Author: Alan Weissberger
MTN Consulting on Telco Network Infrastructure: Cisco, Samsung, and ZTE benefit (but only slightly)
By Matt Walker
Cisco, Samsung, and ZTE benefit most from Huawei bans in 2021 in the telco Network Infrastructure market. (However, the market share gains were miniscule= <1% for each network equipment vendor).
Introduction:
2021 results for the 100+ vendors selling into the telco market are just about finalized. Contrasting 2021 telco network infrastructure (NI) market share with 2020, we note the following NI Equipment Vendor Market Share Changes:
Cisco clearly came out on top, gaining 0.7% share in a market worth $231.4 billion (B). Cisco was helped both by a telco shift in 5G spending towards core networks, and Huawei’s entity list troubles.
Samsung’s share growth of 0.3% was due to a big win with Verizon and a growing telco interest in seeking RAN alternatives beyond Ericsson and Nokia. ZTE, which has escaped the US entity list to date, also picked up some unexpected 5G wins but its growth is more broad-based due to optical, fixed broadband, and emerging market 4G LTE business.
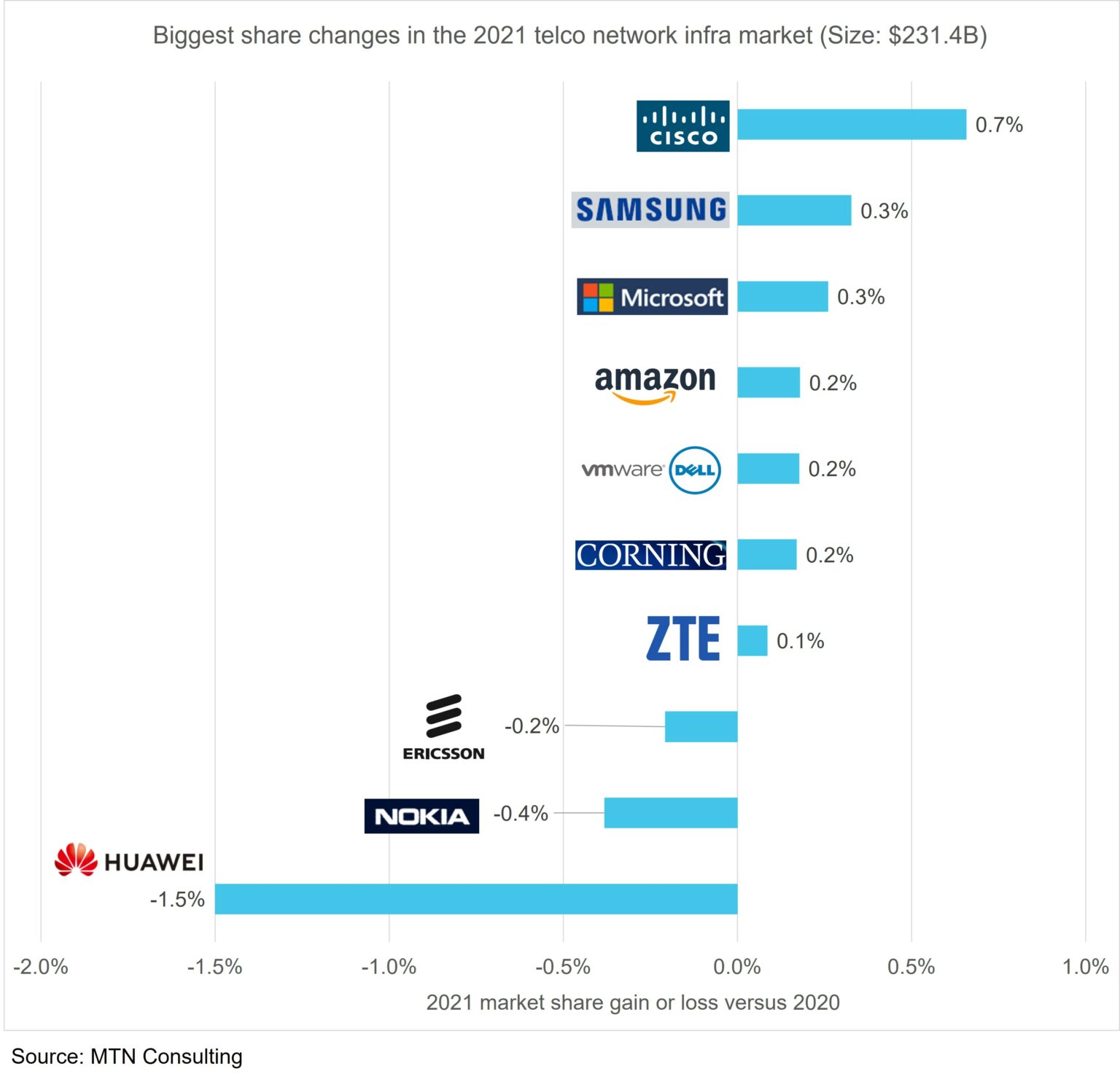
Dell (including VMWare), Microsoft, and Amazon also picked up share as telcos have begun investing in 5G core and cloud technologies. Their growth has little to do with Huawei, and more due to telcos’ ongoing changes to network architecture and service deployment patterns. Corning was an unexpected winner in 2021, gaining 0.2% share on the back of fiber-rich wireless deployments and government support for rural fiber builds.
On the flip side, both Nokia and Ericsson lost share in the overall telco NI market in 2021. Their RAN revenues benefited from Huawei’s troubles in 2020 but telco spending has since shifted towards product areas with more non-Huawei competition. Both vendors are attempting to diversify beyond the telco market, with Nokia so far having more success; its non-telco revenues grew 12% in 2021.
Huawei’s share of telco NI declined to 18.9% in 2021, down from a bit over 20% in both 2019 and 2020. The US Commerce Department’s entity list restrictions were issued in May 2019 but hit the hardest in late 2020 and 2021, after Huawei’s inventory stockpiles began running out.
Huawei’s messaging on its recent fall is muddled. During its annual report webcast yesterday, it cited three factors behind its 2021 revenue decline: supply continuity challenges, a drop in Chinese 5G construction, and COVID. In MTN Consulting’s opinion, supply continuity was the main factor. A related factor were the many government-imposed restrictions on using Huawei gear around the world, especially in Europe where 5G spending was strong in 2021. The other two factors cited by Huawei’s CFO, however, are misleading. Chinese telco network spending, overall, was relatively strong in 2021: total capex for the big three telcos was $52.8B, up 8% from 2020. Without this rise, Huawei’s 2021 results would have been worse. As for COVID, few other vendors cite the pandemic as a factor restraining 2021 telco spend. More vendors cite the opposite: 2021 spending was strong in part because telcos were forced to delay many projects during COVID’s early spread.
To date, Huawei’s troubles have impacted RAN markets the most, but in 2022 and 2023 will begin spreading more clearly to IP infrastructure, optical, microwave, fixed broadband, and other areas. A number of vendors are eager to pursue new opportunities as this happens, including Adtran/ADVA, Ciena, Cisco, CommScope, DZS, and Infinera. The CEO of Infinera, in fact, said on its 4Q21 earnings call that “it was a nice taste, a nice appetizer in 2021, but…we said all along that we would see the design wins and RFPs really scaling and we thought that we’d see revenues from that really beginning to take hold as we got into 2023.”
To date, Huawei has been unable to fully adapt to the supply chain restrictions put in place in 2019. It remains the global #1 in telco NI, however, due to dominance in China and a huge installed base across the globe. The company is investing heavily in carrier services & software, Huawei Cloud and new product areas. One certainty is that it won’t simply fade away, despite the current decline.
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
Editor’s Note:
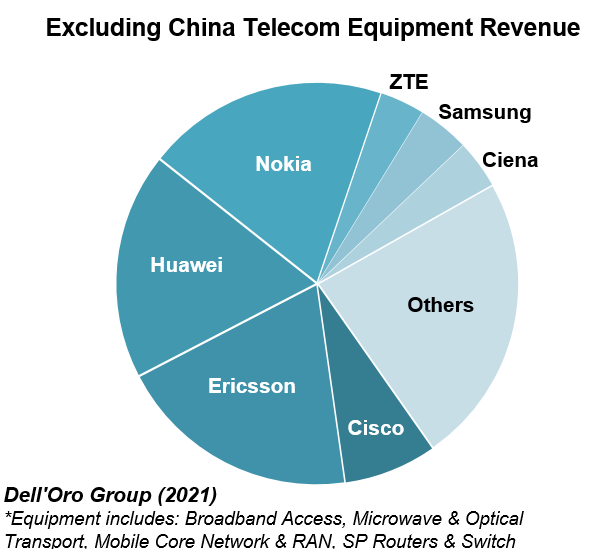
In contrast, Dell’Oro estimates suggest the overall telecom equipment market advanced 7% in 2021, recording a fourth consecutive year of growth, underpinned by surging wireless revenues and healthy demand for wireline-related equipment spurred on by double-digit growth both in RAN and Broadband Access. Total worldwide telecom equipment revenues approached $100 B, up more than 20% since 2017.
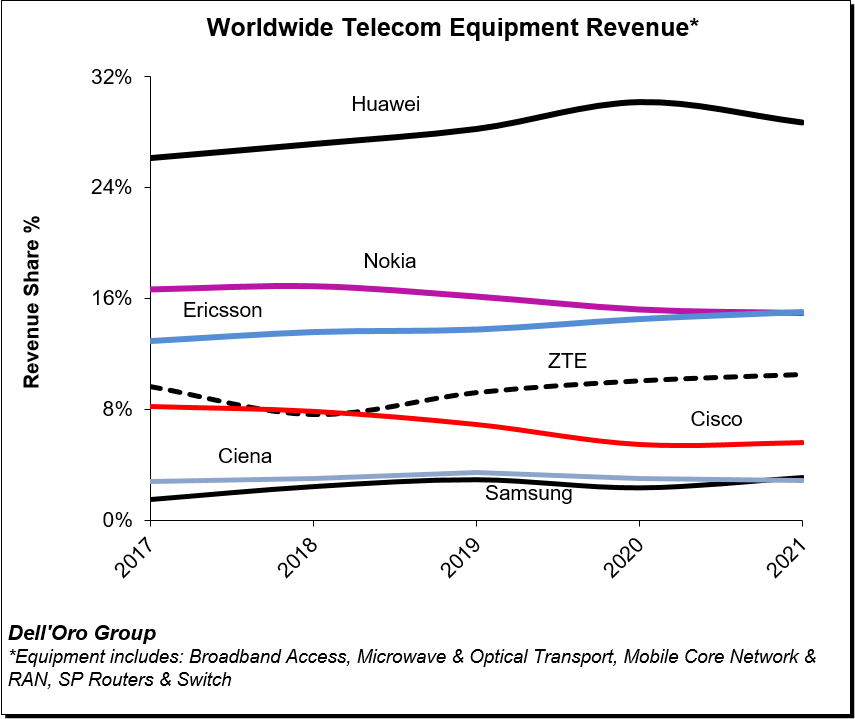
Initial readings suggest the playing field is more even outside of China, with Ericsson and Nokia essentially tied at 20% and Huawei accounting for around 18% of the market.
References:
Cisco, Samsung, and ZTE benefit most from Huawei bans in 2021 telco NI market
Dell’Oro: PONs boost Broadband Access; Total Telecom & Enterprise Network Equipment Markets
MTN Consulting: : 4Q2021 review of Telco & Webscale Network Operators Capex
by Matt Walker
Webscale revenues surge 25% to $2.1 trillion in 2021; capex of $175B drives global data center demand.
Introduction:
Revenues for the webscale sector of network operators ended 2021 at $2.14 trillion. That’s up 25% from 2020, and nearly 3x the total recorded in 2011. One reason for this is a dramatic uptick in cloud services revenues: cloud revenues for the top 3 (AWS, GCP and Azure) climbed 42% YoY, to $120.3B (per MTN Consulting). Still, this accounts for less than 6% of total webscale sector revenues. Larger factors behind 2021’s growth include: digital ad revenues for Alphabet and Facebook (Meta); ecommerce sales at Amazon, JD.Com, and Alibaba; and, 5G device revenue sales at Apple. The webscale sector is now comfortably larger than telecom, which recorded just under $1.9 trillion in 2021 revenues.
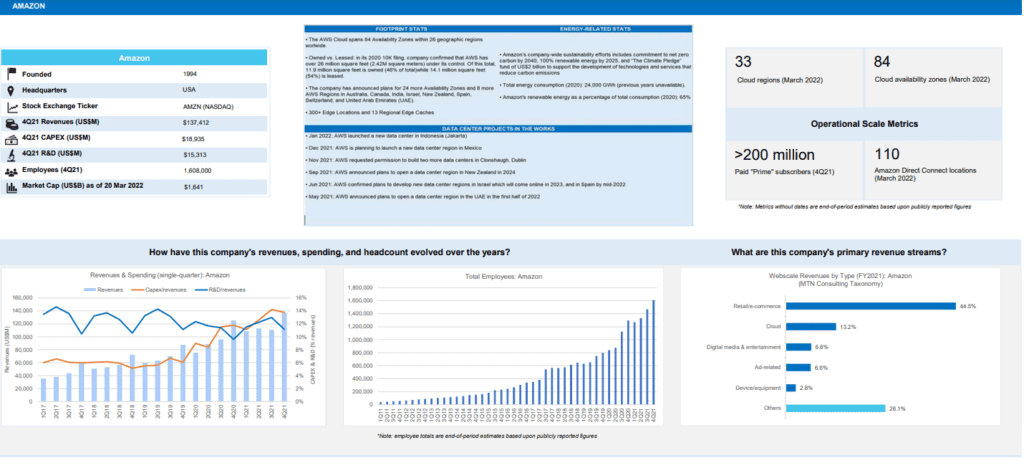
Here’s the profile for Amazon:
Capex- Telcos vs Webscalers:
On a capex basis, telecom remains far ahead, with nearly $325B in 2021 annualized capex, or nearly double the webscale total of $175B. Excluding China/HK-based companies (which haven’t finished reporting), the top 10 biggest telco capex spenders in 2021 were AT&T, DT, Verizon, NTT, Comcast, Vodafone, Orange, Charter, America Movil, and Telefonica. The biggest capex gains in 2021 were seen at America Movil (+$2.54B versus 2020 total), Telecom Italia (+$2.49B), Verizon (+$2.09B), AT&T (+$1.93B), Deutsche Telekom (+$1.74B), BT (+$1.63B), and Rakuten ($1.47B). The DT jump is inflated slightly by its Sprint acquisition, which closed in April 2020.
However, webscale is gradually bridging the capex gap with telcos: webscale capex spiked 30% YoY in 2021, versus an approximate 10% rise for telco capex. Capex in 4Q21 for webscalers was $50B, up 23% YoY. Webscalers also invest heavily in R&D, and have bleeding-edge requirements for the technology they deploy in their network. That has led them to drive the creation of many new innovations in network infrastructure over the last few years. These span semiconductors, optical transmission and components, intent-based routing, network automation, and other areas.
Facebook (Meta) is perhaps the most influential of all webscalers due in part to its openness and support for the OCP and TIP organizations.
Asia Pacific records best recent revenue growth in 2021
Regionally, the strongest growth in 2021 was in Asia Pacific, where revenues grew 29% YoY. The more mature Americas region lagged, with growth of just over 21% YoY. That pushed Americas down to about 44% of global webscale revenues, from 45% in 2020. Asia Pacific follows, with a 36% global revenue share, then Europe (17%) and MEA (3%). The Americas still account for the majority of webscale capex, with the US at the center. For instance, both Alphabet and Facebook (Meta) say well over 70% of their “long-lived assets” are in the US. Going forward, the non-US portion should rise as the cloud providers within the webscale market build out their global data center footprints. In January 2022, for example, AWS launched its first data center in Jakarta, Indonesia, and is planning a new region in Mexico.
Profitability still relatively high, but weaker than 2020:
Using a standardized definition of free cash flow (cash from operations less capex), the webscale sector’s FCF was $347.4B in 2021, or 16.2% of revenues. That is down significantly from a 19.7% margin in 2020. This ratio is still high relative to many sectors, however. The decline is due largely to a webscaler choice to accelerate capex during the COVID dislocation; that should pay off over the long run. Oracle, for instance, saw its FCF drop from 30.8% in 2020 to 17.2% in 2021, due mainly to its rapid cloud expansion. Nonetheless, Oracle says it will continue capex at a roughly $1B per quarter run rate, as it aspires to be the fourth major cloud provider with global scope. Amazon is actually the worst hit company in terms of FCF margin drop, due directly to its enormous 2021 capex outlays: Amazon’s FCF in 2021 was -3.1%, from 6.7% in 2020. Amazon, however, says its 2022 infrastructure (AWS) capex will likely rise.
Cash on hand, including short-term liquid investments, amounted to $747B for the webscale sector at the end of 4Q21, down 2% from the end of 2020. Total debt increased by 7%, to $518B. As a result, net debt (debt minus cash) in Dec. 2021 was -$228B for the webscale sector, from -$280B in December 2020. The companies with the biggest stockpiles of cash (and equivalents) are Alphabet ($139.6B), Microsoft ($125.4B), Amazon ($96.0B), and Apple ($63.9B). Facebook has just $48B, but no debt at all. Apple, IBM, and Oracle all have significantly more debt than cash.
Top 8 webscalers remain the biggest spenders, but Oracle and Twitter also important
This webscale tracker considers a “Top 8” group of companies as being, traditionally, the most influential in the market’s overall technology development and investments. These include three Chinese Internet companies (Alibaba, Baidu and Tencent), the world’s leading smartphone provider (Apple), the world’s biggest social media company (Facebook), and the leading three cloud providers: Alphabet, Amazon, and Microsoft. Ranking webscalers based on their share of tech capex, Amazon tops the list easily, accounting for 27.0% of network/IT capex in 2021. Amazon is followed by Alphabet (16.2%), Microsoft (14.0%), Facebook (10.0%), Tencent (6.3%), Apple (5.0%), Alibaba (4.1%), Oracle (2.9%), Baidu (2.1%), IBM (1.7%), HPE (1.5%), and Twitter (1.3%). Amazon’s recent capex surge is well known, and has supported expansion of the company’s AWS footprint and service offerings. Oracle has been quieter but its capex growth is equally impressive, from a smaller base: 2021 capex was $3.1B, up 70% from 2020. Twitter, a new addition to our webscale coverage, spends more on network/IT capex as a percentage of revenues (over 19%) than all other webscalers, due to ongoing software development and construction of its first owned data center.
The facilities these webscale players are building can be immense. For instance, Microsoft started construction recently on two new data centers in Des Moines Iowa, each of which costs over $1B and measures over 167K square meters (1.8 million square feet). These two are part of a cluster in the area, as is often the case; Microsoft already has three facilities around Des Moines. Facebook is working on a project in DeKalb, Illinois, roughly half the size at 84.2K square meters, costing US$800M and spreading across 500 acres of land. This construction project was announced in 2020 but won’t complete until 2023. These are just two examples of the many big facilities in the works in the webscale sector.
Who benefits from webscale capex?
The network spending of big webscalers is centered around immense, “hyperscale” data centers and undersea cable systems that support network traffic from the tech companies’ online retail, video, and social media platforms, along with cloud services. Webscale network operators (WNOs) may also own access networks, typically using fiber, microwave or mmWave, and even fixed satellite. WNOs exploring outer space for providing connectivity include Amazon, Apple, Alphabet, Facebook, and Microsoft.
A broad set of vendors are benefiting from WNO capex spending – from semiconductor players selling into the data center market (Intel, AMD, Nvidia, Broadcom, etc), to optical components & transport vendors selling into data center interconnect markets (e.g. Infinera, II-VI, Lumentum/Neophotonics), to contract manufacturers of white box/OCP servers (e.g. Wistron and Quanta). Cisco, for instance, recorded approximately $4.0B in 2021 sales to the webscale sector, up from about $2.1B in 2020. The construction industry also sees webscale as important, as much of their capex is for development of data center properties.
Network investment outlook:
Our current forecast calls for $187B of webscale capex in 2022, and further growth in the out-years until capex hits about $252B in 2026. For now, we are maintaining these targets. Despite a modest slippage in profitability, cash/debt and top-line growth in 4Q21, the sector retains many strengths which won’t go away overnight. Cloud services revenue growth remains strong, as does profitability for most players. Moreover, 2022 capex guidance from the major webscalers suggests modest growth; a summary follows:
- Amazon: 4Q21 earnings call confirmed that network/IT (“infrastructure” for AWS) is about 40% of total, consistent with MTN Consulting assumptions. Other components are fulfillment/logistics and transportation. For future capex, it says “we’re still working through some of our plans for 2022, but it’s coming into focus a bit. We see the CapEx for infrastructure going up…we’re adding regions and capacity to handle usage that still exceeds revenue growth in that business. So we feel good about making those investments.”
- Facebook (Meta): still calling for 2022 capex, including principal payments on finance leases, in the range of $29-34 billion (2021 actual: $19.2 billion). Says capex is driven by investments in data centers, servers, network infrastructure, and office facilities, and next year’s figure “reflects a significant increase in our AI and Machine Learning investments, which will support a number of areas across our Family of Apps.”
- Alphabet: projects a “meaningful increase in CapEx” for 2022, due to both technical infrastructure (mainly servers) and office facilities, where the company says it is “reaccelerating investment in fit-outs and ground-up construction.”
- Microsoft: expects 1Q22 capex to decline sequentially versus 4Q21, a change from the prior year period when 1Q21’s total capex was up 22% versus 4Q20. Does not provide any longer-term guidance. Its pending acquisition of Activision Blizzard is likely a factor in future plans, for two reasons. First, the deal consumes a lot of cash, and second, absorbing Activision would likely come with some changes in data center strategy. Currently Activision does not have any of its own data centers, rather, it rents colocation space in third-party facilities. The combined company will clearly want to see benefits from Microsoft’s data center footprint.
- Oracle: expects capex to continue in the roughly $1B per quarter range through the end of its current fiscal year (May 2022).
- Tencent: no concrete guidance but has hinted at Facebook-like investments in the “metaverse,” says it has a lot of the building blocks needed, for example, “a lot of gaming experiences…very strong social networking experience…engine capability, we have AI capability, we have the capability to build a large server architecture that can serve a huge number of concurrent users. We are very experienced in managing digital content economies as well as real-life digital assets.”
- Apple: nothing concrete on capex specifically, but in April 2021 it announced “$430 billion in contributions to the US economy include direct spend with American suppliers, data center investments, capital expenditures in the US, and other domestic spend…”
- Alibaba: no concrete guidance but 4Q21 call said it will continue to “invest in expanding its international infrastructure,” saying it now provides cloud services in 25 regions globally and that it is “committed to serving the real economy for the long term and the digitalization of all industries”. At its Apsara conference in October 2021, the company unveiled several new proprietary products, including Yitian 710 server chip, the X-Dragon architecture, Panjiu cloud-native server series, Alibaba AI and big data platform and a new generation of PolarDB database. It has global aspirations for its IaaS and PaaS services.
- Baidu: hasn’t addressed capex recently but on 4Q21 earnings call cited strong cloud demand growth, and said it is “trying to retain rapid revenue growth for 2022 and beyond,” which will require infrastructure investments.
- Twitter: its capex appears to be moderating now that it has (largely) completed construction of its new data center.
While we are maintaining the forecast outlook as published in Dec 2021, Amazon is a wildcard. It provides no specific guidance, and is clearly the market leader. Its quarterly outlays will be watched carefully. Even if its total capex does moderate, it is possible that the network/IT % of total will rise.
Implications for carrier-neutral market segment:
Webscalers with cloud operations are building out their data center footprints, and most webscalers are deploying more complex functionality into their networks (video, gaming, AI, metaverse). However, webscalers do have some financial pressures, and more important have an increasingly rich range of options for how they expand. The carrier-neutral segment (CNNO) of data center players is investing heavily in larger, more hyperscale-friendly and energy efficient facilities. Further, the sector is consolidating with help from private equity. MTN Consulting expects webscalers to continue to lean heavily on these third-parties for expansion in 2022 and beyond. As a result, data center CNNOs like Digital Realty, Equinix and its JV partners, QTS/Blackstone, CyrusOne/KKR/GIP, American Tower/CoreSite, and GDS will become more attractive to vendors as they invest more in network technology of their own.
References:
MTN Consulting: Network Infrastructure market grew 5.1% YoY; Telco revenues surge 12.2% YoY
MTN Consulting: Network operator capex forecast at $520B in 2025
Light Counting: Large majority of CSPs remain skeptical about Disaggregated Open Routers
LightCounting’s second annual report provides an update on the emergence of the Disaggregated Open Routers (DOR) market in wireless infrastructure. DOR are white-box cell site, aggregation and core routers based on an open and disaggregated architecture for existing 2G/3G/4G and future 5G network architectures.
The DOR architecture was hailed as a new paradigm as early as 2012, using open source software for a centralized SDN Controller from the Open Network Foundation and Linux Foundation. The “open networking architecture” was envisioned to be used by tier 1 telcos and hyperscale cloud service providers and later extend to enterprise/campus networks. Well, that never happened!
Instead, hyperscalers developed their own proprietary versions of SDN, sometimes using a bit of open sourced software (e.g. Microsoft Azure). A few start-ups (e.g. Pica 8 and Cumulus Networks) developed their own software to run on white boxes and bare metal switches, including network operating systems, routing and network management.
One company that’s succeeded at customized software running over white boxes is
Israel based DriveNets. Indeed, the DriveNets software (see References below) is custom built- not open source! It’s an “unbundled” networking software solution, which runs over a cluster of low-cost white box routers and white box x86 based compute servers. DriveNets has developed its own Network Operating System (NOS), rather than use open source or Cumulus’ NOS as several other open networking software companies have done.
LightCounting’s research indicates that the overall DOR market remains incipient and unless proof of concept (PoC), testing and validation accelerate, volumes will take some time to materialize.
“Despite TIP’s (Facebook’s Telecom Infra Project) relentless efforts to push network disaggregation to all network elements and domains, and a flurry of communication service providers (CSPs) taking the lead with commercial DOR deployments like AT&T with DriveNets (NOS), UfiSpace (hardware) and Broadcom (networking silicon), a large majority of CSPs (Communications Service Providers) remain skeptical about the potential opex reduction, the maturity of transport disaggregation, and the impact on operations, administration, maintenance, procurement and support.” said Stéphane Téral, Chief Analyst at LightCounting Market Research.
Source: Light Counting
That quote is quite different from Stephane’s comment one year ago that the DOR market was poised for imminent growth:
“Still incipient, the DOR market is just about to take off and is here to stay but requires more CSPs (Communications Service Providers) to take the plunge and drive volumes. And with China’s lack of appetite for DOR, North America is taking the lead.”
Major findings in the report are the following:
- The open RAN ascension brought router disaggregation to the spotlight and paved the way to four fundamental routes. This phenomenon would have never happened without TIP’s initiative.
- Although NOS software vendors are mushrooming and by far outnumbering the white box hardware suppliers dominated by UfiSpace, there have been some casualties down the DOR road. In the networking silicon domain, Broadcom remains predominant.
- CSPs remain cautiously optimistic about router disaggregation but have yet to see more maturity and the full benefits. As AT&T is showing the DOR way, KDDI and LG U+ could be DriveNets’ next major customers.
- With all inputs from all vendors and CSPs with DOR rollout plans taken into consideration, our cell site-based model produced a forecast showing a slow start that reflects the early stage of this market and an uptick at the end of the 2021-2026 forecast period marked by a double digit CAGR.
About the report:
LightCounting’s Disaggregated Open Routers report explores the emergence of the Disaggregated Open Routers (DOR) market. Disaggregated open routers are white-box routers based on separated white box hardware and software with cloud enabled software functions for existing 2G/3G/4G and future 5G network architectures. The report analyzes the disaggregated open routers’ (aggregation and core) architectures and implementations in wireless infrastructure, including the emerging vendor ecosystem, and tracks white box hardware units and sales, and software sales, all broken down by region including North America, Europe Middle East Africa, Asia Pacific, and Caribbean Latin America. It includes the total number of cell sites worldwide and a 5-year market forecast.
Historical data accounts for sales of the following vendors:
| Vendor | Software | Hardware/White Box | Source of Information | |
| Adva | Ensemble Activator | Survey data and estimates | ||
| Altran | Intelligent Switching Solution (ISS) | |||
| Alpha Networks | Hardware platform | |||
| Arrcus | ArcOS | |||
| Aviat Networks & Metaswitch (Microsoft) | AOS | |||
| Cisco | IOS XR7 | |||
| Datacom | DmOS | |||
| Dell Technologies | NOS | Hardware platform | ||
| Delta Electronics | AGCXD40V1, AGCV208S/AGCV208SV1, AGC7008S | Estimates | ||
| DriveNets | DNOS | |||
| Edgecore Networks | AS7316-26XB, AS7315-27X, AS5915-18X | Survey data and estimates | ||
| Exaware | ExaNOS | |||
| IP Infusion | OcNOS, DANOS | Estimates | ||
| Infinera | CNOS | DRX Series | Survey data and estimates | |
| Niral Networks | NiralOS | |||
| UfiSpace | S9700-53DX, S9700-23D, S9705-48D, S9500-30XS | Survey data and estimates | ||
| Volta Networks (now in IBM) | VEVRE | |||
| Note: Not all vendors provide services |
References:
https://www.lightcounting.com/report/march-2022-disaggregated-open-routers-135
AIS Thailand, Qualcomm and ZTE showcase 1st 5G NR-DC at 2.6GHz and 26GHZ
Advanced Info Service Pcl (AIS) Thailand [1.], Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and ZTE have jointly announced the world’s first 5G NR-DC (New Radio Dual Connectivity) [2.] showcase in the field with 2.6GHz and 26GHz. The trial achieved 8.5Gbps peak downlink speed and 2.17Gbps peak uplink speed with a single mobile device.
Note 1. AIS is Thailand’s largest mobile operator. It’s owned by INTOUCH Company (40.45%) and Singtel (23.32%)
Note 2. NR-DC is the use of two frequency bands in 3GPP’s 5G NR to improve coverage and data speeds.
As part of the joint effort, this collaboration combines two major 5G frequency bands, sub-6GHz and 26GHz (5G mmWave frequencies have yet to be standardized in ITU-R M.1036 by ITU-R WP5D), to enhance the capabilities of Thailand’s 5G network and extend the 5G application landscape.
The trial was conducted at the AIS commercial 5G site in Korat, Thailand, using a smartphone form-factor test device powered by Snapdragon® X65 5G Modem-RF System, and ZTE’s latest mmWave AAU network infrastructure equipment.
The NR-DC was implemented with one 100MHz carrier in 2.6GHz, and four 200MHz carriers in 26GHz. The test achieved 8.5Gbps peak downlink speed and 2.17Gbps peak uplink speed demonstrating the extraordinary capability and flexibility of NR-DC for diversified requirements from individual consumers and industry leaders.
This NR-DC showcase drives the commercial progress of 5G mmWave into the fast lane in Thailand. AIS, Qualcomm Technologies and ZTE are together committed to accelerating and growing 5G for capability enhancement, efficiency improvement and application boundary extension.

“AIS’s key goal is to develop the smart 5G network as a national infrastructure with investments of 30,000-35,000 MB,” Wasit Wattanasap, head of nationwide operation and support business unit at Advanced Info Service Pcl. (AIS), commented, “We are the licensee holding the most spectrum in low band, mid band and high band or mmWave, which has the outstanding feature of rapid data transmission with low latency. We have never stopped deploying innovations to level up the network, including 5G Non NSA/SA Voice over new radio (VoNR) and 5G carrier aggregation (CA), to provide increasingly improved experiences to Thai customers, which was our intention when we joined the auction for spectrum.”
“Most recently, we have continued our collaboration with ZTE and Qualcomm Technologies, to jointly trial 5G NR-DC technology. It is a crucial step to combine different 5G spectrum, 2600 MHz (mid Band) and 26GHz (high Band) in a world-first. This enables downloads of up to 8.5 Gbps, and uplinks of up to 2.17 Gbps. This trial gave us a wider channel for the signal and extremely low latency. For instance, there could be streaming games online (cloud game), controlling driverless vehicles and commanding robots remotely in real-time. Moreover, the trial supports the development of new models of chipsets in the future, to speed up data transfer even more.”
“This cooperation highlights how AIS is the only provider using its licensed spectrum of every waveband for development to support business growth in various dimensions. It is also continuous transformation and updates for Thai consumers. Taking this joint-trial as a good start, we are confident that AIS 5G network is ready to expand the use of mmWave technology and support growth of the business sector in various aspects,” concluded Wasit.
“Our collaboration with AIS and ZTE proves the feasibility of deploying 5G mmWave in Thailand,” said ST Liew, vice president, Qualcomm CDMA Technologies Asia-Pacific Pte. Ltd. and president, Qualcomm South East Asia. “Qualcomm Technologies believes that 5G mmWave will be the key to unlocking the full potential of 5G. The possibility is endless and we are proud to take the first step in bringing the full benefits of 5G mmWave to the country.”
“We’re pleased to work with AIS and Qualcomm Technologies to achieve this milestone, which lays a technology validation foundation for 5G mmWave commercialization,” said Mei Zhong Hua, senior vice president, ZTE Corporation. “With broader 5G opportunities enabled by mmWave, we will join hands with partners to continuously drive mmWave development, create ultimate experiences and usher in a wonderful 5G era.”
References:
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/20220331e1.html
Altice USA transition to fiber access; MoffettNathanson analysis of low population growth on cablecos broadband growth
Altice USA recently disclosed a plan to overbuild its hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) network to blanket 6.5 million locations with fiber by 2025. The NYC based cableco/MSO operates the Optimum and Suddenlink brands, which it plans to rebrand under the Altice USA name.
During a New Street Research investor conference, Altice USA EVP of corporate finance and development Nick Brown said the decision to make that move was a “no brainer” for the company, but acknowledged that it’s in a slightly different position than fellow cable giants Comcast and Charter Communications. Brown stated Altice USA’s own experience and that of its sister companies in Europe gave it better insight into what the transition to fiber would look like in terms of costs and returns, leaving it unafraid to take the leap. But it also already faces “a lot of fiber-based competition relative to others,” especially from Verizon Fios in its legacy Cablevision footprint in the eastern part of the country.
Altice has already upgraded its head ends and backbone rings with fiber. Since DOCSIS would require it to push fiber deeper and deeper into the network anyway, Brown said it made sense to go all-in to pull forward the benefits full fiber has to offer. “The FTTH end-to-end glass network that we’re deploying here in the U.S. for us is pretty much the end state, the logical end state, of a coax upgrade anyway,” Brown argued.
Brown said the move to fiber will allow Altice USA to save in the “low hundreds of millions” of dollars in operating expenses and “materially” reduce its capital expenditures over time. It’s also expected to help Altice more effectively compete by allowing it to offer a better product, reduce churn and improve network reliability. He also pointed out it’ll make future network upgrades easier. Today, it has around half a million active components in its coax network, nearly all of which need to be touched for a DOCSIS upgrade. But with fiber “the equivalent is about 1,000 to 2,000 pieces of equipment that you would need to upgrade to go to next generations of fiber technology as we’re doing this year as we’re moving to XGS-PON,” he said, noting its current fiber footprint of more than 1 million locations was originally built with GPON technology.
“I think it’s just a lot more scalable, a lot more future-proof in our mind, and a lot more cost effective to move to future broadband technologies,” Brown concluded.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
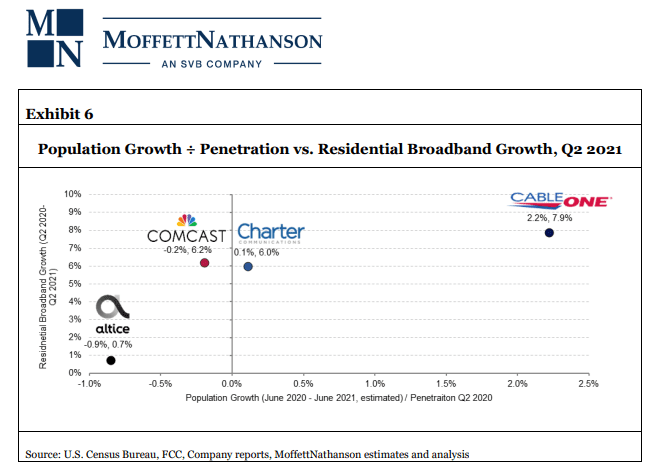
To determine which operators might have been most negatively affected by low population growth (and therefore likely low household growth) from July 2020 to July 2021, and which might have been net beneficiaries of the fastest growth, analysts at MoffettNathanson aggregated the population by county in each cable operator’s footprint using FCC Form 477 data as of Q4 2020. Using those totals, we calculated a weighted average population growth for each operator’s total footprint based on the county-level annual estimates published by the Census Bureau. The weighted-average population growth implies a meaningful headwind to Altice USA (at -0.4% growth), and a significant tailwind to Cable One (at 0.7% growth).
Craig concluded: “Again, there’s a lot more at work in broadband subscriber growth rates than just population (new household formation) growth or starting penetration. Different operators have different demographics. They face different overlaps with fiber, and some will face more FWA than others. They have different pricing strategies.”
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/altice-usa-exec-fiber-logical-end-state-coax
U.S. 4 big cloud companies lead world in hyperscale data centers and capacity
The U.S. continues to lead the world in total hyperscale data centers and worldwide capacity through at least 2026, according to Synergy Research Group. “The United States currently accounts for almost 40% of operational hyperscale data centers and half of all worldwide capacity,” John Dinsdale, chief analyst at Synergy Research Group, wrote in a new report. Synergy’s new hyperscale forecasts show continued rapid growth in the number of large data centers to be used by hyperscale operators in order to support their ever-expanding business operations.
With a current known pipeline of 314 future new hyperscale data centers, the installed base of operational data centers will pass the 1,000 mark in three years’ time and continue growing rapidly thereafter.
The United States currently accounts for almost 40% of operational hyperscale data centers and half of all worldwide capacity. By a wide margin, it is also the country with the most data centers in the future pipeline, followed by China, Ireland, India, Spain, Israel, Canada, Italy, Australia and the UK.
As the installed base of operational data centers continues to grow each year at double-digit percentage rates, the capacity of those data centers will grow even more rapidly as the average size increases and older facilities are expanded.

By data center capacity the leading companies are the usual suspects: Amazon, Microsoft, Google and Facebook, though it is the Chinese hyperscalers that are growing the fastest, most notably ByteDance, Alibaba and Tencent.
The companies that feature most heavily in the future new data center pipeline are Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook and Google. Each has 60 or more data center locations with at least three in each of the four regions – North America, APAC, EMEA and Latin America. Oracle, Alibaba and Tencent also have a notably broad data center presence.
“The future looks bright for hyperscale operators, with double-digit annual growth in total revenues supported in large part by cloud revenues that will be growing in the 20-30% per year range. This in turn will drive strong growth in capex generally and in data center spending specifically,” said John Dinsdale, a Chief Analyst at Synergy Research Group.
“While we see the geographic distribution, build-versus-lease distribution, average data center size and spending mix by data center component all continuing to evolve, we predict continued rapid growth throughout the hyperscale data center ecosystem. Companies who can successfully target that ecosystem with their product offerings have plenty of reasons for optimism.”
Synergy’s Hyperscale Market Tracker research service provides key data and metrics on 19 companies that meet Synergy’s hyperscale definition criteria. The data includes information on the hyperscale data center footprint, a full data center listing, analysis of critical IT load, future data center pipeline, hyperscale operator capex, hyperscale data center spending, company revenues, and five-year forecasts for the key metrics.
Synergy Research Group tracks the data center footprints and expansion plans of 19 of the world’s largest cloud and internet service companies, including the largest providers of infrastructure, platforms, software, search, social media, e-commerce, and gaming.

About Synergy Research Group:
Synergy provides quarterly market tracking and segmentation data on IT and Cloud related markets, including vendor revenues by segment and by region. Market shares and forecasts are provided via Synergy’s uniquely designed online database SIA ™, which enables easy access to complex data sets. Synergy’s Competitive Matrix ™ and CustomView ™ take this research capability one step further, enabling our clients to receive on-going quantitative market research that matches their internal, executive view of the market segments they compete in.
Synergy Research Group helps marketing and strategic decision makers around the world via its syndicated market research programs and custom consulting projects. For nearly two decades, Synergy has been a trusted source for quantitative research and market intelligence.
References:
Synergy Research: Hyperscale Operator Capex at New Record in Q3-2020
Synergy Research: Strong demand for Colocation with Equinix, Digital Realty and NTT top providers
Synergy Research: Ethernet Switch & Router revenues drop to 7 year low in Q1-2020
Synergy Research: Cloud Service Provider Rankings (See Comments for Details)
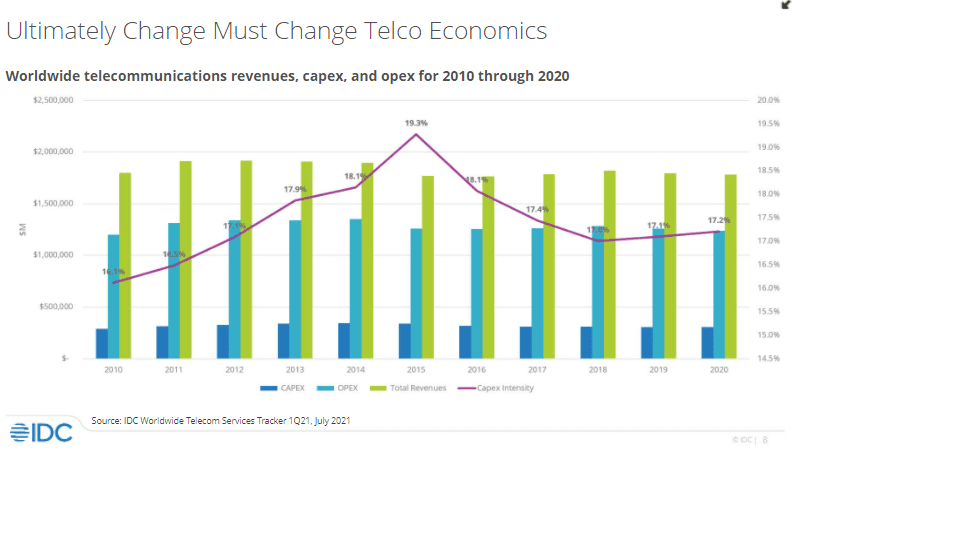
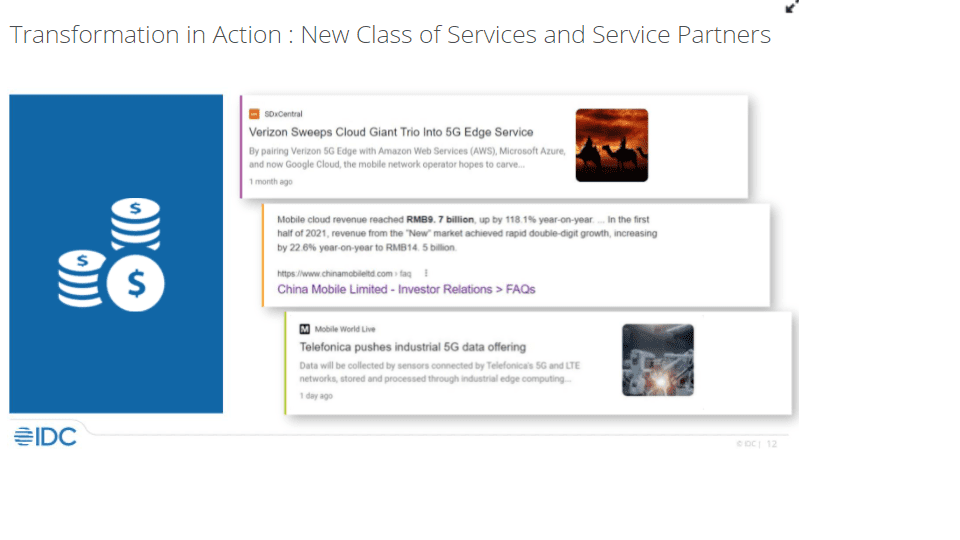
IDC Directions 2022: Telecom Renaissance, by Daryl Schooler
Intelsat and PCCW Global combine networks; Intelsat achieves MEF 3.0 Carrier Ethernet (CE) Certification
Intelsat and PCCW Global Combine Networks:
Satellite communications specialist Intelsat and Hong Kong based PCCW Global have announced a new collaboration to extend the reach, resiliency, and quick delivery of on-demand enterprise connectivity offerings.
The integration of Intelsat’s FlexEnterprise global connectivity fabric with PCCW Global’s Console Connect Software Defined Interconnection® platform enables organizations to deliver enterprise connectivity to locations around the globe while leveraging an easy-to-use platform underpinned by one of the world’s largest private MPLS networks.
The combined solution addresses two key obstacles to delivering reliable, agile services across all of an enterprise’s locations: limited local telecom infrastructure that can challenge traditional network deployments in developing or hard-to-reach places, and lengthy lead times typically associated with creating high-performance networks and services. The collaboration brings together FlexEnterprise’s reach and reduced network deployment speed and Console Connect’s real-time quoting, ordering and provisioning of high-performance connectivity.
Mr. Frederick Chui, Chief Commercial Officer, PCCW Global, said, “The collaboration with Intelsat brings together the latest innovations in fixed network and satellite network technologies to deliver more flexible enterprise connectivity solutions. By integrating Intelsat’s FlexEnterprise solution with the Console Connect digital platform, our global customers can access satellite connected locations wherever they need to and effortlessly turn up services across all sites.”
FlexEnterprise leverages the world’s largest and most advanced integrated satellite fleet and ground infrastructure to enable service providers to integrate the reach and reliability of Intelsat services without the need to manage wholesale satellite capacity. The connectivity-as-a-service solution offers packaged service that makes it quicker and more cost-effective to add resiliency to existing sites and extend the reach of enterprise networks to even the most remote areas.
The Console Connect digital platform puts users in control of one of the world’s largest MPLS and Tier 1 IP networks, providing them with private, on-demand connections between over 750 data centres across more than 50 countries worldwide. Console Connect is home to a growing ecosystem of cloud, SaaS, IX, IoT, carrier and enterprise partners, which are directly interconnected by the platform’s private high-performance network, delivering higher levels of network performance, speed, and security. Through the platform’s MeetingPlace feature, users can also directly order and provision partner services, such as remote peering, colocation and business applications, as well as access native services from Console Connect.
Mr. Brian Jakins, General Manager and Vice President of Networks, Intelsat, said, “Our Sales and Product teams work closely with the telecom ecosystem to make satellite services more relevant and easier to adopt for a broader set of customers. With the integration into the Console Connect platform, Intelsat is able to more easily meet customers anywhere on the PCCW Global network, while enterprises leverage the platform to extend applications and services to their most remote users and outposts.”

Intelsat’s Global Network is First to Achieve MEF 3.0 Carrier Ethernet Certification for New Performance Tier:
Intelsat has become the first satellite operator to achieve MEF 3.0 Carrier Ethernet (CE) Certification for services delivered through its integrated space and global terrestrial network. Intelsat’s achievement means that customers can dependably integrate Intelsat’s global network solutions into their network solutions with assurance of performance and security. This also represents continued progress towards Intelsat’s Unified Network vision to enable seamless, end-to-end orchestrated services, driven by our integration of 5G and other open standards.
“Intelsat’s achievement of MEF 3.0 certification ensures that customers can rely on Intelsat to provide Ethernet services that meet the demands of enterprise, government and wholesale use cases with key performance indicators that define the industry standard for high-quality,” said Lance Hassan, Director of Terrestrial Network Innovation at Intelsat. “This achievement also demonstrates Intelsat’s leadership as a satellite communications company and global provider of network solutions.
MEF service definitions help telecom service providers accelerate product development and service implementations, with definitive measures to ensure consistency of the quality of the services they provide. As part of Intelsat’s continued efforts to drive open standards development and adoption across the satellite industry, the company worked with MEF member companies to amend MEF 23 with a new Performance Tier (PT5) that defines new Class of Service performance objectives for satellite-based networks.
“Intelsat, in achieving our industry’s first MEF 3.0 certification for GEO satellite-based Carrier Ethernet services, is adding a dimension to MEF’s important work that will benefit users no matter where they stand on the globe,” said Bob Mandeville, president and founder of Iometrix, MEF’s testing partner for carrier ethernet certifications.
“Companies in the satellite community are crucially important in enabling accessibility of carrier ethernet services anywhere on the planet,” said Kevin Vachon, chief operating officer, MEF. “Achieving MEF 3.0 certification facilitates interoperability with terrestrial networks and lays the groundwork to ultimately achieve service automation with MEF’s Lifecycle Service Orchestration (LSO) framework and APIs. We congratulate Intelsat on their certification achievements.”
Intelsat services are provided by the company’s integrated satellite and terrestrial network. For more information and to check availability, click here.
References:
India Data Center firms seek captive fiber for faster and more efficient connectivity
India data center providers have urged the government to allow them to lay their own captive fiber optic networks to offer faster and more efficient connectivity to companies. India’s current laws around fiber usage require data center operators to depend on telecom service providers for the fiber. That increases prices, makes the process time consuming and impacts ease of business, senior industry executives told ET.
–>The data center sector does not want to be governed by the same rules as telecom operators since it will become expensive and onerous to lay the fiber.
IT industry body Nasscom has also supported the data center industry’s demands through a recent submission to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (Trai). Nasscom has called for allowing data center companies to lay their own dark fiber between two or more data centers of the same company, to connect customers’ equipment located within such centers.
The biggest challenge affecting data center operations and services in India is around the telecom licenses to connect data centers that are not part of the same campus, Vimal Kaw, NTT’s head of data center services, told the Economic Times (ET).
“In India, telecom is regulated, and a license is required for data center providers to be able to create a network of connected data centers spanning across locations within a city or across cities. Thus, provisions need to be made by the Department of Telecommunication (DoT) and government in the current regulatory framework to enable data center providers to connect DCs using dark fiber to offer services to DC customers,” Kaw said. Typically, companies pay licensed telecom/internet service providers (TSPs/ISPs) on an annual contract basis.
TSPs, in turn, pay a share of their revenue to the government, irrespective of public or private use of the services. If data center businesses want to set up their own dark fiber networks, they will have to come to a similar revenue share arrangement under current laws, which companies say is not feasible for business-to-business networks.“
Sourcing fiber networks through ISPs/ TSPs can lead to exorbitant prices for data center providers, plus it is a time-consuming process. Meanwhile, getting an ISP license for captive usage is even more expensive. Acknowledging the specific need of the data center ecosystem can go a long way in enabling us to extend our services to newer regions,” said Piyush Somani, CEO of ESDS Software.
Nasscom told Trai that traditional networks operated by TSPs are principally designed for voice or public data services, not for cloud services, which require very high availability, bandwidth, and low latency for extremely high amounts of data.

India IT industry body Nasscom has also supported the data center industry’s demands through a recent submission to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (Trai).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Data centers depend on captive dark fiber connectivity sourced from telecom operators to expand their presence, Ashish Aggarwal, head of policy, Nasscom told ET. But the process is time consuming and inefficient for the data center ecosystem. “Laying dark fiber is not a TSP activity in the traditional sense because it’s a captive network. For the benefit of ease of business, data centres should be allowed to lay their own fibre networks,” Aggarwal said.
Sunil Gupta, co-founder and CEO of Yotta Infrastructure, said the government can possibly set up a mechanism – either a mandatory obligation or subsidization/incentivization, or both — for this purpose.“ Additionally, data center operators should be allowed to lay their fiber optic cable and develop their own managed network to connect to other data centers, landing stations, and other key buildings of interest like stock exchanges,” he added.
Meanwhile, telecom operator Reliance Jio, in its submission to Trai has urged the regulator to only back fiber connectivity to data centers via licensed entities. Bharti Airtel has said that if right of way issues around fiber connectivity are resolved, the process can become more efficient.
References:
India’s 5G may lag due to low telecom infrastructure growth rate and insufficient fiber for backhaul
ICRA: Indian Telecom Industry Must Migrate from Copper to Dense Fiber Optic Networks
IBD – Controversy over 5G FWA: T-Mobile and Verizon are in; AT&T is out
Two of the three biggest U.S. telecom network providers, T-Mobile US and Verizon Communications, contend that selling 5G FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) broadband services to homes will prove to be a good business. However, AT&T has no plans to make a big push into that space. We wrote about this topic earlier this year, but it remains a conundrum as debate continues.
Whether these 5G FWA services will heat up broadband competition with cable TV companies — who dominate in high-speed internet services — is a controversial issue for telecom stocks. The fixed 5G wireless services also may compete with local phone companies in areas still served by copper line-based “DSL” services.
“Verizon and T-Mobile think the service can be a growth driver and will have attractive economics,” UBS analyst John Hodulik told Investor’s Business Daily (IBD). “FWA (fixed wireless access) is likely to do better where there are limited options for broadband and among subscribers used to lower speeds, so that means legacy DSL subscribers and slower speed cable. The big question is whether FWA has staying power over the next 5 to 10 years given necessary speed increases.”
AT&T has downplayed the potential of fixed 5G wireless. AT&T contends that as data usage surges over time, FWA will become increasingly uneconomic vs. fiber-optic landline alternatives.
“I think it stems from a genuinely different view of the engineering and capacity constraints,” MoffettNathanson analyst Craig Moffett told IBD. “The divergence in views about fixed wireless access between AT&T and Verizon or T-Mobile speaks to a genuine controversy in the telecom industry.” Craig added that telecom companies are scrambling to make money from huge investments in 5G radio spectrum.
Moffett said: “The renewed appetite for FWA may be a sign of a dawning realization that the gee-whizzy use cases of 5G may never materialize. That could be forcing operators to revisit every possible source of incremental revenue in a bid to earn at least some return on their huge investments in 5G spectrum.”
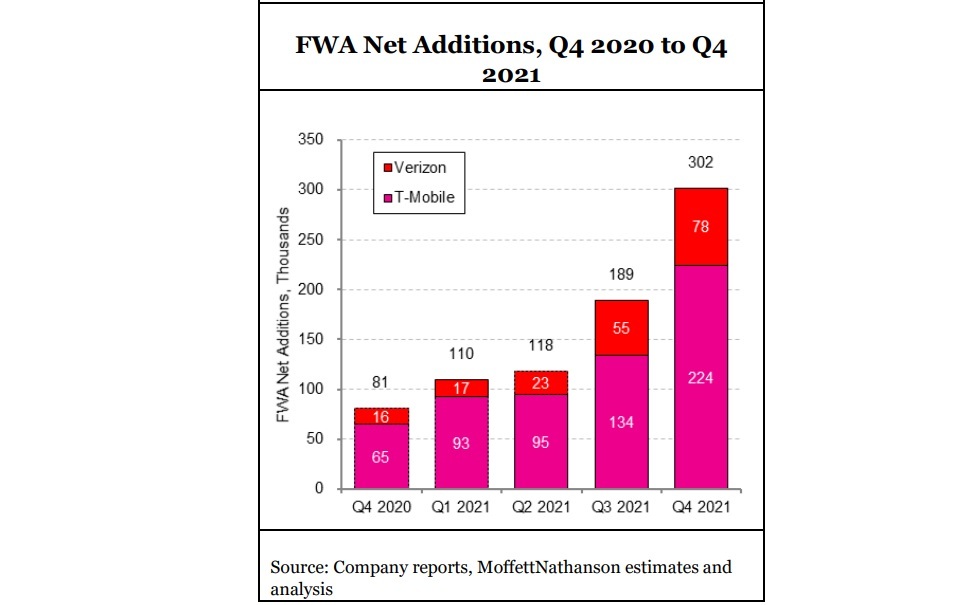
U.S. fixed wireless access (FWA market) captured ~ 38% share of broadband industry net adds in the fourth quarter of 2021. Approximately half of Verizon’s FWA customers are coming from commercial accounts, T-Mobile has indicated that about half its FWA customers are coming from former cable Internet subscribers. FWA’s strong Q4 showing left cable’s flow share at just 66%, about the same as cable’s share of installed US broadband households. “In other words, Cable likely neither gained nor lost share during the quarter, and instead merely treaded water,” Moffett noted. FWA “has gone from low-level background noise to suddenly a major force, with Verizon and T-Mobile alone capturing more than 300K FWA subscribers in the fourth quarter,” Craig noted. However, he isn’t sure that wireless network operators will allocate enough total bandwidth capacity for FWA to fully scale.
In a government auction that ended in early 2021, Verizon spent $45.45 billion on 5G “C-band” airwaves while T-Mobile invested $9.3 billion. AT&T spent $23.4 billion on the auction but it’s putting its 5G investments in areas other than FWA, like industrial 5G applications.
Meanwhile, there are cable TV firms looming with high-speed, coaxial cable. Comcast says it’s not worried about broadband competition from fixed 5G wireless services to homes.
“Time will tell, but it’s an inferior product,” Comcast Chief Executive Brian Roberts said at a recent Morgan Stanley conference. “And today, we can say we don’t feel much impact from (it). It’s lower speeds. And in the long run, I don’t know how viable the technology holds up.”
Cable companies offer hard landlines while 5G wireless services provide high-speed internet to homes mainly via indoor antennae that consumers self-install.
Eighty-seven percent of U.S. households subscribe to an internet service at home, compared with 83% in 2016, according to Leichtman Research Group. Also, cable TV firms comprise 70% of the broadband market, LRG said.
Verizon ended 2021 with 223,000 fixed wireless broadband customers, but most connected via 4G wireless networks. Meanwhile, T-Mobile had 646,000 fixed 5G broadband subscribers.
T-Mobile has told Wall Street analysts it expects to serve in a range of 7 million to 8 million fixed 5G wireless subscribers by 2025. Verizon has projected 3 million to 4 million subscribers over the same period.
T-Mobile charges $50 monthly for its home internet service. Verizon’s pricing starts at $50 or $70 monthly, depending on the data speeds provided. Verizon mobile phone customers with unlimited data plans get a discount.
T-Mobile’s 5G internet to home services provides data speeds up to 115 megabits per second, or Mbps. Verizon plans to provide speeds up to 300 Mbps.
T-Mobile uses mid-band radio spectrum to deliver fixed 5G broadband to homes. Verizon uses a mix of mid-band and high-band radio spectrum. In urban areas, Verizon may be able to deliver higher internet speeds with high-band spectrum, analysts say.
One area of debate remains whether fixed 5G broadband finds more success in suburban/urban markets or in rural areas.
“FWA is definitely a threat to cable companies,” Peter Rysavy, head of Rysavy Research, said in an email. “Particularly with (high frequency) mmWave, 5G can compete directly with cable. Mid-band spectrum is also effective but is best suited for lower density population areas. In these deployments, even T-Mobile limits the number of fixed wireless subscribers it can support in any geographical area.”
At UBS, Hodulik says that even if positioned as a low-end service, fixed 5G broadband still has a potential market of 20 million to 30 million homes.
AT&T, whose forerunner was regional Bell SBC Communications, has a sizable wireline local service area in 22 states. So it will face competition from fixed 5G broadband, just like cable TV firms. Verizon is based mainly in the northeast. T-Mobile doesn’t sell local phone services.
“AT&T has a huge wireline asset base that is only 25% upgraded to fiber,” Oppenheimer analyst Tim Horan told IBD. “So they are very exposed to competition from fixed wireless.”
At an analyst day on March 11, AT&T said it plans to upgrade 50% of its local markets, about 30 million customer locations, to high-speed fiber-optic broadband service by year-end 2025.
Meanwhile, AT&T CEO John Stankey commented on the controversy over FWA. AT&T sees FWA as playing a limited role for mobile small business and enterprise applications as well as in rural areas.
“We’re not opposed to fixed wireless, and I’m sure there’s going to be segments of the market where it’s going to be acceptable and folks are going to find it to be adequate right now,” Stankey said.
Fixed 5G broadband services to homes isn’t the only potential moneymaker for telecom network providers. Verizon, AT&T and T-Mobile aim to upgrade mobile phone users to unlimited data plans. They also plan to sell “private 5G” connections to businesses, Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G connections to industrial devices.
References:
Will 2022 be the year for 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) or a conundrum for telcos?
MoffettNathanson: Robust broadband and FWA growth, but are we witnessing a fiber bubble?