Month: January 2023
High Tech Layoffs Explained: The End of the Free Money Party
Thanks to the Federal Reserve Board’s “free money party” (aka Quantitative Easing/QE and Zero Interest Rate Policy/ZIRP) from 2009-March 2022, investors desperate for returns sent their money to Silicon Valley, which pumped it into a wide range of start-ups that might not have received any funding in other times. Extreme valuations of both public and private companies made it easy to issue stock or take on loans to expand aggressively or to offer sweet deals to potential customers that quickly boosted market share.
“The whole tech industry of the last 15 years was built by cheap money,” said Sam Abuelsamid, principal analyst with Guidehouse Insights. “Now they’re getting hit by a new reality, and they will pay the price.”
Cheap money funded many of the tech acquisitions that were a substitute for internal growth. Two years ago, as the pandemic raged and many office workers were confined to their homes, Salesforce bought the office communications tool Slack for $28 billion, a sum that some analysts thought was way too high. Salesforce borrowed $10 billion to do that deal. This month, Salesforce said it’s laying off 8,000 employees, about 10% of its staff, many of them from Slack.
More than 46,000 workers in U.S.-based tech companies have been laid off in mass job cuts so far in 2023, according to a Crunchbase News tally. Last year, more than 107,000 jobs were slashed from public and private tech companies Here are just a few:
- Amazon is laying off 18,000 office workers and shuttering operations that are not financially viable. More below.
- Google parent Alphabet is cutting 12,000 jobs.
- Microsoft, which has been riding high on cloud revenues for years, is eliminating 10,000 jobs.
- Cisco plans to cut 5% of workforce – approximately 4,100 people will lose their jobs.
- Facebook parent Meta announced in November that it plans to eliminate 13% of its staff, which amounts to more than 11,000 employees.
- Shortly after closing his $44 billion purchase of Twitter in late October, new owner Elon Musk cut around 3,700 Twitter employees.
- IBM said today it would eliminate about 1.5% of its global workforce, which amounts to a “ballpark” figure of 3,900 job cuts.
The easy money era (which started shortly after the Lehman Brothers bankruptcy in September 2008) had been well established when Amazon decided it had mastered e-commerce enough to take on the physical world. Its plans to expand into bookstores was a rumor for years and finally happened in 2015. The media went wild. According to one well-circulated story, the retailer planned to open as many as 400 bookstores. Instead, the eRetail and cloud computing leader closed 68 stores last March, including not only bookstores but also pop-ups and so-called four-star stores. It continues to operate its Whole Foods grocery subsidiary, which has 500 U.S. locations, and other food stores. Amazon said in a statement that it was “committed to building great, long-term physical retail experiences and technologies.”
“High rates are painful for almost everyone, but they are particularly painful for Silicon Valley,” said Kairong Xiao, an associate professor of finance at Columbia Business School. “I expect more layoffs and investment cuts unless the Fed reverses its tightening.”
Addendum (Feb 26, 2023):
Ericsson will lay off 8,500 employees globally as part of its plan to cut costs, according to a memo sent to employees and seen by Reuters. “The way headcount reductions will be managed will differ depending on local country practice,” Chief Executive Borje Ekholm wrote in the memo. “In several countries the headcount reductions have already been communicated this week,” he said. “It is our obligation to take this cost out to remain competitive,” Ekholm said in the memo. “Our biggest enemy right now may be complacency.”
Ericsson to lay off 8,500 employees as part of cost cutting plan
References:
https://news.crunchbase.com/startups/tech-layoffs/
The Rise of New Tech Companies – Fiendbear Unicorns, FANGs, and the Nifty Nine
Update on 5G Stand-Alone (SA) Core Networks
Statista:
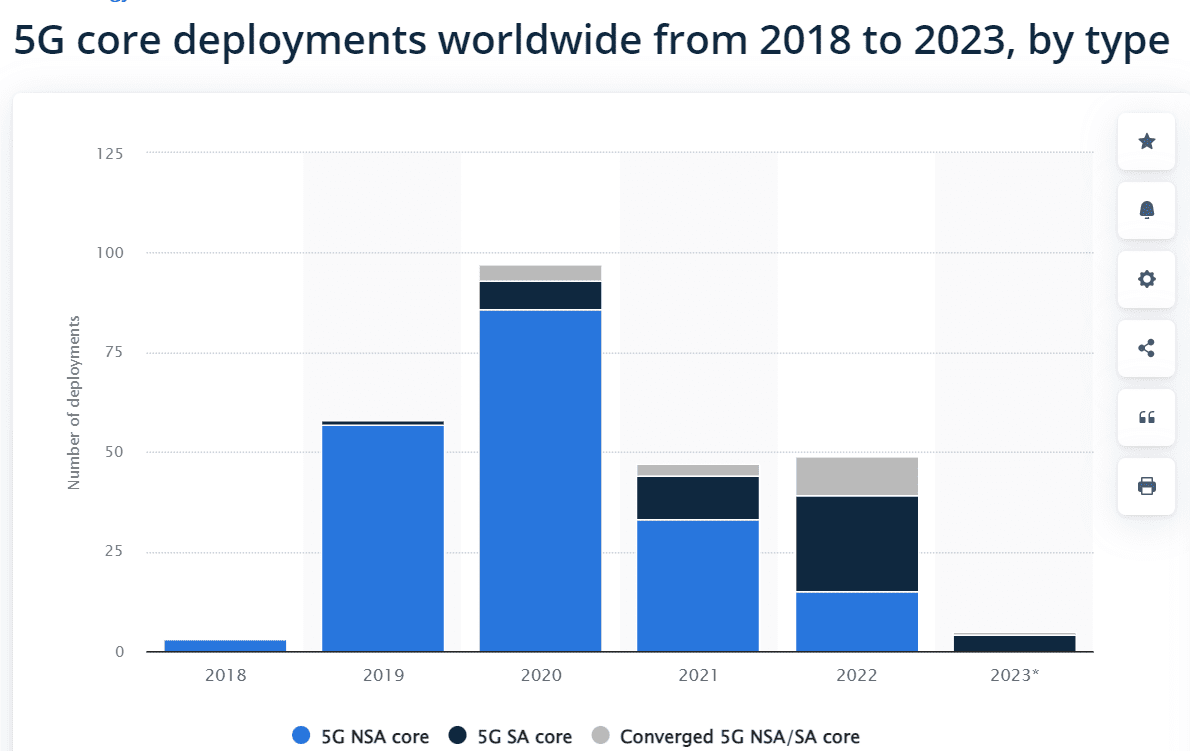
The type of 5G cores currently deployed remains dominated with about 75% of non-standalone (NSA) cores, or cores using the preexisting 4G network infrastructure. However, 5G standalone (SA) cores, which require more up-front costs and development yet may provide faster and more scalable connection, are forecast to outstrip NSAs and consist of 24 of the 49 5G core launches in 2022. All but one of the 5G launches announced for 2023 are standalone.
GSA:
Network Operators are increasingly experimenting with and deploying 5G standalone (SA) networks. With a totally new, cloud-based, virtualized, microservices-based core infrastructure, some of the anticipated benefits of introducing 5G SA technologies include faster connection times (lower latency), support for massive numbers of devices, programmable systems enabling faster and more-agile creation of services and network slices, with improved support for management of service-level agreements within those slices, and the advent of voice over New Radio (VoNR) technology. The introduction of 5G SA is expected to facilitate simplification of architectures, improve security and reduce costs.
The 5G SA technology is expected to enable customisation and open up new service and revenue opportunities tailored to enterprise, industrial and government customers.
GSA is tracking the emergence of the 5G SA system, including the availability of chipsets and devices for customers, plus the testing and deployment of 5G SA networks by public mobile network operators as well as private network operators. This report is the latest in an ongoing series summarizing market trends, drawing on data collected in GSA’s various databases covering chipsets, devices, spectrum and networks.
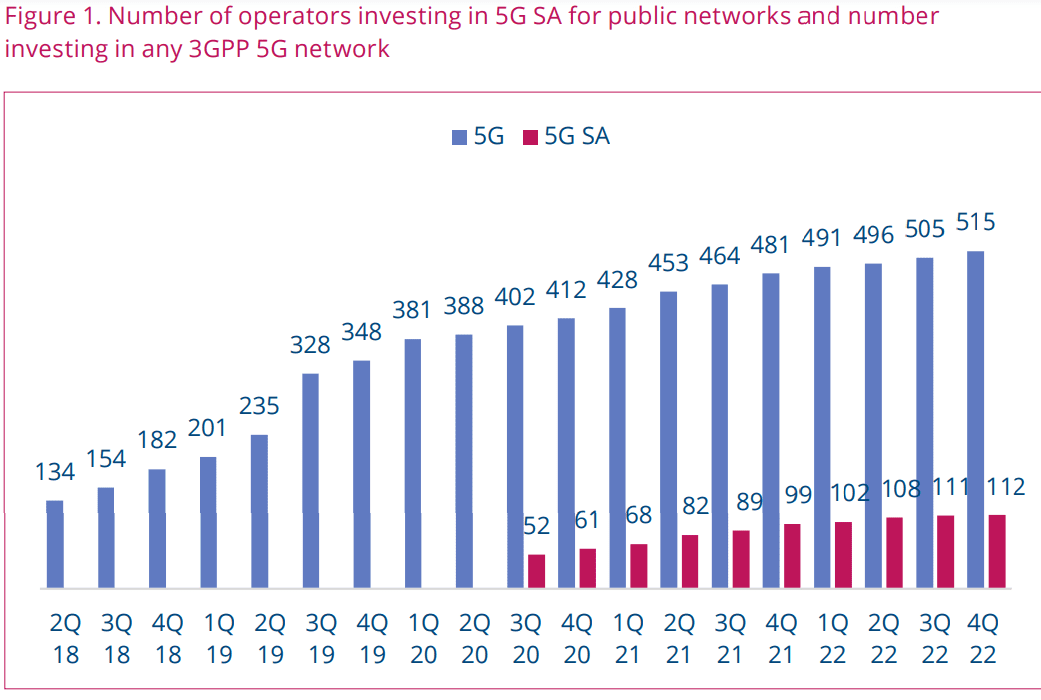
GSA has identified 112 operators in 52 countries and territories worldwide that have been investing in public 5G SA networks in the form of trials, planned or actual deployments . This equates to almost 21.7% of the 515 operators known to be investing in 5G licences, trials or deployments of any type.
At least 32 operators in 21 countries and territories are now understood to have launched public 5G SA networks, two of which have only soft-launched their 5G SA networks. In addition to these, 21 operators have been catalogued as deploying or piloting 5G SA for public networks, and 31 as planning to deploy the technology, showing that launches of 5G SA look set to continue apace. GSA has also recorded 19 operators as being involved in evaluations, tests or trials of 5G SA.
As of the last update in December 2022, GSA had collated information about 955 organisations known to be deploying LTE or 5G private mobile networks.
Countries and territories with operators identified as investing in public 5G SA networks have been granted a licence suitable for the deployment of a private LTE or 5G network so far. Of those, 391 are known to be using 5G networks (excluding those labelled as 5G-ready) for private mobile network pilots or deployments. Of those, 41 (slightly more than 10% of them) are known to be working with 5G SA already. They include manufacturers, academic organizations, commercial research institutes, construction, communications and IT services, rail and aviation organizations.
Dell’Oro Group:
At the close of 2022, we identified 39 mobile network operators that have commercially launched 5G SA eMMB networks.
References:
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1330511/5g-core-deployments-worldwide-by-type/
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/5g-system-overview
https://www.ericsson.com/en/core-network/5g-core
ITU-R WP5D: Studies on technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 100 GHz
The development of IMT for 2030 and beyond is expected to enable new use cases and applications with extremely high data rate and low latency, which will benefit from large contiguous bandwidth spectrum resource with around tens of GHz. This suggests the need to consider spectrum in higher frequency ranges above 92 GHz as a complementary of the lower bands.
Report ITU-R M.[IMT.ABOVE 100 GHz] investigates technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 92 GHz including propagation characteristics, potential new enabling IMT technologies, which could be appropriate for operation in these bands, and relevant deployment scenarios.
The Report describes a series of propagation measurement activities carried out by academia and industry aiming at investigating the propagation characteristics in these bands under several different environments (such as outdoor urban and indoor office). It also includes a summary of the measurement activities collected for these bands, noting that bands of interest are more concentrated in 100, 140-160, 220-240, and around 300 GHz. Characteristics of IMT technologies in bands above 92 GHz, including coverage, link budget, mobility, impact of bandwidth and needed capabilities to support new use cases, have been presented in this Report.
To overcome major challenges of operating in bands above 92 GHz such as limited transmission power, the obstructed propagation environment due to high propagation losses and blockage, it describes enabling antenna and semiconductor technologies, material technologies including reconfigurable intelligent surfaces and MIMO and beamforming technologies as potential solutions.
Given the large bandwidth and high attenuation characteristics of bands above 92 GHz, some typical use cases are also envisaged in this Report, such as indoor/outdoor hot spots, integrated sensing and communication, super-sidelink, flexible wireless backhaul and fronthaul.
The radio wave propagation assessment, measurements, technology development and prototyping described in the Report indicate that utilizing the bands above 92 GHz is feasible for studied IMT deployment scenarios, and could be considered for the development of IMT for 2030 and beyond.
This ITU-R report is expected to be completed and approved in 2023.
References:
ITU-R Report in Progress: Use of IMT (likely 5G and 6G) above 100 GHz (even >800 GHz)
Research & Markets: Global Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) Chipset Market Expected to Reach $7.7B by 2028
Executive Summary:
The “Global Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) Chipset Market Size, Share & Industry Trends Analysis Report By Application, By Deployment, By Offering (Hardware (Processor, Memory, and Power Management Unit) and Software), By Vertical, By Regional Outlook and Forecast, 2022 – 2028” report has been published by ResearchAndMarkets.com.
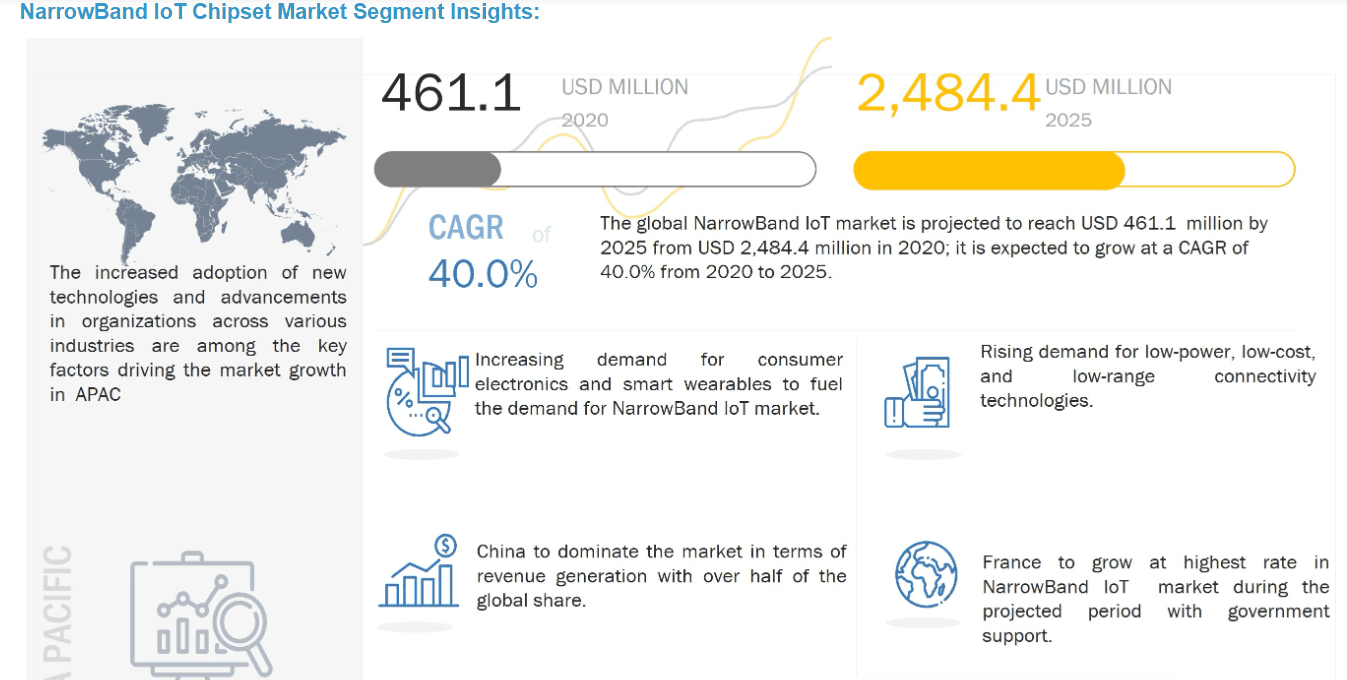
The Global Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) Chipset Market size is expected to reach $7.7 billion by 2028, rising at a market growth of 51.6% CAGR during the forecast period. A Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) chipset is used in many machines, electronic gadgets, and physical items.
Due to numerous advantages of the technology, including low power consumption for user devices, high system capacity, and improved spectrum efficiency enabling deep coverage of an area, the narrowband IoT chipset market is expanding at a rapid rate. A wide variety of new Internet of Things (IoT) devices and services are made possible by the standards-based low power wide area (LPWA) technology known as narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT).
In deep coverage, NB-IoT dramatically increases spectrum efficiency, system capacity, and user device power consumption. A variety of use cases can accommodate a battery life of more than 10 years. The technologies utilized to transport data nowadays range widely. Each has distinct advantages and disadvantages, and the appropriate technology is selected based on the specific circumstances.
The most discussed in recent years and one that will be widely used in future years across multiple industries is NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things). A lot of devices can communicate data using the NB-IoT technology even in areas without coverage from a typical mobile network. A more reliable data transport is ensured by the use of a licensed frequency band where there is no interruption from other devices. A network that can span over big regions while using less energy is an LPWAN, and this is what the NB-IoT is.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis:
As lockdowns were imposed all over the world and the continuity of operations for the majority of industries is significantly compromised, the COVID-19 pandemic is having a significant impact on global supply chains and logistics. Several nations have halted all imports as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic out of concern for further viral spread.
The pandemic is anticipated to cause a decrease in the availability of connectivity devices, which is expected to cause the rate of growth of the NB-IoT chipset market to be slower than anticipated. Moreover, the market for smart street lighting has been impacted by the expansion of COVID-19, which has also had an impact on investments in smart cities and infrastructure projects for roads and highways.
Market Growth Factors:
Increasing Adoption of IoT Along With Better Battery Life for Other Connected Devices:
Battery life is a major aspect in the world of IoT devices as well as other connected devices today. Smartphone makers are continuously striving to improve their devices’ massive battery life because modern smartphones are so different from their models from only a few years ago.
Technologies are evolving and becoming more advanced and sophisticated every year. The market for connected devices is expanding, particularly in the industrial sector, as M2M communications become more prevalent. In addition, connectivity has been made possible by market trends, like IoT in practically every sector, encompassing healthcare, consumer electronics, or retail.
Lesser Initial and Maintenance Costs Along With Increasing Reliability:
Companies is expected to not make significant investments in new technology if it does not improve their bottom line in the long run. That is actually how it should be because a business is fundamentally a living entity that is trying to survive in a hostile market where cost is a very significant factor for the growth and revenue of any business.
With the rapidly expanding information infrastructure and the world’s economy being so interconnected, this is more relevant than ever. NB-IoT and similar technologies use a fairly straightforward waveform, which uses less power. But it’s not only about power savings. As NB-IoT becomes more and more popular, making NB-IoT chips will become more and more affordable.
Market Restraining Factors:
Incompatibility with High Data Speeds Along With the Availability of Alternatives Across The Market
Compared to LTE-M, NB-IoT is less suitable for situations where very low network latency is required. In situations where near-real-time data could be necessary, where LTE-M is a better fit, it will therefore be less common. In the transition to 5G, both NB-IoT and LTE-M play a role in enabling use cases that demand speed and are frequently crucial.
Not all of this depends on the communication standard that is selected. For fixed or mobile devices, NB IoT was created as a pure data transfer method. It cannot seamlessly switch between cells and cannot serve applications that need low latency.
Media Contact:
Research and Markets
Laura Wood, Senior Manager
[email protected]
Reference:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Companies making NB-IoT Chip Sets:
Huawei, Qualcomm, Nordic Semiconductor, Samsung, Mediatek, Intel, among others
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/narrowband-iot-market-59565925.html
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
Samsung Electronics and KDDI announced the successful demonstration of Service Level Agreements (SLA) assurance network slicing in a field trial conducted in Tokyo, Japan. For the first time in the industry, the companies proved their capabilities to generate multiple network slices using a RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) on a live commercial 5G Standalone (SA) network. The RIC, provided by Samsung in this field trial, is a software-based component of the Open RAN architecture that optimizes the radio resources of the RAN to improve the overall network quality.
Network slicing (which requires a 5G SA core network) enables multiple virtual networks to be created within a single physical network infrastructure, where each slice is dedicated for a specific application or service — serving different purposes. For instance, 5G SA network operators can create a low latency slice for automated vehicles, an IoT slice for smart factories and a high bandwidth slice for live video streaming — all within the same network. This means that a single 5G SA network can support a broad mix of use cases simultaneously, accelerating the delivery of new services and meeting the tailored demands of various enterprises and consumers.
“Network slicing will help us activate a wide range of services that require high performance and low latency, benefitting both consumers and businesses,” said Toshikazu Yokai, Managing Executive Officer, General Manager of Mobile Network Technical Development Division at KDDI. “Working with Samsung, we continue to deliver the most innovative technologies to enhance customer experiences.”
Through this field trial conducted in Q4 of 2022, KDDI and Samsung proved their capabilities of SLA assurance to generate multiple network slices that meet SLA requirements, guaranteeing specific performance parameters — such as low latency and high throughput — for each application. Samsung also proved the technical feasibility of multiple user equipment (UE)-based network slices with quality assurance using the RIC, which performs advanced control of RAN as defined by the O-RAN Alliance.
“Network slicing will open up countless opportunities, by allowing KDDI to offer tailor-made, high-performance connectivity, along with new capabilities and services, to its customers,” Junehee Lee, Executive Vice President, Head of Global Sales & Marketing, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “This demonstration is another meaningful step forward in our efforts to advance technological innovation and enrich network services. We’re excited to have accomplished this together with KDDI and look forward to continued collaboration.”
For more than a decade, the two companies have been working together, hitting major 5G networks milestones that include: KDDI’s selection of Samsung as a 5G network solutions provider, end-to-end 5G network slicing demonstration in the lab, 5G network rollout on 700MHz and the deployment of 5G vRAN on KDDI’s commercial network.
Samsung has pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions including chipsets, radios and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio from virtualized RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company is currently providing network solutions to mobile operators that deliver connectivity to hundreds of millions of users around the world.
References:
Ericsson and Nokia demonstrate 5G Network Slicing on Google Pixel 6 Pro phones running Android 13 mobile OS
Nokia and Safaricom complete Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial
Deutsche Telekom demos end to end network slicing; plans ‘multivendor’ open RAN launch in 2023
Is 5G network slicing dead before arrival? Replaced by private 5G?
Telefonica in 800 Gbps trial and network slicing pilot test
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
Network Slicing and 5G: Why it’s important, ITU-T SG 13 work, related IEEE ComSoc paper abstracts/overviews
Ericsson warns profit margins at RAN business set to worsen
Ericsson on Friday reported lower than expected 4th-quarter core earnings as sales of 5G equipment slowed in high-margin markets such as the United States, sending the Swedish company’s shares to their lowest since 2018.
Ericsson is the latest tech company to show the impact of customers tightening belts amid concerns about a global economic slowdown. Others have been cutting staff, including Microsoft (10,000) and Google parent Alphabet (12,000) which have announced thousands of job cuts this week while Amazon had announce 10,000 layoffs several weeks ago.
Ericsson has already announced plans to cut costs by 9 billion crowns ($880 million) by the end of 2023.

Chief Financial Officer Carl Mellander told Reuters that would involve reducing consultants, real estate and also employee headcount. “It’s different from geography to geography, some are starting now, and we’ll take it unit by unit, considering the labour laws of different countries,” Mellander said, referring to the cuts.
Mellander declined to say if the job cuts would be similar to 2017 when Ericsson laid off thousands of employees and focused on research to return the company to profitability.
Last week, the company said it would book a 2.3 billion Swedish crown ($220 million) provision for an expected fine from U.S. authorities for breach of a settlement reached in 2019.
Ericsson’s net sales rose in the fourth quarter, but margins, net income and core earnings fell. Its gross margin for the fourth quarter of 2022 fell to 41.4% from 43.2%.
Ericsson said it expected a fall in margin in its Networks business to persist through the first half of 2023, but the effect of cost savings to emerge in the second quarter.
JPMorgan analysts said given the fall in margins and higher investments, they would expect 2023 earnings to decline by a double digit percentage.
Inge Heydorn, partner and fund manager at investment firm GP Bullhound, said: “The fourth quarter shows once again that the U.S. has a big impact on Ericsson’s margins.”
With U.S. customers such as Verizon tightening their purse strings, Ericsson is hoping newer markets such as India can provide some growth. Its South East Asia, Oceania and India market was the only one to grow in the quarter, rising 21%, accounting for 13% of the company’s business.
The company’s fourth-quarter adjusted operating earnings, excluding restructuring charges, fell to 9.3 billion Swedish crowns from 12.8 billion a year earlier. That was short of the 11.22 billion expected by analysts, Refinitiv Eikon data showed. Net sales rose 21% to 86 billion crowns, beating estimates of 84.2 billion.
A settlement of a patent deal with Apple (AAPL.O) last month resulted in revenue of 6 billion crowns, but Ericsson also took 4 billion crowns in charges, including a provision for a potential fine from U.S. regulators and divestments.
However, there was some good news.
- Ericsson said it expects significant patent revenue growth over the coming 18-24 months.
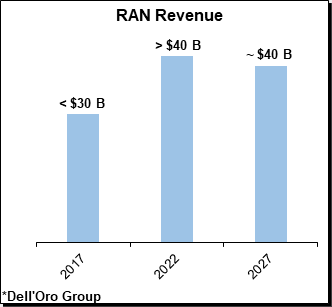
- Ericsson, outside China, remains the company to beat in 5G. Its share of the market for radio access networks (RANs) appears to have increased several years in a row – from 33% in 2017 to 39% now.
- Ericsson is healthily profitable, which could not be said when CEO Ekholm took charge in 2017.
- Boosted by recent takeover activity and a major licensing deal with Apple, its headline sales for the final quarter of 2022 were up 21%, to 86 billion Swedish kronor (US$8.4 billion), compared with the same period a year before.
However, Ericsson has experienced one of its biggest profit slumps since the first half of Ekholm’s tenure. Hurt by higher costs and SEK4 billion ($390 million) worth of one-off charges – relating to US fines, write-downs and divestiture – its net income dropped by 39%, to SEK6.2 billion ($600 billion). Worse, all the various profit margins thinned, with Ericsson’s closely monitored EBIT (earnings before interest and tax) margin shrinking to just 9.1%, from 16.1% a year earlier. And the outlook is frosty.
The mini-boom in 5G spending appears to be over – temporarily, at least. Last year, the market for RAN products, where Ericsson now generates about 70% of its revenues, grew by around 5%, according to data from Dell’Oro, a market research firm that Ericsson uses. This year, RAN market sales are expected to fall by 1%. And in North America, responsible for nearly 30% of Ericsson’s overall revenues, Dell’Oro predicts they will drop by a worrying 7%.
After investing heavily in network rollouts during the last couple of years, many operators are cutting their expenditure amid signs of an economic downturn, and reducing the equipment stockpiles they built up when supplies were tight. “We expect operators to adjust inventory levels as the supply situation eases and we plan for these trends to continue during the first half of 2023,” said Ekholm on Ericsson’s earnings call today.
“The first half is really where we’ll see the sizeable inventory adjustments,” said Ekholm, answering questions asked by analysts. “Operators can sweat assets for a couple of quarters but it cannot be done much more [than that] because of the traffic growth underneath. That is the way to model it.” Ericsson’s expectation is that total mobile data traffic worldwide will grow by a factor of five between 2022 and 2028.
Given the market slowdown, turbulence of the last year and seemingly endless difficulties at smaller units, it is easy to forget that Ericsson remains a solid and successful business. But it has become more reliant on RAN sales under Ekholm – generating more than 70% of its revenues in that market last year, compared with just 47% in 2016. Ekholm clearly restored Ericsson’s reputation as a RAN provider. Amid the slowdown in that sector (zero growth forecast by Dell’Oro through 2027), his big challenge now is to prove it can thrive elsewhere.
Andrew Gardiner, analyst at Citi, said the announcements demonstrated the “significant challenges” the company faced this year. “We view Ericsson’s outlook as one of fundamentals deteriorating in the next quarter or two, as it aims to improve in the second half and beyond,” he added.
References:
https://www.reuters.com/technology/ericsson-quarterly-earnings-miss-expectations-2023-01-20/
https://www.ft.com/content/dd5cb329-f5bd-4b78-bde1-ca7510daaa7a
Dell’Oro: 5G RAN growing; total RAN growth is slowing over next 5 years
According to a newly published forecast report by Dell’Oro Group, after four years of extraordinary growth that propelled the radio access network (RAN) market to reach new record levels, the RAN market is now transitioning from the expansion phase to the next phase in this 5G journey with more challenging comparisons and slower growth.
“It is still early days in the 5G journey but at the same time, the coverage and capacity phases that have shaped the capex cycles with previous technology generations still hold,” said Stefan Pongratz Vice President and analyst with the Dell’Oro Group. “Still, even with the expected changes in capital intensities as the operators reach their initial 5G coverage targets, the plethora of 5G frequencies taken together with the upside from FWA and eventually private 5G, will curb the peak-to-trough decline relative to 2G-4G,” continued Pongratz.
Editor’s Note: In December, Ericsson said it expects the RAN market to be flat with 5G build-out still in its early days.
Additional highlights from the Mobile RAN 5-Year January 2023 Forecast Report:
- Global RAN is projected to grow at a zero percent CAGR outside of China by 2027. See chart below.
- The less advanced MBB regions are expected to grow while RAN investments in both China and North America are expected to decline at mid-single digit CAGRs over the forecast period.
- 5G RAN is expected to grow another 25 percent to 30 percent by 2027, though this will barely be enough to offset steep declines in LTE.
- mmWave projections have been revised downward over the near term and upward in the outer part of the forecast to reflect the potential upside with higher EIRP solutions.
- Small cell RAN revenue growth has been outpacing macros for some time now and these trends are expected to extend throughout the forecast period, with small cell RAN revenues growing more than 20 percent by 2027.
Dell’Oro Group’s Mobile RAN 5-Year Forecast Report offers a complete overview of the Mobile RAN industry by region – North America, Europe, Middle East & Africa, Asia Pacific, China, and Caribbean & Latin America, with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue and unit shipments for 5GNR, 5G NR Sub 6 GHz, 5G NR mmW and LTE pico, micro, and macro base stations. The report also covers Open RAN, Virtualized RAN, small cells, and Massive MIMO. To purchase this report, please contact by email at [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, security, enterprise networks, and data center infrastructure markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com
References:
5G RAN is Growing but Total RAN Growth is Slowing over Next Five Years, According to Dell’Oro Group
\
Fiber Build-Out Boom Update: GTT & Ziply Fiber, Infinera in Louisiana, Bluebird Network in Illinois
This week GTT Communications, Infinera, and Bluebird Network all announced network expansions within the U.S. The various announcements follow AT&T’s deal last month with venture capital firm BlackRock to deploy a multi-gigabit fiber network to 1.5 million customer locations using a commercial open access platform.
GTT Communications, Inc., a leading global provider of managed network and security services to multinational organizations, has announced that it has expanded its partnership with Ziply Fiber, a provider of fiber networks purpose-built for the internet, to establish a new network Point of Presence (PoP) to serve the fast-growing data center market in Portland, Oregon. The two companies linked in hopes to “serve the fast-growing data center market” in the city, according to the announcement.
The new PoP is providing an initial 400G of capacity to customers in the U.S. Pacific Northwest region and will expand the power of GTT’s global Tier 1 IP network by offering an additional option for customers to connect in 11 major data centers and the Hillsboro subsea cable landing station, expanding the reach of GTT via Ziply Fiber’s high-count Silicon Forest fiber cross connection service.
“We are pleased to expand our partnership with GTT to establish a new network PoP in Portland to help customers in the region and beyond to connect to area data centers as well as other geographies,” said Mike Daniel, vice president of Enterprise Sales at Ziply Fiber. “Our regional fiber network, combined with GTT’s global Tier 1 network and suite of leading managed networking and security services, will give enterprises new options to improve connectivity securely and reliably.”
GTT’s global Tier 1 IP backbone is ranked among the largest in the industry1 and connects more than 260 cities on six continents. With the addition of the new Portland PoP, GTT customers in the region can benefit from the improved connectivity, security and scalability available through GTT’s suite of managed connectivity services.
Ziply Fiber’s network was architected to meet today’s increasing digital demands and was engineered to be fully redundant, with a dual infrastructure that maintains customer connections even when issues arise. Ziply Fiber maintains a four-state footprint in Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana and has built redundancies into its network to avoid service interruptions, while updating routing to steer clear of congestion across the broader internet. This ensures content is accessible directly on the fiber backbone and can be accessed more quickly.
“This new PoP deployment creates an exciting opportunity to use the Ziply Fiber network to allow our regional data center customers to easily connect to and take advantage of GTT’s global Tier 1 IP network and our full suite of managed services offerings,” said Jim Delis, president, Americas Division, GTT. “Our work with Ziply Fiber demonstrates GTT’s continued focus on investment to expand the reach of our network for customers with locations in the Pacific Northwest.”
GTT will offer additional customer options to connect in 11 data centers and the Hillsboro subsea cable landing station. Jim Delis, president for GTT’s Americas Division, stated the PoP deployment will enable the network provider’s data center customers to link into its tier-one IP network.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Infinera announced today that the Louisiana Board of Regents, acting on behalf of the statewide Louisiana Optical Network Infrastructure (LONI) and the Board of Supervisors of Louisiana State University (LSU) and Agricultural and Mechanical College, has selected and deployed Infinera’s advanced coherent optical networking solutions to upgrade LONI. Also announced today is the initial deployment of four 400G optical channels along a 220-mile intrastate route in Louisiana.
LONI connects 38 university campuses and data centers and provides connectivity to additional research and education networks in other states. The solution, which increases LONI’s network capacity by a factor of 10, comprises Infinera’s XTM Series open line system and GX Series transponders. The upgraded network expands the ability for the research and education community to share and access information, resources, and remote instruments in real time.
LONI promotes scientific computing and technology across Louisiana and is the backbone infrastructure to the state’s heroic research efforts. These efforts are made possible by utilizing cutting-edge technology to push the limits of scientific discovery at leading university campuses and achievable with LONI’s high-bandwidth optical network. Infinera’s XTM Series line system coupled with GX Series high-performance transponders equips LONI with a 200G/400G/600G solution that offers unmatched high-bandwidth services to its customers today and is scalable to 800G in the future. Infinera’s combined solution delivers superior performance, increasing LONI’s service offering with more bandwidth, greater flexibility, and faster data transfer capabilities.
“A high-capacity state-of-the-art network is critical to enabling breakthrough discoveries that can only be achieved through multi-site collaboration and cloud connectivity,” said Lonnie Leger, LONI’s Executive Director. “We are committed to offering our members up to 100G and deploying Infinera’s innovative solutions, which exceeded both our expectations and commitment, enabling us to exceed what other state universities can offer.”
“LONI operates with a small staff, which requires a highly automated network and cost-effective solution that enables them to meet their bandwidth growth requirements,” said Nick Walden, Senior Vice President, Worldwide Sales, Infinera. “The Infinera team worked closely with LONI to deliver a solution that met their needs now and positions them to meet future bandwidth needs with minimal maintenance and manpower to operate.”
“As bandwidth continues its relentless growth driven by new high-speed applications such as 5G, [augmented reality], [virtual reality], and cloud services, legacy copper-based networks – such as DSL and cable – are simply not capable [of] meeting the bandwidth requirements,” Robert Shore, SVP of marketing at Infinera, told SDxCentral.
Shore added that the current fiber boom “reinforces Infinera’s focus on continuing to innovate and manufacture optical transport solutions that can help network operators effectively leverage their fiber deployments from the core of their network all the way to the very edge.”
Infinera also announced that its ICE6 solution was deployed along the trans-Pacific Unity Submarine Cable System connecting Japan and the U.S., doubling the capacity of that connection.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Bluebird Network completed a 126-mile fiber buildout in Illinois. The route connects the towns of Aurora, Dixon, DeKalb, Sterling, and Rock Falls to Bluebird’s network and services, and provides a “diverse route” to Chicago, the company stated.
Bluebird’s management noted the deployment builds on its recently acquired middle-mile fiber network assets from Missouri Telecom, and expansion into Salina, Kansas, and Waterloo, Iowa.
“Bluebird has no plans to slow down its fiber expansions any time soon,” Bluebird Network President and CEO Michael Morey stated in the release tied to its Kansas and Iowa expansion. “To foster even more growth and strengthen connectivity for businesses in the Midwest, we have builds underway for additional expansions coming online this summer.”
Those moves come on the heels of the AT&T/BlackRock JV that is looking to deploy fiber to more than 30 million locations within AT&T’s 21-state wireline footprint by the end of 2025, and positions the newly created Gigapower entity to boost its reach outside of those initial 21 states.
The deal also prompted a predication from Analysys Mason, saying the move further indicates “that the [U.S.] wireline market is entering a period of profound transformation that will leave it more aligned with the market structures seen in Europe.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/us-fiber-build-booms/2023/01/
AT&T and BlackRock’s Gigapower fiber JV may alter the U.S. broadband landscape
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network & MEC revenues to be > $50 billion by 2027
According to a recently published report from Dell’Oro Group, the Mobile Core Networks (MCN) [1.] and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) market revenues are expected to reach over $50 billion by 2027.
Note 1. The Mobile Core Network is in a transitional stage from 4G to 5G and a new type of core network called the 5G Core Service Based Architecture (SBA). The 5G Core SBA is designed to be a universal core that can be the core for mobile and fixed wireless networks, wireline networks, and Wi-Fi networks. This includes the ability to be the core for 2G/3G/4G, so only one core is necessary for the long term. In addition, the IMS Core will migrate into the 5G Core SBA.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“The MNC and MEC market revenues are expected to grow at a 2 percent CAGR (2022-2027). We expect the MCN market for the China region to reach maturity first—due to its early start on 5G SA deployments—and is projected to have -4 percent CAGR throughout the forecast period,” stated Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group.
“The worldwide market, excluding China, is projected to have a 3 percent CAGR. The Asia Pacific (APAC) and the Europe, Middle, East, and Africa (EMEA) region are expected to have the highest CAGRs throughout the forecast period as MNOs accelerate the deployments of 5G SA networks and expand their respective coverage footprints.
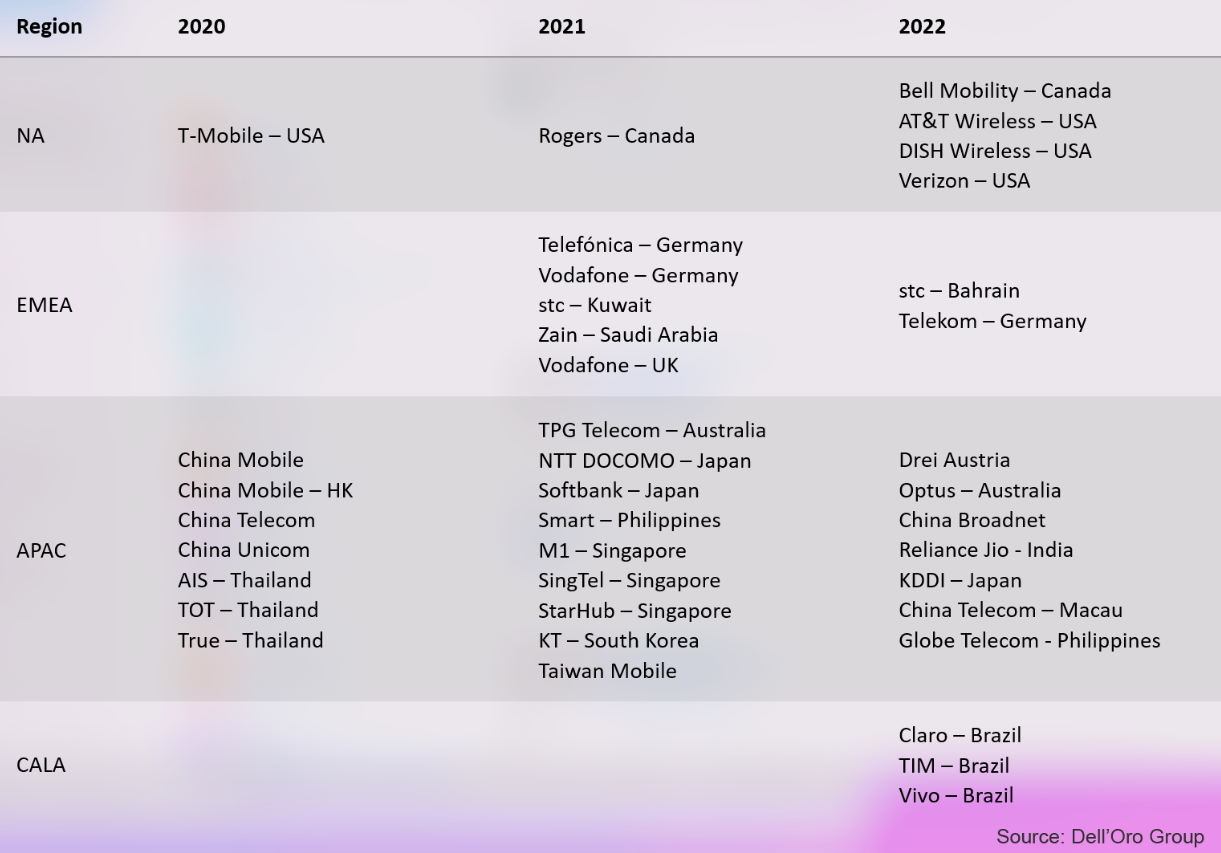
“There were hopes early in the year that many more [SA networks] would be launched in 2022, but the hopes were lowered as the year progressed,” Bolan explained. At the close of 2022, Dell’Oro identified 39 MNOs (Mobile Network Operators) that have commercially launched 5G SA eMMB networks.
“Reliance Jio, China Telecom-Macau, and Globe Telecom were new MNOs added to the list of 39 MNOs launching 5G SA eMMB networks in the fourth quarter of 2022. Reliance Jio has announced a very aggressive deployment schedule to cover most of India by the end of 2023. In addition, AT&T and Verizon plan large expansions to their 5G SA coverage in 2023, raising the projected Y/Y growth rate for the total MCN and MEC market for 2023 higher than 2022,” added Bolan.
Additional highlights from the January 2023 MCN and MEC 5-Year forecast report:
- The MEC segment of the MCN market will have the highest CAGR, followed by the 5G MCN market and the IMS Core market.
- As networks migrate to 5G SA, the 4G MCN market is expected to decline at a double-digit percentage CAGR.
The Dell’Oro Group Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Computing Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, shipments, and average selling prices for Evolved Packet Core, 5G Packet Core, Policy, Subscriber Data Management, and IMS Core including licenses by Non-NFV and NFV, and by geographic regions. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
From Deloitte:
“The coming migration to 5G standalone core networks is expected to allow for increased device density, reliability, and latency, opening the door to advanced enterprise applications,” according to several analysts from Deloitte’s Technology, Media & Telecommunications industry group.
“5G SA’s big attraction for MNOs are the new service and revenue opportunities it creates, Along with near-zero latency and massive device density, 5G SA enables MNOs to provide customers – specifically enterprise customers – access at scale to fiber-like speeds, mission-critical reliability, precise location services, and tailored network slices with guaranteed service levels.”
Deloitte expects the number of mobile network operators investing in 5G SA networks – with trials, planned deployments, or rollouts – to double from more than 100 operators in 2022 to at least 200 by the end of 2023.

References:
Mobile Core Network Market to Reach over $50 billion by 2027, According to Dell’Oro Group
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market driven by 5G SA networks in China
Hawaiian carrier Mobi to deploy a cloud-native 4G/5G core network as a fully managed service on AWS
Mobi, a leading wireless network provider in Hawaii, is now expanding into the continental United States and beyond. Mobi is one of only four full mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) in the United States. According to Mike Dano of Light Reading, they have approximately 55,000 customers.
To support a cost-effective, scalable and innovation-friendly expansion strategy, Mobi partnered with Oslo, Norway based Working Group Two (WG2) to move its core network to the cloud. The WG2 mobile core runs cloud-natively on Amazon Web Services (AWS) and empowers Mobi to build a compelling, app-first customer experience on the largest 5G nationwide network (which is assumed to be the AWS cloud native 5G core network). Mobi plans to use its nationwide capabilities to ensure that its Hawaiian customer base won’t need to sign up for another cellular network provider if they move to the continental U.S.
A pilot solution goes live today – January 17, 2022.

By choosing a scalable and flexible cloud architecture, Mobi can offer more competitive rates and faster time-to-market with new services. The Network-as-a-Service approach reduces the time it takes to develop and deploy new features and upgrades. In contrast to legacy solutions, which include only a few network updates per year, Mobi will benefit from continuous, daily upgrades. Further, with a mobile core from WG2 that is agnostic to any generation of wireless, Mobi can future-proof its network with no end-of-life and continuous maintenance and support.
With a programmable, cloud-native core, Mobi will gain unprecedented flexibility, and will realize significantly faster time-to-market with new services. Once the WG2 mobile core is integrated with the radio network, Mobi can leverage simple APIs to determine which services to activate for every SIM or user. The network is delivered fully as-a-service and the cost is based on consumption, defined by the number and type of users/SIM cards, changing as needs and traffic fluctuate. This allows for lower barriers of entry, and a core network that can scale from single users to hundreds of millions of users.
WG2 says their core offers a full MNO core for 4G and 5G, as well as a full MVNO functionality for 2G/3G. This allows operators to build full modern 4G/5G core networks while leveraging national roaming for 2G/3G where necessary. WG2’s 4G/5G/IMS mobile core network provides Mobi with a web-based portal, through which the company can quickly and easily manage existing services and offer new ones. The WG2 core offers the full set of capabilities related to authentication and provisioning, voice, messaging, and data services.
Quotes:
Justen Burdette, CEO of Mobi:
“Our ambition is to disrupt and challenge the status quo in the wireless industry by delivering a seamless, app-first, and engaging customer experience. By working with WG2 and AWS, we not only get access to a scalable, secure, and future-proof core network, we also improve our ability to meet the demands of our customers. It’s all about making it simple to join, affordable to use, and fun to explore what our network can offer. We’re building a brand that resonates with our customers by working with a strong ecosystem of partners.”
“We’re able to do a modern, cloud-based, AWS-focused core from WG2. It’s a sight to behold.”
“You have complete API [application programming interface] control of the core. That makes it really amazing for us because we built our stack around APIs.”
Erlend Prestgard, CEO of WG2:
“Mobi is a standout example of a carrier that’s ready to unlock the benefits of a network-as-a-service, achievable with a consistent, programmable mobile core running on the cloud. This allows them to go live in new geographical markets in record time. The simplicity of the as-a-service operating model means that Mobi can focus on meeting customer expectations and spend their time dreaming about innovation, rather than managing complexity. We’re truly excited about joining Mobi on this journey.”
Fabio Cerone, Managing Director EMEA, Telco Business Unit at AWS:
“Embracing the cloud helps carriers simplify network operations, deploy networks more rapidly, scale more easily – while still retaining full control over the network and gaining additional agility and innovation capabilities. Now the core network is only one API away from the global community of developers, which can help deliver new value for Mobi’s customers.”
As an app-first company, wholly focused on user experience, Mobi embraces an open, API-enabled core network approach. Access to WG2’s global ecosystem of developers offers Mobi a selection of pre-integrated, ready-to-deploy applications for voice, messaging and data services, built by WG2’s development partners from all over the world. Following the continental U.S. rollout, Mobi also plans to leverage the same model to expand to markets including Canada, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
About Mobi:
Mobi, Inc. launched as the regional wireless provider for Hawaii in 2005 — becoming the first carrier in the United States to offer affordable, simple, unlimited mobile service at a time when activation, overage, and hidden fees were the norm. Anyone can switch to Mobi in just seconds using the Mobi app, Apple Pay, and eSIM — with smart, friendly Mobi customer care geeks ready to help at any time digitally and at Mobi stores in Hawaii. All Mobi team members are proudly represented by the Communications Workers of America (the CWA). Learn more at mobi.com, or on Facebook, Twitter, or LinkedIn.
About Working Group Two:
Working Group Two has rebuilt the mobile core for simplicity, innovation, and efficiency – leveraging the web-scale playbook and operating models. Today, Working Group Two innovation enables MVNO, MNO, and Private Network Operators a secure, scalable, and reliable telco connectivity backbone that scales across all generations of mobile technologies. Our mission is to create programmable mobile networks to allow our customers and their end users to create more valuable and useful products and services.
Media Contact:
Tor Odland
Working Group Two
+47 9909 0872
[email protected]
References:
https://www.wgtwo.com/blog/mobi-expansion-with-wg2-aws/