Author: Alan Weissberger
Future Market Insights: Telecom Cloud Market CAGR at 15.2% from 2022-2032
The Telecom Cloud Market revenues were estimated at US$ 19.8 Bn in 2021 and are anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 15.2% from 2022-2032, according to a recently published Future Market Insights (FMI) report. By the end of 2032, the market is expected to reach a valuation of US$ 24 Bn. Globally, the cloud services market is expected to reach a valuation of 2.5 Bn by 2030, as per a new study by FMI.

During the pandemic, as individuals lived at home during the shutdown and businesses opted to work remotely, massive data consumption led to a spike in demand for telecom cloud installations, which significantly contributed to the market growth. Cloud has been one of the key themes of conversation in the telecom business in 2021 with the development of cloud-native 5G technology.
The public cloud solution provides on-demand infrastructure, lowering capital expenditure as well as continuous operational and life-cycle control. The public cloud may be a terrific incubator environment for not just developing new apps and services, but also bringing them to market and scaling them quickly.
Many corporate firms rely on the public cloud as their base. Telecom companies are increasingly looking to collaborate using public cloud services to use their computational capacity and use their strong network skills on the back end.
Hyperscalers such as Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and Oracle often establish and manage a uniform tech environment with public cloud platforms. CSPs, on the other hand, buy solutions from a variety of vendors who compete and advance in different directions, sometimes marginally, sometimes significantly.
Also, The BFSI sector outsources non-core functions to save money and enhance efficiency. As a consequence, targeted content views and precise financial data are required, which may be merged via a telecommunications cloud service.
Competitive Landscape:
The market is fiercely competitive, where key players are increasingly focused to obtain a competitive advantage. The key companies in the Telecom Cloud Market are focused on R&D to produce innovative technological solutions.
- In April 2021, Momentum Telecom, a global provider of managed network and clouds voice, revealed that it had accomplished its purchase of Atlus Technology, a Tennessee-based leader in the development of cloud-based unified communications solutions.
- In December 2020, Cisco announced the purchase of IMImobile, a cloud telecommunications software and service provider, allowing Cisco to provide its customers with an end-to-end client engagement management solution.
Multi Cloud Management Market Trend: Multi cloud management is similar to the use of best-of-breed applications from multiple developers on a personal computer, rather than the defaults offered by the operating system vendor.
Cloud Business Email Market Demand: The global cloud business email market is expected to acquire a market value of nearly USD 2.15 Bn, proliferating at a CAGR of 10.4% during the forecast period from 2017 to 2027.
More Insights Available
Future Market Insights, in its new offering, presents an unbiased analysis of the Telecom Cloud Market, presenting historical market data (2015-2021) and forecast statistics for the period of 2022-2032.
ABOUT FUTURE MARKET INSIGHTS, INC:
Future Market Insights, Inc. is an ESOMAR-certified business consulting & market research firm, a member of the Greater New York Chamber of Commerce and is headquartered in Delaware, USA. A recipient of Clutch Leaders Award 2022 on account of high client score (4.9/5), we have been collaborating with global enterprises in their business transformation journey and helping them deliver on their business ambitions. 80% of the largest Forbes 1000 enterprises are our clients. We serve global clients across all leading & niche market segments across all major industries.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Public Cloud Based Telecom Cloud Market to Register a CAGR (globenewswire.com)
https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/telecom-cloud-market
Telecom Cloud Market Size, Share, Sales & Trends – 2032 | FMI (futuremarketinsights.com)
Request a Sample Copy of Report:
https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-3353
Dell partners with Wind River on modular cloud-native telecommunications infrastructure
Dell Technologies, together with Wind River (owned by Intel and Delphi Automotive), is introducing a new telecom cloud infrastructure solution to help communications service providers (CSPs) reduce complexity and accelerate their “cloud-native” network deployments.
To facilitate these solutions, Dell’s telecom partner certification program simplifies the process for technology partners to validate and integrate their products within a rapidly growing open technology ecosystem.
Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks help accelerate open, cloud-native network deployments. Dell is taking an entirely new approach to solve the complexities of cloud-native network deployments with Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks. The fully engineered, cloud-native infrastructure blocks simplify telecom cloud network deployment and management, while accelerating the introduction of new technologies and lowering operational expenses (OpEX).
As the fastest way to deploy the Dell Telecom Multicloud Foundation, launched earlier this year, these blocks include Dell PowerEdge servers, Dell Bare Metal Orchestrator management software, and a CSP’s choice of integrated telecom cloud software platforms, beginning with Wind River Studio.
Dell is the first company to launch a co-engineered system with Wind River, designed and factory integrated to host telecom workloads that can be scaled easily with automation, with streamlined support from Dell for the entire infrastructure stack3. The validated and pre-packaged blocks of hardware and software are designed to meet specific telecom workload requirements and use cases, spanning the network core to Open RAN Distributed Units (DU) and Centralized Units (CU).
Wind River delivers mature production-ready offerings based on proven Wind River Studio technology, live in deployments with leading operators. Wind River Studio provides the Containers-as-a-Service layer for a distributed cloud and the tools to automate and optimize “Day 2” operations at scale.
Holger Mueller of Constellation Research Inc. said today’s partnership with Wind River is all about making it easier for telecommunications firms to go live on Dell’s hardware and services. “What’s really of note is the new partner self-certification program,” the analyst said. “Partner certification can be slow and is normally always very expensive. So unleashing a self-service process for partners can be a huge accelerator, as long as the quality of the certification is not compromised.
Dennis Hoffman, senior vice president and general manager, Dell Technologies Telecom Systems Business:
As the telecom network disaggregates, network operators are challenged to effectively acquire, deploy, test and operate a myriad of open, cloud-native solutions. With our portfolio of software, solutions, development labs and partner programs, including our first open, telecom cloud engineered system with Wind River, a leader in Open RAN deployments, we can partner with communications service providers globally to simplify their transition to cloud-native technologies.
Kevin Dallas, president and chief executive officer, Wind River:
Our collaboration with Dell will help address complex CSP challenges in deploying and managing a physically distributed, ultra-low-latency cloud-native infrastructure for intelligent edge networks. As the de facto infrastructure for OpenRAN and 5G vRAN and only 5G solution that is commercially deployed at scale, Wind River Studio enables flexible networks and offers validated architectures to help service providers quickly and reliably deploy new services with industry-leading total cost of ownership for a cloud native future.
References:
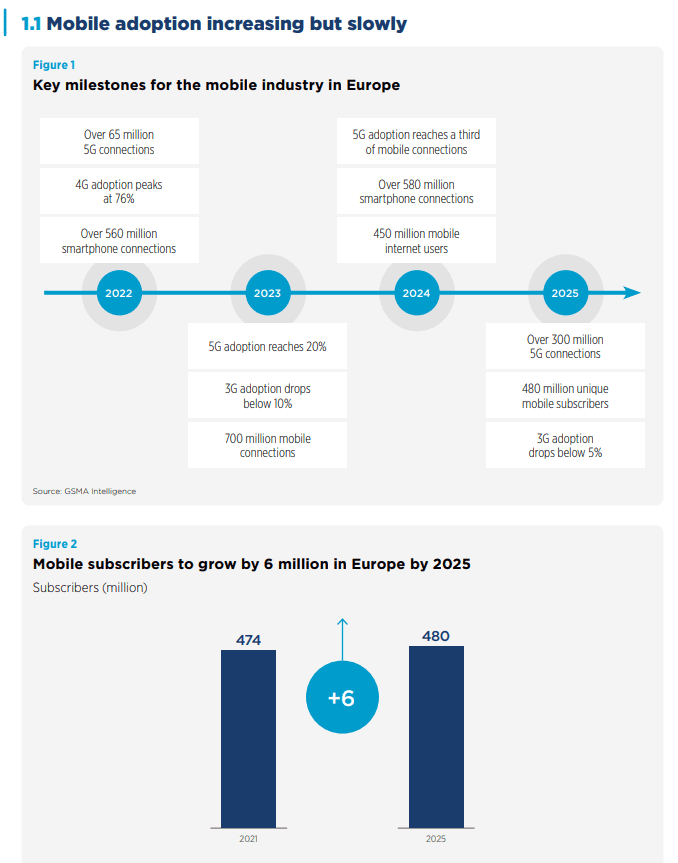
GSMA: Europe’s 5G rollout is too slow at 6% of mobile customer base
GSMA says in order to stay competitive European economies must ‘digitalize’ themselves through faster 5G rollouts and make a fair contribution. The telco trade body and owner of MWC event has released its 2022 Mobile Economy Report for Europe, in which it states the EU will not meet its ‘digital decade goals’ unless it starts rolling out 5G faster across the continent.
In 2021, 474 million people in Europe (86% of the population) were subscribed to mobile services, and this is expected to grow to 480 million by 2025.
The majority of countries in Europe have now deployed commercial 5G services, and nearly two thirds of wireless network operators in the region have launched 5G networks. At the end of June 2022, 108 operators in 34 markets across Europe had launched commercial 5G services, while consumer uptake was at 6% of the mobile customer base. Norway trended above this with 16% of its citizens using 5G, followed by Switzerland (14%), Finland (13%), the UK (11%) and Germany (10%).
GSMA forecasts that by 2025, there will be 311 million 5G connections across Europe, a 44% adoption rate. However, European markets still lag behind global peers such as Japan, South Korea and the U.S. in the adoption of 5G technology. In 2025, the UK and Germany will have the highest 5G adoption rates in Europe at 61% and 59% respectively, compared to 73% in South Korea and 68% in Japan and the U.S. 4G adoption in Europe will peak in 2022 and then decline. However, it is set to remain the dominant technology across the region, accounting for just over half of total connections by 2025.
The pace of 5G coverage expansion across Europe will be a key factor in the transition from 4G to 5G. Although 5G network coverage in Europe will rise to 70% in 2025 (from 47% in 2021), nearly a third of the population will remain without 5G coverage. This compares to 2% or less in South Korea and the U.S.
SOURCE: GSMA
“Europe is adopting 5G faster than ever before, but greater focus on creating the right market conditions for infrastructure investment is needed to keep pace with other world markets. This should include the implementation of the principle of fair contribution to network costs,” said Daniel Pataki, GSMA Vice President for Policy & Regulation, and Head of Europe.
Which of course is a reference to the ‘fair contribution’ argument that telcos and now the GSMA itself has been making for some time now, which in a nutshell says that since internet firms like Netflix and Facebook make tons of money, they should contribute to the building of physical network infrastructure because it is expensive and telcos don’t make as much cash as they used to.
This announcement from the GSMA goes a bit further than saying it’s unfair that content providers make much more margin streaming TV shows that telcos do on digging holes and dragging up cell towers, and seems to be asserting that unless something is done about all this then the entire continent of Europe will become uncompetitive on the world stage.
As economies and societies around the world digitalize, the acceleration of 5G in Europe is necessary to ensure that traditional industrial and manufacturing strengths are not dragged down by weaknesses in the ICT sector. To achieve this, it is vital to create the right conditions for private infrastructure investment, network modernization and digital innovation. A financially sustainable mobile sector is key to the delivery of innovative services and the deployment of new networks.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.gsma.com/mobileeconomy/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/051022-Mobile-Economy-Europe-2022.pdf
How 5G network operators can stay competitive and grow their business
By Shekar Ayyar (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
Introduction:
New services enabled by 5G and the cloud present a significant business opportunity, but upgrading existing network infrastructure to deliver these services can be a challenge amid the ongoing supply-chain disruptions and significant economic volatility.
But that’s exactly what communications service providers (CSPs) need to do to stay competitive and ensure that they have the right infrastructure for success in the future.
This article suggests how this can be accomplished. Let’s first look at 5G use cases as illustrated below:
Image Credit: https://www.rajarshipathak.com/2020/01/requirements-for-5g-network-monetization-solution.html
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Discussion:
1. Introduce new services while being smart about infrastructure investments
5G requires an upgrade in network infrastructure to deliver more bandwidth, faster processing and lower latency. This transition impacts all parts of the network, from the access layer to the edge, across the transport layer and into the network core. And increasingly, it requires connectivity to multi-cloud environments, as several workloads are hosted there.
CSPs that are deploying 5G need to adopt agile, open, software-driven approaches and modern networks that are cost effective, efficient and programmable and allow them to deploy services at the edge all the way into the cloud. With the right technology, CSPs (and enterprises) are better positioned for new service creation to drive topline improvement, increase performance, enable quality of service and reduce costs to deliver bottom line improvement.
The right infrastructure can enable CSPs to launch new services like network slicing, multi-access edge computing (MEC) and multi-cloud networking (MCN), which can boost the top line in a world of declining average revenue per user (ARPU). Manufacturing automation is just one example of network slicing delivering benefits through dedicated bandwidth for IoT devices. And when network operators combine that with MEC in a low-latency environment, they can get much faster response rates to enable automation and machine learning in real time. In addition, MCN enables CSPs and co-location providers to offer secure multi-cloud connectivity to enterprises, on demand and as a service.
Software-based infrastructure that leverages compute resources delivers operational savings because it allows CSPs to use their infrastructure for many different use cases, which makes their networks much more efficient. This is akin to the efficiencies that virtual machines (VMs), which let multiple applications or instances run on a single server, brought to the data center.
2. Avoid doubling down on outdated tech, opt for next-gen programmable networks
Yet many network operators continue to rely on legacy networking equipment. That’s problematic because legacy networking technology is hardware-centric and tied to specific silicon choices, and does not deliver protection against supply-chain shortages and volatility. When CSPs and enterprises experience vendor lock-in, they become completely reliant and stake all aspects of their network on that one vendor: speed of innovation, pricing power and supply availability. This is risky, as evidenced by the recent chip shortages that all industries have witnessed.
But software-based networking can run on merchant silicon and purpose-built switch and router hardware, or on servers. It disaggregates the network stack, making it highly programmable for maximum agility; scales based on consumption; and works across the access network, edge and core. And it does all of the above using a single operating system, without requiring costly integration and in a way that lowers TCO and supply chain risk.
3. Disaggregated solutions break the stronghold that a single vendor can have on a CSP or enterprise.
By adopting this approach, CSPs and enterprises now have a broad choice of silicon as well as a wide range of off-the-shelf white-box platforms. Vendor diversification mitigates any supply-chain challenges. It also gives buyers greater pricing leverage.
And while CSPs and enterprises are controlling their costs and avoiding vendor lock-in, they get the modern networks that they need to move fast and effectively monetize 5G infrastructure.
CSPs and enterprises now have an important choice to make. Do they remain locked into legacy technology or attempt to integrate piecemeal open networking solutions? Or do they want to move into the future with minimal risk and maximum revenue potential and ease?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Shekar Ayyar is chairman and CEO of Arrcus, the hyperscale networking software company and a leader in core-to-edge network infrastructure.
Understanding security threats for telco edge and private 5G networks
Author: Adil Baghir (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
Introduction:
Telcos and enterprises realize the need to move toward the network edge to deploy cloud-like solutions to leverage the massive advances in transmission offered by 5G. Benefits such as speed, low latency, and capacity will drive major transformation for telcos and enterprises, opening new revenue opportunities from new business models. We’ll examine several 5G deployment scenarios and security threats in this article.
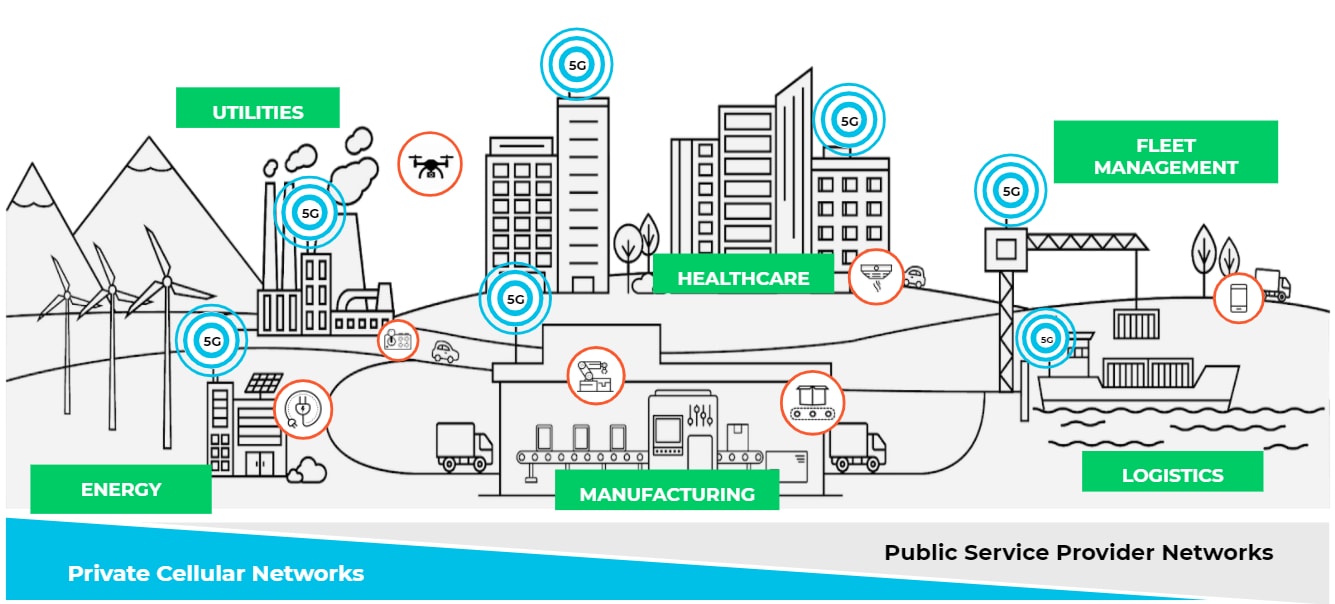
Image Credit: Palo Alto Networks
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Discussion:
Telcos and enterprises are exploring new use cases by deploying edge clouds and bringing content and applications closer to the users and billions of IoT devices to meet the low-latency requirements. The Ericsson 2022 Mobility Report forecasts that over 30 billion Internet of Things (IoT) devices will be connected by 2027.
The 5G core network functions could be deployed as a microservice in a private data centre of the communications service provider (CSP) and enterprise network or in a public cloud (like AT&T-Microsoft Azure and Dish Network-Amazon AWS).
The shift to the edge and deploying telco cloud edge services and enterprise hybrid private 5G networks introduce new security threats associated with the 5G and edge deployment.
Even though there are security risks with 3G/4G, these risks are mainly associated with external attacks. However, with 5G/MEC/IoT architecture, these risks become more serious. 5G core and edge sites can be attacked from the internal network in an “inside-to-outside” approach. Considering that 5G provides high-speed internet broadband, connecting a massive number of consumer and IoT devices, this can be viewed as a new point of attack for the 5G cloud edge architecture.
Such massive transformation forces telcos and enterprises are deploying cloud edge and private 5G services to rethink their security and network protection. There are many challenges in how telcos and enterprises deploy security solutions today as they cannot provide integrated 5G core and security solutions to adapt with cloud-edge use cases. For example, moving to the edge will require a low footprint, automation, scaling and simplified lifecycle management (LCM). Given the increase in the number of edge sites deployed, it will be very complex to manage and scale different security solutions manually. The typical deployments of security solutions are not optimised for distributed and cloud-edge architectures.
The impact of security compromise on an operator or enterprise edge network could be massive because edge sites usually have less capacity than core sites and host mission-critical applications to accommodate low latency requirements, including IoT use cases. For example, a 10/20G volumetric DDoS attack could have a major impact on the network availability and low-latency requirements, and it would lead to a critical service interruption and result in brand damage.
The shift to cloud and edge for telcos and enterprises is an evolved approach to deploying and delivering services and solutions, and introducing a more dynamic environment. The security measures in place today are not aligned with the cloud-edge requirements for the footprint for physical security solutions, increasing number of edge sites, cloud-native strategy and other required capabilities to improve TCO.
DDoS-based IoT Botnet
Most IoT devices have limited computing resources to provide security functionality and typically are not securely coded. MOZI is an example of a DDoS-focused IoT botnet that utilises a large set of remote code executions (RCEs) to leverage common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs) in IoT devices for infection. These devices include network gateways, CCTVs, DVRs, etc. Once the IoT device is successfully infected, the botnet uses protocols/apps, such as TCP/UDP/HTTP, to send and receive configuration updates and attack commands. Eventually, the infected IoT nodes begin generating attack traffic, leading to a massive and sudden spike in UDP traffic going back and forth with peer-to-peer networks. Such volumetric attacks from compromised IoT devices will make it very challenging to guarantee a level of service and maintain low-latency requirements.
Even though it’s always recommended to keep the IoT devices running the latest firmware with all the necessary security patches applied. However, we can’t rely entirely on securing or updating IoT devices. Therefore the network should also be equipped with modern security solutions like DDoS baselining techniques to see anomalous behaviour versus historical norms, and AI/ML techniques, for detection and zero-day attack prevention.
Mobile Edge Cloud and Private 5G Requires New Security Approaches
Security for mobile cloud edge and enterprise hybrid private 5G must be measured carefully to align with the new and increasing security threats. This requires securing the mobile core infrastructure and modern network protection to deliver mission-critical applications while maintaining low latency requirements. Ultimately, this will help telcos and enterprises achieve their desired business outcomes.
In addition, the security implementation for telcos should consider security-as-a-service so that operators may offer secure IoT services leveraging network slicing and provide the flexibility for end customers to manage their security policies with complete network isolation. This requires security integration with the 5G ecosystems to ensure subscriber and device awareness for more agile security control.
Enterprises that deploy private 5G networks may lack the telco experience and knowledge to secure that mobile infrastructure. They might rely entirely on the MNO or their mobile network equipment providers (NEPs) to ensure the infrastructure is fully secured and protected. However, enterprises must extend their network and IT security standards and take all the necessary considerations when they move their critical systems and applications to the edge.
Although 5G comes with embedded security standards, it also introduces potential security risks associated with the deployment model and communications systems. In this post, I have focused on one of the security risks associated with 5G deployment: a DDoS-based IoT botnet. In Part II, I will cover other potential security areas:
- 5G deployment in Hyperscale Cloud Providers (HCP)
- HTTP/2 and exposure of API
- Inert-PLMN
Resources:
Threat Intelligence Report, A10 Global State of DDoS Weapons, H1 2021
Ericsson 2022 Mobility Report, June 2022
Evolving 5G Security for the Cloud, 5G Americas White Paper, Sept 2022
MoffettNathanson: 5G use cases and revenue streams have not yet materialized
Status of 5G Use Cases:
- Multi-access Edge Compute (MEC) remains relatively intangible, and is likely to be fiercely competitive (hyper-scalers/cloud services, and even tower operators, likely better positioned).
- IoT similarly has not demonstrated material revenue upside potential for carriers.
- Private 5G networks may not include carriers at all; and when they do, it is unclear that carriers will achieve attractive revenue splits with the (many) other participants in the value chain (systems integrators, software providers, hardware providers, security providers, hyperscalers).
- Fixed wireless access has emerged as a “consolation prize,” with incremental revenue but at very low revenue/bit, potentially significantly taxing network resources in a way other 5G applications do not.
Editor’s Notes:
The URLLC use case envisioned by the ITU does not exist because the 3GPP Release 16 URLLC in the RAN spec has still n not been completed and the ITU-R M.2150 recommendation uses 3GPP Release 15 URLLC which does not meet the ITU-R M.2410 performance requirements.
Also, the true 5G features, such as network slicing, automation/virtualization and security, can only be realized via a 5G SA core network for which there are relatively few.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Telco incumbents always believe the answer is to “move up the (protocol) stack”… but they face much better-equipped competitors in the cloud service providers (Amazon, Microsoft, Google etc.).
Summary and Conclusions:
In our view, the broadband slowdown appears to owe more to a broad market deceleration than to significant shifts in market share…
• Cable broadband churn is at all-time lows
• TelCo broadband gains have not accelerated
• A significant portion of FWA appears to be market expansion
…so pricing and capital intensity do not appear to be at significant risk.
Footprint expansion initiatives are likely sufficient to keep broadband net add growth at least narrowly positive.
Wireless is now Cable’s Act III
Reference:
Moffett Nathanson Oct 2022 Slide Deck (subscribers only)
At long last: India enters 5G era as carriers spend $ billions but don’t support 5Gi
After years of 5G auction delays, India became the last major Asian economy to launch a 5G network, marking a new wave of spending by indebted Indian carriers. Prime Minister Narendra Modi made the first 5G video call on Saturday to school students to demonstrate use of the service in education. “5G is the beginning of an infinite space of opportunities,” especially for the country’s youth, he said. Well, that has yet to be proven!

Though 5G mobile technology — first introduced in South Korea three years ago — has been viewed by consumers as underwhelming so far because of a dearth of matching applications, local operators led by billionaire Mukesh Ambani’s Reliance Jio Infocomm Ltd. are betting that will change. They are counting on the nation’s 600 million-plus smartphone users to switch to the new network in due course and also on industries gearing for a digital transformation.
Carriers agreed to fork out $19 billion just two months ago for airwaves at a government auction, with Reliance’s $11 billion bid topping the list. The conglomerate proposes to invest 2 trillion rupees ($25 billion) more. Billionaire Sunil Mittal’s Bharti Airtel Ltd. and Vodafone Idea Ltd. haven’t disclosed their spending plans as yet.
While Reliance raised more than $25 billion from marquee investors in 2020 to help fund digital expansion, the need to spend big on 5G could weigh on the finances of rivals. Bharti and unprofitable Idea have a combined net debt of $37 billion, and the latter staved off bankruptcy by giving 36% of its equity to the Indian government earlier this year in lieu of back fees it couldn’t pay.
At the launch event on Saturday, Ambani said Jio’s 5G network will cover the entire country by December next year, while Mittal said Bharti Airtel plans to do so by 2024. Given the scale of spending, some experts said carriers are unlikely to undercut each other on prices once again — something that was tried in 2016 when Jio entered the market by offering free calls and cheap 4G data plans, which ended up putting some rivals out of business.
“They will likely provide 5G services to those segments of the market that are willing to pay higher and try and recover as much as possible before making it available to others,” said Rajat Kathuria, a senior visiting professor at the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations in New Delhi.
5G’s long road to India has been dogged by several controversies. The main one was about how secure Chinese equipment is — a crucial issue for a country engaged in a border conflict with its northern neighbor. Last year, carriers decided to avoid Chinese vendors such as Huawei Technologies Co. and ZTE Corp., and opted instead to tie up with makers like Ericsson AB, Nokia Oyj and Samsung Electronics Co., potentially adding to their costs.
“India may have started a little late, but we’ll finish first by rolling out 5G services that are of higher quality and more affordable,” Ambani said at the launch event. The technology can bring affordable, superior education and skill development to ordinary Indians and deliver high-quality healthcare to rural and remote areas, he said.
Despite India’s TSDSI getting 5Gi (5G for India or Low Mobility Large Cell) included in ITU M.2150 (previously known as IMT 2020), no Indian carrier has announced support of it. That is a major disappointment for TSDSI. Please refer to the numerous references below.
Offering low latency (that does not meet ITU-R M.2410 URLLC performance requirements) and data speeds about 100 times faster than 4G (depending how close your 5G endpoint is to the cell tower or small cell), the technology may someday have the potential to enable a variety of advanced applications such as holograms, 3D avatars of people in metaverses and telemedicine, in which near-instantaneous transmission of video and data would allow surgeons to operate remotely using a robotic scalpel. So far, such applications have been too slow to evolve. For average users, 5G has mostly meant faster video games and content streaming.
To capitalize on 5G, China has been rolling out smartphone apps and industrial projects such as super high-definition live streaming, remote manufacturing, virtual reality and robotic surgery arms. The country’s three state-owned carriers have introduced more than 25,000 such applications, according to a news article posted by the State Council on its website in August. In South Korea, despite mobile operators’ efforts to come up with killer apps, average revenue per person has only climbed slightly since the 4G era.
In India’s race to roll out 5G, the only winner to emerge so far has been the government: The airwave auction was set to raise a record amount, Telecom Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw said in July.
Proceeds from the spectrum auction could provide a big financial boost to Modi’s administration, which has been seeking to tame inflation and rein in fiscal deficits as economists warn of a looming global recession.
References:
https://ieeetv.ieee.org/2020-5g-world-forum-keynote-radha-krishna-ganti
https://tsdsi.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/LMLC_ver1_RIT-Prof-Ganti.pdf
TSDSI’s 5G Radio Interface spec advances to final step of IMT-2020.SPECS standard
India lagging in 5G unless spectrum prices decrease & 5Gi standard debate is settled
Jio and Airtel against 5Gi standard; 2 GHz of mid-band needed for India 5G demand
India’s Success in 5G Standards; IIT Hyderabad & WiSig Networks Initiatives
Ericsson to build 5G network in Greenland; demos 5G microwave backhaul with O2 Telefónica
Swedish telecom equipment maker Ericsson has been contracted to build a 5G network in Greenland, initially covering three towns, local telecom service provider Tusass said on Friday.
Deploying Ericsson equipment and Netgear routers, Tusass will bring high-speed wireless internet to the sparsely populated island without resorting to expensive and hard-to-deploy cables, the company said. A further 10 towns, including Greenland’s capital Nuuk, are set to follow next.
Tusass said it plans to invest around 1 billion Danish crowns ($131.3 million) to secure and expand Greenland’s infrastructure and improve communication.
Greenland, an island of just 56,000 people, is part of the Kingdom of Denmark but has broad autonomy.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Ericsson and O2 Telefónica successfully demo 5G wireless backhaul for non-urban areas. In the latest of their joint projects in mobile transport, Ericsson and O2 Telefónica have successfully demoed 5G wireless backhaul for rural and suburban coverage. This technology milestone has shown that the companies can deliver speeds of up to 10 Gbps over a distance of more than 10 km and demonstrate fiber-like microwave connectivity.

The result of this important demo showed that microwave backhaul over traditional bands can support the continued build-out of high-performing 5G networks and enhanced mobile broadband services from urban to suburban and rural areas – one of the key challenges facing communications service providers in scaling up their 5G deployment.
“We deliver fast mobile 5G connections to millions of customers across Germany. Bringing digitalization to suburban and rural areas through mobile connectivity and fast 5G network rollout has therefore priority for us,” says Aysenur Senyer, Director of Transport Networks at O2 Telefónica.
“Together with our partner Ericsson, we are pioneering new powerful microwave solutions using Carrier Aggregation and MIMO technology to backhaul 5G traffic over long distances in rural areas, when fiber is not an option. This type of technology enables us to deliver fiber-like connectivity via microwave and further accelerate our 5G deployment.”
Ricardo Queirós, Head of Microwave Systems, Business Area Networks, Ericsson, says: “Access to high-speed mobile services is key to bridging the digital divide. This joint demo with O2 Telefónica in Germany demonstrates how microwave backhaul can efficiently spread high-performing 5G to regions outside the traditional dense urban areas.”
“Wireless backhaul has been instrumental to the success of mobile networks and their nationwide coverage. Now it is time to push the boundaries and evolve microwave transmission technology to enable high-performance 5G coverage on a much broader scale,” Queirós adds.
The shift to working from home during the Covid-19 pandemic illustrated the need for fast and reliable connectivity in non-urban environments, and the challenge has been to maintain telecom-grade availability beyond distances of two to three kilometers.
The ability to deliver such high data speeds over distances of more than 10 km – the cruising altitude of a commercial jet – opens up a new world of possibilities for the delivery of low-latency, reliable broadband in harder-to-reach areas.
Traditionally, such areas have been difficult to service, as high capacities require broad bandwidths that usually only have been available in millimeter wave frequency bands (E-band). The E-band is more impacted by rain compared to the lower frequency bands, which makes it more difficult to deliver consistent service over long distances during adverse weather conditions.
Technical details
In the joint demo with O2 Telefónica in Germany, the key innovation is the ability to use MIMO with high modulation in the 112MHz channels (commercial MIMO solutions support up to 56 MHz channels), which were combined with Carrier Aggregation to enable similar capacities to E-band in the lower frequency bands. The demo solution has extended the hop-length with extremely high capacity even in less favorable weather conditions.
The backhaul link utilized the 18GHz frequency band, dual antennas in a MIMO configuration, and commercial MINI-LINK radios together with a pre-commercial baseband algorithm that allowed the use of MIMO in 2x 112 MHz channels. MIMO ensures the efficient use of limited spectrum resources. The same capacity without MIMO would demand a 448 MHz bandwidth in a cross-polar setup.
Microwave backhaul is commonly seen as a more cost- and time-efficient option compared to fiber deployment. The O2 Telefónica demo has shown that high availability and high capacity can also be achieved with wireless transport.
The demo is the latest in a series of collaborations with O2 Telefónica in Germany stretching back over several years. Ericsson is one of the service provider’s main suppliers in all areas of microwave technology and the two companies have carried out several successful joint projects around microwave technology, with more planned for the future.
References:
https://www.reuters.com/business/media-telecom/ericsson-wins-greenland-5g-deal-2022-09-30/
Deutsche Telekom Achieves End-to-end Data Call on Converged Access using WWC standards
Wireline and wireless services are delivered today from two distinct technology implementations with separate network cores. 5G WWC standards offer a path to a fully converged broadband access network that integrates wireless and wireline operations on a common 5G Core.
Using these 5G Wireless Wireline Convergence (WWC) standards [1.] in an industry first proof-of-concept, Deutsche Telekom has validated in a lab trial the feasibility of converging the fixed network control plane into a 5G Core to steer traffic from a 5G residential gateway in its Bonn laboratory. The traffic was then routed along the entire wireline access chain to the core network.
Note 1. The GSMA’s 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), the Broadband Forum (BBF) and CableLabs have united to create technical reports and specifications defining the services and systems required to support 5G wireless and wireline convergence (5G WWC) architectures. Their resulting work is detailed within BBF’s TR-456 (Fixed Mobile Convergence / FMC) and CableLabs WR-TR-5WWC-ARCH and rolled-up within 3GPP Release 16 Technical Specification TS 23.316. The IETF have also been engaged in providing guidance around user plane protocol revisions while the IEEE, ITU-T SG15 and Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) have been engaged with timing/synchronization requirements and other service specifications.
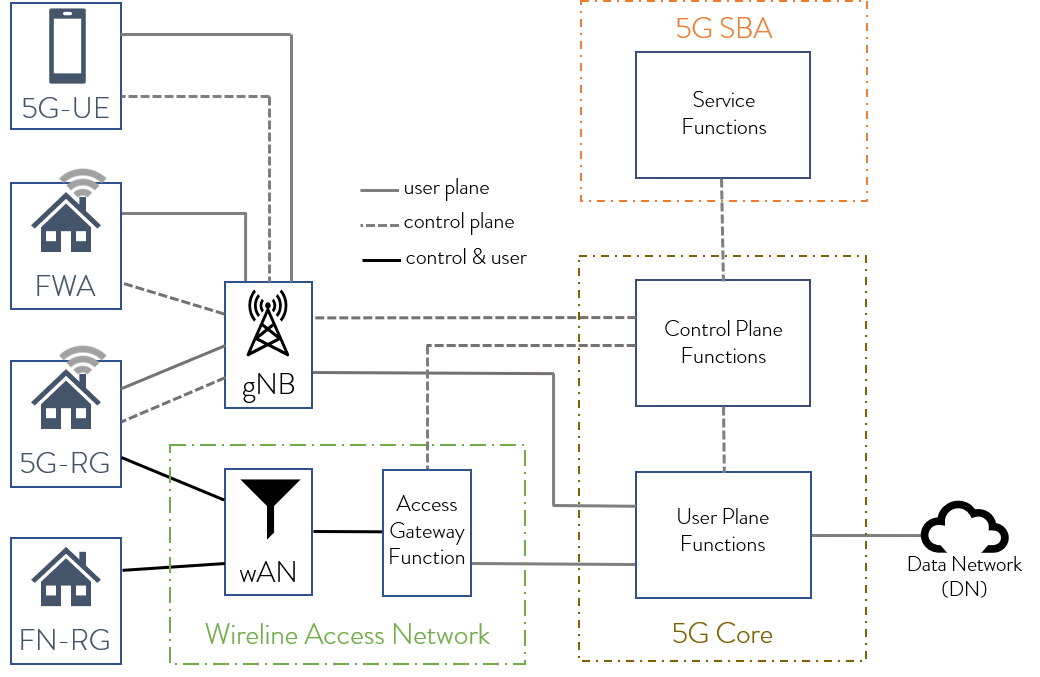
The Access Gateway Function (AGF) supporting wireless wireline convergence in a 5G Core
“Convergence will allow us to optimize our network assets and deliver new, differentiated service experiences to our customers regardless of the access used,” says Ahmed Hafez, VP Network Convergence, Deutsche Telekom. „Our tests prove the feasibility of the convergence architecture by controlling residential gateways in our fixed network from a common 5G Core.
It is critical now that the vendor ecosystem implements the standards into their product roadmaps, speeding up the time to market for end-to-end convergent solutions.”
The proof of concept was conducted on a trial system in Deutsche Telekom’s lab environment. For the 5G residential gateway, which provides the connection between the networked equipment within a home or small office to the 5G Core, a Deutsche Telekom developed prototype was used.
5G Core as common core:
CCA Conference: U.S. Regional Carriers Deploying 5G, actively looking at Fixed Wireless+ CTIA on 5G
Competitive Carriers Association (CCA) conference :
Small and regional carriers are taking different approaches to 5G and fixed wireless, said Eric Boudriau, Ericsson North America head-customer unit regional carriers, at the Competitive Carriers Association (CCA) [1.] conference on September 28th in Portland, OR. “Everybody starts from a different position,” he said. Fixed wireless is “really, really accelerating” in the U.S. and internationally, he said. Other executives stressed the importance of addressing federal infrastructure rules to better fund wireless. The discussion was streamed live from Portland, Oregon.
Note 1. CCA was founded in 1992 by nine rural and regional wireless carriers as a carrier centric organization. Since its founding, CCA has grown to become the nation’s leading association for competitive wireless providers serving all areas of the United States.
Alaska’s GCI deployed 5G in its first market in the spring of 2020, in the middle of the COVID-19 pandemic, said John Myhre, vice president-wireless technology. “We’ve done very well,” he said. “We are continuing to roll out 5G as we roll through different markets.” GCI hasn’t decided what spectrum bands it will use for a fixed-wireless offering, Myhre said. “As a fixed and mobile provider, we have options,” he said. “It’s making sure that we fit the market and the requirement against the technology, not try to force it. In Alaska, everything is just really big. Any project that we do is a big project.” GCI is laying fiber to reach the Aleutian Islands, he noted, in a $58 million project requiring more than 800 miles of undersea cable to reach rural markets.
“We are actively looking at fixed (wireless),” with trials to start in the next 18 months, he said. Wisconsin-based Cellcom launched 5G in February, said CEO Brighid Riordan. The carrier is deploying some fixed wireless using 4G and citizens broadband radio service spectrum and has found the roll out challenging, she said. “We love our trees in Wisconsin, we love the lakes,” she said. “When there’s a valley, when there are trees, it provides a challenge,” she said. Small carriers need government funding to reach some markets, Riordan said. “If it were easy to provide broadband to every rural person in America, it would already be done,” she said: “There’s not necessarily a business case for these very rural customers.”
UScellular is still deploying 5G, market-by-market, said Rebecca Thompson, vice president-government affairs. The carrier started with high-band, she said. “As we get access to some more of our mid-band spectrum we’ll have a much more robust 5G product in the future,” she said. When the provider will get some of its licenses remains to be determined. “There’s some clearing and coordination … and we will still have to actually get the licenses for some of that spectrum,” she said. Mid-band “has proven to really help with geographic reach in a cost effective way” and “is really critical to deploy in rural areas,” The “good news” is fixed wireless is “mature — it’s ready, it’s reliable, it’s offering speeds that people want at home,” Thompson said. It shouldn’t be a foregone conclusion” that the NTIA’s broadband, equity, access and deployment program won’t fund fixed wireless, she added.
UScellular wants to see “less of the thumb on the scale” favoring fiber, she said. Federal funds so far are biased toward fiber and the wireless industry has to fight for more neutral rules for making awards, Boudriau said. Fixed wireless may see the most deployment “where the government isn’t involved,” Myhre said: “We have areas where we may not get funding, but we still have a need.”
References:
https://www.cca-convention.org/
https://www.ccamobile.org/about-cca#AboutUs
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
CTIA at MWC-Las Vegas:
CTIA President Meredith Baker said Wednesday at the start of the Mobile World Congress in Las Vegas. “We’re here to talk about what 5G is,” she said: “5G is innovation. 5G is competition, and most importantly, 5G is here.”
Baker said the wireless industry needs “the right policies” from the government. “Take C band as proof,” she said. “Turning on a portion of that spectrum saw speeds increase up to 50%, and that was 100 MHz. Imagine what 150 or 200 more could do. Well, we shouldn’t have to imagine. … We need more mid-band — licensed mid-band in large contiguous blocks.” The wireless industry also needs Congress to extend the FCC’s auction authority, set to expire Friday, and designate more bands for auction, she said.
Baker also discussed the importance of fixed wireless. “For many Americans, the first 5G killer app is home broadband,” she said. “The fastest growing broadband provider is now a wireless company,” she said. U.S. wireless carriers already offer fixed service to 70 million homes, she noted.
More than 300 million AT&T customers are covered by 5G, all of the company’s major handsets support the new generation of wireless “and we’ve got business models being created,” said David Christopher, executive vice president-business development and strategic alliances. “But it is early days,” he said. Christopher spoke with Recon Analytics’ Roger Entner.
“We’re two years in,” Entner responded: “At this point in the 4G period we still thought that sending pictures was the killer app for 4G. We were wrong.” Deploying a new G “is not a 100-meter dash,” he said. “This will take years.”
“There’s a very good chance that we don’t know what the killer app for 5G is,” Christopher said. Augmented reality and the massive IoT will be important. The median speeds of 5G are already four times that of 4G two years ago, he said: “Latency is a stickier wicket. … It’s something that will certainly get better.” In some cases, better speed is “masking” the need for improved latency, he said.
Reference:
https://communicationsdaily.com/article/view?search_id=595619&id=1374622