AWS
Gartner: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud top rankings for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services
Gartner’s latest Magic Quadrant report for cloud infrastructure and platform services (CIPS) ranks Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud as the top cloud service providers.
Beyond the top three players, Gartner placed Alibaba Cloud in the “visionaries” box, and ranked Oracle, Tencent Cloud, and IBM as “niche players,” in that order.
The scope of Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for CIPS includes infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and integrated platform as a service (PaaS) offerings. These include application PaaS (aPaaS), functions as a service (FaaS), database PaaS (dbPaaS), application developer PaaS (adPaaS) and industrialized distributed cloud offerings that are often deployed in enterprise data centers (i.e. private clouds).
Figure 1: Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services
 ……………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
1. Gartner analysts praise Amazon AWS for its broad support of IT services, including cloud native, edge compute, and processing mission-critical workloads. Also noteworthy is Amazon’s “engineering prowess” in designing CPUs and silicon. This focus on owning increasingly larger portions of the supply chain for cloud infrastructure bolsters the No. 1 cloud provider’s long-term outlook and earns it advantages against competitors, according to the Gartner report.
“AWS often sets the pace in the market for innovation, which guides the roadmaps of other CIPS providers. As the innovation leader, AWS has materially more mind share across a broad range of personas and customer types than all other providers,” the analysts wrote.
AWS, which recently achieved $59 billion in annual revenues, contributed 13% of Amazon’s total revenue and almost 54% of its profit during second-quarter 2021.
AWS’s future focus is on attempting to own increasingly larger portions of the supply chain used to deliver cloud services to customers. Its operations are geographically diversified, and its clients tend to be early-stage startups to large enterprises.
……………………………………………………………………………………
2. Microsoft Azure, which remains the #2 Cloud Services Provider, sports a 51% annual growth rate. It earned praise from Gartner for its strength “in all use cases, which include the extended cloud and edge computing,” particularly among Microsoft-centric organizations.
The No. 2 public cloud provider also enjoys broad appeal. “Microsoft has the broadest set of capabilities, covering a full range of enterprise IT needs from SaaS to PaaS and IaaS, compared to any provider in this market,” the analysts wrote.
Microsoft has the broadest sets of capabilities, covering a full range of enterprise IT needs from SaaS to PaaS and IaaS, compared to any provider in this market. From the perspective of IaaS and PaaS, Microsoft has compelling capabilities ranging from developer tooling such as Visual Studio and GitHub to public cloud services.
Enterprises often choose Azure because of the trust in Microsoft built over many years. Such strategic alignment with Microsoft gives Azure advantages across nearly every vertical market.
“Strategic alignment with Microsoft gives Azure advantages across nearly every vertical market,” Gartner said. However, Gartner criticized Microsoft for very complex licensing and contracting. Also, Microsoft sales pressures to grow overall account revenue prevent it from effectively deploying Azure to bring down a customer’s total Microsoft costs.
Microsoft Azure’s forays in operational databases and big data solutions have been markedly successful over the past year. Azure’s Cosmos DB and its joint offering with Databricks stand out in terms of customer adoption.
………………………………………………………………………………………
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is strong in nearly all use cases and is slowly improving its edge compute capabilities. Google continues to invest in being a broad-based provider of IaaS and PaaS by expanding its capabilities as well as the size and reach of its go-to-market operations. Its operations are geographically diversified, and its clients tend to be startups to large enterprises.
The company is making gains in mindshare among enterprises and “lands at the top of survey results when infrastructure leaders are asked about strategic cloud provider selection in the next few years,” Gartner analysts wrote. Google is also closing “meaningful gaps with AWS and Microsoft Azure in CIPS capabilities,” and outpacing its larger competitors in some cases, according to the report.
The analysts also noted that Google Cloud “is the only CIPS provider with significant market share that currently operates at a financial loss.” The No. 3 public cloud provider reported a 54% year-over-year revenue increase and a 59% decrease in operating losses during Q2.
………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, Dell’Oro Group Research Director Baron Fung recently said that hyperscalers make up a big portion of the overall IT market, with the 10 largest cloud-service providers, including AWS, Google, and Alibaba, accounting for up to 40% of global data center spending, and “some of these companies can have really tremendous weight on the ecosystem.”
The Dell’Oro report noted that some providers have deployed accelerated servers using internally developed artificial intelligence (AI) chips, while other cloud providers and enterprises have commonly deployed solutions based on graphics processing units (GPUs) and FPGAs.
Fung explained that this model has also spilled over into those cloud providers also building their own servers and networking equipment to better fit their needs while “moving away from the traditional model in which users are buying equipment from companies like Dell and [Hewlett Packard Enterprise]. … It’s really disrupting the vendor landscape.”
Certain applications—such as cloud gaming, autonomous driving, and industrial automation—are latency-sensitive, requiring Multi-Access Edge Compute, or MEC, nodes to be situated at the network edge, where sensors are located. Unlike cloud computing, which has been replacing enterprise data centers, edge computing creates new market opportunities for novel use cases.
…………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.gartner.com/doc/reprints?id=1-26YXE86I&ct=210729&st=sb
Google Cloud revenues up 54% YoY; Cloud native security is a top priority
Google Cloud revenues increased 54% year over year to $4.62 billion during the second quarter of 2021, parent company Alphabet reported today. Google Cloud’s operating loss shrunk 59%, from $1.42 billion a year ago to $591 million last quarter.
Google Cloud includes both Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and its Workspace (formerly G Suite) cloud computing services and collaboration tools.
Like previous quarters, “GCPs revenue growth was, again, above cloud overall, reflecting significant growth in both infrastructure and platform services,” the company said in a statement.
“As for Google Cloud, we remain focused on revenue growth, and are pleased with the trends we’re seeing across cloud,” Google CFO Ruth Porat said on the company’s 2Q-2021 earnings call today. Porat added that growth in its Google Cloud Platform segment again surpassed overall cloud gains “reflecting significant growth in both infrastructure and platform services.”
“We will continue to invest aggressively, including expanding our go-to-market organization, our channel expansion, our product offerings, and our compute capacity,” she said.
Also on today’s earnings call, Google CEO Sundar Pichai cited security as a competitive differentiator and “our strongest product portfolio.” Google will continue to invest in security and continue its work to integrate its various security products such as Beyond Corp and Chronicle, he added.
“Cyber threats increasingly are on the mind of not just CIOs but CEOs across our partners. So it’s definitely an area where we are seeing a lot of conversations, a lot of interest…so a definite source of strength and you’ll see us continue to invest here,” he said.
“We are cloud native, we pioneered … zero trust and built the architecture out from a security-first perspective. Particularly, over the course of the last couple of years, with the recent attacks, [companies] really started thinking deeply about vulnerabilities, supply chain security has been a major source of consensus, cyber threats are increasingly on the mind of, not just CIOs, but CEOs across our partners. So it’s definitely an area where we are seeing a lot of conversations, a lot of interest.”
Google Cloud, along with its other business units, boosted Alphabet’s revenue 62% year over year, to $61.9 billion. As usual, Google ad revenue represented the biggest piece of the pie. It grew 69% to $50.44 billion. Retail was the biggest contributor to advertising growth.
Google Cloud holds around 7% market share in the cloud services segment, according to a Canalys report released in April 2021. It trails Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, which hold 32% and 19% market share, respectively.
Microsoft posted financial results Tuesday, its Intelligent Cloud revenue increased 30% to $17.4 billion. The company stated Azure revenue grew of 51%, but did not break out a dollar figure. Amazon is set to report earnings on Thursday.
Along with their hyper-scale cloud competitors Google Cloud is partnering with telecom companies all over the world to help them drive transformation and accelerate 5G adoption and monetization.
Here are a few of their telco partners:
………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://abc.xyz/investor/static/pdf/2021Q2_alphabet_earnings_release.pdf?cache=4db52a1
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/financial/google-cloud-revenue-climbs-54-q2
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/google-cloud-losses-shrink-59-revenue-hits-4-6b/2021/07/
Mavenir to deploy cloud-based 4G/5G radio units & telco software on Amazon Web Services
Less than one month after Dish Network disclosed it is collaborating with Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) for its “cloud native” 5G core network [1.], Mavenir has announced support for deployments and integration of its “cloud-native” telecom network functions with telco infrastructure solutions on AWS.
Mavenir’s collaboration with AWS allows Communications Service Providers (CSPs) to deploy Mavenir’s 4G and 5G products and applications with AWS’s computing infrastructure, state of the art container deployment and management technologies, and big data analytics services.
Note 1. Both Mavenir and AWS are vendors for Dish Network’s (DISH) greenfield 5G wireless network which is comprised of a virtualized RAN (vRAN) and a “cloud native” 5G core network (which includes highly touted functions such as network slicing, orchestration/automation, virtualization, etc).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Mavenir’s “cloud-native” Open RAN, 5G packet core, IMS, and messaging will be combined with Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) anywhere, supporting AWS Outposts. There will also be options for existing deployments to migrate Mavenir’s IMS core, voice, and messaging to Amazon EKS and Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) infrastructure.
AWS will also be able to run Mavenir’s orchestration and network slicing solutions. The two companies will combine their technologies to centrally manage data for network-wide insights and optimization. Mavenir and AWS will also work together to provide private networks and edge deployments.
The solution is designed to scale and leverages the same tools and technologies offered by AWS to enterprise applications today. These tools are the backbone for visibility and automation for any AWS-based offering and generally referred to as Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
That, in effect, results in offloading some of the telco application business to cloud functions. Mavenir says that will reduce complexity, put service providers at par with organizations which are realizing cost savings from cloud migrations without losing insight, performance, and control on their networks.
Opinion: The above claims remain to be proven! Time will tell. However, this partnership provides a well respected host environment (AWS) for Mavenir’s cloud resident 4G/5G software. That certainly lowers the risk for service providers that want to deploy Mavenir’s products and applications.
Another key element from this collaboration is the enablement of Private Networks and Edge deployments on AWS, powered by Mavenir’s Digital Enablement platform. With a digital app store for enterprise and various industry 4.0 applications such as IVA, AR/VR, IIoT and Robotics control, Mavenir’s Edge AI application suite is empowering an ecosystem of developers, service providers, partners, and enterprises to create and deploy applications in AWS to power digitalization and industry 4.0 with 5G.
This collaboration also lowers the network deployment time and cost for Mobile Network Operators and enterprises equally fulfilling use cases of either adding 5G and edge capabilities to an existing network or a greenfield 4G/5G network launch leveraging public clouds.
“The collaboration with Mavenir and AWS allows us to build out our 5G network and messaging platforms in a true cloud-native manner, harnessing the speed and agility that the AWS cloud brings along with Mavenir’s expertise in deploying and operating cloud-native network functions,” said Sidd Chenumolu, Vice President of Technology Development, DISH. “Together, we will enable our customers to take full advantage of the potential of 5G, reimagining wireless connectivity and giving our customers the ability to customize their network experience.”
“Working with AWS enables us to bring new customer-focused 5G use cases and 5G deployments to the market faster and with unique capabilities to realize true 5G potential,” said Bejoy Pankajakshan, Mavenir’s Chief Strategy Officer. “Mavenir’s solutions are designed to support full public cloud as well as hybrid cloud deployments.”
“We’re delighted to collaborate with Mavenir to offer voice and messaging solutions for core network and RAN customers along with AI/ML solutions for orchestration and observability.” said Amir Rao, General Manager Telco Solution Portfolio and Tech Alliances, AWS. “Together, we are providing true cloud native benefits to CSP customers, combining Mavenir’s expertise in the NFV market with the global scale of the AWS infrastructure to meet industry challenges of agility, scaling, slicing, and resiliency.”
Mavenir’s 4G and 5G deployments on AWS provides unique capabilities, including:
- Integration of Mavenir’s cloud-native Open RAN (vDU, vCU-CP, vCU-UP), Converged 4G/5G Packet Core, IMS, and Messaging with Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) anywhere supporting AWS Outposts.
- Use of AWS platform services and tools to deploy and manage cloud native network functions.
- Options for existing deployments to migrate Mavenir’s IMS core, voice, and messaging solutions to Amazon EKS and Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) infrastructure.
- Mavenir’s Orchestration and Network Slicing solutions to manage hybrid cloud workloads running on AWS.
- Adoption of AWS for centrally managed telco workloads on far-edge, network edge and core simultaneously.
- Deployment of Mavenir’s standards compliant observability framework, RIC, NWDAF, AIOps and Analytics platform in AWS to collect the data from various AWS nodes in a centrally managed data lake and process the data using AI/ML for network wide insights and optimization.
- Integration of Mavenir’s telecom adaptation layer (Telco PaaS) as a common open source-based platform adaptation layer designed for telco specific workloads to support various carrier grade requirements on top of Amazon EKS and AWS PaaS functions.
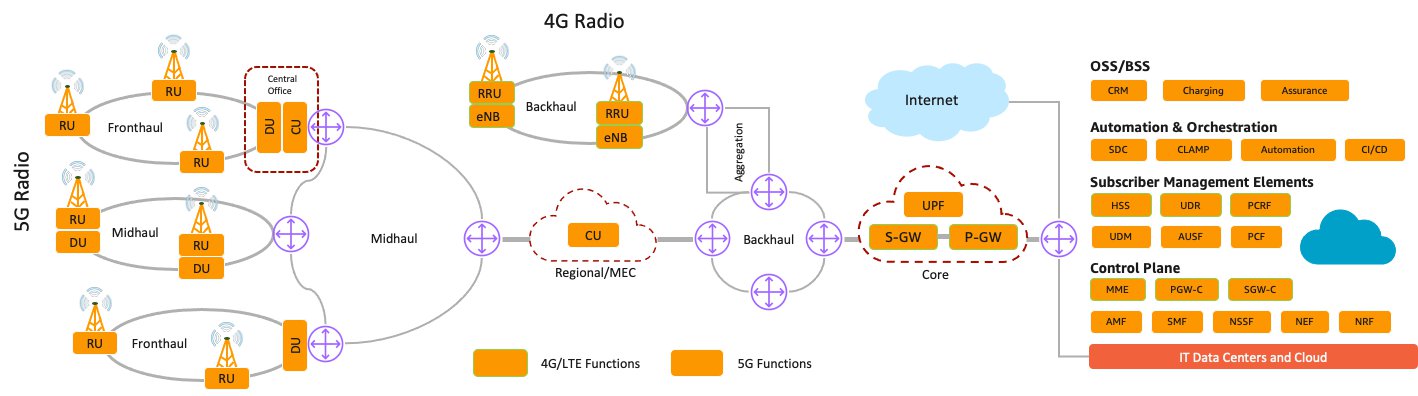
Chart Courtesy of Amazon Web Services
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.mavenir.com/press-releases/mavenir-to-deliver-cloud-based-5g-solutions-on-aws/
Mavenir’s In-House Radio Units Show Open RAN Ecosystem’s Growing Pains
https://partners.amazonaws.com/partners/0010L00001u5BBiQAM/Mavenir
https://www.fiercewireless.com/tech/mavenir-aws-deliver-cloud-based-5g-functions-to-telcos
Analysis of Dish Network – AWS partnership to build 5G Open RAN cloud native network
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/cicd_for_5g_networks_on_aws/5g-networks-on-aws.html
Analysis of Dish Network – AWS partnership to build 5G Open RAN cloud native network
On its Q1-2021 earnings call, Dish Network Chairman and Co-founder Charlie Ergen did not provide any specifics regarding Dish’s deal with Amazon/AWS or its overall plan to build a nationwide 5G Open RAN, “cloud native” core network. Are you a bit tired of cliché’s like this:
“We’re building a Netflix in a Blockbuster world.” All Netflix did was put video on the cloud. Instead of going to a physical store, you put it in the cloud. Right. All the business plans in the world, all the numbers, all the thought if they just did something simple they put it in the cloud and the technology was they were a little ahead of the technology but the technology got there. All we’re doing is taking all those towers that you see as you drive down the highway, we basically put them in the cloud. And so instead of driving to physical store and rent a movie, you’re going to get all your data and information and automation everything from the cloud. And so it’s a dramatic paradigm shift in the way network is built and it should and it’s an advantage over legacy carriers who have 30-year-old architecture.” Of course, that’s incorrect as almost all 5G carriers plan to build a 5G cloud native core network.
Dish is planning to build the world’s first standalone, cloud-based 5G Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN), starting with the launch of a 5G wireless network for enterprise customers in Las Vegas, NV later this year.
Dish says it will leverage AWS’s architecture and services to deploy a cloud-native 5G network that includes O-RAN—the antennas and base stations that link phones and other wireless devices to the network. Also existing in the cloud will be the 5G core, which includes all the computer and software that manages the network traffic. AWS will also power Dish’s operation and business support systems.
“Amazon has made massive investments over the years in compute storage transport and edge, [and] we’ll be sitting on top of that and as we tightly integrate telco into their infra, then we can expose APIs to their development community, which we think makes and enables third-party products and services to have network connectivity, as well as enterprise applications,” said Tom Cullen, executive VP of corporate development for Dish, explaining some of the technical details of the arrangement during Thursday’s earnings call.
Ergen reiterated Dish’s plan to spend up to $10 billion on its overall 5G network and provided milestone date for completion of the first phase of the 5G build-out.
“All of that $10 billion isn’t spent by June of 2023, which is our major milestone,” Ergen said, pointing to the company’s agreement with the U.S. government to cover at least 70% of the population with 5G no later than June 14, 2023. However, Ergen has an escape hatch:
“The agreement we have [with the FCC] recognizes that [there could be] supply chain issues outside of our control, and that the timelines could be adjusted. But we don’t look at it that way internally. There is always unforeseen circumstances, and this one might be particularly acute. But we’re not going to let anything stop us. We’re focused on meeting our timelines, and regardless of what the challenges are. And we’ll have to reevaluate that from time to time, but we’re focused right now on Las Vegas and we’re focused on the 20% build-out by June of next year.”
“We’re not going to let anything stop us, he added. The $10 billion “does take us through the complete (5G) buildout.”
On the 5G cloud native aspect, Ergen said:
“Yes, we anticipated a cloud native network from the beginning, he said. “So the $10 billion total build-out cost that we announced a couple of years ago–I think people are probably still skeptical … But you can see where we’re headed. Most of your models will probably take a lot of capex off the board when you understand the architecture, and we’re not going to go through all the architecture in this call, but it’s certainly has a material impact on capex.”
Dish said last week it plans to run all of its network computing functions inside the public AWS cloud – a plan that represents a dramatic break from the way most 5G networks around the world run today. Many analysts think that’s a huge cyber-security risk as the attack surface is much greater in a virtual, cloud based network.
Marc Rouanne — Executive Vice President and Chief Network Officer:
“Yeah, the way to think of our cloud native network is a network of networks, that’s the way it’s architected. So when a customer comes to us, it’s easy for us to offer one sub network, which we can call it private network and there are techniques behind that like slicing, like automation, like software defined, so I’m not going to go into the techniques, but natively the way to think of it is really this network of networks. Right. And then, as Stephen, you’ve seen that you plan this to the postpaid customers and telling you how they would shake lose sub networks.”
“Absolutely, yeah. No, I think we’ve talked to a number of customers across multiple verticals in different industry segments and is an increasing appetite in demand for the kind of network that we’re building, which is really to enable them to have more security, more control and also more visibility into the data that’s coming off the devices, so that they can control their business more effectively. So we’re seeing a terrific demand. And the network architecture, we’re putting in place actually enables and unlocks that opportunity for those enterprise customers and it’s again not restricted to any specific vertical.
We’re touching a lot of different companies and a lot of different vertical segments across the country and the other aspect of the opportunity that we see for ourselves is that while we build out a nationwide network, we are in the process of working with customers and prospective customers on private networks that are not limited by the geography of our national footprint. So we can deploy those within their environments to support their business operations as well. So the demand we’re seeing is terrific and we’re already engaged with a number of customers today.”
Ergen chimed in again:
“The cloud infrastructure as it existed a couple of years ago, really didn’t handle telco very well, there has been a lot of R&D and investment that they’ve had to make to transform their network into something that where a telco can operate in the cloud, because it’s a little bit different than their traditional IT infrastructure. And then today they are, they were best in class room for what we needed and whether it be their APIs and the documentation and discipline and vendor at the — community that supports them and their — the developers and then of course obviously reach into the enterprise business. So it was — so that’s the first and foremost.
And then the second thing I think is, is the company committed? I’m not going to put words in Amazon’s mouth, I’ll let them talk to their commitment, but they’ve done a lot of work for us to help us without knowing where they have the deal or not and very appreciative that it. I think it’s helpful that Andy will become the CEO because he’s owned this project from the start and he can — he will be able to move all the pieces within Amazon to focus on this. And so I think at the end of the day, I think we’re going to be their largest customer in cloud and I think they’re going to — they may be the largest customer in our network. I mean, but we have to build a network and prove it, and they have to build and prove it. I think that all other carriers around the world will, including the United States will look at Amazon as a real leader here because we’re just doing something different.”
Stephen Bye — Executive Vice President, Chief Commercial Officer
“Yeah. So just in terms of what the Las Vegas build looks like. I think there are several attributes that are really important to what we’re doing to build on Charlie’s comment. One is we are building a cloud native infrastructure. We are using an Open Radio Access architecture. But it’s also a 5G native network. We’re not trying to put 5G on top of 2G, 3G and 4G, the infrastructure that we’re deploying is optimized for 5G and the way we’ve designed the network from an RF perspective and a deployment perspective is to take advantage of the 5G architecture as well as the 5G platform. And so, what does that look like?
It’s basically a new network, it’s new infrastructure, it’s designed using all of the spectrum bands that we have and the RF is optimized to take advantage of that. So we’re on a path to launching that in the third quarter, but it’s one of a number of markets we have coming on. We just have announced those markets through the end of the year, but it’s the first, obviously a number that we have in flight today and we’ve got activity going on across the country to actually build out this network. So it will be the first one that people can touch and feel and get the experience, but it is really a 5G native network and we’ve proven that O-RAN from a technology perspective can work compared to that at the end of last year. Now we are in the execution phase, now we’re in the deployment phase and so you know Vegas will have to be the first one that it will be a fully deployed market that people will be able to touch and feel and experience.”
Bye added that the 5G build-out will be done in phases but the network is designed to support all customers across all segments.

5G Network End-to-End Architecture. Image courtesy of AWS.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In a note to clients, analyst Craig Moffett said that Dish was purchasing services from AWS rather than Amazon investing in Dish’s 5G network:
“It was a purchase agreement, albeit one freighted with lots of rather fuzzy jargon, and nothing more. Notably, Verizon already has its own relationship with AWS, and theirs does call for AWS to co-market Verizon services to AWS’s enterprise customers. By contrast, the Dish agreement calls only for Dish to market AWS services to Dish’s customers, not the other way around. Objectively, it is Verizon, not Dish, that has the more strategic relationship.
Amazon isn’t likely to market a service to its customers unless they are highly confident that its quality is first rate and that its staying power is assured. Perhaps Dish will get there. But it won’t be clear that they have arrived at that point until their network is successfully serving customers… without the safety net of the T-Mobile MVNO agreement. That’s not until 2027. That feels to us like a long time to wait.”
Regarding Dish Network’s new business model, Craig said “It is now fair to say that Dish’s core business is wireless rather than satellite TV. Not by revenues, of course; the wireless business is today but the modest reseller stub of what once was Boost (Mobile). But certainly by valuation….What does matter, however, is the extent to which the satellite TV business can serve as a source of funds for financing the wireless business.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://d1.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/5g-network-evolution-with-aws.pdf
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/cicd_for_5g_networks_on_aws/5g-networks-on-aws.html
SK Telecom and AWS launch 5G edge cloud service and collaborate on other projects
South Korea’s #1 wireless network operator SK Telecom (SKT) has launched a 5G edge cloud service in partnership with Amazon Web Services (AWS). ‘SKT 5GX Edge’ uses AWS Wavelength at the edge of SKT’s 5G network. SKT said that SKT 5GX Edge will enable customers to develop mobile applications that require ultra-low latency.
With SKT 5GX Edge, applications are connected to ‘AWS Wavelength Zones’, which are located at the edge of SK Telecom’s 5G network, making it unnecessary for application traffic to hop through regional aggregation sites and the public internet.
SKT 5GX Edge with AWS Wavelength is expected to enable SK Telecom’s enterprise customers and developers to build innovative services in areas including machine learning, IoT, video games and streaming using the AWS services, APIs, and tools they already use.
SK Telecom and AWS started operating the first AWS Wavelength Zone in South Korea in the central city of Daejeon (140 kilometers south of Seoul) earlier this month. They plan to expand the SKT 5GX Edge infrastructure to other parts of the country, including Seoul in 2021.

SK Telecom has been cooperating with AWS since February of this year to deploy AWS Wavelength Zones on SK Telecom’s 5G network and worked with 20 enterprise customers to test the service.
SKT and AWS are actively cooperating in the area of non-face-to-face services as demand grows due to the pandemic. The two companies have been working with video conferencing solution provider Gooroomee to build an environment where two-way video conferencing and remote education services are provided without delay, and have realized a service with a latency of less than 100 milliseconds for multiple simultaneous sessions.
“With AWS Wavelength on SKT’s 5G network, customers in South Korea can develop applications that take advantage of ultra-low latencies to address use cases like machine learning inference at the edge, smart cities and smart factories, and autonomous vehicles – all while using the same familiar AWS services, API, and tools to deploy them to 5G networks worldwide,” said Matt Garman, Vice President of Sales and Marketing, AWS.
“In collaboration with AWS, SK Telecom has successfully integrated private 5G and edge cloud. By leveraging this new technology, we will lead the efforts to create and expand innovative business models in game, media services, logistics, and manufacturing industries,” said Ryu Young-sang, President of MNO at SK Telecom.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
SK Telecom and AWS also report that they have been working to improve operational stability of autonomous robots and efficiency in remote monitoring and control. Together with Woowa Brothers, the operator of food delivery app ‘Baedal Minjok,’ the two companies have completed tests of applying the 5G MEC service to outdoor food delivery robot Dilly Drive. Meanwhile, work continues with local robotics company Robotis to test run autonomous robots in the 5G cloud environment.
SK Telecom and AWS have also signed an agreement with Shinsegae I&C and Maxst to build an AR navigation and guidance system in the Coex Starfield shopping mall in Seoul. They are also working on potential use of the 5G cloud service with Deep Fine, an AR glass solution developer, and Dabeeo, a spatial recognition service provider. With the National IT Industry Promotion Agency (NIPA), SK Telecom has launched an open lab to develop realistic contents optimized for the 5G network and to support the growth of the related ecosystem.
Collaboration is also ongoing with Looxid Labs, a provider of real-time analysis for eye-gaze tracking and brain wave data, to develop services on the 5G MEC for a senior citizen center in Busan.
SK Telecom and AWS are also cooperating in the area of non-face-to-face services as demand grows due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The two companies have been working with video conferencing services provider Gooroomee to develop an environment where 2-way video conferencing and remote education services are provided without delay, and claim they have achieved a service with a latency of less than 100 milliseconds for multiple simultaneous sessions.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?page.page=1&idx=1494&page.type=all&page.keyword=
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/sk-telecom-launches-5gx-edge-cloud-service-with-aws–1366915
Will Hyperscale Cloud Companies (e.g. Google) Control the Internet’s Backbone?
Rob Powell reports that Google’s submarine cable empire now hooks up another corner of the world. The company’s 10,000km Curie submarine cable has officially come ashore in Valparaiso, Chile.
The Curie cable system now connects Chile with southern California. it’s a four-fiber-pair system that will add big bandwidth along the western coast of the Americas to Google’s inventory. Also part of the plans is a branching unit with potential connectivity to Panama at about the halfway point where they can potentially hook up to systems in the Caribbean.
Subcom’s CS Durable brought the cable ashore on the beach of Las Torpederas, about 100 km from Santiago. In Los Angeles the cable terminates at Equinix’s LA4 facility, while in Chile the company is using its own recently built data center in Quilicura, just outside of Santiago.
Google has a variety of other projects going on around the world as well, as the company continues to invest in its infrastructure. Google’s projects tend to happen quickly, as they don’t need to spend time finding investors to back their plans.

Curie is one of three submarine cable network projects Google unveiled in January 2018. (Source: Google)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Powell also wrote that SoftBank’s HAPSMobile is investing $125M in Google’s Loon as the two partner for a common platform, and Loon gains an option to invest a similar sum in HAPSMobile later on.
Both companies envision automatic, unmanned, solar-powered devices in the sky above the range of commercial aircraft but not way up in orbit. From there they can reach places that fiber and towers don’t or can’t. HAPSMobile uses drones, and Loon uses balloons. The idea is to develop a ‘common gateway or ground station’ and the necessary automation to support both technologies.
It’s a natural partnership in some ways, and the two are putting real money behind it. But despite the high profile we haven’t really seen mobile operators chomping at the bit, since after all it’s more fun to cherry pick those tower-covered urban centers for 5G first and there’s plenty of work to do. And when they do get around to it, there’s the multiple near-earth-orbit satellite projects going on to compete with.
But the benefit both HAPSMobile and Loon have to their model is that they can, you know, reach it without rockets.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
AWS’s Backbone (explained by Sapphire):
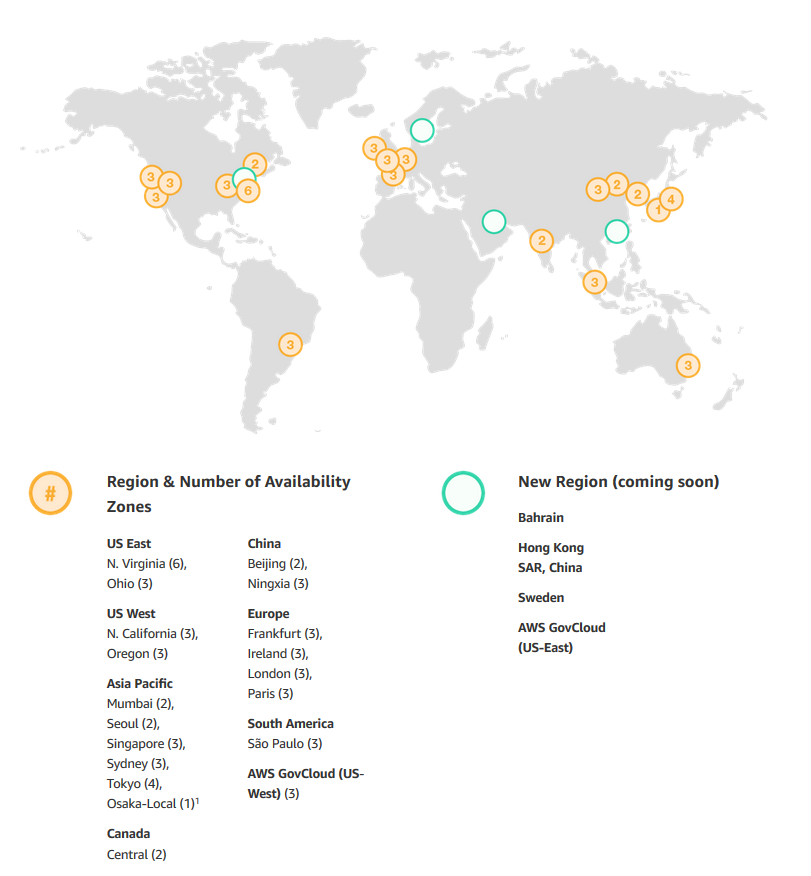
An AWS Region is a particular geographic area where Amazon decided to deploy several data centers, just like that. The reason behind a chosen area is to be close to the users and also to have no restrictions. At the same time, every Region is also connected through private links with other Regions which means they have a dedicated link for their communications because for them is cheaper and they also have full capacity planing with lower latency.
What is inside a Region?
- Minimum 2 Availability Zones
- Separate transit centers (peering the connections out of the World)
How transit centers work?
AWS has private links to other AWS regions, but they also have private links for the feature AWS Direct Connect – a dedicated and private & encrypted (IPSEC tunnel) connection from the “xyz” company’s datacenters to their infrastructures in the Cloud, which works with the VLANs inside (IEEE 802.1Q) for accessing public and private resources with a lower latency like Glacier or S3 buckets and their VPC at the same time between <2ms and usually <1ms latency. Between Availability Zones (inter AZ zone) the data transit there’s a 25TB/sec average.
From AWS Multiple Region Multi-VPC Connectivity:
AWS Regions are connected to multiple Internet Service Providers (ISPs) as well as to Amazon’s private global network backbone, which provides lower cost and more consistent cross-region network latency when compared with the public internet. Here is one illustrative example:

,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
From Facebook Building backbone network infrastructure:
We have strengthened the long-haul fiber networks that connect our data centers to one another and to the rest of the world.
As we bring more data centers online, we will continue to partner and invest in core backbone network infrastructure. We take a pragmatic approach to investing in network infrastructure and utilize whatever method is most efficient for the task at hand. Those options include leveraging long-established partnerships to access existing fiber-optic cable infrastructure; partnering on mutually beneficial investments in new infrastructure; or, in situations where we have a specific need, leading the investment in new fiber-optic cable routes.
In particular, we invest in new fiber routes that provide much-needed resiliency and scale. As a continuation of our previous investments, we are building two new routes that exemplify this approach. We will be investing in new long-haul fiber to allow direct connectivity between our data centers in Ohio, Virginia, and North Carolina.
As with our previous builds, these new long-haul fiber routes will help us continue to provide fast, efficient access to the people using our products and services. We intend to allow third parties — including local and regional providers — to purchase excess capacity on our fiber. This capacity could provide additional network infrastructure to existing and emerging providers, helping them extend service to many parts of the country, and particularly in underserved rural areas near our long-haul fiber builds.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Venture Beat Assessment of what it all means:
Google’s increasing investment in submarine cables fits into a broader trend of major technology companies investing in the infrastructure their services rely on.
Besides all the datacenters Amazon, Microsoft, and Google are investing in as part of their respective cloud services, we’ve seen Google plow cash into countless side projects, such as broadband infrastrucure in Africa and public Wi-Fi hotspots across Asia.
Elsewhere, Facebook — while not in the cloud services business itself — requires omnipresent internet connectivity to ensure access for its billions of users. The social network behemoth is also investing in numerous satellite internet projectsand had worked on an autonomous solar-powered drone project that was later canned. Earlier this year, Facebook revealed it was working with Viasat to deploy high-speed satellite-powered internet in rural areas of Mexico.
While satellites will likely play a pivotal role in powering internet in the future — particularly in hard-to-reach places — physical cables laid across ocean floors are capable of far more capacity and lower latency. This is vital for Facebook, as it continues to embrace live video and virtual reality. In addition to its subsea investments with Google, Facebook has also partnered with Microsoft for a 4,000-mile transatlantic internet cable, with Amazon and SoftBank for a 14,000 km transpacific cable connecting Asia with North America, and on myriad othercable investments around the world.
Needless to say, Google’s services — ranging from cloud computing and video-streaming to email and countless enterprise offerings — also depend on reliable infrastructure, for which subsea cables are key.
Curie’s completion this week represents not only a landmark moment for Google, but for the internet as a whole. There are currently more than 400 undersea cables in service around the world, constituting 1.1 million kilometers (700,000 miles). Google is now directly invested in around 100,000 kilometers of these cables (62,000 miles), which equates to nearly 10% of all subsea cables globally.
The full implications of “big tech” owning the internet’s backbone have yet to be realized, but as evidenced by their investments over the past few years, these companies’ grasp will only tighten going forward.
China Permits Virtual Telecom Operators vs Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
China has granted the official go ahead for virtual telecom operator businesses after piloting the practice for almost five years. The China Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has issued official licenses to 15 private virtual telecoms to resell internet access, the ministry said in a statement released Monday on its website. These virtual operators, including Chinese tech giants Alibaba and Xiaomi, do not maintain the network infrastructure but rent wholesale services like roaming and text messages from the country’s three major telecom infrastructure operators China Mobile, China Unicom, and China Telecom.
In a move to further open up the telecom sector, China started to issue pilot licenses in May 2013 to private companies to allow them to offer repackaged mobile services to users. It issued pilot operation licenses to eleven ‘mobile virtual network operators’, or MVNOs, at the end of 2013 which has gradually increased to A 42 virtual telecom businesses.
Granting virtual telecom operators official licenses is aimed at encouraging mobile telecom business innovation and improving the sector’s overall service quality, the statement said.
Reference:
http://usa.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201807/23/WS5b559eb4a310796df4df82ed.html
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
While Amazon is not a virtual ISP, they do offer Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) service:
To securely transfer data between an on-premises data center and Amazon Web Services (AWS), consider implementing a transit Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Transit VPCs not only manage your networks more efficiently, but also add dynamic routing and secure connectivity in your cloud environment. Because these transit VPCs are deployed with high availability on AWS, downtime is limited.
Amazon’s VPC lets a company or enterprise provision a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network that the user defines. The user has complete control over the enterprise virtual networking environment, including selection of IP address range, creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and network gateways. You can use both IPv4 and IPv6 in your VPC for secure and easy access to resources and applications.
These AWS resource requests are implemented virtually and can be used to connect Amazon VPCs, whether they are running in different parts of the world and/or running in separate AWS accounts, to a common Amazon VPC that serves as a global network transit center. This approach uses host-based Virtual Private Network (VPN) appliances in a dedicated Amazon VPC and helps to simplify network management by reducing the amount of connections required to connect multiple Amazon VPCs and remote networks.
Simplify network management and reduce your total number of connections by deploying a highly available, scalable, and secure transit Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) on AWS.
Download the eBook to learn more about:
- How to build a private network that spans two or more AWS Regions
- Sharing connectivity between multiple Amazon VPCs and on-premises data centers
- How transit VPCs enable you to share Amazon VPCs and AWS resources across multiple AWS accounts
For more info please refer to https://aws.amazon.com/networking/partner-solutions/featured-partner-solutions/




