Month: March 2021
Evaluating Gaps and Solutions to build Open 5G Core/SA networks
by Saad Sheikh, Vice President and Chief Architect, SouthTel, South Africa
Since the “freezing” of the much awaited 3GPP Release-16 in July 2020, many network equipment vendors have sought to develop 5G core/5G stand alone (5G SA) network capabilities. Those includee network slicing. massive IoT. uRLLC (ultra reliable, ultra low latency communications), edge network computing, NPN (non public network) and IAB (Integrated Access and Backhaul), etc.
It is just natural that all of the big telco’s in APAC and globally have started their journey towards 5G Standalone (5G SA) core network. However, most of the commercial deployments are based on vendor E2E stack which is a good way to start the journey and offer services quickly.
Yet there’s a big caveat: With the type of services and versatility of solution specially on the industry verticals required and expected from both 3GPP Release16 and 5G SA core network it is just a matter of time when network equipment vendors cannot fulfill all the solutions and that is when a dire need to build a Telco grade Cloud platform will become a necessity.
During the last two years we have done a lot of work and progress in both better understanding of what will be the Cloud Native platforms for the real 5G era. As of now, the 5G Core container platforms from an open cloud perspective are not fully ready but we are also not too far from making it happen.
2021 is the year that we expect a production ready open 5G native cloud platform avoiding all sorts of vendor lock ins.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Let’s try to understand top issues enlisted based on 5G SA deployments in Core and Edge network:
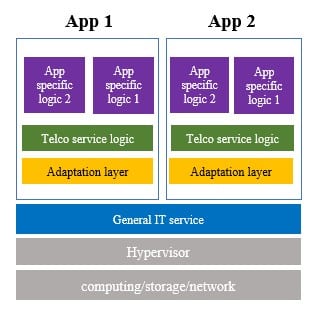
- Vendors are mostly leveraging existing NFVI to evolve to CaaS by using a middle layer shown Caas on Iaas. The biggest challenge is this interface is not open which means there are many out of box enhancements done by each vendor. This is one classic case of “When open became the new closed.”
Reference: https://cntt-n.github.io/CNTT/doc/ref_model/chapters/chapter04.html
The most enhancement done on the adaptors for container images are as follows:
- Provides container orchestration, deployment, and scheduling capabilities.
- Provides container Telco enhancement capabilities: Huge page memory, shared memory, DPDK, CPU core binding, and isolation
- Supports container network capabilities, SR-IOV+DPDK, and multiple network planes.
- Supports the IP SAN storage capability of the VM container.
- Migration path from Caas on IaaS towards BMCaaS is not smooth and it will involve complete service deployment, it is true with most operators investing heavily in last few years to productionize the NFVi no body is really considering to empty pockets again to build purely CaaS new and stand-alone platform however smooth migration must be considered.
- We are still in early phase of 5G SA core and eMBB is only use case so still we have not tested the scaling of 5G Core with NFVi based platforms.
- ETSI Specs for CISM are not as mature as expected and again there are a lot of out of the box. customizations done by each vendor VNFM to cater this.
Now let’s consider where the open platforms are lacking and how that might be fixed.
Experience #1: 5G Outgoing traffic from PoD:
The traditional Kubernetes and CaaS Platforms today handles and scales well with ingress controller however 5G PoD’s and containers outgoing traffic is not well addressed as both N-S and E-W traffic follows same path and it becomes an issue of scaling finally.
We know some vendors like Ericsson who already bring products like ECFE and LB in their architecture to address these requirements.
Experience#2: Support for non-IP protocols:
PoD is natively coming with IP and all external communication to be done by Cluster IP’s it means architecture is not designed for non-IP protocols like VLAN, L2TP, VLAN trunking
Experience#3: High performance workloads:
Today all high data throughputs are supported CNI plugin’s which natively are like SR-IOV means totally passthrough, an Operator framework to enhance real time processing is required something we have done with DPDK in the open stack world
Experience#4: Integration of 5G SBI interfaces:
The newly defined SBI interfaces became more like API compared to horizontal call flows, however today all http2/API integration is based on “Primary interfaces” .
It becomes a clear issue as secondary interfaces for inter functional module is not supported.
Experience#5: Multihoming for SCTP and SI is not supported:
For hybrid node connectivity at least towards egress and external networks still require a SCTP link and/or SIP endpoints which is not well supported
Experience#6: Secondary interfaces for CNF’s:
Secondary interfaces raise concerns for both inter-operability, monitoring and O&M, secondary interfaces is very important concept in K8S and 5G CNF’s as it is needed during
- For all Telecom protocols e.g BGP
- Support for Operator frameworks (CRD’s)
- Performance scenarios like CNI’s for SR-IOV
Today, only viable solution is by NSM i.e. a service mesh that solves both management and monitoring issues.
Experience#7: Platform Networking Issues in 5G:
Today in commercial networks for internal networking most products are using Multus+VLAN while for internal based on Multus+VxLAN it requires separate planning for both underlay and overlay and that becomes an issue for large scale 5G SA Core Network
Similarly, top requirements for service in 5G Networks are the following:
- Network separation on each logical interface e.g VRF and each physical sub interface
- Outgoing traffic from PoD
- NAT and reverse proxy
Experience#8: Service Networking Issues in 5G:
For primary networks we are relying on Calico +IPIP while for secondary network we are relying ion Multus
Experience#9: ETSI specs specially for BM CaaS:
Still I believe the ETSI specs for CNF’s are lacking compared to others like 3GPP and that is enough to make a open solution move to a closed through adaptors and plugin’s something we already experienced during SDN introduction in the cloud networks today a rigorous updates are expected on
- IFA038 which is container integration in MANO
- IFA011 which is VNFD with container support
- Sol-3 specs updated for the CIR (Container image registry) support
Experience#10: Duplication of features on NEF/NRM and Cloud platforms:
In the 5G new API ecosystem operators look at their network as a platform opening it to application developers. API exposure is fundamental to 5G as it is built into the architecture natively where applications can talk back to the network, command the network to provide better experience in applications however the NEF and similarly NRF service registry are also functions available on platforms. Today it looks a way is required to share responsibility for such integrations to avoid duplicates.
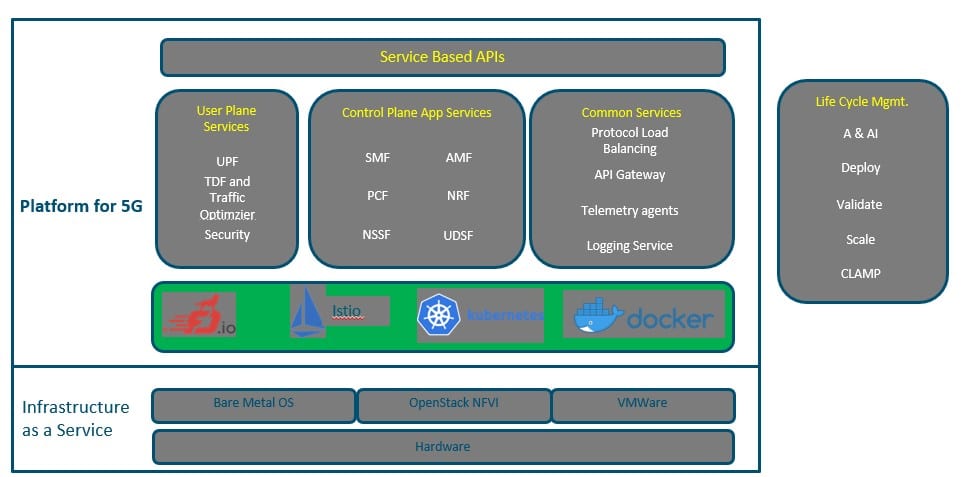
Reference Architectures for the Standard Platform:
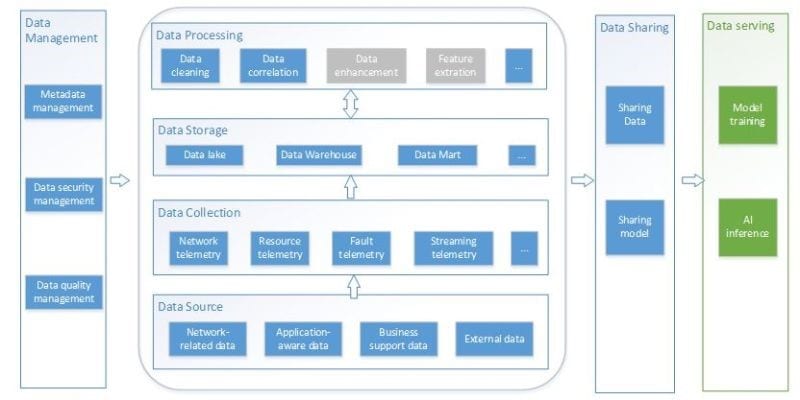
Sol#1: Solving Data Integration issues
Real AI is the next most important thing for telco’s as they evolve in their automation journey from conditional #automation to partial autonomy . However to make any fully functional use case will require first to solve #Data integration architecture as any real product to be successful with #AI in Telco will require to use Graph Databases and Process mining and both of it will based on assumption that all and valid data is there .
Sol#2: AI profiles for processing in Cloud Infra Hardware profiles
With 5G networks relying more on robust mechanisms to ingest and use data of AI , it is very important to agree on hardware profiles that are powerful enough to deliver AI use cases to deliver complete AI pipe lines all the way from flash base to tensor flow along with analytics .
Sol#3: OSS evolution that support data integration pipeline
To evolve to future ENI architecture for use of AI in Telco and ZSM architecture for the closed loop to be based on standard data integration pipeline like proposed in ENI-0017 (Data Integration mechanisms).
Sol#4: Network characteristics
A mature way to handle outgoing traffic and LB need to be included in Telco PaaS.
Sol#5: Telco PaaS
Based on experience with NFV it is clear that IaaS is not the Telco service delivery model and hence use cases like NFVPaaS has been in consideration for the early time of NFV . With CNF introduction that will require a more robust release times it is imperative and not optional to build a stable Telco PaaS that meet Telco requirements. As of today, the direction is to divide platform between general PaaS that will be part of standard cloud platform over release iterations while for specific requirements will be part of Telco PaaS.
The beauty of this architecture is no ensure the multi-vendor component selection between them. The key characteristics to be addressed are discussed below.
Paas#1: Telco PaaS Tools
The agreement on PaaS tools over the complete LCM , there is currently a survey running in the community to agree on this and this is an ongoing study.
Reference: https://wiki.anuket.io/display/HOME/Joint+Anuket+and+XGVELA+PaaS+Survey
Paas#2: Telco PaaS Lawful interception
During recent integrations for NFV and CNF we still rely on Application layer LI characteristics as defined by ETSI and with open cloud layer ensuring the necessary LI requirements are available it is important that PaaS include this part through API’s.
Paas#3: Telco PaaS Charging Characteristics
The resource consumption and reporting of real time resources is very important as with 5G and Edge we will evolve towards the Hybrid cloud.
Paas#4: Telco PaaS Topology management and service discovery
A single API end point to expose both the topology and services towards Application is the key requirement of Telco PaaS
Paas#5: Telco PaaS Security Hardening
With 5G and critical services security hardening has become more and more important, use of tools like Falco and Service mesh is important in this platform
Paas#6: Telco PaaS Tracing and Logging
Although monitoring is quite mature in Kubernetes and its Distros the tracing and logging is still need to be addressed. Today with tools like Jaeger and Kafka /EFK needs to be include in the Telco PaaS
Paas#7: Telco PaaS E2E DevOps
For IT workloads already the DevOps capability is provided by PaaS in a mature manner through both cloud and application tools but with enhancements required by Telco workloads it is important the end-to-end capability of DevOps is ensured. Today tools like Argo need to be considered and it need to be integrated with both the general PaaS and Telco PaaS
Paas#9: Packaging
Standard packages like VNFD which cover both Application and PaaS layer.
Paas#8: Standardization of API’s
API standardization in ETSI fashion is the key requirement of NFV and Telco journey and it needs to be ensured in PaaS layer as well. For Telco PaaS it should cover VES , TMForum,3GPP , ETSI MANO etc . Community has made following workings to standardize this
- TMF 641/640
- 3GPP TS28.532 /531/ 541
- IFA029 containers in NFV
- ETSI FEAT17 which is Telco DevOps
- ETSI TST10 /13 for API testing and verification
Based on these features there is an ongoing effort with in the LFN XGVELA community and I hope more and more users, partners and vendors can join to define the Future Open 5G Platform
Reference: https://github.com/XGVela/XGVela/wiki/XGVela-Meeting-Logistics
 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Glossary:
|
Term |
Description |
|
NFV |
Network Function Virtualization |
|
VNF |
Virtual Network Functions |
|
CNF |
Containerized Network Functions |
|
UPF |
User Plane Function |
|
AMF |
Access Management Function |
|
TDF |
Traffic Detection Function |
|
PCF |
Policy Charging Function |
|
NSSF |
Network Slice Subnet Function |
|
UDSF |
Unstructured Data Storage Function |
|
A & AI |
Active and Available Inventory |
|
CLAMO |
Control Loop Automation Management Function |
|
NFVI |
Network Function Virtualized Infrastructure |
|
SDN |
Software Defined Networks |
|
VLAN |
Virtual LAN |
|
L2TP |
Layer2 Tunneling Protocol |
|
SBI |
Service Based Interface |
|
NRF |
Network Repository Function |
|
NEF |
Network Exposure Function |
|
NAT |
Network Address translation |
|
LB |
Load Balance |
|
HA |
High Availability |
|
PaaS |
Platform as a Service |
|
ENI |
Enhanced Network Intelligence |
|
ZSM |
Zero touch Service Management |
|
EFK |
Elastic search, FLuentd and Kibana |
|
API |
Application Programming Interface |
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Saad Sheikh:
Saad Sheikh is an experienced telecommunications professional with more than 18 years of experience for leading and delivering technology solutions . He is currently Vice President and Chief Architect with Southtel, which is the leading System integrator in South Africa. There he is leading 5G, Cloud, Edge Networking, Open RAN, Networking and Automation units. He is helping to bring the power of innovative solutions to Africa.
Prior to this he was Chief Architect with STC (Saudi Telecom Company) where he lead the company Cloud Infrastructure Planning and Architecture Design to deliver large scale 5G , NFV , SDN and Cloud projects in Middle East. Previously, he held senior positions with both vendors and operators in Asia, Africa and APAC driving large scale projects in IT and Telecom.
India’s BSNL Selects NOVELSAT Hub System for Remote Islands Connectivity
NOVELSAT’s High Performance Hub Will Enhance Broadband Connectivity to Lakshadweep, Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The contract was awarded by System Integrator Precision Electronics Ltd (PEL) on behalf of BSNL.
State-run telecoms provider (BSNL) selected Israeli satellite transmission company Novelsat to provide high-capacity satellite-based backhaul and broadband services to Lakshadweep, Andaman, and Nicobar Islands under a Universal Service Obligation (USO) project funded by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT). The contract was awarded by System Integrator Precision Electronics Ltd (PEL) on behalf of BSNL.
Under the partnership, BSNL will use Novelsat’s Xnet Data Hub system [1.] for flexibility in its growing network. BSNL will also use Novelsat’s DynamiX technology for dynamic allocation of network resources in MCPC/Point-to-Multi-Point networks on top of Novelsat’s NS4 waveform for improved network economics, the company said.
Note 1. The Xnet Data Hub is for Point-to-Multi-Point satellite network data applications requiring high performance connectivity. Addressing multiple applications including enterprise, backhaul & trunking, government & defense, aero and maritime, NOVELSAT Xnet Data Hub delivers highly integrated and optimized and efficient hub solution.
Satellite backhaul more practical than fiber backhaul for remote islands:
Satellite has always been the advantageous solution for remote and hard to reach locations. As cost of satellite capacity continues to sharply decrease, satellite connectivity cost now rivals terrestrial solutions in a growing number of use cases, making satellite connectivity a viable and economical solution for providing connectivity to more locations and more users. Offering compressive point-to-point and point-to-multi-point solutions, NOVELSAT provides high data rate broadband connectivity for demanding telecom and enterprise applications including: backhaul, trunking, backbone networks, enterprise networks, maritime and aero connectivity.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
BSNL is looking to increase its network capacity to address growing demand for broadband amidst sharp rise in data consumption across users and locations. PEL along with its technology partner NOVELSAT addressed the BSNL requirement, and in turn their customer BSNL selected NOVELSAT’s Xnet Data hub system for the exceptional efficiency and flexibility it offers for growing BSNL network.
Designed to support the growing needs of hub network operators, NOVELSAT’s Xnet optimizes and maximizes both performance and usage of satellite and network resources. Utilizing NOVELSAT’s DynamiX technology for dynamic allocation of network resources in MCPC/Point-to-Multi-Point networks on top of the most bandwidth-efficient waveform, NOVELSAT NS4™, significantly improves network economics.
NOVELSAT partnered with Precision Electronics Limited, a listed company in India to offer its solution to BSNL. Precision Electronics Limited brings in network elements like networking gear, antenna & indoor/outdoor electronics, and overall systems integration beyond the core satellite hub and remote solution from NOVELSAT.
“BSNL’s network requires the highest levels of network quality and flexibility. NOVELSAT’s proven track record, combined with its leading-edge technology, allow us to rapidly expand our network and offer better services to our customers,” said Sh. Sanjay Kumar, GM (Radio) at BSNL. “NOVELSAT has been selected to meet our challenge of providing highly efficient and reliable broadband connectivity between our country’s islands and the mainland. With this solution we are supporting the goal of accelerating the economic growth and bettering the life of the islands population”.
“We are honored to play a part in the rollout of enhanced broadband connectivity to the people of Lakshadweep, Andaman, and Nicobar Islands, and we are committed to supporting BSNL during these challenging times, as it implements its network development,” said Gary Drutin, CEO of NOVELSAT. “The BSNL deployment is a great example of the benefits offered by NOVELSAT’s Xnet data hub system, delivering a high capacity, scalable solution with maximum performance and efficiency.”
Last month, U.S.-based ST Engineering iDirect inked a partnership with BSNL to provide satellite broadband to the Indian islands of Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep.
About BSNL
BSNL is an Indian state-owned telecommunications company, headquartered in New Delhi, India. It was incorporated by the Department of Telecommunications (DOT), Ministry of Communications, Government of India in 2000. It provides mobile voice and internet services through its nationwide network across India. It is the largest government owned telecom company in India offering variety of services in retail and enterprise segment.
About PEL
Precision Electronics Ltd. (PEL) is a listed company that is focused to provide customized mission critical solutions to its customers. Backed by a strong Design & Engineering team and a state of art manufacturing infrastructure, PEL designed products are being used by the Indian defence/paramilitary forces, TSPs, Railways, Healthcare sector to name a few. It is strongly poised to garner substantial business in the near future.
About Novelsat
NOVELSAT is an innovator and a leading provider of next-generation content connectivity solutions over satellite. Powered by our innovative technology, our solutions are transforming network capabilities to drive new experiences and expand growth potential.
Our leadership foundations are built around our proprietary waveform and premier system architecture, combined with cutting-edge video capabilities and best-in-industry content security. Pioneering, expanding and enhancing core and end-to-end capabilities, we outperform competitive solutions and products, delivering new levels of performance, efficiency and flexibility. Our high-performance solutions are setting the industry standards in spectral efficiency, transmission performance, media processing, video delivery, and content protection, powering mission-critical and demanding applications for the broadcast, cellular, government, and mobility markets.
World’s leading service and content providers have recognized the unique value of our state-of-the-art technology, selecting our solutions for their most demanding applications, including: Video transmission for the world’s leading broadcasters and content rights holders, as well as for the world’s major sports events; Broadband connectivity for backhaul/trunking networks of leading network operators and services providers; Mission critical communications for military, defense, security and emergency organizations; and Earth observation connectivity for leading earth observation constellation.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
BSNL Selects NOVELSAT Hub System for Remote Islands Connectivity
IBM, Samsung Electronics, and M1 Unveil Singapore’s 1st 5G Industry 4.0 Studio
IBM, Samsung Electronics and Singapore network operator M1 opened the IBM Industry 4.0 Studio, which will combine advanced 5G connectivity with artificial intelligence, hybrid cloud and edge computing functionalities to make and test innovative Industry 4.0 products for enterprises in Singapore and across the Asia Pacific region.
The Studio simulates operational use cases that demonstrate how businesses can harness the power of hybrid cloud and AI technologies and advanced 5G capabilities to transform critical operations and drive new value – from improving quality and productivity in production lines to empowering service and quality control personnel. The Studio will develop, test and benchmark real-world Industry 4.0 use cases involving autonomous guided vehicles, collaborative robots, 3-D augmented reality, and real-time AI visual and acoustic recognition and classification.
IBM worked with Samsung and M1 to deliver products that take advantage of the ultra-low latency, high reliability, and security of 5G connectivity, combining Samsung’s standalone 5G network products and mobile devices with IBM’s hybrid cloud, edge computing, and AI technologies, as well as M1’s engineering and network services expertise in the designing and integration of 5G SA products and formulation of 5G test cases to meet regulatory requirement.
Built on Red OpenShift, the Industry 4.0 use cases employ IBM’s AI products for visual and acoustic analysis and augmented reality technologies.
Supported by Singapore’s Infocomm Media Development Authority as part of Singapore’s 5G journey, the Studio is hosting the country’s first 5G Industry 4.0 trial, testing real-world applications that can be applied in the manufacturing sector, while measuring and optimising the performance of enterprise 5G for industrial use.
With full-fledged 5G standalone functionality covering at least half of Singapore by end 2022, Singapore will drive more businesses to evaluate the ways in which they can integrate 5G into their existing operations, but they need a way to trial new use cases to evaluate their adoption strategies and return on investment.
The launch is the next step in Samsung and IBM’s global strategic partnership to advance 5G and edge industry innovation through enterprise networks and through cross collaboration with global mobile operators.

“5G presents an enormous opportunity for enterprises to drive new value and transform their operations to harness the next era of industrial connectivity. This project builds on IBM’s longstanding strategic partnership with Samsung, and a shared vision with M1 and IMDA, to help businesses tap into emerging hybrid cloud and AI technologies that will define their future success. It is crucial these businesses have an opportunity to test and evaluate these technological investments, and we are committed to working shoulder to shoulder with them to ensure they make the best decisions that will truly propel their businesses forward,” said Brenda Harvey, General Manager, IBM APAC.
There are seven focus areas being explored via the Studio that could deliver transformative value for customers by applying ultra-low latency, high-bandwidth, stable and secure 5G connectivity to Industry 4.0 applications:
1. Visual Recognition solutions using IBM Maximo Visual Inspection. With 5G, this enables real-time, streaming video analytics to power use cases such as faster identification of defects on the manufacturing line or rapid sorting of parts in a warehouse environment.
2. Acoustic Insights. Applies AI to analyze audio captured by phones and tablets to uncover potential defects in server fans, for example. Combined with 5G, this enables audio streaming and more rapid analysis to enable continuous monitoring in real time.
3. Augmented reality (AR) solution, a collaboration between IBM Singapore and IBM Haifa Research Lab. For example, users can point the camera of their mobile device at equipment and view step-by-step instructions that are superimposed on the image on their screen to walk them through a procedure such as setup, testing, or repair. 5G enables rapid, dynamic access to multiple procedure models, so a technician could browse quickly from step to step without long delays to download new models. If the technician encounters a problem not covered in the procedure model, 5G enables a remote expert to provide real-time, live, peer-to-peer assistance using on-screen AR guidance.
4. Complex use cases for automated guided vehicles and collaborative robots, enabled by the low latency of 5G. For example, a robot arm uses a phone to visually scan an item; the visual is sent to the server, analysed and the result returned; the robot arm then takes action to sort or reject the item based on the Visual Inspection result. The low latency of 5G enables this process to take place in near-real-time, allowing the robot arm to immediately sort or reject parts.
5. AI models developed and deployed on edge servers, with flexibility and dynamic resource scalability via Red Hat OpenShift.
6. Container-based applications with continuous monitoring and automated management, integration, and control of multiple deployed solutions at the edge, via IBM Edge Application Manager.
7. 5G end-to-end solutions and vertical use cases for private networks. Delivering private networks that combine Samsung’s latest 5G end-to-end solutions, including the RAN and the Core, with IBM’s open hybrid cloud technologies. Additionally, exploring new vertical use cases to enable enterprises to adopt emerging technologies crucial to Industry 4.0.
Quotes:
“5G is a potential game changer for Industry 4.0. It is the critical connectivity layer that can enable smart manufacturing. I would like to congratulate IBM for the opening of its 5G-enabled Industry 4.0 studio here in Singapore. It is important for Singapore to be the place where innovative 5G solutions can be developed and deployed globally. A strong 5G ecosystem will provide more opportunities for businesses and our people. We will work with industry to forge ahead with 5G, as we architect Singapore’s digital future,” said Lew Chuen Hong, Chief Executive, IMDA.
“As a forerunner in Singapore’s 5G development, M1 is the first network operator to roll out 5G trials as early as 2018 and has developed more than 15 5G use cases, trials and partnerships – a record in the industry, in the areas of autonomous vehicles, robotics, AI and more. The endless possibilities that 5G SA network can bring to Industry 4.0 manufacturing in Singapore is set to benefit enterprises. M1’s 5G hyper-connectivity, end-to-end network slicing, ultra-low latency, as well as highly reliable and secured communications will enable businesses to work not just faster, more efficiently and securely, but smarter too. The use cases being tested and developed out of this project will help more Singapore businesses to adopt 5G, value-adding to the acceleration of Industry 4.0 and building a vibrant 5G ecosystem for Singapore,” said Manjot Singh Mann, CEO of M1.
KC Choi, Executive Vice President & Global Head of B2B Business, Mobile Communications Business, Samsung Electronics commented, “The opening of the Studio in Singapore is an important milestone in applying 5G-enabled mobile and network solutions with Industry 4.0 capabilities to help transform manufacturing. Mobile and 5G capabilities like these are empowering workers and changing the way factories and warehouses operate, bringing new efficiency and productivity to operations. Samsung is pleased to be collaborating with IBM, IMDA, and M1 in this groundbreaking project to help make 5G a reality for customers.”
References:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/ibm-samsung-m1-open-5g-industry-40-studio-in-singapore–1376197
FCC Notice of Inquiry to discuss Open and Virtualized RANs (vs Vendor Lock-in 2.0)
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) today adopted a Notice of Inquiry to start a formal discussion on the opportunities and potential challenges presented by open and virtualized radio access networks (RANs), and how the FCC might leverage these concepts to support network security and 5G leadership.
The FCC seeks comment on the current status of development and deployment, whether and how the FCC might foster the success of these technologies, and how to support competitiveness and new entrant access to this emerging market.
The Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN) concept promotes the use of open interface
specifications (not standards as the FCC incorrectly stated) in the portion of the telecommunications network that connects wireless devices—like mobile phones—to the core of the network.
This can be implemented in vendor-neutral hardware and software-defined technology based on open interfaces and standards. In addition, Open RAN allows disaggregation of the radio access network, which can enable the use of interchangeable technologies that promote network security and public safety. The FCC is seeking input from academics, industry, and the public on what steps are required to deploy Open RAN networks broadly and at scale.
The Notice of Inquiry (NOI) seeks comment on the current status of Open RAN development and deployment in networks in the U.S. and abroad. It asks about the role of established large manufacturers and new entrants in setting standards for this new network architecture. It seeks input on what steps should be taken by the FCC, federal partners, industry, academia, and others to accelerate the timeline for Open RAN standards development. Further, it seeks comment on any challenges or other considerations related to the deployment, integration, and testing of systems based on Open RAN specifications. The NOI also requests comment on the costs and benefits associated with Open RAN development and deployment.
The FCC’s Technological Advisory Committee, a group of industry representatives that provides technical advice to the Commission, recently recommended that the Commission encourage the development of the Open RAN ecosystem by supporting Open RAN innovation, standardization, testing, and security and reliability. The Commission also hosted a Forum on 5G Open Radio Access Networks in September 2020.
This Notice of Inquiry seeks input on the status of Open RAN and virtualized network environments: where the technology is today and what steps are required to deploy Open RAN networks broadly and at scale. It also seeks comment on whether and, if so, how deployment of Open RAN-compliant networks could further the Commission’s policy goals and statutory obligations, advance legislative priorities, and benefit American consumers by making state-of-the-art wireless broadband available more quickly and to more people in more parts of the country.
What the Notice of Inquiry Would Do:
- Describe the relationship of recent government action to Open RAN development, including through Commission and other U.S. government action, legislative developments, and international activity.
- Seek comment on the current status of Open RAN development and deployment domestically and internationally.
- Seek comment on potential public interest benefits in promoting Open RAN development and deployment, including increased competition, network vendor diversity, affordability for consumers, network security and public safety, and other potential benefits.
- Seek comment on additional considerations regarding Open RAN development and deployment, including potential software vulnerabilities or risks posed by a virtualized operating environment. o Seek comment on barriers to Open RAN development and deployment and whether and what Commission efforts could be undertaken to promote Open RAN development and deployment.
- Seek comment on how the Commission can collaborate with and/or leverage ongoing Open RAN research and development activities in academia and other federal agencies.
- Discuss and seek comment on the costs and benefits of Open RAN deployment.
Diagram courtesy of TIP Open RAN Project
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Author Notes:
It’s important to note that there is no Open RAN work ongoing within SDOs like ITU-R, ITU-T, ETSI or IEEE. Nor is there any Open RAN activity within 3GPP. Instead, there are three consortia/forums that are working on Open RAN specifications and market awareness. They are: O-RAN Alliance, TIP Open RAN project and GSMA which will surely be the marketing arm for this technology.
In addition, there are several consortiums in the U.S., Europe, and Asia that are trying to promote Open RAN technology.
In the U.S., the Open RAN Policy Coalition “represents a group of companies formed to promote policies that will advance the adoption of open and interoperable solutions in the Radio Access Network (RAN) as a means to create innovation, spur competition and expand the supply chain for advanced wireless technologies including 5G.”
“Coalition members believe that by standardizing or “opening” the protocols and interfaces between the various subcomponents (radios, hardware and software) in the RAN, we move to an environment where networks can be deployed with a more modular design without being dependent upon a single vendor.”
The above statement is quite strange, considering that 1) There is NO ongoing standardization work on Open RAN (consortiums produce specs but NOT standards) and 2) An “open” network should not exclude vendors (e.g. Huawei, ZTE) or cause vendor lock-in.
However, it seems vendor lock-in is how Open RAN technology is being deployed today with various vendors and operators banding together to offer Open RAN technology solutions. Some examples of that include:
- Rakuten-NEC “RCS” which has been endorsed by Telefonica and supposedly sold to 15 network operators.
- Mavenir, a U.S. based software developer, has teamed up with MTI, a Taiwanese maker of radio units.
- Parallel Wireless, a Mavenir rival, has a similar partnership with China’s Comba.
- NTT DoCoMo’s open RAN ecosystem includes some prominent names in the IT and telecom sectors, such as Dell, Fujitsu, Intel, Mavenir, NEC, Nvidia, Qualcomm, Red Hat, VMware, Wind River and Xilinx.
- Telefonica, Deutsche Telekom, Orange and Vodafone pledged in a MoU to back Open RAN systems that take advantage of new open virtualized architectures, software and hardware with a view to enhancing the flexibility, efficiency and security of European networks in the 5G era.
Light Reading’s Iain Morris coined the term “Vendor Lock-in 2.0.” He says that Open RAN deployment is all about trading one form of vendor lock-in for another, as depicted in this illustration, courtesy of Light Reading:

Market research firm Omdia’s view is that “preferred partnerships” will take shape between software developers and hardware manufacturers. Its latest forecast is that open and “virtualized” radio access network products will account for roughly 9% of the total market by the end of 2024, up from just 1% in 2020.
However, rather than encouraging new RAN companies, Omdia believes the big five – Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung – will “probably seize the majority” of this business. The challengers, it says, simply “cannot achieve the same economies of scale as the incumbents.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-seeks-comment-open-radio-access-networks
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-370266A1.pdf
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2021/01/20/analysis-telefonica-vodafone-orange-dt-commit-to-open-ran/
FCC Votes to Move Forward on 3.45-3.55GHz Spectrum Auction
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) said today that it will make mid-band spectrum in the 3.45-3.55 GHz band available for auction to facilitate 5G deployment across the U.S. The FCC consulted last year on allowing flexible use of the 3.45-3.55 GHz band. The latest action means the FCC is on track for a 5G mid-band auction this year. Bidding in FCC Auction 110 is expected to begin in early October 2021.
Auction 110 will offer up to 100 megahertz of spectrum divided into ten 10-megahertz blocks licensed by geographic areas known as Partial Economic Areas (PEAs), for a total of 4,060 flexible-use licenses across the contiguous United States. The proposed auction procedures would include a clock phase for bidding on generic blocks in each geographic area followed by an assignment phase for bidding on frequency-specific license assignments. The Public Notice proposes bidding credit caps and specific upfront payment and minimum opening bid amounts. Flexible-use licenses made available through this auction are subject to cooperative sharing requirements to protect federal incumbents, so the Public Notice proposes a reserve price of over $14.7 billion in order to meet the requirement that auction proceeds cover the expected sharing and relocation costs for federal users in the band.
Today’s Public Notice works in concert with new rules for the 3.45 GHz band that were also adopted today, establishing a framework for coordination of non-federal and federal use and establishing a band plan. In legislation passed last year, Congress required the Commission to commence a system of competitive bidding for licenses in the 3.45 GHz band by the end of 2021. Today’s actions position the Commission to fulfill that mandate.
Last year’s Consolidated Appropriations Act required the commission to start an auction for licenses in the 3.45-3.55 GHz band by the end of 2021. The rules now adopted will reallocate 100 MHz of spectrum in the 3.45 GHz band for flexible use wireless services.
The FCC also established a framework for the 3.45 GHz band which will enable commercial use by different cellular network providers, while also ensuring that federal incumbents are protected from interference. Together, the 3.45 GHz band and the neighboring 3.5 GHz and 3.7 GHz bands represent 530 MHz of contiguous mid-band spectrum for 5G.
The FCC is now inviting comments on procedures for the auction of 100 MHZ of mid-band spectrum in the 3.45–3.55 GHz. Bidding in Auction 110 is expected to start in early October.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Forward Reference:
Separately, the FCC Seeks Comment on Open Radio Access Networks, which we cover in a companion post.
Session Border Controller (SBC) for Enterprises and VoIP Service Providers
by Nellie Marteen
Introduction:
If you are new to Unified Communications (UC), it could be challenging to learn its many components. Some acronyms could be confusing. For example, SBC- Session Border Controller.
SBC is a network element used to protect Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) based VoIP (most enterprises use VoIP as the telephony service over the Internet). SBC may be deployed in the enterprise/customer premises (see Figure below), the VoIP carrier network or in the cloud as discussed later in this article.
SIP is used to initiate, maintain, and pause the working of VoiP and SIP services. The primary purpose of SBC is to enhance connectivity and address safety problems. However, some companies do not use SBC despite knowing its many benefits.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
SBC in the enterprise/customer premises is shown in this Figure:
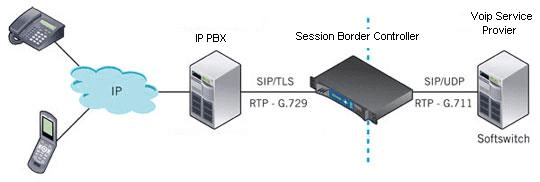
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Advantages of using SBC:
1. Quality of Calls
Session Border Controller can enhance call quality and provide ease of use. SBC enables the IP Private Branch Exchange (PBX) to be placed on the LAN among a separate IP address. They can do significant things such as normalizing hosted PBX signaling between the PBX as well as the service provider and providing critical routing capacities.
SBCs also assure interoperability of VoIP and video gadgets, examine VoIP lines, analyze call quality, and many more to name. SBC is a must if you get complaints about dropped or missed calls, reduced call quality, or both.
2. Connectivity
The primary function of SBC is to connect a company’s communications infrastructure to the hosted PBX service providers, private vendor network, and public internet. Additionally, SBCs have various essential roles, such as maintaining and securing networks.
An organization can save time and money by using SBCs. They can easily route their phone traffic via internal IPs rather than conventional circuit switched phone networks. Organizations can route phone calls instantly without paying for individual, traditional phone lines.
3. Safety
This is the benefit that many companies do not recognize. If a SBC recognizes a potential security threat, it can instantly remove/block that problem. After spotting the threat, it will alert the host computer(s) with the threat details and the protocols applied to normalize it. Also, SBCs can send the threat date to other businesses’ branches to look out for the same security breach. IT teams can be aware and utilize the data to look out for future security threats.
4, Mitigation of DoS Attacks and Continuity of Service
SBCs use pattern recognition technology to find unusual activities like a strange traffic surge while a DoS (Denial of Service) attack [1.] is ongoing. DoS strikes can take down entire networks resulting in unexpected downtime. Firewalls are generally not sufficient to prevent DoS attacks.
SBCs decrease threats and defend business communication systems from DoS attacks. DoS strikes can interpret phone and video conferences and steal important information or infect systems with malware and viruses. And if the system gets down due to a DoS attack, the organization may have to suffer for an unknown amount of time.
You can watch a short video on how SBCs detect and defend against DoS attacks.
Note 1. A denial-of-service (DoS) attack occurs when legitimate users are unable to access information systems, devices, or other network resources due to the actions of a malicious cyber threat actor. The most common method of attack occurs when an attacker floods a network server with traffic. In this type of DoS attack, the attacker sends several requests to the target server, overloading it with traffic. These service requests are illegitimate and have fabricated return addresses, which mislead the server when it tries to authenticate the requestor. As the junk requests are processed constantly, the server is overwhelmed, which causes a DoS condition to legitimate requestors.
5. Security
Hackers and other bad actors have found new ways to interrupt business communications services and upgrade their ways to disrupt older security measures. Here, SBCs take care of the protection. It is crucial to have up-to-date methods supported. Additionally, an extra layer of security from SBCs are crucial to safely maintaining VoIP solutions.
SBC Challenges:
SBC can be a complex piece of technology – one that demands a certain amount of expertise to set up and maintain. It is not a set-and-forget technology; as additions, moves and changes of voice service occur, the SBC must be configured to recognize them. Also, the IT department must actively manage SBC devices adding to their workload.
Who controls the session border?
For the enterprise, it is obviously desirable to be able to secure network connections, so their IT department should manage the SBC. Yet the VoIP carrier — whose network is being connected to — is also concerned about such things as QoS, lawful intercept of voice traffic and management of the voice connection.
For these reasons, communications carriers who offer VoIP connectivity often want to manage the session border controller or specify the controller that the enterprise will use. This is clearly at odds with an enterprise that wants to mask its internal networks from external intrusion. SBC, from the standpoint of the carrier, breaks the end-to-end management of call completion and complicates regulatory obligations such as access to 911 services and call intercept.
SBC in two VoIP carrier networks is depicted in this diagram:

Complicating this situation is the introduction of cloud-based session control. In this scenario, the SBC functionality is provided through a cloud service. Advantages are that the enterprise can offload a great deal of the management overhead associated with SBC maintenance. The drawback is that VoIP traffic latency can increase dramatically as it transits a much larger network.
Conclusions:
We have described and detailed all the significant benefits of SBC in this article, along with the challenges an IT department must deal with to effectively use SBCs. The important topic of whether the enterprise or carrier should control the session border was discussed along with cloud based session control.
It should be crystal clear that enterprises using VoIP should integrate SBC within their business communications system – either directly or via their VoIP service provider.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.voip-info.org/session-border-controller/
https://ribboncommunications.com/company/get-help/glossary/session-border-controller-sbc
https://www.ir.com/guides/a-complete-guide-to-session-border-controllers
https://us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/tips/ST04-015
https://www.ecosmob.com/session-border-controller/#1
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Nellie Marteen:
Nellie is also a blogger who writes about a variety of topics.
Huawei or Samsung: Leader in 5G declared Standard Essential Patents (SEPs)?
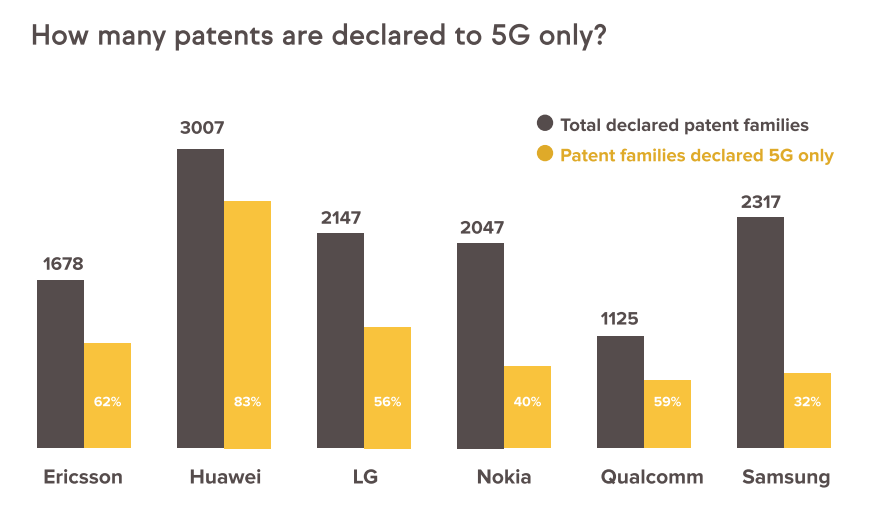
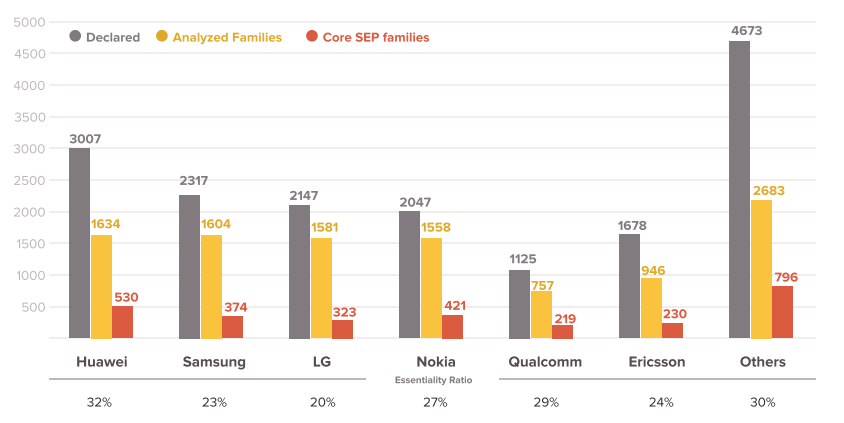
A new report, jointly released by IP consulting and analysis companies, Amplified and GreyB, disclosed that the top 6 companies (Huawei, Samsung, LG, Nokia, Ericsson, Qualcomm) account for 64.9% in 18,887 declared patent families. In granted 10,763 declared patent families, 2,893 families have been identified as core SEPs where top 6 companies account for 72.5%.
Huawei was first with 530 patent families and a ratio 18.3%. Nokia and Samsung were ranked No. 2 and No. 3 with 14.6% and 12.9%. respectively.
The report is an update of the previous report “Exploration of 5G Standards and Preliminary Findings on Essentiality” released on May 26, 2020.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. announced on March 10th that it has ranked first in 5G Standard Essential Patent (SEP)¹ shares according to a patent essentiality study conducted by IPlytics2, a Berlin-based market intelligence firm comprised of economists, scientists and engineers. The findings were published in IPlytics’ recent report: “Who is leading the 5G patent race? A patent landscape analysis on declared SEPs and standards contributions.”

Samsung also ranked second in two other categories: share of 5G granted3 and active patent4 families5, and share of 5G granted and active patent families with at least one of them granted by the EPO (European Patent Office) or USPTO (United States Patent and Trademark Office).
Last year, Samsung also led in 5G patents as a result of its research and development of 5G standards and technologies.
the top 10 companies own more than 80% of all granted 5G patent families, while the top 20 own more than 93% of all 5G granted patent families. These numbers confirm that there are only a few major large 5G patent owners, but looking at overall 5G declarations, the IPlytics Platform database identified more than 100 independent companies, which have declared ownership of at least one 5G patent.
The 5G patent family statistics presented in Table 1 are not based on verified SEP families. Neither ETSI nor the declaring companies have published independent assessments of the essentiality or validity of the declared 5G patents. Thus, the 5G patent families presented are only potentially essential. Many well-known SEP studies estimate that between 20% and 30% of all declared patents are essential. However, the essentiality rate differs across patent portfolios. To better understand the essentiality rate across portfolios, IPlytics created a data set of 1,000 5G-declared patent families (EPO/USPTO granted), which independent experts have mapped to 5G specifications. Here, the experts mapped the patents for six hours in a first check and then EPO/USPTO patent attorneys double-checked the mapping for a further three hours.
Table 1. Top 5G patent declaring companies (with >1% share)
| Current Assignee | 5G families | 5G granted and active families | 5G EPO/USPTO granted and active families | 5G EPO/USPTO granted and active families not declared to other generations |
| Huawei (CN) | 15.39% | 15.38% | 13.96% | 17.57% |
| Qualcomm (US) | 11.24% | 12.91% | 14.93% | 16.36% |
| ZTE (CN) | 9.81% | 5.64% | 3.44% | 2.54% |
| Samsung Electronics (KR) | 9.67% | 13.28% | 15.10% | 14.72% |
| Nokia (FN) | 9.01% | 13.23% | 15.29% | 11.85% |
| LG Electronics (KR) | 7.01% | 8.7% | 10.3% | 11.48% |
| Ericsson (SE) | 4.35% | 4.59% | 5.25% | 3.79% |
| Sharp (JP) | 3.65% | 4.62% | 4.66% | 5.50% |
| Oppo (CN) | 3.47% | 0.95% | 0.64% | 1% |
| CATT Datang Mobile (CN) | 3.44% | 0.85% | 0.46% | 0.68% |
| Apple (US) | 3.21% | 1.46% | 1.66% | 2.15% |
| NTT Docomo (JP) | 3.18% | 1.98% | 2.25% | 1.9% |
Source: IPlytics
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Superscript Notes:
[1] “A patent that protects technology essential to a standard”, European Commission report – “Setting out the EU approach to Standard Essential Patents”, p1, November 2017.
[2] “IPlytics derived the “essential rate” by creating a random data set of 1,000 5G-declared patent families (EPO/USPTO granted) and mapping it to 5G specifications.” . Available : https://www.iam-media.com/who-leading-the-5g-patent-race-patent-landscape-analysis-declared-seps-and-standards-contributions
[3] “a patent that is granted by at least one of patent offices”, IPlytics report – “who is leading the 5G patent race”, p5, November 2019.
[4] “in active status, which means it has not lapsed, been revoked or expired”, IPlytics report – “who is leading the 5G patent race”, p3, November 2019.
[5] “a collection of patent applications covering the same or similar technical content”, . Available: https://www.epo.org/searching-for-patents/helpful-resources/first-time-here/patent-families.html
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.amplified.ai/news/
https://www.greyb.com/5g-patents/
https://news.samsung.com/us/samsung-extends-leadership-5g-patents/
Omnispace Demonstrates 5G Satellite Capability with U.S. Navy & Marine Corps
Omnispace, the company that is building a global hybrid network, today announced the successful demonstration of 5G satellite capability with the National Security Innovation Network (NSIN), along with the Navy and Marine Corps. Omnispace was selected by NSIN in 2020 to pilot its technology in connection with Verizon’s new 5G “Living Lab.”
This week, Omnispace successfully tested an initial 5G-via-satellite capability in a LinQuest lab demonstration for the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps. A number of commercial-off-the-shelf 5G devices successfully communicated voice and data services via an emulated 5G radio access network (RAN), to Omnispace’s on-orbit satellite, leveraging LinQuest Corporation’s lab facility in Northern Virginia.
“Omnispace is honored to have been selected to work with the U.S. Navy and Marines to demonstrate 5G capability from space,” said Campbell Marshall, Vice President, Government and International Markets, Omnispace LLC. “The development of standards-based 5G non-terrestrial network (NTN) technology powered by Omnispace’s S-band spectrum will allow small tactical 5G devices to communicate directly and seamlessly with 5G-capable satellites and terrestrial networks, giving our warfighters ubiquitous global connectivity and true comms-on-the-move.”
“5G will be a critical technology for our military operations in the very near future, and those operations aren’t limited to dense urban environments where most 5G infrastructure is being deployed,” said Marine Corps Lieutenant Colonel Brandon Newell, Director, SoCal Tech Bridge, Naval X, a driving force behind some of the U.S. Department of Defense’s (DoD) 5G initiatives. “Truly global, mobile 5G connectivity in aero, maritime and remote areas will be essential across a broad spectrum of our government and military operations.”
Omnispace is continuing the development of a global hybrid 5G communications network based on 3GPP standards, which will the ensure security and interoperability of devices all over the world for a wide array of enterprise and government customers.
The company plans to make its direct-to-satellite 5G NTN connectivity solutions available through its ‘one global network,’ which will utilize the company’s existing 2 GHz priority spectrum rights. Initial elements of the Omnispace network will enter into service in 2022.
About Omnispace
Headquartered in the Washington D.C. area, and founded by veteran telecommunications and satellite industry executives, Omnispace is redefining mobile connectivity for the 21st century. By leveraging 5G technologies, the company is combining the global footprint of a non-geostationary satellite constellation with the mobile networks of the world’s leading telecom companies to bring an interoperable “one network” connectivity to users and IoT devices anywhere on the globe.
Learn more at: Omnispace.com and follow on LinkedIn or Twitter @omnispace.
AT&T Provides Update on Fiber Rollouts, 5G Expansion, and Financial Outlook
Here are the highlights of AT&T Investor Day Announcements:
3 million new fiber locations:
AT&T plans to deploy fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) to another 3 million-plus residential and business locations across more than 90 metro areas in 2021, and is already sizing up plans to push that to an additional 4 million locations in 2022, Jeff McElfresh, CEO of AT&T Communications, said today during the company’s investor day event.
“The margin economics are attractive. These areas are adjacent to our current footprint, driving cost efficiencies in our build as well as our marketing and distribution efforts.”
McElfresh expects its fiber subscriber volumes increase in the second half of the year after the initial buildouts, but noted that he likes what AT&T is seeing in the early part of 2021. The company noted that about 70% of its gross broadband adds in fiber buildout areas are new AT&T customers.
“And if we keep up with that pace, our vision would be to have over half of our portfolio, or 50% of our network, covered by that fiber asset. As our integrated fiber plan improves the yield performance on that fiber it will further give us conviction on continuing that investment in the coming years.”
AT&T is also looking to broaden its reach of fiber amid rising data demand and network usage that has occurred during the pandemic, and isn’t expected to stop any time soon. That’s shown in the graph’s below:
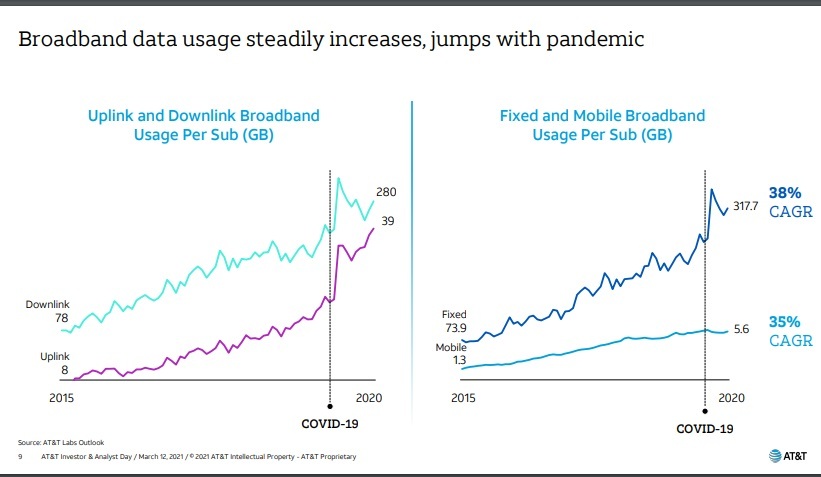
References:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
AT&T’s 5G Strategy:
AT&T’s 5G network now covers 230M Americans in 14,000 cities and towns and AT&T 5G+ is now available in parts of 38 cities in the U.S.
Note: AT&T may temporarily slow data speeds if the network is busy.
“Connectivity is at the heart of everything we do – 140 years and counting. From our fiber network backbone to the layers of wireless spectrum technology, we provide 5G network coverage that delivers the speeds, security and lower latency connections that customers and businesses need,” said Jeff McElfresh, CEO – AT&T Communications. “Over the past five years, AT&T has invested more capital in the U.S. than any other public company.”
Here is what the company said about its 5G Strategy:
AT&T has planned a balanced approach to 5G. Our strategy of deploying 5G in both sub-6 (5G) and mmWave (5G+) spectrum bands provides a great mix of speeds, latency and coverage for consumers and businesses. We rolled out nationwide 5G that now covers 230 million people, and offer 5G+ providing ultra-fast speeds to high-density areas where faster speeds can have huge impacts for our customers. So far, AT&T has deployed 5G+ nodes in parts of 38 cities across the U.S.
AT&T 5G is opening up some impressive opportunities for businesses and consumers and mid-band and mobile edge computing will help us go even further. There is an emerging multi-sided business model across 5G, edge computing and a variety of use cases from healthcare to gaming.
Our mobile edge computing plus 5G network will help satisfy the need for ultra-responsive networks and open up new possibilities for consumers and businesses. With our investments, we will take advantage of new technologies like spatial computing to enable applications across industries from manufacturing automation to watching immersive sports.
Reference: https://about.att.com/story/2021/5g_strategy.html
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
C-band spectrum deployment to begin in 2021:
- AT&T acquired 80 MHz of C-band spectrum in the FCC’s Spectrum Auction 107. The company plans to begin deploying the first 40 MHz of this spectrum by the end of 2021.
- AT&T expects to spend $6-8 billion in capex deploying C-band spectrum, with the vast majority of the spend occurring from 2022 to 2024. Expected C-band deployment costs are already included in the company’s 2021 capex guidance and in its leverage ratio target for 2024.
- AT&T expects to deliver 5G services over its new C-band spectrum licenses to 70 to 75 million people in 2022 and 100 million people in “early” 2023.
- Funding C-band spectrum: AT&T’s investment in C-band spectrum via Auction 107 totals $27.4 billion, including expected payments of $23 billion in 2021.
- To meet this commitment and other near-term priorities, in 2021 the company expects to have access to cash totaling at least $30 billion, including cash on hand at the end of 2020 of $9.7 billion, commercial paper issued in January 2021 of $6.1 billion and financing via a term loan credit agreement of $14.7 billion.
Jeff McElfresh, CEO of AT&T Communications, explained the operator’s focus on both 5G and fiber: “Our value proposition is to serve customers how they want to be served with enough bandwidth and capacity and speed, and we’ll let the technology service architecture meet that demand or that need.”
“When you get up into the midband segment of spectrum, while it offers us really wide bandwidth for speed and capacity, its coverage characteristics don’t penetrate [buildings and other locations] as effectively as the lowband does,” he said. “And so as we design our network and our offers in the market, you will see us densify our wireless network on the top of our investments in fiber.”
–>Yet McElfresh didn’t really address how AT&T Communications would overcome those challenges.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2021/att_analyst_day.html
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Financial Targets and Guidance:
- End-of-year 2021 debt ratio target of 3.0x. The company expects to end 2021 with a net debt-to-adjusted EBITDA ratio of about 3.0x,3 reflecting an anticipated increase in net debt of about $6 billion to fund the C-band spectrum purchase.
- 2024 debt ratio of 2.5x or lower. During 2024, AT&T expects to reach a net debt-to-adjusted EBITDA ratio of 2.5x or lower.3 To achieve this target, the company expects to use all cash flows after total dividends to pay down debt and will continue to look for opportunities to monetize non-strategic assets. The company also does not plan to repurchase shares during this period.
- 2021 guidance unchanged. AT&T’s 2021 financial guidance, announced in January 2021, is unchanged on a comparative basis. For the full year, the company continues to expect:
- Consolidated revenue growth in the 1% range
- Adjusted EPS to be stable with 20204,5
- Gross capital investment6 in the $21 billion range, with capital expenditures in the $18 billion range
- 2021 free cash flow7 in the $26 billion range, with a full-year total dividend payout ratio in the high 50’s% range
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2021/att_analyst_day.html
Verizon Outlines Plans for C-Band and mmWave 5G, Business Internet and MEC
C-Band auction results:
Verizon has outlined its plans to expand 5G network coverage using the spectrum it acquired in the recent C-band auction. The company pledged to cover 100 million Americans with its new C-band 5G network—which it will brand as “ultra wideband”—by next March
Verizon succeeded in more than doubling its existing mid-band spectrum holdings by adding an average of 161 MHz of C-Band nationwide for $52.9 billion including incentive payments and clearing costs.
Verizon won between 140 and 200 megahertz of C-Band spectrum in every available market. Specifically, Verizon:
- Secured a minimum 140 megahertz of total spectrum in the contiguous United States and an average of 161 megahertz nationwide; that’s bandwidth in every available market, 406 markets in all.
- Secured a consistent 60 megahertz of early clearing spectrum in the initial 46 markets – this is the swath of spectrum targeted for clearing by the end of 2021, home to more than half of the U.S. population.
- Secured up to 200 megahertz in 158 mostly rural markets covering nearly 40 million people. This will further enhance Verizon’s broadband solution portfolio for rural America.
The auction results represent a 120 percent increase in Verizon’s spectrum holdings in sub-6 gigahertz bands. The quality of this spectrum and Verizon’s depth of licensed holdings represent the premier asset in the industry. In addition, C-Band is a widely used spectrum band throughout the world and will allow for roaming opportunities and economies of scale. The spectrum bands Verizon won are contiguous, which will streamline deployment of this spectrum across the mainland United States.
At an analysts meeting on Wednesday evening, the company said the improved services will help it accelerate wireless network service revenue growth. Verizon expects growth of at least 2 percent this year, 3 percent in 2022 and 2023 and 4 percent or more in 2024. It’s committed an extra $10 billion in capex over the next three years to support the additional 5G network roll-out. Projected spending this year is in the range of $17.5-18.5 billion.
5G mmWave: The super-fast 5G mmWave network that Verizon launched two years ago has seen slow growth, even though Verizon has put up 17,000 cell sites. It’s a very short-range technology, and it’s best used in places like stadiums, concert halls, and convention centers—all the places that have been hardest hit by the pandemic.
Only 5% of Verizon’s total network usage will be on millimeter-wave by the end of 2021, although that could double if stadiums fill up again, according to Verizon CTO Kyle Malady. Only 9% of the carrier’s postpaid customer base has mmWave-capable phones.
Ultimately, he sees as much as 50% of 5G network usage moving to mmWave in dense cities. Of course, that involves people going outside to use it, because mmWave requires line of sight communications so can’t penetrate building walls or other structures.
Verizon is looking at using millimeter-wave for focused backhaul, which will let it put up more rural sites quickly without worrying about running fiber to them.
The company intends to put up another 14,000 millimeter-wave sites this year, Malady said. There’s still technical room for improvement with millimeter-wave, he added. Verizon is working with three different repeater vendors to improve range without adding entire new sites, and he has a “roadmap with Qualcomm” for better beamforming and software features to improve both range and latency.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In the next 12 months, Verizon expects to have incremental 5G bandwidth via the new spectrum available to 100 million people in the initial 46 markets, delivering 5G Ultra Wideband performance on C-Band spectrum. Over 2022 and 2023, coverage is expected to increase to more than 175 million people and by 2024 and beyond, when the remaining C-Band is cleared, more than 250 million people are expected to have access to Verizon’s 5G Ultra Wideband service on C-Band spectrum.
In addition, Verizon is committing to an additional $10 billion in capital expenditures over the next three years to deploy C-Band as quickly as possible. This spend will be in addition to the current capital expenditure guidance of $17.5B-$18.5B for 2021, which is expected to be at comparable levels through 2023.
C-Band spectrum in Verizon’s Network:
More than 70% of the 5G devices in the hands of customers today are C-Band compatible. Every iPhone 12 model is C-Band compatible. The Samsung Galaxy S21 series and Google Pixel 5 are also compatible. Going forward, all new 5G handsets Verizon brings to market to postpaid customers will be C-Band compatible, with more than 20 C-Band compatible devices offered by the end of the year.
The acquisition of this C-Band spectrum will be a critical component in Verizon’s 5G broadband strategy — 5G Home and 5G Business Internet.
5G Home: By the end of this year, Verizon expects to cover nearly 15 million homes with its home broadband product, and by the end of 2023, 30 million homes, using both 4G and 5G.
To accompany the growth in fixed broadband offerings, the company introduced new 5G Home devices which will be simple for customers to install in their homes – including the Internet Gateway, and the Verizon Smart Display, which join the Verizon 5G Internet Gateway. All three devices will have a sleek design and ‘self setup’ featuring AR guidance, simple instruction videos, and in-app chat and call support.
5G Home internet, the super fast service with download speeds up to 1 Gbps, depending on location, is currently available in 18 markets, with one to two million households expected to be covered via mmWave by end of 2021 and a total of 15 million with LTE Home and the arrival of the first tranche of C-Band. Verizon has teamed up with some of the best content providers in the industry to bring customers plenty of options for all their gaming and streaming needs.

5G Business Internet: 5G Business Internet complements the full suite of Verizon Business tools and offerings, including OneTalk voice communications, BlueJeans by Verizon video-collaboration platform, advanced security and other business services.
By using a high powered fixed 5G receiver, business customers will be able to access the broadband speeds they need with the reliability from Verizon they have come to expect. 5G Business Internet is now available in three markets on mmWave with plans to bring the product to 20 more before the end of the year.
Accelerate 5G Edge:
Verizon Business is well positioned to capture significant edge compute share and is in-market today with both public and private MEC models in collaboration with leading cloud providers. With the addition of C-Band spectrum, the company expects a wider and faster path to monetization.
By the end of 2022, the total edge compute addressable market in the U.S. is estimated to reach $1 billion, and by 2025, rapid adoption of Edge Compute is estimated to create a $10 billion addressable marketplace.
Public MEC Model: Last year, the company partnered with AWS: Wavelength and immediately connected AWS’s 1 million plus developer community to the nearly 170 million end-devices across Verizon’s 4G and 5G Nationwide networks at the edge. Developers today are building use cases spanning a wide array of commercial applications – all through an easy on-ramp in the AWS portal where they can move their workloads to the edge of our network, automatically triggering a recurring revenue share for Verizon and AWS. This partnership enables Verizon Business to be a key participant in this growing opportunity with C-Band accelerating our reach and time to market.
Private MEC Model: Last year, Verizon Business announced a collaboration with Microsoft to deliver a Private MEC model for customers that want a completely dedicated edge compute infrastructure on-premise to provide unique connectivity for their employees, enable data-intensive applications and benefit from solutions like computer vision, augmented reality and machine learning – all built to increase productivity, provide enhanced security and reduce latency in ways that wi-fi cannot.
This fully integrated Verizon 5G solution includes:
- Verizon Private Edge, which combines the power of Microsoft Azure cloud and edge capabilities with 5G on the customer premise.
- Verizon Private network connectivity, which is forecast to be a $10 billion dollar global market by 2025.
- Co-developed real-time enterprise solutions like Intelligent Logistics, Predictive Maintenance, Robotics and Factory Automation, which give Verizon Business a direct line of sight to another $12 billion applications and solutions addressable opportunity by 2025 that will be commercialized through a growing partner ecosystem, including IBM, Cisco, Deloitte and SAP.
The demand for MEC services unlocks an estimated Verizon total market that is forecast to exceed $30 billion by 2025, revenue that will be shared with partners.

Verizon expects to increase service revenues by shifting people to higher-tier unlimited (text, talk, Internet) cellular plans.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Quotes from Executives:
Hans Vestberg, Chairman and CEO of Verizon
FCC C-Band auction results
“Today is one of the most significant days in our 20-year history. This was a highly successful auction for Verizon – a once in a lifetime opportunity – and I am thrilled with what we were able to accomplish.”
Verizon’s strategy
“Our growth model is based on a clear vision: We are a multi-purpose network company with the best networks architected by the best engineers on the planet. This idea of a multi-purpose network at scale is our strategic foundation to maximize growth and put us in a position to realize the best return on investment in the fully-networked economy.”
Verizon’s competitive advantage
“Since we began building 5G, we have had a first mover advantage. We are more than a year ahead in building and selling mmWave with our 5G Ultra Wideband service and still the only company with commercial Mobile Edge Compute. Now we intend to extend our lead by accelerating our deployment of C-Band. Our new C-Band position combined with our mmWave, means we are the only carrier suited to deploy the fastest, most powerful 5G experience to the most people – or as we call it, 5G built right.”
Ronan Dunne, CEO of Verizon Consumer Group
5G adoption
“Customers are migrating to 5G in earnest. As of YE 2020, 9% of our Consumer postpaid phone base were on a 5G device. With the exciting device lineup we have in store, and the superior 5G experience that we deliver, we expect to reach 50% some 18 months ahead of GSMA forecast, and end 2023 ahead of even the more ambitious Ericsson Mobility Report forecast.”
5G devices
“Overall we have 10M 5G Ultra Wideband devices in the hands of customers on our network today. And of those, approximately 70% are already C-Band compatible. Going forward all new 5G handsets we sell to postpaid customers will be C-Band compatible.”
Step ups
“We have seen tremendous step-ups from our customers from Metered to Unlimited and Unlimited to Premium Unlimited as we discussed back in November. We continue to see this with over 20% of our postpaid accounts ending the year on a Premium Unlimited plan. We expect this number to grow to over 30% this year and approximately 50% by 2023. With C-Band included, we think step-ups to premium will only accelerate.”
5G Home acceleration
“By the end of 2021 we will have between 1 and 2 million millimeter wave 5G Homes open for sale and some 15 million in total with the arrival of the first tranche of C Band. By the end of 2023 this will have risen to more than 30 million households we can serve.”
Tami Erwin, CEO of Verizon Business
Mobile Edge Compute
“Verizon Business has a strong first-mover advantage to build a nationwide Mobile Edge Compute platform and be both a market leader and a market maker. This is not just an idea, it’s happening. Companies in every industry are finding exciting ways to bring 5G and 5G Edge to life – leveraging the full capabilities of 5G from throughput and ultra-low latency to sensor densification and rock solid reliability.”
Kyle Malady, CTO of Verizon
Auction results
“We secured a game-changing amount of C-Band spectrum to go along with our leadership in millimeter wave spectrum. We’ve been planning for many months, and are already working to make this the fastest deployment of new spectrum ever. As the leader in the wireless industry, we have consistently deployed a deep portfolio of strong spectrum holdings with best in class technology capabilities. This same focus will continue to position us for growth for years to come.”
Matt Ellis, CFO of Verizon
“Our Network as a Service strategy is our foundation when considering significant investments. We’ve leveraged that framework, investing in key strategic areas, such as spectrum, network assets, partnerships, and disciplined M&A, to position us for this next technology era.”
“Our strategy is working. Our core business is producing revenue growth today. More customers are experiencing the benefits of 5G Ultra Wideband every month on our millimeter wave spectrum and C-Band helps us accelerate the timeline and expand upon that growth.”