fiber optics
Deutsche Telekom’s fiber optic expansion in 140 of the 179 municipalities within the Gigabit region of Stuttgart
Deutsche Telekom said it has deployed its fiber optic network in more than 140 of the 179 municipalities covered by its agreement with the “gigabit region” of Stuttgart. The German network operator has developed its network in the districts of Boeblingen, Esslingen, Goeppingen, Ludwigsburg and Rems-Murr districts.With ongoing expansion efforts at over 58 construction sites, the company is making significant progress, particularly in nine districts in Stuttgart, according to the statement from the company.
Since 2019, Telekom has accounted for more than 90 percent of the growth in fiber optic infrastructure. As the sole company expanding into both rural and urban areas, Telekom has established itself as a reliable partner, delivering on all construction projects and cooperation agreements, according to the broadband officer of the region and managing director of Gigabit Region Stuttgart (GRS).
In Ludwigsburg and Esslingen alone, Telekom has already been awarded contracts for 76 funding projects. The recent collaboration with Stadtwerke Nuertingen serves as a prime example of Telekom’s cooperative efforts.
Currently, approximately 30,000 households in expansion areas under this partnership can already subscribe to Telekom’s fibre optic connections. The long-term goal is to enable 185,000 households within cooperative areas with municipal utilities to choose their preferred communication provider for fibre optic connections by 2030.
The combined efforts of self-expansion, collaborations, and subsidized projects have granted around 335,000 households throughout the region access to the fibre optic network, Telekom said.
The core focus of the gigabit project is to expand the ultra-fast fiber optic network through strategic partnerships. Currently, 177 municipalities, including Stuttgart and the neighbouring districts of Boeblingen, Esslingen, Goeppingen, Ludwigsburg, and Rems-Murr, are participating in the expansion program.
The project aims to provide 50 percent of households, all companies, and schools with fiber optic connectivity by 2025. By 2030, the target is to achieve 90 percent household coverage. With a population of approximately 2.8 million in the conurbation, other companies in the Stuttgart region are also actively involved in fiber optic expansion initiatives said Telekom.

Telekom includes provisions for rapidly expanding the performance of its 5G network. Presently, almost 95 percent of households can already access 5G in Telekom’s mobile network, while over 99 percent of the population can utilize 4G/LTE connectivity.
Significance of DT Tower Sales:
Deutsche Telekom said proceeds from the sale of its tower business helped reduce net debt excluding leases by over 10 billion euros compared with the end of 2022, to 93 billion euros. The transaction was also the main factor behind the near quadrupling of net profit, to 15.4 billion euros, compared with the same period last year, the company said.
Deutsche Telekom had agreed in July 2022 to sell 51% of its tower business in Germany and Austria to a consortium of Canada’s Brookfield and U.S. private equity firm DigitalBridge after they made a surprise last-minute bid that valued the unit at 17.5 billion euros ($17.5 billion).
References:
Infinera trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project delivered 61.3 Tbps between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia
Infinera has completed a simulated intercity network trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project in Australia. The trial delivered 61.3 Tbps of unregenerated data transmission capacity on a fiber pair over the equivalent of 1,240 route km between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia. The network trial was implemented using Infinera’s 800G-capable ICE6 coherent solution [1.] and Corning Incorporated’s SMF-28® ULL fiber with advanced bend, demonstrating the high-performance capability of the express network, which is part of the intercity fiber network Telstra InfraCo is building across Australia.
Note 1. The sixth-generation Infinite Capacity Engine (ICE6), from Infinera’s Advanced Coherent Optical Engines and Subsystems, is a 1.6 Tb/s optical engine that delivers two independently programmable wavelengths at up to 800 Gb/s each. Utilizing a 7-nm CMOS process node DSP and advanced PIC technology, ICE6 leverages ultra-high baud rates, high modem SNR, and innovative features to break performance and spectral efficiency barriers, including 800G single-wavelength performance over 1000+ km in a commercial network. ICE6 is also beating optical transmission expectations at lower rates, including 600 Gb/s and 400 Gb/s per wavelength.

Image Credit: Infinera
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The trial was performed with real-world configurations, including 1,240 kilometers of ultra-low-loss fiber simulating one of Telstra InfraCo’s planned express Melbourne-Sydney routes. Infinera performed an in-service, non-traffic-impacting upgrade from C-band to combined C-band plus L-band as part of the capacity expansion process. With Infinera’s ICE6 and Corning’s optical fiber, Telstra InfraCo achieved 61.3 Tbps total capacity with 6.2 milliseconds latency across the combined C-band and L-band, with wavelengths up to 700 Gbps.
Telstra InfraCo’s express network is designed to be a high-performance national network for customers who need reliable, ultra-high bandwidth between capital cities and international submarine cable landing stations. For hyperscalers, global cloud providers, content companies, and governments, this means access to scalable high capacity and more direct routes, with optional route redundancy.
“Based on these results, Telstra InfraCo’s express network and overall intercity fiber build will lead the world in scale, low latency, and high data transmission performance rate,” said Kathryn Jones, Fiber Executive at Telstra InfraCo. “The simulation exceeds our expectations, offering almost seven times today’s typical capacity of 8.8 Tbps per fibre pair and validates our selection of Corning’s SMF-28 ULL fiber in the cable design. This will enable Telstra to develop market-leading solutions for our customers today and for years to come – a key element of Telstra’s ambitious T25 strategy and transformation goals.”
“To meet the rigorous demands of a vast network over Australia’s unique terrain, Telstra InfraCo needed fiber infrastructure with advanced bend capability and minimal signal loss to deliver ultra-high cable capacity. That’s why they turned to Corning,” said Sharon Bois, Division Vice President, Product Line and Marketing, Corning Optical Fiber and Cable. “Our SMF-28® ULL fiber with advanced bend is designed to meet exactly those needs.”
“Infinera’s 800G-capable ICE6 solution demonstrated industry-leading performance, maximizing fiber capacity and reach on Telstra InfraCo’s express network configuration,” said Nick Walden, Senior Vice President of Worldwide Sales at Infinera. “This achievement underscores the enhanced performance Infinera’s technology can bring to meet Telstra InfraCo’s express network requirements for bandwidth today and into the future.”
Media Contact:
Anna Vue
Tel. +1 (916) 595-8157
[email protected]
Referencs:
Fiber Build-Out Boom Update: GTT & Ziply Fiber, Infinera in Louisiana, Bluebird Network in Illinois
Frontier Communications fiber build-out boom continues: record number of fiber subscribers added in the 1st quarter of 2023
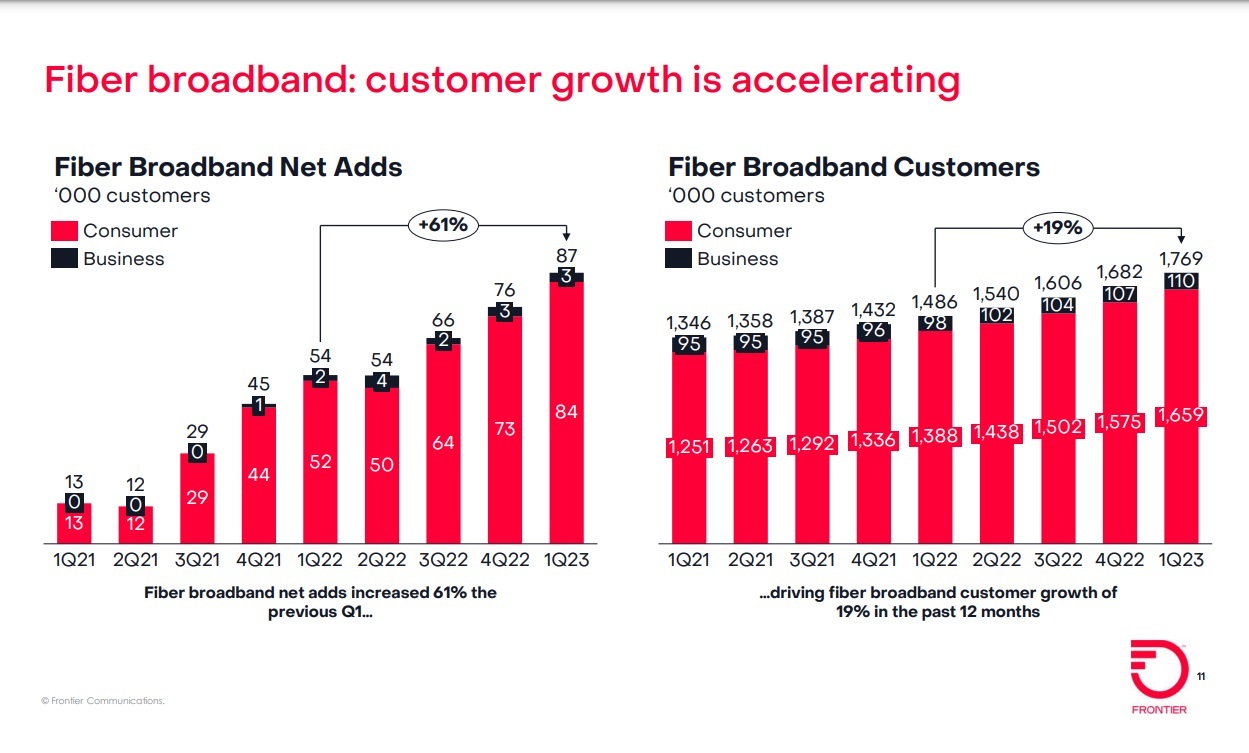
Frontier Communications added record number of fiber broadband customers in the 1st quarter of 2023. The fiber facility based network operator added 87,000 fiber subscribers (including 83,000 residential subs) in the first quarter of 2023, up from +54,000 in the year-ago quarter. Those results beat the 76,000 residential fiber subs Frontier was expected to add in the period. Frontier ended the quarter with 1.76 million fiber customers: 1.65 million residential subscribers and 110,000 business customers.
“We delivered another strong quarter and reached a critical milestone in our transformation. Thanks to our team’s consistent operational performance, we achieved EBITDA growth for the first time in five years,” said Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier.
“We are creating an internet company that people love. Over the last two years, we have rallied around our purpose of Building Gigabit America, invested in fiber, enhanced our product, put the customer at the center of everything we do and made it easier to do business with us. We are quickly becoming an agile, digital infrastructure company, and I’m confident we will return to growth this year.”
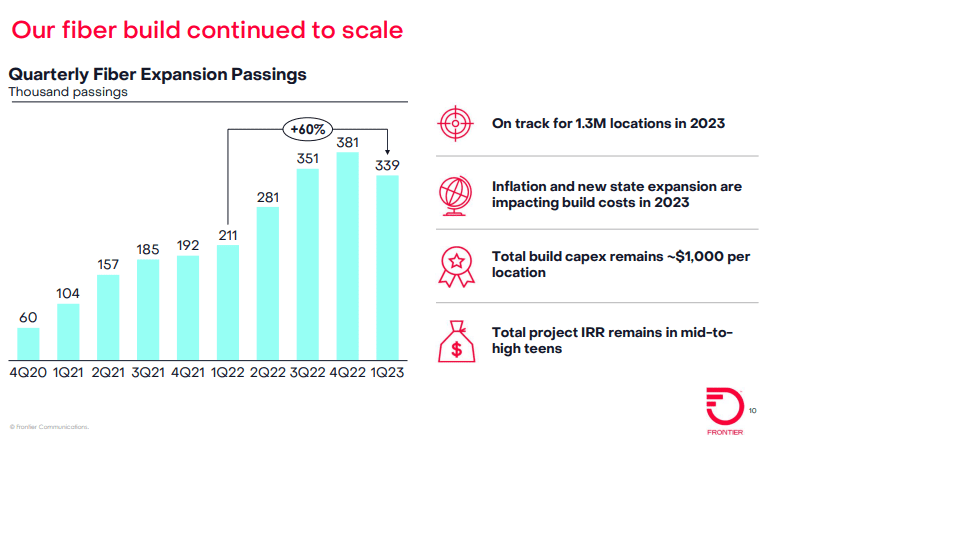
Frontier said it built fiber to an additional 339,000 locations in Q1 2023, up 60% from the 211,000 it built in the year-ago period. Frontier’s Q1 buildout was better than the 300,000 locations expected by the analysts at New Street Research. Frontier ended the quarter with 5.5 million fiber passings and 15.4 million total passings.
First-Quarter 2023 Consolidated Financial Results:
• Revenue of $1.44 billion decreased 0.5% from the first quarter of 2022 as growth in consumer, business and wholesale fiber was more than offset by declines in legacy copper
• Operating income was $143 million and net income was $3 million
• Adjusted EBITDA of $519 million increased 2.0% over the first quarter of 2022 as revenue declines were more than offset by lower content, selling, general and administrative expenses, and cost-saving initiatives
• Adjusted EBITDA margin of 36.0% increased from 35.2% in the first quarter of 2022
• Capital expenditures of $1.15 billion increased from $0.45 billion in the first quarter of 2022 as fiber expansion initiatives accelerated First-Quarter 2023
Consumer Results:
• Consumer revenue of $761 million decreased 1.9% from the first quarter of 2022 as strong growth in fiber broadband was more than offset by declines in legacy copper broadband and voice
• Consumer fiber revenue of $448 million increased 10.1% over the first quarter of 2022 as growth in consumer broadband, voice, and other more than offset declines in video
• Consumer fiber broadband revenue of $298 million increased 17.3% over the first quarter of 2022 driven by growth in fiber broadband customers
• Consumer fiber broadband customer net additions of 84,000 resulted in consumer fiber broadband customer growth of 19.5% from the first quarter of 2022
• Consumer fiber broadband customer churn of 1.20% was roughly flat with churn of 1.19% in the first quarter of 2022
• Consumer fiber broadband ARPU of $61.44 decreased 1.1% from the first quarter of 2022 driven primarily by the autopay and gift-card incentives introduced in the third quarter of 2021 First-Quarter 2023
Business and Wholesale Results:
• Business and wholesale revenue of $657 million decreased 1.4% from the first quarter of 2022 as growth in fiber was more than offset by declines in copper
• Business and wholesale fiber revenue of $281 million increased 6.0% over the first quarter of 2022 as growth in business was partly offset by modest declines in wholesale
• Business fiber broadband customer churn of 1.45% increased from 1.24% in the first quarter of 2022
• Business fiber broadband ARPU of $104.38 decreased 1.2% from the first quarter of 2022
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
While Frontier’s fiber growth engine continues to hum along, the company is dealing with higher costs related to its fiber initiative. The company raised its 2023 capex guidance to a range of $3 billion to $3.2 billion, up from an original outlook of $2.8 billion.
Frontier blamed the increase on a couple of factors – a decision to build inventory opportunistically where it saw supply chains ease a bit in the quarter and higher build costs as it scales its build into new geographies. Frontier is also seeing higher labor costs being driven by general inflation and higher rates as some of its multi-year labor contracts come up for renewal.
The anticipated increase in capex this year concerned investors. Frontier shares were down $2.33 (-10.94%) to $19.13 each in Friday morning trading.
Overall, Frontier expects fiber build costs in 2023 to be in the range of $1,000 to $1,100. But it’s confident that total project build costs will remain at about $1,000 per location as it mixes in lower-cost locations in some new-build states and benefits from aerial builds and an increased focus on multiple dwelling units (MDUs), Frontier CFO Scott Beasley said on Friday’s earnings call.
The current capex picture isn’t expected to impact Frontier’s overall fiber buildout/upgrade plan. “We’re confident that the 10 million locations is still attractive to build out,” Beasley said. Frontier is also continuing to explore an additional 1 million to 2 million additional fiber passings beyond the original 10 million target.
Frontier says it’s too early to tell how this year’s cost headwinds might impact future opportunities coming by way of the $42.5 billion Broadband Equity, Access and Deployment (BEAD) program. New Street Research estimates that there are 1.2 million BEAD-eligible locations in Frontier’s footprint. New Street Research expects ARPU pressure at Frontier to ease in the second quarter of the year and return to growth in the third quarter.
Frontier recently initiated several consumer pricing changes for value-added services that were previously free. Whole-home Wi-Fi, for example, now costs $10 per month, its Home Shield Elite product is now $6 per month extra and the company is now charging $50 for professional installs. Those actions are driving new fiber customer monthly ARPU to a range of $65 to $70, the company said.
Frontier is also speeding up its original cost savings target to $500 million by the end of 2024. Its prior target was $400 million by the end of 2024. Frontier is approaching that target through a range of streamlining and simplification initiatives, including improved field operations, self-service capabilities, the consolidation of call centers and an ongoing reduction in copper infrastructure.
Frontier’s guidance for the full year 2023:
• Adjusted EBITDA of $2.11 – $2.16 billion, unchanged from prior guidance
• Fiber build of 1.3 million new locations, unchanged from prior guidance
• Cash capital expenditures of $3.00 – $3.20 billion, an increase from prior guidance of $2.80 billion, reflecting higher inventory levels and fiber build costs
• Cash taxes of approximately $20 million, unchanged from prior guidance
• Net cash interest payments of approximately $655 million, an increase from prior guidance of $630 million, reflecting the $750 million of debt raised in March 2023
• Pension and OPEB expense of approximately $50 million (net of capitalization), unchanged from prior guidance
• Cash pension and OPEB contributions of approximately $125 million, unchanged from prior guidance
References:
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Frontier Communications adds record fiber broadband customers in Q4 2022
Frontier’s Big Fiber Build-Out Continued in Q3-2022 with 351,000 fiber optic premises added
Frontier Communications sets another fiber buildout record; raises FTTP buildout target for 2022
“Fiber is the future” at Frontier, which added a record 54K fiber broadband customers in 1Q-2022
Frontier’s FTTP to reach 10M locations by 2025; +192,000 FTTP passings in 4Q-2021
Frontier Communications reports added 45,000 fiber broadband subscribers in 4Q-2021 – best in 5 years!
Zayo announces “Waves on Demand,” security enhancements, and network growth
Zayo Group Holdings, Inc (Zayo) today announced a series of expansions and enhancements to its network and services. These include enhanced network protection and an industry-first, on-demand connectivity service, as well as significant growth of its long-haul dark fiber and 400G-enabled routes and modernization of its IP core network. In particular, Zayo plans to build eight new long-haul fiber routes and debuted a new Waves on Demand service for customers looking to rapidly light up added bandwidth. Waves on Demand will initially focus on providing 100G services across eight routes, though a 400G route between Newark, NJ and New York is available. Five additional routes are planned. More details below.
“Yesterday’s network can’t deliver tomorrow’s ideas,” said Andrés Irlando, President of Zayo. “Zayo’s global network provides game-changing performance, scale, security, resilience and value for our customers. Our goal is to revolutionize the industry by constantly improving our network and prioritizing our customers’ needs. Our teams are focused on providing them with the best possible experience.”
Providing an On-Demand Network:
For large bandwidth customers who need data center connectivity quickly and easily, Zayo is launching Waves on Demand to enable same-day turn-up on the most in-demand routes, with significantly shortened delivery times. Zayo will be the only provider to enable customers to provision wavelengths within a day.
This industry-first means customers can quickly provision “Wavelength on Demand” between key data center locations across its market-leading network footprint, including its highest-demand routes. In 2023, Zayo launched 8 new Waves on Demand routes, with 5 additional routes planned for the future.
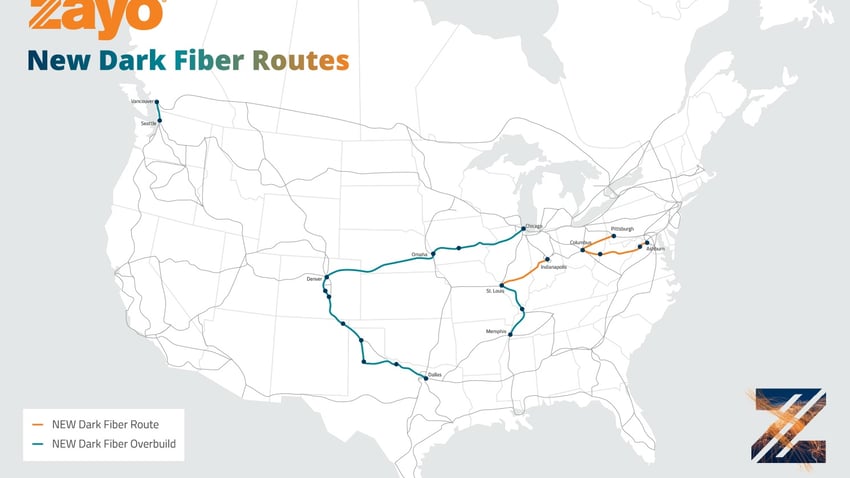
Zayo’s Completed Waves on Demand routes include:
- Newark, NJ – New York, NY (up to 400G)
- Ashburn, VA – New York, NY
- Hillsboro, OR – Seattle, WA
- Ashburn, VA – Newark, NJ
- Atlanta, GA – Dallas, TX
- Los Angeles, CA – San Jose, CA
- Inter-Los Angeles, CA
- Los Angeles, CA – San Jose, CA (alt)
Zayo’s Planned Waves on Demand Routes include:
- Toronto, ON – Chicago, IL
- San Jose, CA – Seattle, WA
- Newark, NJ – Chicago, IL
- Chicago, IL – Secaucus, NJ
- Englewood, FL – Chicago, IL
Chaz Kramer, Zayo’s VP of Product Management, told Fierce that Waves on Demand will cut the time required to add wavelengths from 45 days or more to just hours. said, “80% of our services right now are 100G services at the moment. Our focus is trying to solve the customer requirement for that time lag in terms of service delivery,” he said.
“The only way to stay ahead of the digital curve is to continuously transform. Transformative ideas need a reliable, resilient and on-demand network,” said Bill Long, Chief Product Officer at Zayo. “Zayo is leading the industry with network automation and self-service options, ensuring customers have unprecedented speed and resilience with more flexibility and elasticity, while enhancing security and value, so our customers can focus on making progress toward their business goals instead of worrying about their network.”
Security Enhancements:
Security has never been more important across the tech industry, and beyond. As more and more companies face the realities of route hijacking, Zayo has taken security protection for customers one step further.
In addition to deploying Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) filtering – a component of Mutually Agreed Norms for Routing Security (MANRS) compliance designed to secure the internet’s routing infrastructure – Zayo now requires two-factor authentication process for Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) route management. As one of the first communications infrastructure providers to implement a two-factor authentication process for BGP updates, this will provide improved security for the broader internet community and prevent inadvertent or malicious route hijacks from bad actors.
Network Growth and Modernization
This year Zayo began IP Core upgrades to support 400G connectivity, providing better routing performance, stability, high bandwidth and reduced pricing for customers. Zayo has partnered with Juniper Networks®, a global leader in IP networking, cloud and connected security solutions for next-gen IP Core connectivity.
“Juniper Networks is dedicated to delivering state-of-the-art solutions, including systems optimized for our customers’ current and future core throughput demands. We are pleased to partner with Zayo as they construct and fortify their next-generation IP Core network, equipped with 400G,” said Sally Bament, Vice President of Service Provider Marketing at Juniper Networks. “By employing Juniper’s core routers, Zayo can ensure their customers enjoy high-speed bandwidth services that can support growing performance and capacity demands of end users.”
The Growth of Zayo’s Network:
- In 2022, Zayo added 5,200 route miles to its network, resulting in more than 1.35M fiber miles.
- Zayo now has 224 400G-enabled wavelength points of presence (PoPs) and 145 100G-enabled PoPs.
- Zayo deployed 24 long-haul waves routes in 2022 with 926TB of wavelength capacity, enabling 400G services across these routes, spanning more than 20,000 route miles. In 2023, Zayo will exceed the number of new Long Haul Dark Fiber routes deployed in 2022.
- Zayo will complete 8 long-haul construction projects in 2023, totaling 2,951 route miles and 708,000 fiber miles.
- Zayo is estimated to complete 32 400G routes in 2023 with 14 completed in the first half of the year.
Zayo’s 2023 planned new and augmented dark fiber routes:
- New – St. Louis, MO to Indianapolis, IN
- Overbuild – Denver, CO to Dallas, TX
- Overbuild – Chicago, IL to Omaha, NE
- Overbuild – Omaha, NE to Denver, CO
- Overbuild – Seattle, WA to Vancouver, WA
- New – Columbus, OH to Pittsburgh, PA
- Overbuild – St. Louis, MO to Memphis, TN
- New – Columbus, OH to Ashburn, VA
Zayo’s New Tier 1 400G Routes:
- Albany, NY – Newark, NJ
- Bend, OR – Umatilla, OR
- Chicago, IL – Cleveland, OH
- Albany, NY – Boston, MA
- Atlanta, GA – Washington, DC
- Dallas, TX – St. Louis, MO
- Denver, CO – Dallas, TX
- Kansas City, MO – Indianapolis, IN
- Las Vegas, NV – Phoenix, AZ
- Montreal, QC (Canada) – Quebec City, QC (Canada)
- Columbus, OH – Ashburn, VA
- Columbus, OH – Cleveland, OH
- Columbus, OH – Pittsburg, PA
- Chicago, IL – Clinton, KY
- Clinton, KY – Ponchatoula, LA
- Toronto, ON (Canada) – Waterloo, ON (Canada) (Crosslake)
- Toronto, ON (Canada) – Montreal, QC (South) (Canada)
- Toronto, ON (Canada) – Montreal, QC (North) (Canada)
- Indianapolis, IN – Columbus, OH
- Ashburn, VA – Baltimore, MD
- Salt Lake City, UT – Seattle, WA
- Los Angeles, CA – San Jose, CA
Additional tier 2 and 3 routes will also be added throughout 2023, totaling 32 new routes.
“We believe that technology plays a critical role in preparing students for the future. We chose Zayo’s future-ready network because of its resilience and performance,” said Dr. Thomas Weeks, Chief Technology Officer at Hillsborough County Public Schools. “We trust Zayo because they invest in their world-class network. The Zayo team worked with us to tailor a solution that met the unique needs of our school district and enhances our effectiveness to help students and staff achieve.”
Enhancing Service Delivery and Customer Experience:
Zayo has also set out to change the trajectory of customer experience. Zayo optimized its service delivery with rebuilt processes that utilize automation to make working with Zayo easier for customers. Since implementing these changes, Zayo had its largest install quarter in history in Q4 2022.
To learn more about Zayo’s network and how it can help you connect what’s next, please visit https://www.zayo.com/info/network-expansion/
About Zayo Group Holdings, Inc:
For more than 15 years, Zayo has empowered some of the world’s largest and most innovative companies to connect what’s next for their business. Zayo’s future-ready network spans over 16 million fiber miles and 139,000 route miles. Zayo’s tailored connectivity and edge solutions enable carriers, cloud providers, data centers, schools, and enterprises to deliver exceptional experiences, from core to cloud to edge. Discover how Zayo connects what’s next at www.zayo.com and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter.
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/zayo-slashes-time-turn-bandwidth-waves-demand
Zayo to deploy 400G b/s network across North America and Western Europe
Digital Realty & Zayo plan next gen fiber interconnection and security capabilities
Telekom Malaysia Berhad launches fiber optic network hub
Telekom Malaysia Berhad (TM) [1.] announced the completion of its new fiber optic network hub or point of presence (PoP) project phase one installations, across northern region, Sabah and Sarawak.
Note 1. Telekom Malaysia Berhad (TM) is a Malaysian telecommunications company founded in 1984. Beginning as the national telecommunications company for fixed line, radio, and television broadcasting services, it has evolved to become the country’s largest provider of broadband services, data, fixed line, pay television, and network services.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The launch ceremony, which was officiated by YB Fahmi Fadzil, Minister of Communications and Digital, took place at SMK Padang Terap, Kuala Nerang, Kedah. Also present were Dato’ Haji Pkharuddin Bin Haji Ghazali, Director-General of Education and Dato’ Sri Haji Mohammad Bin Mentek, Secretary-General, Ministry of Communications and Digital.
PoP is the location where different devices connect to each other and to the internet. In simple terms, PoP brings fiber optics closer to users. By setting up PoP locations near schools, people in rural and remote areas can get better and faster internet services in their homes, instead of relying on mobile internet. This will improve internet access and connectivity for more people in the community.
During the ceremony, YB Fahmi highlighted the significant benefits and opportunities that the new PoPs would bring. The new PoPs represent a major step forward in the Government’s efforts to narrow the digital gap and promote digital inclusion across Malaysia.
A total of 4,370 PoPs had been planned under the 12th Malaysia Plan (12MP) where 4,323 PoPs will be installed near rural schools and 47 PoPs near industrial area.
Phase one of the project, involves 677 sites. The remaining will be implemented under phase two over the span of three years, 2022-2025. A total of 233 PoP circuits were installed under phase 1, with 100% completion achieved by TM, ahead of other industry players.
“We are thrilled to see the progress and achievements of this project, which will bring significant benefits and opportunities to the community, including improved internet quality, economic development and the development of new infrastructures,” said Shazurawati Abdul Karim, Executive Vice President of TM One.
The PoP will create a more balanced and inclusive regional development, boosting the growth of new technologies like 5G and future generations of communication technologies. Through this initiative, users in TM’s PoP area have now reached over 9,000 and are increasing. A total of 58 of its users are schools that have subscribed to Unifi services. The widespread internet accessibility will not only help to develop the rural economy but more importantly allow learning materials to be downloaded, to improve the quality of education in schools, equipping the future generations with a wealth of knowledge.
“As the nation’s telecommunications leader, and enabler of Digital Malaysia, TM is committed to support the nation’s development agenda through the benefits brought by hyperconnectivity and digital solutions, which will accelerate digital adoption and new economic growth,” added Shazurawati.
“The presence of PoP can attract technology companies, start-ups and other businesses that require a high-speed internet connection to operate. This can create more job opportunities, increase innovation, and stimulate economic growth in local communities,” Shazurawati concluded.
The collaboration between TM and the Government demonstrates the shared commitment to deliver digital inclusivity throughout Malaysia. For phase two of PoP project, TM has been awarded with 174 sites in the central region. This phase is expected to further boost digital connectivity and economic development for Malaysia.
The extensive internet access that PoP provides will not only enhance the rural economy but also enable the download of educational materials, elevating the quality of education in schools and equipping the younger generation with a vast range of knowledge.
References:
https://www.tm.com.my/news/TM%E2%80%99S%20NEW%20FIBRE%20OPTIC%20NETWORK%20HUB
Telekom Malaysia Completes Fibre Optic Network Hub Across Sabah and Sarawak
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
Frontier Communications Parent, Inc. (“Frontier”) reported impressive 4th quarter and full-year 2022 results today. The fiber facilities based carrier added a record 76,000 fiber subs in the last quarter, more than two times what it added in the year-ago quarter. The bulk of those fiber subscriber gains are coming from cable competitors, execs said.
Frontier ended 2022 with 1.7 million fiber customers, a figure that represents the majority of its total base of 2.8 million broadband subs. Frontier also built out a record 381,000 new fiber locations in Q4, ending 2022 with 5.2 million fiber locations. That gets Frontier past the halfway point toward a goal of building fiber-to-the-premises to 10 million locations by 2025.
Total revenues were down year-over-year, but consumer fiber revenues rose 7.7% to $436 million versus the prior year period, offsetting declines in video. Consumer fiber broadband revenues surged 15.5%, to $283 million.
“We ended the year strong with another quarter of record operational results. We now have the fiber engine we need to power our growing digital infrastructure business. This is how we advance our purpose of Building Gigabit America,” said Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier.
“This year, we will accelerate our fiber build and give customers more reasons to choose the un-cable provider. The team is fired up and ready to return to growth in 2023.”
Frontier expects to accelerate its fiber build to 1.3 million homes in 2023 – about 20% faster than its 2022 pace – and end the year with 6.5 million fiber locations. Frontier is also exploring fiber builds beyond its initial goal of 10 million. The company has identified 1 million to 2 million copper locations where it can upgrade to fiber cost-effectively. There’s another 3 million to 4 million locations in its footprint that remain financially unattractive but could get over the hump with government subsidies or partnerships.
Even with its faster build pace, Frontier expects 2023 capital expenditures to reach $2.8 billion, essentially flat versus 2022’s $2.74 billion. Frontier anticipates its fiber buildout costs will stay in its envelope of $900 to $1,000 per location passed.
Frontier believes it’s set to grow its average revenue per user (ARPU) by 2% to 3% in 2023. Tied in, it’s updating its pricing and looking to upsell customers to higher speeds (more than half of new subs are choosing speeds of 1-Gig or more) while also reducing its reliance on perks such as gift cards.

Source: Frontier Q4 2022 earnings presentation
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
On the wholesale side, Frontier has fiber tower deals with AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile and recently inked an expanded deal with AT&T to connect it to Frontier’s central offices. Company President and CEO Nick Jeffery suggested that the same model could apply to the likes of Amazon, Microsoft and other cloud companies that are distributing data and could make use of cache locations where data is being consumed.
But that handwork with wireless network operators has yet to drive Frontier toward deals that could enable it to add mobile services to the bundle, and follow the path being taken by major cable operators such as Comcast and Charter Communications.
Jeffery reiterated a position that Frontier is keeping close watch on potential MVNO partnerships but that no such agreement is imminent. Such a deal could be a “distraction of our capital,” he said.
“For the moment, we don’t see the need to launch with an MVNO and bundle with our core broadband offer,” Jeffery explained. “We think it’s something we could spin up relatively quickly and efficiently if we needed to.”
Full-Year 2022 Highlights:
- Built fiber to 1.2 million locations, bringing total fiber passings to 5.2 million by the end of 2022 – more than halfway to our target of 10 million fiber locations.
- Added a record 250,000 fiber broadband customer net additions, resulting in fiber broadband customer growth of 17.5% from 2021.
- Revenue of $5.79 billion, net income of $441 million, and Adjusted EBITDA of $2.08 billion.
- Capital expenditures of $2.74 billion, including $1.52 billion of non-subsidy-related build capital expenditures and $0.06 billion of subsidy-related build capital expenditures.
- Surpassed our $250 million gross annualized cost savings target more than one year ahead of plan and raised our target to $400 million by the end of 2024.
4th-Quarter 2022 Highlights:
- Built fiber to a record 381,000 locations
- Added a record 76,000 fiber broadband customers
- Revenue of $1.44 billion, net income of $155 million, and Adjusted EBITDA of $528 million
- Capital expenditures of $878 million, including $517 million of non-subsidy-related build capital expenditures and $33 million of subsidy-related build capital expenditures
- Net cash from operations of $360 million, driven by strong operating performance and increased focus on working capital management
- Achieved annualized run-rate cost savings of $336 million
4th-Quarter 2022 Consolidated Financial Results:
- Frontier reported revenue for the quarter ended December 31, 2022, of $1.44 billion, a 6.9% decline compared with the quarter ended December 31, 2021, as growth in consumer, business and wholesale fiber was more than offset by declines in copper and subsidy.
- Revenue growth was negatively impacted by the expiration of CAF II funding at the end of the fourth quarter of 2021.
- Excluding subsidy-related revenue, revenue for the quarter ended December 31, 2022, declined 2.5% compared with the quarter ended December 31, 2021, an improvement in the year-over-year rate of decline reported for the quarter ended September 30, 2022.
- Fourth-quarter 2022 operating income was $136 million and net income was $155 million.
- Capital expenditures were $878 million, an increase from $559 million in the fourth quarter of 2021, as fiber expansion initiatives accelerated.
4th-Quarter 2022 Consumer Results:
- Consumer revenue of $764 million declined 2.3% from the fourth quarter of 2021, as strong growth in fiber broadband was more than offset by declines in legacy video and voice.
- Consumer fiber revenue of $436 million increased 7.7% over the fourth quarter of 2021, as growth in consumer broadband, voice, and other more than offset declines in video.
- Consumer fiber broadband revenue of $283 million increased 15.5% over the fourth quarter of 2021, driven by growth in fiber broadband customers.
- Consumer fiber broadband customer net additions of 73,000 resulted in consumer fiber broadband customer growth of 17.9% from the fourth quarter of 2021.
- Consumer fiber broadband customer churn of 1.32% was flat with the fourth quarter of 2021.
- Consumer fiber broadband ARPU of $61.20 declined 1.6% from the fourth quarter of 2021, as price increases and speed upgrades were more than offset by the autopay and gift-card incentives introduced in the third quarter of 2021.
- Excluding the impact of gift-card incentives, consumer fiber broadband ARPU increased 0.9% over the fourth quarter of 2021.
4th-Quarter 2022 Business and Wholesale Results:
- Business and wholesale revenue of $659 million declined 2.6% from the fourth quarter of 2021, as growth in our fiber footprint was more than offset by declines in our copper footprint.
- Business and wholesale fiber revenue of $285 million increased 5.5% over the fourth quarter of 2021, driven by growth in both business and wholesale.
- Business fiber broadband customer churn of 1.33% increased from 1.23% in the fourth quarter of 2021.
- Business fiber broadband ARPU of $107.68 increased 0.8% from the fourth quarter of 2021.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, Frontier introduced its Fiber Innovation Labs yesterday – National Innovation Day – designed for inventing and testing new patents, technologies and processes that will advance its fiber-optic network. Improving the customer experience and driving efficiencies are key to accelerating Frontier’s fiber-first strategy. Frontier’s labs serve as a testing ground to find new technologies and procedures to advance the way it delivers blazing-fast fiber internet to consumers and businesses across the country.
“The work we are doing in our Fiber Innovation Labs will change the way we serve our customers and will ultimately change the industry,” said Veronica Bloodworth, Frontier’s Chief Network Officer. “We have the best team in the business – they live and breathe innovation. They have been awarded several patents and are in the process of bringing those new inventions to life to deliver the best ‘un-cable’ internet experience to our customers. Be prepared to be amazed.”
As part of Frontier’s Fiber Innovation Labs, the company has launched its first-ever outside plant facility in Lewisville, Texas. The facility is designed as a miniature suburban neighborhood that mimics the real-life experiences of its techs serving customers every day. It features roads, sidewalks, a state-of-the-art central office, a small house and a reconstructed manhole system. It also simulates weather elements and temperature changes. Here, the Frontier team can test and learn new methods in real-world environments to install and maintain its fiber-optic network.
References:
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
\
BT’s CEO: Openreach Fiber Network is an “unstoppable machine” reaching 9.6M UK premises now; 25M by end of 2026
BT’s chief executive said its broadband network is now an “unstoppable machine” that will ultimately “end in tears” for many of its fiber optic competitors. “There is only going to be one national network,” Philip Jansen told the Financial Times. “Why do you need to have multiple providers?” BT said on Thursday that its networking division Openreach had laid fiber to 9.6M premises, with 29% of people in those areas opting to move over to its fiber optic connectivity offering.
BT has long provided the main wholesale network in Britain, giving access to TalkTalk and Sky among other OTT players. BT is ploughing billions of pounds into its network, extending its fiber offerings to 25M premises by end of 2026.
Competitors to Openreach, backed by billions in private capital, are racing to lay full fiber across the UK before the incumbent gets there. They include Virgin Media O2 and more than 100 alternative networks known as “altnets.”

Virgin Media O2 is seeking to upgrade its network to fiber by 2028 and has formed a joint venture between its owners, Spain’s Telefónica and Liberty Global, as well as infrastructure fund Infravia, to lay fiber to an additional 7M premises across the UK and offer wholesale access to other broadband providers. That’s in areas not already covered by the existing Virgin Media network. Industry insiders say network operators need to sign up about 40% of customers in any given location where they are building to make their business viable.
“Building is irrelevant — it’s how many people you’ve got on the network,” Jansen said. “No one else has got a machine anywhere near ours. It’s . . . unstoppable.” He said that the market would probably shake out to be just a “couple of big players” as well as a smattering of specialist providers for things like rural areas and multi-occupancy buildings — a process that would “end in tears” for many of the other operators. Jansen added that while BT had been spending large amounts of cash this year to fund its build efforts, once the construction phase ends he hopes the company will generate “a lot more cash” and could increase the dividend offered to shareholders.
“BT was on the back foot five years ago, we’re unquestionably on the front foot now,” he added. “Investors who own the company need a return.” BT maintained its full-year outlook on Thursday as it posted third-quarter revenue and earnings in line with analysts’ expectations. Revenue fell 3% in the third quarter compared with the same period in the previous year, to £5.2bn, which it attributed in part to lower sales in its global division and a loss of income from BT Sport following the completion of a joint venture with Warner Bros Discovery.
In November BT announced that it would increase its cost-savings target by £500mn to £3bn by 2025 as it sought to mitigate higher energy and inflation costs. As part of the cost-cutting drive, Jansen said there would be fewer people working at BT over the next five years, although he refused to be drawn on numbers. BT has already reduced its net headcount by 2,000 over the past two years, despite significant recruitment at Openreach. It has pushed ahead with inflation-linked price rises in 2023 for the majority of its consumer and wholesale customers in spite of cross-party calls for telecoms companies to reverse the decision during a cost of living crisis. “Right now the [capital expenditure] has to be paid for somehow,” Jansen said. “Hopefully inflation comes down and it won’t be so painful for everyone.”
References:
https://www.ft.com/content/031dcf72-dfaf-4e90-85d2-335ef703dbd1
Openreach on benefit of FTTP in UK; Full Fiber rollouts increasing
Super fast broadband boosts UK business; Calls to break up BT & sell Openreach
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
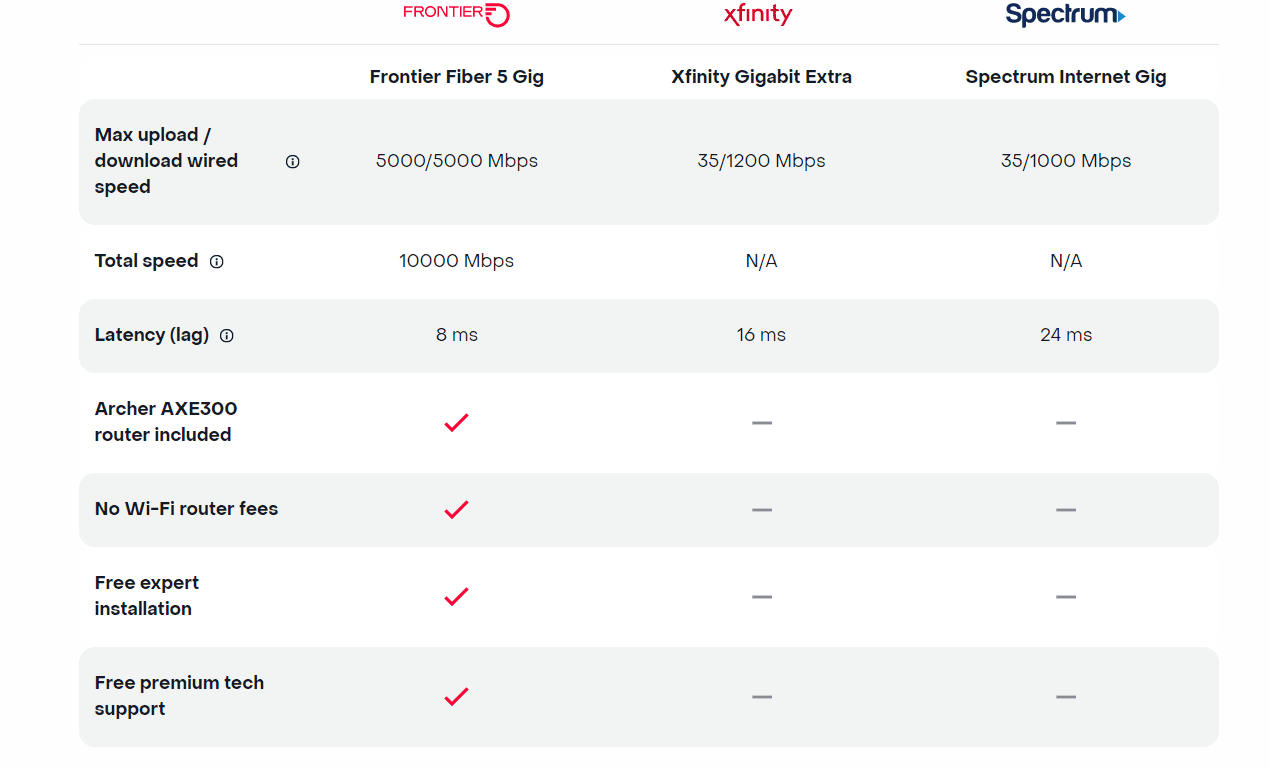
Today, Frontier Communications launched the nation’s only network-wide 5 Gig fiber internet service. With the launch of 5 Gig, Frontier will provide customers across its 25 state fiber network – not just select markets – the opportunity to sign up for the new premium service with blazing-fast speeds. The company says that 5 Gig internet has 125x faster upload speeds, 5x faster download speeds and 2.5x less latency than cablecos [1.], but they don’t specify the cable network speeds or latency.
Note 1. Comcast currently offers 1 and 2 Gig Internet. The company announced a successful trial of the world’s first live, multigigabit symmetrical Internet connection powered by 10 Gbps and Full Duplex DOCSIS 4.0 last December. Charter Communications is also planning a DOCSIS 4.0 upgrade to deliver download speeds of 5 Gbps and 10 Gbps over the coming years, but isn’t currently planning to bring symmetrical service offerings to market.
Frontier’s 5 Gig fiber internet service enables customers to run multiple connected devices at their fastest possible speeds. This means:
- Symmetrical download and upload speeds at up to 5 gigabits per second
- 125x faster upload speed than cable
- 1.6 seconds to download Adobe Photoshop on PC (1GB)
- <36 seconds to download a House of Dragons episode in 4K (22 GB)
- <2 minutes to download a 100-minute 8K movie (67 GB)
- 99.9% network reliability
The 5 Gig internet offer starts at $154.99 a month with autopay and includes uncapped data + Wi-Fi router + free installation + premium tech support. There are no additional Wi-Fi or router fees, no data caps or overage charges. The inclusion of a Archer AXE300 Wi-Fi 6E router is a major advantage, because most installed WiFi routers are WiFi 5= IEEE 802.11ac which won’t support giga bit speeds.
Frontier also dropped the price of its 2-gig internet service, which debuted in February 2022 at a cost of $149.99 per month. That service is now priced at $109.99 per month.
New Street Research stated that Frontier’s 5-gig rollout will “help establish Frontier as a leader in network capabilities and drive the message that this is a new Frontier.” The analysts added, “It also helps drive the message that they are delivering a product that Cable can’t.” Furthermore, New Street noted the move could contribute to growth in average revenue per user (ARPU) given the price drop for the 2-gig plan could “drive some incremental demand for that too.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
On Frontier’s Q3 2022 earnings call, CEO Nick Jeffrey noted 45% to 50% of new customers were taking its 1 Gbps and 2 Gbps plans. Among its installed base, uptake of 1-gig or faster speeds stood at 15% to 20%. That was up sequentially from 10% to 15% in Q2, Jeffrey said at the time.
Frontier is set to report Q4 2022 earnings on February 24th. In a 4Q 2022 earnings preview, the ISP disclosed it added 75,000 new fiber customers and 8,000 total broadband subscribers in the quarter. That was 17% more fiber broadband customers than it had at the end of 2021. For the fifth consecutive quarter, fiber broadband customer additions outpaced copper broadband customer losses, resulting in 8,000 total broadband customer net additions in the fourth quarter of 2022.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Other Competition:
AT&T, Altice USA, Lumen Technologies and Ziply Fiber all already provide symmetrical speeds of 5 Gbps or faster. And Google Fiber has announced plans to debut 5-gig and 8-gig plans early this year. But Frontier claimed it is the only operator thus far to roll out such speeds networkwide.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About Frontier Communications:
Frontier is a leading communications provider offering gigabit speeds to empower and connect millions of consumers and businesses in 25 states. It is building critical digital infrastructure across the country with its fiber-optic network and cloud-based solutions, enabling connections today and future proofing for tomorrow. Rallied around a single purpose, Building Gigabit America™, the company is focused on supporting a digital society, closing the digital divide, and working toward a more sustainable environment. Frontier is preparing today for a better tomorrow. Visit frontier.com.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Media Contact:
Chrissy Murray, VP, Corporate Communications
+1 504-952-4225 [email protected]
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://frontier.com/shop/internet/fiber-internet/5-gig
Frontier Communications adds record fiber broadband customers in Q4 2022
Frontier Communications sets another fiber buildout record; raises FTTP buildout target for 2022
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport market to hit $17B by 2027; Lumen Technologies 400G wavelength market
According to a recent forecast report by Dell’Oro Group, the Optical Transport equipment demand is forecast to increase at a 3 percent compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) for the next five years, reaching $17 billion by 2027. The cumulative revenue during that five year period is expected to be $81 billion.
“We expect annual growth rates to fluctuate in the near term before stabilizing to a more typical 3 percent growth rate,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “There is still a large amount of market uncertainty this year due to the economic backdrop—economists are predicting a high chance of a recession in North America and Europe. However, at the same time, most optical systems equipment manufacturers are reporting record levels of order backlog entering the year, and we expect that most of this backlog could convert to revenue when component supply improves this year,” added Yu.
Additional highlights from the Optical Transport 5-Year January 2023 Forecast Report:
- Optical Transport market expected to increase in 2023 due to improving component supply.
- WDM Metro market growth rates in next five years are projected to be lower than historic averages due to the growing use of IP-over-DWDM.
- DWDM Long Haul market is forecast to grow at a five-year CAGR of 5 percent.
- Coherent wavelength shipments on WDM systems forecast to grow at 11 percent CAGR, reaching 1.2 million annual shipments by 2027.
- Installation of 400 Gbps wavelengths expected to dominate for most of forecast period.
About the Report
The Dell’Oro Group Optical Transport 5-Year Forecast Report offers a complete overview of the Optical Transport industry with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, unit shipments, wavelength shipments (by speed up to 1.2+ Tbps). The report tracks DWDM long haul, WDM metro, multiservice multiplexers, optical switch, Disaggregated WDM, DCI, and ZR Optics.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Lumen Technologies is expanding its 400G wavelength network across North America. Lumen said it has now deployed the network in 70 markets. More than 240 data centers have access to Lumen’s 400G Wavelength Services, and the network has over 800 Tbit/s of capacity.
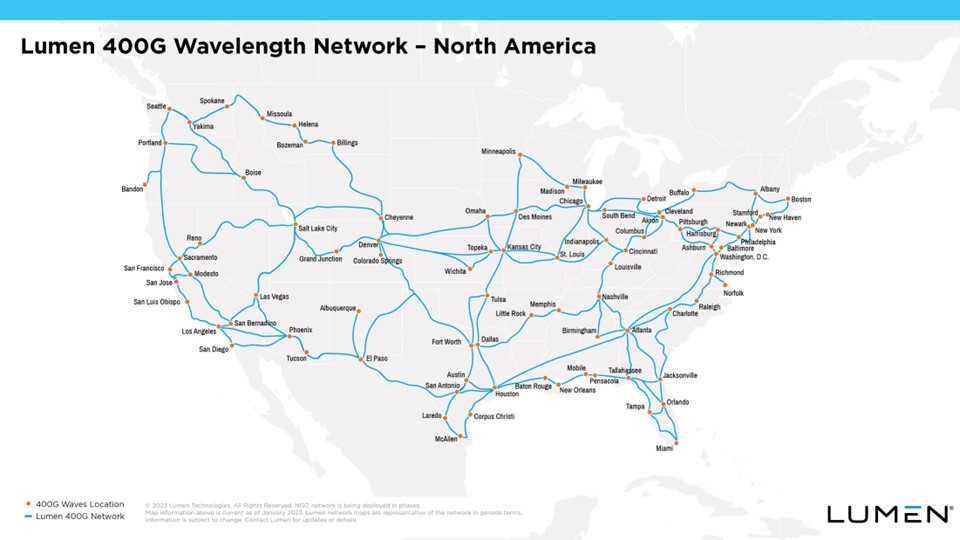
Lumen said it plans to continue its intercity 400G expansion this year, pushing the network “deeper into the metro edge.” The company noted that wavelength services will assist customers in moving workloads to the cloud, and provide private, dedicated connections.
Enterprise customers can also examine network options, plan out their wavelengths and get cost estimates with Lumen’s Topology Viewer.
References:
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/lumen-kicks-up-its-400g-offering-across-the-us-301730126.html
Fiber Build-Out Boom Update: GTT & Ziply Fiber, Infinera in Louisiana, Bluebird Network in Illinois
This week GTT Communications, Infinera, and Bluebird Network all announced network expansions within the U.S. The various announcements follow AT&T’s deal last month with venture capital firm BlackRock to deploy a multi-gigabit fiber network to 1.5 million customer locations using a commercial open access platform.
GTT Communications, Inc., a leading global provider of managed network and security services to multinational organizations, has announced that it has expanded its partnership with Ziply Fiber, a provider of fiber networks purpose-built for the internet, to establish a new network Point of Presence (PoP) to serve the fast-growing data center market in Portland, Oregon. The two companies linked in hopes to “serve the fast-growing data center market” in the city, according to the announcement.
The new PoP is providing an initial 400G of capacity to customers in the U.S. Pacific Northwest region and will expand the power of GTT’s global Tier 1 IP network by offering an additional option for customers to connect in 11 major data centers and the Hillsboro subsea cable landing station, expanding the reach of GTT via Ziply Fiber’s high-count Silicon Forest fiber cross connection service.
“We are pleased to expand our partnership with GTT to establish a new network PoP in Portland to help customers in the region and beyond to connect to area data centers as well as other geographies,” said Mike Daniel, vice president of Enterprise Sales at Ziply Fiber. “Our regional fiber network, combined with GTT’s global Tier 1 network and suite of leading managed networking and security services, will give enterprises new options to improve connectivity securely and reliably.”
GTT’s global Tier 1 IP backbone is ranked among the largest in the industry1 and connects more than 260 cities on six continents. With the addition of the new Portland PoP, GTT customers in the region can benefit from the improved connectivity, security and scalability available through GTT’s suite of managed connectivity services.
Ziply Fiber’s network was architected to meet today’s increasing digital demands and was engineered to be fully redundant, with a dual infrastructure that maintains customer connections even when issues arise. Ziply Fiber maintains a four-state footprint in Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana and has built redundancies into its network to avoid service interruptions, while updating routing to steer clear of congestion across the broader internet. This ensures content is accessible directly on the fiber backbone and can be accessed more quickly.
“This new PoP deployment creates an exciting opportunity to use the Ziply Fiber network to allow our regional data center customers to easily connect to and take advantage of GTT’s global Tier 1 IP network and our full suite of managed services offerings,” said Jim Delis, president, Americas Division, GTT. “Our work with Ziply Fiber demonstrates GTT’s continued focus on investment to expand the reach of our network for customers with locations in the Pacific Northwest.”
GTT will offer additional customer options to connect in 11 data centers and the Hillsboro subsea cable landing station. Jim Delis, president for GTT’s Americas Division, stated the PoP deployment will enable the network provider’s data center customers to link into its tier-one IP network.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Infinera announced today that the Louisiana Board of Regents, acting on behalf of the statewide Louisiana Optical Network Infrastructure (LONI) and the Board of Supervisors of Louisiana State University (LSU) and Agricultural and Mechanical College, has selected and deployed Infinera’s advanced coherent optical networking solutions to upgrade LONI. Also announced today is the initial deployment of four 400G optical channels along a 220-mile intrastate route in Louisiana.
LONI connects 38 university campuses and data centers and provides connectivity to additional research and education networks in other states. The solution, which increases LONI’s network capacity by a factor of 10, comprises Infinera’s XTM Series open line system and GX Series transponders. The upgraded network expands the ability for the research and education community to share and access information, resources, and remote instruments in real time.
LONI promotes scientific computing and technology across Louisiana and is the backbone infrastructure to the state’s heroic research efforts. These efforts are made possible by utilizing cutting-edge technology to push the limits of scientific discovery at leading university campuses and achievable with LONI’s high-bandwidth optical network. Infinera’s XTM Series line system coupled with GX Series high-performance transponders equips LONI with a 200G/400G/600G solution that offers unmatched high-bandwidth services to its customers today and is scalable to 800G in the future. Infinera’s combined solution delivers superior performance, increasing LONI’s service offering with more bandwidth, greater flexibility, and faster data transfer capabilities.
“A high-capacity state-of-the-art network is critical to enabling breakthrough discoveries that can only be achieved through multi-site collaboration and cloud connectivity,” said Lonnie Leger, LONI’s Executive Director. “We are committed to offering our members up to 100G and deploying Infinera’s innovative solutions, which exceeded both our expectations and commitment, enabling us to exceed what other state universities can offer.”
“LONI operates with a small staff, which requires a highly automated network and cost-effective solution that enables them to meet their bandwidth growth requirements,” said Nick Walden, Senior Vice President, Worldwide Sales, Infinera. “The Infinera team worked closely with LONI to deliver a solution that met their needs now and positions them to meet future bandwidth needs with minimal maintenance and manpower to operate.”
“As bandwidth continues its relentless growth driven by new high-speed applications such as 5G, [augmented reality], [virtual reality], and cloud services, legacy copper-based networks – such as DSL and cable – are simply not capable [of] meeting the bandwidth requirements,” Robert Shore, SVP of marketing at Infinera, told SDxCentral.
Shore added that the current fiber boom “reinforces Infinera’s focus on continuing to innovate and manufacture optical transport solutions that can help network operators effectively leverage their fiber deployments from the core of their network all the way to the very edge.”
Infinera also announced that its ICE6 solution was deployed along the trans-Pacific Unity Submarine Cable System connecting Japan and the U.S., doubling the capacity of that connection.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Bluebird Network completed a 126-mile fiber buildout in Illinois. The route connects the towns of Aurora, Dixon, DeKalb, Sterling, and Rock Falls to Bluebird’s network and services, and provides a “diverse route” to Chicago, the company stated.
Bluebird’s management noted the deployment builds on its recently acquired middle-mile fiber network assets from Missouri Telecom, and expansion into Salina, Kansas, and Waterloo, Iowa.
“Bluebird has no plans to slow down its fiber expansions any time soon,” Bluebird Network President and CEO Michael Morey stated in the release tied to its Kansas and Iowa expansion. “To foster even more growth and strengthen connectivity for businesses in the Midwest, we have builds underway for additional expansions coming online this summer.”
Those moves come on the heels of the AT&T/BlackRock JV that is looking to deploy fiber to more than 30 million locations within AT&T’s 21-state wireline footprint by the end of 2025, and positions the newly created Gigapower entity to boost its reach outside of those initial 21 states.
The deal also prompted a predication from Analysys Mason, saying the move further indicates “that the [U.S.] wireline market is entering a period of profound transformation that will leave it more aligned with the market structures seen in Europe.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/us-fiber-build-booms/2023/01/
AT&T and BlackRock’s Gigapower fiber JV may alter the U.S. broadband landscape