fiber optics
Analysts: Combined ADTRAN & ADVA will be a “niche player”
ADTRAN is positioning its acquisition of ADVA as building a complementary combination of assets that can better capitalize on what it sees as an unprecedented investment cycle in fiber. However, analysts argue that the new combined company would still be just a “niche player” in the market.
On Monday, ADTRAN wrote in an email to this author (and many others):
ADTRAN has entered into a business combination agreement with ADVA, a Germany-based global leader in business ethernet, metro WDM, Data Center Interconnect and network synchronization solutions, to combine our two companies.We believe our combination will create many opportunities to better serve end-to-end fiber networking solutions spanning metro edge, aggregation, access and subscriber connectivity. Additionally, we anticipate that by utilizing our collective world-class R&D teams, we will be better positioned to accelerate innovation and offer differentiated solutions.Going forward, it will be business as usual and all existing customer, partner and supplier relationships will remain intact. Until we receive all required regulatory approvals and close the transaction, ADVA and ADTRAN will continue to operate as separate companies. As we integrate the two companies, we will be focused on the best ways to offer our enhanced value proposition and partner with you.
Highlights of the Deal:
- Combination expands product offering and strengthens position as a global fiber networking innovation leader with combined revenue of $1.2B
- Highly complementary businesses create a global, scaled end-to-end provider to better serve customers with differentiated fiber networking solutions, spanning metro edge, aggregation, access and subscriber connectivity
- Creates a stronger and more-profitable company, poised to benefit from the unprecedented investment cycle in fiber, an expanded market opportunity and increased scale
- Meaningful value creation with over $50 million in annual run-rate cost synergies
- All-stock transaction with ADTRAN shareholders to own approximately 54% and ADVA shareholders to own approximately 46% of the combined company, assuming a tender of 100% of ADVA shares
- Combined company to be dual-listed on the NASDAQ and Frankfurt Stock Exchange
 The two vendors produced a combined $1.2 billion in revenues last year. However, ADTRAN’s presentation in support of the deal showed that market heavyweights Nokia, Ciena, and smaller player Infinera had much higher revenues over that same time period.
The two vendors produced a combined $1.2 billion in revenues last year. However, ADTRAN’s presentation in support of the deal showed that market heavyweights Nokia, Ciena, and smaller player Infinera had much higher revenues over that same time period.
“It’s not going to reshape the optical networking industry,” John Lively, principal analyst at LightCounting, told SDxCentral about the deal. “ADTRAN and ADVA are going to improve their position in combination, [but] don’t really threaten the large players.”
Companies that are potentially threatened by this deal are smaller competitors such as Infinera ($1.4 billion in 2020 revenues) and Calix ($500 million in 2020 revenues), Lively noted.
“The challenges pressured by the global pandemic have clearly shown that fiber connectivity has become an essential foundation for the modern digital economy,” ADTRAN Chairman and CEO Thomas Stanton explained to investors about the deal. “This transformation will significantly increase the scale of the combined businesses, enhancing our ability to serve as a trusted supplier to our customers and worldwide.”
Stanton added that “our combination will make us one of the largest western suppliers for the markets we serve. Our greater size will increase cross-selling opportunities to existing customers, accelerating our combined growth, and allowing us to further penetrate our target markets.”
Although ADTRAN will remain a mid-tier player after the deal closes, LightCounting’s Lively and Dell’Oro Group VP Jimmy Yu both think in general, “it’s a good move.”
Yu noted that industry mergers can destroy value if too many products and workforces overlap. But in this case, ADTRAN and ADVA are from adjacent markets of fixed access and optical layer, and both sides will help each other grow the product line, so “it seems like a complementary combined company that’s going to come out of this,” he added.
Jimmy had this general comment on optical network trends:
“Disaggregated DWDM systems outperformed the broader market, demonstrating the growing adoption of this platform type. Really what we see is that this type of platform architecture, where transponder units are independent of the line systems, is being more widely embraced beyond the Internet content providers. Also, it is no longer just for metro applications. Recently, the highest growth rates have been from long-haul applications,”
Lively noted that there is almost no overlap in the product line, and “for the networks, the two companies logically fit together [as] ADTRAN makes access to equipment and ADVA makes the gear that connects the access equipment to the core.”
“So if you are a smaller service provider, and you want to upgrade to 10 Gb/s internet service for your customers, you could potentially buy everything you need from the new ADTRAN, from the passive optical networking, all the way through to connect to the core,” he said.
Yu also mentioned that the deal will help increase the scale and diversity in products as ADTRAN will be able to offer access and a backhaul solution, especially in tier-two and tier-three markets where most service providers want to work with one solution company instead of multiple vendors.
“2022 should be positive for sales,” argued the analysts at WestPark Capital in a note to investors earlier this month, following the release of Adtran’s second quarter results.
The WestPark Capital analysts pointed out that ADTRAN stands to gain ground in part from government broadband funding, as well as moves by some American and European network operators away from China’s Huawei.
The Raymond James analysts concurred on the Huawei opportunity. “We believe that the Huawei backlash outside of China presents among the largest opportunities,” they wrote on Monday.
The combined company will maintain ADTRAN’s global headquarters in Huntsville, Alabama. It will maintain ADVA’s headquarters in Munich, Germany, as its European base. Currently, ADTRAN has a geographical revenue split of 74% in the Americas, 21% in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, and 5% in Asia Pacific, while ADVA is split 62% in EMEA, 29% in the Americas, and 9% in Asia Pacific, according to Stanton.
The deal expands ADVA’s presence in North America and ADTRAN’s ability to reach the European market more effectively, Lively said. One of the drivers for this combination is “we see our customers making significant capital investments to transition their supply chains to trusted vendors with our roots in the U.S. and Germany, our company will be viewed favorably by customers who increasingly specify Western vendors,” Stanton explained.
“It’s kind of a race to build out their digital infrastructure to make the country competitive,” which presents a real opportunity for the new ADTRAN and also its competitors, Lively added.
Zayo to deploy 400G b/s network across North America and Western Europe
Zayo Group Holdings today announced the planned deployment of 31 high capacity, 400G b/s enabled long haul routes across North America and Western Europe.
The availability of 400G b/s client-side wavelength capabilities will enable Zayo to deliver multi-terabit capacity across its underlying global network, enabling higher transmission rates, reduced cost per bit, increased data transfer speeds and significantly greater bandwidth capacity — key features that support enterprises on their digital transformation journeys. Up to 800G transmission will be available in select areas as Zayo deploys significant speed enhancements in anticipation of future network needs.
This optimized wavelength network is designed to provide a direct route for multi-cloud and multi-market connectivity, ideal for content providers, hyper-scalers, carriers and data centers. The upgrade will also enable reduced physical space requirements as well as reduced operation and maintenance costs resulting from a 40% reduction in power consumption.
The race to 400Gb/s has accelerated in recent years, with an increasing number of users, applications and devices driving exponential demand for increased bandwidth. Exceeding the current standard of 100G, Zayo’s new routes will provide a fourfold increase in maximum data transfer speed, supporting 5G technologies including Internet of Things, cloud-based computing, edge computing, virtual reality, high-definition video streaming and artificial intelligence.
“400G is rapidly becoming the prevailing requirement for networks and Zayo is breaking new ground with its 800G capabilities,” said Brian Lillie, Zayo Chief Product and Technology Officer. “This deployment underscores Zayo’s commitment to maintaining the leading edge of communications infrastructure and providing state-of-the art network solutions critical to our customers’ digital transformation journeys.”
C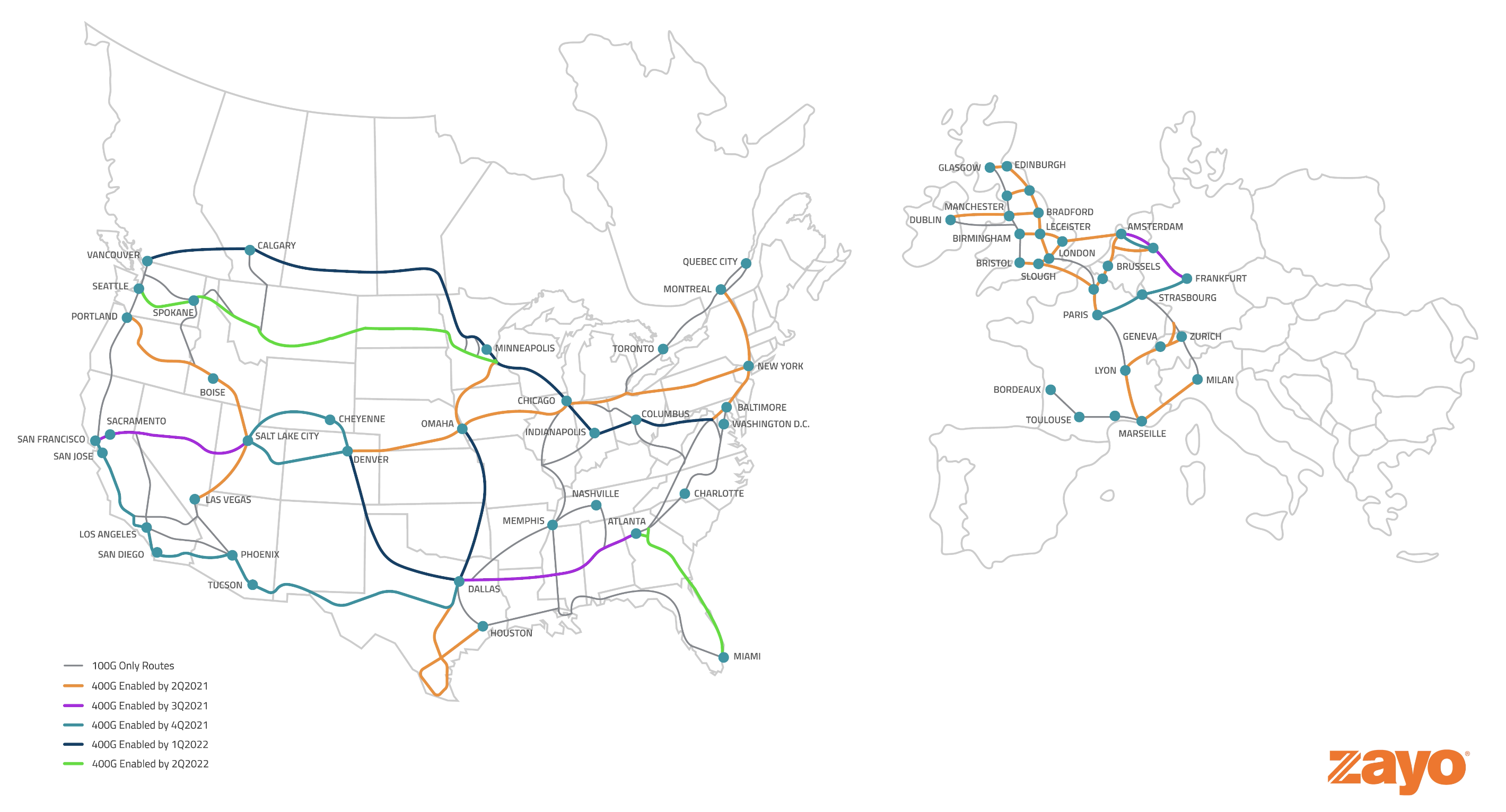 Chart courtesy of Avery Anderson of Zayo Group
Chart courtesy of Avery Anderson of Zayo Group
About Zayo Group:
Zayo’s 126,000-mile network in North America and Europe includes extensive metro connectivity to thousands of buildings and data centers. Zayo’s communications infrastructure solutions include dark fiber, private data networks, wavelengths, Ethernet, dedicated internet access and data center connectivity solutions.
Zayo owns and operates a Tier 1 IP backbone and through its CloudLink service, Zayo provides low-latency private connectivity that attaches enterprises to their public cloud environments. Zayo serves wireless and wireline carriers, media, tech, content, finance, healthcare and other large enterprises. For more information, visit https://zayo.com
References:
AT&T’s fiber buildout reduced due to supply constraints
AT&T has experienced recent disruptions in the supply of fiber optic cable, which has caused the company to trim back its planned fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) buildout for 2021, according to senior EVP and CFO Pascal Desroches.
AT&T had previously said it would build out its fiber network to an additional 3 million homes passed this year. But that’s now been reduced by 1/2 million.
“Since the start of the third quarter, we are seeing dislocation across the board, including in fiber supply. We’re probably going to come in a little bit light of 3 million homes passed, probably around 2.5 million,” Desroches said Tuesday at the Oppenheimer Technology, Internet & Communications Conference, according to this transcript.

An AT&T technician working on a fiber project
………………………………………………………………………………………….
Specifically, this is what Pascal said:
But since the start of the third quarter, we are seeing dislocation across the board, including in fiber supply. And as a result of those dislocations, we had previously provided guidance of 3 million homes past this year (unedited- very bad grammar). We’re probably going to come in a little bit in light of that, probably around 2.5 million. We don’t think it’s going to impact us long term. But I think it’s really important context because if we’re feeling the pain of this, I can only imagine what others in the industry are experiencing.
John Stankey (AT&T CEO) has always been a believer in fiber. I think when he took over he identified that as a priority area because he understood from a technology standpoint, there is no better technology for connectivity. And therefore, in a world where the demands for symmetrical speed are increasing significantly, this is the technology to bet heavily on. And so we have a great position, and we are leaning into adding to that position. So it’s really a function of when you — and I think others are now recognizing it as a result of what you’ve seen in the last year in the pandemic, the need to do what we’re doing now, 2-way communication can only happen with symmetrical speed. So I think everyone has had an aha moment, like we need to deploy fiber. And so we’ve long believed that. John has long believed that, and this is just really leading into that opportunity.
As we deploy fiber, our goal is to get at least 40% penetration on homes passed. And we think in certain markets, we’ll have an opportunity to do better than that. And the other thing that is great about is when you lay fiber, you lay fiber to a community where there is both homes and businesses. So it also helps boost returns in your enterprise business. And so that’s why it is so critical that we roll this out because the ability to grow both your enterprise and your consumer business is attractive. And we think these investments will provide us with mid-teen returns over time.
I know we’re largest fiber purchaser in the country. And we have prices that are at the best and most competitive among the industry. So we feel really good about the ability to secure inventory, fiber inventory and at attractive price points and the ability to execute and the build-out at scale, something that many others don’t have.
Oppenheimer moderator question: “Can you talk a little bit about where your supply comes from, I guess, both the fiber and the optical components or any other key suppliers? Is that U.S. sourced? Or is it a lot of it outsourced internationally?”
Pascal’s answer: “It is a U.S. company which has locations both domestically and outside the U.S.” [We suspect that it’s Corning].
AT&T typically has had no problem getting fiber at a low cost, Desroches said. “We’re the largest fiber purchaser in the country and we have prices that are the best and most competitive in the industry,” he said. “We feel really good about the ability to secure fiber inventory at attractive price points and the ability to execute the buildout at scale, something that many others don’t have.”
AT&T expects to catch up to its original fiber-construction estimates in the years after 2021, largely because of what Desroches called its “preferred place in the supply chain” and “committed pricing.” As AT&T said in a news release yesterday, AT&T is “working closely with the broader fiber ecosystem to address this near-term dislocation” and “is confident it will achieve the company’s target of 30 million customer locations passed by the end of 2025.”
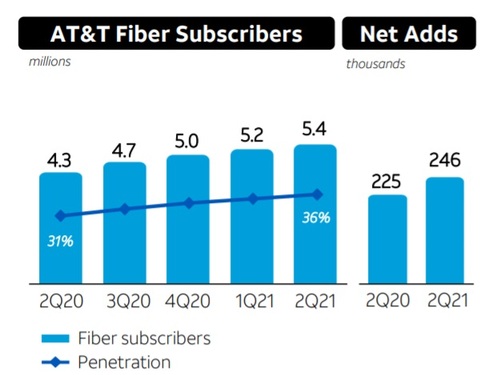
AT&T added another 246,000 fiber broadband subs in Q2 2021, extending its total to 5.43 million, and said last month it was on pace to add about 1 million net fiber subscribers for all of 2021.
AT&T has estimated that nearly 80% of new fiber subscribers are also new AT&T customers, reversing a previous trend that saw a sizable portion of its FTTP customer net adds coming from upgrades of existing AT&T high-speed Internet customers on older VDSL and DSL platforms (which have been largely discontinued).
Speaking on AT&T’s 2Q-2021 earnings call last month, Desroches stated that the company’s consumer wireline business had reached a “major inflection point” as broadband revenues continue to surpass legacy declines. Meanwhile, AT&T’s broadband average revenue per user (ARPU) reached $54.76 in Q2 2021, improving from $51.61 in the year-ago period.
References:
Will AT&T’s huge fiber build-out win broadband market share from cablecos/MSOs?
Frontier Communications Accelerates Fiber Build Out -10 Million locations passed by 2025
On August 5th, Frontier Communications announced an accelerated fiber optics buildout plan that will result in their fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) network passing 10 million locations (homes/offices) by 2025. Frontier says they will end 2021 with 4 million locations passed by fiber and will then add another 6 million in a revised, multi-year “Wave 2” plan.
Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier, said, “The acceleration of our fiber network expansion is clear evidence that Frontier’s transformation is taking hold. Over the past several months, we’ve made real progress in executing our strategy – by adding world-class leadership, introducing a purpose-driven culture, improving the customer experience, and making our operations more efficient and sustainable.
“Demand for high-speed broadband is growing rapidly, and fiber is the best product to meet the needs of consumers and businesses. Frontier is already doing what customers want and cable can’t – delivering symmetrical download and upload speeds with far lower latency than our competition. Early next year, we will start delivering 2 gigabit per second services, further stretching our performance lead to where only fiber can compete. We have hard work ahead of us, but momentum is increasing as we rally the Frontier team around our mission to Build Gigabit America.”
Jeffery added, “Our second-quarter results reflect continuing momentum in our fiber expansion strategy, with all key fiber metrics in line or above expectations. In particular, we accelerated our fiber build out, continued our customer momentum with another strong quarter of consumer fiber net adds, and reduced our consumer churn. Taken together, it was another strong quarter that positions Frontier well as we head into the second half of the year.”
At its virtual investor day, Frontier provided an update on the fiber buildout and other priorities resulting from its strategic review. These include:
- Frontier’s current ability to provide a best-in-class offering featuring symmetrical 1 gigabit per second download and upload speeds;
- Plans to launch a symmetrical 2 gigabit per second offering in the first quarter of 2022 that will unlock next-generation digital experiences for customers;
- Plans to deploy fiber to reach 10 million locations by 2025; and
- A new target of $250 million run rate savings by 2023 from simplifying the Company’s operations and improving the customer experience.
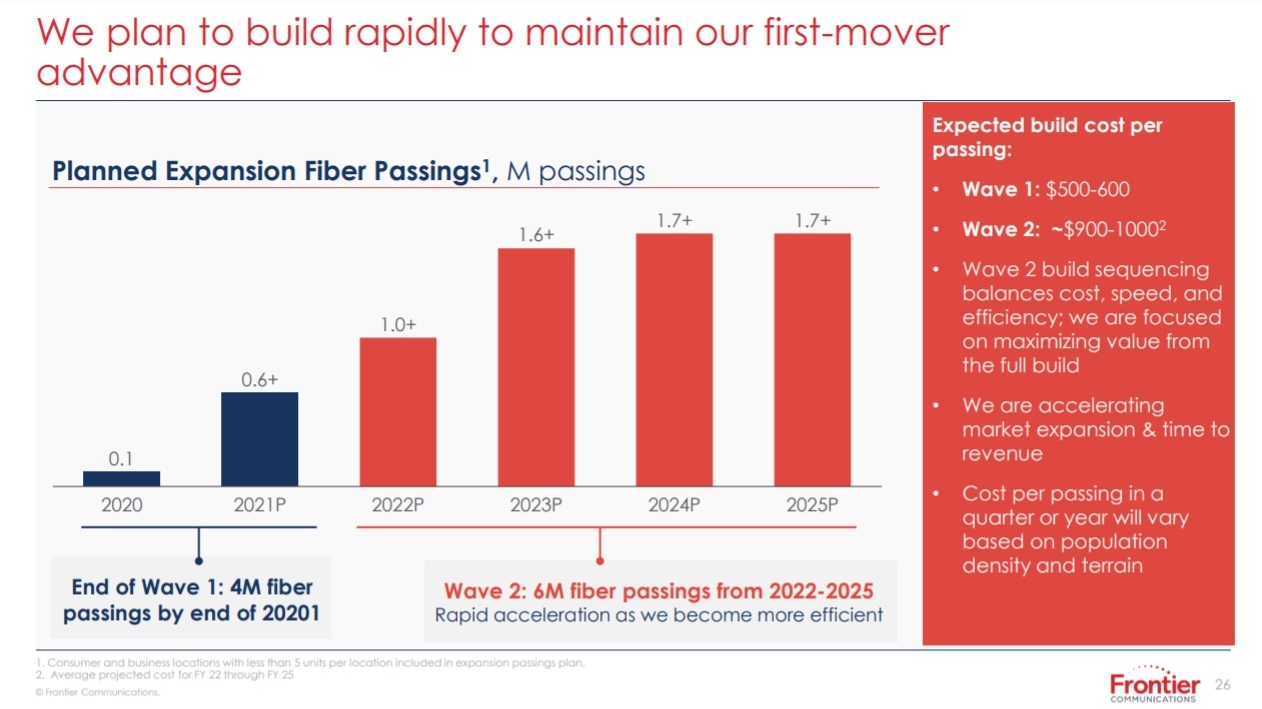
Image Credit: Frontier Communications
……………………………………………………………………………………….
Frontier also offered some revised predictions on service penetration, expecting them to be in the mid-teens to 20% at the end of year one, rise to 25% to 30% at the end of year two, and then on up to 45%. Frontier introduced new pricing for residential fiber broadband service, with entry-level service at 500 Mbit/s.
MoffettNathanson analyst Nick Del Deo (a colleague) wrote in a note to clients:
The single most important data points from today’s analyst day relate to Frontier’s FTTH deployment plans (Exhibit 1). For 2021, the company increased its expectation for new passings from 495K to >600K, which will complete “wave one” of its fiber upgrade project and leave it with ~4M total FTTH passings. Between 2022 and 2025, the company plans to build to another 6M passings, bringing its total to 10M, or about two thirds of its broadband-enabled locations. The remaining 5M, part of wave three, are currently in a holding pattern, with the company working through the optimal approach: do nothing, upgrade, upgrade with government assistance, divest, swap, or do something more creative that we haven’t come up with.

Image Credit: Frontier Communications
…………………………………………………………………………………….
The company also announced it will start to introduce 2-Gig services over FTTP in early 2022, but didn’t disclose pricing.
Del Deo summarized his assessment of Frontier’s fiber buildout (emphasis added):
Frontier plans to build FTTH to 7M incremental homes through 2025, a rapid acceleration from its current pace. This will leave two thirds of its broadband-enabled footprint served by fiber, with the status of the remaining one third TBD. The deployment costs appear somewhat higher, and returns a bit lower, than what we would have expected, but we had haircut the value of its FTTH expansion in our prior work to account for such risks. The faster pace and certainty now reduce the need for such haircuts. The path to financing the build remains open, but the company will need at least a couple of billion dollars in fresh funding. It’s not clear to us that management’s optimism regarding the commercial unit is warranted, but time will tell whether it can engineer a turnaround.
Management has high hopes for the commercial part of its business, and we don’t doubt that growth can get better from where it is today, but we think this will continue to be a segment that weighs on the company’s overall results.
Light Reading’s Jeff Baumgartner opines that “Frontier’s accelerated FTTP buildout plan, revised pricing and plans for 2-Gig service should pressure cable competitors to match up with speeds and pricing. Frontier’s moves might also cause those cable operators to give more consideration to “mid-split” or “high-split” upgrades that dedicate more upstream capacity to their DOCSIS 3.1 networks, accelerate their pursuit of new DOCSIS 4.0 technologies, or shift to full FTTP upgrades in select areas.”
………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
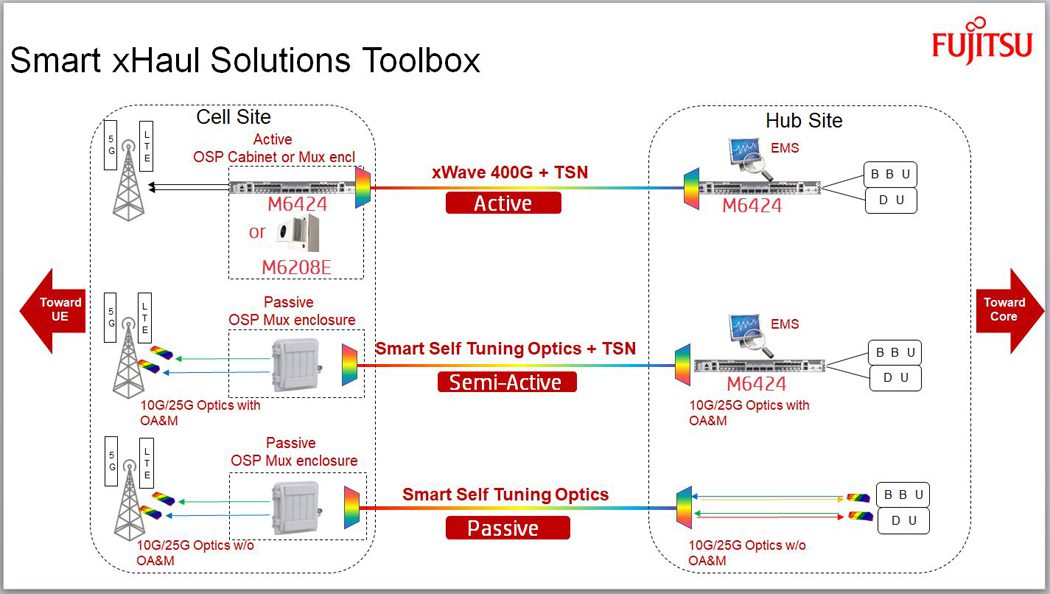
Fujitsu and HFR unveil Smart xHaul optical transport for 5G traffic

Digital Realty & Zayo plan next gen fiber interconnection and security capabilities
Digital Realty, the largest global provider of carrier- and cloud-neutral data center, colocation and interconnection solutions, announced today a significant step in its plan to create next-generation interconnection and security capabilities and build the largest open fabric-of-fabrics interconnecting key centers of data exchange.
As part of this development strategy, Digital Realty is working with Zayo Group Holdings, Inc., a leading global provider of fiber-based communications solutions, to lay the physical and virtual foundations of a new open fabric.
This collaboration represents a significant milestone on the cross-industry roadmap outlined earlier this year in Digital Realty’s industry manifesto for open interconnection and next-generation colocation solutions. The collaborative approach aims to unlock trapped value and remove legacy barriers to digital transformation by more closely aligning with the hybrid IT and security considerations of multinational enterprises. 
“As businesses continue to shift globally towards hybrid IT to enable new digital workplace models, create new lines of business, and control costs, Zayo and Digital Realty are in an excellent position to enable customers’ growth through a shared interest in globally secure, software-defined interconnection,” said Brian Lillie, Chief Product and Technology Officer at Zayo. “We look forward to working together to power next-generation interconnection and security capabilities that will unlock the true potential of digital transformation.”
This initiative builds upon new and existing innovative capabilities, including PlatformDIGITAL®, Digital Realty’s first of its kind global data center platform, which already brings together over 4,000 participants in connected data communities around the world, as well as Zayo’s extensive global fiber network. The new collaboration also follows Digital Realty’s recent announcement of its plan to build native SDN-enabled multi-platform orchestration and global fabric connectivity across its global platform.
“We’re excited to advance our roadmap for removing the legacy interconnection barriers that continue to impede enterprise digital transformation initiatives,” said Digital Realty Chief Technology Officer Chris Sharp. “Our platform capabilities and the steps we are taking in collaboration with Zayo will serve as a force-multiplier in building the industry’s largest open fabric-of-fabrics to effectively address the growing intensity of enterprise data creation and its gravitational impact on IT architectures.”
Digital Realty’s Data Gravity Index DGx™ projects that Forbes global 2000 enterprises will be adding storage at a combined rate of more than 620 terabytes per second for data aggregation and exchange across 53 metros by 2024. This rapid growth reflects a growing trend among global customers towards deploying and connecting large, private data infrastructure footprints across multiple global locations.
Gartner® predicts that by 2023, over 50%1 of the primary responsibility of data and analytics leaders will comprise data created, managed, and analyzed in edge environments. As a result, a new pervasive data center infrastructure is needed to enable digitized endpoints and mobile users to fully participate in globally distributed workflows. By removing legacy barriers across the interconnection industry, the consortium approach seeks to enable connected data communities and to support transformative outcomes for customers across all industries.
References:
Media & Industry Analyst Relations:
Marc Musgrove, Digital Realty, +1 (415) 508-2812
[email protected]
Lightpath to deploy 800Gb/sec links using Ciena’s WaveLogic 5 Extreme technology
Fiber-optic network services provider Lightpath has rolled out 800-Gbps capabilities via implementation of Ciena’s WaveLogic 5 Extreme technology. The company also will deploy Ciena’s Waveserver Ai platform, which will pair with a flexible-grid optical transport network based on Ciena’s 6500 RLS platforms.
The Lightpath Network consists of over 18,000 route miles of fiber providing connectivity to over 12,000 service locations. Lightpath provides a variety of connectivity and business services to customers in the metro New York area, including financial services firms (e.g. “Lightpath intros 100-Gbps optical transport service” and “Lightpath raises New York metro fiber-optic network footprint”). Using Ciena’s coherent optical solution, Lightpath’s network becomes more adaptive, allowing it to respond quickly to ever-changing bandwidth demands while maximizing operational efficiencies, providing customers with more reliable, high-speed services.
The enhanced optical transport technology will increase fiber network flexibility and efficiency as well as support Physical Layer encryption for data security. Cable MSO Altice USA owns a controlling interest in the company (see “Altice USA to sell almost 50% of Lightpath fiber enterprise business to Morgan Stanley Infrastructure Partners”).

“In order for our customers to execute on their own digital innovations, we need to provide them with fast and reliable connectivity. With Ciena’s solutions, our customers in the New York and Boston metro areas will now experience next-level digital services with high bandwidth and minimal latency,” commented Phil Olivero, CTO at Lightpath.
“As users consume more digital content, it is crucial for service providers to ensure their network can adapt to these surging and often unpredictable demands. With Ciena’s technology, Lightpath is adding scalability to meet bandwidth demands and also gaining real-time visibility into the performance of its network,” added Kevin Sheehan, CTO, Americas, for Ciena.
WaveLogic 5 Extreme is now available in three different product implementations to meet network architecture preferences: 6500 Packet-Optical Platform, Waveserver 5 compact interconnect platform, and the WaveLogic 5 Extreme 800G transceiver module

The WaveLogic 5 Extreme chip is 12mm x 16mm CMOS device. Here are some of its remarkable features:
- It is the industry’s first commercial 7nm CMOS device for optical networks.
- Based on 7nm FinFET technology, it includes 3km of wiring and contains 800 Trillion operations per second, which is about as much horsepower as 400,000 laptops!
- Some of the capabilities that are packed into the ASIC include nonlinear probabilistic constellation shaping, throughput-optimized forward error correction, frequency division multiplexing, and encryption.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Ciena
Ciena is a networking systems, services and software company. We provide solutions that help our customers create the Adaptive Network™ n response to the constantly changing demands of their end-users. By delivering best-in-class networking technology through high-touch consultative relationships, we build the world’s most agile networks with automation, openness and scale. For updates on Ciena, follow us on Twitter @Ciena, LinkedIn, the Ciena Insights blog, or visit www.ciena.com.
About Lightpath
Lightpath is revolutionizing how customers connect to their digital destinations by combining our next-generation network with our next-generation customer service. Lightpath’s advanced fiber-optic network offers a comprehensive portfolio of custom-engineered connectivity solutions with unparalleled performance, reliability, and security. Our consultative customer service means we work with you to design, deliver, and support the solution for your unique needs, faster and more easily than ever before. For over 30 years, thousands of enterprises, governments, and educators have trusted Lightpath to power their organization’s innovation. Altice USA (NYSE: ATUS) owns a 50.01% controlling interest in Lightpath and Morgan Stanley Infrastructure Partners (MSIP) owns 49.99% of the Company.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Facebook and Liquid Intelligent Technologies to build huge fiber network in Africa
Facebook Inc. and Africa’s largest fiber optics company, Liquid Intelligent Technologies, are extending their reach on the continent by laying 2,000 kilometers (1,243 miles) of fiber in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The two companies intend to build an extensive long haul and metro fiber network. Apparently, this is part of Facebook’s effort to “connect the unconnected,” especially in 3rd world countries.
The move will make Facebook one of the biggest investors in fiber networks in the region. The cable will eventually extend the reach of 2Africa, a major sub-sea line that’s also been co-developed by Facebook, the two companies said in a July 5th statement.

Facebook will invest in the fiber build and support network planning. Liquid Technologies will own, build and operate the fiber network, and provide wholesale services to mobile network operators and internet service providers. The network will help create a digital corridor from the Atlantic Ocean through the Congo Rainforest, the second largest rainforest after the Amazon, to East Africa, and onto the Indian Ocean. Liquid Technologies has been working on the digital corridor for more than two years, which now reaches Central DRC. This corridor will connect DRC to its neighboring countries including Angola, Congo Brazzaville, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia.
The new build will stretch from Central DRC to the Eastern border with Rwanda and extend the reach of 2Africa, a major undersea cable that will land along both the East and West African coasts, and better connect Africa to the Middle East and Europe. Additionally, Liquid will employ more than 5,000 people from local communities to build the fiber network.
“This is one of the most difficult fiber builds ever undertaken, crossing more than 2,000 kilometers of some of the most challenging terrain in the world” said Nic Rudnick, Group CEO of Liquid Intelligent Technologies. “Liquid Technologies and Facebook have a common mission to provide affordable infrastructure to bridge connectivity gaps, and we believe our work together will have a tremendous impact on internet accessibility across the region.”
Liquid Intelligent Technologies is present in more than 20 countries in Africa, with a vision of a digitally connected future that leaves no African behind.
“This fiber build with Liquid Technologies is one of the most exciting projects we have worked on,” said Ibrahima Ba, Director of Network Investments, Emerging Markets at Facebook. “We know that deploying fibre in this region is not easy, but it is a crucial part of extending broadband access to under-connected areas. We look forward to seeing how our fibre build will help increase the availability and improve the affordability of high-quality internet in DRC.”
Facebook has been striving to improve connectivity in Africa to take advantage of a young population and the increasing availability and affordability of smartphones. The social-media giant switched to a predominantly fiber strategy following the failed launch of a satellite to beam signal around the continent in 2016.
About Liquid Intelligent Technologies:
Liquid Intelligent Technologies is a pan-African technology group present in more than 20 countries, mainly in Sub-Saharan Africa. Liquid has firmly established itself as the leading provider of pan-African digital infrastructure with an extensive network covering over 100,000 km. Liquid Intelligent Technologies is redefining network, cloud, and cybersecurity offerings through strategic partnerships with leading global players, innovative business applications, smart cloud services and world-class security on the African continent. Liquid Intelligent Technologies is now a comprehensive, one-stop technology group that provides customized digital solutions to public and private sector companies across the continent under several business units including Liquid Networks, Liquid Cloud and CyberSecurity and Africa Data Centers. For more information contact: Angela Chandy [email protected]
References:
Will AT&T’s huge fiber build-out win broadband market share from cablecos/MSOs?
AT&T added 235,000 fiber connections in the first quarter, ending the period with nearly 5.2 million total fiber customers. AT&T says they have a total of around 15 million fiber and non-fiber customers, so fiber access is approximately 1/3 of total customers now.
The company recently announced it plans to build fiber to 3 million new customer locations this year and 4 million next year. AT&T plans to double the number of locations where it offers fiber Internet, from approximately 15 million to about 30 million, by 2025. To do that, AT&T is planning to increase its annual capital expenses from $21 billion to around $24 billion.
AT&T’s new focus on connectivity over content is a direct result of its spinning off Warner Media to Discovery, as we chronicled in this IEEE Techblog post. Thaddeus Arroyo, head of AT&T’s consumer business, made that crystal clear at a recent BoA investor event:
“We expect capital expenditures of about $24 billion a year after the Warner Media discovery transaction closes. That’s an incremental investment that’s going to go to fiber to 5G capacity and 5G C-band deployment.
We have another great opportunity, the one we continue to talk around fiber. So as part of this capital, we’re going to be investing in fiber expansion to meet the growing needs for bandwidth that require a much more robust fiber network regardless of the last mile serving technology. Fiber is the foundation that fuels our network. Expanding our fiber reach serves multiple services hanging off at each strand of fiber. It includes macro cell sites, small cell sites, wholesale services, enterprise, small business, and fiber that’s extended directly into our customers’ homes and into businesses.
We plan to reach 30 million customer locations passed with fiber by the end of 2025. That’s going to double our existing fiber footprint. And investing in fiber drives solid returns because it’s a superior product. Where we have fiber we win, we’re improving share in our fiber footprint, and the penetration rates are accelerating and growing, given our increased financial flexibility. We’re comfortable in our ability to invest and achieve our leverage targets that we outlined of getting to 2.6% at close and below 2.5% by the end of 2023.”
Mo Katibeh, the AT&T executive responsible for fiber and 5G build-outs, added on via a recent post on LinkedIn: “We are building MORE Fiber to MORE homes and businesses. And we’re talking A LOT of fiber – MILLIONS of new locations every year, planning to cover 30 MILLION customer locations by the end of 2025! And you know what comes with all that investment in America? JOBS. Our AT&T Network Build team is GROWING..”
Previously, Katibeh wrote on LinkedIn : “Contributing to a large portion of the $105B Capital spend between 2016 and 2020 – our team is building out AT&T #Fiber to MILLIONS of new customer locations in 2021, as well as augmenting America’s best mobility network with more capacity, more speed – and more #5G (you know I love 5G!).”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
So with all that said, will AT&T’s fiber build-out keep pace with cable companies/MSOs DOCSIS networks?
Tom Rutledge, Charter’s CEO, made a brief comment about plant upgrades on the earnings call (note – Dave Watson made similar comments on the Comcast earnings call):
“We’re continuously increasing the capacity in our core and hubs and augmenting our network to improve speed and performance at a pace dictated by customers in the marketplace. We have a cost-effective approach to using DOCSIS 3.1, which we’ve already deployed, to expand our network capacity 1.2 gigahertz, which gives us the ability to offer multi-gigabit speeds in the downstream and at least 1 gigabit per second in the upstream.”
According to Leichtman Research Group, the top cable companies had 68 million broadband subscribers, and top wireline telecom companies had 33.2 million subscribers at the end of 2019.
“Based on the currently available information, cable stole wired broadband market share in Verizon and AT&T markets as well. Oy vey!” said Jim Patterson of Patterson Advisory Group in his May 2, 2021 newsletter. “Think about Comcast and AT&T as having roughly the same number of homes passed (AT&T probably closer to 57 million homes versus the nearly 60 million shown for Comcast),” he added. Patterson noted that top cable companies Comcast, Charter and Altice managed to capture 86% of broadband customer growth in the U.S. in the first quarter of this year.
“(AT&T) fiber connections simply aren’t growing fast enough to keep up,” wrote colleague Craig Moffett of MoffettNathanson in a recent note to clients. Here’s more:
To be sure, there are questions about the extent to which these deployments will overlap cable (or will instead be focused on unserved rural communities), and the extent to which labor and supply chain contraints might limit acheivability of announced targets. Still, taken together, these deployments suggest that, after a precipitous decline in new fiber construction in 2020, planned fiber deployments do, indeed, rise over the next two years; we expect that both 2021 and 2022 will represent new all-time peaks in total number of fiber homes passed. Typically, the competitive impact from overbuilds is felt with some lag, suggesting the impact on cable operators will peak in 2024/2025.
At the same time, we expect that federal stimulus to accelerate broadband market growth in 2021 and 2022, perhaps significantly, with new household formation, in particular, driving upside to 2021 and 2022 forecasts.
Longer term, however, Cable operators will have to contend with more fiber overbuilds, as TelCos increasingly see both more favorable economics for fiber deployment and increasingly acknowledge that their copper plant faces imminent obsolescence without it. The forecasts for fiber deployment in this note suggest that 2021 will be a record for fiber construction – assuming labor and materials capacity can accommodate the TelCos’ own forecasts – and 2022 will step up higher still. After that, deployments are expected to abate, at least to a degree.
“Cable can upgrade its plant quickly and at low cost to offer at least 4.6Gbit/s down and 1.5Gbit/s up, well beyond current fiber offerings. They can do this before the move to DOCSIS 4.0, which is still years off,” wrote the financial analysts at New Street Research in a recent note to investors. The result, according to the New Street analysts, is that fiber providers like AT&T won’t necessarily be able to dominate the fiber market with a 1 Gbit/s FTTH/FTTP connection and take market share from cable incumbents.
“Cable will face new fiber competition in more of its markets over the next few years; however, there is little to no prospect of fiber delivering a service in those markets that cable can’t easily match or beat,” New Street concluded.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“Looking back and being a little critical, we probably allowed the cable companies to execute and to take share in that market in a significant way,” AT&T CFO Pascal Desroches said at a recent Credit Suisse investor event.
AT&T executives have said that the company’s fiber investment ultimately will generate internal returns of around 15%. Desroches said that return on investment will be due to a variety of factors. Fiber “supports not only consumer needs, it supports needs for our enterprise businesses as well as needs for potentially our reseller business. So being able to look across and integrate the planning for fiber deployment such that it not only serves consumer needs, but it serves these other market adjacencies as well is something that we haven’t been very good at historically, That’s why we’re really bullish and we believe we’re going to be able to execute really well here,” AT&T’s CFO concluded.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/opticalip/is-atandts-fiber-investment-good-idea/d/d-id/770468?
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:6813211481950318592/
Ciena demo’s 45 wavelengths @400G; Joins Google’s Cloud’s 5G/Edge ISV Program
During OFC 2021 last week, Ciena and Lumenisity Ltd. said that they had partnered to demonstrate transmission of 45 wavelengths, each at 400G, over 1,000 km of hollowcore fiber cable.
The demonstration paired Lumenisity’s CoreSmart hollowcore cable with Ciena’s WaveLogic 5 Extreme and Nano coherent optical engines, with the transmission occurring in a recirculating loop. The companies say their work indicates that hollowcore fiber cable can be used for high-bandwidth, long-reach applications such as data center interconnect (DCI) in addition to edge and 5G xHaul applications Lumenisity had previously cited (see “Lumenisity, BT drive 400ZR DWDM transmission over hollowcore fiber“ and “BT testing hollowcore fiber for 5G support”).
Lumenisty said that it has been working over the past six months with ecosystem partners to test the CoreSmart low-latency hollowcore cable in its System Lab in Romsey, UK (see “Startup Lumenisity unveils hollowcore fiber cables for DWDM applications, new funding” for more on Lumenisity’s fiber). Ciena participated in at least some of those exercises, including a second trial in which the two companies achieved a capacity of 38.4 Tbps with 48x800G channels over greater than 20 km without in line amplification using the current generation of CoreSmart. Lumenisity says the next generation of CoreSmart will be able to extend reach in such an application to between 50-100 km with no inline amplification when paired with the WaveLogic 5 Extreme.
“The results obtained both internally and with Ciena commercial WaveLogic 5 systems show further evidence that we are bringing our world-class hollowcore fiber cable technology to market at an accelerating rate for multiple high-capacity applications, that solve real world latency issues for our customers,” commented Tony Pearson, business development director at Lumenisity.
“System characterization results of WaveLogic 5 Extreme programmable 800G and WaveLogic 5 Nano 400ZR coherent pluggables running over CoreSmart show promising results with hollowcore fiber now proven to preserve high-capacity while materially reducing latency,” added Steve Alexander, senior vice president and CTO of Ciena. “We are proud to be at the forefront of this breakthrough technological achievement where we can enable a 50% increase in reach for latency-sensitive data center interconnects.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, CTO Alexander wrote a blog titled, “Ciena has joined Google Cloud’s 5G/Edge ISV Program to help enterprises accelerate migration of their IT resources to the cloud“
Here’s an excerpt:
To facilitate the migration of enterprise IT workloads to the cloud, there is a requirement for higher speed connections from the enterprise edge to cloud provider that are scalable with enhanced security to best protect critical business data. Shared IP network connections to the cloud are acceptable for lower speed (10Gb/s) connections and below. However, when secure, higher speed connections are required to the cloud, connectivity via the IP network can become overly complex, expensive, and inefficient when compared to the optical network (Optical Fast Lane) that can provide a more efficient, cost-effective, and secure option for enterprises needing to reduce their workload migration times to support their evolving business objectives.
For the multi-cloud market to succeed, it must reduce the friction for enterprises to migrate their workloads to a cloud provider, as well as between cloud providers – on demand. This is analogous to the days when you had a mobile plan with one carrier, and to switch to another carrier, you had to switch mobile numbers, which was too complex for most customers, so they stuck with their existing carrier. Only when consumers could keep their phone number when they switched carriers (through Local Number Portability), did it make the mobile market truly competitive leading to improved choice, pricing, and innovation. This is what we’re trying to achieve in the multi-cloud market.
Google Cloud is one of the leading cloud providers in the market that embraces an architecture that enables their enterprise customers to gracefully migrate their workloads to Google Cloud via an Optical Fast Lane that enables Enterprise to develop and leverage the Google Cloud for new and innovative applications. Ciena is excited to be a key player in this program and in addressing this opportunity in the industry. This builds off Ciena’s long standing relationship with Google and other Cloud Providers serving both private and managed high-capacity optical transport networks – principally dominated by subsea, long-haul, metro and DCI connectivity.
Ciena is also a major supplier to Communication Service Providers (CSPs) and MSOs – serving all segments of the network – including high-speed access connectivity for Enterprises as well as cell-site routing and backhaul. In partnership with CSPs, Google Cloud is helping customers leverage their edge real-estate assets to facilitate low latency connectivity to Google Cloud and reduce the friction required for enterprises to improve their mean time to the cloud for their data and workloads.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References: