T-Mobile US
5G Advanced offers opportunities for new revenue streams; 3GPP specs for 5G FWA?
A Mobile World Live webinar on 5G-advanced upgrades identified new opportunities for network operator revenue streams, mostly due to improved network efficiencies and reduced costs. 5G Advanced, the next step in 5G evolution, will be specified in 3GPP Release 18 and 19. There is no work on it in ITU-R which is now focused on IMT-2030 (6G).

Egil Gronstad, T-Mobile senior director-technology development and strategy, said 5G Advanced will present opportunities for new revenue streams: 5G IoT will have lower cost and lower power consumption of endpoint devices (Redcap). Another 5G Advanced capability will be Ambient IoT (coming in Rel 19) which has a lot of opportunities via lower cost and no battery required in IoT devices. A bit further out is Integrated sensing and communications -using the network as a radar system to detect objects of interest. Improved spectrum efficiency will be improved using AI/ML for beam management.
Egil said 3GPP should develop specs for fixed wireless access (FWA). He’s disappointed with 3GPP not pursuing 5G FWA. “We haven’t really done anything in the 3GPP specs to specifically address fixed wireless,” he said. Neither has ITU-R WP 5D, which is responsible for developing all ITU-R recommendations for IMT (3G, 4G, 5G, 6G). FWA was not identified as an ITU use case for 5G and that hasn’t changed with 5G Advanced.
References:
https://www.nokia.com/about-us/newsroom/articles/5g-advanced-explained/
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
Huawei pushes 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) but there are no completed 3GPP specs or ITU-R standards!
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
ABI Research: 5G-Advanced (not yet defined by ITU-R) will include AI/ML and network energy savings
FWA a bright spot in otherwise gloomy Internet access market
Parks Associates’ newly launched Broadband Market Tracker, states that U.S. Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) adoption from a mobile network operator hit 7.8 million U.S. residential home internet connections in Q1-2024. That’s in comparison to 106.3 million U.S. households that had home internet service at the end of 2023.
Kristen Hanich, director of research at Parks Associates, told Fierce Network FWA and satellite internet are the “fastest growing” segments of the broadband market, “attracting consumers who were previously unserved or underserved by traditional providers.” She noted for the past several years, the FWA base has grown by 700,000 to 900,000 subscribers per quarter while cable connections have declined.
T-Mobile in Q1-2024 passed the 5 million mark for FWA subscribers and Verizon reported a total FWA tally of 3.4 million subscribers. These figures include both residential and business FWA customers.
Key FWA Findings from OpenSignal:
- 5G FWA has reshaped the U.S. broadband market. It has allowed U.S. mobile operators to rapidly expand their broadband footprints for minimal incremental network investment. This has seen 5G FWA absorb all broadband subscriber growth in the market since mid-2022.
- FWA is the secret sauce for 5G monetization. FWA benefits from lower prices compared to wireline competition, access to existing mobile retail channels and subscribers, and the ability to deliver a “good enough” broadband service.
- U.S. mobile networks have proven to be resilient. Despite adding millions of 5G FWA subs since 2021, 5G speeds on T-Mobile and Verizon’s mobile networks have continued to improve. Their success in managing FWA traffic is due to a variety of factors, including plentiful access to mid-band spectrum, localized load management, and differences in peak usage time of day patterns between mobile and FBB usage.
- Elsewhere, there are mixed results. In India, Jio is seeing no discernible impact from FWA on the mobile experience of its users, while in Saudi Arabia Zain is seeing the additional load on its network from FWA having a greater influence on mobile users’ experience, depending on the time of day or the level of FWA penetration.
“Despite adding more than eight million 5G FWA subs using 400+ GB per month of data since Q1 2021, the overall mobile network experience on T-Mobile and Verizon’s mobile networks has not been compromised,” Opensignal analyst Robert Wyrzykowski wrote in the firm’s new assessment of FWA technology.

In its new report, Opensignal found that areas in the U.S. with a larger number of FWA customers actually showed better networking performance than areas with fewer FWA customers. Meaning, Verizon and T-Mobile offered increasingly speedy connections even in geographic locations with higher concentrations of FWA users.
“We would expect low-FWA penetration areas to see better mobile and FWA performance because of less load on the network. However, our data demonstrates the opposite trend,” Wyrzykowski explained.

Other Opensignal findings:
- Around 6% of urban Internet customers subscribe to FWA; in rural areas that figure is 7%.
- Some 74% of FWA customers pay less than $75 per month for their services.
- 35% of FWA customers are between 18-34 years old, whereas that age range is 25% for cable.
Opensignal’s findings provide an important view into the FWA industry in the US as its subscriber growth begins to slow. For example, T-Mobile added 405,000 FWA customers during the first quarter, far less than the 541,000 FWA customers it added during the fourth quarter of 2023.
“5G FWA services have been on a dramatic growth trajectory in the U.S., absorbing all broadband subscriber growth in the market since mid-2022 and amassing more than 600-700 thousand net adds per quarter,” wrote Opensignal’s Wyrzykowski. “This is despite the USA being a mature broadband market with nearly 97% broadband adoption and modest household growth.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
U.S. cable companies have recorded historic declines in their core Internet businesses amid the growth of FWA in the U.S. Financial analysts at TD Cowen predict the U.S. cable industry will collectively lose more than half a million customers in the second quarter of this year. They attribute that decline to FWA competition as well as other factors including the end of the U.S. government’s Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP).
The situation for cable might get even worse if FWA providers like T-Mobile and Verizon decide to invest further into their fixed wireless businesses.
“The pain for cable may continue for longer than expected as the ability for cable to return to broadband subscriber growth may take longer (if ever),” wrote the TD Cowen analysts in a recent note to investors.
Others agree. For example, the analysts at S&P Global wrote that cable service providers in general have been losing value to wireless network operators despite cable’s efforts to bundle mobile services into cable offerings.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Parks’ Hanich said fiber optic access technology is on an upswing and Parks is seeing “excellent growth in the markets where it is available and high customer satisfaction with the customers who have it.”
“But the numbers are not quite as dramatic as what’s been going on with T-Mobile, Verizon and Starlink,” she said, noting the “growing convergence” of satellite and mobile networks is something else to keep an eye on.
Asked whether the demise of the Affordable Connectivity Program has had any impact on Parks’ findings, Hanich said, “we are concerned that the end of the program will result in households and families needing to disconnect from the internet for financial reasons.”
“For a good percentage of Americans, household budgets have been hit by rising inflation and lower-income families especially are having to cut back,” she said. “Thankfully we are seeing ISPs step up, try and transition people onto other plans and initiatives.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Parks found adoption of mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) services reached over 15 million residential customer mobile lines in the quarter. In an MVNO model, broadband operators lease spectrum capacity from a wireless network to stand up their own mobile offering.
NTIA published some findings from its latest Internet Use Survey. Unsurprisingly, internet usage in the U.S. has gone up, with 13 million more people using the internet in 2023 compared to 2021. However, a lot of that usage is coming from lower-income households. Specifically, internet adoption among households making less than $25,000 per year increased from 69% in 2021 to 73% in 2023.
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/fixed-wireless-continues-its-climb-among-us-homes-parks
https://www.lightreading.com/fixed-wireless-access/fwa-in-the-usa-getting-ready-for-phase-2
Fiber and Fixed Wireless Access are the fastest growing fixed broadband technologies in the OECD
Summary of Verizon Consumer, FWA & Business Segment 1Q-2024 results
Verizon’s 2023 broadband net additions led by FWA at 375K
AT&T’s fiber business grows along with FWA “Internet Air” in Q4-2023
Ericsson: Over 300 million Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) connections by 2028
T-Mobile to acquire UScellular’s wireless operations in $4.4 billion deal
T-Mobile will buy almost all of regional carrier UScellular’s wireless operations including customers, stores and 30% of its spectrum assets [1.] in a deal valued at $4.4 billion, the company said on Tuesday. The announcement comes nearly ten months after UScellular and its parent company TDS disclosed that they were undertaking a strategic review of the mobile business, suggesting a possible sale.
Note 1. UScellular stated that it will retain around 70% of its spectrum assets following the T-Mobile deal “and will seek to opportunistically monetize these retained assets.”
The transaction, which is subject to the satisfaction of customary closing conditions and receipt of certain regulatory approvals, is expected to close in mid-2025.
T-Mobile’s 5G SA network will expand to provide millions of UScellular customers, particularly those in underserved rural areas, a superior connectivity experience, moving from a roaming experience outside of the UScellular coverage area to full nationwide access on the country’s largest and fastest 5G network. Additionally, UScellular customers will have the ability to fully participate in the T-Mobile’s industry-leading value-packed plans filled with benefits and perks, and best-in-class customer support with the opportunity to save UScellular customers hundreds of millions of dollars. T-Mobile customers will also get access to UScellular’s network in areas that previously had limited coverage and the benefit of enhanced performance throughout UScellular’s footprint from the addition of the acquired UScellular spectrum to T-Mobile’s network.
“With this deal T-Mobile can extend the superior Un-carrier value and experiences that we’re famous for to millions of UScellular customers and deliver them lower-priced, value-packed plans and better connectivity on our best-in-class nationwide 5G network,” said Mike Sievert, CEO of T-Mobile. “As customers from both companies will get more coverage and more capacity from our combined footprint, our competitors will be forced to keep up – and even more consumers will benefit. The Un-carrier is all about shaking up wireless for the good of consumers and this deal is another way for us to continue doing even more of that.”
“T-Mobile’s purchase and integration of UScellular’s wireless operations will provide best-in-class connectivity to rural Americans through enhanced nationwide coverage and service offerings at more compelling price points,” said Laurent Therivel, CEO of UScellular. “The transaction provides our customers access to better coverage and speeds, as well as unlimited texting in more than 215 countries, content offers, device upgrades and other T-Mobile benefits.”
Best-in-Class Network Experience
The combination of both companies’ spectrum and assets will provide UScellular customers a superior connected experience on T-Mobile’s industry-leading nationwide 5G network that offers best-in-class performance, coverage, and speed. Customers of both companies, particularly those in underserved rural areas, will receive access to faster and more reliable 5G service they would not otherwise have.
Value-Packed Plans
UScellular customers will have the option to stay on their current plans or move to an unlimited T-Mobile plan of their choosing with no switching costs, which include beloved Un-carrier benefits such as streaming and free international data roaming. If UScellular customers choose to switch to T-Mobile, they could save hundreds of millions of dollars combined annually. Some will also have access to plans with increased savings previously not available to them, including T-Mobile’s 5G Unlimited 55+ plans. All customers will be able to take advantage of T-Mobile’s award-winning customer service team, and have better, more accessible in-person and digital retail support.
More Choice and Increased Competition
This transaction will create a much-needed choice for wireless in areas with expensive and limited plans from AT&T and Verizon, and for those that have been limited to one or no options for home broadband connectivity. By tapping into the additional capacity and coverage created through the combined spectrum and wireless assets, T-Mobile will spur competition and expand its fast-growing home broadband offering and fixed wireless products to communities without competitive broadband options, further bridging the digital divide for hundreds of thousands of customers in UScellular’s footprint.
Proven Un-carrier Playbook
T-Mobile has a proven industry-leading track record of bringing companies together in the name of enhanced connectivity, choice, and value for consumers. The integrations of MetroPCS in 2013 and Sprint in 2020 have been noted as two of the most successful merger combinations in wireless history that resulted in competition-enhancing shifts benefiting millions of consumers. Leveraging its tried-and-true playbook for successful integrations, T-Mobile will continue to deliver exceptional value and experiences to more people across the country, while forcing others to follow suit, for the good of customers.
Transaction Details and Financial Profile
T-Mobile will pay approximately $4.4 billion for the assets being acquired from UScellular in the transaction in a combination of cash and up to $2.0 billion of debt to be assumed by T-Mobile through an exchange offer to be made to certain UScellular debtholders prior to closing. To the extent any debtholders do not participate in the exchange, their bonds will continue as obligations of UScellular and the cash portion of the purchase price will be correspondingly increased. Following the closing of the transaction, UScellular will retain ownership of its other spectrum as well as its towers, with T-Mobile entering into a long-term arrangement to lease space on at least 2,100 additional towers being retained.
T-Mobile does not expect the transaction to impact the company’s 2024 guidance or 2024 authorized shareholder return program. T-Mobile expects this transaction will yield approximately $1.0 billion in effective total opex and capex annual run rate cost synergies upon integration, with total cost to achieve the integration currently estimated at between $2.2 billion to $2.6 billion. The company plans to reinvest a portion of synergies toward enhancing consumer choice, quality and competition in the wireless industry.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/business/uscellular-acquisition-operations-assets
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/t-mobile-buy-uscellulars-wireless-114507766.html
UScellular adds NetCloud from Cradlepoint to its 5G private network offerings; Buyout coming soon?
Betacom and UScellular Introduce 1st Private/Public Hybrid 5G Network
UScellular’s Home Internet/FWA now has >100K customers
UScellular Launches 5G Mid-Band Network in parts of 10 states
UScellular adds NetCloud from Cradlepoint to its 5G private network offerings; Buyout coming soon?
UScellular has added NetCloud Private Networks from Cradlepoint (part of Ericsson) to expand its portfolio of private cellular solutions. The company now offers Ericsson Private 5G and Ericsson’s Mission Critical Networks to its customers. By building on these capabilities, UScellular is able to support even more customers across varying areas of business.
Some existing private cellular network ecosystems are pulled together piece by piece from different providers, which requires additional training and agreements. This makes it difficult for enterprise IT teams to have seamless visibility across the entire network. NetCloud Private Networks is an end-to-end private cellular network solution that removes these complexities to simplify building and operating 5G private networks.
“With the addition of NetCloud Private Networks to our portfolio, we can better address business challenges for customers of all sizes to connect business, industry and mission critical applications,” said Kim Kerr, senior vice president, enterprise sales and operations for UScellular. “The agility, flexibility and scalability of NetCloud Private Networks helps improve coverage, security, mobility, and reliability for applications where Wi-Fi may not be enough.”
NetCloud Private Networks supports enterprises who need more scalable, reliable and secure connectivity than they are getting today with traditional Wi-Fi solutions. There is significant opportunity in warehouses, logistics facilities, outdoor storage yards, manufacturing and retail operations environments to provide more connectivity. This will alleviate manual work, improve safety, and provide increased visibility.
“UScellular is a leader in this space by showing how a public carrier enhances the value of private network solutions,” said Manish Tiwari, head of private cellular networks, Cradlepoint and Ericsson Enterprise Wireless Networks.
“By adding NetCloud Private Networks to their portfolio of Ericsson private networks solutions, UScellular unlocks new opportunities for organizations to have local network coverage and address their reliability and security challenges. With solutions available to cater to both OT and IT in industrial and business environments, their customers have a choice in adopting the right private network solution for their use-cases with secure, policy-based wireless connectivity at scale.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, The Wall Street Journal reported Thursday that T-Mobile is seeking to buy $2 billion worth of UScellular and take over some operations and wireless spectrum licenses. A deal could be announced this month, according to people familiar with the matter.
Meanwhile, Verizon is considering a deal for some of the rest of the company which is 80% owned by Telephone & Data Systems (TDS). Last year, TDS put the wireless company’s operations up for sale, as it struggled with competition from national wireless telco rivals and cable-broadband providers.
Verizon is the biggest U.S. cellphone carrier by subscribers, while T-Mobile became the second largest soon after it bought rival Sprint. T-Mobile gained more customers this month after it completed its purchase of Mint Mobile, an upstart brand.
The rising value of wireless licenses is a driving force behind the deal. U.S. Cellular’s spectrum portfolio touches 30 states and covers about 51 million people, according to regulatory filings.
U.S. companies have spent more than $100 billion in recent years to secure airwaves to carry high-speed fifth-generation, or 5G, signals and are hunting for more. But the Federal Communications Commission has lacked the legal authority to auction new spectrum for more than a year. The drought has driven up the price of spectrum licenses at companies that already hold them.
The U.S. wireless business has also matured: Carriers have sold a smartphone subscription to most adults and many children, which leaves less room for expansion as the country’s population growth slows. AT&T and Verizon have meanwhile retreated from expensive bets on the media business to focus on their core cellphone and home-internet customers.
A once-crowded field of small, midsize and nationwide cellphone carriers in the U.S. is now split among Verizon, T-Mobile and AT&T, leaving few players left to take over. As one of the last pieces left on the board, U.S. Cellular has long been an attractive takeover target. For many years, the home of the Chicago White Sox has been UScellular field.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About UScellular:
UScellular offers wireless service to more than four million mostly rural customers across 21 states from Oregon to North Carolina. It also owns more than 4,000 cellular towers that weren’t part of the latest sale talks. The company has a market value of about $3 billion.
UScellular provides a range of solutions from public/private hybrid networks, MVNO models, localized data (aka CUPS) and custom VPN approaches. Private 5G offers unparalleled reliability, security and speed, enabling seamless communication and automation. For more information:
https://business.uscellular.com/products/private-cellular-networks/
References:
https://www.wsj.com/business/telecom/t-mobile-verizon-in-talks-to-carve-up-u-s-cellular-46d1e5e6
Betacom and UScellular Introduce 1st Private/Public Hybrid 5G Network
T-Mobile & EQT Joint Venture (JV) to acquire Lumos and build out T-Mobile Fiber footprint
T-Mobile and EQT, a purpose-driven global investment organization, today announced they have entered into a joint venture (JV) with EQT’s Infrastructure VI fund (EQT) that will acquire fiber-to-the-home platform Lumos from EQT’s predecessor fund EQT Infrastructure III.
The JV will bring T-Mobile’s retail, marketing, brand and customer experience strengths together with EQT’s fiber infrastructure investment expertise. Together they will acquire Lumos’ scalable fiber network build capabilities to deliver best-in-class high-speed fiber internet connectivity to customers across the U.S. without access to fiber today. After the transaction closes, Lumos, which currently reaches 320,000 households over 7,500 route miles with fiber optic internet and home wi-fi service in the Mid-Atlantic, will transition to a wholesale model with T-Mobile as the anchor tenant owning customer relationships and leveraging its brand to attract new subscribers. The JV will focus on market identification and selection, network engineering and design, network deployment, and customer installation.
“As the demand for reliable, low-latency connectivity rapidly increases, this deal is a scalable strategy for T-Mobile to take a significant step forward in expanding on our broadband success and continue shaking up competition in this space to bring even more value and choice to consumers,” said Mike Sievert, CEO of T-Mobile. “Together with EQT and Lumos, T-Mobile is building on our position as the fastest growing broadband provider in the country in a value-accretive way that complements our sustained growth leadership in wireless. Customers – homes and businesses – who get the fast, affordable, and reliable internet they need will be the real winners,” he added.
T-Mobile provides a unique value proposition and much-needed reliable connectivity to homes and businesses across the country through its 5G Internet, a fixed wireless internet service on its 5G network that is available to more than 50 million households and businesses nationwide and serves over 5 million customers, as well as T-Mobile Fiber, which has launched in parts of 16 U.S. markets. Those launches have shown consumer demand for broadband that T-Mobile cannot meet through its fallow capacity fixed wireless product alone, and many customers want the speed and reliability that only fiber can provide.

Jan Vesely, Partner within EQT’s Infrastructure Advisory Team said, “We are proud to have partnered with Lumos over the past six years to rapidly scale the company and roll out fiber to underserved markets, and we look forward to continuing to leverage EQT’s considerable digital infrastructure and fiber expertise to support the significant fiber buildout ambitions of T-Mobile and the JV. This new effort will build critical fiber broadband infrastructure that will enable remote work, education, and healthcare use cases across the country. We have worked with T-Mobile as a customer across many of our existing digital infrastructure investments and are delighted to build on that relationship and partner with T-Mobile on this opportunity to roll out fiber to underserved Americans.”
“Lumos takes great pride in our achievements, as we have successfully delivered fiber to hundreds of thousands of homes and businesses, marking a significant acceleration in our growth. Our commitment to enhancing customers’ lives through the development of a network prepared for the demands of tomorrow remains steadfast,” Brian Stading, CEO of Lumos. “With the support of our private equity partner, EQT, and leveraging the strength of the T-Mobile brand and unrivaled customer experience, Lumos is set to expedite our network expansion. This joint venture will amplify our ability to change lives through the transformative power of fiber optic internet.”
The transaction is expected to close in late 2024 or early 2025, subject to customary closing conditions and regulatory approvals. At closing, T-Mobile is expected to invest approximately $950 million in the JV to acquire a 50% equity stake and all existing fiber customers, with the funds invested by T-Mobile being used by Lumos for future fiber builds. The next capital contribution by T-Mobile out of an additional commitment of approximately $500 million is anticipated between 2027 and 2028. These combined investments are expected to allow Lumos to reach 3.5 million homes passed by the end of 2028. T-Mobile continues to expect to complete its remaining authorization for share repurchases and dividends in 2024.
With this transaction, EQT Infrastructure VI is expected to be 35-40% percent invested (including closed and/or signed investments, announced public offers, if applicable, and less any expected syndication) based on target fund size and subject to customary regulatory approvals.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/business/t-mobile-eqt-jv-to-acquire-lumos
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
Ookla: T-Mobile and Verizon lead in U.S. 5G FWA
T-Mobile combines Millimeter Wave spectrum with its 5G Standalone (SA) core network
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
T-Mobile US, in a partnership with Ericsson and Qualcomm Technologies, has successfully tested the aggregation of six component carriers in sub-6 GHz spectrum in its live production 5G network.
The test involved aggregating two channels of 2.5 GHz, two channels of PCS spectrum and two channels of AWS spectrum, according to T-Mobile US, which produced an “effective 245 MHz of aggregated 5G channels.”
T-Mo said that they were able to “achieve download speeds of 3.6 Gbps in sub-6 GHz spectrum. That’s fast enough to download a two-hour HD movie in less than 7 seconds!”
5G carrier aggregation allows T-Mobile to combine multiple 5G channels (or carriers) to deliver greater speed and performance. In this test, the Un-carrier merged six 5G channels of mid-band spectrum – two channels of 2.5 GHz Ultra Capacity 5G, two channels of PCS spectrum and two channels of AWS spectrum – creating an effective 245 MHz of aggregated 5G channels.
Image Courtesy of Qualcomm Technologies
“We are pushing the boundaries of wireless technology to offer our customers the best experience possible,” said Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology at T-Mobile. “With the first and largest 5G standalone network in the country, T-Mobile is the only mobile provider serving 10s of millions of customers to unleash new capabilities like 5G carrier aggregation nationwide, and I am so incredibly proud of our team for leading the way.”
T-Mobile US announced in May of 2023 that it was rolling out four component-carrier aggregation across its 5G Standalone network, which it said at the time can achieve peak speeds of 3.3 Gbps. In that case, T-Mobile US relies on two 2.5 GHz channels, one 1.9 GHz channel and one 600 MHz channel. The first device able to access 4CA capabilities was the Samsung Galaxy S23.
The carrier also touted its testing of five-component-carrier aggregation in sub-6 GHz spectrum at last year’s Mobile World Congress Barcelona. In that trial, working with Nokia and Qualcomm, T-Mo aggregated two FDD and three TDD carriers and achieved peak downlink throughput speeds that exceeded 4.2 Gbps.
T-Mobile claims to be the leader in 5G, delivering the country’s largest, fastest and most awarded 5G network. The Un-carrier’s 5G network covers more than 330 million people across two million square miles — more coverage area than AT&T and Verizon combined. 300 million people nationwide are covered by T-Mobile’s super-fast Ultra Capacity 5G with over 2x more square miles of coverage than similar offerings from the Un-carrier’s closest competitors.
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/ran/carrier-aggregation
Ookla: T-Mobile and Verizon lead in U.S. 5G FWA
T-Mobile combines Millimeter Wave spectrum with its 5G Standalone (SA) core network
Verizon, T-Mobile and AT&T brag about C-band 5G coverage and FWA
T-Mobile and Charter propose 5G spectrum sharing in 42GHz band
ABI Research: 5G Network Slicing Market Slows; T-Mobile says “it’s time to unleash Network Slicing”
T-Mobile US at “a pivotal crossroads” CEO says; 5,000 employees laid off
Ookla Q2-2023 Mobile Network Operator Speed Tests: T-Mobile is #1 in U.S. in all categories!
T-Mobile and Google Cloud collaborate on 5G and edge compute
T-Mobile combines Millimeter Wave spectrum with its 5G Standalone (SA) core network
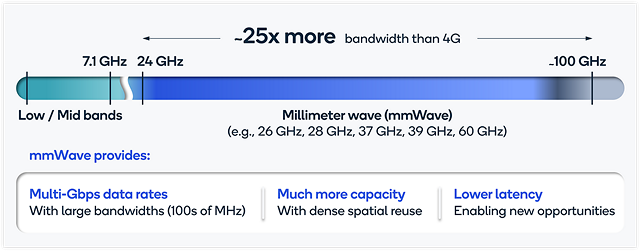
T-Mobile, with the help of with Ericsson and Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., has tested millimeter wave (mmWave) on its production 5G SA network (note that mmWave identifies higher frequencies used on a 5G RAN, while 5G SA refers to a true 5G core network). The Un-carrier aggregated eight channels of mmWave spectrum to reach download speeds topping 4.3 Gbps without relying on low-band or mid-band spectrum to anchor the connection. T-Mobile also aggregated four channels of mmWave spectrum on the uplink, reaching speeds above 420 Mbps.
In the latest revision of ITU-R M.1036- Frequency Arrangements for IMT-the following mmWave bands were approved:
-Frequency arrangements in the band 24.25-27.5 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 45.5-47 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 47.2-48.2 GHz
-Frequency arrangements in the band 66-71 GHz
In the U.S., Verizon has historically been the carrier promoting 5G mmWave, which they dubbed “5G Ultra Wideband.” The telco claims they’ve achieved 1.26 Gbps upload speed using 5G Ultra Wideband. With uploading data becoming increasingly important for video chats, uploading large files or live streaming video. “We have achieved remarkable speed in downloading using various combinations of spectrum in our world-class spectrum portfolio,” said Adam Koeppe, Senior Vice President of Technology Planning at Verizon. “This new achievement indicates how much additional performance we can unleash for our customers on the uplink as we aggregate different combinations of spectrum.”
T-Mobile took the opposite path, focusing on mid and low-band spectrum for its 5G network…until now. 5G mmWave can deliver very fast speeds because it offers massive capacity. But the signal doesn’t travel very well through obstacles, making it less ideal for mobile phone users who aren’t sitting still. That’s why T-Mobile has implemented a multi-band spectrum strategy using low-band to blanket the country and mid-band and high-band (Ultra Capacity) to deliver insanely fast speeds to nearly everyone. Now the Un-carrier is testing 5G mmWave on 5G SA for crowded areas like stadiums and, potentially, for fixed wireless service.
“We’ve been industry leaders – rolling out the first, largest and fastest 5G standalone network across the country – and now we’re continuing to push the boundaries of wireless technology,” said Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology at T-Mobile. “We’ve always said we’ll use millimeter wave where it makes sense, and this test allows us to see how the spectrum can be put to use in different situations like crowded venues or to power things like fixed-wireless access when combined with 5G standalone.”
T-Mobile is the U.S. leader in 5G [1.] delivering the largest, fastest and most awarded 5G network in the country. The Un-carrier’s 5G network covers more than 330 million people across two million square miles — more than AT&T and Verizon combined. 300 million people nationwide are covered by T-Mobile’s super-fast Ultra Capacity 5G with over 2x more square miles of coverage than similar mid-band 5G offerings from the Un-carrier’s closest competitors. According to Ookla’s quarterly speed test reports, T-Mobile’s 5G network has consistently outperformed AT&T’s and Verizon’s when it comes to median download speed.
Note 1. AT&T is the leading provider of mobile services in the U.S. with 229.1 subscribers as of Q2 2023, followed by: Verizon: 143.3 million (Q2 2023),,T-Mobile US: 117.9 million (Q3 2023), Dish Wireless: 7.5 million (Q3 2023), and uscellular: 4.6 million (Q3 2023).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
T-Mobile also offers wireless solutions to connect homes and businesses. 5G Home Internet (FWA) is available to over 50 million homes today, plus Small Business Internet and Business Internet is available across the country. This means millions of homes and businesses can finally ditch traditional ISPs for fast, reliable and hassle-free internet service with T-Mobile. The telco’s FWA customer base increased by 557,000 during Q3, giving it a total of 4.2 million. It has allowed T-Mobile to offer a compelling alternative to fixed broadband, but its service comes with the caveat that speeds will fluctuate depending on demand.
The extra capacity offered by mmWave could help to offer a faster, more consistent connection, making it even more appealing. However, the propagation challenges of mmWave spectrum means customers will have to ensure their FWA hub is sitting on the right shelf or window sill to establish a fast, reliable connection. Addressing complaints as customers struggle to put their hub in the right spot may be a problem for the Un-carrier.
Editor’s Note:
The NTIA will study the following bands in the next two years, noting that the spectrum could support a range of uses, including mobile broadband (IMT), drones and satellite operations:
- 3.1 GHz-3.45 GHz
- 5.03 GHz-5.091 GHz
- 7.125 GHz-8.4 GHz
- 18.1 GHz-18.6 GHz
- 37.0 GHz-37.6 GHz
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/network/t-mobile-revs-up-millimeter-wave-with-5g-standalone
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-achieves-upload-speeds-surpassing-1-gbps
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/t-mobile-finally-puts-mmwave-to-work-in-5g-sa-network
https://www.telecoms.com/wireless-networking/t-mobile-network-speeds-still-way-ahead-of-verizon-at-t
U.S. Launches National Spectrum Strategy and Industry Reacts
Verizon, T-Mobile and AT&T brag about C-band 5G coverage and FWA
Verizon says it has approximtely 222 million people covered with its mid-band C-band network, [1.] a figure the company hopes to increase to 250 million by the end of next year. “C-band is a game change for our business,” CEO Hans Vestberg said on the telco’s 3rd quarter earnings call. “Our network is winning.”
Note 1. C-band sits between the two Wi-Fi bands, which are at 2.4GHz and 5GHz. It’s slightly above and very similar to the 2.6GHz band that Clearwire and then Sprint used for 4G starting in 2007, and which T-Mobile currently uses for mid-band 5G. And it adjoins CBRS, a band from 3.55 to 3.7GHz that’s currently being deployed for 4G. ITU-R divided C-band into three chunks, referred to as band n77, band n78, and band n79.

……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Verizon officials said the company is using the capacity in its mid-band 5G network to pursue opportunities like fixed wireless access (FWA) and private wireless networks. “We see demand for the product continuing to grow,” Vestberg said of Verizon’s private wireless network offerings. He added that Verizon is working to transition its private wireless customers from pilots to commercial deployments. He also said the company is growing its ecosystem of suppliers for that business.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
T-Mobile announced Tuesday it now covers 300 million people with its 2.5GHz mid-band network, reaching that goal three months earlier than the company had planned. T-Mobile’s overall 5G footprint has expanded as well, now covering more than 330 million people or 98% of the population.
“We have been leaders in the 5G era from the start, deploying the largest, fastest, most awarded and most advanced 5G network in the country faster than anyone else,” said Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology at T-Mobile. “While the other guys are playing catch-up, finally beginning to build out their mid-band 5G networks, we are maintaining our lead and will continue offering customers the best network – paired with the best value – for years to come.”
“T-Mobile’s turnaround story is incredible, going from network underdog a decade ago to the undeniable network leader today,” said Anshel Sag, Principal Analyst at Moor Insights and Strategy. “T-Mobile has not only built out a robust 5G network with unmatched coverage and capacity, but the Un-carrier is also leading the way in rolling out new capabilities that will unlock the true promise of 5G.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Last week, AT&T said it ended the third quarter covering 190 million subscribers for its mid-band 5G network, and said it remains on track to cover 200 million by the end of the year. On the telco’s 3-2023 earnings call, CEO John Stankey said, “we continue to enhance the largest wireless network in North America and expand the nation’s most reliable 5G network. It’s no surprise that when you combine our high-value customer growth and rising revenues per user, we continue to grow profits in our wireless business.”
Regarding FWA, Stankey touted the company’s Internet Air offering. “We have no issues selling Internet Air into the business segment. It’s a really attractive thing for us to do. It’s a really helpful product on a number of different fronts. It meets a particular need.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/private-networks/verizon-jumps-too-as-mobility-biz-surprises-in-q3
https://www.pcmag.com/news/what-is-c-band
https://www.fool.com/earnings/call-transcripts/2023/10/19/att-t-q3-2023-earnings-call-transcript/
https://www.att.com/internet/internet-air/
T-Mobile and Charter propose 5G spectrum sharing in 42GHz band
This June, we noted that the FCC was exploring shared use of the 42 GHz band using in 500 megahertz of spectrum. Recently, T-Mobile and Charter voiced support for some kind of spectrum sharing scenario.
“While wireless carriers continue to require additional spectrum that is licensed on an exclusive-use basis, T-Mobile agrees that the technical characteristics of the 42GHz band, along with its separation from other millimeter wave spectrum that has already been licensed, means that the commission may wish to consider a different approach here,” T-Mobile wrote in an August 30th FCC filing.
“The commission, however, should avoid applying untested, novel sharing approaches to the 42GHz band. Instead, it should implement the nationwide non-exclusive licensing framework currently used in the 70/80/90GHz bands, with a few modifications to ensure that the spectrum will be used efficiently and may be deployed for [a] variety of advanced communications services.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Charter has long eyed the 37GHz band as a way to bolster mobile operations in its planned 3.5GHz CBRS network. The MSO/cableco has said it could offer speeds up to 1 Gbit/s via concurrent operations in the CBRS and 37GHz bands.
Charter’s FCC filing is similar to T-Mobile’s, as it supports a “unified nationwide, non-exclusive simple shared licensing regime.” The company urged the FCC to implement the same spectrum sharing design across both the lower 37GHz band and the 42GHz band.
“Allocating the lower 37GHz band for non-exclusive use would offer 600 megahertz for innovative new wireless connectivity in the United States,” Charter noted. “The allocation of the 42GHz band alongside the lower 37GHz band would of course increase the total spectrum available for innovative new deployments by 500 megahertz.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Backgrounder:
The 42GHz band resides in what is known as millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum. 5G transmissions in those bands are at very high speeds, but they typically travel just a few thousand feet, and generally cannot pass through obstructions like walls, trees, glass or concrete, i.e. they require line of sight communications.
WRC 19 identified mmWave frequencies for 5G, but ITU-R WP 5D did not complete and agree on the frequency arrangements for same (revision 6 of ITU-R M.1036) until very recently. WRC 19 identified the frequency bands: 24.25-27.5 GHz, 37-43.5 GHz, 45.5-47 GHz, 47.2-48.2 and 66-71 GHz for the deployment of 5G networks and the frequency arrangements for them is in draft recommendation ITU-R M.1036 which is expected to be approved this November. Note that 42GHz is not included!
Some analysts are quite positive on mmWave communications. For example, “mmWave 5G offers a way to improve on the current situation because the bands have extremely high capacity that are able to support very large amounts of data traffic and users, although in a small area,” wrote OpenSignal analyst Ian Fogg in a post on the network-monitoring firm’s website.
Qualcomm is also an advocate of spectrum sharing in mmWave bands since at least July 2022.
Image Credit: Qualcomm
Qualcomm’s filings to open the Lower 37 GHz band to shared licensed access ask the FCC to adopt a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) to allocate six 100-MHz-wide priority licenses in the Lower 37 GHz band and allow each priority operator—which may be a federal government or a commercial operator—to use the rest of the band on a secondary basis. To enable these secondary operations on an interference-free basis, each priority operator would implement a technology-neutral, equipment-based rule to provide coordinated, periodic listening of the channel, referred to as long term sensing (LTS), to determine whether its secondary operations on spectrum outside its priority licensed spectrum may cause harmful interference to the priority license holder of that swath of spectrum.
Secondary operations are only allowed for communications links that sensing determines will not cause interference to the priority licensee. The coordinated sensing procedure allows each priority license holder to access all other channels (i.e., the other 500 MHz) on a secondary – and interference-free – basis, increasing overall spectrum utilization while not degrading the QoS for the priority licensee.
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/ecfs/document/10830309419380/1
https://www.fcc.gov/ecfs/document/10830021467677/1
WRC 19 Wrap-up: Additional spectrum allocations agreed for IMT-2020 (5G mobile)
T-Mobile US at “a pivotal crossroads” CEO says; 5,000 employees laid off
T-Mobile US Chief Executive Mike Sievert says the company is at a “pivotal crossroads.” Sievert’s comments come in a letter to staff in which he says the company is laying off 5,000 employees, or some 7% of the company.
T-Mobile CEO Mike Sievert argued the new job cuts would better position T-Mobile for the future. Sievert also cited increasing customer acquisition and retention costs. He described the layoffs as a “large change, and an unusual one for our company.”
Sievert wrote in a letter to T-Mobile employees:
“What it takes to attract and retain customers is materially more expensive than it was just a few quarters ago. We’ve been out-running this trend by accelerating merger synergies, and building our high-speed Internet business faster than expected, and out-performing in a few other areas. However, it is clear that doing everything we are doing and just doing it faster is not enough to deliver on these changing customer expectations going forward.
Today’s changes are all about getting us efficiently focused on a finite set of winning strategies, so that we can continue to out-pace our competitors and have the financial capability to deliver a differentiated network and customer experience to a continually growing customer base, while simultaneously meeting our obligations to our shareholders.”

T-Mobile CEO Mike Sievert (Source: UPI/Alamy Stock Photo)
T-Mobile’s layoffs will come over the next five weeks. Sievert wrote that the cuts would primarily affect corporate and back-office roles, along with some technology positions. These job cuts should come as no surprise. T-Mobile has been steadily reducing the number of its employees since it merged with Sprint in 2020. Earlier this year T-Mobile laid off an unspecified number of employees as it worked to overhaul its retail sales strategy. Can Sievert be trusted when he wrote, “After this process is complete, I do not envision any additional widespread company reductions again in the foreseeable future.”???
Telecom layoffs this year are surging. AT&T, Verizon, Crown Castle, Ericsson, Airspan, Cambium Networks, Cisco Systems and Dish Network are among telecom companies cutting jobs. Moreover, both AT&T and Verizon have recently embarked on new cost-cuttingprograms on top of previous cost reduction campaigns.
The layoffs come as T-Mobile and its rival cell carriers face increased competition from cable companies that are offering mobile plans and piggybacking on the carrier’s networks via MVNO relationships. Other MVNOs, or mobile virtual network operators, unrelated to the cable companies are also offering lower-priced cell plans.
References:
https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1283699/000119312523219679/d507613dex991.htm
https://www.lightreading.com/5g-and-beyond/how-and-why-t-mobile-is-cutting-5000-jobs/d/d-id/786245?
https://www.wsj.com/business/telecom/t-mobile-us-to-lay-off-7-of-workforce-df368047
Inside AT&T’s newly expanded $8 billion cost-reduction program & huge layoffs
T-Mobile and Google Cloud collaborate on 5G and edge compute
Ookla Q2-2023 Mobile Network Operator Speed Tests: T-Mobile is #1 in U.S. in all categories!