Author: Alan Weissberger
Kaleido Intelligence: eSIMs for smartphones and IoT at 21% CAGR from 2023-2028
A new report from Kaleido Intelligence predicts that 1.4 billion eSIMs will be shipped in 2028, while CAGR will rise 21% between now and then. The market research firm forecasts a robust average growth of 77% in smartphone eSIM activations between 2023 and 2028.
Market disruption will come in the form of ‘travel eSIM’ as well as increased ability to transfer an eSIM from one device to another, ‘forcing the market to take new shape.’
However, the most profound transformation is anticipated in the IoT space. An IoT specification for eSIMs will see ‘commercialization as pre-compliant solutions’ in 2024, and will lower the technical and investment burden of setting up IoT systems.
The press release also states: “Although many MNOs may not have a concrete strategy for IoT connectivity at retail, support for eSIM via the new specification will offer considerable opportunities at the wholesale level. With well over half of active IoT eSIMs using the new specification by 2028, demand for connectivity profiles will be greater than ever before.”
Kaleido’s research found that the combined migration towards ‘ijo,hudfwe4’ smartphones and the ability to offer a more seamless journey to travel SIM purchasing is likely to help accelerate travel SIM adoption and erode the existing physical travel SIM market.
Nitin Bhas, Chief of Strategy & Insights at Kaleido commented:
“High roaming costs, growing traveller awareness of eSIM, and the future ratification of GSMA eSIM specifications for smartphones in China will further drive this adoption surge for alternative eSIM solutions. Nevertheless, the market landscape presents mobile operators with the opportunity to reshape their traditional roaming strategies, attract new customers through similar travel eSIM services and to drive usage amongst existing customers with compelling roaming deals.”
500% Growth in Spend:
Travel eSIM retail spend predicted to rise 500% between 2023 and 2028, as leisure and business travellers embrace cheaper esim travel plans outside core rlah markets.
$10 billion in Retail Spend:
The global travel eSIM market will be worth close to $10 billion in 2028, accounting for over 80% of total travel SIM spend by then. ‘
$30 billion Travel Market:
Retail spend on travel connectivity services, including roaming packages and travel SIMs, to be worth over $30 billion by 2028.

“The eSIM market has seen several developments recently that smooth the path to adoption, and address many lingering ecosystem challenges,” said Steffen Sorrell, Chief of Research at Kaleido. “The effect of this will mean eSIM or iSIM form factors will gradually become a de facto requirement by 2028 for most cellular devices.”
A recent survey by Omdia would seem to back up this projection of growth for the IoT and eSIM sector – of the hundreds of enterprise professionals polled over 70% of said they are planning to use 5G connectivity for IoT, while, eSIM/iSIM technology has already been or will be adopted by nearly 90% over the next two years. 95% of them expected to see measurable benefits from IoT within two years of deployment, and 90% said existing IoT projects have met or exceeded their expectations.
References:
https://telecoms.com/523216/esim-shipments-will-grow-77-by-2028/
Counterpoint Research: eSIM adoption now entering high-growth phase; +11% YoY in 2022
3GPP Release 16 5G NR Enhancements for URLLC in the RAN & URLLC in the 5G Core network
Introduction:
3GPP Release 16 was “frozen” July 3, 2022. However, two key work items were not completed: Enhancement of the 5G RAN and the 5G Core network to support ultra-high reliability and low-latency communications (URLLC).
The enhancements, especially in the RAN, are essential for 3GPP New Radio (NR) to meet the ITU-R M.2410 Minimum Performance Requirements for the URLLC use case. That was to enable a whole new set of mission critical applications that required either ultra high reliability or ultra low latency (< or =1 ms in the data plane and < or =10ms in the control plane) or both.
Yet URLLC in the RAN and the associated URLLC in the RAN Conformance Test specification still have not been completed (more below)!
Overview of URLCC Enhancements:
The main functionalities introduced were the support of redundant transmission, QoS monitoring, dynamic division of the Packet Delay Budget, and enhancements of the session continuity mechanism.
The 3GPP Rel 16 URLLC in the RAN spec, once complete and performance tested, is needed to meet the ITU-R M.2410 URLLC Performance Requirements.
The 5G NR Physical Layer is improved for the support of URLLC in the RAN in several ways: new DCI formats, Enhanced PDCCH monitoring capability, Sub-slot based HARQ-ACK feedback, Two HARQ-ACK codebooks constructed simultaneously, PUSCH enhancements, Enhanced inter UE Tx prioritization/multiplexing and Multiple active configured grant configurations for a BWP.
3GPP Rel-17 URLLC work is mostly contained in the feature “Enhanced Industrial IoT and URLLC support for NR.” This covers mostly some “Physical Layer feedback enhancements for HARQ-ACK and CSI reporting” and the “Intra-UE multiplexing and prioritization of traffic with different priority.”
Current Status:
The most recent URLLC in the RAN spec dated December 2022 is 96% complete as per:
| 830074 | NR_L1enh_URLLC | Physical Layer Enhancements for NR Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC) | Rel-16 | R1 | 22/12/2022 | RP-191584 | history | 2019/03/26 | 26/06/2019 | 26/6/19: WID:RP-190726->RP-191584 |
The URLLC in the RAN Conformance Test spec is only 90% complete as per:
| 900054 | NR_L1enh_URLLC-UEConTest | … UE Conformance Test Aspects – Physical Layer Enhancements for NR URLLC | Rel-16 | R5 | 22/12/2022 | RP-202566 | history | 2021/01/06 | 20/06/2022 | 22/3/22: Compl:16 ; 20/6/22: Rapporteur: Huawei->Chunying GU, Huawei; Rap eMail: ->guchunying@huawei. |
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Here are the key 3GPP Rel16 URLLC work items from https://www.3gpp.org/dynareport?code=WI-List.htm
- 830074 NR_L1enh_URLLC Physical Layer Enhancements for NR Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC)
- 800095 FS_NR_L1enh_URLLC… Study on physical layer enhancements for NR UR Low Latency Cases
- 830174 NR_L1enh_URLLC-Core… Core part: Physical Layer Enhancements for NR URLLC
- 830274 NR_L1enh_URLLC-Perf… Perf. part: Physical Layer Enhancements for NR URLLC (R4)
- 900054 NR_L1enh_URLLC-UEConTest… UE Conformance Test Aspects – Physical Layer Enhancements for NR URLLC (R5)
References:
https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3498
https://www.3gpp.org/dynareport?code=WI-List.htm
https://www.3gpp.org/dynareport?code=status-report.htm
https://www.3gpp.org/dynareport?code=FeatureOrStudyItemFile-830074.htm
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/urlcc-2022
https://techblog.comsoc.org/category/3gpp-release-16
Executive Summary: IMT-2020.SPECS defined, submission status, and 3GPP’s RIT submissions
5G Specifications (3GPP), 5G Radio Standard (IMT 2020) and Standard Essential Patents
Another Opinion: 5G Fails to Deliver on Promises and Potential
Ericsson and Vodafone enable Irish rugby team to use Private 5G SA network for 2023 Rugby World Cup
Ericsson and Vodafone Ireland have partnered to install a cutting-edge 5G Standalone Mobile Private Network (MPN) solution for the Irish rugby team to supply fast and reliable in-play data analysis ahead of the 2023 Rugby World Cup in September.
Previously the team relied on standard WiFi across stadiums and training facilities both at home and away. Now giving instant feedback on team plays and tactics, the 5G Standalone MPN solution and artificial intelligence technology ensures faster download and upload speeds and lower latency, which can be utilised for real-time performance analysis and decisions on the pitch.
Using this reliable connectivity, up to eight high-resolution video streams are captured by multiple cameras and a 5G connected drone and then analysed in real-time to collate data on team performance. The technology helps to improve the communication between management, coaches and players and maximises the time on pitch where the smallest tweak to a running line or defensive position, can have a significant impact on the weekend’s game.
Vodafone Ireland and Ericsson have worked closely with the IRFU and their Head of Analytics and Innovation, Vinny Hammond and his analysis team of John Buckley, Alan Walsh and Jack Hannon. This collaboration has led to a clear understanding of the specific performance outcomes sought by such an elite sports team and has supported the design and installation of the Ericsson Private 5G solution, which now enables the management team, coaches and players to feel the real benefit of instant feedback to enhance the ability to make decisions quikcly.
The new solution has been tested at the Irish team’s High Performance Centre and will be brought to France in a bespoke 5G connected van for the World Cup in September.
Vodafone Ireland Network Director, Sheila Kavanagh says: “At Vodafone, we are so proud of our support for the Irish Rugby team, so we’re delighted to bring further value through the delivery of this cutting-edge technology solution. Performance analysis has experienced massive changes in the past couple of decades. What started with pen and paper-based methods for collecting notational data has evolved to using cutting-edge computer-based technologies and artificial intelligence to collect ever increasing amounts of real-time information. Distilling and delivering this data back to the team at top speed requires a reliable, secure and scalable connectivity solution.”
“This 5G MPN, drone and additional technology will support Vinny Hammond and his analytics team to quickly breakdown and organise unstructured data and present it back in a clear manner to other coaching staff and management – helping them understand the performance of the plays and overall team, without delay. It’s fantastic to see it in use in the HPC, but we’re also really excited to support the team with 5G connectivity throughout their time at the World Cup in France with our fully kitted Connected Van. Our 5G MPN technology is a demonstration of how technology and connectivity innovation can enhance the business of sport and the performance of teams, bringing added layers of data and analysis to coaches, management, and their players.”
IRFU Head of Analytics and Innovation, Vinny Hammond says: “So much of our roles revolve around moving large quantities of data so we can analyse performance to understand what is working and what is not. Vodafone’s 5G MPN stretches the boundaries of what we can do in terms of how quickly we can analyse multiple high-resolution cameras and drone footage which ultimately informs our strategic decision making. The work John and Alan have done on this project in conjunction with Vodafone and Ericson has enabled us to push new boundaries at this years RWC. Being on our own 5G network also gives us that level of security and reliability that we really need, and we’ll have the added benefit of that connectivity with our 5G Connected Van, linking back to our High Performance centre, to reduce reliance on third party connectivity.”
John Griffin, Head of Ericsson Ireland, says: “5G is the ultimate platform of future innovation and our successful partnership with Vodafone continues to ensure new organisations like the IRFU can benefit from the low latency, high bandwidth, and secure connectivity of a 5G standalone private network. Our global leadership in 5G technology and accelerated software availability mean the IRFU will be one step ahead of their competitors on and off the field, giving them the best chance of success at an elite level of performance and revolutionizing the future of a key function within the sports industry.”
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/3/2023/ericsson-and-vodafone-help-irish-rugby-team-adopt-5g-technology-to-get-fast-in-play-data-analysis
South Korea government fines mobile carriers $25M for exaggerating 5G speeds; KT says 5G vision not met
South Korea’s antitrust regulator said it had imposed a total of 33.6 billion won ($25.06 million) in fines on three domestic mobile carriers for exaggerating their 5G network speeds. The Korea Fair Trade Commission (KFTC) said the three South Korean firms – SK Telecom Co Ltd, KT Corp, and LG Uplus Corp – had also unfairly advertised that they were the fastest relative to their competitors.
“The three telecom companies advertised that consumers could use target 5G network speeds, which cannot be achieved in real-life environment … companies advertised that their 5G network speed was faster than competitors without evidence,” the KFTC said in a statement.
In support of ongoing civil lawsuits filed by consumers, the advertisements released by the three mobile carriers have been presented by the regulator to a local court.
SK Telecom and KT Corp declined to comment. A spokesperson at LG Uplus said the company is reviewing the sanctions.
The KFTC imposed a fine of 16.8 billion won on SK Telecom, 13.9 billion won on KT and 2.8 billion won on LG Uplus.
There were 30.76 million 5G network users in South Korea in June, accounting for about 38% of the total 80.23 million mobile subscriptions in the country, according to data from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Source: Reuters
In a paper issued last week, SK Telecom states correctly the industry is far from achieving its 5G goals even four years after commercialization. There were “misunderstandings” about network performance and problems such as device form factors and lack of market demand, it said. “A variety of visionary services were expected, but there was no killer service,” the paper stated. “We should have taken a more objective perspective,” it added. In particular:
A variety of visionary services were expected, but there was no killer service Even at the time when preparing for 5G, services such as autonomous driving, UAM, XR, hologram, and digital twin had appeared and expected, but most of them did not live up to expectations. We should have taken a more objective perspective. For example, whether 5G technology alone could change the future, or whether the overall environment constituting the service was prepared together. If so, the gap between the public’s expectations for 5G and the reality would not have been large. 3D video, UHD streaming, AR/VR, autonomous driving, remote surgery, etc. are representative services that are not still successful presented by the 5G Vision Recommendation. Most of them are the result of a combination of factors such as form factor constraints, immaturity of device and service technology, low or absent
market demand, and policy/regulation issues, rather than a single factor of the lack of 5G performance.
The authors concluded that instead of expecting that the new technology alone could create successful services, it would have been more effective to have collaborated with partners to build a broader 5G ecosystem.
Gap between 5G Vision Recommendations and customer expectations:
Although the usage scenarios and capability goals presented in the 5G Vision Recommendation are future goals to be achieved in the long term, misunderstandings have been created that can lead to excessive expectations of 5G performance and innovative services based on it from the beginning of commercialization. To prevent this misunderstanding from recurring in 6G, it is necessary to consider various usage scenarios of 6G, set achievable goals, and communicate accurately with the public. In particular, there were issues raised about the maximum transmission speed of 20Gbps, which was considered an icon of 5G key performance indicators. As 3G evolved into LTE, the radio access technology also evolved from WCDMA to OFDMA, and with the introduction of CA and multi-antenna technology, it became possible to use a much wider bandwidth than 3G. This can be seen as a ‘revolutionary’ improvement. On the other hand, 5G is considered as an ‘evolutionary’ improvement that supplements the performance of LTE based on the same radio access technology, CA, and multi-antenna system technology. Due to this, it was difficult to implement the increase in transmission speed shown in LTE in 5G at once. Moreover, the difference in technology perception was further revealed in the initial stage of 5G commercialization. Early commercialization was promoted for 5G, however, 5G required more base station compared to LTE to build a nationwide network due to frequency characteristics, requiring more efforts in terms of cost and time.
SK Telecom has made significant efforts to expedite 5G nationwide rollout, but customers wanted the same level of coverage as LTE in a brief period.
References:
https://newsroom-prd-data.s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/SKT6G-White-PaperEng_v1.0_web.pdf
Barriers for telcos deploying AI in order to improve network operations
Communications service providers (CSPs) face a host of barriers, such as accessing high-quality data, that impede thesir ability to effectively deploy AI which could improve network and service operations, according to new research commissioned by Nokia and conducted by Analysys Mason.
“CSPs are unable to access high-quality data sets (which will enable them to make more accurate decisions) because they are using legacy systems with proprietary interfaces. This will restrict how quickly they can integrate AI into their networks,” according to the research, which is based on responses from 84 CSPs surveyed globally.
Almost 50 percent of Tier-1 CSPs ranked data collection as the most challenging stage of the telco AI use case development cycle.
Further, the research found that only six percent of CSPs surveyed believe they are at the most-advanced level of automation, or zero-touch automation, which relies on AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms to manage and improve network operations. The high-quality data issue is also impacting CSPs’ ability to retain AI talent.
Still, 87 percent of CSPs have started to implement AI into their network operations, either as proof of concepts or into production; with 57 percent saying they have deployed telco AI use cases to the point of production.
CSP respondents said they believe AI will help improve network service quality, top-line growth, customer experience, and energy optimisation to meet their sustainability goals.
The research said CSPs should evaluate their telco AI implementation strategies and develop a clear roadmap for AI implementation to overcome their data challenge and other impediments, such as an inability to scale AI use case deployments. The report can be found here.
Adaora Okeleke, Principal Analyst, at Analysys Mason said: “CSPs must transition to more-autonomous operations if they are to manage networks more efficiently and deliver on their main business priorities. But as this research demonstrates, accessing high-quality data remains a critical obstacle to deploying telco AI within their networks. They need to really examine their AI implementation strategies to work around this data quality issue.”
Andrew Burrell, Head of Business Applications Marketing, Cloud and Network Services at Nokia, said: “AI has a crucial role in driving step changes in network performance, including cutting carbon footprints. CSPs are aware of the challenges of more deeply embedding AI into their operations and, as this research points out, the steps they can take to positively alter that situation, including building the right ecosystem of vendor partners with the right skillsets that can better cater to their network needs.”
Resources and additional information:
Webpage: https://www.nokia.com/networks/ai-ops/
References:
ETSI NFV evolution, containers, kubernetes, and cloud-native virtualization initiatives
Backgrounder:
NFV, as conceived by ETSI in November, 2012, has radically changed. While the virtualization and automation concepts remain intact, the implementation envisioned is completely different. Both Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) [1.] and Management, Automation, and Network Orchestration (MANO) [2.] were not commercially successful due to telco’s move to a cloud native architecture. Moving beyond virtualization to a fully cloud-native design helps push to a new level the efficiency and agility needed to rapidly deploy innovative, differentiated offers that markets and customers demand. An important distinguishing feature of the cloud-native approach is that it uses Containers [3.] rather than VNFs implemented as VMs.
Note 1. Virtual network functions (VNFs) are software applications that deliver network functions such as directory services, routers, firewalls, load balancers, and more. They are deployed as virtual machines (VMs). VNFs are built on top of NFV infrastructure (NFVI), including a virtual infrastructure manager (VIM) like OpenStack® to allocate resources like compute, storage, and networking efficiently among the VNFs.
Note 2. Management, Automation, and Network Orchestration (MANO) is a framework for how VNFs are provisioned, their configuration, and also the deployment of the infrastructure VNFs will run on. MANO has been superseded by Kubernetes, as described below.
Note 3. Containers are units of a software application that package code and all dependencies and can be run individually and reliably from one environment to another. Some advantages of Containers are: faster deployment and much smaller footprint, factors that can help in improving the resource utilization and lowering resource consumption.
An article which compares Containers to VMs is here.
High Level NFV Framework:
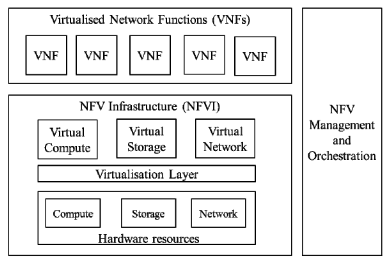
Kubernetes Defined:
Each application consisted of many of these “container modules,” also called Pods, so a way to manage them was needed. Many different container orchestration systems were developed, but the one that became most popular was an open source project called Kubernetes which assumed the role of MANO. Kubernetes ensured declarative interfaces at each level and defined a set of building blocks/intents (“primitives”) in terms of API objects. These objects are representation of various resources such as Pods, Secrets, Deployments, Services. Kubernetes ensured that its design was loosely coupled, which made it easy to extend it to support the varying needs of different workloads, while still following intent-based framework.

The traditional ETSI MANO framework as defined in the context of virtual machines along with 3GPP management functions.

ETSI MANO Framework and Kubernetes and associated constructs
Source of both diagrams: Amazon Web Services
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
ETSI NFV at 2023 MWC-Shanghai Conference:
During the 2023 MWC-Shanghai conference, ETSI hosted a roundtable discussion of its NFV and cloud-native virtualization initiatives. There were presentations from China Telecom, China Mobile, China Unicom, SKT, AIS, and NTT DOCOMO. Apparently, telcos want to leverage opportunities in cloud-based microservices and network resource management, but it also has become clear that there are “challenges.”
Three reoccurring themes during the roundtable were the following:
1) the best approach to implement containerization (i.e., Virtual Machine (VM)-based containers versus bare-metal containers) which have replaced the Virtual Network Machine (VNF) concept
2) the lack of End-to-End (E2E) automation;
3) the friction and cost that is incurred from the presence of various incompatible fragmented solutions and products.
Considering the best approach to implement containerization, most attendees present suggested that having a single unified backward-compatible platform for managing both bare metal and virtualized resource pools would be advantageous. Their top three concerns for selecting between VM-based containers and bare-metal containers were performance, resource consumption, and security. The top three concerns for selecting between VM-based containers and bare-metal containers were performance, resource consumption, and security.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
ETSI NFV Evolution:
While the level of achievements and real benefits of NFV might not equate among all service providers worldwide, partly due to the particular use cases and contexts where these operate. Based on the ETSI NFV architecture, service providers have been able to build ultra-largescale telco cloud infrastructures based on cross-layer and multi-vendor interoperability. For example, one of the world’s largest telco clouds based on the ETSI NFV standard architecture includes distributed infrastructure of multiple centralized regions and hundreds of edge data centers, with a total of more than 100,000 servers. In addition, some network operators have also achieved very high ratios of virtualization (i.e., amount of virtualized network functions compared to legacy ATCA-based network elements) in their targeted network systems, e.g., above 70% in the case of 4G and 5G core network systems. In addition, ETSI NFV standards are continuously providing essential value for wider-scale multivendor interoperability, also into the hyperscaler ecosystem as exemplified by recent announcements on offering support for ETSI NFV specifications in offered telco network management service solutions.
ETSI ISG NFV Release 5, initiated in 2021, had “consolidation and ecosystem” as its slogan. It aimed to address further operational issues in areas such as energy efficiency, configuration management, fault management, multi-tenancy, network connectivity, etc., and consider new use cases or technologies developed by other organizations in the ecosystem
Work on ETSI NFV Release 6 has started. It will focus on: 1) new challenges, 2) architecture evolution, and 3) additional infrastructure work items.
Key changes include:
- The broadening of virtualization technologies beyond traditional Virtual Machines (VMs) and containers (e.g., micro VM, Kata Containers, and WebAssembly)
- Creation of declarative intent-driven network operations
- Integrating heterogenous hardware, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), and cloud platforms through a unified management framework
All changes aim for simplification and automation within the NFV architecture. The developments are preceded by recent announcements of standards-based applications by hyperscalers: Amazon Web Services (AWS) Telco Network Builder (TNB) and Microsoft Azure Operator Nexus (AON) are two new NFV-Management and Orchestration (NFV-MANO)-compliant platforms for automating deployment of network services (including the core and Radio Access Network (RAN)) through the hybrid cloud.
As more network operators and vendors are already leveraging the potential of OS container virtualization (containers) technologies for deploying telecom networks, the ETSI ISG NFV also studied how to enhance its specifications to support this trend. During this work, the community has found ways to reuse the VNF modeling and existing NFV management and orchestration (NFV-MANO) interfaces to address both OS container and VM virtualization technologies, hence ensuring that the VNF modeling embraces the cloud-native network function (CNF) concepts, which is now a term commonly referred in the industry.
This has been achieved despite OS container and VM technologies having somewhat different management logic and resource descriptions. However, diverse and quickly changing open source solutions make it hard to define unified and standardized specifications. Nevertheless, due to the fact that both kind of virtualization technologies can and will still play a major role in the future to fulfill the various and broad set of telecom network use cases, efforts to further evolve them as well as to complement them with other newer virtualization technologies (e.g., unikernels) are needed.
Furthermore, driven by new application scenarios and different workload requirements (e.g., video, Cloud RAN, etc.), new requirements for deploying diversified heterogeneous hardware resources in the NFV system are becoming a reality. For example, to meet high-performance VNFs, requirements for heterogeneous acceleration hardware resources such as DPUs, GPUs, NPU, FPGAs, and AI ASIC are being brought forward. In another example, to meet the ubiquitous deployment of edge devices in the future, other types of heterogeneous hardware resources, such as integrated edge devices and specialized access
devices, are also starting to be considered.
NFV architectures have and will continue to evolve, especially with the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) automation. Data centers, either cloud-based or “on-premises” are becoming complex, heterogeneous environments. In addition to Central Processing Units (CPUs), complementary Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) handle parallel processing functions for accelerated computing tasks of all kinds. AI, Deep Learning (DL), and big data analytics applications are underpinned by GPUs. However, as data centers have expanded in complexity, Digital Processing Units (DPUs) have become the third member of this data-centric accelerated computing model. The DPU helps orchestrate and direct the data around the data center and other processing nodes on the network.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Updates in ETSI NFV for Accelerating the Transition to Cloud (abiresearch.com)
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
Virtual Network Function Orchestration (VNFO) Market Overview: VMs vs Containers
Qualcomm and BT open 5G Lab in Farnborough, UK
BT Group and Qualcomm have together formed a new 5G laboratory located at Qualcomm Technologies’ offices in Farnborough, United Kingdom. The 5G test lab will have BT Group’s live environment installed; BT Group runs the EE mobile network in the U.K.
From the early days of 4G to the development of 5G, this collaboration has grown from strength to strength they say. While the companies have not disclosed many details regarding which technologies and use cases are being explored at the lab, they did state that enabling faster deployment and commercialization of 5G features and services is a key focus area.
Vikrant Jain, Director, Business Development, Qualcomm Technologies International, Ltd. says: “We are excited to announce our collaboration with BT for testing and validation of new 5G features / next generation 5G services. Our state-of-the-art lab facilities will help facilitate and speed up the time-to-market, which means customers can benefit from the new technology sooner. We value our relationship and that has been running for over a decade, and we would like to thank BT for their continued support on this advancing innovation and we look forward to what else is to come for us in the technology space in the future.”
Naveen Khapali, Senior Manager, Device Technology at BT Group, says: “By working directly with Qualcomm Technologies in an embedded 5G lab, we’ll be able to realize the benefits of closer working, helping to bring the next generation of technology to our customers sooner.”
About Qualcomm:
Qualcomm is enabling a world where everyone and everything can be intelligently connected. Our one technology roadmap allows us to efficiently scale the technologies that launched the mobile revolution – including advanced connectivity, high-performance, low-power compute, on-device intelligence and more – to the next generation of connected smart devices across industries. Innovations from Qualcomm and our family of Snapdragon platforms will help enable cloud-edge convergence, transform industries, accelerate the digital economy, and revolutionize how we experience the world, for the greater good.
Qualcomm Incorporated includes our licensing business, QTL, and the vast majority of our patent portfolio. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., a subsidiary of Qualcomm Incorporated, operates, along with its subsidiaries, substantially all of our engineering, research and development functions, and substantially all of our products and services businesses, including our QCT semiconductor business. Snapdragon and Qualcomm branded products are products of Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries. Qualcomm patented technologies are licensed by Qualcomm Incorporated.
About BT Group:
BT Group is the UK’s leading provider of fixed and mobile telecommunications and related secure digital products, solutions and services. We also provide managed telecommunications, security and network and IT infrastructure services to customers across 180 countries.
BT Group consists of three customer-facing units: Business covers companies and public services in the UK and internationally; Consumer serves individuals and families in the UK; Openreach is an independently governed, wholly owned subsidiary wholesaling fixed access infrastructure services to its customers – over 650 communications providers across the UK.
British Telecommunications plc is a wholly owned subsidiary of BT Group plc and encompasses virtually all businesses and assets of the BT Group. BT Group plc is listed on the London Stock Exchange.
For more information, visit www.bt.com/about
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.qualcomm.com/news/releases/2023/08/qualcomm-and-bt-group-announce-5g-lab-r-d-facilities
BT and Ericsson wideband FDD trial over live 5G SA network in the UK
BT tests 4CC Carrier Aggregation over a standalone 5G network using Nokia equipment
BT and Ericsson in partnership to provide commercial 5G private networks in the UK
Qualcomm CEO: AI will become pervasive, at the edge, and run on Snapdragon SoC devices
Qualcomm Introduces the World’s First “5G NR-Light” Modem-RF System for new 5G use cases and apps
Nokia to open 5G and 6G research lab in Amadora, Portugal
AT&T Lab to research 5G use cases, 5G+ available in Houston, TX
Leichtman Research Group: U.S. added 840,000 broadband subs in 2Q-2023
Leichtman Research Group, Inc. (LRG) found that the largest cable and wireline phone providers and fixed wireless services in the U.S. – representing about 96% of the market – acquired about 840,000 net additional broadband Internet subscribers in 2Q 2023, compared to a pro forma gain of about 700,000 subscribers in 2Q 2022.
These top broadband providers now account for over 112.9 million subscribers, with top cable companies having about 76.2 million broadband subscribers, top wireline phone companies having about 30.7 million subscribers, and top fixed wireless services having about 5.9 million subscribers.
Findings for the quarter include:
- Overall, broadband additions in 2Q 2023 were 120% of those in 2Q 2022
- The top cable companies added about 10,000 subscribers in 2Q 2023 – compared to a loss of about 60,000 in 2Q 2022
- The top wireline phone companies lost about 60,000 total broadband subscribers in 2Q 2023 – similar to about 60,000 net losses in 2Q 2022
- Wireline Telcos had about 450,000 net adds via fiber in 2Q 2023, and about 510,000 non-fiber net losses
- Fixed wireless/5G home Internet services from T-Mobile and Verizon added about 890,000 subscribers in 2Q 2023 – compared to 815,000 net adds in 2Q 2022
“Top broadband providers added about 840,000 subscribers in 2Q 2023, led by another strong quarter from fixed wireless,” said Bruce Leichtman, president and principal analyst for Leichtman Research Group, Inc. “Fixed wireless services have acquired over 800,000 net adds in each of the past five quarters, accounting for about 4.45 million net adds in that period.”
| Broadband Providers | Subscribers at end of 2Q 2023 | Net Adds in 2Q 2023 |
| Cable Companies | ||
| Comcast | 32,305,000 | (19,000) |
| Charter | 30,586,000 | 77,000 |
| Altice | 4,576,100 | (36,600) |
| Cable One | 1,057,900 | (5,100) |
| Breezeline* | 680,785 | (6,734) |
| Other major private companies** | 7,035,000 | 0 |
| Total Top Cable | 76,240,785 | 9,566 |
| Wireline Phone Companies | ||
| AT&T | 15,304,000 | (41,000) |
| Verizon | 7,562,000 | 34,000 |
| Lumen | 2,909,000 | (72,000) |
| Frontier | 2,865,000 | 2,000 |
| Windstream^ | 1,175,000 | 0 |
| TDS | 523,600 | 8,200 |
| Consolidated | 376,829 | 6,967 |
| Total Top Wireline Phone | 30,715,429 | (61,833) |
| Fixed Wireless Services | ||
| T-Mobile | 3,678,000 | 509,000 |
| Verizon* | 2,260,000 | 384,000 |
| Total Top Fixed Wireless | 5,938,000 | 893,000 |
| Total Top Broadband | 112,894,214 | 840,733 |
Leichtman Research Group, Inc. (LRG) specializes in research and analysis on broadband, media and entertainment industries. LRG combines ongoing consumer surveys with industry tracking and analysis, to provide companies with a richer understanding of current market conditions, and the potential impact and adoption of new products and services. For more information about LRG, please call (603) 397-5400 or visit www.LeichtmanResearch.com.
Leichtman Research Group: Fixed Wireless Services Accounted for 90% of the Broadband Net Adds in 2022!
AT&T, Verizon and Comcast all lost fixed broadband subscribers in 2Q-2023
ABI Research joins the chorus: 5G FWA is a competitive alternative to wired broadband access
Leichtman Research Group: U.S. broadband growth returns to pre-pandemic levels in Q3-2021
Omdia: Global smartphone shipments decline in 2Q23 for 8th consecutive quarter
According to Omdia, smartphone shipments totaled 265,9 million units in the second quarter of 2023. This represents a decline of 9.5% compared to the previous year and a decrease of 1.2% compared to the previous quarter. This is the eighth consecutive quarter of year-on-year decline in overall smartphone shipments.
The three largest OEMs, Apple, Samsung and Xiaomi, all saw their shipments fall more than 10% from 2Q22 to 2Q23.
Samsung had the most shipments in 2Q23, reporting 53.3 million shipments. This is a 11.5% dip from 1Q23, following the release of the S23-series, but more worryingly is a 14.3% fall year-on-year. This result follows the weak demand for mid/low-end smartphones due to the ongoing economic recession, and sales of Samsung’s Galaxy A series significantly declining. Despite this, Samsung smartphones maintained its market share of 20%, and its position as the largest player in the smartphone industry.
Apple had a big quarter-on-quarter fall following a successful 1Q23 for its iPhone 14 series. It recorded 43.2 million shipments, a 24.6% fall from 1Q23 and a 11.7% fall year-on-year from 2Q22. As such, Apple’s market share has fallen back down to its usual level for the second quarter of each year, at 16%. While it previously seemed that Apple was more resilient to the negative down-winds of the economy, it has now begun to feel the squeeze.
“Apple has strong sales of premium models such as the iPhone 14 Pro and Pro Max, while the standard and Plus models sluggish sales compared to their predecessors. Normally, from the second quarter, the standard model should drive up the overall quantity, but this year it is different. Demand for Pro and Pro Max is increasing, especially among high-income consumers.” said Jusy Hong, Senior Research Manager at Omdia.
Xiaomi’s shipments continue to fall globally, falling to 33.2 million, a 15.7% fall year-on-year – from 39.4 million in 2Q22. It still occupies the third spot globally but is facing stiff competition from other Chinese OEMs Oppo and vivo. The weak Indian market remains a problem for Xiaomi, as their biggest market. However, it is further establishing itself in Western Europe, something many other Chinese brands have failed to do.
Oppo Group (including OnePlus) recorded 25.0 million shipments in 1Q23, a fall of 10.5% from the previous year. This fall isn’t as far as Xiaomi’s and as a result, Xiaomi’s lead over Oppo Group has diminished from 11.5 million in 2Q22 to just 8.3 million in 2Q23.
Transsion Holding has recorded a combined total of 24.5 million – a 38.4% increase year-on-year from the 17.7 million shipped in 2Q22. This pushes Transsion Holdings ahead of vivo to be the fifth largest smartphone OEM in 2Q23, coming after a period of long stagnation as it was digesting the inventories from 1Q23. Its efforts to expand into more markets is also proving successful.
Zaker Li, Omdia Principal Analyst says, ‘The main reason for the increase in shipments was that Transsion completed inventory adjustment in the first quarter this year and increased supply of new products from 2Q. Transsion is targeting the low-end smartphone market in more countries in Asia and Oceania.’
Hong concludes: “The smartphone industry remains in a slump, and we are expecting the market to contract year-on-year until 3Q23. But there is hope for a recovery in the fourth quarter this year. Apple and Samsung have both faced challenges and have revised their targets down as a result. But these problems will ease come the end of the year and into 2024. Inflation and the resulting squeeze on wage packets and the economy is already easing globally, and high inventory levels is already being tackled by many OEMs. The growing popularity of recycled smartphones is hindering the growth of new smartphone shipments. In particular, it is the main reason for the recent decline in demand in the mid-range smartphone market. Overall shipment forecasts for this year have been revised down over the past several months. However, we expect the smartphone shipments will also recover as the economy recovers.”
References:
IDC: Global smartphone market will remain challenged through 1st half of 2023
GfK: Global telecom market (x-North America) posts 9.7% revenue drop; smartphone revenues -10.2% in 2022
Omdia and IDC: Samsung regains lead in global smartphone market
Trendforce: Global Smartphone Market to Reach 1.36 Billion Units in 2021 as Samsung regains #1 position
Counterpoint & Canalys: Global Smartphone Market Shows Signs of Recovery in Q3-2020
TPG, Ericsson launch AI-powered analytics, troubleshooting service for 4G/5G Mobile, FWA, and IoT subscribers
Australia telco TPG Telecom and Ericsson today announced a new multi-year agreement to deliver an Australian-first cloud-native and AI-powered analytics tool to pinpoint and improve mobile network performance for customers. Based on Ericsson Expert Analytics and EXFO Adaptive Service Assurance, the solution gives TPG Telecom’s Technology, Network and Care teams an in-depth, end-to-end understanding of subscriber’s experience at an individual level. Through the new agreement, TPG Telecom will gain insights from its 4G and 5G Mobile, Fixed Wireless Access and IoT subscribers using smart data collection with embedded intelligence to predict, prioritise, and resolve performance issues as they arise in real-time.
These insights will enable TPG Telecom to react quicker to network issues, improve performance and reduce the need for infrastructure-based diagnoses, allowing the telco to enhance its service experience for customers.
The solution integrates Ericsson Expert Analytics, EXFO adaptive service assurance and Ericsson software probes, provided as part of Ericsson’s dual-mode 5G Core, to deliver end-to-end network visibility and reduced total costs.
TPG Telecom is the first in Australia and one of the first communication service providers (CSP) globally to deploy Ericsson Expert Analytics in a commercial network using cloud-native technologies. As a cloud-native software, its embedded scalability, agility and resilience means it is designed to flexibly handle TPG Telecom’s requirements as its network and use-cases evolve, adapting to any unexpected challenges.

TPG Telecom General Manager Cloud/Infrastructure NW Services, Chris Tsigros, said: “TPG Telecom is committed to investing in cutting edge technology designed to provide superior network experience to every single one of our customers. The analytics and troubleshooting solution we’re implementing with Ericsson will help ensure we deliver a great experience for our customers. This new technology will change the way in which the TPG Telecom customer care team interacts with our customers, leading to greater effectiveness and increased customer satisfaction. It’s just another way we’re putting our customers first.”
Emilio Romeo, Head of Ericsson, Australia and New Zealand, says: “Embarking on this multi-year deployment of advanced analytics and troubleshooting capabilities with TPG Telecom further demonstrates our commitment to bringing the best mobile telecommunications experience to all Australians. It is the latest in a long history of working side by side with TPG Telecom to bring groundbreaking technology to Australia and a new level of service experience to the Australian people. With the Ericsson Expert Analytics solution implementation, and the real-time access to the data from the dual-mode 5G Core thanks to its built-in software probes, TPG Telecom can gain greater network visibility at a lower cost, passing on the benefits to its customers as they enjoy its services across the country.”
The initial deployment phase focused on acquiring profound insights and troubleshooting capabilities through the software probes built into Ericsson’s cloud-native dual-mode 5G Core. The state-of-the-art solution delivered to TPG adopts an innovative approach that combines probing and event-based monitoring, ensuring rapid and effective issue resolution.
One of the standout features of this deployed solution is its capacity to provide comprehensive troubleshooting across the entire network, all within a unified application. TPG benefits from a range of advanced functionalities, including On-Demand Troubleshooting and robust filtering capabilities, significantly expediting the identification and resolution of network challenges.
With this implementation, TPG Telecom gains the ability to trace and monitor subscriber sessions handled by the core network, which forms the foundation of TPG Telecom’s mobile network. Currently, the solution successfully monitors approximately 5 million subscribers, and its coverage continues to expand
The full solution will continue to be rolled out in phases of further enhancements, and will give TPG Telecom the ability to automatically detect issues from captured network and subscriber insights. TPG Telecom will also benefit from AI-powered recommendations for correction of any network or customer issues found.
Ericsson Expert Analytics is an open system designed for ease of integration in multi-vendor hybrid environments. The software solution is powered by anomaly detection techniques based on machine learning and artificial intelligence, transforming data at scale into actionable insights for better business outcomes. It is designed and used to analyze the real-time network data of more than 250 million subscribers of mobile telecommunications operators all over the world.
The solution follows the 2021 completion of the virtualisation of TPG Telecom’s core network and a new partnership to deploy Ericsson’s dual-mode 5G Core for standalone 5G networks.
About TPG TELECOM:
TPG Telecom Limited, formerly named Vodafone Hutchison Australia Limited, was listed on the Australian Securities Exchange on 30 June 2020. On 13 July 2020, this newly listed company merged with TPG Corporation Limited, formerly named TPG Telecom, to bring together the resources of two of Australia’s largest telecommunications companies, creating the leading challenger full-service telecommunications provider. TPG Telecom is home to some of Australia’s most-loved brands including Vodafone, TPG, iiNet, AAPT, Internode, Lebara and felix. https://www.tpgtelecom.com.au/
Resources:
Securing 5G experience with software probes
Data and Analytics for better business outcomes
Cloud native is transforming the telecom industry
TPG Telecom and Ericsson announce 5G Core partnership for standalone 5G networks
TPG Telecom’s ground-breaking cloud transformation
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/press-releases/7/2023/tpg-telecom-and-ericsson-launch-australian-first-analytics-and-troubleshooting-solution-to-boost-network-performance-for-customers
Cloud Service Providers struggle with Generative AI; Users face vendor lock-in; “The hype is here, the revenue is not”
Global Telco AI Alliance to progress generative AI for telcos
Park Place Technologies on network monitoring, predictive fault diagnosis and repair; Entuity acquisition adds analytics
Bain & Co, McKinsey & Co, AWS suggest how telcos can use and adapt Generative AI
Forbes: Cloud is a huge challenge for enterprise networks; AI adds complexity



