Author: Alan Weissberger
GSMA announces Open Gateway with 21 carriers, Microsoft Azure and AWS
Today, GSMA (the association representing the world’s major mobile operators) announced a new initiative called Open Gateway, a framework to provide universal, open-source-based APIs into carrier networks for developers to access and use a variety of mobile network services.
GSMA Open Gateway is a framework of common network Application Programmable Interfaces (APIs) designed to provide universal access to operator networks for developers. Launched with the support of 21 mobile network operators, the move represents a paradigm shift in the way the telecoms industry designs and delivers services in an API economy world. GSMA Open Gateway will help developers and cloud providers enhance and deploy services more quickly across operator networks via single points of access to the world’s largest connectivity platform.
Applications like location or identity verification and carrier billing, previously would have been more complicated or more expensive (if not impossible) to integrate and use. The plan is to be able to kick off more development using APIs in applications like immersive mixed-reality experiences and web3 applications that will in turn give more 5G business to the 21 mobile carriers that are part of Open Gateway.
The 21 carriers that have signed up for Open Gateway are: America Movil, AT&T, Axiata, Bharti Airtel, China Mobile, Deutsche Telekom, e& Group, KDDI, KT, Liberty Global, MTN, Orange, Singtel, Swisscom, STC, Telefónica, Telenor, Telstra, TIM, Verizon and Vodafone. These carriers have signed a memorandum of understanding, and the plan is to build and work on these APIs by way of CAMARA, an open source project co-developed by the Linux Foundation and the GSMA for this purpose: to help developers access “enhanced” network capabilities.
The carriers have invested billions in new networking technology, but they don’t really have a lot of usage on those networks. This move is being driven in part by them trying to kick-start activity on them.
GSMA Open Gateway APIs are defined, developed and published in CAMARA, the open source project for developers to access enhanced network capabilities, driven by the Linux Foundation in collaboration with the GSMA. Working in CAMARA, APIs between telcos and developers can be delivered quickly, using developer-friendly tools and software code. However, no details were provided about which services we might see rolled out first.
José María Álvarez-Pallete López, GSMA Board Chairman and Chairman & CEO of Telefónica, said: “GSMA Open Gateway will enable single points of access to ultra-broadband networks and provide a catalyst for immersive technologies and Web3 – giving them the ability to fulfill their potential and reach critical mass. Telcos have come a long way in developing a global platform to connect everyone and everything. And now, by federating open network APIs and applying the roaming concept of interoperability, mobile operators and cloud services will be truly integrated to enable a new world of opportunity. Collaboration amongst telecom operators and cloud providers is crucial in this new digital ecosystem.”
“By applying the concept of interconnection for operators to the API economy developers can utilise technology once, for services such as identity, cybersecurity or billing, but with the potential to be integrated with every operator worldwide. This is a profound change in the way we design and deliver services,” said Mats Granryd, Director General of GSMA. “In 1987, representatives from 13 countries worked together to harmonise mobile voice services and enable roaming, and I believe that 35 years on, GSMA Open Gateway has the potential to deliver a similar impact for digital services.”
GSMA Open Gateway will help developers and cloud providers enhance and deploy services more quickly via single points of access to operator networks. This is achieved via common, northbound service APIs that simply expose mobile operators’ network capabilities within a consistent, interoperable and federated framework.
Ishwar Parulkar, Chief Technologist for the Telco Industry at Amazon Web Services (AWS), said: “GSMA Open Gateway is a significant step in enriching the cloud developer experience. Developers using AWS’s more than 200 services will also be able to leverage APIs from telco operators. This allows the developer community to create new applications, and for telcos to open up new models of consumption and monetisation for their networks. We believe this will help accelerate innovation in the telecom industry.”
Erik Ekudden, CTO & SVP, Ericsson, said: “Together with Vonage, we enable operators to take their advanced mobile network capabilities to developers via easy-to-use APIs. The QoD API that we are demonstrating at MWC Barcelona 2023 – live on the networks of Orange, Telefónica and Vodafone – shows how GSMA Open Gateway APIs are highly scalable across operators and with different app developers. This places 5G as an innovation platform at the heart of digital transformation and we are excited to be part of the GSMA Open Gateway initiative.”
“At Microsoft, we are focused on extending a distributed computing fabric from the cloud to the edge, together with our operator partners,” said Satya Nadella, Chairman and CEO, Microsoft. “We look forward to bringing the GSMA Open Gateway initiative to Microsoft Azure, to empower developers and help operators monetise the value of their 5G investments.”
The GSMA Open Gateway initiative launches with eight universal network APIs, including SIM Swap, QoD, Device Status (Connected or Roaming Status), Number Verify, Edge Site Selection and Routing, Number Verification (SMS 2FA), Carrier Billing – Check Out and Device Location (Verify Location). The initiative plans to launch further APIs throughout 2023.
Examples of services supported by the introduction of GSMA Open Gateway include Edge Site Selection and Routing to support autonomous vehicles and Verify Location for fleet management and incident reporting; SIM Swap to combat financial crime and QoD for drones, robotics, eXtended Reality (XR) and immersive online gaming.
The GSMA Open Gateway demonstrations available to see at MWC Barcelona 2023 include:
- At the GSMA Pavilion, Axiata is showcasing its first ever immersive music concert on the Axiata Digital Concert Platform, powered by Dialog and Axiata Digital Labs’ Axonect, designed in association with GSMA Open Gateway APIs for Number Verification (SMS 2FA), Device Location and Carrier Billing.
- At MWC’s startup showcase, 4YFN, Deutsche Telekom (DT) will announce details of its developer marketplaces and Early Adopter Programmes for CAMARA APIs in association with GSMA Open Gateway. In addition, DT will be demonstrating applications of APIs, including QoD, alongside Matsuko and Orange in Hall 3 on stand 3M31.
- The 5G Future Forum (5GFF) will take collaboration to the next level across three operator networks – Rogers, Verizon and Vodafone. Musicians from around the world will jam over 5G, using Mobile Edge Compute (MEC) and the GSMA Open Gateway’s Edge Site Selection API. See the show on Wednesday, 1st March at 12pm in Theatre 1, Hall 6.
- At the GSMA Pavilion, KDDI, Telefónica, Mawari and Sturfee will showcase a revolution in online shopping with the 5G MEC powered XR Digital Twin Store. This allows shoppers in a physical store, and online shoppers in its Digital Twin, to share an immersive retail experience together. This project will explore opportunities based on the GSMA Open Gateway QoD API.
- On stand 4A60 in Hall 4, KT will be showing a demonstration of B2B use cases – built on the GSMA Open Gateway APIs for Edge Site Selection and Routing – with MEC. Titled ‘5G Connectivity & Cloud Federation’ this demonstration enables enterprise customers to receive the best service experience anywhere in the world by discovering optimal edge resources.
- Orange, Telefónica, Vodafone, Vonage and Ericsson are showing how user experience in mobile cloud gaming – and interactive high definition video applications – can be significantly enhanced by leveraging advanced network functionality through global network APIs. Application developers from Blacknut, Zoom and Vonage utilised the GSMA Open Gateway QoD API to add innovative features and enhance the mobile experience.
- Singtel, AIS, Summit Tech and Bridge Alliance will be showing their live broadcast demonstration at the GSMA Pavilion, leveraging 5G and MEC to provide a hyper-personalised view in 8K resolution. Participants are able to interact in real-time within live events across different country networks.
- Demonstrations at Telefónica’s booth will show GSMA Open Gateway API availability in Telefónica Kernel, in collaboration with Microsoft. Microsoft will also be announced as a partner in Telefónica’s Early Adopter Programme for developers and experience creators, which also features AWS, Google and Vonage.
- In addition, at its booth, Microsoft will present a solution for developers to build network-aware applications through a unified interface across operator networks.
Over the next 12 months the initiative will support engagement via Early Adopter Programmes for developers and it will promote GSMA Open Gateway APIs via significant developer channels, including Microsoft events such as Ignite and Build; and AWS’ re:Invent.
References:
Nvidia Survey Reveals How Telcos Plan to Use AI; Quantifying ROI is a Challenge
A Nvidia sponsored survey of more than 400 telecommunications industry professionals from around the world found a cautious tone in how they plan to define and execute on their AI strategies. Virtually every telco is already engaged with AI in some way, although mostly at an early stage. NVIDIA’s first “State of AI in Telecommunications” survey consisted of questions covering a range of AI topics, infrastructure spending, top use cases, biggest challenges and deployment models. The survey was conducted over eight weeks between mid-November 2022 and mid-January 2023.
Amid skepticism about the money-making potential of 5G, telecoms see efficiencies driven by AI as the most likely path for returns on investment. 93% of those responding to questions about undertaking AI projects at their own companies appear to be substantially underinvesting in AI as a percentage of annual capital spending.
Some 50% of respondents reported spending less than $1 million last year on AI projects; a year earlier, 60% of respondents said they spent less than $1 million on AI. Just 3% of respondents spent over $50 million on AI in 2022.
The reasons cited for such cautious spending? Some 44% of respondents reported an inability to adequately quantify return on investment, which illustrates a mismatch between aspirations and the reality in introducing AI-driven solutions. 34% cited an insufficient number of data scientists as the second-biggest challenge.
The biggest telco objectives for AI are to: optimize operations (60%), lower costs (44%) and enhance customer engagement (35%). Respondents cited use cases ranging from cell site planning and truck-route optimization to recommendation engines.
Just over a third of respondents said they had been using AI for more than six months. 31% said they’re still weighing different options, 18% reported being still in a trial phase and only 5% said they had no AI plans at all. Most industry execs say they see AI technologies will positively impact their business – 65% agreed AI was important to their company’s success, and 59% said it would become a source of competitive advantage.
Operators are spending a fraction of their capex budgets on AI projects – last year half said they spent less than $1 million on AI. At the top end, 2% spent more than $50 million in 2021, with that number rising to 3% in 2022.
The latest AI Index compiled by Stanford University puts telcos at the forefront of AI deployment. Using its own data and that from a McKinsey study, it found that the highest level of AI adoption is in product or service development by hi-tech companies and telcos (45%), followed by AI in service operations (45%).
The biggest single application in any industry was natural language text understanding deployed by 34% of hi-tech and telco firms, with 28% implementing AI-based computer vision and 25% using virtual agents.
- Moving from proof of concept to production/scale 47%
- Economic uncertainty 46%
- Infrasctructure upgrades 46%
- Market differentiation 34%
- Change in priority of data science 20%
- 92% will either increase or maintain their AI spend in 2023.
References:
https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2023/02/21/telco-survey-ai/
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/lp/industries/telecommunications/state-of-ai-in-telecom-survey-report/
https://aiindex.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/2022-AI-Index-Report_Master.pdf
Allied Market Research: Global AI in telecom market forecast to reach $38.8 by 2031 with CAGR of 41.4% (from 2022 to 2031)
Global AI in Telecommunication Market at CAGR ~ 40% through 2026 – 2027
The case for and against AI in telecommunications; record quarter for AI venture funding and M&A deals
SK Telecom inspects cell towers for safety using drones and AI
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
Nokia launches anyRAN to drive CloudRAN partnerships for mobile network operators and enterprises
Overview:
On the eve of MWC 2023 in Barcelona, Nokia today announced that it has signed go-to-market agreements with the world’s leading cloud infrastructure and server providers giving mobile network operators and enterprises flexibility in their choice of hardware, cloud infrastructure, and data center solutions for running Cloud RAN. To support this Nokia has also announced the launch of anyRAN, a new concept to help mobile operators and enterprises extend their options for building and evolving their radio access networks. Nokia’s approach supports the evolution of today’s purpose-built networks to Cloud RAN and hybrid solutions, ensuring performance consistency across all network environments.
anyRAN was introduced by Nokia’s President of Mobile Networks Tommi Uitto at the Intercontinental Hotel in Barcelona, Spain.

Image Credit: Nokia
The Collaborative Advantage: Nokia launches anyRAN:
Nokia anyRAN is designed to help mobile operators and enterprises extend their options for building and evolving their radio access networks. The software can run on any partner’s Cloud and Server infrastructure in addition to Nokia AirScale base stations and Nokia AirFrame servers. This approach removes the complexity from deployments by allowing a mix of purpose-built, hybrid, and fully Cloud-based RAN solutions, enabling deep multi-level disaggregation at the Cloud Infrastructure layer and data center (server) hardware layer. Close collaboration with partners also ensures performance consistency of Cloud RAN with Nokia’s field-proven purpose-built RAN.
Future-ready performance: Cloud RAN SmartNIC for anyRAN:
Underpinning these high-performance solutions is the Nokia Cloud RAN SmartNIC, a Layer 1 (fronthaul) In-Line acceleration card that integrates seamlessly with all leading Cloud or server infrastructures. L1 acceleration needs specialized silicon with extreme computing capacity, which is beyond the capabilities of general-purpose processors. Nokia Cloud RAN SmartNIC uses dedicated and optimized silicon technology, which is more energy efficient and provides higher performance. Nokia and its partners have already successfully performed end-to-end 5G data calls (Layer 3 calls) in multi-vendor setups powered by Nokia’s solution.
Nokia 5G Cloud RAN:
While Nokia’s AnyRAN solution offers deep multi-level vertical disaggregation, Nokia also continues to serve the mobile operator and enterprise market with its optimized Nokia AirFrame OpenEdge server family. Benefitting from the SmartNIC, the enhanced AirFrame Open Edge server delivers a 50 percent performance boost compared to the system shown at Mobile World Congress 2022. Nokia’s solutions offer network performance consistency between purpose-built AirScale baseband and Cloud RAN and secures the best possible feature performance parity, with the fastest time-to-market for cloud/hybrid networks.
Sue Rudd, Director Networks and Service Platforms at TechInsights: “As service providers evolve on the path towards disaggregated RAN, Nokia’s anyRAN offers them a solution with standard O-RAN fronthaul and 3GPP midhaul interfaces under seamless control that can operate across multiple Cloud partner data centers. Combined with acceleration from a new Layer 1 SMARTNIC and a ‘host neutral’ Container as a Service (CaaS) layer for DU and CU processing, this flexible open approach will allow operators to leverage Nokia’s powerful new ecosystem of platform and cloud partners to deliver very cost effective, high performance Cloud RAN service.”
Tommi Uitto, President of Mobile Networks at Nokia: “The strength of our industry partnerships and the launch of anyRAN unlocks more choice and higher performance in Cloud RAN for our mobile network operator and enterprise customers. Server-based Cloud RAN will have to co-exist with purpose-built RAN in the short-to-medium term which calls for performance consistency and service continuity between the two. Together with our leading industry partners, we have made huge progress towards this goal by driving consistent performance across any partner’s Cloud Infrastructure or server hardware. Our collaborative approach to Cloud RAN means we can drive efficiency, innovation, openness, and scale by jointly delivering competitive advantage to organizations embracing Cloud RAN.”
Mobile World Congress 2023:
At MWC 2023 in Barcelona, Nokia will showcase anyRAN as well as the future-ready SmartNIC solution, its enhanced AirFrame Open Edge server as well as the progress made in Cloud RAN with its best-in-class partners. Additional demonstrations will also be included on our partner’s stands. Please visit Hall 3 to see our industry-leading technology solutions.
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/mobile-networks/anyran/
Comcast selects Nokia’s 5G SA Core software to support its mobile connectivity efforts
Resources and additional information:
Nokia AirScale Cloud RAN
Nokia anyRAN
Cloud RAN: A Guide to Acceleration Options
In-Line architecture: bringing efficiency and performance to Cloud RAN
Ericsson to lay off 8,500 employees as part of cost cutting plan
After warning in January that profit margins at its RAN business would worsen, telecom equipment maker Ericsson will lay off 8,500 employees globally as part of its plan to cut costs, according to a memo sent to employees and seen by Reuters.
“The way headcount reductions will be managed will differ depending on local country practice,” Chief Executive Borje Ekholm wrote in the memo. “In several countries the headcount reductions have already been communicated this week,” he said. “It is our obligation to take this cost out to remain competitive,” Ekholm said in the memo. “Our biggest enemy right now may be complacency.”
While technology companies such as Microsoft, Meta and Alphabet have laid off thousands of employees citing economic conditions, Ericsson’s move would be the largest layoff to hit the telecoms industry.
On Monday, the company, which employs more than 105,000 worldwide, announced plans to cut about 1,400 jobs in Sweden. While Ericsson did not disclose which geography would be most affected, analysts had predicted that North America would likely be most affected and growing markets such as India the least.
The company said in December it would cut costs by 9 billion crowns ($880 million) by the end of 2023 as demand slows.
“Our aim is to manage the process in every country with fairness, respect, professionalism and in line with local labor legislation,” Ericsson said in a statement.
“We are also working on our service delivery, supply, real estate and IT. We have already started to implement and accelerate various initiatives to help us reach” the cost-cutting goal, Ericsson said.
Many telecom companies had beefed up their inventories during the height of the pandemic which is now leading to slowing orders for telecom equipment makers like Ericsson and Nokia.
References:
https://www.reuters.com/business/media-telecom/ericsson-lay-off-8500-employees-memo-2023-02-24/
https://apnews.com/article/technology-stockholm-covid-business-07bda439ac93836817a00d0d54892d0a
Ericsson Mobility Report: 5G monetization depends on network performance
High Tech Layoffs Explained: The End of the Free Money Party
HPE acquires private cellular network provider Athonet (Italy) to strengthen HPE Aruba’s networking portfolio
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) today announced the expansion of its connected edge-to-cloud offering with the acquisition of Athonet, a private cellular network technology provider that delivers mobile core networks to enterprises and communication service providers. Combined with the HPE telco and Aruba networking portfolios, Athonet will put HPE at the forefront of a growing market that is predicted by IDC to increase to more than $1.6 billion1 by 2026.
Based in Vicenza, Italy, Athonet has more than 15 years of experience delivering 4G and 5G mobile core solutions to customers and partners globally. Athonet is an award-winning technology pioneer with more than 450 successful customer deployments in various industries, including leading mobile operators, hospitals, airports, transportation ports, utilities, government and public safety organizations.
With enterprises facing complex connectivity challenges across large and remote sites, private 5G offers high levels of coverage, reliability and mobility across campus and industrial environments. It also augments the cost-effective, high-capacity connectivity provided by Wi-Fi. The incorporation of Athonet’s technology will allow HPE to deliver private networking capabilities directly to enterprises as part of HPE’s Aruba networking portfolio, while also enabling communications service providers (CSPs) to quickly deploy private 5G networks for their customers.

“Telco customers are looking for simpler ways to deploy private 5G networks to meet growing customer expectations at the connected edge,” said Tom Craig, global vice president and general manager, Communications Technology Group at HPE. “At the same time, enterprise customers are demanding a customized 5G experience with low-latency, segregated resources, extended range and security across campus and industrial environments that complement their existing wireless networks. With the acquisition of Athonet, HPE now has one of the most complete private 5G and Wi-Fi portfolios for CSP and enterprise customers – and we will offer it as a service through HPE GreenLake.”
HPE expands private 5G solutions for both telcos and the enterprise:
HPE will integrate Athonet’s technology into its existing CSP and Aruba networking enterprise offerings to create a private networking portfolio that accelerates digital transformation from edge-to-cloud. The networking portfolio will provide the following benefits:
- Enhanced private networks that combine the high capacity of Wi-Fi with the coverage and mobility of 5G
- Accelerated private 5G deployments that improve agility and innovation to help telco B2B teams and enterprise customers
- New enterprise revenue streams for telcos with differentiated services leveraging 5G and Wi-Fi
- Alignment of costs to revenues with consumption-based models for enterprises and telcos through HPE GreenLake, reducing the risk of entering new markets
- Management of operational complexity and cost efficiency with 5G orchestration and zero-touch automation to deliver new workloads from edge-to-cloud
With 5G investments running into the billions of dollars, CSPs are looking for simple ways to meet customer needs and drive new B2B revenue by deploying both edge compute and private 5G networks. The addition of Athonet’s software to HPE’s telco portfolio enhances one of the broadest communications portfolios in the market, which serves a base of more than 300 customers across 160 countries and connects more than one billion mobile devices worldwide. Building on its existing private 5G solutions, HPE’s enhanced offering for CSPs will support private 4G and 5G networks and include telco-grade orchestration and automation capabilities. These capabilities will help launch new B2B services that meet growing customer expectations for the connected edge.
“Athonet was founded to provide customers with private 4G and 5G solutions that deliver carrier-grade reliability and performance to suit their increasing and more challenging connectivity needs,” said Gianluca Verin, CEO and co-founder of Athonet. “We are excited to join HPE and combine our highly skilled teams as we expand our joint service provider offerings for the rapidly growing private 5G market and build on HPE’s strategy to be the leading edge-to-cloud solutions provider.”
Private 5G offers enterprises new capabilities that are ultra-secure, easy to deploy and manage, ready for highly specialized applications such as robotics and industrial IoT, data networks and pipelines, and security systems facilitation. The acquisition of Athonet strengthens Aruba’s connected edge portfolio, providing the unique and highly sought-after ability to deliver fully integrated Wi-Fi and private 5G networks. Integration with Aruba Central will enable network managers to administer Wi-Fi and private 5G through a single pane of glass and bring to bear the power of AI-powered insights, workflow automation, and robust security.
HPE GreenLake, HPE’s edge-to-cloud platform, will offer Athonet private 5G offerings, combining all costs for Wi-Fi and private 5G into one single monthly subscription with no capital expenditure. Flexible consumption options, including HPE’s networking as a service, mean private 5G networks can be deployed with reduced risk, little upfront investment and scaled according to demand.
HPE portfolio integration and availability:
HPE will integrate Athonet’s solutions with its existing telco software assets and plans to make them available to customers some time following the close of the transaction. HPE will also integrate the solutions with the Aruba networking portfolio in the near future. The transaction is expected to close at the beginning of the third quarter of HPE’s 2023 fiscal year, subject to regulatory approvals and other customary closing conditions.
About Hewlett Packard Enterprise:
Hewlett Packard Enterprise is the global edge-to-cloud company that helps organizations accelerate outcomes by unlocking value from all of their data, everywhere. Built on decades of reimagining the future and innovating to advance the way people live and work, HPE delivers unique, open and intelligent technology solutions as a service. With offerings spanning Cloud Services, Compute, High Performance Computing & AI, Intelligent Edge, Software, and Storage, HPE provides a consistent experience across all clouds and edges, helping customers develop new business models, engage in new ways, and increase operational performance. For more information, visit: www.hpe.com
Media Contacts for U.S. & Canada:
Ben Stricker [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Analysis from Channel Futures:
While HPE already offers a 5G cloud-native software core, Athonet gives deeper in-house capabilities to more quickly and directly deploy private 5G networks.
“Given HPE’s Wi-Fi and security assets – like Aruba – I’d say this makes a clear play to simplify management for key enterprise digital assets. And this is the kind of issue that enterprises are often bringing up to us,” Omdia chief analyst of enterprise services Camille Mendler told Channel Futures. (Omdia and Channel Futures share a parent company, Informa.)
Patrick Filkins, IDC‘s research manager for IoT and telecom network infrastructure, said Athonet can give HPE customers an improved option for deploying a private 5G network together with Wi-Fi. Filkins said that integrated portfolio could well serve an enterprise that has already done the heavy legwork of building a Wi-Fi network.
“This is a very complicated task, and one the enterprise itself controls. They don’t want to start from scratch or be forced to have someone else tinkering in their systems, so this acquisition will hopefully provide some assurance to enterprise customers that the vendors will help ensure their customers can repurpose work they’ve already done to integrate a new network technology, and hopefully new use cases,” Filkins said.
Filkins said the acquisition will immediately improve the HPE 5G core and gradually work its way into Aruba portfolio improvements. For example, HPE will integrate Athonet into the Aruba Central network management platform.
“Specifically, we expect HPE/Aruba to over time release follow-on solutions which help enterprises manage the two technologies seamlessly. Enterprises are not interested in deploying both 5G and Wi-Fi networks in a silo. They want a combined solution that can help tackle the integration and management issues from a single pane. This means you’ll see HPE’s telco and Aruba teams working together more closely over time,” Filkins said.
Mendler said one might see a U.S. equivalent in Celona, despite Athonet’s age (founded 2004) compared to that of Celona (founded in 2019). Filkins added that although many vendors provide private and public LTE/5G cores in the U.S., most run their headquarters abroad. He pointed to Cisco and Microsoft-acquired Mavenir, Affirmed Networks and MetaSwitch as 5G core providers in the U.S.
“However, from a competitive standpoint, Athonet competes globally against Nokia, Ericsson, Mavenir, Microsoft Azure, Cisco, etc., among others,” Filkins told Channel Futures. He described Athonet as “no slouch” in the wireless market. He calls the company’s customer base deep, though consisting of smaller customers. HPE said in an announcement that Athonet has performed 450 customer deployments in various verticals. Athonet’s customers include SpaceX, which uses a private cellular network in Antarctica.
Filkins called the Athonet technology offerings “relatively advanced for 5G.” For example, the cloud-native 5G core meets almost all of 3GPP‘s listed functions. He also said Athonet’s core augments HPE’s 5G core offerings.
“The cloud-native part means it can be deployed fully on-site, fully in the cloud, or in a hybrid format. This should cover any scenario the customer wants. [Athonet] has specialized in selling mobile core software to enterprises, and smaller, regional operations for years. It knows the needs of the enterprise well,” Filkins said.
Athonet CEO and co-founder Gianluca Verin said his team looks forward to joining HPE. Moreover, he said he wants to enhance HPE’s goal of being “the leading edge-to-cloud solutions provider.” Verin worked in support and solution engineer positions at Ericsson for eight years before starting Athonet.
HPE’s GreenLake edge-to-cloud services platform will host the private 5G service. HPE executives have said GreenLake as-a-service consumption model will “simplify” enterprises’ entrance into 5G and lower risk.
“I think this is an important step HPE is taking. For the most part, private 5G and Wi-Fi networks have been offered as point solutions, but HPE/Aruba intend to do the ‘under-the-hood’ work to make them as integrated as possible, which is what enterprise customers want,” Filkins said.
In December, HPE said 80% of its top 100 customers have adopted the GreenLake platform. The vendor is also equipping Aruba partners to deliver its network-as-a-service offering.
When HPE unveiled a private 5G offering one year ago, an executive said HPE preferred to go to market though system integrators, telcos and service providers rather than straight to the enterprise. HPE’s telco business serves 300 customers across the world, the company said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
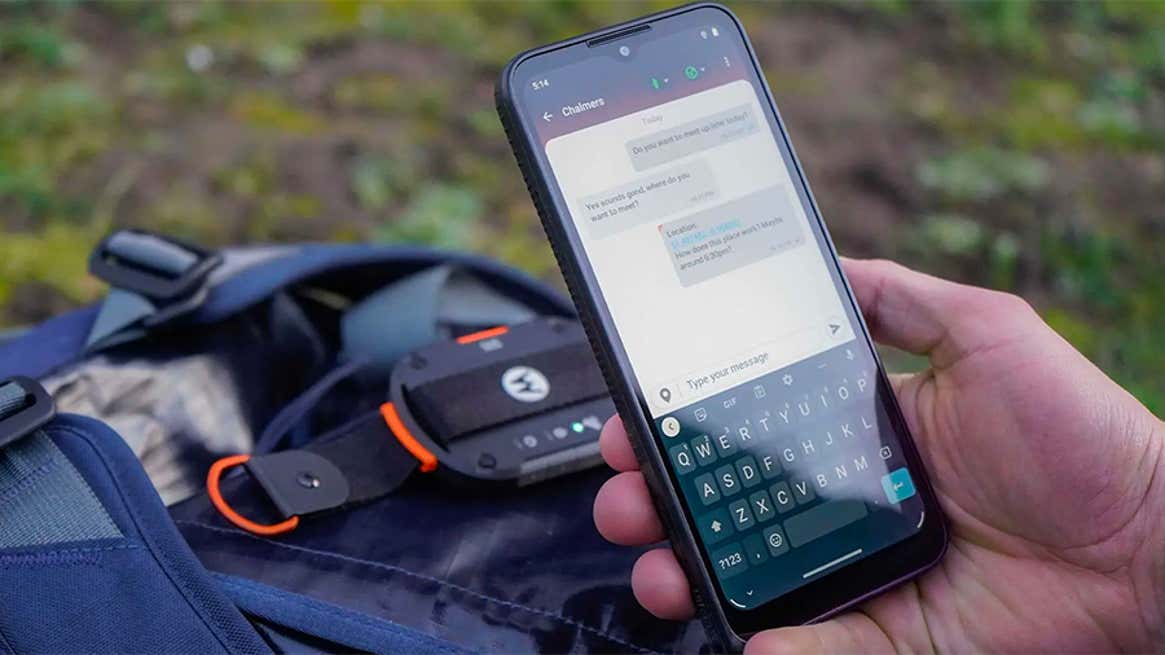
Bullitt Group & Motorola Mobility unveil satellite-to-mobile messaging service device
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
Frontier Communications Parent, Inc. (“Frontier”) reported impressive 4th quarter and full-year 2022 results today. The fiber facilities based carrier added a record 76,000 fiber subs in the last quarter, more than two times what it added in the year-ago quarter. The bulk of those fiber subscriber gains are coming from cable competitors, execs said.
Frontier ended 2022 with 1.7 million fiber customers, a figure that represents the majority of its total base of 2.8 million broadband subs. Frontier also built out a record 381,000 new fiber locations in Q4, ending 2022 with 5.2 million fiber locations. That gets Frontier past the halfway point toward a goal of building fiber-to-the-premises to 10 million locations by 2025.
Total revenues were down year-over-year, but consumer fiber revenues rose 7.7% to $436 million versus the prior year period, offsetting declines in video. Consumer fiber broadband revenues surged 15.5%, to $283 million.
“We ended the year strong with another quarter of record operational results. We now have the fiber engine we need to power our growing digital infrastructure business. This is how we advance our purpose of Building Gigabit America,” said Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier.
“This year, we will accelerate our fiber build and give customers more reasons to choose the un-cable provider. The team is fired up and ready to return to growth in 2023.”
Frontier expects to accelerate its fiber build to 1.3 million homes in 2023 – about 20% faster than its 2022 pace – and end the year with 6.5 million fiber locations. Frontier is also exploring fiber builds beyond its initial goal of 10 million. The company has identified 1 million to 2 million copper locations where it can upgrade to fiber cost-effectively. There’s another 3 million to 4 million locations in its footprint that remain financially unattractive but could get over the hump with government subsidies or partnerships.
Even with its faster build pace, Frontier expects 2023 capital expenditures to reach $2.8 billion, essentially flat versus 2022’s $2.74 billion. Frontier anticipates its fiber buildout costs will stay in its envelope of $900 to $1,000 per location passed.
Frontier believes it’s set to grow its average revenue per user (ARPU) by 2% to 3% in 2023. Tied in, it’s updating its pricing and looking to upsell customers to higher speeds (more than half of new subs are choosing speeds of 1-Gig or more) while also reducing its reliance on perks such as gift cards.

Source: Frontier Q4 2022 earnings presentation
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
On the wholesale side, Frontier has fiber tower deals with AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile and recently inked an expanded deal with AT&T to connect it to Frontier’s central offices. Company President and CEO Nick Jeffery suggested that the same model could apply to the likes of Amazon, Microsoft and other cloud companies that are distributing data and could make use of cache locations where data is being consumed.
But that handwork with wireless network operators has yet to drive Frontier toward deals that could enable it to add mobile services to the bundle, and follow the path being taken by major cable operators such as Comcast and Charter Communications.
Jeffery reiterated a position that Frontier is keeping close watch on potential MVNO partnerships but that no such agreement is imminent. Such a deal could be a “distraction of our capital,” he said.
“For the moment, we don’t see the need to launch with an MVNO and bundle with our core broadband offer,” Jeffery explained. “We think it’s something we could spin up relatively quickly and efficiently if we needed to.”
Full-Year 2022 Highlights:
- Built fiber to 1.2 million locations, bringing total fiber passings to 5.2 million by the end of 2022 – more than halfway to our target of 10 million fiber locations.
- Added a record 250,000 fiber broadband customer net additions, resulting in fiber broadband customer growth of 17.5% from 2021.
- Revenue of $5.79 billion, net income of $441 million, and Adjusted EBITDA of $2.08 billion.
- Capital expenditures of $2.74 billion, including $1.52 billion of non-subsidy-related build capital expenditures and $0.06 billion of subsidy-related build capital expenditures.
- Surpassed our $250 million gross annualized cost savings target more than one year ahead of plan and raised our target to $400 million by the end of 2024.
4th-Quarter 2022 Highlights:
- Built fiber to a record 381,000 locations
- Added a record 76,000 fiber broadband customers
- Revenue of $1.44 billion, net income of $155 million, and Adjusted EBITDA of $528 million
- Capital expenditures of $878 million, including $517 million of non-subsidy-related build capital expenditures and $33 million of subsidy-related build capital expenditures
- Net cash from operations of $360 million, driven by strong operating performance and increased focus on working capital management
- Achieved annualized run-rate cost savings of $336 million
4th-Quarter 2022 Consolidated Financial Results:
- Frontier reported revenue for the quarter ended December 31, 2022, of $1.44 billion, a 6.9% decline compared with the quarter ended December 31, 2021, as growth in consumer, business and wholesale fiber was more than offset by declines in copper and subsidy.
- Revenue growth was negatively impacted by the expiration of CAF II funding at the end of the fourth quarter of 2021.
- Excluding subsidy-related revenue, revenue for the quarter ended December 31, 2022, declined 2.5% compared with the quarter ended December 31, 2021, an improvement in the year-over-year rate of decline reported for the quarter ended September 30, 2022.
- Fourth-quarter 2022 operating income was $136 million and net income was $155 million.
- Capital expenditures were $878 million, an increase from $559 million in the fourth quarter of 2021, as fiber expansion initiatives accelerated.
4th-Quarter 2022 Consumer Results:
- Consumer revenue of $764 million declined 2.3% from the fourth quarter of 2021, as strong growth in fiber broadband was more than offset by declines in legacy video and voice.
- Consumer fiber revenue of $436 million increased 7.7% over the fourth quarter of 2021, as growth in consumer broadband, voice, and other more than offset declines in video.
- Consumer fiber broadband revenue of $283 million increased 15.5% over the fourth quarter of 2021, driven by growth in fiber broadband customers.
- Consumer fiber broadband customer net additions of 73,000 resulted in consumer fiber broadband customer growth of 17.9% from the fourth quarter of 2021.
- Consumer fiber broadband customer churn of 1.32% was flat with the fourth quarter of 2021.
- Consumer fiber broadband ARPU of $61.20 declined 1.6% from the fourth quarter of 2021, as price increases and speed upgrades were more than offset by the autopay and gift-card incentives introduced in the third quarter of 2021.
- Excluding the impact of gift-card incentives, consumer fiber broadband ARPU increased 0.9% over the fourth quarter of 2021.
4th-Quarter 2022 Business and Wholesale Results:
- Business and wholesale revenue of $659 million declined 2.6% from the fourth quarter of 2021, as growth in our fiber footprint was more than offset by declines in our copper footprint.
- Business and wholesale fiber revenue of $285 million increased 5.5% over the fourth quarter of 2021, driven by growth in both business and wholesale.
- Business fiber broadband customer churn of 1.33% increased from 1.23% in the fourth quarter of 2021.
- Business fiber broadband ARPU of $107.68 increased 0.8% from the fourth quarter of 2021.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, Frontier introduced its Fiber Innovation Labs yesterday – National Innovation Day – designed for inventing and testing new patents, technologies and processes that will advance its fiber-optic network. Improving the customer experience and driving efficiencies are key to accelerating Frontier’s fiber-first strategy. Frontier’s labs serve as a testing ground to find new technologies and procedures to advance the way it delivers blazing-fast fiber internet to consumers and businesses across the country.
“The work we are doing in our Fiber Innovation Labs will change the way we serve our customers and will ultimately change the industry,” said Veronica Bloodworth, Frontier’s Chief Network Officer. “We have the best team in the business – they live and breathe innovation. They have been awarded several patents and are in the process of bringing those new inventions to life to deliver the best ‘un-cable’ internet experience to our customers. Be prepared to be amazed.”
As part of Frontier’s Fiber Innovation Labs, the company has launched its first-ever outside plant facility in Lewisville, Texas. The facility is designed as a miniature suburban neighborhood that mimics the real-life experiences of its techs serving customers every day. It features roads, sidewalks, a state-of-the-art central office, a small house and a reconstructed manhole system. It also simulates weather elements and temperature changes. Here, the Frontier team can test and learn new methods in real-world environments to install and maintain its fiber-optic network.
References:
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
\
Comcast selects Nokia’s 5G SA Core software to support its mobile connectivity efforts
Today, Comcast announced it will roll out Nokia’s 5G Stand Alone Core networking software to support its deployment of CBRS and 600MHz spectrum to Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile customers in its service areas across the United States.
Comcast will deploy that spectrum in select, high-traffic areas in support of both residential and business customers that take mobile services from the operator. Deploying fresh spectrum in those areas will give Comcast a greater degree of ownership economics with wireless and help to offset a portion of the MVNO costs associated with its pact with Verizon. Those deployments will also build on Comcast’s current Wi-Fi offload strategy that involves millions of access points deployed in customer homes and in certain metro areas.
Nokia will supply Comcast with its 5G Stand Alone Core networking software, including Packet Core, delivering near zero touch automation and ultra low latency capabilities, as well as operations software and consulting services. These offerings will support Comcast’s efforts to deliver enhanced 5G access to consumer and business customers in the U.S. using Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) and 600 MHz spectrum.
By combining Nokia’s software with Comcast’s targeted, capital-light network design, Comcast can cost-effectively deliver enhanced 5G and WiFi mobile connectivity to its more than five million Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile customers. Comcast and Nokia are currently conducting field trials, which includes Comcast employee testing.
As the demand for reliable Internet access inside and outside of the home and office rapidly increases, Comcast’s mid-band (CBRS) and low-band (600MHz) spectrum enable the company to supplement its existing Xfinity WiFi network and cellular network partnership with additional targeted 5G coverage in certain high-traffic areas within its service territory.
Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile services are built for the way people use mobile today, with the Internet at the core of the experience. Calls and texts are free, and customers can experience the freedom of paying by the gig or unlimited, and switch between payment options at any time for any line on their account. For complete pricing and availability details, please visit Xfinity Mobile or Comcast Business Mobile.
Nokia claims to be leading the 5G Standalone Core market, with over 80 communication service provider (CSP) customers around the world. In addition, 25 of the top 40 CSPs by revenue rely on Nokia Core network products.

Comcast and Nokia are currently conducting field trials, including tests with Comcast employees. Comcast didn’t reveal the location of its test markets, but the announcement indicates the operator is finally starting to gear up this important piece of its wireless strategy.
This deal comes more than two years after the company bid for and won licensed CBRS spectrum. Comcast also spent $1.7 billion on 600MHz spectrum licenses in 2017.
Though Comcast has no plans to deploy a national wireless network, it estimates that its current spectrum holdings cover roughly 80% of its homes passed and about 50% of the US population.
Tom Nagel, SVP, Wireless Strategy at Comcast, said: ”We are pleased to be working with Nokia to enable Comcast’s advanced 5G mobile products and services for our customers. Combining Nokia’s industry-leading solutions with Comcast’s targeted network design and new dual SIM technology allows us to create exciting next-generation wireless offerings.”
Fran Heeran, SVP & General Manager of Core Networks, Cloud and Network Services, at Nokia, said: “We are delighted to partner with Comcast and provide Nokia’s advanced 5G Core portfolio to deliver innovative 5G customer offerings securely, at scale, and with advanced operational efficiencies.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Last fall, Comcast announced it would use Samsung radios, including strand-mounted small cells, for its targeted 5G network. Comcast will deploy separate Samsung radios for the CBRS and 600MHz bands and use its wireline network to help backhaul traffic.
At the time, Comcast confirmed to Light Reading that its wireless network deployment is “using a multi-vendor solution but not within an open RAN framework.”
Comcast’s wireless network evolution is underway as the operator continues to grow a mobile business that launched almost six years ago. Comcast added a record 365,000 mobile lines in Q4 2022, raising its total to 5.31 million.
Meanwhile, Comcast recently introduced a limited-time service convergence bundle for new customers that offers one unlimited mobile line and a 200Mbit/s home broadband service (with the Wi-Fi gateway included) for $50 per month – for a period of 24 months.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g-and-beyond/comcast-shares-wireless-wealth-with-nokia/d/d-id/783415
Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core/5g-core/
Samsung announces 5G NTN modem technology for Exynos chip set; Omnispace and Ligado Networks MoU
Samsung Electronics, a leader in advanced semiconductor technology, today announced that it has secured standardized 5G non-terrestrial networks (NTN) [1.] modem technology for direct communication between smartphones and satellites, especially in remote areas. Samsung plans to integrate this technology into the company’s Exynos modem solutions, accelerating the commercialization of 5G satellite communications and paving the way for the 6G-driven Internet of Everything (IoE) era. That’s noteworthy considering Samsung’s latest flagship smartphone, the Galaxy S23, does not use Samsung’s Exynos platform and instead only uses Qualcomm’s Snapdragon chipset.
Note 1. There are no ITU or ETSI standards for 5G NTN– only for 5G terrestrial networks. It is not even under consideration for the next revision o the 5G RAN standard– ITU-R M.2150-1.
NTN is a communications technology that uses satellites and other non-terrestrial vehicles to bring connectivity to regions that were previously unreachable by terrestrial networks, whether over mountains, across deserts or in the middle of the ocean. It will also be critical in assuring operability in disaster areas and powering future urban air mobility (UAM) such as unmanned aircraft and flying cars.

Source: Samsung
“This milestone builds on our rich legacy in wireless communications technologies, following the introduction of the industry’s first commercial 4G LTE modem in 2009 and the industry’s first 5G modem in 2018,” said Min Goo Kim, Executive Vice President of CP (Communication Processor) Development at Samsung Electronics. “Samsung aims to take the lead in advancing hybrid terrestrial-NTN communications ecosystems around the world in preparation for the arrival of 6G.”
By meeting the latest 5G NTN specifications defined by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP Release 17), [2.] Samsung’s NTN technology will help ensure interoperability and scalability among services offered by global telecom carriers, mobile device makers and chip companies.
Note 2. 3GPP Release 17 contains specs for 5G-NR over Non terrestrial Networks (NTN) and NB-IoT over NTN,
Impacts on 5GC of Satellite NG-RAN used as new RAN 3GPP access
In 3GPP Rel-17, only direct access with transparent satellite is considered, as shown in following figure:
Source: 3GPP
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
For highly reliable NTN communication with low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, Samsung has developed and simulated 5G NTN standard-based satellite technology using its Exynos Modem 5300 reference platform to accurately predict satellite locations and minimize frequency offsets caused by the Doppler shift. Based on this technology, Samsung’s future Exynos modems will support two-way text messaging as well as high-definition image and video sharing. That would be an important development considering today’s phone-to-satellite services generally support only slow-speed emergency messaging (e.g. Apple iPhone 14). An offering that supports high-bandwidth services like video calling would presumably require far more satellites than today’s services use – and it could also pose a challenge to terrestrial mobile network operators looking to make profits from offering high-bandwidth services in remote or rural areas.
Additionally, Samsung said it plans to secure a standardized NB-IoT NTN technology for use in its next-generation modem platforms. With integrated satellite connectivity, Samsung’s NB-IoT solutions will eliminate the need for a separate high-power wireless antenna chip inside smartphones, providing mobile device makers with much greater design flexibility.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Samsung has not disclosed when the company might begin offering satellite services in its 5G NTN equipped phones, how much the service might cost, and which satellite operators might support the offering.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In a related development, Omnispace and Ligado Networks today announced a new Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to combine their respective spectrum holdings in order to offer “space-based, direct-to-device (D2D) solutions for global voice, text and data connectivity.”
The companies pledged to merge Ligado’s 40MHz of L-band satellite spectrum in the U.S. and Canada with Omnispace’s 60MHz of S-band satellite spectrum. “The combination of L- and S-band spectrum is a unique opportunity to expand the ecosystem of D2D applications and technologies, enhance user experience and extend service globally. For consumer smartphones, the offering will have enough bandwidth to go beyond emergency satellite texting by offering ubiquitous roaming mobile coverage with two-way voice, messaging and data capabilities,” according to the companies’ press release.
However, there are plenty of obstacles to the companies’ ambitions. For example, Ligado has spent years working to free its spectrum of interference concerns, and its financial footing remains a question. “Ligado has no cash and an overwhelming debt load,” tweeted analyst Tim Farrar with TMF Associates following the announcement from Ligado and Omnispace.
References:
https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3937
https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-17
GfK: Global telecom market (x-North America) posts 9.7% revenue drop; smartphone revenues -10.2% in 2022
The 9.7% year-over-year drop in the global telecom market is based on GfK’s exclusive POS (point of sale) data for retailers in 67 countries worldwide, excluding North America. The industry had $360 billion (U.S. $) in revenue from January to December 2022.
The smartphone segment, including phablets, experienced a 10.2% drop year over year, but still accounted for $330 billion (US) in revenue. One of the few market drivers in 2022 was consumers with higher and middle incomes. These shoppers now account for 48% of all smartphone buyers, up 4 percentage points compared to 2021. Demand for premium devices also increased; revenue for 5G models, for example, grew by 1.2% in 2022 versus the year before. The same applies to devices with more storage; smartphones with a capacity of over 256GB recorded an increase of 19% and accounted for 41% of total market revenue in 2022.
“While we had already predicted saturation effects in 2022 after the strong telecom sales in pandemic years, the additional weakness of the Chinese market significantly impacted the results,” explains Jan Lorbach, GfK expert for the Telecom industry. “But GfK expects a stabilization of the telecom market in 2023.”
While consumers who are still buying smartphones are opting for premium devices, the total number of purchases decreased in 2022. One reason may be that people are keeping their smartphones for a longer time. Data from gfknewron Consumer shows that, from January to September 2019, only 48% of consumers used their smartphones for two years or longer; for the same period in 2022, that increased to 57% (an increase of plus 9 percentage points).
This new longevity in ownership can especially be observed in Generation Z (15 to 25 years old), where the share of Gen Z consumers keeping their smartphones for two-plus years now stands at 14 percentage points above the average. This younger generation has a clear focus on sustainability and therefore may be consciously extending the lifecycle of their devices.
Wearables Hold Steady:
One of the few telecom segments that managed to survive the difficult year 2022 in a stable manner is wearables. With $13.9 billion (US $) in revenue, the wearables market achieved almost the same level in 2022 as in the previous year (minus 1.1% compared to 2021). Although popular segments have lost ground, this has been offset by growth in other product lines.
GfK also saw significant year-over-year (2022 vs. 2021) increases and declines in revenue in specific wearables categories:
• Health and Fitness tracker: -31%
• Smartwatches: +21%
• Wrist Sport Computers: -43%
These shifts have been driven by increasing consumer demand for greater control of their health, via smart features. Accordingly, wearables with a sleep tracking feature (plus 4%) or blood oxygen sensors (plus 20%) showed strong growth. This trend also led to innovations, such as the new feature of stress level measuring (EDA). Launched in the fourth quarter of 2021, these devices already account for 16% of revenue in the wearables market and continue to grow.
AR/VR headsets: First decline ever, but potential is still high:
Further hot topics for MWC are virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and the metaverse — made possible by devices such as VR headsets. While awareness and discussions around the metaverse have risen, retail sales of VR headsets in the European market* actually declined by 15% year-over-year in 2022. This is the first decline ever, as the market has previously recorded double-digit growth for years.
“The European market seems to have accomplished initial consumer penetration of VR headsets,” says Sohjin Baek, GfK expert for global IT hardware industry. “The industry should now focus on providing more content, as well as better visual quality and security, to drive the market based on this initial penetration. Convincing consumers about the use cases will be key to drive VR/metaverse forward.”
Outlook 2023:
GfK experts forecast a stronger year 2023 for the global Telecom market overall compared to the relatively weak 2022. At a regional level, China, which is the largest single market, is expected to pick up again and significantly drive global market growth. Additionally, developments within the three main product categories will have a positive impact:
- Although replacement cycles are extending, smartphone purchases made at the height of the pandemic in 2020 and 2021 are entering the expected renewal cycle window this year.
- In wearables the next generation of Health Tracking sensors, which will expand the scope of applications, will drive the market. In addition, positive revenue growth is expected for the smartwatches segment.
- VR/AR is expected to become more tangible and grow into areas beyond gaming. This is one of the segments with the greatest potential in the coming years.
To remain competitive in the market and differentiate from competitors in terms of quality, retailers and manufacturers should continue to innovate for more powerful or faster devices that make consumers’ lives easier. “Innovation will further drive consumer’s demand,” says Jan Lorbach, GfK expert for the Telecom market. “When the holding time of smartphones is extending and budgets are tight, consumers will more than ever ask for value for money.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About the GfK method:
Through its retail panels, GfK regularly collects POS data in more than 70 countries worldwide for the consumer electronics, photography, telecommunications, information technology, office equipment, and small and large household appliances sectors. All figures are according to GfK panel market, with global data excluding North America and presented in US dollars. Revenues are presented in US dollars Non Subsidized Prices (NSP).
gfknewron is an always-on platform that combines market, consumer and brand data supercharged with AI-powered recommendations. It enables companies to gain actionable and connected insights and act at speed to ignite sustainable growth. The platform offers three specific modules: “gfknewron Market” for market and competitor insights, “gfknewron Consumer” for an in-depth consumer understanding and “gfknewron Predict” that delivers recommendations for companies based on market data and AI-powered intelligence.
* European market data include Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, United Kingdom, Greece, Italy, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Russia, Spain, Sweden
U.S. media contact: David Stanton +1 (908) 875-9844; [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, ReportLinker forecasts that the Global IoT Telecom Services Market size is expected to reach $97.9 billion by 2028, rising at a market growth of 31.8% CAGR during the forecast period. IoT protocols and 5G interconnection can broadcast information from thousands of devices to a large number of consumers without slowing communication speed or limiting capacity. The market for IoT telecom services is driven by these factors, which are anticipated to increase in the future. The growth of the IoT telecom services market is primarily driven by the increasing acceptance of technological advancement and innovation, as well as IoT-powered smart security cameras.
Based on connectivity, the IoT telecom services market is segmented into cellular technology, LPWAN, NB-IoT, and RF-based. In 2021, the LPWAN segment garnered a substantial revenue share in the IoT telecom service market. This is due to the widespread acceptance of the IoT telecom service market to strengthen LPWA Network (LPWAN) technologies, which offer a low-cost, low-power wireless option with global reach and robust security. In the telecom industry, machine-to-machine connections are crucial; for this, WiFi and GSM technologies are typically employed.
References:
https://www.gfk.com/press/telecom-global-trends-mwc
Allied Market Research: Global AI in telecom market forecast to reach $38.8 by 2031 with CAGR of 41.4% (from 2022 to 2031)
IDC: Global Telecoms Market at $1.53T in 2020; Meager Growth Forecast