percent less energy, according to trials on the Vodafone network. Following successful tests in the North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) region, the telecommunications group is now successively activating the technology in the live network together with its technology partner Ericsson.
The new energy-saving radio from Ericsson has been intensively tested in the live network in Wachtendonk in the Lower Rhine region over the past few weeks. The positive test results demonstrate an energy-saving potential of up to 40 percent per 5G base station and are the reason for today’s large-scale rollout. The new technology will be installed and automatically activated in NRW, Rhineland-Palatinate, Hesse, Saarland and Baden-Württemberg during routine maintenance and modernization work.
Test results on the Vodafone network show that energy requirements can be reduced by more than 2,500 kilowatt hours (kWh) per mobile phone site per year by bundling the active technology. This is roughly equivalent to the annual energy requirement of a two-person household per mobile phone station. If the technology is activated on a large scale in the network, significantly more than 30 million kilowatt hours of electricity can be saved each year. At the same time, stable and reliable network coverage will also be strengthened in rural regions.
Vodafone Germany CEO Philippe Rogge, says: “For the first time, we are bundling the active antenna technology of different area frequencies in mobile communications. This is good for smartphone users in rural areas and good for our planet. Because with the new technology, we are bringing fast and reliable 5G networks even better to people in rural areas and deep into buildings. At the same time, we are reducing the energy requirements of our mobile phone antennas. We expect to be able to save more than 30 million kilowatt hours of electricity per year with large-scale activation in our network.”
Daniel Leimbach, Head of Western Europe at Ericsson, says: “Energy consumption reduced by up to 40 percent, weight reduced by 60 percent – around a year ago, we celebrated a world premiere at the launch of the Radio 6646 at the Eurolab in Aachen. At the Imagine Live Innovation Day in the research and development center, our experts presented the innovative 5G technology for the first time. We are all the more pleased that Vodafone is convinced of its performance and energy efficiency and is installing the technology in the area. Because only innovations that are scalable, economical and powerful at the same time deliver the full benefits for mobile customers and sustainability.
The technology in Ericsson’s new radio:
Ericsson’s new remote radio combines the different 5G area frequencies 900, 800 and 700 MHz as well as the components of several radio cells into one compact system in a more sustainable way. By bundling three frequencies and several radio cells, the transmission technology consumes significantly less energy for each individual frequency range at full power. In addition, the new radio is 60 percent lighter and therefore requires less energy and material in the manufacturing process.
On the way to CO2 neutrality:
The new antenna product is another building block on Vodafone’s path to becoming more sustainable step by step. The Düsseldorf-based company has set itself specific targets to be CO2-neutral by 2025. The network is the biggest and most important lever here. Vodafone Germany has therefore been sourcing 100 percent of its electricity from renewable sources since 2020. It is also constantly testing new technologies and solutions to make the German mobile network more sustainable and conserve resources. For example, the dynamic energy-saving mode in the mobile network has already been ensuring an intelligent adjustment between actual energy demand and consumption around the clock for over a year.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Ericsson and Vodafone deploy new energy-efficient, light 5G radio in London
Ericsson and U.S. PAWR 5G SA network for rural agricultural research
TDC NET with Ericsson launch first 5G Standalone network in Denmark
Ericsson powers Singtel 5G SA core network; lightest and smallest Massive MIMO radio
Ericsson announces 5G standalone NR software and 2 new Massive MIMO radios
Grandview Research: global telecom services market to compound at 6.2% from 2023 to 2030
According to Grandview Research, the global telecom services market size was valued at USD 1,805.61 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030.
Rising spending on the deployment of 5G infrastructures due to the shift in customer inclination toward next-generation technologies and smartphone devices is one of the key factors driving this industry. An increasing number of mobile subscribers, soaring demand for high-speed data connectivity, and the growing demand for value-added managed services are the other potential factors fueling the market growth. The global communication network has undoubtedly been one of the prominent areas for continued technological advancements over the past few decades.
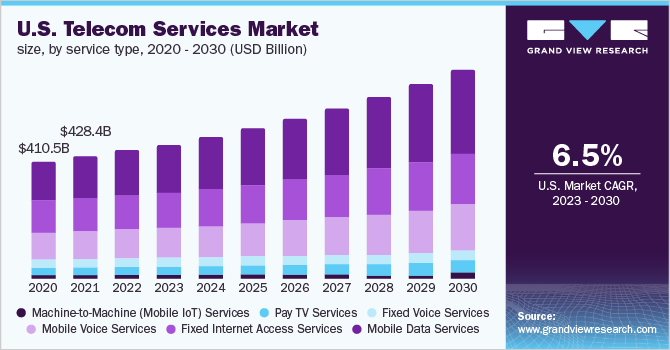
In 2022, the wireless networks accounted for a market share of more than 76.0% in the global market. The advent of cloud-computing technologies, artificial intelligence, and IoT is presumed to majorly contribute to the growth of wireless communication channels worldwide. Over the years, there has been a rapid deployment of systems for Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) that has enabled internet access to cellular devices in private homes, public spaces, airports, office buildings, cafeterias, and other areas. Such wireless densification to simplify work processes and automate routine test actions is presumed to prove beneficial, hence registering a robust CAGR in the forthcoming years.
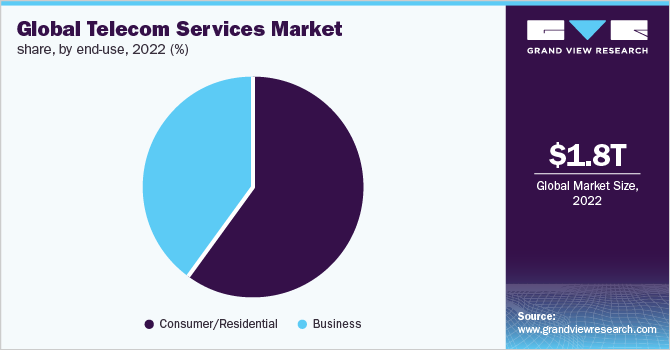
In 2022, the consumer/residential segment accounted for the largest revenue share of more than 59.0% and is projected to maintain its lead over the forecast period. The significant growth is ascribed to the proliferation of smartphones worldwide. There were more than 8 billion mobile subscribers recorded globally in 2020, wherein more than 60% of the population was using smartphones. The private telecom operators account for a larger subscriber base as compared to government-owned companies. In addition, the growing demand for OTT applications is contemplating the users to subscribe to wireless internet offerings, thereby significantly contributing to the deployment of communication networks at a broader level. Additionally, the growing trend of using ultra-high-definition videos and online gaming is expected to boost the segment growth over the forecast period.
In 2022, the Asia Pacific captured more than 33.0% of share and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.0% from 2023 to 2030. The region is likely to attract more than half of the new mobile subscribers by 2030. The regional market is primarily driven by e-commerce and retailer buy-in platforms, smartphone ubiquity, and investments in 5G networks. China, Japan, and India have emerged as significant contributors to regional market growth. According to industry expert analysis, in February 2022, China recorded 1.02 billion internet users, which is more than three times the number of the third-placed United States, which had just over 307 million. India recorded the second highest internet users in February 2022.
Some prominent players in the global telecom services market include:
- AT&T Inc.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT)
- China Mobile Ltd.
- Deutsche Telekom AG
- SoftBank Group Corp.
- China Telecom Corp Ltd.
- Telefonica SA
- Vodafone Group
- KT Corporation
- Bharati Airtel Limited
- Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited
- KDDI Corporation
- Orange SA
- BT Group plc
- Comcast Corporation
Telecom Services Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size value in 2023 | USD 1,885.41 billion |
| Revenue forecast in 2030 | USD 2,874.76 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030 |
| Base year for estimation | 2022 |
| Historical period | 2017 – 2021 |
| Forecast period | 2023 – 2030 |
| Quantitative units | Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2023 to 2030 |
| Report coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Segments covered | Service type, transmission, end-use, region |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Country scope | U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; France; Italy; China; Japan; India; South Korea; Brazil; Mexico |
| Key companies profiled | AT&T Inc.; Verizon Communications Inc.; NTT; China Mobile Ltd.; Deutsche Telekom AG; SoftBank Group Corp.; China Telecom Corp Ltd.; Telefonica SA; Vodafone Group; KT Corporation; Bharati Airtel Limited; Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited; KDDI Corporation; Orange SA; BT Group plc; Comcast Corporation |
| Customization scope | Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
| Pricing and purchase options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
References:
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/global-telecom-services-market
Technavio: APAC region leads global telecom services market with 33% growth
Canalys: Global cloud infrastructure services spending up 16% in Q3-2023
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom to Jointly Develop Telco-specific Large Language Models (LLMs)
Canalys: Global cloud infrastructure services spending up 16% in Q3-2023
Global spending on cloud infrastructure services reached US$73.5 billion in Q3 2023, a 16% year-on-year increase. Q3 growth remained consistent with the previous quarter, showing we are entering a stable phase. The impact of enterprise IT spending cuts on the cloud services market is slowly easing. In Q3 2023, the top three cloud providers – AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud – jointly grew by 20%, slightly outpacing the overall market and accounting for 65% of total spending. AWS mirrored its performance in the previous quarter, while Microsoft saw an uptick in its growth rate. Google Cloud, however, saw a drop in its rate in Q3 2023.
In August, Canalys said that AI would be a major driver of cloud service provider investments.
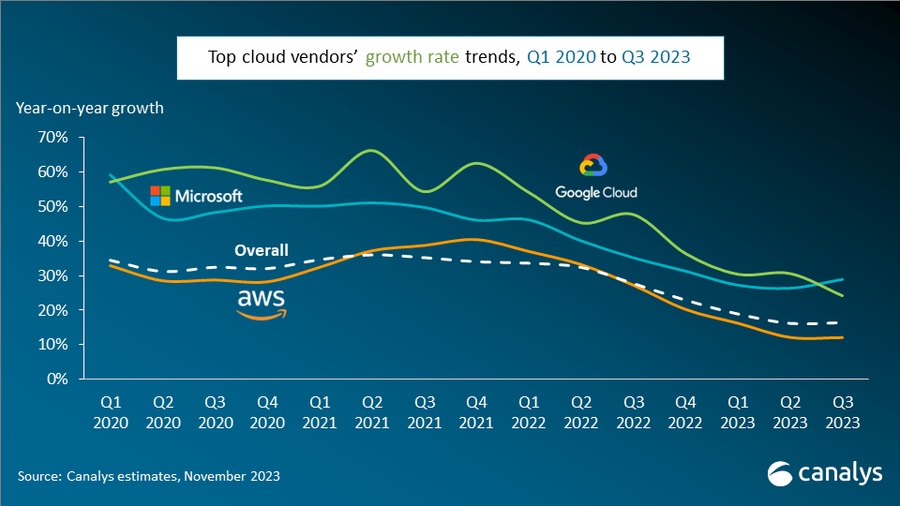
Cloud market showing signs of resilience – helped by growing interest in AI
Despite enterprises continuing to optimize overall IT spending, the cloud market is beginning to show signs of resilience, helped in part by a growing interest in AI. While the broader market continues to grapple with the repercussions of cost-cutting behavior, the performance of the leading cloud vendors hints at a shift in the market dynamic. Growing demand for AI solutions is gradually offsetting the impact of reduced IT spending as enterprises begin to invest in cloud computing to support AI strategies.
Top three vendors launch AI-focused partner programs
Microsoft’s efforts to commercialize its AI products are gaining momentum, with the recent introduction of Copilot driving significant customer and partner interest. Looking ahead to next year and beyond, discussions around GenAI will take center stage, and it will become a key growth driver for the channel. Following AWS’ and Microsoft’s recent AI-focused partner program launches, Google Cloud introduced the Generative AI Partner Initiative in Q3, as it seeks to work with partners to drive enterprise adoption of its AI solutions, including Duet AI.
“Generative AI unlocks a wealth of opportunities for channel partners to venture into new areas of business growth,” said Alex Smith, VP at Canalys. “The big cloud players and their partners can seize this exponential growth opportunity by identifying customers with an appetite for AI solutions, while simultaneously strengthening their AI capabilities and offering comprehensive portfolios of AI-related products and services to address these evolving needs.”
“Apart from capitalizing on new business opportunities arising from GenAI, channel partners can incorporate GenAI internally to boost productivity,” said Yi Zhang, Analyst at Canalys. “To succeed in this rapidly evolving landscape, channel partners must stay ahead of the game by establishing robust AI strategies and investing in strategic AI partnerships.”
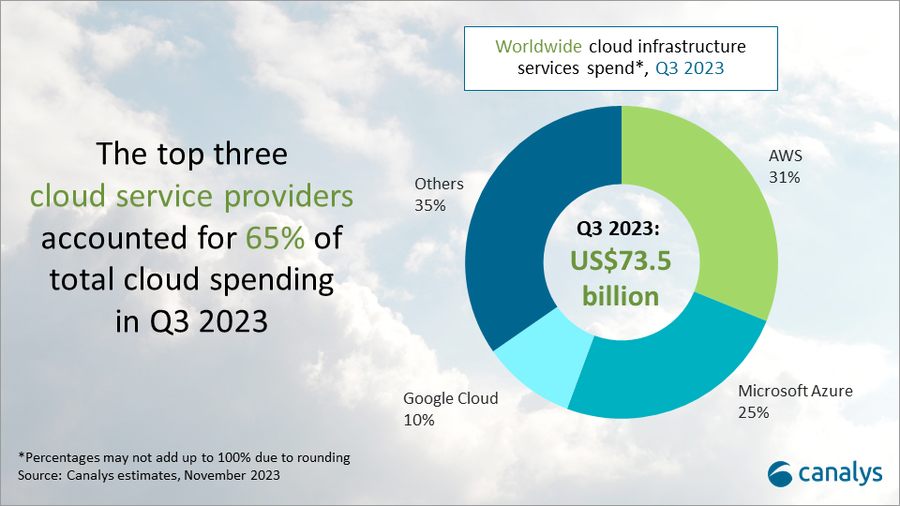
AWS continues to reign supreme with 31% market share
Amazon Web Services (AWS) continued to dominate the cloud infrastructure services market in Q3 2023, with a stable market share of 31%. Year-on-year growth of 12% was in line with the previous quarter but still below the overall market’s growth rate. The company’s efforts to cut costs and enhance efficiency resulted in substantial profit improvements in Q3 2023. AWS unveiled plans to open new data centers in South Korea and Malaysia, responding to the increasing demand for cloud computing in these regions. It also enhanced its cloud marketplace, as growing numbers of ISVs are seeing transactions accelerate via AWS Marketplace. AWS has committed to improving the AWS Marketplace and Partner Central in the coming months, aiming to empower partners to use AWS Marketplace to accelerate sales.
Microsoft Azure bounces back with 25% market share and rising growth rate
Microsoft Azure held second place in the cloud infrastructure services market in Q3 with a 25% market share. Following seven consecutive quarters of slowing year-on-year growth, it saw an uptick in its growth rate, which was up 29% compared with Q3 last year. The impact of the AI surge is palpable – marked by increased demand for cloud following the launch of Microsoft Copilot for Windows in September. Business performance is expected to remain steady, given the 18% increase in its cloud order backlog, which reached US$212 billion in Q3 2023. Since August, partners have had access to the new Microsoft AI Cloud Partner Program, designed to support partners in harnessing the advantages of incorporating AI capabilities into their organizations and capitalizing on the business opportunities presented by Microsoft AI-related products and Microsoft Azure.
Google Cloud takes 10% market share with growth below expectations
Google Cloud reached a market share of 10% in Q3 2023 after growing 24% year on year, securing third place in the cloud infrastructure services market. Growth was below expectations, and this was the first time that Google Cloud’s growth rate dipped below that of Microsoft Azure’s in the last three years. The dip was primarily due to the delayed impact of enterprises’ IT cost-cutting measures. Emphasizing its partner-first vision, Google Cloud is highlighting the Google Cloud partner ecosystem, particularly in the context of AI. It also committed to an open approach to GenAI development, facilitating the integration of partner-developed AI models into the Google Cloud Platform.
Canalys defines cloud infrastructure services as those services that provide infrastructure-as-a-service and platform-as-a-service, either on dedicated hosted private infrastructure or shared public infrastructure. This excludes software-as-a-service expenditure directly but includes revenue generated from the infrastructure services being consumed to host and operate them.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
According to Nick Wood at telecoms.com, the overall cloud infrastructure services market – which for Canalys encompasses infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) and platform-as-a-service (IaaS) – is on course to fall short of Canalys’ full-year expectations. In February, Canalys predicted that cloud spending in 2023 would grow 23% on last year, when it reached $247.1 billion. That makes for a projected total of around $304 billion.
However, since then, macroeconomic conditions have taken their toll on spending, tempering expectations for this year. The year to date total for 2023 is $212.3 billion, which means there is $91.7 billion worth of ground to make up in Q4 if spending is going to meet that target.
Achieving this looks like a tall order, because it would mean the year-on-year growth rate in Q4 would need to be 39.7%. Given the market grew by 19% in Q1, and 16% in both Q2 and Q3, a sudden surge in spending is unlikely.
References:
https://canalys.com/newsroom/global-cloud-services-q3-2023
https://telecoms.com/524974/cloud-spending-set-to-miss-full-year-forecast-despite-solid-q3-growth/
Cloud infrastructure services market grows; AI will be a major driver of future cloud service provider investments
Canalys: Cloud marketplace sales to be > $45 billion by 2025
Canalys: Global cloud services spending +33% in Q2 2022 to $62.3B
Gartner Forecast: Worldwide Public Cloud End-User Spending ~$679 Billion in 2024; GenAI to Support Industry Cloud Platforms
IDC: Public Cloud services spending to hit $1.35 trillion in 2027
Canalys: Global cloud services spending +33% in Q2 2022 to $62.3B
Synergy: Q3 Cloud Spending Up Over $11 Billion YoY; Google Cloud gained market share in 3Q-2022
AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud account for 62% – 66% of cloud spending in 1Q-2022



