Author: Alan Weissberger
AI RAN Alliance selects Alex Choi as Chairman
Backgrounder:
The AI RAN Alliance, formed earlier this year, is a groundbreaking collaboration aimed at revolutionizing the RAN industry. Partnering with tech giants, the goal is to transform traditional Radio Access Networks (RANs) into intelligent, self-optimizing systems using advanced AI technologies. Their website states:
Bringing together the technology industry leaders and academic institutions, the AI-RAN Alliance is dedicated to driving the enhancement of RAN performance and capability with AI. Moreover, we aim to optimize RAN asset utilization, and unlock new revenue streams. By pioneering AI-based innovations in RAN, we aspire to profitably propel the telecom industry towards 6G.
The alliance’s founding members include Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS), Arm, DeepSig Inc. (DeepSig), Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (Ericsson), Microsoft Corporation (Microsoft), Nokia, Northeastern University, NVIDIA, Samsung Electronics, SoftBank Corp. (SoftBank) and T-Mobile USA, Inc. (T-Mobile).
The group’s mission is to enhance mobile network efficiency, reduce power consumption, and retrofit existing infrastructure, setting the stage for unlocking new economic opportunities for telecom companies with AI, facilitated by 5G and 6G.

Image Courtesy of the AI RAN Alliance.
Purpose:
The AI RAN Alliance is dedicated to eliminating the inefficiencies of traditional RAN systems by embedding AI directly into network infrastructures. This shift will enable, for example, dynamic resource allocation, predictive maintenance, and proactive network management.
Industry Benefits:
Enhanced Network Efficiency: Real-time optimized bandwidth allocation and improved user experiences.
Economic Advantages: Cost savings from AI-driven automation and reduced energy consumption.
Innovative Revenue Opportunities: New services such as real-time AI Assistants on your mobile devices.
Key Focus Areas:
- AI for RAN
- AI on RAN (RAN for AI)
- AI and RAN
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
New AI RAN Alliance Chairman:
On August 15, 2024, the AI RAN Alliance appointed Dr. Alex Jinsung Choi, Principal Fellow of SoftBank Corp.’s Research Institute of Advanced Technology as Chairman.
“The AI-RAN Alliance is set to transform telecommunications through AI-RAN advancements, increased efficiency, and new economic opportunities,” said Choi. “As Chair, I’m excited to lead this AI-RAN initiative, working with industry leaders to enhance mobile networks, reduce power consumption, and modernize infrastructure with 5G and 6G with AI/ML. Our goal is to drive societal progress through AI-RAN, transitioning from traditional to next-generation communications infrastructure.”
Satadal Bhattacharjee, Sr. Director of Marketing, Infrastructure BU, ARM, said, “We’re excited to collaborate with Choi, the Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. Like Choi, we believe that AI will fundamentally change the way wireless services are deployed, fostering broad innovation and enhancing operational efficiency. We look forward to working with key industry leaders from silicon to software to fulfill the promise of ubiquitous AI and 6G.”
Jim Shea, Co-founder and CEO of DeepSig, said, “As a pioneer in AI-native communications together with his prior experience growing the O-RAN ALLIANCE, Choi will lead this important initiative that is shaping the future of intelligent radio access networks. DeepSig’s extensive AI/ML wireless expertise will play a key role in this exciting collaboration to leverage advanced technologies to help the industry unlock unprecedented network efficiency and accelerate innovation.”
Mathias Riback, VP & Head of Advanced Technology U.S., Ericsson, said, “I’m thrilled to welcome Dr. Choi as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. As a non-standardization organization, the Alliance can uniquely complement the work of existing SDOs by focusing on shaping innovative use cases that integrate AI with RAN. In addition to realizing benefits from AI in RAN implementations, it will be important to advance ‘AI on RAN’ use cases, where mobile networks play a critical role in enabling AI applications. Ericsson is fully committed to fostering a collaborative environment that unites all players in the evolving AI ecosystem to shape the future of telecom together.”
Shawn Hakl, VP of 5G Strategy, Microsoft, said, “At Microsoft, we recognize artificial intelligence (AI) as a pivotal technology of our era. We are excited to be a part of the AI-RAN Alliance and are particularly pleased to see Choi step into the role of Chair. Choi’s leadership will be key as we collaborate to leverage AI in optimizing RAN infrastructure investments and expanding the capabilities of RAN to introduce new AI-driven services for modern mobile applications.”
Ari Kynäslahti, Head of Strategy and Technology, Mobile Networks at Nokia commented, “Nokia is proud to be part of the AI-RAN Alliance and contribute towards integrating AI into radio access networks. The potential of AI to optimize networks, predict and resolve issues, and enhance performance and service quality is significant. As we embark on this transformative journey, collaboration is essential to harness our collective expertise. We are pleased to see Dr. Alex Choi appointed to this role, and look forward to him guiding our efforts to achieve these goals.”
Tommaso Melodia, William L. Smith Professor, Northeastern University, said, “We are pleased to have Choi as the Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance, leading our efforts to transform the industry. Choi has been a strong advocate for the evolution towards a more open, software-driven, and AI-integrated future. Under Choi’s leadership, the AI-RAN Alliance is set to fast-track the development of new services and use cases by leveraging openness, softwarization, and AI integration to enhance network performance, energy efficiency, spectrum sharing, and security, ultimately redefining the landscape of global communications.”
Soma Velayutham, GM, AI and Telecoms, NVIDIA, said, “The AI-RAN Alliance is a critical initiative for advancing the convergence of AI and 5G/6G technologies to drive innovation in mobile networks. The consortium’s new leadership will bring a fresh perspective and focus on delivering the next generation of connectivity.”
Dr. Ardavan Tehrani, Samsung Research, AI-RAN Alliance Board of Directors Vice Chair, said, “We are excited to have Dr. Alex Choi leading the AI-RAN Alliance as the Chair of the Board. The Alliance will play a pivotal role in fostering collaboration, driving innovation, and transforming future 6G networks utilizing AI. Under Dr. Choi’s leadership, the Alliance will strive to deliver substantial value to end users and operators through pioneering AI-based use cases and innovations.”
Ryuji Wakikawa, VP and Head of Research Institute of Advanced Technology, SoftBank Corp., said, “SoftBank is committed to realizing an AI-powered network infrastructure, and we strongly believe that Choi’s extensive background and expertise will be a great force in advancing AI-RAN technology and driving significant progress for the mobile industry in this AI era with lightning speed.”
John Saw, EVP and CTO, T-Mobile, said, “We are thrilled to have Alex Choi as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. AI is advancing at an unprecedented rate and with our 5G network advantage we have a unique opportunity to harness this momentum. By developing solutions that make the most of both RAN and AI on GPUs — and working alongside Choi and the top industry leaders within the Alliance — we believe there is potential for change that will revolutionize the industry.”
Dr. Akihiro Nakao, Professor, The University of Tokyo, said, “Dr. Alex Jinsung Choi’s appointment as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance represents a pivotal step in advancing AI within the telecommunications sector. His leadership is expected to unite academic and industry efforts, nurturing the next wave of innovators who will drive the future of AI and telecommunications. This initiative will not only fast-track the adoption of AI across diverse applications but also foster international collaboration and set new standards for efficiency, energy management, resilience, and the development of AI-driven services that will reshape the telecommunications industry and benefit society worldwide.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://ai-ran.org/news/industry-leaders-in-ai-and-wireless-form-ai-ran-alliance/
AI sparks huge increase in U.S. energy consumption and is straining the power grid; transmission/distribution as a major problem
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Tech layoffs continue unabated: pink slip season in hard-hit SF Bay Area
A combination of strategic pivots toward the red-hot AI sector and corrections after pandemic-era over hiring have pushed companies across the tech sector to lay off massive number of employees, according to outplacement firm Challenger, Grey & Christmas. Tech companies including Cisco Systems, Intel and Dell have cut tens of thousands of jobs in August, the latest in a year that began with layoffs at companies such as Amazon and Google.
On Wednesday, Cisco announced in a notice posted with the Securities and Exchange Commission that it was laying off 5,500 workers (7% of its employees) as part of an effort to invest more in AI. In a short statement, CEO Chuck Robbins used the term “AI” five times, highlighting the company’s efforts to keep up in the ongoing AI race. Earlier this year, Cisco also laid off 4,000 or 5% of its workforce, saying that the company wanted to “realign the organization and enable further investment in key priority areas.” Cisco joins a litany of other companies like Microsoft and Intuit that have used AI as the justification for mass layoffs.
- As of August 17, 2024, 404 tech companies have laid off 132,498 workers this year, according to layoffs.fyi, a website that tracks tech industry job cuts. This includes major tech companies like Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Tesla, TikTok, and Snap, as well as smaller startups and apps.
- Crunchbase says that in 2023, more than 191,000 workers in U.S.-based tech companies (or tech companies with a large U.S. workforce) were laid off in mass job cuts. In 2022, more than 93,000 jobs were slashed from public and private tech companies in the U.S.
The SF Bay Area has been particularly hard-hit, with companies such as Twitter, Meta, and Salesforce announcing significant job cuts. The layoffs are sending shockwaves through the region’s economy. The tech industry has long been a major driver of growth and employment in the Bay Area, accounting for a significant portion of tax revenue and supporting numerous ancillary businesses. The sudden loss of jobs has raised concerns about a potential economic downturn. Many of the affected workers are highly skilled in areas such as software engineering, product development, and data science.
Here are the largest Bay Area tech company layoffs in 2024 and 2023:
| March 14, 2023 | Meta/FB |
21,000
|
13% | Menlo Park |
| August 1, 2024 | Intel |
18,720
|
15% | Santa Clara |
| January 20, 2023 | Alphabet |
12,000
|
6% | Mountain View |
| Feb 14 & Aug14, 2024 | Cisco Systems | 9,500 | 13% | San Jose |
The tech layoffs have created a fiercely competitive job market, with many qualified individuals seeking new employment. This has put pressure on salaries and benefits, further exacerbating the economic impact. The tech layoffs have also had a psychological toll on the Bay Area community. Many workers have lost their sense of stability and are worried about their financial future. The uncertainty has created a climate of anxiety and stress, particularly among those who are still employed.
Government officials and economic development agencies are working to mitigate the effects of the layoffs. They are providing support services to displaced workers, such as job retraining and placement assistance. However, the full extent of the economic impact remains to be seen. The surge in tech layoffs underscores the cyclical nature of the industry. While the Bay Area has weathered economic downturns in the past, the unprecedented scale of the current tech job cuts raises questions about the long-term health of the tech sector. As companies adapt to a changing economic landscape, the region’s economy is struggling to evolve to meet the challenges and perceived opportunities (e.g. AI).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.wsj.com/finance/investing/tech-media-telecom-roundup-market-talk-12947dd6
https://futurism.com/the-byte/cisco-layoff-ai-profit
https://news.crunchbase.com/startups/tech-layoffs/
https://www.challengergray.com/tags/job-cut-report/
Massive layoffs and cost cutting will decimate Intel’s already tiny 5G network business
Cisco to lay off more than 4,000 as it shifts focus to AI and Cybersecurity
Cisco restructuring plan will result in ~4100 layoffs; focus on security and cloud based products
AI Echo Chamber: “Upstream AI” companies huge spending fuels profit growth for “Downstream AI” firms
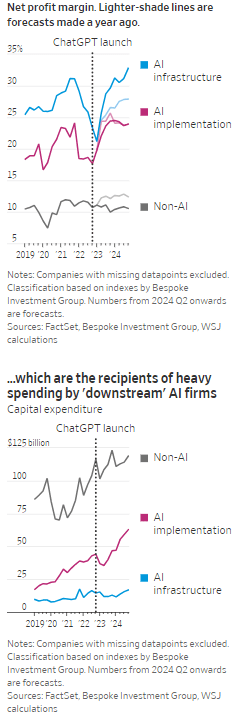
According to the Wall Street Journal, the AI industry has become an “Echo Chamber,” where huge capital spending by the AI infrastructure and application providers have fueled revenue and profit growth for everyone else. Market research firm Bespoke Investment Group has recently created baskets for “downstream” and “upstream” AI companies.
- The Downstream group involves “AI implementation,” which consist of firms that sell AI development tools, such as the large language models (LLMs) popularized by OpenAI’s ChatGPT since the end of 2022, or run products that can incorporate them. This includes Google/Alphabet, Microsoft, Amazon, Meta Platforms (FB), along with IBM, Adobe and Salesforce.
- Higher up the supply chain (Upstream group), are the “AI infrastructure” providers, which sell AI chips, applications, data centers and training software. The undisputed leader is Nvidia, which has seen its sales triple in a year, but it also includes other semiconductor companies, database developer Oracle and owners of data centers Equinix and Digital Realty.
The Upstream group of companies have posted profit margins that are far above what analysts expected a year ago. In the second quarter, and pending Nvidia’s results on Aug. 28th , Upstream AI members of the S&P 500 are set to have delivered a 50% annual increase in earnings. For the remainder of 2024, they will be increasingly responsible for the profit growth that Wall Street expects from the stock market—even accounting for Intel’s huge problems and restructuring.
It should be noted that the lines between the two groups can be blurry, particularly when it comes to giants such as Amazon, Microsoft and Alphabet, which provide both AI implementation (e.g. LLMs) and infrastructure: Their cloud-computing businesses are responsible for turning these companies into the early winners of the AI craze last year and reported breakneck growth during this latest earnings season. A crucial point is that it is their role as ultimate developers of AI applications that have led them to make super huge capital expenditures, which are responsible for the profit surge in the rest of the ecosystem. So there is a definite trickle down effect where the big tech players AI directed CAPEX is boosting revenue and profits for the companies down the supply chain.
As the path for monetizing this technology gets longer and harder, the benefits seem to be increasingly accruing to companies higher up in the supply chain. Meta Platforms Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg recently said the company’s coming Llama 4 language model will require 10 times as much computing power to train as its predecessor. Were it not for AI, revenues for semiconductor firms would probably have fallen during the second quarter, rather than rise 18%, according to S&P Global.
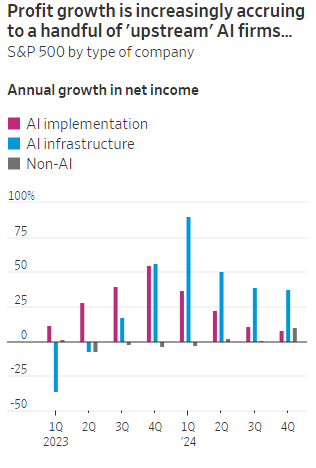 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
A paper written by researchers from the likes of Cambridge and Oxford uncovered that the large language models (LLMs) behind some of today’s most exciting AI apps may have been trained on “synthetic data” or data generated by other AI. This revelation raises ethical and quality concerns. If an AI model is trained primarily or even partially on synthetic data, it might produce outputs lacking human-generated content’s richness and reliability. It could be a case of the blind leading the blind, with AI models reinforcing the limitations or biases inherent in the synthetic data they were trained on.
In this paper, the team coined the phrase “model collapse,” claiming that training models this way will answer user prompts with low-quality outputs. The idea of “model collapse” suggests a sort of unraveling of the machine’s learning capabilities, where it fails to produce outputs with the informative or nuanced characteristics we expect. This poses a serious question for the future of AI development. If AI is increasingly trained on synthetic data, we risk creating echo chambers of misinformation or low-quality responses, leading to less helpful and potentially even misleading systems.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In a recent working paper, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) economist Daron Acemoglu argued that AI’s knack for easy tasks has led to exaggerated predictions of its power to enhance productivity in hard jobs. Also, some of the new tasks created by AI may have negative social value (such as design of algorithms for online manipulation). Indeed, data from the Census Bureau show that only a small percentage of U.S. companies outside of the information and knowledge sectors are looking to make use of AI.
References:
https://deepgram.com/learn/the-ai-echo-chamber-model-collapse-synthetic-data-risks
https://economics.mit.edu/sites/default/files/2024-04/The%20Simple%20Macroeconomics%20of%20AI.pdf
AI wave stimulates big tech spending and strong profits, but for how long?
AI winner Nvidia faces competition with new super chip delayed
SK Telecom and Singtel partner to develop next-generation telco technologies using AI
Telecom and AI Status in the EU
Vodafone: GenAI overhyped, will spend $151M to enhance its chatbot with AI
Data infrastructure software: picks and shovels for AI; Hyperscaler CAPEX
KT and LG Electronics to cooperate on 6G technologies and standards, especially full-duplex communications
In a joint statement, KT (South Korea’s #2 mobile network operator) and LG Electronics will work together to promote 6G technology research and technology standardization. The two companies plan to develop full-duplex communication technology, global standardization cooperation (presumably in 3GPP and ITU-R WP5D for IMT-2030), and 6G application services and next-generation transmission technologies. The companies had previously announced partnerships to develop AI service platforms and AI service robots.
Full-duplex communications will be introduced as part of the 5G-Advanced Release 18 and is expected to increase spectrum efficiency by enabling uplink and downlink data to be simultaneously transmitted and received over a single frequency band. The companies said it can increase frequency efficiency by up to two times. They will design technologies that operate in the 6G candidate frequency bands and transmit and receive simultaneously to verify actual performance. The duo also plan to promote global standardization of 6G (that can only be done by ITU-R IMT-2030 recommendations).
“Through this 6G research and development collaboration with LG Electronics, KT expects to lead the development of 6G mobile communication technology and strengthen its global standardization leadership,” said Lee Jong-sik, executive director of KT Network Research Institute. “We will do our best to secure innovative network technology and capabilities for providing differentiated services.”
Je Young-ho, executive director of LG Electronics C&M Standard Research Institute added: “LG Electronics has been proactively leading research and development to discover core 6G technologies since 2019,” and added, “Through our collaboration with KT, we expect to contribute greatly to not only leading 6G standardization, but also discovering core services.”

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Singtel and SK Telecom announced a partnership last month to collaborate on 6G research, including new network slicing capabilities, a fully disaggregated network, and new telco APIs based on Open Gateway. Earlier this year, Samsung and Arm began conducting joint research into parallel packet processing technology, which it described as one of the ‘key software technologies in next-generation communications’ to accelerate 6G software development, while Nvidia launched its 6G Research Cloud Platform, which includes a a digital twin that can simulate 6G systems, a software-defined, full RAN stack that researchers can play around with the Nvidia Sionna Neural Radio Framework which enables developers to use Nvidia GPUs to generate and capture training data.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.koreaittimes.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=133845
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/kt-and-lg-looking-to-take-the-lead-in-6g
https://news.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20210406000119
https://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/tech/2024/06/129_334571.html
South Korea government fines mobile carriers $25M for exaggerating 5G speeds; KT says 5G vision not met
South Korea has 30 million 5G users, but did not meet expectations; KT and SKT AI initiatives
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia to work on AI assisted “fiber sensing”
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia have agreed to work on artificial intelligence (AI) assisted “fiber sensing,” a wired network technology that employs AI to monitor the environment around optical cables. The two companies signed a memorandum of understanding (see photo below) last Wednesday, with a plan to “accumulate empirical data based on machine learning” from SKT’s commercial network. SKT, South Korea’s largest mobile network carrier, said on Monday that it will utilize Nokia’s product to detect earthquakes, climate changes and other unexpected situations that might arise from nearby construction areas in order to stabilize network conditions. The objective is nationwide deployment in South Korea by the end of this year.
In a joint statement, the companies explained when data runs through an optical cable, the phase of the light can change due to various factors like temperature fluctuations or physical strain on the cable. The changes can be detected and analyzed to provide precise measurements of the environmental conditions affecting the fiber. Using AI-based technology, SKT and Nokia aim to stabilize fiber optic networks in advance by tracking the impact of weather conditions and construction on optical cables. The statement added “fiber sensing” has no distance limitations, unlike some existing wired network monitoring technologies, making it possible to quickly apply the new technology to major backbone networks.
SKT-Nokia monitors wired network status with AI:
– Tracking the impact of weather, earthquakes, construction, etc. on optical cables with ‘fiber sensing’ technology
– Immediately applicable to existing networks and no distance restrictions, making it easy to apply to backbone networks
– Both companies’ capabilities will be combined to quickly internalize new AI-based wired network technology
A signing ceremony for the memorandum of understanding took place at SK Telecom’s headquarters Wednesday in central Seoul. SK Telecom’s Ryu Jung-hwan, head of infrastructure strategy and technology, and John Harrington, Nokia’s senior vice president and head of network infrastructure sales for the Asia-Pacific region, attended the event.

SK Telecom’s Ryu Jung-hwan, head of infrastructure strategy and technology, right, and John Harrington, Nokia’s senior vice president and head of network infrastructure sales for the Asia-Pacific region, pose for a photo after a signing ceremony at SK Telecom’s headquarters in central Seoul on Wednesday, August 7th. Photo Credit: SK TELECOM
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In July, SKT and Singtel announced that they have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to collaborate on building next-generation telecommunications networks that will drive innovation, improve network performance and security and deliver enhanced customer experiences over the next two years. The partners will explore the use of artificial intelligence (AI), orchestration tools, and deepen the domain knowledge of network virtualization and other technologies – central to laying the necessary building blocks for progressing to 6G.
References:
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7228552138988134402/
Cisco to lay off more than 4,000 as it shifts focus to AI and Cybersecurity
Reuters reports that Cisco Systems will cut thousands of jobs in its second round of layoffs this year. The number of people affected could be similar to or slightly higher than the 4,000 employees Cisco laid off in February, and will likely be announced as early as Wednesday with the company’s fourth-quarter results.
The San Jose, CA headquartered networking company plans to shift its product focus to higher-growth areas, such as AI and cybersecurity. It’s current set of products and services are listed here.
Cisco has been contending with weakening demand and persistent supply chain issues in its core business – routers and switches – that are used by ISPs and enterprise private networks. Two reasons for that are: 1.] the major cloud service providers design their own switch/routers or use bare metal switches (made by ODMs in Taiwan and China), and 2.] enterprise private/virtual private networks are being replaced by cloud network solutions.
- Global enterprise network sales have been declining. Dell’Oro Group reported sales contractions in Branch Routing and Campus Switching in 4Q-2023 and that is expected to continue throughout most of 2024. On premises data centers (which use Cisco Ethernet switches) are not growing. In its place……
- Enterprise spending on cloud infrastructure services is growing by leaps and bounds. It’s now nearing $80 billion per quarter. Cloud customers increased their spending on cloud services by $14.1 billion to $79.1 billion in the 2Q-2024, an increase of 22% year-over-year. It’s the third consecutive quarter in which the year-over-year growth rate was 20% or more, with generative AI being one of the factors behind the market acceleration.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
As a result of stagnant sales of its core networking products, Cisco has been pursuing a strategy aimed at diversifying its revenue streams. One of the most significant moves in this direction was the $28 billion acquisition of Splunk, a cybersecurity firm, which was finalized in March. This purchase is expected to boost Cisco’s subscription-based services, reducing its dependence on one-time hardware sales, which have been increasingly susceptible to market volatility.
Cisco’s major shift towards AI is a key part of its long-term strategy. In May, the company reiterated its ambitious goal of achieving $1 billion in AI-related product orders by 2025. This target is supported by a $1 billion fund launched in June, aimed at investing in AI startups such as Cohere, Mistral AI, and Scale AI. Over the past few years, Cisco has made over 20 AI-focused acquisitions and investments, highlighting its commitment to integrating AI into its product offerings.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Over 126,000 employees have been laid off across 393 tech companies since the start of the year, according to data from tracking website Layoffs.fyi. That surely reflects their need to cut costs to balance huge investments in AI, analytics and related technologies.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/index.html#~products-by-technology
Cisco to Implement Second Round of Layoffs Amidst Strategic Shift to AI and Cybersecurity
Worldwide Enterprise Network Spending Follows Roller Coaster Trajectory
Cisco restructuring plan will result in ~4100 layoffs; focus on security and cloud based products
Nokia’s 760 global private networking contracts are mostly 4G-LTE Advanced
Backgrounder:
Private Wireless Radio Access Network (RAN) revenue growth slowed in the fourth quarter of 2023 on a year-over-year basis. However, full-year revenues accelerated by approximately 40% in 2023, propelling private wireless to comprise around 2% of the overall RAN market.
“Private wireless RANs are now growing at a formidable pace, in contrast to public RAN and enterprise WLAN – both segments are projected to contract in 2024,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group in April.
The top 3 Private Wireless RAN suppliers in 2023 were Huawei, Nokia, and Ericsson. Excluding China, they were Nokia, Ericsson, and Samsung.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Nokia leads in Private RANs:
Nokia recently told Fierce Network that it signed 30 new private networking contracts in the second quarter of 2024. Nokia has said that it has signed more than 760 private network contracts around the world. NGIC, Sigma Lithium and Solis are some of the most recent names it has signed.
Nokia said that 78% of its private network business is based on 4G LTE-Advanced [1.], compared to 18% being 5G only, and the remaining 4% combining the two broadband cellular technologies.
Note 1. In October 2010, LTE-Advanced successfully passed the ITU-R’s evaluation process and was found to meet or exceed IMT-Advanced requirements. It was standardized a “IMT Advanced,” which support low to high mobility applications and a wide range of data rates in accordance with user and service demands in multiple user environments. IMT Advanced also has capabilities for high quality multimedia applications within a wide range of services and platforms, providing a significant improvement in performance and quality of service.

Image courtesy of Research Gate
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
David de Lancellotti, VP of enterprise campus edge business at Nokia talked to Fierce about Nokia’s performance in the private networking space. “Thirty in Q2, and roughly 50 — a little more than 50 — in the first half,” he said of contracts signed.
“We kind of jumped into this a bit earlier than anybody else,” Nokia’s de Lancellotti explained. “I think we’ve always taken a real service provider approach in terms of quality, in terms of feature set [and] in terms of roadmap,” while noting Nokia’s “real drive to pick up the enterprise space.”
Industry verticals – transportation, energy and manufacturing – continue to “lead the way” for private networking contracts in Q2. “When we talk about transportation, I think that’s the port side of business, which continues to be strong for us,” David said.
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/wireless/nokia
Private Wireless RAN Revenues up ~40 Percent in 2023, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LTE_Advanced
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-adv/Pages/default.aspx
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Network-architecture-of-LTE-Advanced_fig1_333886291
Highlights of FiberConnect 2024: PON-related products dominate
The Fiber Broadband Association’s flagship conference, FiberConnect 2024, concluded July 31, 2024, in Nashville, Tennessee. It featuring 275 speakers and 286 exhibitors in the Expo Hall, with about half the attendees from operators and half representing vendors. The show provided a great opportunity to gauge the pulse of the fiber based broadband industry in North America.

China Unicom-Beijing and Huawei build “5.5G network” using 3 component carrier aggregation (3CC)
Huawei says it has deployed an “ultra large-scale 5.5G network” (there is no definition, 3GPP approved specs, or ITU-R recommendations/standards for 5.5G) operated by China Unicom in Beijing. The network uses three component carrier (3CC) aggregation to provide 70 percent coverage within Beijing’s 4th urban ring road. Huawei says China Unicom will offer comprehensive 5.5G service (again undefined) across stadiums, metro stations and tunnels, residential areas, scenic spots, business districts, and universities in key areas within the city’s 4th Ring Road and Beijing Municipal Administrative Center.
Editor’s Note: At the 5G Advanced Forum during MWC Shanghai 2023, Huawei’s President of ICT Products & Solutions, Yang Chaobin said, “In 2024, Huawei will launch a complete set of commercial 5.5G network equipment to be prepared for the commercial deployment of 5.5G.” Many believe that 5.5G is another name for 3GPP defined 5G Advanced, which is expected to bring new wireless technology innovations that improve speed, coverage, mobility, power efficiency, and sustainability. 3GPP Release 18 in 2024 is the beginning of 5G Advanced. The second and major release of 5G Advanced, Release 19, will be completed by the end of 2025. This release will focus on enhanced performance and the 5G system’s ability to meet commercial deployment needs.
In the Beijing Action Plan for Promoting 5G-A Technology Evolution and Application Innovation (2024-2026), Beijing Municipal Communications Administration hammered home the importance of Beijing’s role in pioneering 5.5G development. China Unicom Beijing is striving to do its part, with a large-scale 5.5G network demonstration at the beginning of 2024 followed by the ultra-large-scale commercial 5.5G network deployment of recent months, in helping Beijing become a “dual 10 Gbps” city that sets the bar for network construction, device development, and industry enablement. With the first version of 5.5G standards frozen in June 2024 and more than 20 commercial 5.5G devices now on the market, a mature 5.5G industry ecosystem is taking shape.

“Full 5.5G coverage” in Beijing’s core urban areas and the Beijing Municipal Administrative Center. Photo: Huawei
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In August 2022, China Unicom Beijing and Huawei commercialized the world’s largest 3.5 GHz 2CC network, which has brought 200 MHz 2CC coverage to more than 85% of Beijing’s urban area while providing comprehensive coverage for Beijing’s core areas and the Beijing Municipal Administrative Center. In 2023, this was further augmented when China Unicom Beijing and Huawei completed a 2.1 GHz band deployment targeting key urban scenarios. These deployments substantially improved the network experience of users in Beijing while laying a solid foundation for the future evolution to 5.5G, and this year’s 5.5G 3CC deployment paves the way for larger-scale 5.5G deployments in the coming years.
The ultra-large commercial 5.5G 3CC network consists of more than 4,000 base stations and covers well-known landmarks in Beijing, such as Wukesong, Capital Indoor Stadium, Workers’ Stadium, Beijing Railway Station, Guijie Street, Panjiayuan, and Beijing University of Technology. Featuring 5.5G capabilities, the network provides powerful support for services such as immersive video, UHD live streaming, and cloud gaming. In addition to consumer scenarios, China Unicom Beijing is proactively pursuing innovations in UHD shallow compression encoding, IoT, and XR split rendering, unlocking the full potential of 5.5G networks to enable various industries.
Yang Lifan, Deputy General Manager of China Unicom Beijing, remarked: “We have the world’s largest 200 MHz 5G network and it makes our 3CC carrier aggregation much easier. 5.5G 3CC coverage will be extended to match that of our current 200 MHz 5G network. With Huawei’s advanced technologies and our smart operations, we will provide users with a much better network experience.”
David Li, President of Huawei Wireless Network 5G<E TDD Product Line, said: “We are honored to mark a groundbreaking milestone in 5.5G network construction with China Unicom Beijing — large-scale commercial 5.5G. We will continue to innovate and provide more efficient, smarter, and greener network solutions, enabling users to enjoy a superior, smooth experience with 5.5G networks.”
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2024/7/5ga-beijing-3cc#
Huawei pushes 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) but there are no completed 3GPP specs or ITU-R standards!
https://blog.huawei.com/en/post/2023/11/14/5-5g-whats-in-a-number
5G Advanced offers opportunities for new revenue streams; 3GPP specs for 5G FWA?
Nokia, BT Group & Qualcomm achieve enhanced 5G SA downlink speeds using 5G Carrier Aggregation with 5 Component Carriers
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
Finland’s Elisa, Ericsson and Qualcomm test uplink carrier aggregation on 5G SA network
Verizon Business sees escalating risks in mobile and IoT security
Verizon Business released its 2024 Mobile Security Index (MSI) report outlining the top threats to mobile and IoT device security. This year’s report, in its seventh iteration, goes beyond employee-level mobile usage and extends into the usage of IoT devices and sensors and the security concerns the growth of these devices can present especially as remote work continues to be a trend. This expanded view of mobile security concerns for organizations showcases the evolving threat landscape that CIOs and other IT decision makers must contend with.
This annual report surveyed 600 people responsible for security strategy, as well as employee-level mobile usage, the report looked at the use of IoT devices and sensors and the security concerns that come with them as remote work continues to be a trend.
Highlights:
- 80% of responding organizations consider mobile devices critical to their operations, while 95% are actively using IoT devices.
- 96% of critical infrastructure respondents use IoT devices, with % having experienced a significant mobile or IoT device-related security incident.
- 77% of respondents anticipate that AI-assisted attacks, such as deep fakes and SMS phishing, are likely to succeed.
Employees are using more mobile and IoT devices, leading to increased cyber risks
The survey finds that 80% of respondents consider mobile devices critical to their operations, while 95% are actively using IoT devices. However, this heavy reliance comes with significant security concerns. In critical infrastructure sectors, where 96% of respondents report using IoT devices, more than half state that they have experienced severe security incidents that led to data loss or system downtime.
“These findings highlight the continued friction that employers face as more and more work is done on personal mobile devices,” said Phil Hochmuth Research VP, enterprise mobility at IDC. “This is why we are seeing more and more employers move from a pure bring-your-own-device model to employer provided devices where CIO’s can have greater governance to protect critical infrastructure from cyber attacks.”
Additionally, Hochmuth says, organizations should adopt robust frameworks such as Zero Trust and the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) 2.0, and comply with mandates like the European Union’s NIS2 Directive.
Emerging AI cyberthreats meet new AI defenses
Emerging artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are expected to exacerbate the mobile threat landscape, but it also presents opportunities for defense. A striking 77% of respondents anticipate that AI-assisted attacks, such as deepfakes and SMS phishing, are likely to succeed. At the same time, 88% of critical infrastructure respondents acknowledge the growing importance of AI-assisted cybersecurity solutions.
Accounting for IoT growth in cybersecurity planning
With companies increasingly deploying IoT devices, their digital landscapes are evolving, creating a need for cybersecurity strategies to evolve in kind.
“The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is giving rise to a massive expansion in mobile device technology that goes well beyond phones, tablets and laptops. Enterprise networks now include all sorts of sensors and purpose-built devices that monitor, measure, manage and control commercial tasks and data flow,” said TJ Fox, SVP of Industrial IoT and Automotive, Verizon Business. “That IIoT growth brings with it a proportionate need for more knowledge, awareness and IT solutioning to ensure the security of those increasingly sophisticated networks. The growing importance that IoT plays in our customer’s technology ecosystem underscores why it should be a component in any sound cybersecurity program.”
What business leaders should know
The 2024 MSI helps inform cybersecurity decisions for leaders of businesses of all sizes and in key sectors. As mobile and IoT threats rise, the need for robust security measures has never been greater. In response to these growing threats, 84% of respondents have increased their mobile device security spending over the past year, with 89% of critical infrastructure respondents planning further increases.
This year’s MSI includes contributions from Verizon’s partners including Ivanti, Lookout, Jamf among others. Help your organization lower cyber risks by deploying comprehensive security protections, continuous employee education and advanced threat detection capabilities.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Quotes:
Phil Hochmuth Research VP at IDC said: “These findings highlight the continued friction that employers face as more and more work is done on personal mobile devices. This is why we are seeing more and more employers move from a pure bring-your-own-device model to employer-provided devices where CIOs can have greater governance to protect critical infrastructure from cyber attacks.”
TJ Fox, SVP of Industrial IoT and Automotive, Verizon Business added: “The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is giving rise to a massive expansion in mobile device technology that goes well beyond phones, tablets and laptops. Enterprise networks now include all sorts of sensors and purpose-built devices that monitor, measure, manage and control commercial tasks and data flow.
“That IIoT growth brings with it a proportionate need for more knowledge, awareness and IT solutions to ensure the security of those increasingly sophisticated networks. The growing importance that IoT plays in our customer’s technology ecosystem underscores why it should be a component in any sound cybersecurity program.”
References:
Verizon Business 2024 Mobile Security Index
https://www.telecoms.com/security/verizon-warns-of-escalating-risks-in-mobile-and-iot-security